Diagnosis of Desmoplastic Reaction by Immunohistochemical Analysis, in Biopsy Specimens of Early Colorectal Carcinomas, Is Efficacious in Estimating the Depth of Invasion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
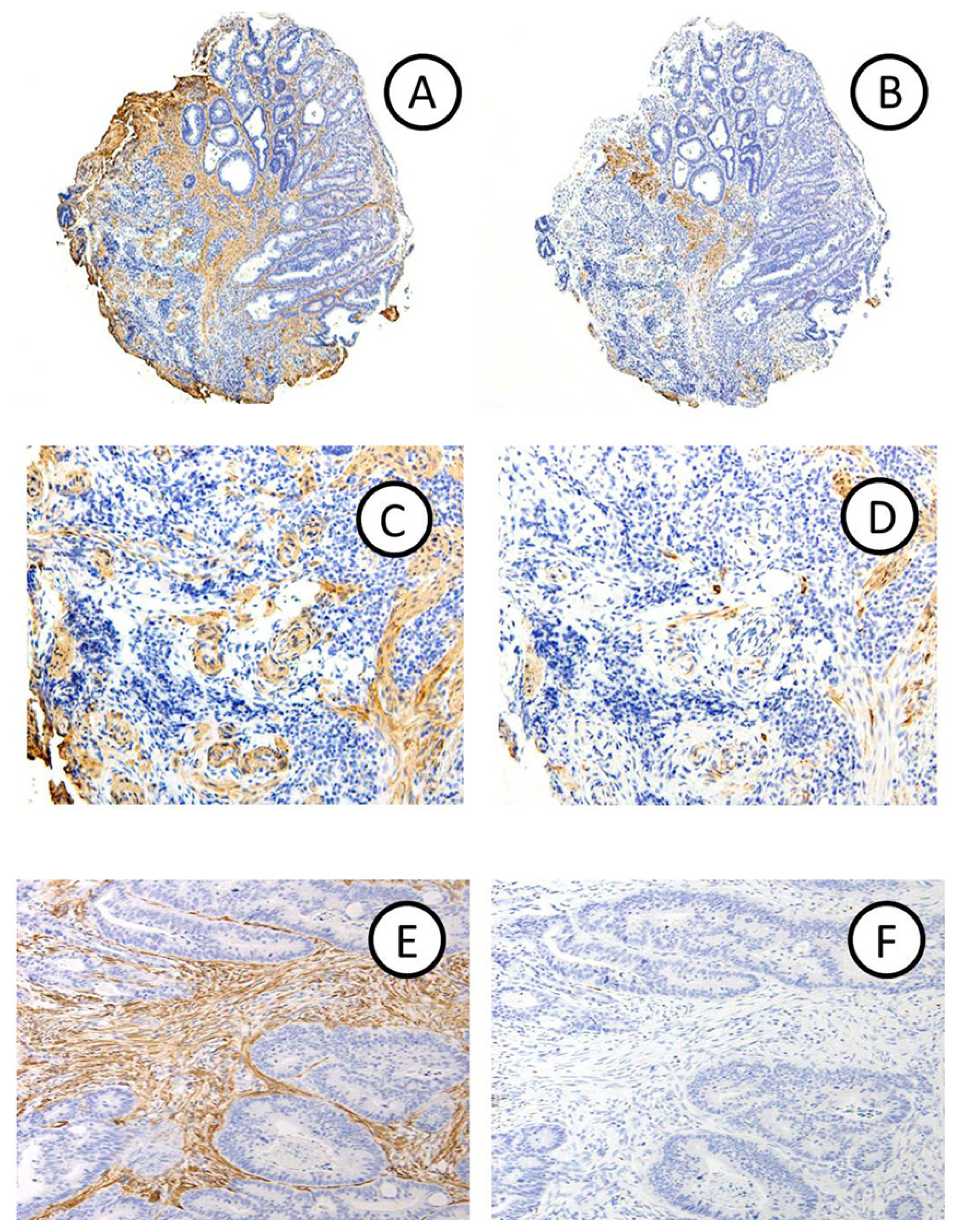
2.1.1. Clinicopathological Features
2.1.2. Relationship between Diagnosis of DR and the Depth of Invasion in Early CRCs
2.2. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Patients and Ethics
3.2. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
3.3. Evaluation of Immunohistochemical Staining
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Kimura, R.; Fujimori, T.; Ichikawa, K.; Ajioka, Y.; Ueno, H.; Ohkura, Y.; Kashida, H.; Togashi, K.; Yao, T.; Wada, R.; et al. Desmoplastic reaction in biopsy specimens of early colorectal cancer: A Japanese prospective multicenter study. Pathol. Int 2012, 62, 525–531. [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima, K.; Fujimori, T.; Fujii, S.; Takeda, J.; Ohkura, Y.; Kawamata, H.; Kumamoto, T.; Ishiguro, S.; Kato, Y.; Shimoda, T.; et al. Correlations between lymph node metastasis and depth of submucosal invasion in submucosal invasive colorectal carcinoma: A Japanese collaborative study. J. Gastroenterol 2004, 39, 534–543. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori, T.; Kawamata, H.; Kashida, H. Precancerous lesions of the colorectum. J. Gastroenterol 2001, 36, 587–594. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, T.; Fukuzawa, M.; Uraoka, T.; Nishi, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Ikematsu, H.; Saito, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Fujii, T.; et al. Risk of lymph node metastasis in patients with pedunculated type early invasive colorectal cancer: A retrospective multicenter study. Cancer Sci 2011, 102, 1693–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, T.; Itabashi, M.; Shimada, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Ito, Y.; Ajioka, Y.; Hamaguchi, T.; Hyodo, I.; Igarashi, M.; Ishida, H.; et al. Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum (JSCCR) guidelines 2010 for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol 2012, 17, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hirose, M.; Fukui, H.; Igarashi, Y.; Fujimori, Y.; Katake, Y.; Sekikawa, A.; Ichikawa, K.; Tomita, S.; Imura, J.; Ajioka, Y.; et al. Detection of desmoplastic reaction in biopsy specimens is useful for predicting the depth of invasion of early colorectal cancer: A Japanese collaborative study. J. Gastroenterol 2010, 45, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori, T. Dokkyo Medical University: Japan; Unpublished observation; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Halvorsen, T.B.; Seim, E. Association between invasiveness, inflammatory reaction, desmoplasia and survival in colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Pathol 1989, 42, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Tsujino, T.; Seshimo, I.; Yamamoto, H.; Ngan, C.Y.; Ezumi, K.; Takemasa, I.; Ikeda, M.; Sekimoto, M.; Matsuura, N.; Monden, M. Stromal myofibroblasts predict disease recurrence for colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res 2007, 13, 2082–2090. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, M.; Pujuguet, P.; Martin, F. Role of stromal myofibroblasts infiltrating colon cancer in tumor invasion. Path. Res. Pract 1996, 192, 708–717. [Google Scholar]
- Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum, Japanese Classification of Colorectal Carcinoma, 2nd ed; Kanehara & Co., Ltd: Tokyo, Japan, 2009.
- Fukui, H.; Fujii, S.; Takeda, J.; Kayahara, T.; Sekikawa, A.; Nanakin, A.; Suzuki, K.; Hisatsune, H.; Seno, H.; Sawada, M.; et al. Expression of Reg Iα protein in human gastric cancers. Digestion 2004, 69, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
| DR-positive | DR-negative | Total | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of lesion, n (%) | 21 (55.3) | 17 (44.7) | 38 (100) | |
| Age (years) | ||||
| Mean (range) | 60.2 (39–79) | 67.4 (53–79) | 63.4 (39–79) | NS |
| Gender | ||||
| Male/Female, n (%) | 12 (57)/9 (43) | 12 (71)/5 (29) | 24(63)/14 (37) | NS |
| Tumor Size (mm) | ||||
| Median (range) | 20 (5–35) | 13 (4–35) | 16.5 (4–35) | NS |
| Location, n (%) | ||||
| Rectum | 4 (19.0) | 5 (29.4) | 9 (23.7) | NS |
| Sigmoid | 6 (28.6) | 6 (35.3) | 12 (31.6) | |
| Descending | 2 (9.5) | 1 (5.9) | 3 (7.9) | |
| Transverse | 4 (19.0) | 5 (29.4) | 9 (23.7) | |
| Ascending | 4 (19.0) | 0 (0) | 4 (10.5) | |
| Cecum | 1 (4.9) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.6) | |
| Histological type, n (%) | NS | |||
| Well-differentiated | 14 (67) | 15 (88) | 29 (76) | |
| Moderately-differentiated | 7 (33) | 2 (12) | 9 (24) | |
| DR | Group A | Group B | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | 0 | 21 | <0.001 |
| Negative | 14 | 3 |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ohno, K.; Fujimori, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Ichikawa, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Imura, J.; Tomita, S.; Mitomi, H. Diagnosis of Desmoplastic Reaction by Immunohistochemical Analysis, in Biopsy Specimens of Early Colorectal Carcinomas, Is Efficacious in Estimating the Depth of Invasion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 13129-13136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140713129
Ohno K, Fujimori T, Okamoto Y, Ichikawa K, Yamaguchi T, Imura J, Tomita S, Mitomi H. Diagnosis of Desmoplastic Reaction by Immunohistochemical Analysis, in Biopsy Specimens of Early Colorectal Carcinomas, Is Efficacious in Estimating the Depth of Invasion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(7):13129-13136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140713129
Chicago/Turabian StyleOhno, Kazuya, Takahiro Fujimori, Yosuke Okamoto, Kazuhito Ichikawa, Takeshi Yamaguchi, Johji Imura, Shigeki Tomita, and Hiroyuki Mitomi. 2013. "Diagnosis of Desmoplastic Reaction by Immunohistochemical Analysis, in Biopsy Specimens of Early Colorectal Carcinomas, Is Efficacious in Estimating the Depth of Invasion" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 7: 13129-13136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140713129
APA StyleOhno, K., Fujimori, T., Okamoto, Y., Ichikawa, K., Yamaguchi, T., Imura, J., Tomita, S., & Mitomi, H. (2013). Diagnosis of Desmoplastic Reaction by Immunohistochemical Analysis, in Biopsy Specimens of Early Colorectal Carcinomas, Is Efficacious in Estimating the Depth of Invasion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(7), 13129-13136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140713129




