Dynamic Variation of Secondary Metabolites from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua Rhizomes During Repeated Steaming–Drying Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
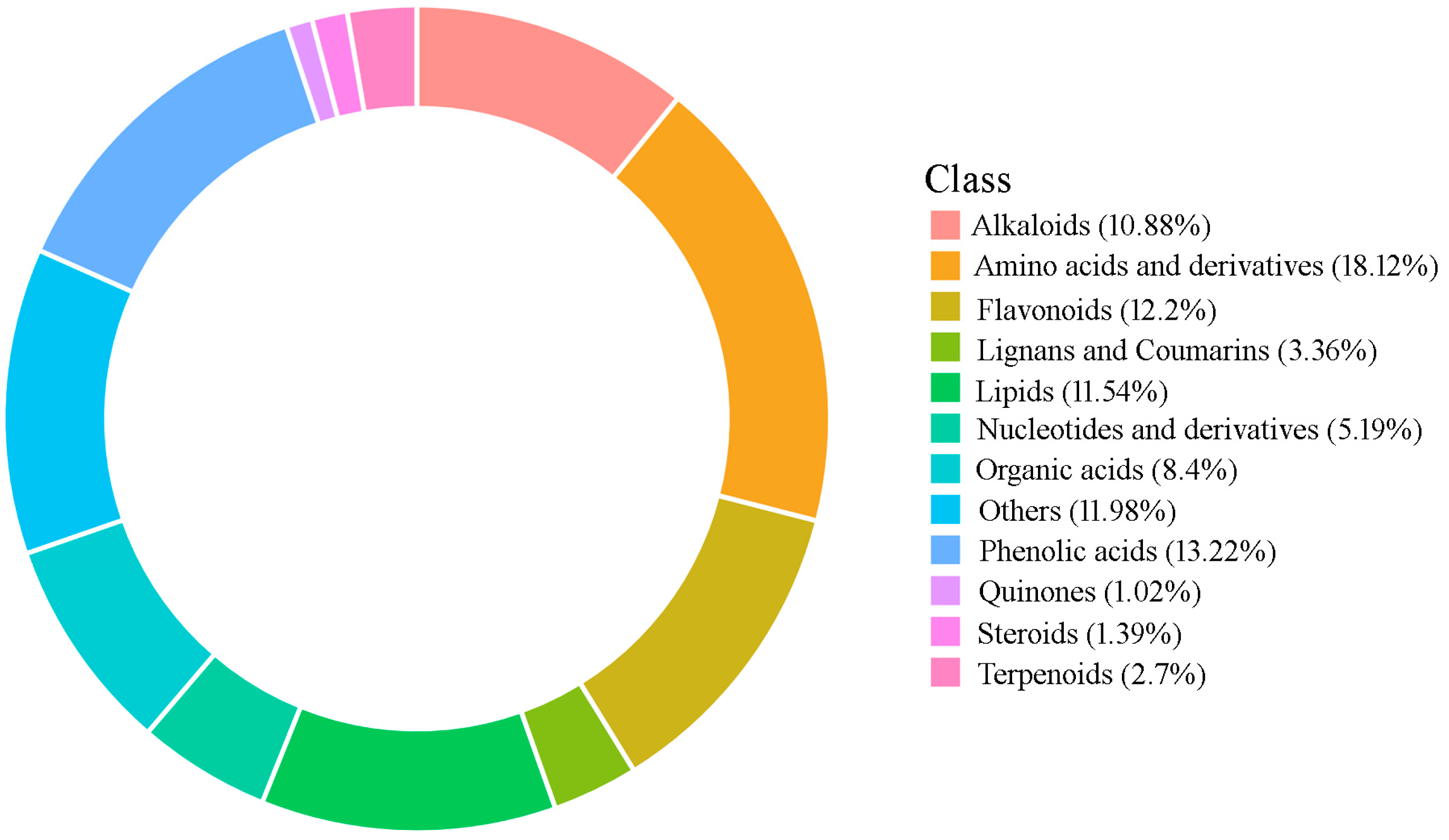
2.1. Metabolite Identification in P. cyrtonema Rhizomes
2.2. Variation Trends of Metabolites During Repeated Cycles of Steaming and Drying
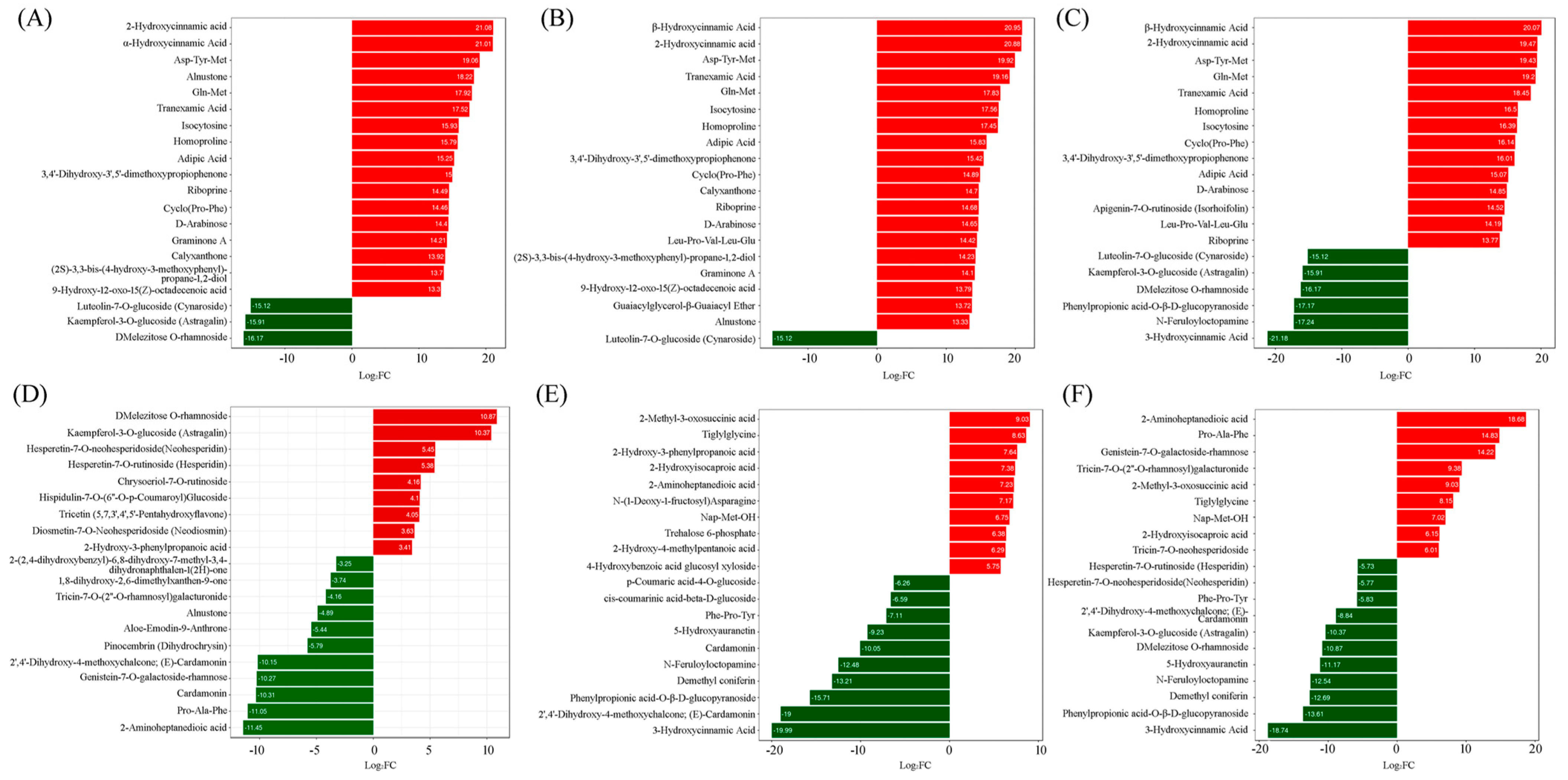
2.3. Screening of Differentially Accumulated Metabolites
2.3.1. ‘Tre-0’ Sample vs. ‘Tre-3’ Sample
2.3.2. ‘Tre-0’ Sample vs. ‘Tre-6’ Sample
2.3.3. ‘Tre-0’ Sample vs. ‘Tre-9’ Sample
2.3.4. ‘Tre-3’ Sample vs. ‘Tre-6’ Sample
2.3.5. ‘Tre-3’ Sample vs. ‘Tre-9’ Sample
2.3.6. ‘Tre-6’ Sample vs. ‘Tre-9’ Sample
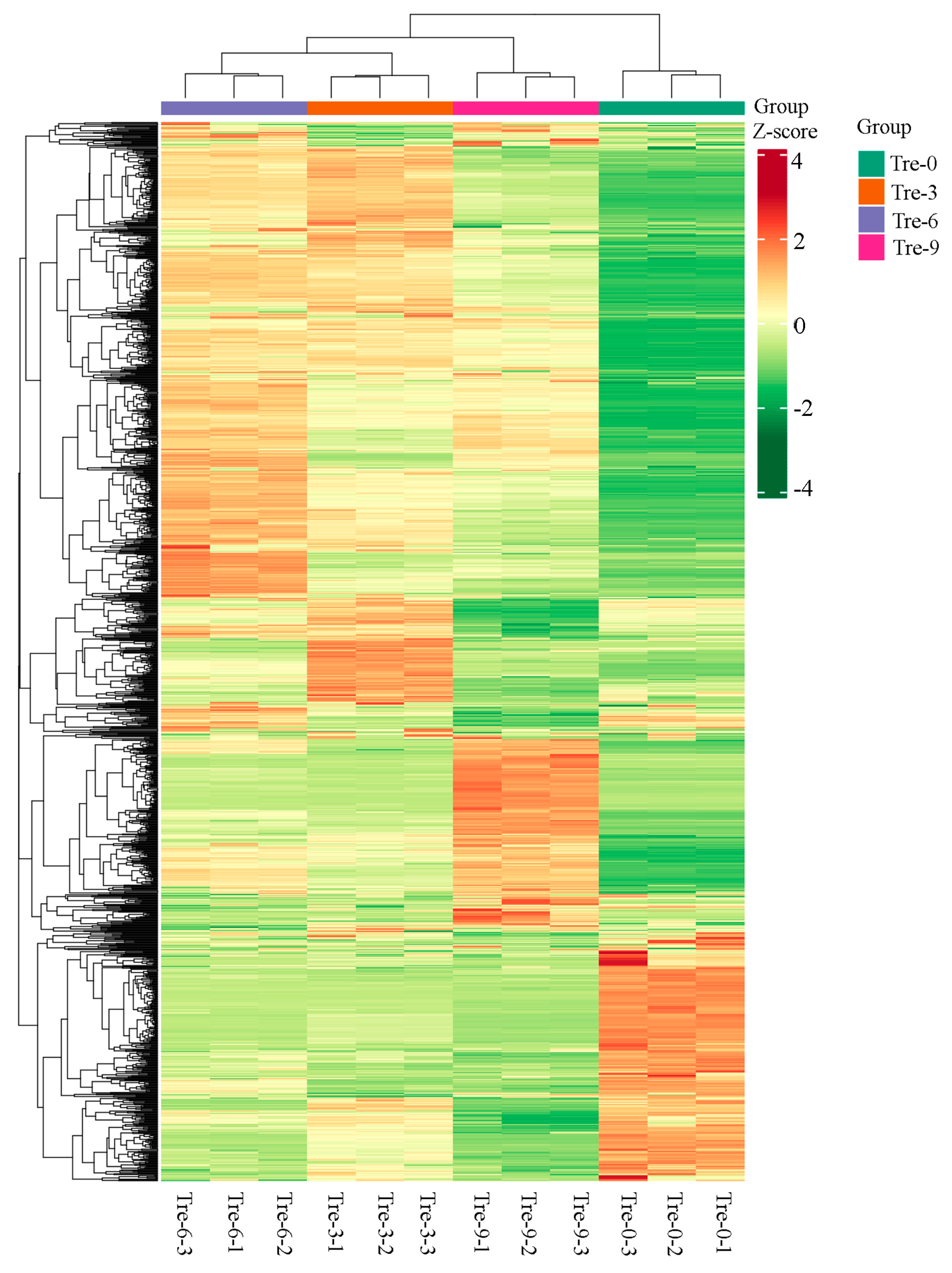
2.4. Cluster Analysis of Different Polygonati Rhizoma Samples
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
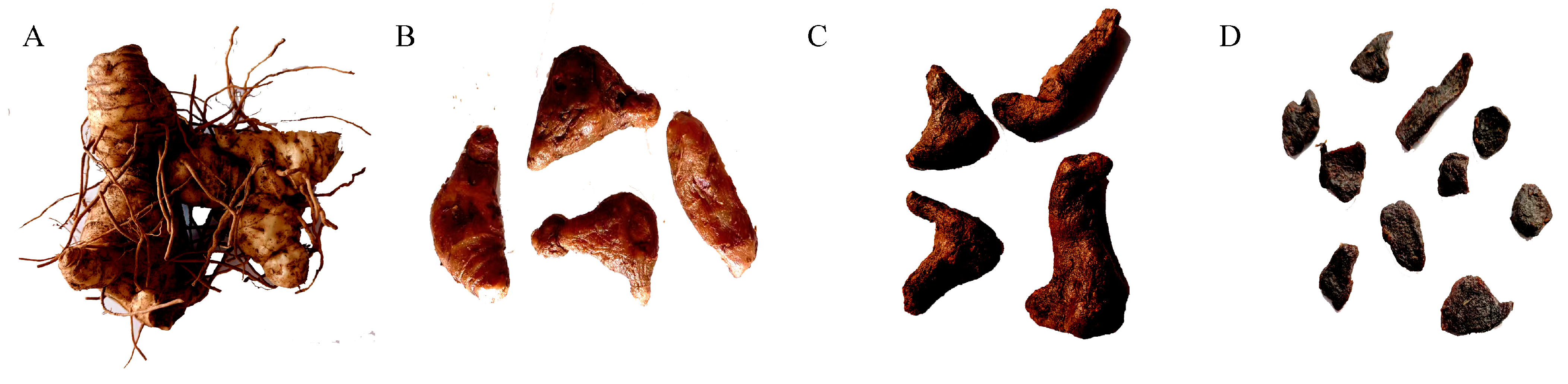
4.1. Material Preparation
4.2. Extraction and LC-MS Analysis
4.3. Identification and Analysis of Metabolites
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; He, F.; Wu, H.; Xiang, F.; Zheng, H.; Wu, W.; Li, S. Health-promoting activities and associated mechanisms of Polygonati Rhizoma polysaccharides. Molecules 2023, 28, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Dabu, X.L.T.; He, J.; Yang, H.X.; Yang, S.C.; Chen, J.W.; Fan, W.; Zhang, G.H.; Cai, J.L.; Ai, H.L.; et al. Polygonatone H, a new homoisoflavanone with cytotoxicity from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Huang, L.; Jiang, P.; Xu, G.; Sun, T. Immunological regulation of the active fraction from Polygonatum sibiricum F. Delaroche based on improvement of intestinal microflora and activation of RAW264.7 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 293, 115240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.J.; Kim, C.Y.; Yoon, K.D.; Min, Y.R.; Kim, J. Steroidal saponins from the rhizomes of Polygonatum sibiricum. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.Y.; Qian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qu, W.; Liang, J.Y. Two new homoisoflavanones from the rhizome of Polygonatum odoratum. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2015, 51, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Fu, S.; Liu, C. Protective effect of Polygonatum sibiricum against cadmium-induced testicular injury in mice through inhibiting oxidative stress and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 261, 113060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Shao, J. Analysis of the genetic structure and morphology of Polygonatum cyrtonema in Anhui province, eastern China revealed three distinct genetic groups. Nord. J. Bot. 2020, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Ji, H.; Cheng, X.; Wang, D.; Li, T.; Ren, K.; Qu, S.; Pan, Y.; Liu, X. Characterization, classification, and authentication of Polygonatum sibiricum samples by volatile profiles and flavor properties. Molecules 2021, 27, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Cheng, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Xing, L.; Shi, S.; Wang, R.; Wu, Z.; Yu, N.; Peng, D. Determination and analysis of monosaccharides in Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua polysaccharides from different areas by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole trap tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 3506–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, J.Z.; Li, X.G.; He, A.G.; Zhong, J. Botrytis cinerea causing gray mold of Polygonatum sibiricum (Huang Jing) in China. Crop Prot. 2021, 140, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Liu, J.Z.; Wu, C.F.; Li, J.; Dai, L.; Damme, E.V.; Balzarine, J.; Clercq, E.D.; Chen, F.; Bao, J.K. Anti-HIV I/II activity and molecular cloning of a novel mannose/sialic acid-binding lectin from rhizome of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2006, 38, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Luo, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, M. Structures of fructan and galactan from polygonatum cyrtonema and their utilization by probiotic bacteria. Carbohyd. Polym. 2021, 267, 118219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Huang, X.F.; Kong, L.Y. Steroidal saponins from Polygonatum cyrtonema. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2013, 49, 888–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yue, Y.D.; Tang, F. Sequential extraction and structural analysis of polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2014, 26, 364–369. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Feng, S.S.; Sun, Y.J.; Hao, Z.Y.; Feng, W.S.; Zheng, X.K. Advances in studies on chemical constituents of three medicinal plants from Polygonatum mill and their pharmacological activities. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2015, 46, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar]
- 16 Wan, K.; Ban, J.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lai, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway involved in rhizome development in Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Plants 2024, 13, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 17 Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant flavonoids: Classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritisha, T.; Padma, A.; Rukam, T. Metabolomics of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) genotypes during groundnut-sclerotium rolfsii interaction at different stages of infection. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 16, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Liao, G.; Wan, D.; Kong, W.; Li, C.; Gu, D.; Pu, Y.; Ge, C.; Wang, G. Combined application of high-throughput sequencing and LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics to evaluate the formation of Zn-protoporphyrin in Nuodeng ham. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162 Pt B, 112209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, D. Comprehensive metabolomics and antioxidant activity of Allium species viz. Allium semenovii, A. sativum and A. cepa: An important spice. Food Res. Int. 2023, 166, 112584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.S.; Ahmed, S.; Zhou, B.; Shi, L. (2024). A review on pharmacological activities and phytochemical constituents of Zanthoxylum armatum DC. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Su, H.; Yin, S.; Han, C.; Hao, D.; Dong, X. The regulatory mechanism of chilling-induced dormancy transition from endo-dormancy to non-dormancy in Polygonatum kingianum Coll.et Hemsl rhizome bud. Plant Mol. Biol. 2019, 99, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.S.; Chen, J.J.; Shi, M.F.; Zhou, C.X. A new homoisoflavanone from the rhizomes of Polygonatum cyrtonema. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 3, 597–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Zhang, X.; Dabu, X.L.T.; He, J.; Yang, S.C.; Chen, J.W.; Fan, W.; Zhang, G.H.; Ai, H.L.; Hai, M.R. Analysis of chemical constituents from Polygonatum cyrtonema after “nine-steam-nine-bask”processing. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 29, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Gong, Q.F. Progress in study on processing of Polygonati rhizome in past decade. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2017, 23, 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M.; Wu, Y.; Sun, C.; Ma, H.; Ye, X.; Li, X. Polygonati Rhizoma: A review on the extraction, purification, structural characterization, biosynthesis of the main secondary metabolites and anti-aging effects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 327, 118002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, S.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Jin, W. Metabolite profiling of violet, white and pink flowers revealing flavonoids composition patterns in Rhododendron pulchrum Sweet. J. Biosci. 2021, 46, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaroson, M.L.; Koutouan, C.; Helesbeux, J.J.; Le Clerc, V.; Hamama, L.; Geoffriau, E.; Briard, M. Role of Phenylpropanoids and Flavonoids in Plant Resistance to Pests and Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, M.; Lam, P.Y.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Dai, L.; Wei, Z. Multifaceted roles of flavonoids mediating plant-microbe interactions. Microbiome 2022, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lv, S.; Zhao, L.; Gao, T.; Yu, C.; Hu, J.; Ma, F. Advances in the study of the function and mechanism of the action of flavonoids in plants under environmental stresses. Planta 2023, 257, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, S.T.; Jia, Q.J.; Liang, Z.S. Advances in chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Polygonati Rhizoma. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2021, 33, 1783–1796. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Lai, G.F.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, B.G.; Luo, S.D. Study on the chemical constituents of Polygonatum kingianum (II). Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2008, 39, 825–828. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Yu, Y.; Guo, P.; Huo, J.; Tang, S. Chemical constituents of Polygonatum sibiricum. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2019, 55, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Tsai, K.L.; Chou, W.C.; Cheng, H.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Ou, H.C.; Chang, Y.C. Quercetin Mitigates cisplatin-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2022, 50, 1281–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wan, R.; Peng, W.; Zhao, X.; Bai, W.; Hu, C. Quercetin alleviates ferroptosis accompanied by reducing M1 macrophage polarization during neutrophilic airway inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 938, 175407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Yin, J.; Yoon, K.H.; Hwang, Y.J.; Lee, M.W. Antiproliferative effects of new dimeric ellagitannin from Cornus alba in prostatecancer cells including apoptosis-related s-phase arrest. Molecules 2016, 21, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Kuang, H.; Yuan, X. Efficacy of Buzhong Yiqi decoction on benign prostatic hyperplasia and its possible mechanism. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 43, 533–541. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Tao, T.; Yao, H.; Zheng, H.; Wang, F.; Gao, Y. Mechanism of action of quercetin in rheumatoid arthritis models: Meta-analysis and systematic review of animal studies. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 1629–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Wei, G.; Gan, X.; Li, T. Study on the varied content of Polygonatum cyrtonema polysaccharides in the processing of steaming and shining for nine times based on HPLC-MS/MS and chemometrics. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.B.; Ge, J.C.; Zhang, W.J.; Liu, W.; Luo, J.P.; Xu, F.Q.; Wu, D.L.; Xie, S.Z. Physicochemical, morpho-structural, and biological characterization of polysaccharides from three Polygonatum spp. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 37952–37965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zeng, J.; Gong, P.; Wu, Y.; Li, H. Effect of steaming process on the structural characteristics and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Polygonatum sibiricum rhizomes. Glycoconjugate J. 2021, 38, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.Y.; Xu, D.P.; Wu, Y.M.; Ou, S.Y. Triterpenoid saponins from the rhizome of Polygonatum sibiricum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 12, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Huang, L.; Xiao, P.; Gao, W. The genus Polygonatum: A review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 214, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Luo, J.; Jia, M.; Chai, Y.; Bao, Y. Polygonatum sibiricum saponin exerts beneficial hypoglycemic effects in type 2 diabetes mice by improving hepatic insulin resistance and glycogen synthesis-related proteins. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, Z.; Nie, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, T.; Zhang, C.; Wu, D.; Zhang, J. Recent advances in polysaccharides from edible and medicinal Polygonati Rhizoma: From bench to market. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 195, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, P.; Wu, W.; Li, D.; Shang, E.X.; Guo, S.; Qian, D.; Yan, H.; Wang, W.; Duan, J.A. Multi-constituents variation in medicinal crops processing: Investigation of nine cycles of steam-sun drying as the processing method for the rhizome of Polygonatum cyrtonema. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2022, 209, 114497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Class (Numbers of Metabolites) | Sub-Class | Numbers in Different Samples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tre-0 | Tre-3 | Tre-6 | Tre-9 | Total | ||
| Alkaloids (149) | Alkaloids | 69 | 71 | 71 | 71 | 71 |
| Benzylphenylethylamine alkaloids | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Isoquinoline alkaloids | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Phenolamine | 36 | 36 | 36 | 35 | 36 | |
| Piperidine alkaloids | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| Plumerane | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | |
| Pyridine alkaloids | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Pyrrole alkaloids | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Quinoline alkaloids | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Tropan alkaloids | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Flavonoids (167) | Chalcones | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 9 |
| Flavanols | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Flavanones | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | |
| Flavanonols | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Flavones | 58 | 62 | 62 | 62 | 63 | |
| Flavonols | 14 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 15 | |
| Isoflavones | 9 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 9 | |
| Other flavonoids | 48 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 49 | |
| Lignans and coumarins (46) | Coumarins | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 |
| Lignans | 33 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | |
| Lipids (158) | Free fatty acids | 79 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 |
| Glycerol ester | 7 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| LPC | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | |
| LPE | 29 | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 | |
| PC | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Sphingolipids | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | |
| Phenolic acids (181) | Phenolic acids | 176 | 181 | 181 | 178 | 181 |
| Quinones (14) | Anthraquinone | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| Quinones | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Steroids (19) | Steroid | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Steroidal saponins | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | |
| Terpenoids (37) | Ditepenoids | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Monoterpenoids | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| Terpene | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Triterpene | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | |
| Triterpene saponin | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Nucleotides and derivatives (71) | Nucleotides and derivatives | 68 | 71 | 71 | 71 | 71 |
| Organic acids (115) | Organic acids | 113 | 114 | 113 | 115 | 115 |
| Amino acids and derivatives (248) | Amino acids and derivatives | 242 | 248 | 247 | 248 | 248 |
| Others (164) | Alcohol compounds | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Aldehyde compounds | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |
| Chromone | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Ketone compounds | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | |
| Others | 41 | 44 | 44 | 44 | 44 | |
| Saccharides | 73 | 73 | 74 | 73 | 74 | |
| Vitamin | 17 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 17 | |
| Total | 1330 | 1365 | 1363 | 1360 | 1369 | |
| No. | Modification | Corresponding Amino Acids |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Acetylation | Arg, Glu, Asp Thr, Gln, Ala, Lys, Phe, Leu, Asp, Tyr, Ser |
| 2 | Cyclo- | Tyr, Ala, Val, Pro, Phe, Leu, Glu, Gly, Ser |
| 3 | Hydroxylation | Phe, Tyr, Pro, Glu, Leu, Met, His |
| 4 | Monomethylation | Glu, Pro,Arg, Cys,His, Met |
| 5 | Dimethylation | Lys, Arg,Gly |
| 6 | Trimethylation | Lys |
| 7 | Homo- | Ser, Ala, Pro, Arg, Cys |
| 8 | Oxo- | Pro, Tyr |
| 9 | Glycosidation | Asp, Glu |
| 10 | Adenosylation | Met, Cys |
| 11 | Esterification | Arg |
| 12 | Ethylation | Gly |
| 13 | Benzylation | Ser |
| 14 | Propylation | Pro |
| 15 | Ribosylation | Cys |
| 16 | Propionylation | Gly |
| 17 | Propenylation | Cys |
| 18 | Allosterism | Leu |
| 19 | Cyano- | Ala |
| 20 | Acylation | Gly |
| 21 | Nitro- | Tyr |
| 22 | Phosphorylation | Tyr |
| Types | Compounds | Molecular Weight (Da) | Formula | Modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| monosaccharide | Dihydroxyacetone phosphate | 169.998 | C3H7O6P | phosphorylation |
| D-threonic acid | 136.0372 | C4H8O5 | oxidation | |
| 3-dehydro-L-threonic acid | 134.0215 | C4H6O5 | oxidation | |
| D-erythrose-4-phosphate | 200.0086 | C4H9O7P | phosphorylation | |
| D-threose | 120.0423 | C4H8O4 | ||
| D-xylonic acid | 166.0477 | C5H10O6 | oxidation | |
| L-xylose | 150.0528 | C5H10O5 | _ | |
| D-arabinose | 150.0528 | C5H10O5 | _ | |
| D-arabinono-1,4-lactone | 148.0372 | C5H8O5 | lactonization | |
| D-fructose-1,6-biphosphate | 339.996 | C6H14O12P2 | phosphorylation | |
| D-glucosamine 1-phosphate | 259.0457 | C6H14NO8P | phosphorylation | |
| D-fructose 6-phosphate | 260.0297 | C6H13O9P | phosphorylation | |
| Gluconic acid | 196.0583 | C6H12O7 | oxidation | |
| D-glucoronic acid | 194.0427 | C6H10O7 | oxidation | |
| D-glucose 6-phosphate | 260.0297 | C6H13O9P | phosphorylation | |
| D-glucurono-6,3-lactone | 176.0321 | C6H8O6 | lactonization | |
| D-glucose | 180.0634 | C6H12O6 | _ | |
| D-glucose 1,6-bisphosphate | 339.996 | C6H14O12P2 | phosphorylation | |
| D-glucosamine | 259.0457 | C6H13NO5 | amination | |
| Glucose-1-phosphate | 260.0297 | C6H13O9P | phosphorylation | |
| D-glucono-1,5-lactone | 178.0477 | C6H10O6 | lactonization | |
| Glucaric acid-1-phosphate | 290.0039 | C6H11PO11 | phosphorylation | |
| 1,6-anhydro-β-d-glucose | 162.0528 | C6H10O5 | dehydration | |
| D-sorbitol | 182.079 | C6H14O6 | reduction | |
| sorbose | 180.0634 | C6H12O6 | _ | |
| Sorbitol-6-phosphate | 262.0454 | C6H15O9P | phosphorylation | |
| D-mannitol | 182.079 | C6H14O6 | reduction | |
| D-mannose | 180.0634 | C6H12O6 | _ | |
| 1,5-anhydro-d-glucitol | 164.0685 | C6H12O5 | dehydration, reduction | |
| D-fucose | 164.0685 | C6H12O5 | _ | |
| L-fucitol | 166.0841 | C6H14O5 | reduction | |
| D-galacturonic acid | 194.0427 | C6H10O7 | oxidation | |
| Dulcitol | 182.079 | C6H14O6 | reduction | |
| D-galactose | 180.0634 | C6H12O6 | _ | |
| D-galactaric acid | 210.0376 | C6H10O8 | oxidation | |
| D-saccharic acid | 210.0376 | C6H10O8 | oxidation | |
| Rhamnose | 164.0685 | C6H12O5 | _ | |
| L-gulono-1,4-lactone | 178.0477 | C6H10O6 | - | |
| Allitol | 182.079 | C6H14O6 | reduction | |
| Inositol | 180.0634 | C6H12O6 | _ | |
| D-sedoheptuiose 7-phosphate | 290.0403 | C7H15O10P | phosphorylation | |
| Sedoheptulose | 210.074 | C7H14O7 | _ | |
| D-pinitol | 194.079 | C7H14O6 | reduction | |
| N-Acetyl-d-galactosamine | 221.0899 | C8H15NO6 | amination | |
| 1-(sn-Glycero-3-phospho)-1D-myo-inositol | 334.0665 | C9H19O11P | reduction | |
| Glucopyranose 6-hydroxydecanoate | 350.1941 | C16H30O8 | esterification | |
| disaccharide | Sucrose-6-phosphate | 422.0825 | C12H23O14P | phosphorylation |
| D-sucrose | 342.1162 | C12H22O11 | - | |
| Galactinol | 342.1162 | C12H22O11 | reduction | |
| D-cellobiose | 342.1162 | C12H22O11 | - | |
| D-trehalose | 342.1162 | C12H22O11 | - | |
| Maltitol | 344.1319 | C12H24O11 | - | |
| Isomaltulose | 342.1162 | C12H22O11 | - | |
| D-maltose | 342.1162 | C12H22O11 | - | |
| Lactobiose | 342.1162 | C12H22O11 | - | |
| Digalacturonate | 370.0747 | C12H18O13 | - | |
| Melibiose | 342.1162 | C12H22O11 | - | |
| Rutinose | 326.1213 | C12H22O10 | - | |
| Trehalose 6-phosphate | 422.0825 | C12H23O14P | phosphorylation | |
| beta-d-Galp-(1->3)-d-GalpNAc | 383.1428 | C14H25NO11 | ||
| trisaccharide | Planteose | 504.169 | C18H32O16 | - |
| Maltotriose | 504.169 | C18H32O16 | - | |
| Manninotriose | 504.169 | C18H32O16 | - | |
| D-Panose | 504.169 | C18H32O16 | - | |
| Solatriose | 488.1741 | C18H32O15 | - | |
| Gentianose | 504.1690 | C18H32O16 | - | |
| Raffinose | 504.169 | C18H32O16 | - | |
| D-melezitose | 504.169 | C18H32O16 | - | |
| GalNAc1-4[Fuc1-3]GlcNAcSp | 639.2599 | C24H41N5O15 | - | |
| Tetrasaccharide | D-maltotetraose | 666.2219 | C24H42O21 | _ |
| Stachyose | 666.2219 | C24H42O21 | - | |
| DMelezitose O-rhamnoside | 650.2269 | C24H42O20 | _ | |
| Nystose | 666.2219 | C24H42O21 | - | |
| Pentasaccharide | Verbascose | 828.2747 | C30H52O26 | - |
| Class | Sub-Class | Numbers of Metabolites with the Highest Contents | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tre-0 | Tre-3 | Tre-6 | Tre-9 | |||
| Alkaloids (149) | Alkaloids | 25 | 22 | 15 | 9 | 71 |
| Benzylphenylethylamine alkaloids | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Isoquinoline alkaloids | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| Phenolamine | 16 | 13 | 2 | 5 | 36 | |
| Piperidine alkaloids | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | |
| Plumerane | 8 | 3 | 7 | 2 | 20 | |
| Pyridine alkaloids | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 | |
| Pyrrole alkaloids | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 4 | |
| Quinoline alkaloids | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 6 | |
| Tropan alkaloids | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | |
| Amino acids and derivatives (248) | Amino acids and derivatives | 67 | 53 | 58 | 70 | 248 |
| Flavonoids (167) | Chalcones | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 9 |
| Flavanols | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | |
| Flavanones | 2 | 9 | 5 | 0 | 16 | |
| Flavanonols | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| Flavones | 10 | 9 | 19 | 25 | 63 | |
| Flavonols | 4 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 15 | |
| Isoflavones | 4 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 9 | |
| Other Flavonoids | 22 | 17 | 5 | 5 | 49 | |
| Lignans and coumarins (46) | Coumarins | 2 | 3 | 6 | 11 | |
| Lignans | 4 | 9 | 17 | 5 | 35 | |
| Lipids (158) | Free fatty acids | 1 | 22 | 51 | 6 | 80 |
| Glycerol ester | 1 | 0 | 7 | 2 | 10 | |
| LPC | 1 | 6 | 23 | 0 | 29 | |
| LPE | 0 | 19 | 11 | 0 | 31 | |
| PC | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Sphingolipids | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 7 | |
| Nucleotides and derivatives (71) | Nucleotides and derivatives | 12 | 31 | 14 | 14 | 71 |
| Organic acids (115) | Organic acids | 24 | 11 | 46 | 34 | 115 |
| Others (164) | Alcohol compounds | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| Aldehyde compounds | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 8 | |
| Chromone | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| Ketone compounds | 5 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 14 | |
| Others | 7 | 16 | 19 | 2 | 44 | |
| Saccharides | 12 | 9 | 19 | 34 | 74 | |
| Vitamin | 2 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 17 | |
| Phenolic acids (181) | Phenolic acids | 39 | 59 | 39 | 44 | 181 |
| Quinones (14) | Anthraquinone | 0 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 9 |
| Quinones | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 5 | |
| Steroids (19) | Steroid | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| Steroidal saponins | 9 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 13 | |
| Terpenoids (37) | Ditepenoids | 0 | 1 | 8 | 6 | 15 |
| Monoterpenoids | 4 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 10 | |
| Terpene | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 4 | |
| Triterpene | 0 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 | |
| Triterpene saponin | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; He, F.; Hu, R.; Wan, X.; Wu, W.; Zhang, L.; Ho, C.-T.; Li, S. Dynamic Variation of Secondary Metabolites from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua Rhizomes During Repeated Steaming–Drying Processes. Molecules 2025, 30, 1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091923
Wang S, He F, Hu R, Wan X, Wu W, Zhang L, Ho C-T, Li S. Dynamic Variation of Secondary Metabolites from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua Rhizomes During Repeated Steaming–Drying Processes. Molecules. 2025; 30(9):1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091923
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuzhen, Feng He, Ruibin Hu, Xuchun Wan, Wei Wu, Lei Zhang, Chi-Tang Ho, and Shiming Li. 2025. "Dynamic Variation of Secondary Metabolites from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua Rhizomes During Repeated Steaming–Drying Processes" Molecules 30, no. 9: 1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091923
APA StyleWang, S., He, F., Hu, R., Wan, X., Wu, W., Zhang, L., Ho, C.-T., & Li, S. (2025). Dynamic Variation of Secondary Metabolites from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua Rhizomes During Repeated Steaming–Drying Processes. Molecules, 30(9), 1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091923









