Identification of Marker Peptides in Gelatins from Sika Deer (Cervus nippon) Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Quadrupole-Exactive-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Selection of Marker Peptide Candidates
2.2. Definition of Marker Peptide of Gelatins from Sika Deer
2.3. Interpretation of Product Ion Spectra for Defined Marker Peptides
2.4. Identification of Gelatin from Sika Deer by Defined Marker Peptides
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Sample Preparations
3.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis
3.4. Data Processing and De Novo Sequencing Identification of Peptides
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Côté, S.D.; Rooney, T.P.; Tremblay, J.P.; Dussault, C.; Waller, D.M. Ecological impacts of deer overabundance. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 113–147. [Google Scholar]
- McCullough, D.R.; Takatsuki, S.; Kaj, K. Sika Deer: Biology and Management of Native and Introduced Populations; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kaji, K.; Uno, H.; Iijima, H. Sika Deer: Life History Plasticity and Management; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of the Environment General Policy Division Minister’s Secretariat; Ministry of the Environment. Annual Report on the Environment, the Sound Material-Cycle Society and Biodiversity in Japan 2023; Ministry of the Environment Government of Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Takai, S. Guidelines on the hygienic management of wild meat in Japan. Meat Sci. 2022, 191, 108864. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rashwan, A.K.; Bai, H.; Osman, A.I.; Eltohamy, K.M.; Chen, Z.; Younis, H.A.; Al-Fatesh, A.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P.S. Recycling food and agriculture by-products to mitigate climate change: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 3351–3375. [Google Scholar]
- Shirai, K. Tyuyakudaiziten; Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers: Tokyo, Japan, 1985; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Li, H.; Jin, L.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; You, J.; Li, S.; Xu, Y. Deer antler base as a traditional Chinese medicine: A review of its traditional uses, chemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. Deer antlers: Traditional Chinese medicine use and recent pharmaceuticals. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2020, 60, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, P.; Liu, D.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zheng, S.; Fang, J.; Hao, L. Health effects of peptides extracted from deer antler. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, H.; He, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, F. Anticancer activity in vitro and biological safety evaluation in vivo of Sika deer antler protein. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, H.; Ruan, H.; Li, W.; He, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J. The protective effect of sika deer antler protein on Gentamicin-iinduced nephrotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Fan, M.; Choi, Y.J.; Yu, Y.; Yao, G.; Deng, Y.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, E.K. Sika deer (Cervus nippon) velvet antler extract attenuates prostate cancer in xenograft model. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 348–356. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Shi, H.; Yang, C.; Wu, M.; Zhang, A. Comparison of the composition, immunological activity and anti-fatigue effects of different parts in sika deer antler. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1468237. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Cheng, X.L.; Wei, F.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Li, M.H.; Ma, S.C. Detection of gelatin adulteration in traditional Chinese medicine: Analysis of deer-horn glue by rapid-resolution liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2015, 2015, 259757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Zhang, M.; Leng, X.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, Y. Antler extracts stimulate chondrocyte proliferation and possess potent anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and immune-modulatory properties. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2018, 54, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, B.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Leng, X.; Zhao, D. Investigating the molecular control of deer antler extract on articular cartilage. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xia, Y.; Hua, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Gong, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y. Functional properties and antioxidant activity of gelatine and hydrolysate from deer antler base. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 3402–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Yang, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Z.S.; Li, W.Q.; Xu, H.C.; Zhang, Z.J. Tortoise plastron and deer antler gelatin prevents against neuronal mitochondrial dysfunction In Vitro: Implication for a potential therapy of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 690256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Long, H.; Yang, C.; Cai, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, W. Anti-inflammatory role of pilose antler peptide in LPS-induced lung injury. Inflammation 2017, 40, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.; Qian, W.; Wu, J.; Yuan, C.; Jiang, S.; Lv, J. Pilose antler peptide promotes osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and mineralization via the insulin signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, K.; Uchino, S.; Li, D.; Kikuchi, T.; Tei, K.; Li, W. Antioxidant activity of gelatins from sika deer (Cervus nippon). Pharmacogn. Res. 2024, 16, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ru, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, X.; Fan, G.; Mao, B.; Zhou, X.; Qin, Y. Chemical constituents and bioactivities of Colla corii asini. Drug Discov. Ther. 2014, 8, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallongeville, S.; Koperska, M.; Garnier, N.; Reille-Taillefert, G.; Rolando, C.; Tokarski, C. Identification of animal glue species in artworks using proteomics: Application to a 18th century gilt sample. Anal. Chem. 2011, 8, 9431–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumazawa, Y.; Taga, Y.; Takashima, M.; Hattori, S. A novel LC–MS method using collagen marker peptides for species identification of glue applicable to samples with multiple animal origins. Herit. Sci. 2018, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumazawa, Y.; Taga, Y.; Iwai, K.; Koyama, Y. A Rapid and simple LC-MS method using collagen marker peptides for identification of the animal source of leather. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6051–6057. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, M.; Collins, M.; Thomas-Oates, J.; Wilson, J.C. Species identification by analysis of bone collagen using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 2, 3843–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Bargen, C.; Dojahn, J.; Waidelich, D.; Humpf, H.U.; Brockmeyer, J. New sensitive high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the detection of horse and pork in halal beef. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11986–11994. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, A.D.; Gunning, Y.; Rigby, N.M.; Philo, M.; Kemsley, E.K. Meat authentication via multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry of myoglobin peptides. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 10315–10322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.T.; Kesmen, Z.; Baykal, B.; Sagdic, O.; Kulen, O.; Kacar, O.; Yetim, H.; Baykal, A.T. A novel method to differentiate bovine and porcine gelatins in food products: NanoUPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS(E) based data independent acquisition technique to detect marker peptides in gelatin. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2450–2458. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, G.; Guo, S.; Zaman, F.; Li, T.; Huang, Y. Recent advances in animal origin identification of gelatin-based products using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry methods: A mini review. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 39, 260–271. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Huang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Yang, M.; Xie, Y.; Wang, K.; Duan, J.A.; et al. A strategy for identifying species-specific peptide biomarkers in deer-hide gelatin using untargeted and targeted mass spectrometry approaches. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1092, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhao, K.; Cai, S.; Jiang, M.; Huang, X.; Chen, S.; Li, S.; Zhao, M.; Duan, J.A.; Liu, R. Discovery of peptide biomarkers by label-free peptidomics for discrimination of horn gelatin and hide gelatin from Cervus nippon Temminck. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130347. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, F.; Wang, B.; Guo, D.X.; Jiao, Y.; Yin, X.; Cui, W.L.; Zhou, Q.Q.; Yu, F.R.; Lin, Y.Q. Peptide biomarkers discovery for seven species of deer antler using LC-MS/MS and label-free approach. Molecules 2022, 27, 4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.J.; Li, L.F.; Fung, H.Y.; Cheng, H.Y.; Kong, H.Y.; Wong, T.L.; Zhang, Q.W.; Liu, M.; Bao, W.R.; Huo, C.Y.; et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of Ejiao-related animal gelatins through peptide markers using LC-QTOF-MS/MS and scheduled multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) by LC-QQQ-MS/MS. Molecules 2022, 27, 4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, D.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, B.; Ding, Y.; Bai, J.; Wen, H.; Wu, H.; Duan, J.A.; et al. Discovery of Elaphuri Davidiani Cornu-specific peptide biomarkers by peptidomics analysis-based method. Electrophoresis 2023, 44, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, F.; Wang, B.; Guo, D.X.; Jiao, Y.; Cui, W.L.; Cheng, X.L.; Wang, Z.B.; Yin, X.; Ma, S.C.; Lin, Y.Q. Discovery of species-specific peptide markers and development of quality-evaluation strategies for deer horn gelatin using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and a label-free methodology. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1705, 464153. [Google Scholar]
- Jannat, B.; Ghorbani, K.; Kouchaki, S.; Sadeghi, N.; Eslamifarsani, E.; Rabbani, F.; Beyramysoltan, S. Distinguishing tissue origin of bovine gelatin in processed products using LC/MS technique in combination with chemometrics tools. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaudel, M.; Burkhart, J.M.; Zahedi, R.P.; Oveland, E.; Berven, F.S.; Sickmann, A.; Martens, L.; Barsnes, H. PeptideShaker enables reanalysis of MS-derived proteomics data sets. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geer, L.Y.; Markey, S.P.; Kowalak, J.A.; Wagner, L.; Xu, M.; Maynard, D.M.; Yang, X.; Shi, W.; Bryant, S.H. Open mass spectrometry search algorithm. J. Proteome Res. 2004, 3, 958–964. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, R.; Beavis, R.C. TANDEM: Matching proteins with tandem mass spectra. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 1466–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Barsnes, H.; Vaudel, M. SearchGUI: A highly adaptable common interface for proteomics search and de novo engines. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2552–2555. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elias, J.E.; Gygi, S.P. Target-decoy search strategy for mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 604, 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D609–D617. [Google Scholar]
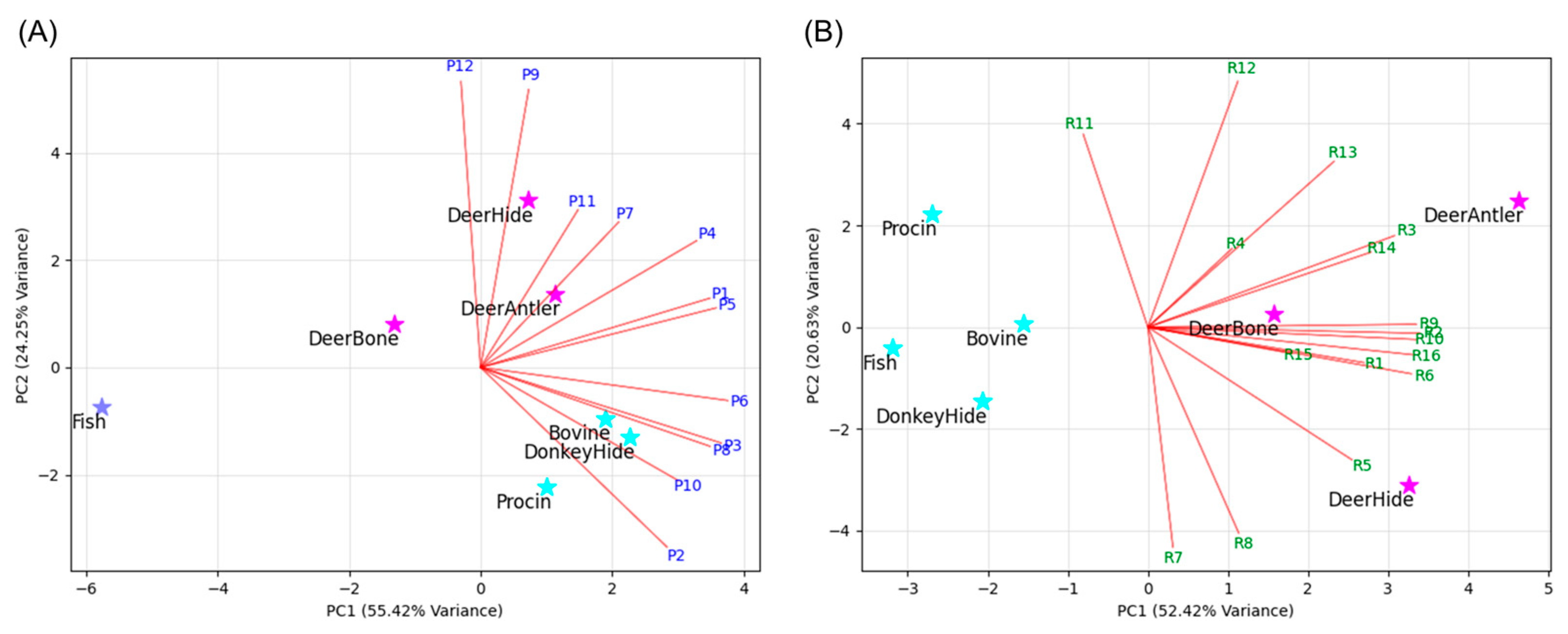
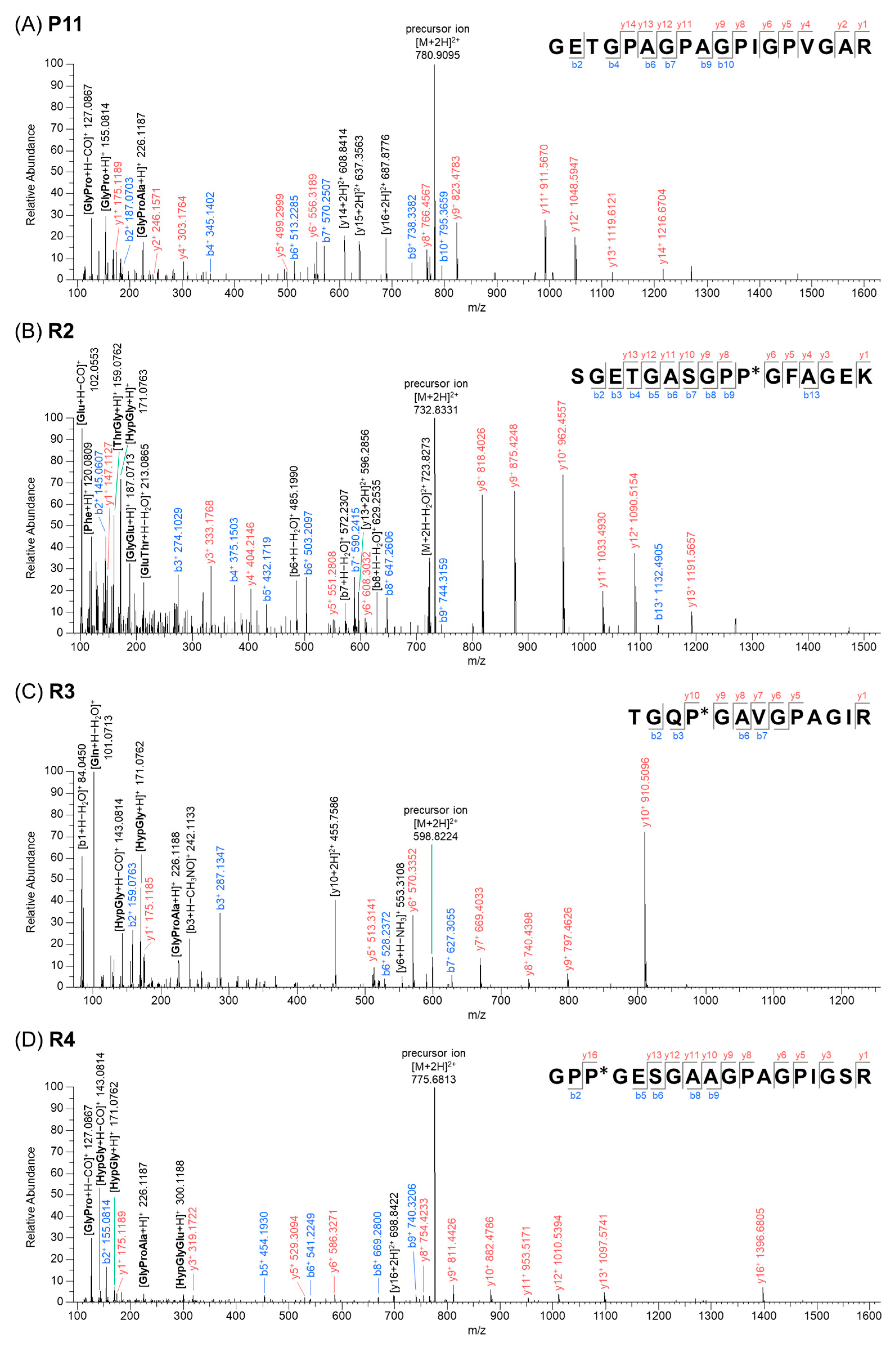

| No. | tR (min) | m/z | Charge | Sequence a | Chain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 2.34 | 418.7223 | 2 | GPAGPQGPR | COL1A1 |
| P2 | 2.48 | 434.7354 | 2 | GPSGPQGIR | COL1A2 |
| P3 | 4.48 | 392.2216 | 2 | GAAGLPGPK(+15.99) | COL1A1 |
| P4 | 4.55 | 666.8308 | 2 | GPSGPQGPSGPP(+15.99)GPK | COL1A1 |
| P5 | 5.04 | 553.2911 | 2 | GVQGPP(+15.99)GPAGPR | COL1A1 |
| P6 | 6.20 | 446.7536 | 2 | PGPIGPAGAR | COL1A2 |
| P7 | 7.77 | 449.7589 | 2 | GVVGLPGQR(+15.99) | COL1A1 |
| P8 | 7.91 | 730.3499 | 2 | GAAGP(+15.99)P(+15.99)GATGFPGAAGR(+15.99) | COL1A1 |
| P9 | 8.40 | 590.8253 | 2 | TGQPGAVGPAGIR | COL1A2 |
| P10 | 10.71 | 793.8815 | 2 | GANG(+0.98)AP(+15.99)GIAGAPGFP(+15.99)GAR(+15.99) | COL1A1 |
| P11 | 11.55 | 780.9101 | 2 | GETGPAGPAGPIGPVGAR | COL1A1 |
| P12 | 11.90 | 908.9360 | 2 | GPPGP(+15.99)MGPPGLAGPPGESGR | COL1A1 |
| R1 | 6.35 | 739.3578 | 3 | GETGPAGRP(+15.99)GEVGPP(+15.99)GPP(+15.99)GPAGEK | COL1A1 |
| R2 | 7.09 | 732.8339 | 2 | SGETGASGPP(+15.99)GFAGEK | COL1A2 |
| R3 | 7.39 | 598.8227 | 2 | TGQP(+15.99)GAVGPAGIR | COL1A2 |
| R4 | 7.45 | 775.8814 | 2 | GPP(+15.99)GESGAAGPAGPIGSR | COL1A2 |
| R5 | 8.32 | 644.3202 | 2 | GFP(+15.99)GSP(+15.99)GNIGPAGK | COL1A2 |
| R6 | 8.57 | 894.9656 | 2 | AGPVGTAGAP(+15.99)GPQGPVGPTGK | COL1A2 |
| R7 | 8.59 | 556.7801 | 2 | GLAGPP(+15.99)GMP(+15.99)GAR | COL1A1 |
| R8 | 10.15 | 536.7750 | 2 | GFP(+15.99)GADGVAGPK | COL1A1 |
| R9 | 10.39 | 1147.5565 | 2 | GYP(+15.99)GNAGPVGTAGAP(+15.99)GPQGPVGPTGK | COL1A2 |
| R10 | 10.39 | 765.3729 | 3 | GYP(+15.99)GN(+0.98)AGPVGTAGAP(+15.99)GPQGPVGPTGK | COL1A2 |
| R11 | 12.25 | 1275.1007 | 2 | GNDGATGAAGPP(+15.99)GPTGPAGPP(+15.99)GFP(+15.99)GAVGAK | COL1A2 |
| R12 | 14.57 | 611.8090 | 2 | GFP(+15.99)GTP(+15.99)GLP(+15.99)GFK | COL1A2 |
| R13 | 15.51 | 863.7582 | 3 | GSDGSVGPVGPAGPIGSAGPP(+15.99)GFP(+15.99)GAP(+15.99)GPK | COL1A2 |
| R14 | 16.32 | 858.4260 | 3 | GSDGSVGPVGPAGPIGSAGPP(+15.99)GFPGAP(+15.99)GPK | COL1A2 |
| R15 | 16.50 | 637.3487 | 2 | LGAP(+15.99)GFLGLP(+15.99)GSR | COL1A2 |
| No. | Peak Area Ratio Relative to the Trypsin-Derived Peptide (m/z 737.7062) | BLAST Search Results a | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sika Deer Antler | Sika Deer Hide | Sika Deer Bone | Donkey Hide | Bovine | Porcine | Fish | Horse | Sheep | Goat | |
| P1 | 4.99 | 4.94 | 3.76 | 6.43 | 4.15 | 3.50 | 0.05 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| P2 | 3.90 | 3.07 | 2.73 | 4.38 | 3.69 | 4.77 | 2.88 | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| P3 | 6.68 | 5.56 | 3.70 | 7.29 | 8.13 | 9.08 | 0.06 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| P4 | 2.09 | 3.21 | 1.30 | 2.53 | 2.50 | 1.53 | 0.07 | - | - | - |
| P5 | 6.81 | 5.45 | 4.94 | 7.32 | 5.85 | 4.40 | 0.05 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| P6 | 3.90 | 4.37 | 2.37 | 5.85 | 5.37 | 4.63 | 0.05 | ✓ | - | ✓ |
| P7 | 9.88 | 6.84 | 4.67 | 9.82 | 1.80 | 1.16 | 0.05 | ✓ | ✓ | - |
| P8 | 3.54 | 3.31 | 2.60 | 3.82 | 4.94 | 5.62 | 0.04 | - | - | - |
| P9 | 1.32 | 2.33 | 0.76 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.54 | 0.02 | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| P10 | 3.47 | 2.13 | 2.31 | 2.71 | 4.61 | 5.58 | 0.03 | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| P11 | 5.69 | 4.91 | 3.96 | 0.01 | 7.71 | 0.48 | 0.03 | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| P12 | 1.70 | 2.37 | 1.25 | 0.01 | 0.58 | 0.76 | 0.89 | - | - | - |
| R1 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.00 | - | - | - |
| R2 | 1.05 | 0.89 | 0.66 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | - | - | - |
| R3 | 1.91 | 0.83 | 1.44 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.29 | 0.00 | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| R4 | 2.59 | 1.99 | 1.35 | 2.24 | 0.03 | 3.32 | 0.07 | ✓ | - | - |
| R5 | 0.91 | 1.25 | 0.74 | 0.95 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.02 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| R6 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | - | - | - |
| R7 | 0.04 | 2.17 | 0.16 | 2.48 | 0.22 | 0.04 | 0.01 | - | - | - |
| R8 | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.00 | ✓ | - | - |
| R9 | 0.32 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | - | - | - |
| R10 | 0.44 | 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | - | - | - |
| R11 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.41 | 0.00 | - | - | - |
| R12 | 0.38 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.32 | 0.00 | ✓ | ✓ | - |
| R13 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| R14 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| R15 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.01 | 0.00 | - | ✓ | - |
| R16 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | - | ✓ | ✓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otsuki, K.; Nomizo, A.; Zhang, M.; Li, D.; Kikuchi, T.; Li, W. Identification of Marker Peptides in Gelatins from Sika Deer (Cervus nippon) Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Quadrupole-Exactive-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2025, 30, 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071528
Otsuki K, Nomizo A, Zhang M, Li D, Kikuchi T, Li W. Identification of Marker Peptides in Gelatins from Sika Deer (Cervus nippon) Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Quadrupole-Exactive-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071528
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtsuki, Kouharu, Aya Nomizo, Mi Zhang, Dongxia Li, Takashi Kikuchi, and Wei Li. 2025. "Identification of Marker Peptides in Gelatins from Sika Deer (Cervus nippon) Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Quadrupole-Exactive-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071528
APA StyleOtsuki, K., Nomizo, A., Zhang, M., Li, D., Kikuchi, T., & Li, W. (2025). Identification of Marker Peptides in Gelatins from Sika Deer (Cervus nippon) Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Quadrupole-Exactive-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 30(7), 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071528







