Enhancement Strategies in Transition Metal Oxides as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Reaction Mechanisms and Performance Regulation
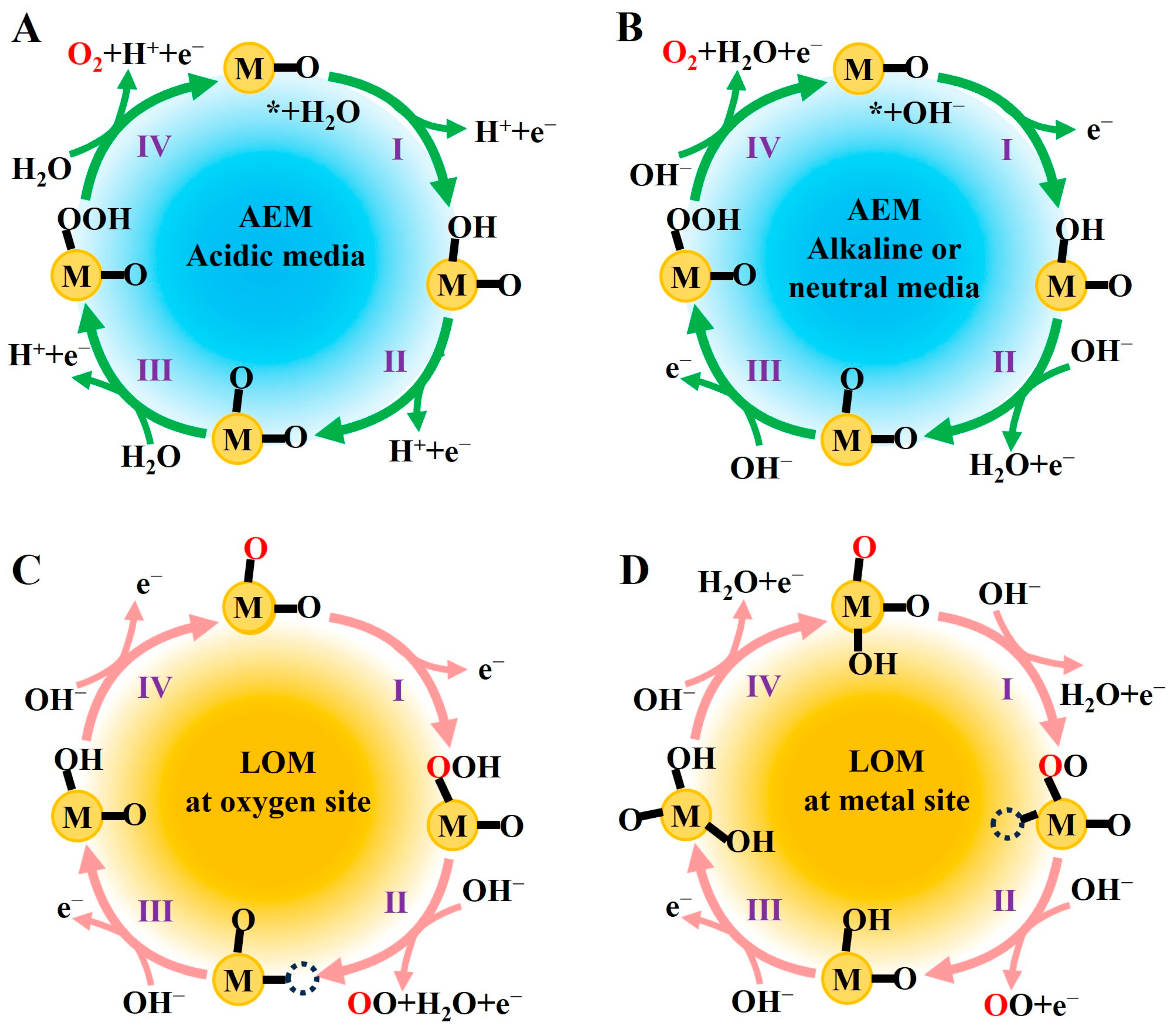
2.1. Fundamental Mechanisms of the OER
- (1)
- H2O dissociation adsorption: H2O adsorbs on the electrode surface and dissociates into H+ and OH−.
- (2)
- Deprotonation of OH*: OH− undergoes further deprotonation, generating O* and H+.
- (3)
- Bond formation: O* combines with another O* to form an O-O bond, producing O-OH*.
- (4)
- Deprotonation of O-OH*: O-OH* loses a proton, generating O2 and H+.
- (1)
- Lattice oxygen activation: Under applied potential, the covalency of the metal–oxygen bond (M-O) strengthens, and oxygen ligands lose electrons to form electrophilic oxygen species.
- (2)
- Nucleophilic attack: OH− or H2O molecules from the electrolyte attack the activated lattice oxygen, forming a superoxide-like group (O2−).
- (3)
- Oxygen vacancy formation: The release of lattice oxygen leads to the generation of surface oxygen vacancies (Ov).
- (4)
- Vacancy repair: Oxygen sources (H2O/OH−) from the solution fill the oxygen vacancies, restoring the catalyst structure.
2.2. Performance Regulation of TMOs
3. Optimization Strategies for the OER Catalytic Performance of TMOs
3.1. Morphology Control
3.1.1. Crystal Orientation Modulation
3.1.2. Architecting Multi-Dimensional Structures
3.2. Crystal Phase Change
3.2.1. Amorphization
3.2.2. Reconstruction
3.3. Support Engineering
3.3.1. Carbon Support
3.3.2. MXene Support
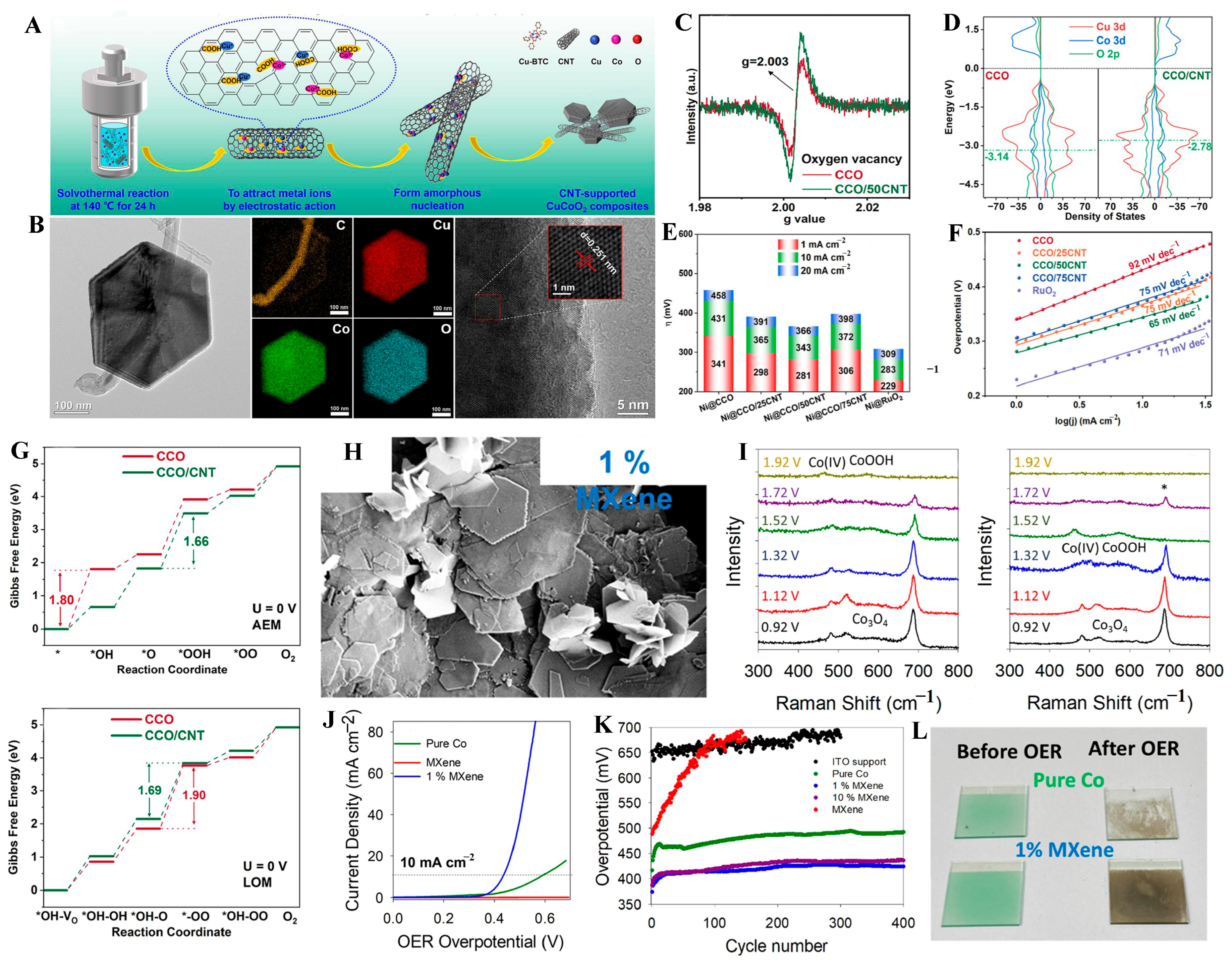
3.3.3. Graphitic C-N Support
3.4. Heteroatom Doping
3.4.1. Cationic Doping
3.4.2. Anionic Doping
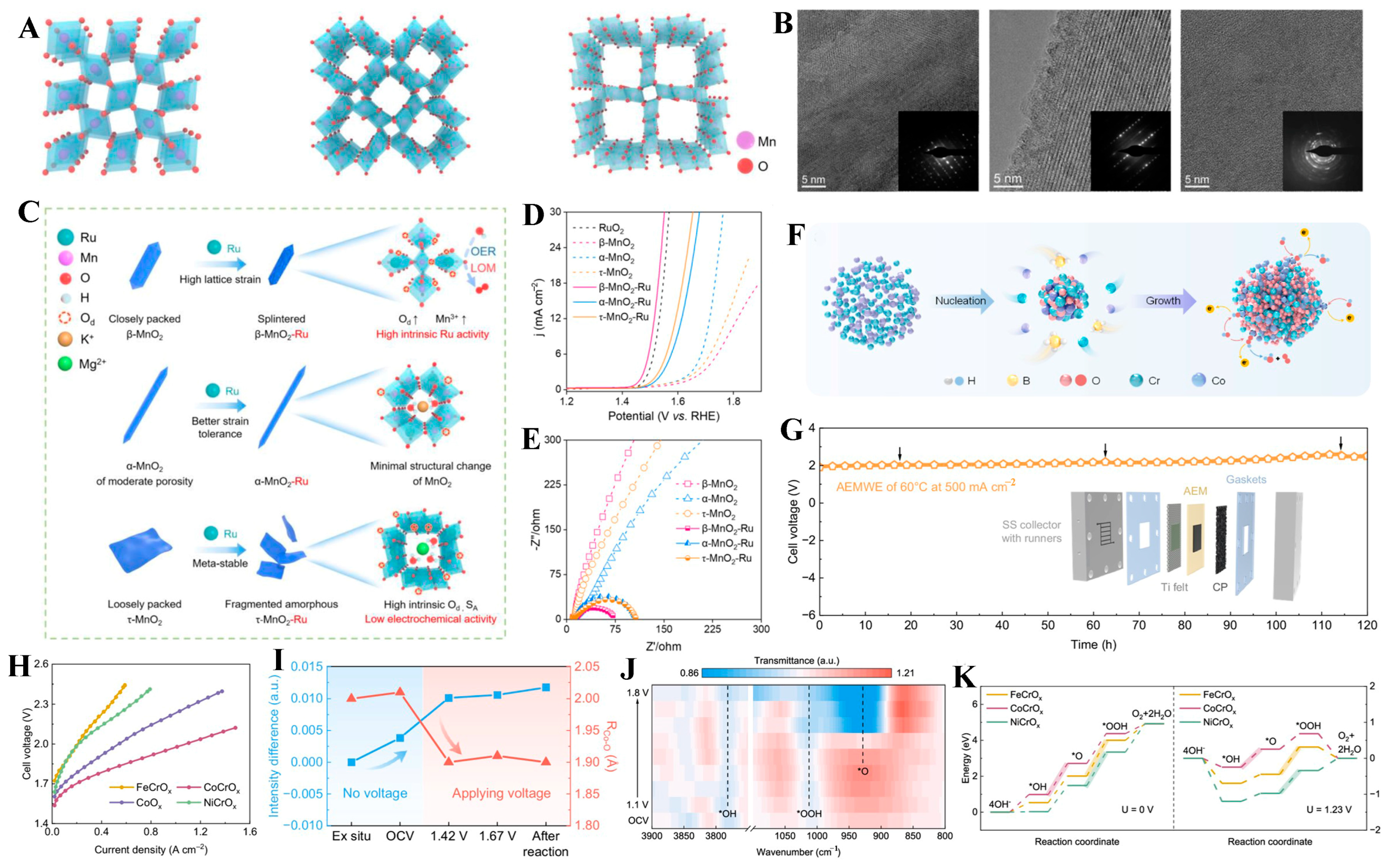
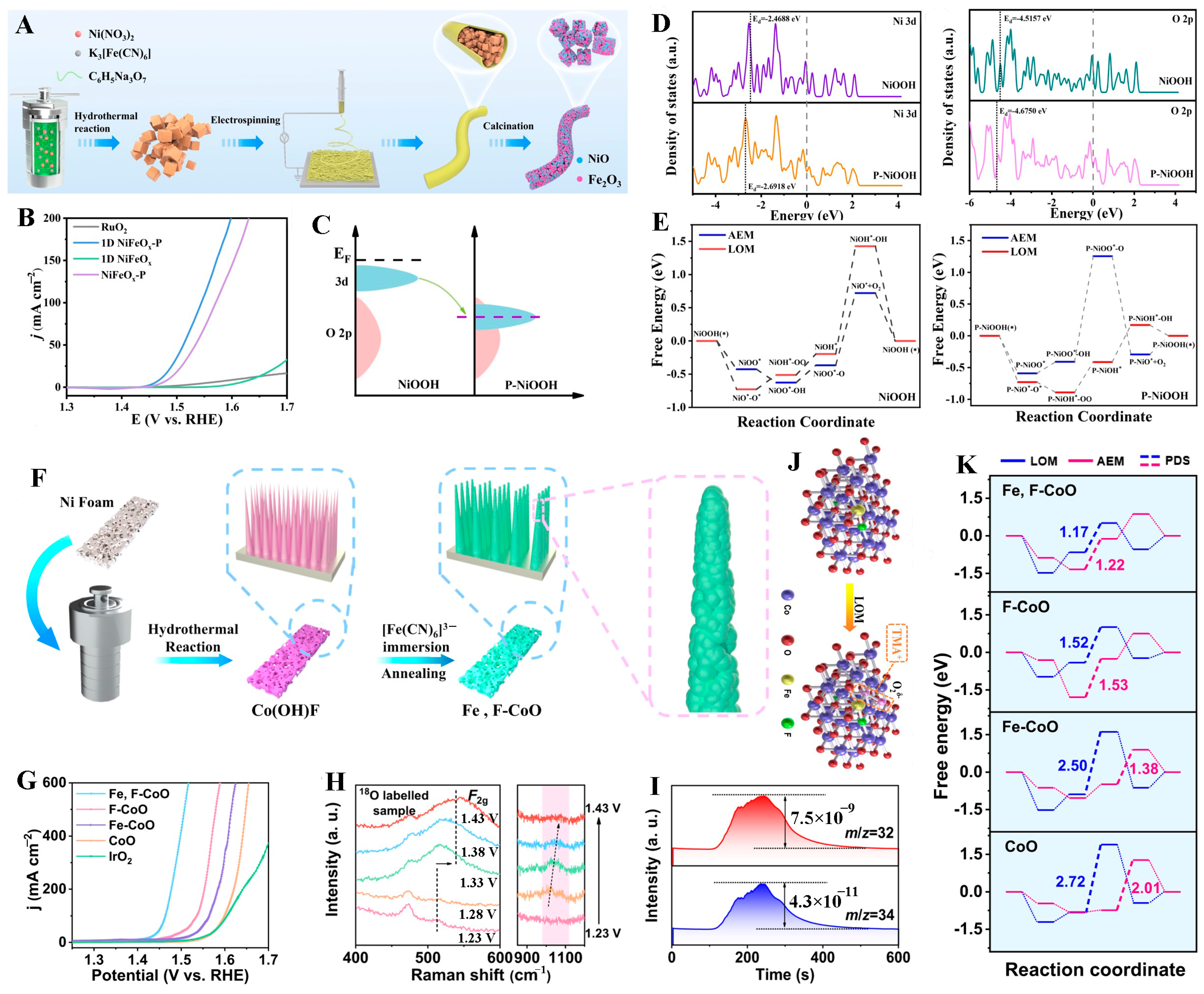
3.5. Heterostructure Construction
4. Conclusions and Outlook
- (1)
- Precise synthesis and structural control: Achieving precise and controllable synthesis of composition, crystal phase, size, morphology, and defect types remains highly challenging. Particularly for multi-metal oxides, the demanding synthesis conditions increase the complexity and unpredictability of preparation. Future efforts require the development of more scientific, precise, and scalable synthetic methods. These methods should be environmentally friendly, possess high atom economy, and enable the direct construction of stable catalyst structures on current collectors to ensure their practical application potential.
- (2)
- Active site identification and mechanism elucidation: The dynamic reconstruction of the catalyst surface during the OER process makes identifying the true active sites and stable phases extremely challenging. In the future, the development of time-resolved rapid in situ characterization technologies (such as time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy, fast-scanning electrochemical microscopy, in situ transient spectroscopy, etc.) will be crucial. These technologies can track the structural evolution of active sites and the formation and transformation of intermediates during the catalytic process on the millisecond or even microsecond scale, thus more accurately revealing the real-time reaction pathway and deactivation mechanism of OER.
- (3)
- Stability and degradation mechanisms: The dissolution kinetics and long-term durability of catalysts remain focal points of debate. Under the high anodic potentials of OER, oxide dissolution is a dynamic process whose mechanisms are not yet fully understood. There is a need to develop characterization protocols capable of tracking changes in catalyst structure, valence state, and composition over extended periods to systematically study degradation mechanisms. Strategies such as introducing vacancy defects to enhance structural stability and corrosion resistance are effective pathways for improving longevity.
- (4)
- Multifunctional application and broad-pH-range adaptability: Currently, high-performance catalysts are mostly confined to alkaline environments, with severely inadequate activity and stability in acidic or neutral media, limiting their application scope. Developing catalysts that exhibit both high activity and high stability across a broad pH range, especially under acidic conditions, is a critical future direction. Simultaneously, designing bifunctional or even trifunctional catalysts that couple OER with the HER and the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) is crucial for realizing next-generation energy conversion devices, such as overall water splitting and metal–air batteries.
- (5)
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies: AI can be applied to high-throughput screening to predict the components of TMOs with desirable electronic structures, stability, and activity; identify key descriptors from multi-dimensional data and establish a “structure–performance” relationship model; and guide the intelligent regulation of experimental conditions (such as temperature, precursor ratio, atmosphere, etc.), so as to realize the precise and controllable preparation of catalysts. In the future, the paradigm shift from “trial-and-error” research to “rational design-experimental validation” will be realized, which will greatly accelerate the development process of TMO catalysts and promote their translation from laboratory to industrial applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hussain, I.; Kathiresan, M.; Singh, K.; Kalidasan, B.; Mendhe, A.C.; Islam, M.N.; Meng, K.; Aslam, M.K.; Hanif, M.B.; Al Zoubi, W.; et al. Interface and surface engineering of MXenes and COFs for energy storage and conversion. InfoMat 2025, 7, e70011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Xing, X.; Qi, Q.; Li, H.; Han, D.; Song, X.; Tang, X.; Ng, Y.H.; Huo, P. Regulation CN reduction of CO2 products selectivity by adjusting the number of V sites and mechanism exploration. Fuel 2025, 388, 134509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Zhu, B.; Cui, Y.; Wei, H.; Bu, J.; Wang, F.; Huo, P.; Li, P.; Yan, Y. Setaria viridis-like hierarchical structure TiN nanofibers for high-performance supercapacitor. J. Power Sources 2024, 618, 235199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsmark, E.; Straus, J.; Granado, P. Developing hydrogen energy hubs: The role of H2 prices, wind power and infrastructure investments in Northern Norway. Appl. Energy 2024, 376, 124130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussmou, B.; Sigue, S.; Abderafi, S. Review of green hydrogen production technologies, to choose the optimal process of electrolysis-renewable energy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2026, 225, 116205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Jiang, J.; Hong, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Dong, H. State-of-the-art advancements in single atom electrocatalysts originating from MOFs for electrochemical energy conversion. Chin. J. Catal. 2024, 59, 38–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tüysüz, H. Alkaline Water Electrolysis for Green Hydrogen Production. Acc. Chem. Res. 2024, 57, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, G. Selenate oxyanion-intercalated NiFeOOH for stable water oxidation via lattice oxygen oxidation mechanism. J. Energy Chem. 2025, 101, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadakkayil, A.; Fahim, F.; Shohl, W.; Vullo, M.; Bloom, B.; Waldeck, D.H. Synergistic Spin-Mediated Catalysis for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 42659–42669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Q.; Singh, S.; Borrmann, H.; Hasse, V.; Yi, C.J.; Li, Y.K.; Schmidt, M.; Li, X.D.; Fecher, G.H.; et al. Topological semimetals with intrinsic chirality as spin-controlling electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. Nat. Energy 2025, 10, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alia, S.; Norman, A.; Miller, E. Fe-Doped Ni-Based Catalysts Surpass Ir-Baselines for Oxygen Evolution Due to Optimal Charge-Transfer Characteristics. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 17347–17359. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Qin, H.; Zhou, P.; Xiang, M.; Lian, Y.; Deng, Y. Regulating Ru-O bond and oxygen vacancies of RuO2 by Ta doping for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution in acid media. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 20584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Cai, Q.; Li, S.; Liang, D.; et al. Research progress on ruthenium-based materials in the oxygen evolution reaction of proton exchange membrane electrolysis water splitting. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2026, 548, 217178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnier, L.; Cossard, G.; Martin, V.; Pascal, C.; Roche, V.; Sibert, E.; Shchedrina, I.; Bousquet, R.; Parry, V.; Chatenet, M. Fe-Ni-based alloys as highly active and low-cost oxygen evolution reaction catalyst in alkaline media. Nat. Mater. 2024, 23, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qin, Z.; Qian, J.; Chen, L.; Shen, K. FeNi-LDH nanoflakes on Co-encapsulated CNT networks for stable and efficient ampere-level current density oxygen evolution. Appl. Catal. B 2024, 359, 124506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera, Z.; Yapur, A.; Rodríguez, O.; Díaz, J.; Martínez, L.; Videa, M. Nickel-Based Electrocatalysts for Water Electrolysis. Energies 2022, 15, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhou, X.; Lv, H.; Yu, H.; Yu, Y. Bimetallic-based electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2212160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Ma, M.; Gao, P.; Cao, D.; Cheng, D. Novel Ru-O3Se4 single atoms regulate the charge redistribution at Ni3Se2/FeSe2 interface for improved overall water splitting in alkaline media. Adv. Energy Mater. 2025, 15, 2402558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, P.; Medhi, H.; Bhattacharyya, K.; Hussain, C. Recent progress in the design and functionalization strategies of transition metal-based layered double hydroxides for enhanced oxygen evolution reaction: A critical review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 483, 215083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cho, J.; Ha, Y.; Haw, S.-C.; Wang, Z.; Lei, J.; Tang, J.; Liu, T.; et al. Heterostructure boosts a noble-metal-free oxygen-evolving electrocatalyst in acid. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 5972–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, K.; Nair, A.N.; Yadav, A.; Enriquez, L.G.; Pollock, C.J.; House, S.D.; Yang, S.; Guo, X.; Sreenivasan, S.T. Nickel-based single-molecule catalysts with synergistic geometric transition and magnetic field-assisted spin selection outperform RuO2 for oxygen evolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2302170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.S.; Vasudevan, S.; Panicker, U.G. Recent developments in CoFe-based materials for enhanced alkaline oxygen evolution reaction catalysis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2025, 200, 109984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Ha, J.S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, M.; Jeong, Y.-H.; Ditter, A.; Shapiro, D.A.; Yu, Y.-S.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, D. Boosting the performance of alkaline anion exchange membrane water electrolyzer with vanadium-doped NiFe2O4. Small 2025, 7, 2410006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, S.; Zhu, M.; Wang, F.; Yang, K.; Dong, B.; Yao, Q.F.; Hu, W. Enhancing water oxidation performance of transition metal oxides by atomically precise heteroatom doping. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 22806–22817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Xue, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, N.; Song, T.; Dong, H.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q. Unraveling the synergistic effect of heteroatomic substitution and vacancy engineering in CoFe2O4 for superior electrocatalysis performance. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 3503–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirizzi, L.; Muhyuddin, M.; Vecchio, C.; Mosca, E.; Baglio, V.; Gatto, I.; Berretti, E.; Lavacchi, A.; Ficca, V.; Viscardi, R.; et al. Amorphous nanostructured Ni-Fe oxide as a notably active and low-cost oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalyst for anion exchange membrane water electrolysis. Ind. Chem. Mater. 2025, 3, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Li, B.; Shao, Z.; Guo, W. Beyond conventional structures: Emerging complex metal oxides for efficient oxygen and hydrogen electrocatalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2025, 54, 1027–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kwon, S.; Ham, K.; Goddard, W.; Cho, K.; Kenis, P. Synergistic coupling of Ni-oxalate prism and layered FeOOH for oxygen evolution reaction in anion exchange membrane water electrolysis. App. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2025, 374, 125393. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, S.; Kang, B.; An, S.; Jung, H.; Kwon, J.; Oh, H.; Lim, J.; Choi, P.; Oh, J.; Cho, K.; et al. High-performance nickel-bismuth oxide electrocatalysts applicable to both the HER and OER in alkaline water electrolysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 11946–11955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Zhou, W.-K.; Qin, H.-F.; Lian, Y.-B.; Bai, J.-R. Recent advances in Co3O4-based electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 177, 151415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Z.; Kennedy, J.V.; Li, J.; Qian, D.; Liu, J.; et al. Fe2O3/P-doped CoMoO4 electrocatalyst delivers efficient overall water splitting in alkaline media. Appl. Catal. B 2024, 346, 123741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hou, J.; Ji, H.; Meng, D.; Qi, J.; San, X. Prediction of oxygen evolution activity for FeCoMn oxide catalysts via machine learning. Catalysts 2024, 14, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boppella, R.; Tan, J.; Manorama, S.; Moon, J. Anion-mediated transition metal electrocatalysts for efficient water electrolysis: Recent advances and future perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 427, 213552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Hu, J. Unveiling mechanistic regulation strategies in transition metal oxide catalysts for enhanced oxygen evolution reaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2026, 701, 138669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Tao, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, F.; Niu, Z.; Fan, M.; et al. Nitrogen-mediated promotion of cobalt-based oxygen evolution catalyst for practical anion-exchange membrane electrolysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 20379–20390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, C.; Menezes, P.; Steven Orthmann, S.; Driess, M. In Situ Formation of Nanostructured Core-Shell Cu3N-CuO to Promote Alkaline Water Electrolysis. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Duan, J.; Wen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhai, T. Stability of electrocatalytic OER: From principle to application. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 10709–10740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, C.; Huang, X.; Arandiyan, H.; Shao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y. Advances in oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalysts via direct oxygen-oxygen radical coupling pathway. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2416362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Goddard, W.; Xiao, H. Potential-dependent transition of reaction mechanisms for oxygen evolution on layered double hydroxides. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seh, Z.W.; Kibsgaard, J.; Dickens, C.F.; Chorkendorff, I.; Nørskov, J.K.; Jaramillo, T.F. Combining theory and experiment in electrocatalysis: Insights into materials design. Science 2017, 355, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svane, K.L.; Rossmeisl, J. Theoretical optimization of compositions of high-entropy oxides for the oxygen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, 202201146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, H.; Xi, S.; Lee, W.S.V.; Xue, J. Understanding of oxygen redox in the oxygen evolution reaction. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Wu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, J.; Cheng, N. Activating lattice oxygen in spinel oxides via engineering octahedral sites for oxygen evolution. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 3504–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, A.; Jayabal, S. Recent advances in transition metal dichalcogenide-based heterostructured materials for electrochemical water splitting applications. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2025, 9, 6324–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Xu, B.; Yu, X.; Ye, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guan, T.; Yang, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, K.; Wang, J. Activation of lattice oxygen in nitrogen-doped high-entropy oxide nanosheets for highly efficient oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 17806–17817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalifah, M.A.; Howchen, B.; Staddon, J.; Celorrio, V.; Tiwari, D.; Fermin, D.J. Correlating orbital composition and activity of LaMnxNi1−xO3 nanostructures toward oxygen electrocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 4439–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Yan, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, K.; An, W.; Chen, H.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zou, X. Electrocatalytic water oxidation activity-stability maps for perovskite oxides containing 3d, 4d and 5d transition metals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, 202311606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Yu, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, S.; Fu, Y.; Li, B. Fe ion doping as an effective strategy to enhance oxygen evolution reaction activity in NiCo2O4. J. Power Sources 2025, 630, 236159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zheng, X.; Huang, C.; Lv, S.; Xiang, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Wei, Z. The strain-mediated orbital synergy in Co3O4 for enhanced oxygen evolution reaction activity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2025, 13, 33188–33195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, H.; Chai, D.-F.; Zhang, W.; Qi, M.; Li, Y.; Dong, G.; Wang, Y.; Guo, D. Rapid and in-depth reconstruction of fluorine-doped bimetallic oxide in electrocatalytic oxygen evolution processes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 684, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X. Understanding the mechanism of the oxygen evolution reaction with consideration of spin. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2021, 4, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.; Ma, Y.; An, H.; Wang, H.; Zou, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. High-spin Co3+ in cobalt oxyhydroxide for efficient water oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Chen, Z.; Sun, S.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Z. Spin-state transition represses the surface reconstruction for efficient water oxidation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 11607–11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Cai, W.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, K.; Huang, B.; Liu, Z. Spin polarization induced rapid reconstruction of transition metal oxide for efficient water electrolysis. Chem. Sci. 2025, 16, 14750–14759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, G.; Zeng, L.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, W. A universal process: Self-templated and orientated fabrication of XMoO4 (X: Ni, Co, or Fe) nanosheets on MoO2 nanoplates as electrocatalysts for efficient water splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 33785–33794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.P.; Rahman, M.S.; Scheideler, W.J. 3D printed microlattices of transition metal/metal oxides for highly stable and efficient water splitting. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2400160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wan, H.; Chen, G.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Ma, W.; Liu, X.; Ma, R. Multi-shelled cobalt-nickel oxide/phosphide hollow spheres for an efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 10918–10927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
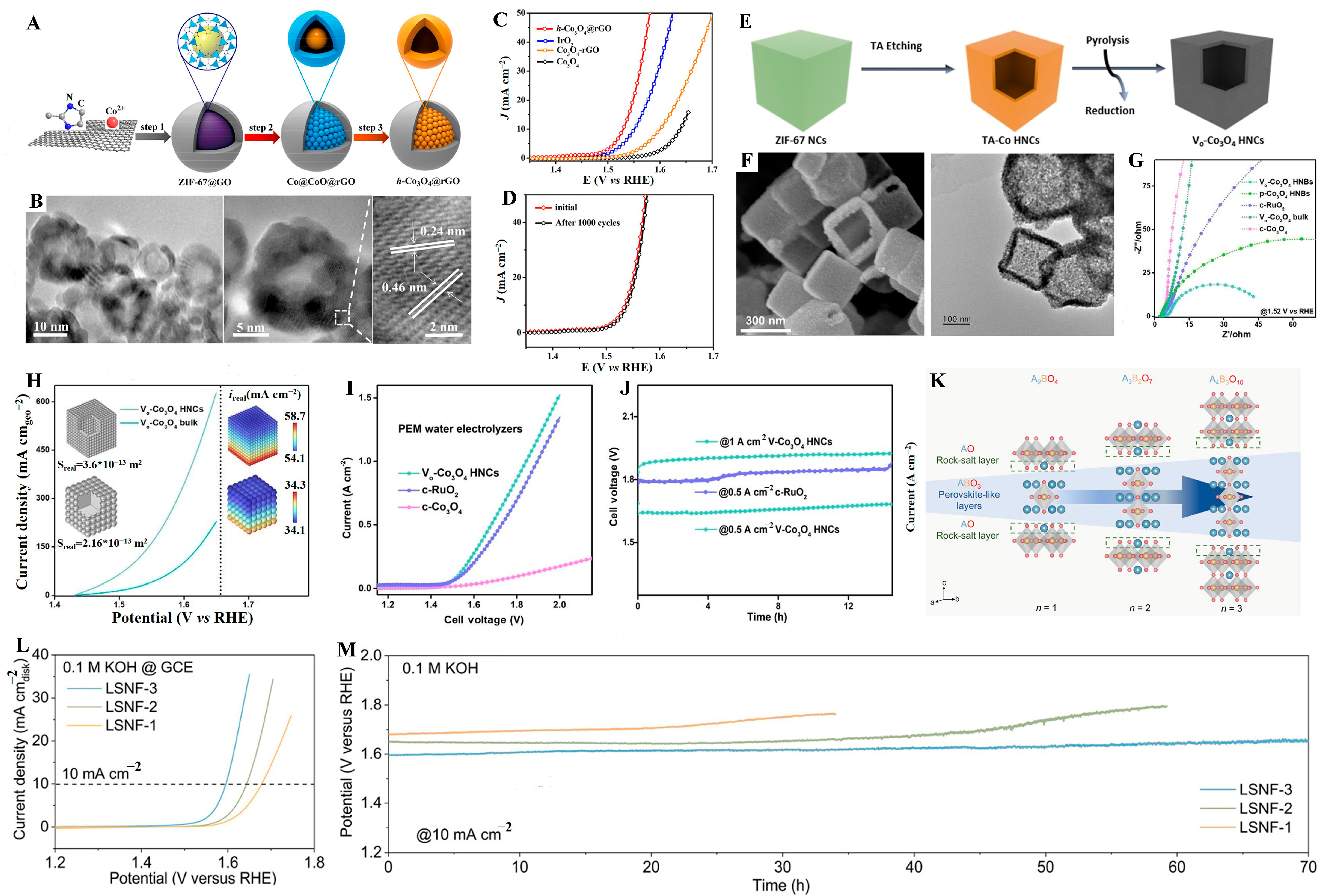
- Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Shao, C.; Ke, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Jin, H.; Da, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, W. Facet-dependent lattice oxygen activation on oxygen-defective Co3O4 for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Energy Lett. 2024, 9, 2182–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Xiao, X.; Shan, Y.; Bai, Y.; Xue, H.; Pang, H.; Tian, Z.; Xu, Q. In situ anchoring polymetallic phosphide nanoparticles within porous Prussian blue analogue nanocages for boosting oxygen evolution catalysis. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 3016–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
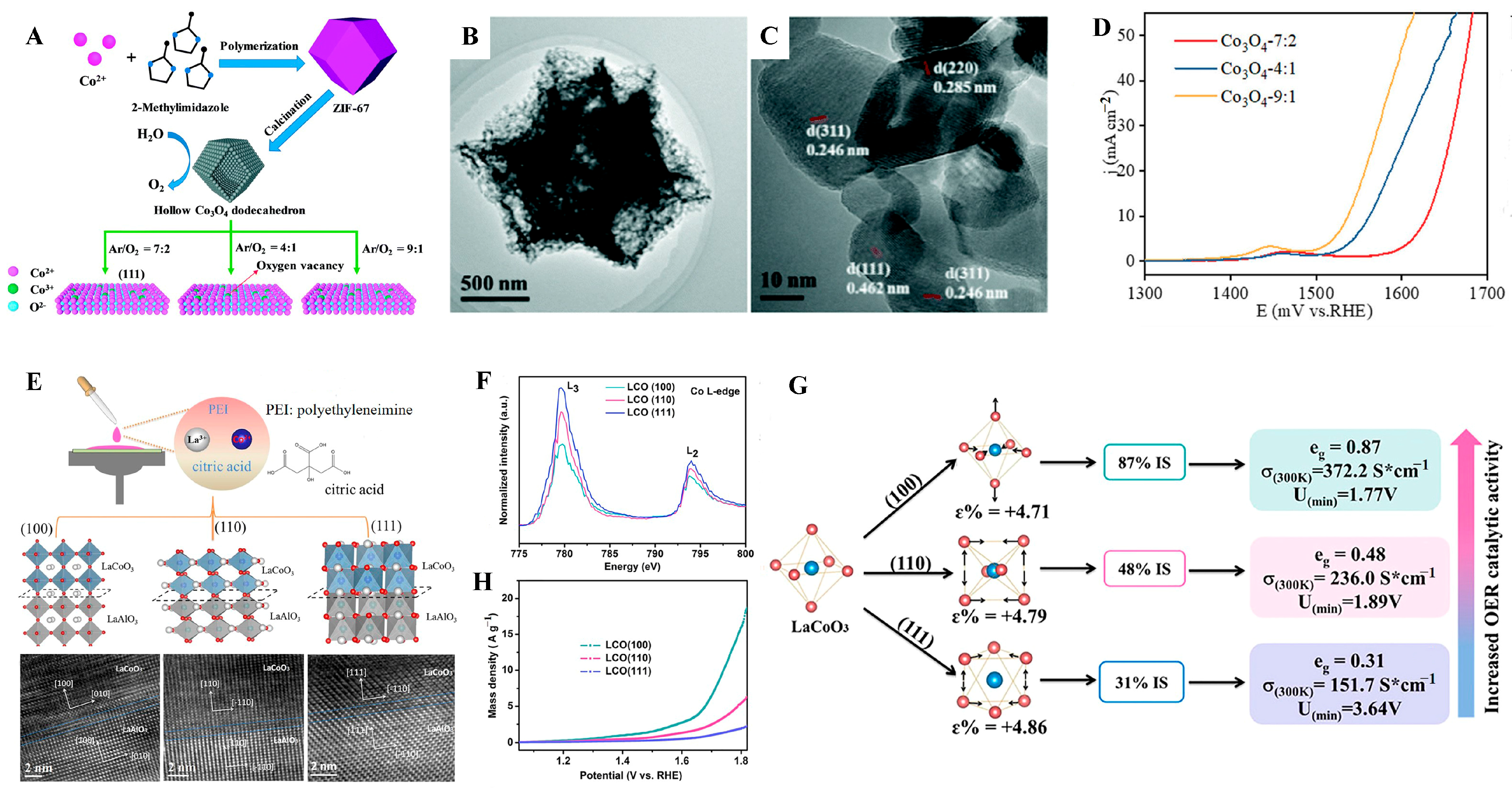
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhen, Y.; Nan, J.; Dong, B.; Chai, Y. Crystal facet engineering of perovskite cobaltite with optimized electronic regulation for water splitting. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 2665–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Huang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Z.; Liao, Y.; Lai, Y.; Chen, C.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, K.; et al. Structural anisotropy determining the oxygen evolution mechanism of strongly correlated perovskite nickelate electrocatalyst. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 4262–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füngerlings, A.; Wohlgemuth, M.; Antipin, D.; van der Minne, E.; Kiens, E.M.; Villalobos, J.; Risch, M.; Gunkel, F.; Pentcheva, R.; Baeumer, C. Crystal-facet-dependent surface transformation dictates the oxygen evolution reaction activity in lanthanum nickelate. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Sun, H.; Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Q.; Lai, X. Hollow Co3O4 dodecahedrons with controlled crystal orientation and oxygen vacancies for the high-performance oxygen evolution reaction. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Guo, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Yan, W.; Chu, W.; Wu, C.; Xie, Y. Spin-state regulation of perovskite cobaltite to realize enhanced oxygen evolution activity. Chem 2017, 3, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gil-Sepulcre, M.; Lee, J.; Bui, V.; Wang, Y.; Rudiger, O.; Kim, M.; DeBeer, S.; Tuysuz, H. Iridium single-atom-ensembles stabilized on Mn-substituted spinel oxide for durable acidic water electrolysis. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2401648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Kuang, S.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X. Boosting oxygen evolution over inverse spinel Fe-Co-Mn oxide nanocubes through electronic structure engineering. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 134446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, S.; Su, F.; Tang, K. Quenching-etching surface engineering of NiO nanosheets with rich defects for highly enhanced electrocatalytic oxygen evolution activity. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 88, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.T.A.; Pawar, S.M.; Inamdar, A.I.; Kim, H.; Im, H. A morphologically engineered robust bifunctional CuCo2O4 nanosheet catalyst for highly efficient overall water splitting. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 7, 1901515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, F.; Ke, F.; Cheng, G.; Luo, W. Carbon encapsulated hollow Co3O4 composites derived from reduced graphene oxide wrapped metal-organic frameworks with enhanced lithium storage and water oxidation properties. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 10649–10655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, C.; Wang, S.; Shen, X.; Jia, C.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C. Defect-balanced active and stable Co3O4−x for proton exchange membrane water electrolysis at ampere-level current density. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 4196–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guan, D.; Gu, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Shao, Z.; Guo, Y. Tuning synergy between nickel and iron in Ruddlesden-Popper perovskites through controllable crystal dimensionalities towards enhanced oxygen-evolving activity and stability. Carbon Energy 2024, 6, e465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Liu, D.; Yan, X.; Guo, P.; Ding, X.; Xiang, K.; Tu, X.; Guo, Y.; Wu, R. Oxygen vacancy-enriched amorphous transition metal ternary oxides toward highly efficient oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Mater. Lett. 2024, 6, 2948–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Hu, P.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Guo, L. Amorphous materials emerging as prospective electrodes for electrochemical energy storage and conversion. Chem 2023, 9, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
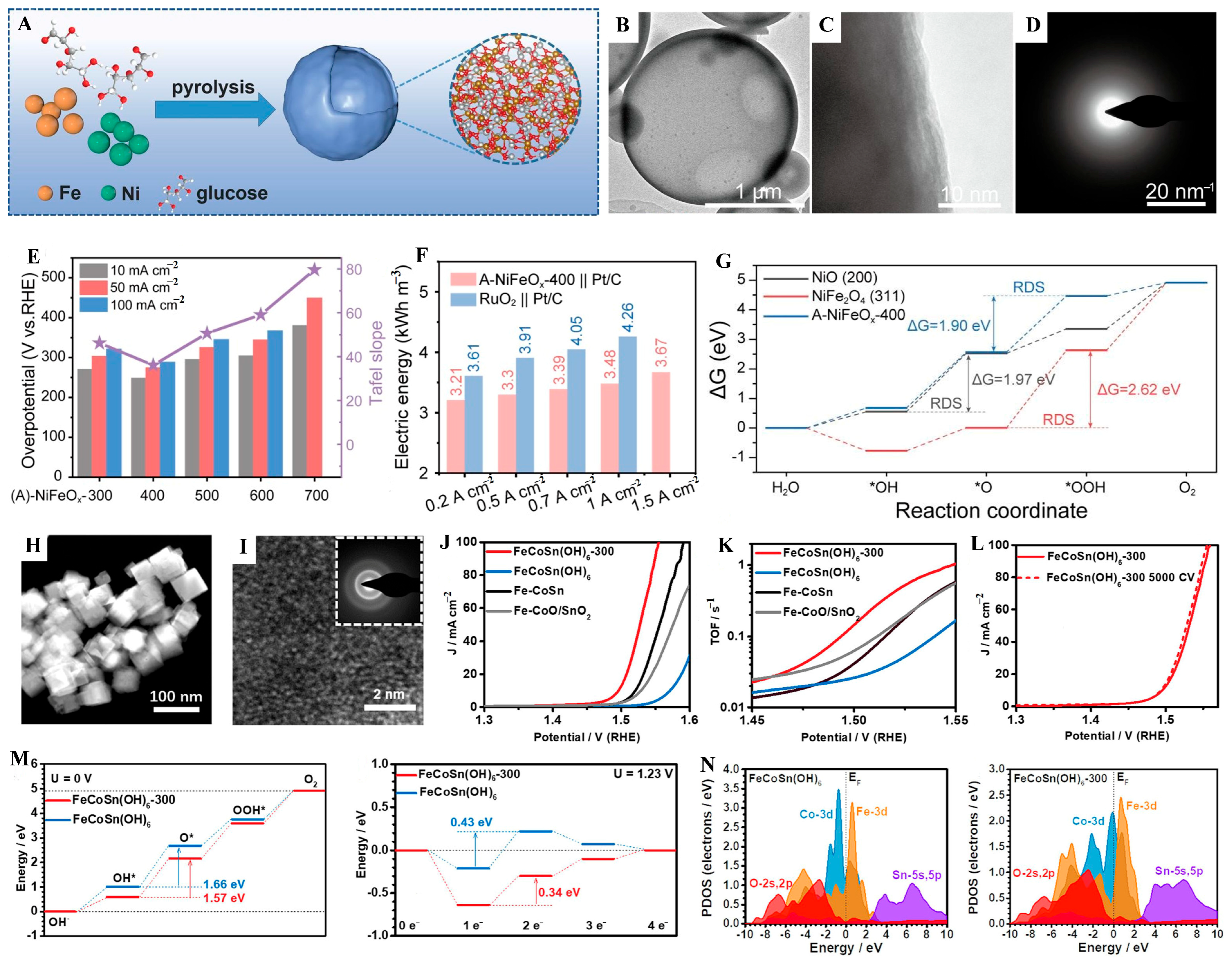
- Duan, Y.; Yu, Z.Y.; Hu, S.J.; Zheng, X.S.; Zhang, C.T.; Ding, H.H.; Hu, B.C.; Fu, Q.Q.; Yu, Z.L.; Zheng, X.; et al. Scale-up synthesis of amorphous NiFeMo oxides and their rapid surface reconstruction for superior oxygen evolution catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 15772–15777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Duan, Z.; Ren, L.; Ji, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Q.; Wu, H.; et al. Unveiling the accelerated water electrolysis kinetics of heterostructural iron-cobalt-nickel sulfides by probing into crystalline/amorphous interfaces in stepwise catalytic reactions. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2201903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Lai, F.; Song, B.; Wang, S.; Singh, H.; Talebi, P.; Zhu, L.; Niu, Y.; King, G.; Huang, Y.; et al. Correction: Scalable synthesis of amorphous NiFe oxide hollow microspheres via glucose-mediated spray pyrolysis for industrial hydrogen production. Energy Environ. Sci. 2025, 18, 8711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Geng, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, G.; Huang, B.; Hu, Z.; Lee, J.-F.; Lai, Y.-H.; Chu, Y.H.; et al. A top-down strategy for amorphization of hydroxyl compounds for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rücker, K.K.; Taffa, D.H.; Bisen, O.; Risch, M.; Hayes, D.; Brim, E.; Richards, R.M.; Harms, C.; Wark, M.; Lorenz, J. Influence of Co and Mn Doping on the Surface Reconstruction of Faceted NiO (111) Nanosheets after the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2025, 129, 9341–9355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasulo, F.; Massaro, A.; Pecoraro, A.; Pavone, M. Role of defect-driven surface reconstructions in transition metal oxide electrocatalysis towards OER/ORR: A quantum-mechanical perspective. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2023, 42, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, A.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Meng, H.; Wang, Z.; Diao, C.; Xue, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Promoting surface reconstruction in spinel oxides via tetrahedral-octahedral phase boundary construction for efficient oxygen evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202409912. [Google Scholar]
- Yeom, K.; Jo, J.; Shin, H.; Moon, S.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; Shim, J.; Mok, D.; Bootharaju, M.; Back, S. Unraveling Surface Reconstruction During Oxygen Evolution Reaction on the Defined Spinel Oxide Surface. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Shi, C.; Xu, H.; Gu, Y.; Sha, Y.; Hu, Z.; Ni, M.; Shao, Z. Simultaneously mastering operando strain and reconstruction effects via phase-segregation strategy for enhanced oxygen-evolving electrocatalysis. J. Energy Chem. 2023, 82, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, J.; Ge, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Dai, L.; Li, S.; Li, W. Carbon-based bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reactions: Optimization strategies and mechanistic analysis. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 71, 234–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, N.; Zhou, X.; Yue, Z.; Shan, Y.; Chen, K.; Yu, X. MXene introduced between CoNi LDH and NiMoO4 nanorods arrays: A bifunctional multistage composite for OER catalyst and supercapacitors. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 86, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Zhang, W.; Yu, B.; Hu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, D. Three-dimensional porous cobalt ferrite and carbon nanorod hybrid network as highly efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 11489–11500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Gong, S.; Ji, L.; Huang, J.; Xu, M.; Chen, Z. Three-dimensional porous ultrathin carbon networks reinforced PBAs-derived electrocatalysts for efficient oxygen evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elayappan, V.; Shanmugam, R.; Chinnusamy, S.; Yoo, D.J.; Mayakrishnan, G.; Kim, K.; Noh, H.S.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, H. Three-dimensional bimetal TMO supported carbon based electrocatalyst developed via dry synthesis for hydrogen and oxygen evolution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 505, 144642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanan, A.; Shu, D.; Aftab, U.; Cao, D.; Laghari, A.J.; Solangi, M.Y.; Abro, M.I.; Nafady, A.; Vigolo, B.; Tahira, A.; et al. Co2FeO4@rGO composite: Towards trifunctional water splitting in alkaline media. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 33919–33937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Jiang, C.; Bai, J.; Sun, L.; Tan, H.; Liu, L.; Zeng, X.; Zhao, X.; Xiong, D. The interaction of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with CuCoO2 nanosheets promotes structural modification and enhances their OER performance. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2024, 11, 3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, T.P.; Shingte, S.R.; Chavan, V.D.; Kim, D.-K.; Mujawar, S.H.; Dongale, T.D.; Patil, P.B. CoFe2O4 nanoparticle embedded carbon nanofibers: A promising non-noble metal catalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 92, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xie, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, R.; Ma, F.; Liu, M.; Zou, J. Fe2O3/spinel NiFe2O4 heterojunctions in-situ wrapped by one-dimensional porous carbon nanofibers for boosting oxygen evolution/reduction reactions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 21329–21343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anne, B.R.; Kundu, J.; Kabiraz, M.K.; Kim, J.; Cho, D.; Choi, S.-I. A review on MXene as promising support materials for oxygen evolution reaction catalysts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2306100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Hassan, M.M.U.; Mehran, M.T.; Baig, M.M.; Hussain, S.; Shahzad, F. 2D MXenes and their heterostructures for HER, OER and overall water splitting: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 2794–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, S.; Hosseini, S.A.; Alishahi, M. CuCo2O4/Ti3C2Tx MXene hybrid electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction of water splitting. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 920, 165811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.M.C.; Quang, T.A.; Gnanasekaran, L.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Vasseghian, Y.; Joo, S.-W. Co3O4-RuO2/Ti3C2Tx MXene electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction in acidic and alkaline media. ChemSusChem 2025, 18, e202402270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, X.; Mao, Y.; Wang, F.; Gao, X.-T.; Qiu, S.; Le, S.; Sun, K.-N. MXene-supported Co3O4 quantum dots for superior lithium storage and oxygen evolution activities. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyndall, D.; Gannon, L.; Hughes, L.; Carolan, J.; Pinilla, S.; Jaśkaniec, S.; Spurling, D.; Ronan, O.; McEvoy, N.; Nicolosi, V.; et al. Understanding the effect of MXene in a TMO/MXene hybrid catalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 2023, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, P.V.; Mane, P.; Chakraborty, B.; Rout, C.S. Spinel NiFe2O4 nanoparticles decorated 2D Ti3C2 MXene sheets for efficient water splitting: Experiments and theories. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 602, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, R.; Paswan, S.K.; Kumar, L.; Singh, G.P.; Haldar, K.K. Ti3C2Tx nanosheet/NiFe2O4 nanoparticle composites for electrocatalytic water splitting. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2025, 8, 1649–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Yang, Y. Graphitic carbon nitride for electrochemical energy conversion and storage. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 2796–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, X.; Shen, H.; Jiang, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, W.; Li, J. Co3O4@g-C3N4 supported on N-doped graphene as effective electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 20687–20695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yu, S.; Ge, R.; Feng, L.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, W. Cobalt oxide supported on phosphorus-doped g-C3N4 as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 4718–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeghan, S.M.N.; Seo, B.; Son, H.; Joo, S.W.; Kim, M.; Lee, G. Exfoliated defects-rich g-C3N4 nanosheets heterointerface engineering with CuCo2O4 as promising bifunctional electrocatalysts for seawater splitting. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, S.; Nam, S.; Kim, H. Interfacial engineering of α-Fe2O3 coupled Co3O4 heterostructures anchored on g-C3N4 structure for enhanced electrocatalytic performance in alkaline oxygen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 53, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararaj, S.B.; Tamilarasan, S.; Kadirvelu, K.; Thangavelu, S. Electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction and methanol oxidation using surface-oriented stable NiSnO3 nanospheres anchored g-C3N4 nanosheets. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 612, 155785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, G.; Han, S.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, J.; Sun, M.; Yu, L. Flower-like NiCo2O4-CN as efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for Zn-air battery. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 341, 135997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Lai, W.; Li, P.; Ye, C.; Liu, N.; Dou, S.; Pan, H.; Sun, W. Enriched d-band holes enabling fast oxygen evolution kinetics on atomic-layered defect-rich lithium cobalt oxide nanosheets. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ede, S.R.; Luo, Z.P. Tuning the intrinsic catalytic activities of oxygen-evolution catalysts by doping: A comprehensive review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 20131–20163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Li, H.; Pei, K.; Wong, L.W.; Zheng, X.; Tsang, C.S.; Chen, H.; Shen, W.; Ly, T.H.; Zhao, J.; et al. Strategic design for high-efficiency oxygen evolution reaction (OER) catalysts by triggering lattice oxygen oxidation in cobalt spinel oxides. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 33718–33728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Gu, Y.D.; Lian, Y.B.; Su, Y.H.; Hu, J.P.; Zhao, X.H.; Peng, Y.; Feng, K.; et al. Ru-substituted MnO2 for accelerated water oxidation: The feedback of strain-induced and polymorph-dependent structural changes to the catalytic activity and mechanism. ACS Catal. 2022, 13, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhong, X.; Hu, Z.; Huang, W.-H.; Pao, C.-W.; Cheng, H.; Alonso-Vante, N.; Ma, J. Universal synthesis strategy for preparation of transition metal oxide electrocatalysts doped with noble metal single atoms for oxygen evolution reaction. Energy Adv. 2024, 3, 2002–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, Z.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, S.; Wang, Y. Self-healing iridium-doped manganese oxide for boosting stability of acidic oxygen evolution. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2417766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Su, Y.; Qin, H.; Cao, Z.; Wei, H.; Wu, F.; Ou, G. Ir-doped Co3O4 as efficient electrocatalyst for acidic oxygen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 14642–14649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Xie, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, S. Synergistic interfacial effect of Ru/Co3O4 heterojunctions for boosting overall water splitting. Small 2024, 20, 2309633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Parreiras, S.O.; Lee, S.; Banjac, K.; Boureau, V.; Gallego, J.M.; Hu, X.; Écija, D.; Lingenfelder, M. Operando Nanoscale Characterization Reveals Fe Doping of Ni Oxide Enhances Oxygen Evolution Reaction via Fragmentation and Formation of Dual Active Sites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202419521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Feng, M.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, Y.; Yue, X.; Huang, S. Constructing oxygen vacancies by doping Mo into spinel CO3O4 to trigger a fast oxide path mechanism for acidic oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 8796–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Debata, S.; Madhuri, R.; Sharma, P.K. Electrocatalytic behavior of transition metal (Ni, Fe, Cr) doped metal oxide nanocomposites for oxygen evolution reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 449, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Qin, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, D.; et al. Highly efficient anion exchange membrane water electrolyzers via chromium-doped amorphous electrocatalysts. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Zhu, A.; Zhao, C.; Yu, M.; Shi, G.; Yan, J.; Sun, S.; Wang, W. Enhancing oxygen evolution reaction by simultaneously triggering metal and lattice oxygen redox pair in iridium loading on Ni-doped CO3O4. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2302537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Jin, S.; Chen, H.; Lee, W.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y. Anionic defect engineering of transition metal oxides for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 5875–5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, C.; Kong, Y.; Huo, Q.; Mi, L.; Sun, J.; Cao, J.; Shao, J.; Chen, X.; Zhou, W.; et al. Unlocking the transition of electrochemical water oxidation mechanism induced by heteroatom doping. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202309732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, X. Preparation of Fe/P co-doped MMoO4 (M=Co, Cu and Zn) as environmentally friendly oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalyst. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 48, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Xie, J.; Tong, Z.; Chi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, X.; Lin, Z.; Wang, L.; Chai, Y. Synergistic effect of metallic nickel and cobalt oxides with nitrogen-doped carbon nanospheres for highly efficient oxygen evolution. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Fang, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Mo, C.; Ning, J.; Hu, Y. Lattice oxygen activation and local electric field enhancement by co-doping Fe and F in CoO nanoneedle arrays for industrial electrocatalytic water oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Lu, Y.; Murad, M.; Pei, C.; Liu, Q.; Park, H.S.; Pang, H.; Yu, X. Dimension-dependent heterostructure catalysts for acidic oxygen evolution reaction: Challenges and prospects. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2026, 547, 217072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, R.; Anandhababu, G.; Xie, J.; Lv, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, M.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. Cobalt/iron(oxides) heterostructures for efficient oxygen evolution and benzyl alcohol oxidation reactions. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhao, M.; Yuan, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, H.; Chen, D.; Fu, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, C. Oxygen vacancies and interface engineering on amorphous/crystalline CrOx-Ni3N heterostructures toward high-durability and kinetically accelerated water splitting. Small 2022, 18, 2106554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.L.; Xu, H.M.; Zhu, H.R.; Shuai, T.Y.; Zhan, Q.N.; Huang, C.J.; Li, G.R. Heterostructured electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 18832–18865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, K.; Xi, S.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; et al. Cation-vacancy-rich NiFe2O4 nanoparticles embedded in Ni3Se2 nanosheets as an advanced catalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Ge, W.; Deng, S.; Zhou, Q.; Deng, S.; Yang, P. In-situ constructing of NiO/CoFe2O4 heterojunction through oxophilicity engineering for efficient water oxidation. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1016, 178952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
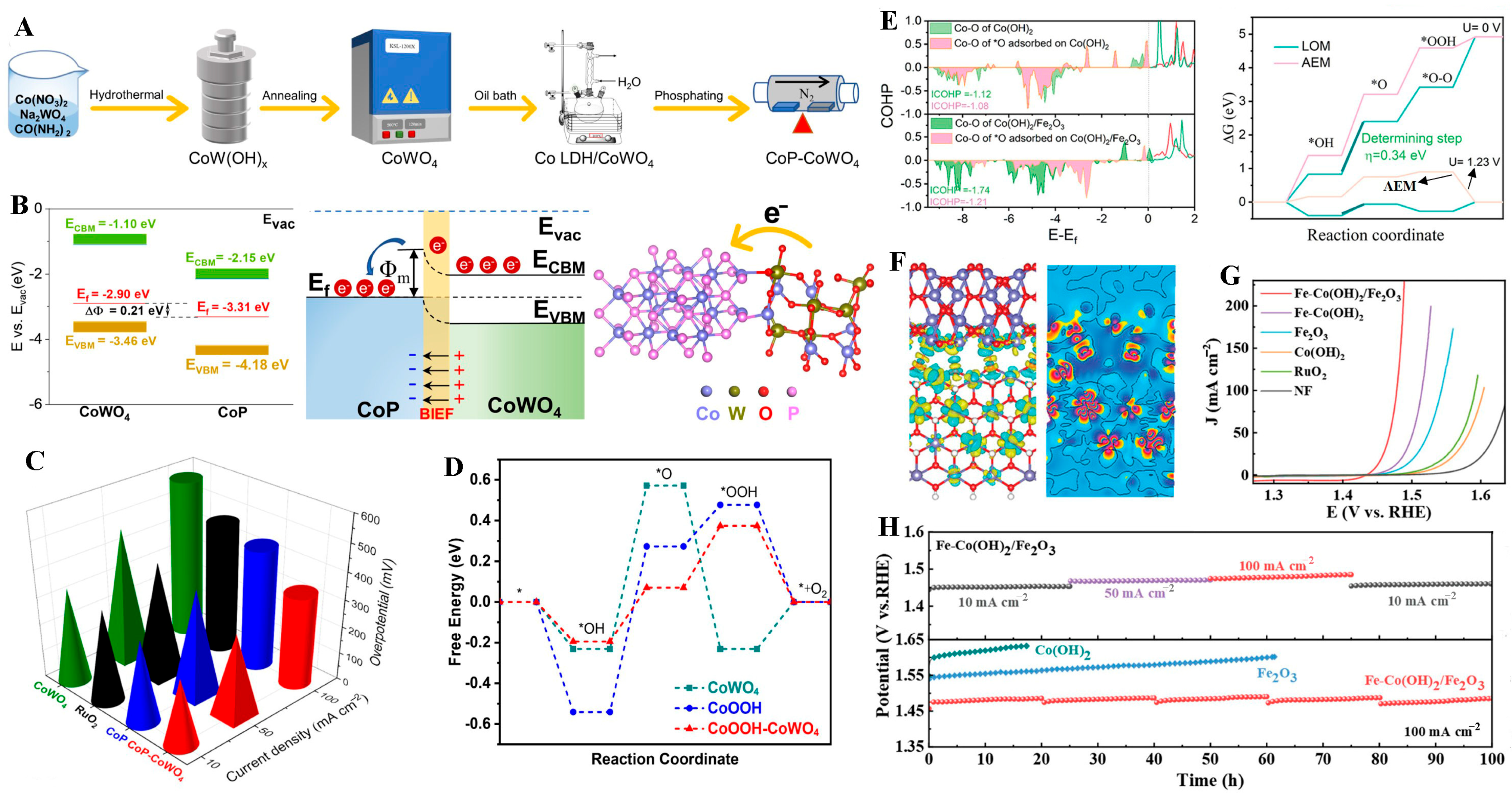
- Yan, L.; Deng, J.; Li, H. Nanoflower-Like CoP-CoWO4 Heterostructures for Enhanced Oxygen Evolution Reaction. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2025, 8, 8702–8711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Tang, Y.; Jia, B.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Bao, R.; Li, C.; Yi, J.; Wang, J.; Ma, T. Coupling adsorbed evolution and lattice oxygen mechanism in Fe-Co(OH)2/Fe2O3 heterostructure for enhanced electrochemical water oxidation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2305243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, P.; Niu, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, W.; Song, B.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, P. Magnetic field enhanced electrocatalytic oxygen evolution of NiFe-LDH/Co3O4 p-n heterojunction supported on nickel foam. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2200084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Catalyst | Modulation | Electrolyte | Mechanism | Overpotential | Stability | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LaCoO3 (100) film | Crystal orientation | 1 M KOH | AEM | 470 mV at 6.58 A g−1 | 20,000 s at 6.58 A g−1 | [64] |
| Vo-Co3O4 HNCs | Hollow structures | 0.50 M H2SO3 | LOM | 265 mV at 10 mA cm−2 | 130 h at 20 mAcm−2 | [70] |
| A-NiFeOx-400 | Amorphization | 1 M KOH | AEM | 248 mV at 10 mA cm−2 | 16 h at 10 mA cm−2 | [76] |
| FeCoSn(OH)6-300 | Amorphization | 1 M KOH | AEM | 266 mV at 10 mA cm−2 | 200 h at 100 mA cm−2 | [77] |
| CCO/50CNT | Carbon Support | 1 M KOH | AEM and LOM | 343 mV at 10 mA cm−2 | 18 h at 10 mA cm−2 | [89] |
| Ti3C2Tx sheets/NiFe2O4 | MXene Support | 1 M KOH | 181 mV at 10 mA cm−2 | [99] | ||
| β-MnO2-Ru | Cationic Doping | 1 M KOH | LOM | 278 mV at 10 mA cm−2 | 50 h at 10 mA cm−2 | [110] |
| CoCrOx | Cationic Doping | 1 M KOH | AEM | 268 mV at 10 mA cm−2 | 120 h at 500 mA cm−2 | [118] |
| NiFeOx-P | Anionic Doping | 1 M KOH | LOM | 237 mV at 10 mA cm−2 | 120 h at 70 mA cm−2 | [121] |
| Fe, F-CoO NNAs | Doping | 1 M KOH | LOM | 169 mV at 10 mA cm−2 | 300 h at 500 mA cm−2 | [124] |
| Fe-Co(OH)2/Fe2O3 | Heterostructure | 1 M KOH | AEM and LOM | 219 mV at 10 mA cm−2 | 100 h at 100 mA cm−2 | [132] |
| NiFe-LDH/Co3O4/NF | Heterostructure | 1 M KOH | AEM | 274 mV at 50 mA cm−2 | 48 h at 50 mA cm−2 | [133] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Song, N.; Wang, N.; He, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, Y. Enhancement Strategies in Transition Metal Oxides as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Molecules 2026, 31, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules31010147
Li P, Song N, Wang N, He Y, Zhu Z, Yan Y. Enhancement Strategies in Transition Metal Oxides as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Molecules. 2026; 31(1):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules31010147
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Pengxin, Ning Song, Naxiang Wang, Yan He, Zhi Zhu, and Yongsheng Yan. 2026. "Enhancement Strategies in Transition Metal Oxides as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction" Molecules 31, no. 1: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules31010147
APA StyleLi, P., Song, N., Wang, N., He, Y., Zhu, Z., & Yan, Y. (2026). Enhancement Strategies in Transition Metal Oxides as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Molecules, 31(1), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules31010147







