Neuropilin Antagonists (NRPas) Block the Phosphorylation of the Cancer Therapeutic Key Factor p38α Kinase Triggering Cell Death
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
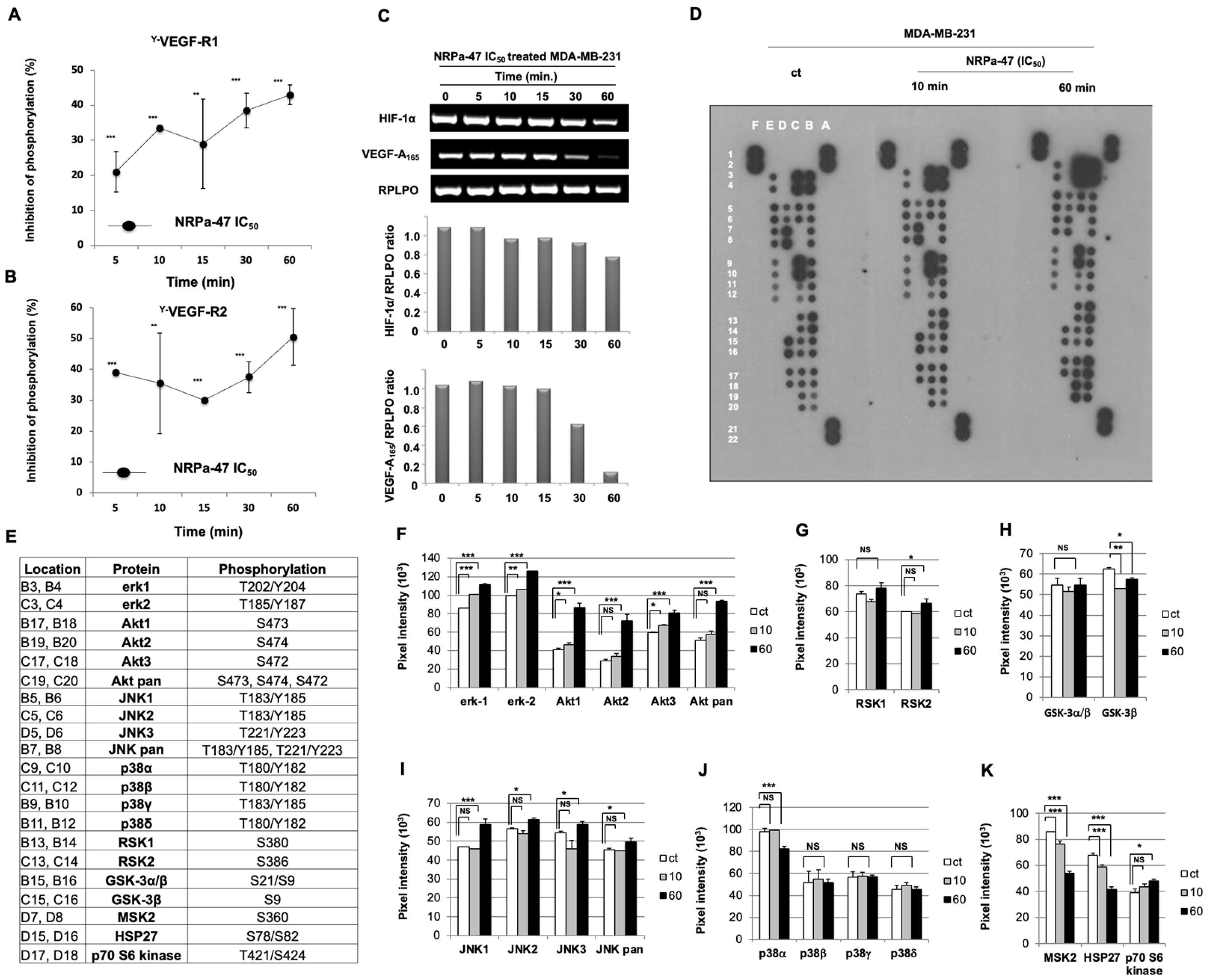
2.1. Neuropilin Antagonist 47 (NRPa-47) Inhibits VEGF-R1/-R2 Phosphorylation
2.2. NRP-1/VEGF-Rs Downstream Signalling Modulation Induced by NRPa-47
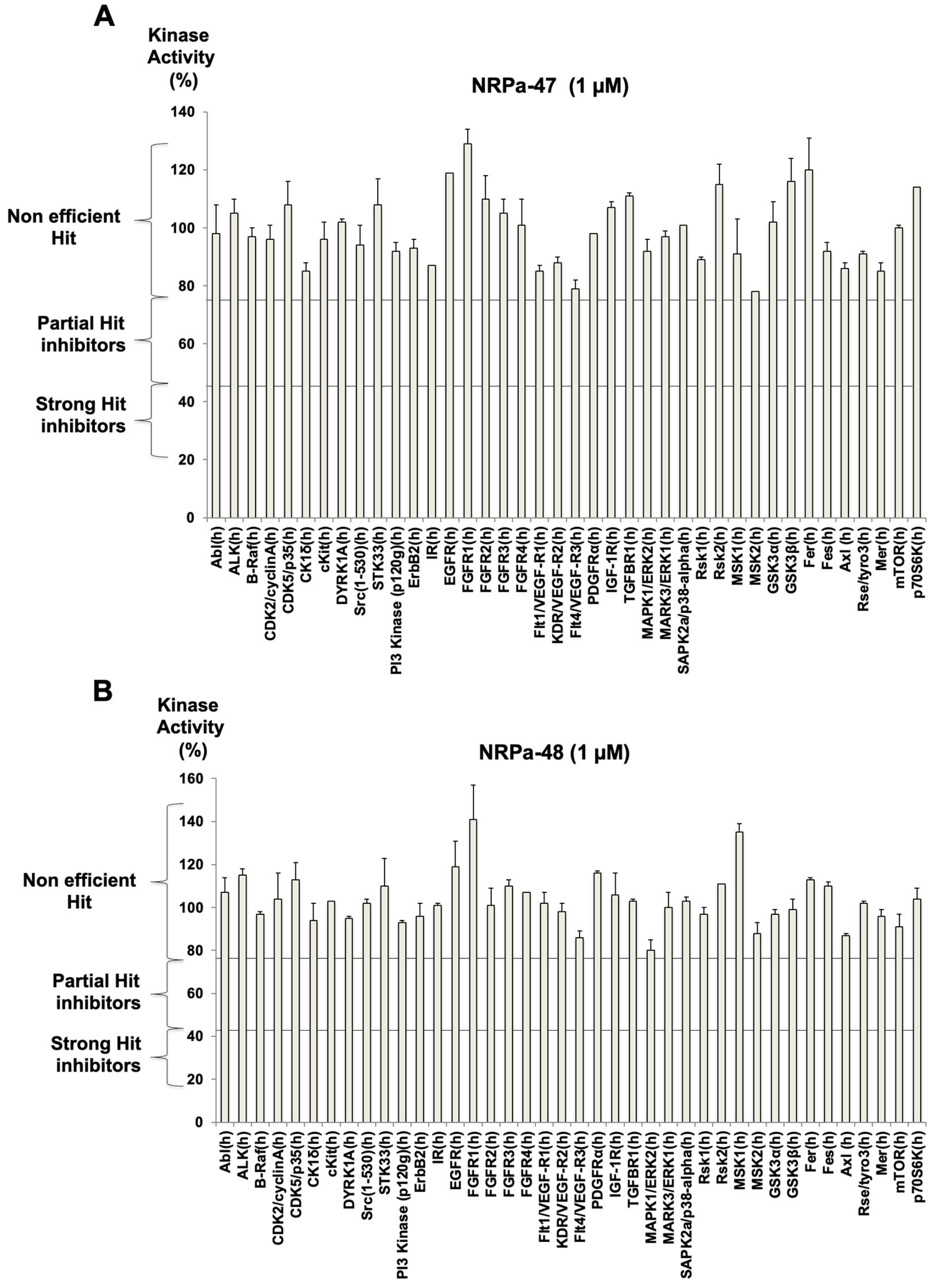
2.3. Modified-NRPa-47 (NRPa-48) and Its Own Effect on NRP-1/VEGF-Rs Downstream Signalling
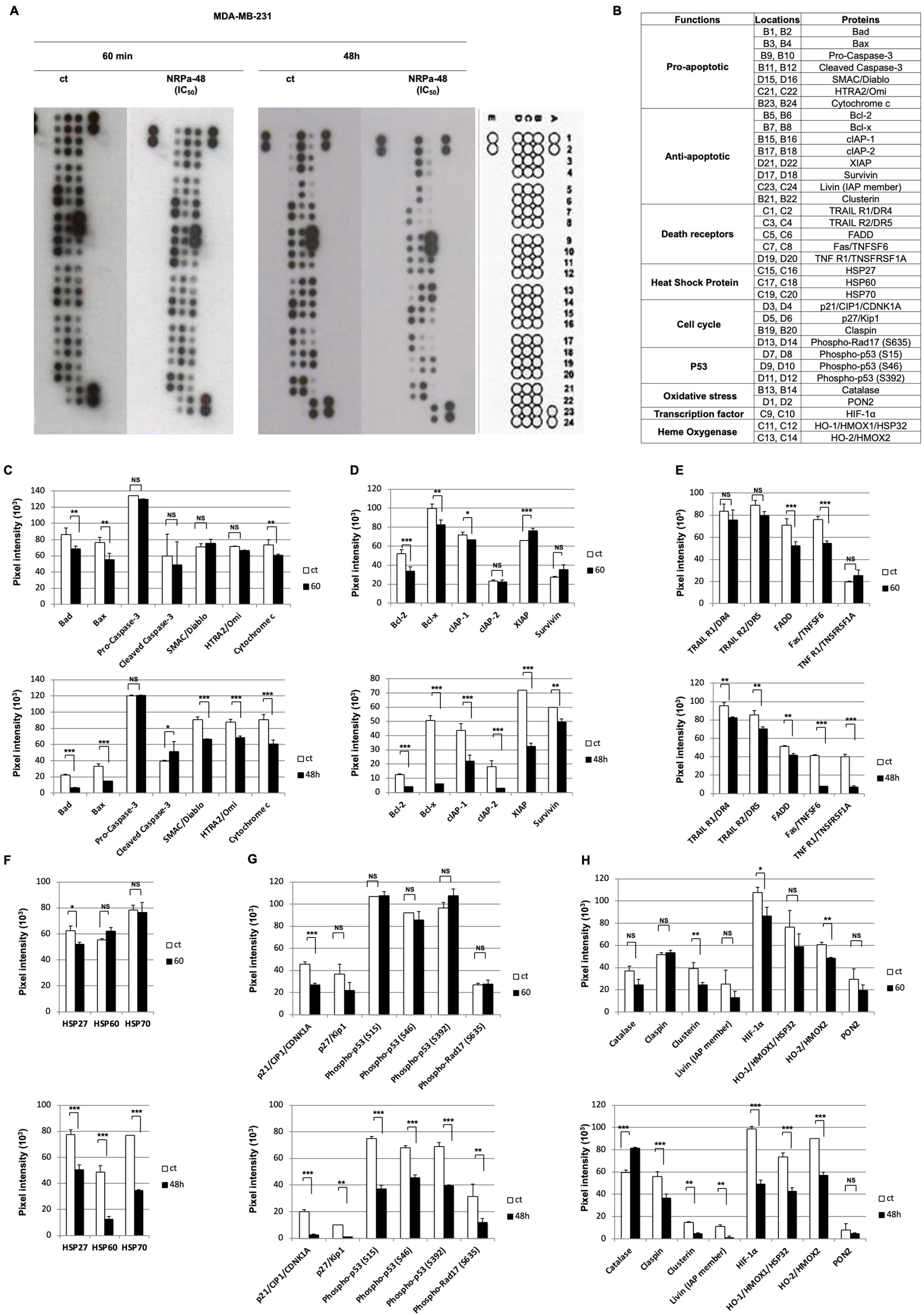
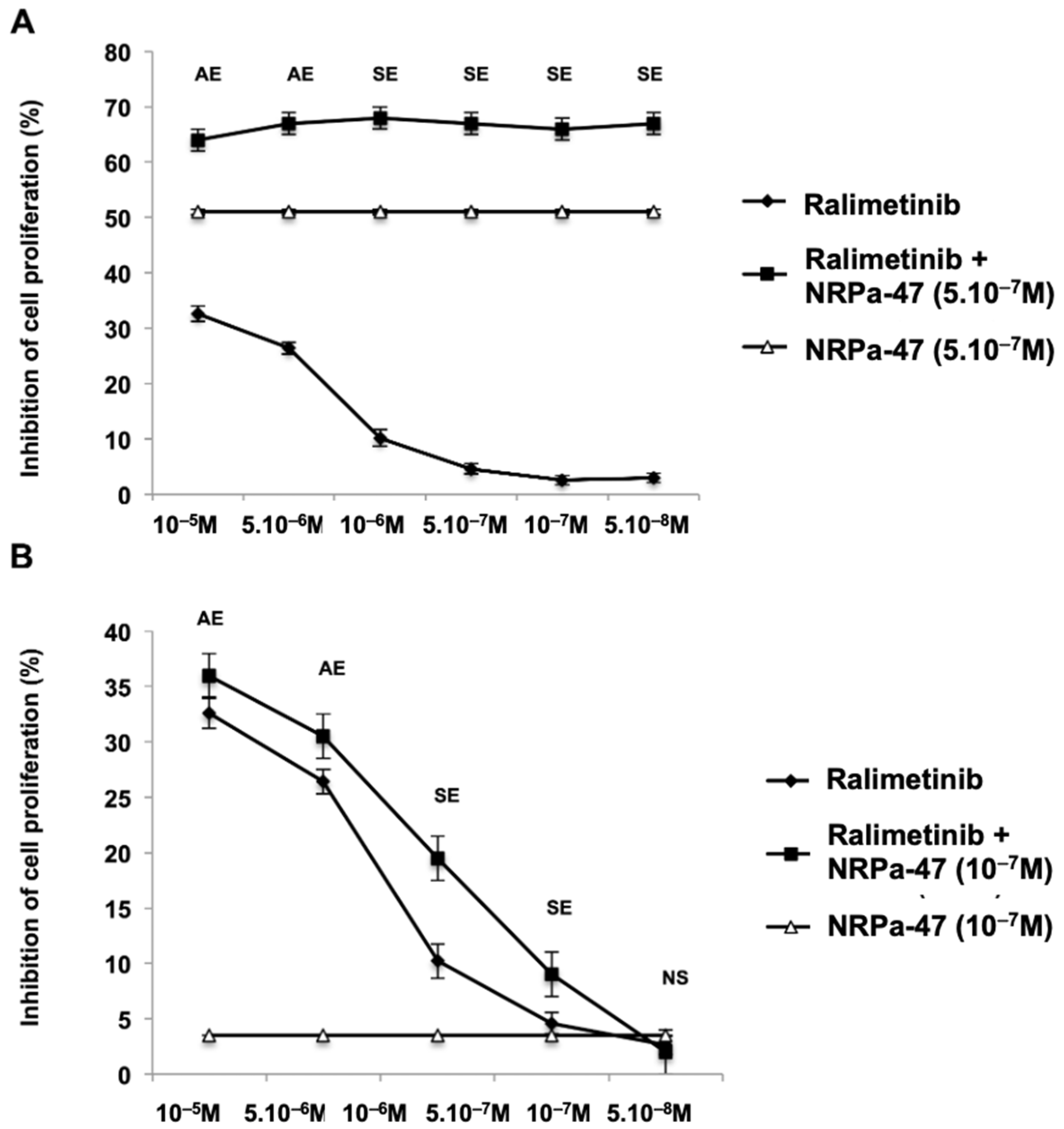
2.4. Apoptotic Pathway Induced by NRPa-47
2.5. Mechanism of NRPa-48-Induced Cell Death
2.6. In Vivo Anti-Tumour Activity of NRPa-48 on Xenografted-NOG Mice
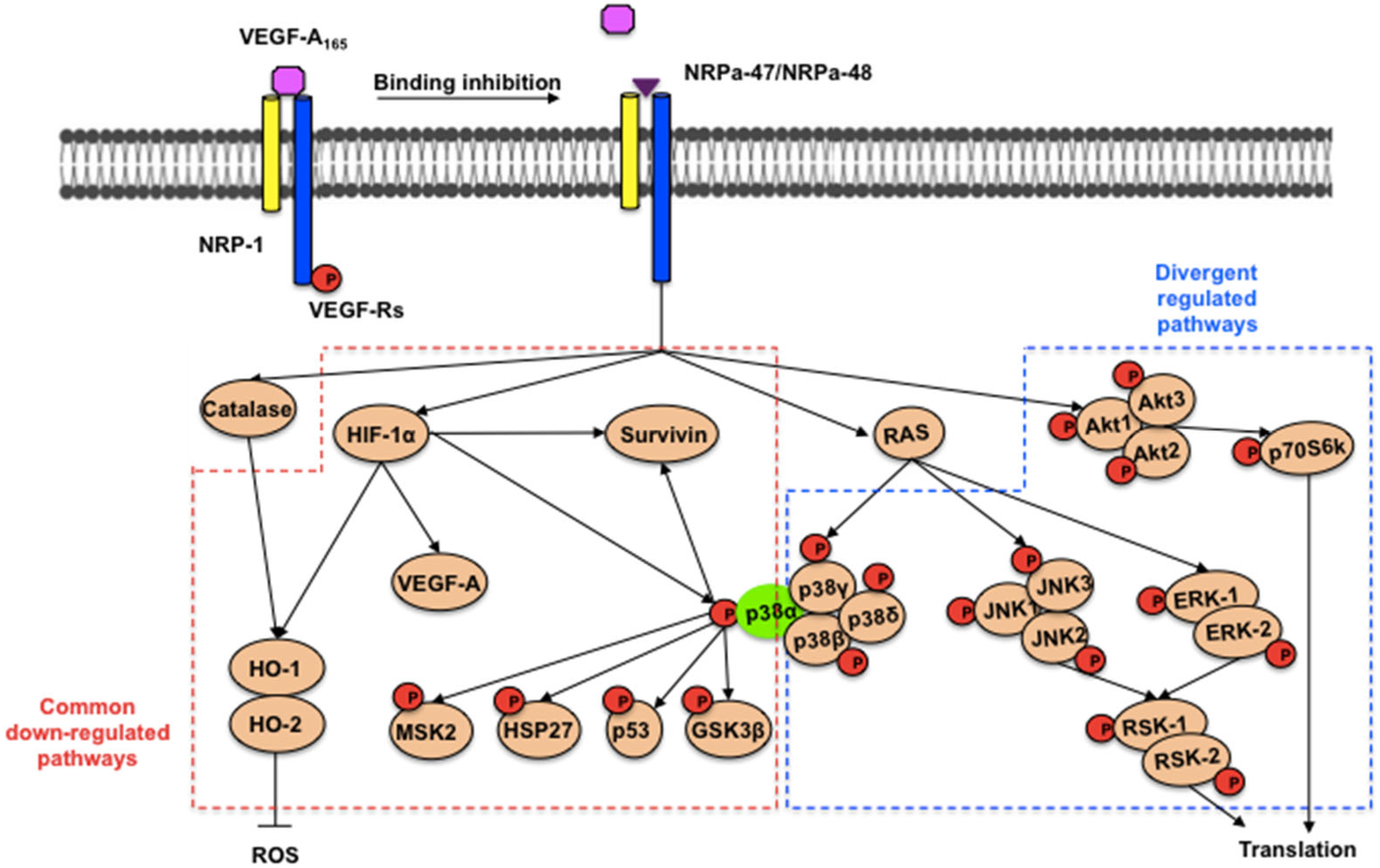
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Synthesis of Compound
4.2. Total RNA Preparation and RT-PCR
4.3. Proteome Profiler Arrays
4.4. Cell Culture Conditions
4.5. VEGF-R Kinase Assay
4.6. Molecular Docking
4.7. Protein Kinase Profiling
4.8. In Vivo Xenografted-Tumour Mouse Model
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, Q.; Chanthery, Y.; Liang, W.C.; Stawicki, S.; Mak, J.; Rathore, N.; Tong, R.K.; Kowalski, J.; Yee, S.F.; Pacheco, G.; et al. Blocking neuropilin-1 function has an additive effect with anti-VEGF to inhibit tumor growth. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodkin, A.L.; Levengood, D.V.; Rowe, E.G.; Tai, Y.T.; Giger, R.J.; Ginty, D.D. Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell 1997, 90, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Tugues, S.; Li, X.; Gualandi, L.; Claesson-Welsh, L. Signal transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Biochem. J. 2011, 437, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prud’homme, G.J.; Glinka, Y. Neuropilins are multifunctional coreceptors involved in tumor initiation, growth, metastasis and immunity. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 921–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, J.R.; Staton, C.A.; Chapple, K.; Corfe, B.M. Neuropilins: Expression and roles in the epithelium. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2012, 93, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumond, A.; Brachet, E.; Durivault, J.; Vial, V.; Puszko, A.K.; Lepelletier, Y.; Montemagno, C.; Pagnuzzi-Boncompagni, M.; Hermine, O.; Garbay, C.; et al. Neuropilin 1 and Neuropilin 2 gene invalidation or pharmacological inhibition reveals their relevance for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Mishra, J.; Bodas, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Batra, S.K.; Dutta, S.; Datta, K. Role of neuropilin-2 signaling axis in cancer progression and therapy resistance. Cancer Metastasis Res. 2022, 41, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, E.M.; Giovanini, A.F.; Ribas, C.A.P.M.; Malafaia, O.; Roesler, R.; Isoan, G.R. The nervous system development regulator neuropilin-1 as a potential marker and therapeutic target in brain cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.; Bai, S.; Damico-Beyer, L.A.; Jin, D.; Liang, W.C.; Wu, Y.; Theil, F.P.; Joshi, A.; Lu, Y.; Lowe, J.; et al. Anti-neuropilin-1 (MNRP1685A): Unexpected pharmacokinetic differences across species, from preclinical models to humans. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 2512–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caunt, M.; Mak, J.; Liang, W.C.; Stawicki, S.; Pan, Q.; Tong, R.K.; Kowalski, J.; Ho, C.; Reslan, H.B.; Ross, J.; et al. Blocking neuropilin-2 function inhibits tumor cell metastasis. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starzec, A.; Ladam, P.; Vassy, R.; Badache, S.; Bouchemal, N.; Navaza, A.; Du Penhoat, C.H.; Perret, G.Y. Structure-function analysis of the antiangiogenic ATWLPPR peptide inhibiting VEGF(165) binding to neuropilin-1 and molecular dynamics simulations of the ATWLPPR/neuropilin-1 complex. Peptides 2007, 28, 2397–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, G.Y.; Starzec, A.; Hauet, N.; Vergote, J.; Le Pecheur, M.; Vassy, R.; Leger, G.; Verbeke, K.A.; Bormans, G.; Nicolas, P.; et al. In vitro evaluation and biodistribution of a 99mTc-labeled anti-VEGF peptide targeting neuropilin-1. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2004, 31, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoa, A.; Pellegrini-Moise, N.; Bechet, D.; Barberi-Heyob, M.; Chapleur, Y. Sugar-based peptidomimetics as potential inhibitors of the vascular endothelium growth factor binding to neuropilin-1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3285–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Bagherzadeh, A.; Hartzoulakis, B.; Jarvis, A.; Lohr, M.; Shaikh, S.; Aqil, R.; Cheng, L.; Tickner, M.; Esposito, D.; et al. Characterization of a bicyclic peptide neuropilin-1 (NP-1) antagonist (EG3287) reveals importance of vascular endothelial growth factor exon 8 for NP-1 binding and role of NP-1 in KDR signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 13493–13502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasarre, C.; Roth, M.; Jacob, L.; Roth, L.; Koncina, E.; Thien, A.; Labourdette, G.; Poulet, P.; Hubert, P.; Crémel, G.; et al. Peptide-based interference of the transmembrane domain of neuropilin-1 inhibits glioma growth in vivo. Oncogene 2010, 29, 2381–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.; Allerston, C.K.; Jia, H.; Herzog, B.; Garza-Garcia, A.; Winfield, N.; Ellard, K.; Aqil, R.; Lynch, R.; Chapman, C.; et al. Small molecule inhibitors of the neuropilin-1 vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2215–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.; Mote, F.; Steadman, D.; Soudy, C.; Miyauchi, J.T.; Crosby, S.; Jarvis, A.; Reisinger, T.; Winfield, N.; Evans, G.; et al. Small molecule neuropili-1 antagonists combine antiangiogenic and antitumor activity with immune modulation through reduction of transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) production in regulatory T-cells. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 4135–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starzec, A.; Miteva, M.A.; Ladam, P.; Villoutreix, B.O.; Perret, G.Y. Discovery of novel inhibitors of vascular endothelial growth factor-A-Neuropilin-1 interaction by structure-based virtual screening. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 4042–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broz, M.; Kolaric, A.; Jukic, M.; Bren, U. Neuropilin (NRPs) related pathological conditions and their modulators. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriello, L.; Montès, M.; Lepelletier, Y.; Leforban, B.; Liu, W.-Q.; Demange, L.; Delhomme, B.; Pavoni, S.; Jarray, R.; Boucher, J.-L.; et al. Structure-based discovery of a small non-peptidic Neuropilins antagonist exerting in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity on breast cancer model. Cancer Lett. 2014, 349, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-Q.; Lepelletier, Y.; Montès, M.; Borriello, L.; Jarray, R.; Grépin, R.; Leforban, B.; Loukaci, A.; Benhida, R.; Hermine, O.; et al. NRPa-308, a new neuropilin-1 antagonist, exerts in vitro anti-angiogenic and anti-proliferative effects and in vivo anti-cancer effects in a mouse xenograft model. Cancer Lett. 2018, 414, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-Q.; Megale, V.; Borriello, L.; Leforban, B.; Montès, M.; Goldwaser, E.; Gresh, N.; Piquemal, J.-P.; Hadj-Slimane, R.; Hermine, O.; et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of non-peptidic antagonists of neuropilin-1 receptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 4254–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, P.S.M.; Franco, L.S.; Fraga, C.A.M. The Magic Methyl and Its Tricks in Drug Discovery and Development. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, E.J.; Kümmerle, A.E.; Fraga, C.A. The methylation effect in medicinal chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5215–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capdeville, R.; Buchdunger, E.; Zimmermann, J.; Matter, A. Glivec (STI571, imatinib), a rationally developed, targeted anticancer drug. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Fu, J. Methyl-containing pharmaceuticals: Methylation in drug design. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 3283–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.R.; Ronco, C.; Demange, L.; Benhida, R. Hypoxia inducible factor down-regulation, cancer and cancer stem cells (CSCs): Ongoing success stories. Med. Chem. Commun. 2017, 8, 21–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, M.M.; Anbar, H.S.; El-Gamal, M.I. Current status and future prospects of p38a/MAPK14 kinase and its inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 213, 113216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.; Diaz, L.; Pous, J.; Baginski, B.; Duran-Corbera, A.; Scarpa, M.; Brun-Heath, I.; Igea, A.; Martin-Malpartida, P.; Ruiz, L.; et al. Characterization of p38a autophosphorylation inhibitors that target the non-canonical activation pathway. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, H.C.; Aslanian, A.S.; Lees, J.A.; Yaffe, M.B. p53-deficient cells rely on ATM- and ATR-mediated checkpoint signaling through the p38MAPK/MK2 pathway for survival after DNA damage. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarray, R.; Pavoni, S.; Borriello, L.; Allain, B.; Lopez, N.; Bianco, S.; Liu, W.-Q.; Biard, D.; Demange, L.; Hermine, O.; et al. Disruption of phactr-1 pathway triggers pro-inflammatory and pro-atherogenic factors: New insights in atherosclerosis development. Biochimie 2015, 118, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarray, R.; Allain, B.; Borriello, L.; Biard, D.; Loukaci, A.; Larghero, J.; Hadj-Slimane, R.; Garbay, C.; Lepelletier, Y.; Raynaud, F. Depletion of the novel protein PHACTR-1 from human endothelial cells abolishes tube formation and induces cell death receptor apoptosis. Biochimie 2011, 93, 1668–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Kooi, C.W.; Jusino, M.A.; Perman, B.; Neau, D.B.; Bellamy, H.D.; Leahy, D.J. Structural basis for ligand and heparin binding to neuropilin B domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6152–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.N. Surflex: Fully automatic flexible molecular docking using a molecular similarity-based search engine. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abagyan, R.; Totrov, M. Biased probability Monte Carlo conformational searches and electrostatic calculations for peptides and proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 235, 983–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borriello, L.; Jarray, R.; Rignault-Bricard, R.; Montes, M.; Lopez, N.; Maciel, T.T.; Hermine, O.; Raynaud, F.; Demange, L.; Lepelletier, Y. Neuropilin Antagonists (NRPas) Block the Phosphorylation of the Cancer Therapeutic Key Factor p38α Kinase Triggering Cell Death. Molecules 2025, 30, 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071494
Borriello L, Jarray R, Rignault-Bricard R, Montes M, Lopez N, Maciel TT, Hermine O, Raynaud F, Demange L, Lepelletier Y. Neuropilin Antagonists (NRPas) Block the Phosphorylation of the Cancer Therapeutic Key Factor p38α Kinase Triggering Cell Death. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071494
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorriello, Lucia, Rafika Jarray, Rachel Rignault-Bricard, Matthieu Montes, Nicolas Lopez, Thiago Trovati Maciel, Olivier Hermine, Françoise Raynaud, Luc Demange, and Yves Lepelletier. 2025. "Neuropilin Antagonists (NRPas) Block the Phosphorylation of the Cancer Therapeutic Key Factor p38α Kinase Triggering Cell Death" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071494
APA StyleBorriello, L., Jarray, R., Rignault-Bricard, R., Montes, M., Lopez, N., Maciel, T. T., Hermine, O., Raynaud, F., Demange, L., & Lepelletier, Y. (2025). Neuropilin Antagonists (NRPas) Block the Phosphorylation of the Cancer Therapeutic Key Factor p38α Kinase Triggering Cell Death. Molecules, 30(7), 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071494






