Green Nanoparticle Synthesis in the Application of Non-Bacterial Mastitis in Cattle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Indetification of Microorganisms
2.2. Physicochemical Analysis of Nanoparticles
2.3. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.4. Minimal F/A Concentration (MFC/MAC)
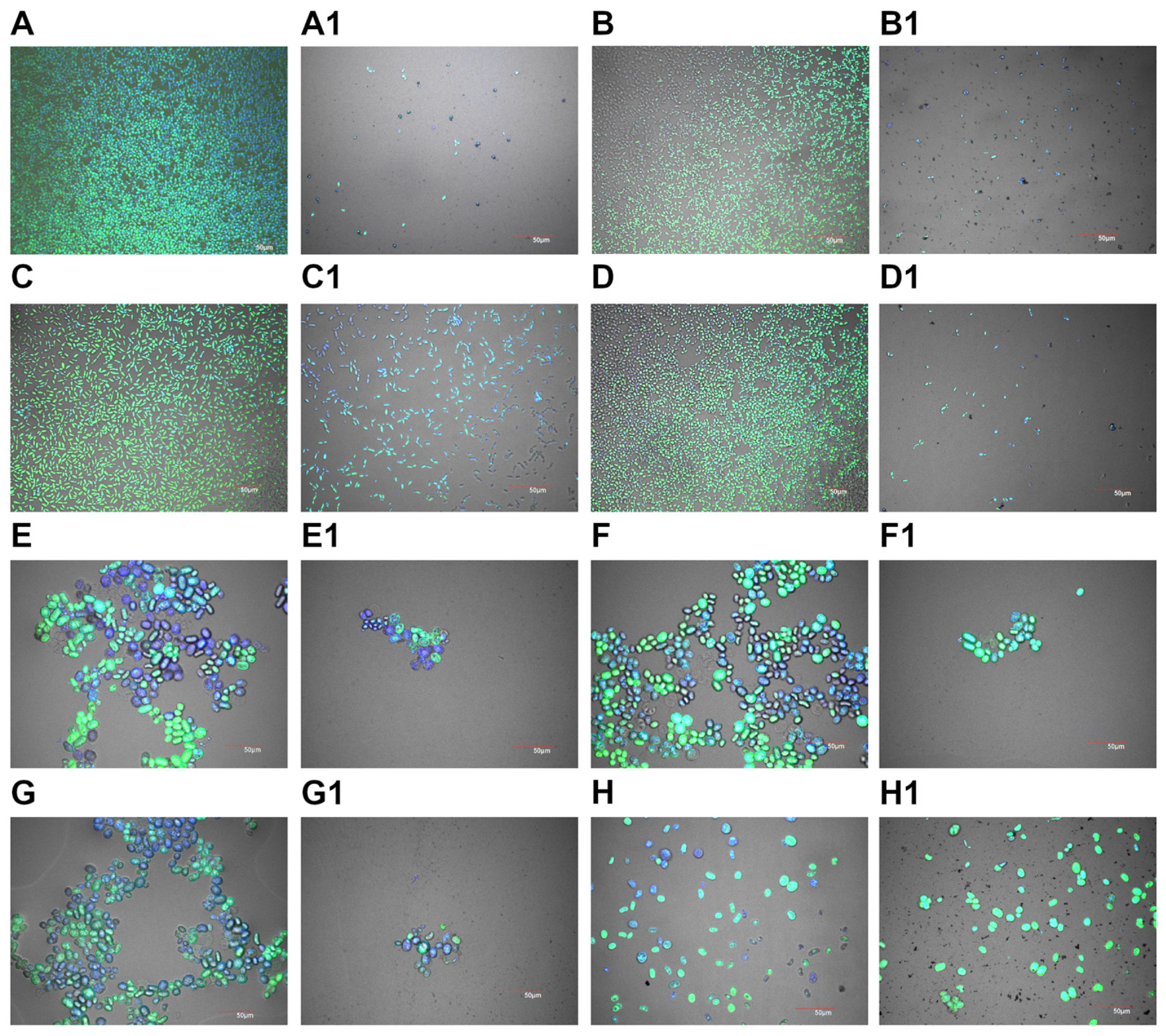
2.5. Viability Analysis
2.6. Biofilm Formation
2.7. Invasion Test
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microorganism Strains
4.2. Synthesis and Physicochemical Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles
4.3. Physicochemical Analysis of Nanoparticles
- LIBS: Studies using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) enabled the identification of elements present in dried suspensions of AgNPs. A laser beam focused on the surface of the dried suspension caused its ablation, followed by heating and ionizing the resulting vapors and generation of plasma. The plasma thus generated was a source of strong radiation, specific to the atoms in the suspension. The study was conducted in the experimental setup shown in the Nasiłowska et al. 2023 [15]. The plasma was generated using a Quantel pulsed Nd/YAG laser, model Brio. The experiments were carried out with radiation at a wavelength of 1064 nm according to the parameters listed in Table 5.
- EDS: The elemental composition of the dried suspensions of AgNPs was also determined using an EDX detector (energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer, FEI, (FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA) coupled to a scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (Quanta 250 FEG SEM, FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA). The accelerating voltage was 30 kV, while the spot was 6.
- FTIR-ATR: The functional groups of the dried suspensions were determined by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The dried suspensions of AgNPs were analyzed by FTIR (Nicolet IS50, FTIR, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Samples were measured three times using ATR (total internal reflection) in the 400–4000 cm−1 range with a resolution of 4 cm−1 and for 64 scans.
4.4. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
4.5. Minimal F/A Concentration (MFC/MAC)
4.6. Viability Analysis
4.7. Biofilm Formation
4.8. Invasion Test
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanek, P.; Żółkiewski, P.; Januś, E. A Review on Mastitis in Dairy Cows Research: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lass-Flörl, C.; Mayr, A. Human Protothecosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagielski, T.; Buzzini, P.; Lassa, H.; Malinowski, E.; Branda, E.; Turchetti, B.; Polleichtner, A.; Roesler, U.; Lagneau, P.-E.; Marques, S.; et al. Multicentre Etest Evaluation of In Vitro Activity of Conventional Antifungal Drugs against European Bovine Mastitis Prototheca spp. Isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1945–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassa, H.; Jagielski, T.; Malinowski, E. Effect of Different Heat Treatments and Disinfectants on the Survival of Prototheca zopfii. Mycopathologia 2011, 171, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huilca-Ibarra, M.P.; Vasco-Julio, D.; Ledesma, Y.; Guerrero-Freire, S.; Zurita, J.; Castillejo, P.; Barceló Blasco, F.; Yanez, L.; Changoluisa, D.; Echeverría, G.; et al. High Prevalence of Prototheca bovis Infection in Dairy Cattle with Chronic Mastitis in Ecuador. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakkori, N.; Rahmani, H.K.; Khoramian, B. Genotypic and Phenotypic Diversity of Prototheca spp. Recovered from Bovine Mastitis in Terms of Antimicrobial Resistance and Biofilm Formation Ability. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luceri, A.; Francese, R.; Lembo, D.; Ferraris, M.; Balagna, C. Silver Nanoparticles: Review of Antiviral Properties, Mechanism of Action and Applications. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallmann, E.J.J.; Cunha, F.A.; Castro, B.N.M.F.; Maciel, A.M.; Menezes, E.A.; Fechine, P.B.A. Antifungal Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Obtained by Green Synthesis. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. 2015, 57, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Tyagi, A.K.; Kumar, P.; Malik, A. Antibacterial Potential of Jatropha Curcas Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles against Food Borne Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic Basis of Antimicrobial Actions of Silver Nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 231711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameh, T.; Gibb, M.; Stevens, D.; Pradhan, S.H.; Braswell, E.; Sayes, C.M. Silver and Copper Nanoparticles Induce Oxidative Stress in Bacteria and Mammalian Cells. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.S.; Shittu, E.O.; Akpor, O.B.; Rotimi, D.; Batiha, G.E.S. Silver Nanoparticles Restrict Microbial Growth by Promoting Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Baek, K.-H. Green Nanobiotechnology: Factors Affecting Synthesis and Characterization Techniques. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 417305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiłowska, B.; Skrzeczanowski, W.; Bombalska, A.; Bogdanowicz, Z. Laser Emission Spectroscopy of Graphene Oxide Deposited on 316 Steel and Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy Suitable for Orthopedics. Materials 2023, 16, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworecka-Kaszak, B.; Krutkiewicz, A.; Szopa, D.; Kleczkowski, M.; Biegańska, M. High Prevalence of Candida Yeast in Milk Samples from Cows Suffering from Mastitis in Poland. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 196347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzo, G.; Bonerba, E.; Di Pinto, A.; Bolzoni, G.; Ceci, E.; Mottola, A.; Tantillo, G.; Terio, V. Occurrence of Prototheca spp. in Cow Milk Samples. New Microbiol. 2014, 37, 459–464. [Google Scholar]
- Dhand, V.; Soumya, L.; Bharadwaj, S.; Chakra, S.; Bhatt, D.; Sreedhar, B. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Coffea Arabica Seed Extract and Its Antibacterial Activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikhao, N.; Ounkaew, A.; Kasemsiri, P.; Theerakulpisut, S.; Okhawilai, M.; Hiziroglu, S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using the Extract of Spent Coffee Used for Paper-Based Hydrogen Peroxide Sensing Device. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejaswini, R.; Athar, D.A. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Roasted Coffea Arabica Bean Extract and Its Antimicrobial Activity. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2021, 5, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavin, T.; Murugaiyah, V.; Tan, J.K.; Kassim, M.N.I.; Ramakrishna, S.; Vigneswari, S. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Coffea Arabica Husk for Enhanced Antibacterial and Anti-Cancer Applications. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 194, 107625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beinhauerova, M.; Moravkova, M.; Seydlova, R.; Crhanova, M. Eradication of Bovine Mastitis Caused by the Pathogenic Microalga Prototheca bovis on a Dairy Cattle Farm: A Case Report. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdal, M.; Gurkok, S. Recent Advances in Nanoparticles as Antibacterial Agent. ADMET DMPK 2022, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Manna, S.; Mandal, S.M. Antimicrobial Nanoparticles: Current Landscape and Future Challenges. RSC Pharm. 2024, 1, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharjeel, A.W.; Rather, I.U.H.; Oveas, R.P.; Qurat, U.A.N.; Mohsina, M.; Riyaz, A.B.; Jalal, U.P.; Sandip, C.; Kuldeep, D.; Mohd, I.Y. A Brief Analysis of Economic Losses Due to Mastitis in Dairy Cattle. Indian. Vet. J. 2022, 99, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Liaqat, N.; Jahan, N.; Khalil-ur-Rahman; Anwar, T.; Qureshi, H. Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles: Optimization, Characterization, Antimicrobial Activity, and Cytotoxicity Study by Hemolysis Assay. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 952006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, M.; Shahzaib, A.; Nishat, N.; Jahan, A.; Bhat, T.A.; Inam, A. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review of Methods, Influencing Factors, and Applications. JCIS Open 2024, 16, 100125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawangkan, A.; Siriphap, A.; Yosboonruang, A.; Kiddee, A.; Pook-In, G.; Saokaew, S.; Sutheinkul, O.; Duangjai, A. Potential Antimicrobial Properties of Coffee Beans and Coffee By-Products Against Drug-Resistant Vibrio Cholerae. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 865684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canci, L.A.; de Toledo Benassi, M.; Canan, C.; Kalschne, D.L.; Colla, E. Antimicrobial Potential of Aqueous Coffee Extracts against Pathogens and Lactobacillus Species: A Food Matrix Application. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velgosova, O.; Dolinská, S.; Podolská, H.; Mačák, L.; Čižmárová, E. Impact of Plant Extract Phytochemicals on the Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles. Materials 2024, 17, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Sharma, S.; Alam, M.K.; Singh, V.N.; Shamsi, S.F.; Mehta, B.R.; Fatma, A. Rapid Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Dried Medicinal Plant of Basil. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.S.; Rai, A.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Rapid Synthesis of Au, Ag, and Bimetallic Au Core–Ag Shell Nanoparticles Using Neem (Azadirachta Indica) Leaf Broth. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, S.P.; Chaudhary, M.; Pasricha, R.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Synthesis of Gold Nanotriangles and Silver Nanoparticles Using Aloevera Plant Extract. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Bulut, O.; Some, S.; Mandal, A.K.; Yilmaz, M.D. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: Biomolecule-Nanoparticle Organizations Targeting Antimicrobial Activity. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2673–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Yadav, S.C.; Yadav, S.K. Syzygium Cumini Leaf and Seed Extract Mediated Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Characterization. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modarresi, M.; Chahardoli, A.; Karimi, N.; Chahardoli, S. Variations of Glaucine, Quercetin and Kaempferol Contents in Nigella Arvensis against Al2O3, NiO, and TiO2 Nanoparticles. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamai, S.; Negi, D.P.S. Cysteine-Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles as a Colorimetric Probe for the Selective Detection of Cysteamine. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 215, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-González, A.; Figueroa-Hernández, C.Y.; González-Rios, O.; Suárez-Quiroz, M.L.; González-Amaro, R.M.; Hernández-Estrada, Z.J.; Rayas-Duarte, P. Coffee Chlorogenic Acids Incorporation for Bioactivity Enhancement of Foods: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, H.; Fan, J.; Li, J.; Warren, A.; Lin, X. Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) in the Model Ciliate Paramecium Multimicronucleatum: Molecular Mechanisms of Activation Are Dose- and Particle Size-Dependent. Eur. J. Protistol. 2021, 81, 125792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbuna, C.; Parmar, V.K.; Jeevanandam, J.; Ezzat, S.M.; Patrick-Iwuanyanwu, K.C.; Adetunji, C.O.; Khan, J.; Onyeike, E.N.; Uche, C.Z.; Akram, M.; et al. Toxicity of Nanoparticles in Biomedical Application: Nanotoxicology. J. Toxicol. 2021, 2021, 9954443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-López, L.Z.; Espinoza-Gómez, H.; Somanathan, R. Silver Nanoparticles: Electron Transfer, Reactive Oxygen Species, Oxidative Stress, Beneficial and Toxicological Effects. Mini Review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Guo, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L. Size-Dependent Cellular Uptake and Localization Profiles of Silver Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4247–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recordati, C.; De Maglie, M.; Bianchessi, S.; Argentiere, S.; Cella, C.; Mattiello, S.; Cubadda, F.; Aureli, F.; D’Amato, M.; Raggi, A.; et al. Tissue Distribution and Acute Toxicity of Silver after Single Intravenous Administration in Mice: Nano-Specific and Size-Dependent Effects. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pate, K.; Safier, P. Chemical Metrology Methods for CMP Quality. In Advances in Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP); Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 299–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyotome, T.; Matsui, S. Analysis of Prototheca and Yeast Species Isolated from Bulk Tank Milk Collected in Tokachi District, Japan. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 8364–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Desouky, N.; Shoueir, K.; El-Mehasseb, I.; El-Kemary, M. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Bio Valorization Coffee Waste Extract: Photocatalytic Flow-Rate Performance, Antibacterial Activity, and Electrochemical Investigation. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 13, 15871–15885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Li, G.; Wan, P.; Shao, Z.; Jin, E.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Long, A.; Qian, Y. Investigation of Prototheca bovis Infection and Its Correlation with Dairy Herd Improvement Data from a Dairy Farm in Central China. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, P.H.F.d.; Garcia, M.T.; Figueiredo-Godoi, L.M.A.; Lage, A.C.P.; da Silva, N.S.; Junqueira, J.C. Metal Nanoparticles to Combat Candida albicans Infections: An Update. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peréz-Través, L.; de Llanos, R.; Flockhart, A.; García-Domingo, L.; Groenewald, M.; Pérez-Torrado, R.; Querol, A. Virulence Related Traits in Yeast Species Associated with Food; Debaryomyces Hansenii, Kluyveromyces Marxianus, and Wickerhamomyces Anomalus. Food Control 2021, 124, 107901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Herai, Y.; Yahaba, M.; Watanabe, A.; Kamei, K.; Igari, H. Fungemia with Wickerhamomyces Anomalus: A Case Report and Literature Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e53550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, P.; Baliou, S.; Kofteridis, D.P. Fungemia by Wickerhamomyces Anomalus—A Narrative Review. Pathogens 2024, 13, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, M. Disinfection of Mycotic Species Isolated from Cases of Bovine Mastitis Showing Antifungal Resistance. Cohesive J. Microbiol. Infect. Disease 2020, 3, 10.31031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Roudbary, M.; Mohammadi, R.; Cernáková, L.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Roudbary, M.; Mohammadi, R.; et al. Overview on the Infections Related to Rare Candida Species. Pathogens 2022, 11, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampanti, G.; Belleggia, L.; Cardinali, F.; Milanović, V.; Osimani, A.; Garofalo, C.; Ferrocino, I.; Aquilanti, L. Microbial Dynamics of a Specialty Italian Raw Ewe’s Milk Cheese Curdled with Extracts from Spontaneous and Cultivated Onopordum tauricum Willd. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, B.M.; Ali, E.M. Therapeutic Effect of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Erodium Glaucophyllum Extract against Oral Candidiasis: In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagielski, T.; Bakuła, Z.; Pleń, M.; Kamiński, M.; Nowakowska, J.; Bielecki, J.; Wolska, K.I.; Grudniak, A.M. The Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Against Microalgae of the Prototheca Genus. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, V.L.; Pereira, D.I.B.; da Costa, M.M.; Panagio, L.; Nakasato, G.; Reis, G.; Cargnelutti, J.F.; Sangioni, L.A.; Botton, S.A. Activity of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Against Isolates of Prototheca Species from Bovine Mastitis. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Orlandi, C.; Sardi, J.; Pitangui, N.; De Oliveira, H.; Scorzoni, L.; Galeane, M.; Medina-Alarcón, K.; Melo, W.; Marcelino, M.; Braz, J.; et al. Fungal Biofilms and Polymicrobial Diseases. J. Fungi. 2017, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunnoo, S.; Paosen, S.; Lethongkam, S.; Sukkurd, R.; Waen-ngoen, T.; Nuidate, T.; Phengmak, M.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Biologically Rapid Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Aqueous Eucalyptus Camaldulensis Leaf Extract: Effects on Hyphal Growth, Hydrolytic Enzymes, and Biofilm Formation in Candida albicans. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 1597–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.; González-Ballesteros, N.; da Costa, A.; Machado, R.; Gomes, A.C.; Rodríguez-Argüelles, M.C. Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Biosynthesized with Cystoseira Algae Extracts. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 28, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahey, M.G.; Gabr, B.M.; Gabr, A.M.; Abo Hagar, A.M.; Hegazy, E.E. Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Different Candida Species Isolated from Patients with Oral Candidiasis. Microbes Infect. Dis. 2024, 5, 1642–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Carrión, C.; Nazarenus, M.; Paradinas, S.S.; Carregal-Romero, S.; Almendral, M.J.; Fuentes, M.; Pelaz, B.; Del Pino, P.; Hussain, I.; Clift, M.J.D.; et al. Metal Ions in the Context of Nanoparticles toward Biological Applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2014, 4, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, E.; Turnbull, G.; Clarke, J.; Picard, F.; Riches, P.; Vendrell, M.; Graham, D.; Wark, A.W.; Faulds, K.; Shu, W. 3D Bioprinting of Mature Bacterial Biofilms for Antimicrobial Resistance Drug Testing. Biofabrication 2019, 11, 045018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierzbicki, M.; Kot, M.; Lange, A.; Kalińska, A.; Gołębiewski, M.; Jaworski, S. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial, Cytotoxic, and Physical Properties of Selected Nano-Complexes in Bovine Udder Inflammatory Pathogen Control. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2024, 17, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, S.; Ilberg, V.; Blum, U.; Langowski, H.C. Nanosilver in Dairy Applications–Antimicrobial Effects on Streptococcus Thermophilus and Chemical Interactions. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2020, 73, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, N.; Henley-Smith, C.J.; De Canha, M.N.; Oosthuizen, C.B.; Berrington, D. Viability Reagent, PrestoBlue, in Comparison with Other Available Reagents, Utilized in Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Assays. Int. J. Microbiol. 2013, 2013, 420601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Matched Pattern | Score Value | NCBI Identifier |
|---|---|---|
| Candida albicans | 2.05 | 5476 |
| Pichia fermentans | 2.21 | 53655 |
| Pichia kudriavzevii | 2.06 | 4909 |
| Wickerhamomyces anomalus | 2.08 | 4927 |
| Wickerhamiella pararugosa | 2.18 | 49331 |
| Strain | Species | Material | Preliminary Indetification | GenBank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRO3 | Prototheca bovis (Isolate 1) | Quarter milk | Phenotypic Characteristics | PQ151373 |
| PRO7 | Prototheca bovis (Isolate 2) | Quarter milk | Phenotypic Characteristics | PQ1513734 |
| PRO32 | Prototheca bovis (Isolate 3) | Quarter milk | Phenotypic Characteristics | PQ151375 |
| Concentration (mg/L) | C. albicans | P. fermentans | P. kudriavzevii | W. anomalus | W. pararugosa | P. bovis Isolate 1 | P. bovis Isolate 2 | P. bovis Isolate 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 320 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 160 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 80 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 40 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 20 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 10 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 5 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 2.5 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1.25 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 0.625 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| PC | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Concen-tration (mg/L) | C. albi-cans | P. fer-mentans | P. kudriavzevii | W. anomalus | W. pararugosa | P. bovis Isolate 1 | P. bovis Isolate 2 | P. bovis Isolate 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 320 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 160 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 80 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 40 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 20 | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | + |
| 10 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 5 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 2.5 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1.25 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 0.625 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| PC | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Accumulation (shots number) | 1 |
| Gate width, ns | 500 |
| Gate delay, ns | 500 |
| Pulse energy, mJ | 46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Motrenko, M.; Lange, A.; Kalińska, A.; Gołębiewski, M.; Kunowska-Slósarz, M.; Nasiłowska, B.; Czwartos, J.; Skrzeczanowski, W.; Orzeszko-Rywka, A.; Jagielski, T.; et al. Green Nanoparticle Synthesis in the Application of Non-Bacterial Mastitis in Cattle. Molecules 2025, 30, 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061369
Motrenko M, Lange A, Kalińska A, Gołębiewski M, Kunowska-Slósarz M, Nasiłowska B, Czwartos J, Skrzeczanowski W, Orzeszko-Rywka A, Jagielski T, et al. Green Nanoparticle Synthesis in the Application of Non-Bacterial Mastitis in Cattle. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061369
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotrenko, Michał, Agata Lange, Aleksandra Kalińska, Marcin Gołębiewski, Małgorzata Kunowska-Slósarz, Barbara Nasiłowska, Joanna Czwartos, Wojciech Skrzeczanowski, Aleksandra Orzeszko-Rywka, Tomasz Jagielski, and et al. 2025. "Green Nanoparticle Synthesis in the Application of Non-Bacterial Mastitis in Cattle" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061369
APA StyleMotrenko, M., Lange, A., Kalińska, A., Gołębiewski, M., Kunowska-Slósarz, M., Nasiłowska, B., Czwartos, J., Skrzeczanowski, W., Orzeszko-Rywka, A., Jagielski, T., Hotowy, A., Wierzbicki, M., & Jaworski, S. (2025). Green Nanoparticle Synthesis in the Application of Non-Bacterial Mastitis in Cattle. Molecules, 30(6), 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061369










