Photoinduced Surface Relief Grating Formation for a Single Crystal of 4-Aminoazobenzene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
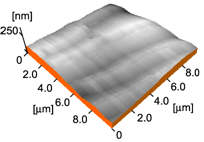
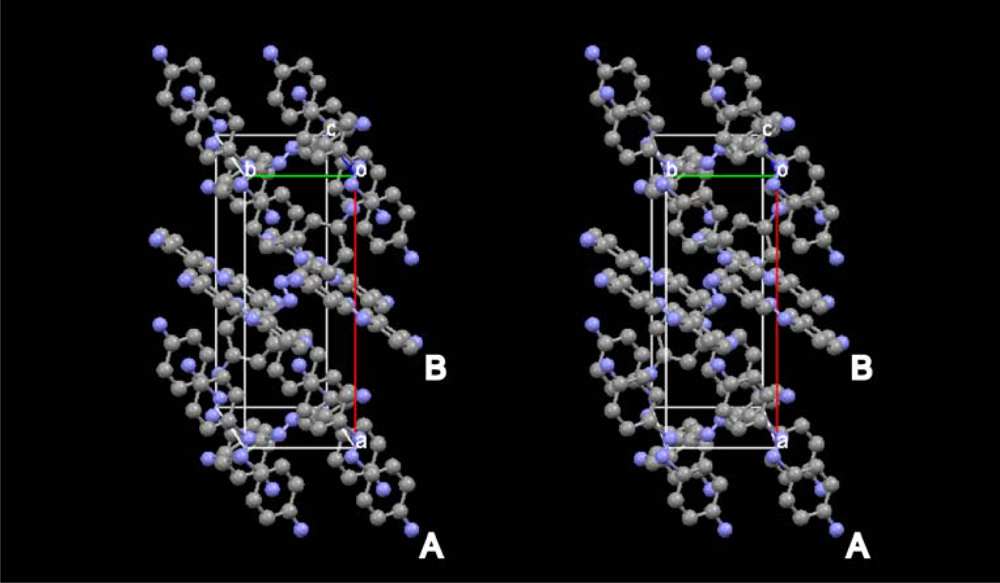
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
4. Calculation
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Reichmanis, E; Nalamasu, O; Houlihan, FM. Organic materials challenge for 193 nm imaging. Acc. Chem. Res 1999, 32, 659–667. [Google Scholar]
- Lippert, T. Laser application of polymers. Adv. Polym. Sci 2004, 168, 51–246. [Google Scholar]
- Rochon, P; Batalla, E; Natansohn, A. Optically induced surface gratings on azoaromatic polymer films. Appl. Phys. Lett 1995, 66, 136–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, DY; Tripathy, SK; Li, L; Kumar, J. Laser-induced holographic surface relief gratings on nonlinear optical polymer films. Appl. Phys. Lett 1995, 66, 1166–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Barret, C; Natansohn, A; Rochon, P. Mechanism of optically inscribed high-efficiency diffraction gratings in azo polymer films. J. Phys. Chem 1996, 100, 8836–8842. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, J; Li, L; Jiang, XL; Kim, DY; Lee, TS; Tripathy, SK. Gradient force: The mechanism for surface relief grating formation in azobenzene functionalized polymers. Appl. Phys. Lett 1998, 72, 2096–2098. [Google Scholar]
- Lefin, P; Fiorini, C; Nunzi, J-M. Anisotropy of the photo-induced translation diffusion of azobenzaene dyes in polymer matrices. Pure Appl. Opt 1998, 7, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, TG; Johansen, PM; Holme, NCR; Ramanujam, PS. Mean-field theory of photoinduced formation of surface reliefs in side-chain azobenzene polymers. Phys. Rev. Lett 1998, 80, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, NK; Kim, DY; Bian, S; Williams, J; Liu, W; Li, L; Samuelson, L; Kumar, J; Tripathy, SK. Surface relief structures on azo polymer films. J. Mater. Chem 1999, 9, 1941–1955. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorini, C; Prudhomme, N; de Veyrac, G; Maurin, I; Raimond, P; Nunzi, J-M. Molecular migration mechanism for laser induced surface relief grating formation. Synth. Met 2000, 115, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata, T; Seki, T; Ichimura, K. Surface relief gratings in host-guest supramolecular materials. Adv Mater 2000, 12, 1675–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K; Yang, S; Kumar, J. Formation mechanism of surface relief structures on amorphous azopolymer films. Phys Rev B 2006, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, H; Takahashi, T; Kadota, T; Shirota, Y. Formation of surface relief grating using a novel azobenzene-based photochromic amorphous molecular material. Adv. Mater 2002, 14, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Shirota, Y; Utsumi, H; Ujike, T; Yoshikawa, S; Moriwaki, K; Nagahama, D; Nakano, H. Photochromic amorphous molecular materials and their applications. Opt. Mater 2003, 21, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, H; Tanino, T; Ando, H; Nakano, H; Shirota, Y. Significant effect of molecular structure on surface relief grating formation for novel azobenzene-based photochromic amorphous molecular materials. Chem. Lett 2004, 33, 1152–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, T; Tanino, T; Ando, H; Nakano, H; Shirota, Y. Surface relief grating formation using a novel azobenzene-based photochromic amorphous molecular material, tris[4-(phenylazo)phenyl]amine. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryat 2005, 430, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, H; Tanino, T; Takahashi, T; Ando, H; Shirota, Y. Photoinduced surface relief grating formation using azobenzene-based photochromic amorphous molecular materials. J. Mater. Chem 2008, 18, 242–246. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, H; Tanino, T; Nakano, H; Shirota, Y. Photoinduced surface relief grating formation using new polymers containing the same azobenzene chromophore as a photochoromic amorphous molecular material. Mater. Chem. Phys 2009, 113, 376–381. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, H; Takahashi, T; Tanino, T; Shirota, Y. Synthesis and photoinduced surface relief grating formation of novel photo-responsive amorphous molecular materials, 4-[bis(9,9-dimethylfluoren-2-yl)amino]-4′-cyanoazobenzene and 4-[bis(9,9-dimethylfluoren-2-yl)amino]-4′-nitroazobenzene. Dyes Pigm 2009, 84, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann, T; Tsutsui, T. Synthesis and properties of a hole-conducting, photopatternable molecular glass. Chem. Mater 1999, 11, 2226–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, C; Kim, M-J; Vak, D; Kim, DY. A. novel azobenzene-based amorphous molecular material with a spiro linked bifluorene. J. Mater. Chem 2003, 13, 2904–2909. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M-J; Seo, E-M; Vak, D; Kim, D-Y. Photodynamic properties of azobenzene molecular films with triphenylamines. Chem. Mater 2003, 15, 4021–4027. [Google Scholar]
- Ishow, E; Lebon, B; He, Y; Wang, X; Bouteiller, L; Galmiche, L; Nakatani, K. Structural and photoisomerization cross studies of polar photochromic monomeric glasses forming surface relief gratings. Chem. Mater 2006, 18, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Ishow, E; Camacho-Aguilera, R; Guerin, J; Brosseau, A; Nakatani, K. Spontaneous formation of complex periodic superstructures under high interferential illumination of small-molecule-based photochromic materials. Adv. Funct. Mater 2009, 19, 796–804. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, WA; Jaeger, HM. Hierarchical self-assembly of metal nanostructures on diblock copolymer scaffolds. Nature 2001, 413, 735–738. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M; Harrison, C; Chaikin, PM; Register, RA; Adamson, DH. Block copolymer lithography: periodic arrays of ∼1011 holes in 1 square centimeter. Science 1997, 276, 1401–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Stoykovich, MP; Müller, M; Kim, SO; Solak, HH; Edwards, EW; de Pablo, JJ; Nealey, PF. Directed assembly of block copolymer blends into nonregular device-oriented structure. Science 2005, 308, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, R; Kamata, K; Iyoda, T. Smart block copolymer masks with molecule-transport channels for total wet nanopatterning. J. Mater. Chem 2008, 18, 5482–5491. [Google Scholar]
- Hirai, T; Leolukman, M; Liu, CC; Han, E; Kim, YJ; Ishida, Y; Hayakawa, T; Kakimoto, M; Nealey, PF; Gopalan, P. One-step direct-patterning template utilizing self-assembly of POSS-containing block copolymers. Adv. Mater 2009, 21, 4334–4338. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, H; Tanino, T; Shirota, Y. Surface relief grating formation on a single crystal of 4-dimethylaminoazobenzene. Appl Phys Lett 2005, 87, 061910:1–061910:3. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, H. Photoinduced surface relief grating formation on a (100) surface of a single crystal of 4-(dimethylamino)azobenzene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 16042–16045. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, H. Photoinduced surface relief grating formation on a co-crystal of 4-[bis(9,9-dimethylfluoren-2-yl)amino]azobenzene and ethyl acetate. ChemPhysChem 2008, 9, 2174–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, H; Seki, S; Kageyama, H. Photoinduced vitrification near the surfaces of single crystals of azobenzene-based molecular materials with glass-forming ability. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker, A. Crystal and molecular structure of C.I. Solvent Yellow 2, 1-phenylazo-4-(N,N-dimethylamine)-phenyl. J. Cryst. Spectr. Res 1992, 22, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Since the optical density for polarized light with polarization direction parallel to the b-axis was somewhat larger than that parallel to the a-axis, the b-axis was selected as a primary axis for determining H and V orientations of the sample crystal according to the previous works of SRG formation using single crystals [30–33].

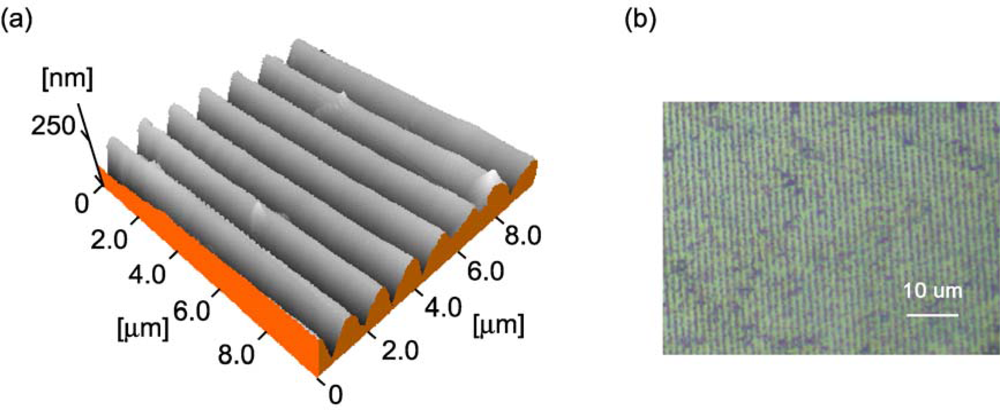
| Entry | Polarization of the writing beams | Orientation of the sample crystal | Modulation depth [nm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | p | H | 30–70 |
| 2 | p | V | 80–250 |
| 3 | s | H | 100–200 |
| 4 | s | V | 40–80 |
| Molecule | ɛrela | ɛrelb |
|---|---|---|
| A | 0.51 | 0.29 |
| B | 0.08 | 0.37 |
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakano, H. Photoinduced Surface Relief Grating Formation for a Single Crystal of 4-Aminoazobenzene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 1311-1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11041311
Nakano H. Photoinduced Surface Relief Grating Formation for a Single Crystal of 4-Aminoazobenzene. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2010; 11(4):1311-1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11041311
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakano, Hideyuki. 2010. "Photoinduced Surface Relief Grating Formation for a Single Crystal of 4-Aminoazobenzene" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 11, no. 4: 1311-1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11041311
APA StyleNakano, H. (2010). Photoinduced Surface Relief Grating Formation for a Single Crystal of 4-Aminoazobenzene. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 11(4), 1311-1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11041311