The Determination of Eight Biogenic Amines Using MSPE-UHPLC-MS/MS and Their Application in Regard to Changes in These Biogenic Amines in Traditional Chinese Dish-Pickled Swimming Crabs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Standards
2.2. UPLC-MS/MS Parameters
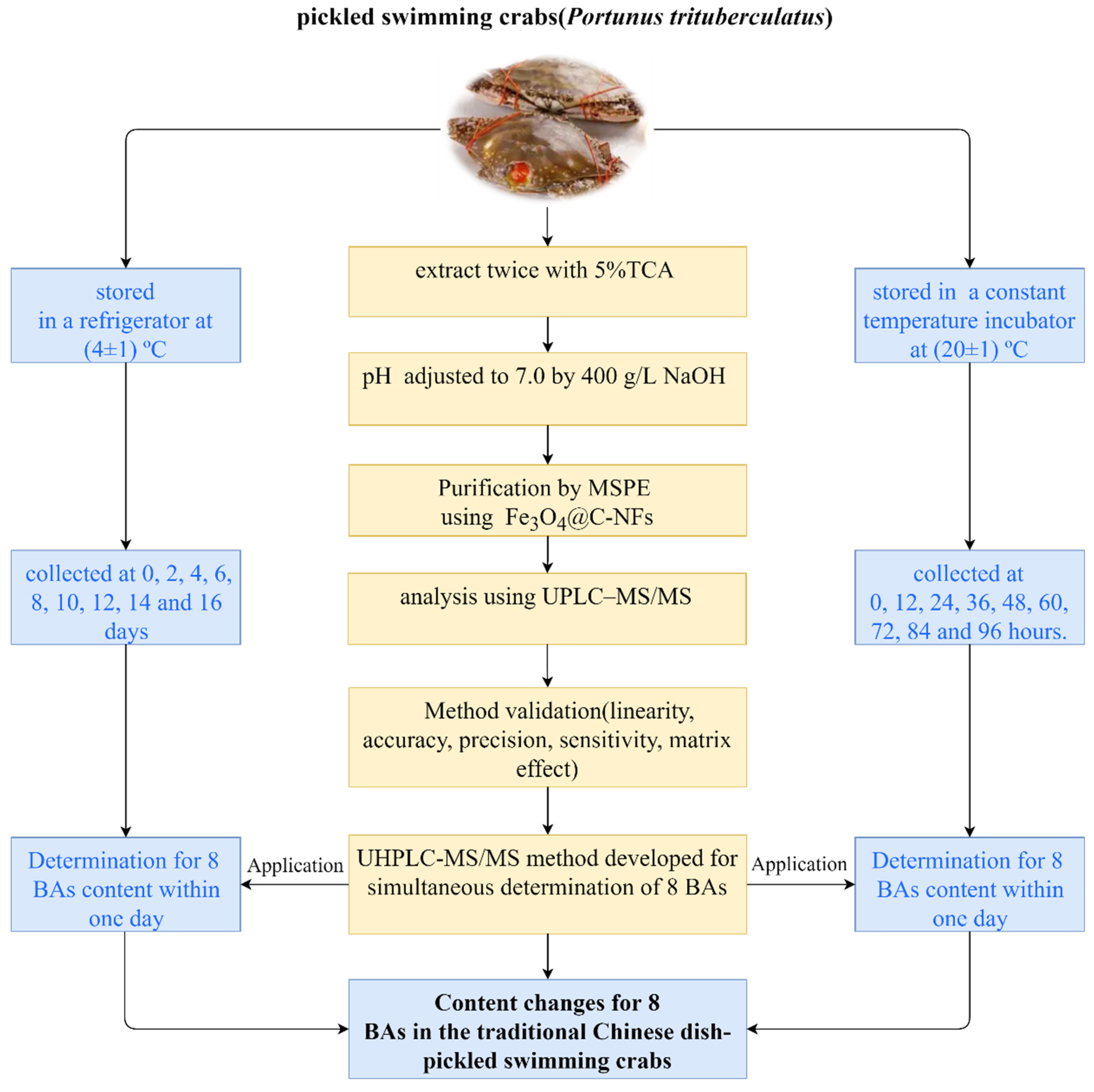
2.3. Samples Preparation
2.4. Sample Pretreatment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Conditions
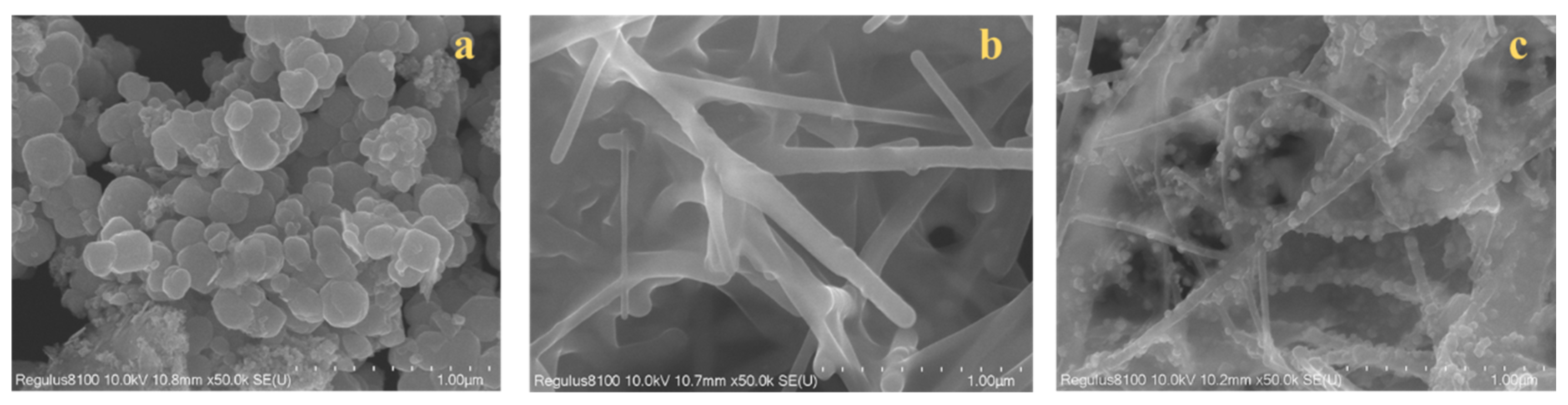
3.2. Characterization of Fe3O4@C-NFs
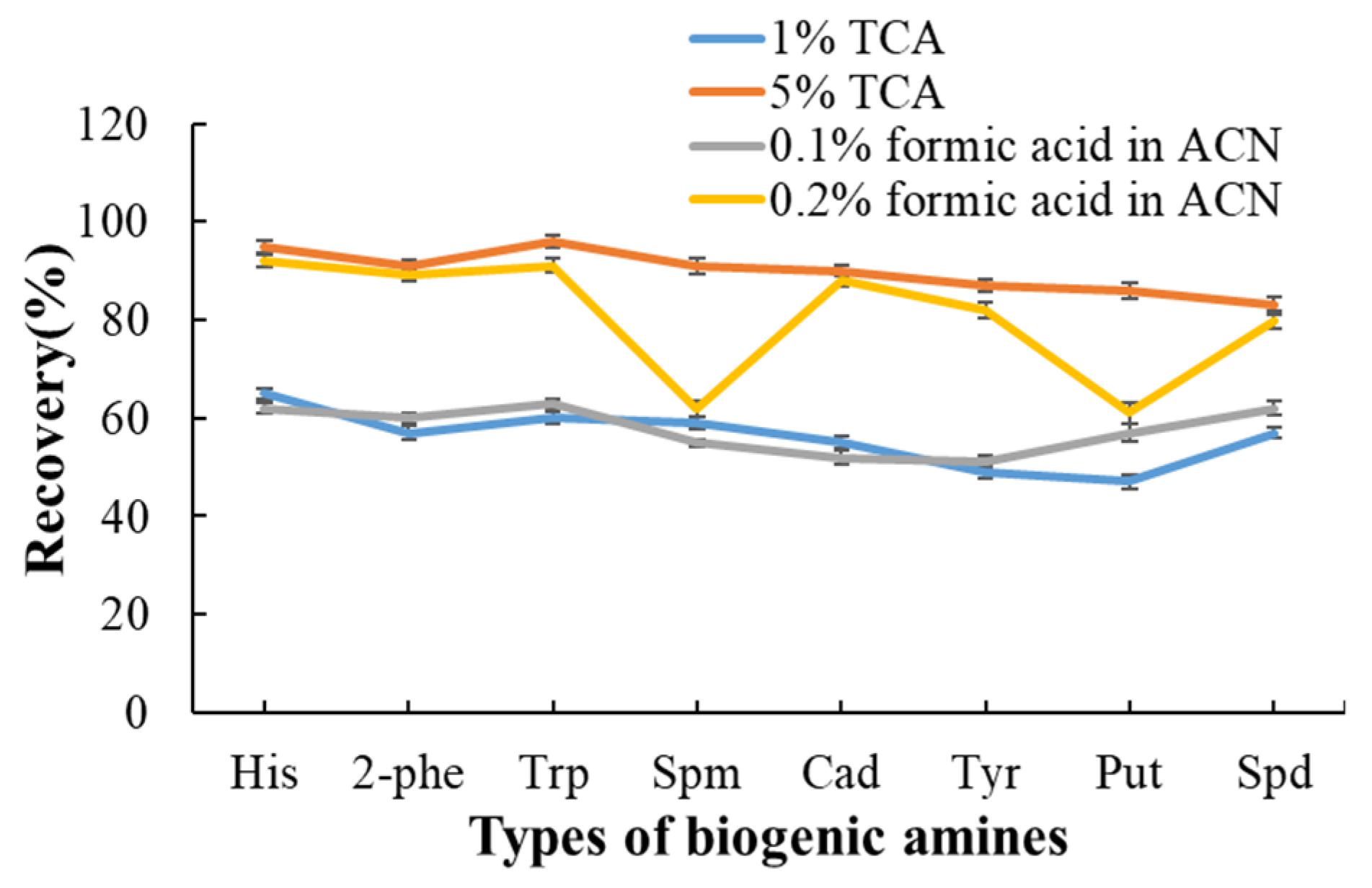
3.3. Selection of Extraction Solvent
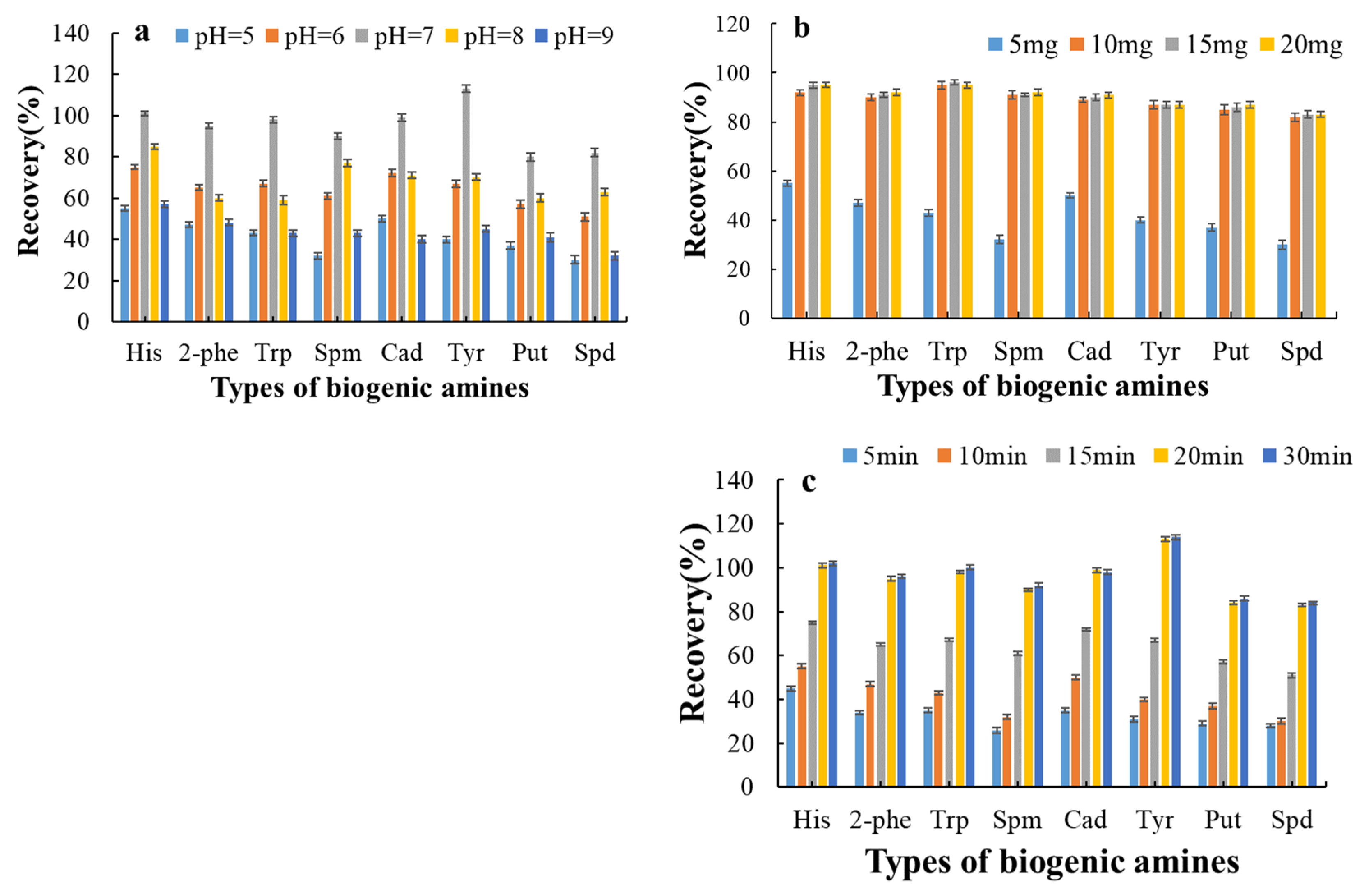
3.4. Optimization of Adsorption and Elution Conditions for Biogenic Amines by Magnetic Materials
3.5. Method Validation
3.6. Reproducibility and Recyclability of Fe3O4@C-NF Composites
3.7. Comparison with Other Methods
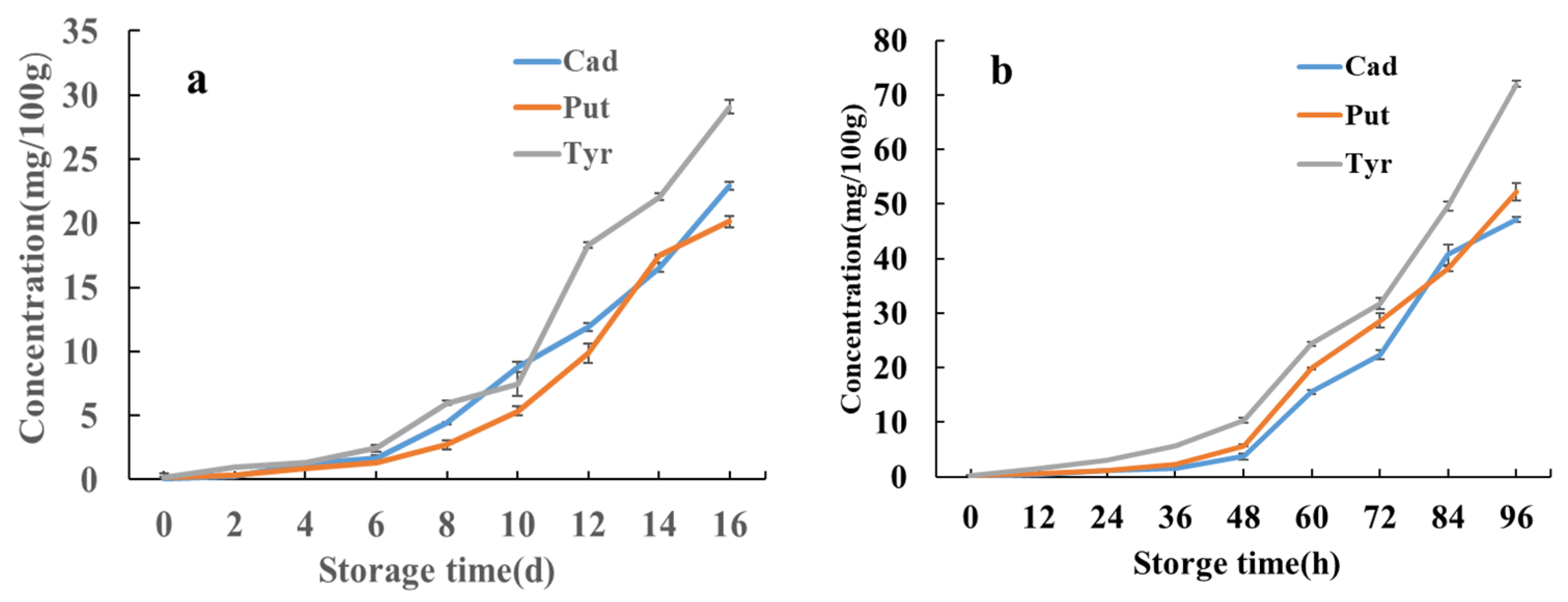
3.8. Changes in Biogenic Amines in Pickled Swimming Crabs Under Different Storage Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Nemati, M.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Mohebbi, A.; Sehatkhah, M.R.; Afshar Mo-gaddam, M.R. Simultaneous application of deep eutectic solvent as extraction solvent and ion-pair agent in liquid phase microextraction for the extraction of biogenic amines from tuna fish samples. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, L.; Xu, J.; Preininger, C.; Bui, B.T.S.; Haupt, K. Competitive fluorescent pseudoimmunoassay exploiting molecularly imprinted polymers for the detection of biogenic amines in fish matrix. Talanta 2018, 181, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniente, M.; Botello-Morte, L.; García-Gonzalo, D.; Pagán, R.; Ontañón, I. Analytical strategies for the determination of biogenic amines in dairy products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3612–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Simeonov, V.; Namieśnik, J. Evaluation of the Impact of Storage Conditions on the Biogenic Amines Profile in Opened Wine Bottles. Molecules 2018, 23, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, D.; Shi, R.; Wang, J.; Xiong, K. Effects of different co-cultures on the amino acid availability, biogenic amine concentrations and protein metabolism of fermented sufu and their relationships. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 113, 108323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Lai, H.; He, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Ge, L. Reduction of biogenic amine and nitrite production in low-salt Paocai by controlled package during storage: A study comparing vacuum and aerobic package with conventional salt solution package. Food Control 2021, 123, 107858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Effects of garlic addition on bacterial communities and the conversions of nitrate and nitrite in a simulated pickle fermentation system. Food Control 2020, 113, 107251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Xiao, K. Modified QuEChERS combined with ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry to determine seven biogenic amines in Chinese traditional condiment soy sauce. Food Chem. 2017, 29, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Liu, T.; Hou, J.; Pan, L.; Sadiq, F.A.; Yuan, L.; Yang, H.; He, G. Analysis of bacterial diversity and biogenic amines content during the fermentation processing of stinky tofu. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Sun, B. Analysis of bacterial diversity and biogenic amines content during fermentation of farmhouse sauce from Northeast China. Food Control 2020, 108, 106861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yamaki, S.; Kawai, Y.; Yamazaki, K. Histamine production behaviors of a psychrotolerant histamine-producer, morganella psychrotolerans, in various environmental Conditions. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.B.; Lu, S.L. The importance of amine-degrading enzymes on the biogenic amine degradation in fermented foods: A review. Process Biochem. 2020, 99, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Huang, W.; You, Y.; Han, B.; Han, X.Y.; Deng, H.; Wu, T.; Li, C. Profiling the occurrence of biogenic amines in wine from Chinese market and during fermentation using an improved chromatography method. Food Control 2022, 136, 108859. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz-Atienza, E.; Landeta, G.; de las Rivas, B.; Gomez-Sala, B.; Munoz, R.; Hernandez, P.E. Phenotypic and genetic evaluations of biogenic amine production by lactic acid bacteria isolated from fish and fish products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 146, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, C.N.; Adams, M.E. Biogenic amines in the nervous system of the cockroach, Periplaneta americana following envenomation by the jewel wasp, Ampulex compressa. Toxicon 2012, 59, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anal, A.K.; Perpetuini, G.; Petchkongkaew, A.; Tan, R.; Wache, Y. Food safety risks in traditional fermented food from South-East Asia. Food Control 2020, 109, 106922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Gupta, M.; Verma, K.K. Salting-out assisted liquid-liquid extraction for the determination of biogenic amines in fruit juices and alcoholic beverages after derivatization with 1-naphthylisothiocyanate and high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1422, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świder, O.; Roszko, M.Ł.; Wójcicki, M.; Szymczyk, K. Biogenic Amines and Free Amino Acids in Traditional Fermented Vegetables-Dietary Risk Evaluation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, L.; Chikweto, A.; Mckibben, J.; Gibson, K. Potential for Scombroid Poisoning from Ingestion of Selar crumenophthalmus Due to Increased Histamine Levels in Grenada. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M. Impact of Biogenic Amines on Food Quality and Safety. Foods 2019, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givanoudi, S.; Heyndrickx, M.; Depuydt, T.; Khorshid, M.; Robbens, J.; Wagner, P. A Review on Bio- and Chemosensors for the Detection of Biogenic Amines in Food Safety Applications: The Status in 2022. Sensors 2023, 23, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargossi, E.; Gardini, F.; Gatto, V.; Montanari, C.; Torriani, S.; Tabanelli, G. The Capability of Tyramine Production and Correlation Between Phenotypic and Genetic Characteristics of Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Wang, F.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, L.; Wang, Y. Ornithine Decarboxylation System of Shewanella baltica Regulates Putrescine Production and Acid Resistance. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Community. Commission Regulation (EC) No. 2073/2005 on microbiological criteria for foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2005, L 338, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- GB 2733-2015; National Food Safety Standard Fresh and Frozen Aquatic Products. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Angulo, M.F.; Flores, M.; Aranda, M.; Henriquez-Aedo, K. Fast and selective method for biogenic amines determination in wines and beers by ultra high performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, C.L.; Huang, D.M.; Yang, G.X.; Tang, Y.Y.; Shi, Y.F.; Kong, C.; Cao, P.; Cai, Y.Q. Determination of 8 biogenic amines in aquatic products and their derived products by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry without derivatization. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiono, K.; Tsutsumi, T.; Nabeshi, H.; Ikeda, A.; Yokoyama, J.; Akiyama, H. Simple and rapid determination of biogenic amines in fish and fish products by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry using 2,4,6-triethyl-3,5-dimethyl pyrylium trifluoromethanesulfonate as a derivatization reagent. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1643, 462046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.Y.; Zang, X.H.; Wu, T.; Wang, M.; Pang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Use of functionalized covalent organic frameword as sorbent for the solid-phase extraction of biogenic amines from meat samples followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.K.; Song, Y.N.; Chen, F.; Jiang, Z.J.; Che, Z.; Yang, X.; Chen, X. Simultaneous determination of eight biogenic amines in the traditional Chinese condiment Pixian Douban using UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, R.L.; Wu, W.H.; Marks, H.S. Simultaneous quantification of eight biogenic amine compounds in tuna by matrix solid-phase dispersion followed by HPLC-orbitrap mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5906–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.; Dong, H.; Wu, Y.; Guo, X.; Hou, X.; Wang, B. QuEChERS-based purification method coupled to ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) to determine six quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs) in dairy products. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, C.M.; Schieberle, P. Development of stable isotope dilution assays for the simultaneous quantitation of biogenic amines and polyamines in foods by LC-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3026–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redruello, B.; Ladero, V.; Cuesta, I.; Álvarez-Buylla, J.R.; Martín, M.C.; Fernández, M.; Alvarez, M.A. A fast, reliable, ultra high performance liquid chromatography method for the simultaneous determination of amino acids, biogenic amines and ammonium ions in cheese, using diethyl ethoxymethylenemalonate as a derivatising agent. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuran, B.; Ulusoy, H.I.; Sarp, G.; Yilmaz, E.; Morgül, U.; Kabir, A.; Tartaglia, A.; Locatelli, M.; Soylak, M. Determination of chloramphenicol and tetracycline residues in milk samples by means of nanofiber coated magnetic particles prior to high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection. Talanta 2021, 230, 122307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, R.; Yu, H.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Chan, T.D. Magnetic solid-phase extraction of sulfonamide antibiotics in water and animal-derived food samples using core-shell magnetite and molybdenum disulfide nanocomposite adsorbent. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1610, 460543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, D.H.; Du, K.Z.; Li, J.; Fang, S.M.; He, J.; Tian, F.; Chang, Y.X. A vortex enhanced magnetic solid phase extraction for the selective enrichment of four quaternary ammonium alkaloids from Zanthoxyli Radix. J. Chromatogr. B 2023, 1217, 123617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, G.Y.; Yin, S.J.; Chen, L.X.; Gao, P.; Xiao, S.Y.; Yang, F. Magnetic porous carbon derived from NH2-MIL-101(Fe) as an adsorbent for the magnetic solid-phase extraction of anthraquinones. Sep. Sci. Plus 2022, 5, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selahle, S.K.; Mpupa, A.; Nomngongo, P.N. Combination of zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 and magnetic porous porphyrin organic polymer for preconcentration of neonicotinoid insecticides in river water. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1661, 462685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.X.; Yin, S.J.; Chai, T.Q.; Wang, J.L.; Chen, G.Y.; Zhou, X.; Yang, F.Q. Ultra-high adsorption capacity of core-shell-derived magnetic zeolite imidazolate framework-67 as adsorbent for selective extraction of theophylline. Molecules 2023, 28, 5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.P.; Bai, J.L.; He, P.F.; Zeng, J.J. One Pot Synthesis of Nanofiber-Coated Magnetic Composites as Magnetic Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction Adsorbents for Rapid Determination of Tetracyclines in Aquatic Food Products. Molecules 2023, 28, 7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.R.; Zhao, X.E.; Wang, R.J.; Wei, N.; Sun, J.; Dang, J.; Chen, G.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhu, S.Y.; You, J.M. Simultaneous determination of food-related biogenic amines and precursor amino acids using in situ derivatization ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8225–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, R.; Tajik, H.; Moradi, M.; Forough, M. Application of novel Fe3O4-g-GO-g-RAFT agent nanoabsorbents for D-SPME of biogenic amines in smoked fish. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 87, 103400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laly, S.J.; Anupama, T.K.; Kumar, K.A.; AshokSankar, T.V.; Ninan, G. Changes in biogenic amines, biochemical and microbial attributes of three spotted crab (Portunus sanguinolentus) during iced and refrigerated storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Y. The evaluation of the three edible tissues of dead adult Chinese mitten crabs (Eriocheir sinensis) freshness in harvest season, based on the analysis of TVBN and biogenic amine. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anupama, T.K.; Laly, S.J.; Kumar KN, A.; Sankar, T.V.; Ninan, G. Biochemical and microbiological assessment of crucifix crab (Charybdis feriatus) stored at 4 °C. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2018, 27, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.S.; Xia, W.S.; Kim, J.M. Biogenic and volatile amines in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) stored at different temperatures. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulkumar, A.; Paramasivam, S.; Rameshthangam, P.; Rabie, M.A. Changes on biogenic, volatile amines and microbial quality of the blue swimmer crab (Portunus pelagicus) muscle during storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2503–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Montazeri, N.; Ershad-Langrudi, H.; Mokhayer, B.; Parviz, M.; Nazarinia, A. The biogenic amines and bacterial changes of farmed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) stored in ice. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, E.R.; Jeyalakshmi Kala, K.L.; Ravichandran, S.; Chandran, M. Variation of amino acids in the muscle of Crab Portunus sanguinolentus during storage. Asian J. Biochem. 2015, 10, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Lehane, L.; Olley, J. Histamine fish poisoning revisited. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 58, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, H.S.; Anderson, C.R. Determination of putrescine and cadaverine in seafood (finfish and shellfish) by liquid chromatography using pyrene excimer fluorescence. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1094, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalaby, A.R. Significance of biogenic amines to food safety and human health. Food Res. Int. 2005, 29, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, S.M.A.; Khanzadi, S.; Fazlara, A.; Najafzadehvarzi, H.; Azizzadeh, M. Effect of lactic acid and ajwain (Carum copticum) on the biogenic amines and quality of refrigerated common carp (Cyprinus carpio). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 97, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
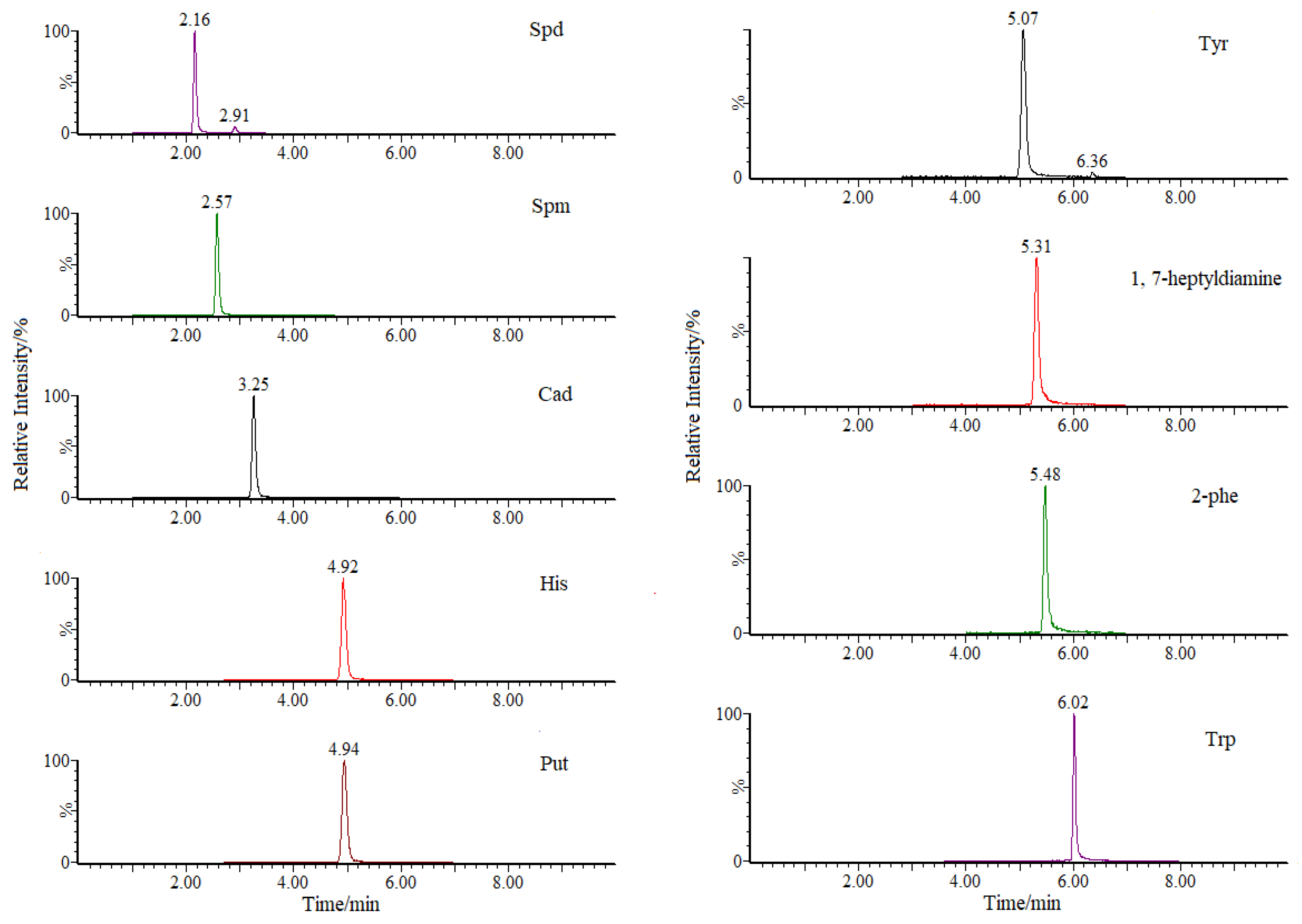

| Analyte | RT (min) | Parention Ion (m/z) | Daughter Ion (m/z) | Cone Voltage (V) | Collision Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| His | 4.92 | 111.9 | 95.1 *, 68 | 15 | 15, 22 |
| 2-phe | 5.48 | 121.9 | 105 *, 77 | 15 | 10, 25 |
| Trp | 6.02 | 160.9 | 122 *, 77 | 10 | 10, 22 |
| Spm | 2.57 | 202.9 | 112.1 *, 129 | 20 | 20, 15 |
| Cad | 3.25 | 102.9 | 86 *, 69 | 19 | 15, 22 |
| Tyr | 5.07 | 137.9 | 144.1 *, 117 | 13 | 10, 21 |
| Put | 4.94 | 88.9 | 72 *, 30 | 12 | 12, 20 |
| Spd | 2.16 | 145.9 | 112 *, 72 | 15 | 15, 15 |
| 1,7-heptyldiamine | 5.31 | 130.9 | 114.1 *, 55.1 | 15 | 10, 15 |
| Analyte | Spiked Levels (μg/kg) | Accuracy (%) | Intra-Day RSD (%) | Inter-Day RSD (%) | Analyte | Spiked Levels (μg/kg) | Accuracy (%) | Intra-Day RSD (%) | Inter-Day RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| His | 2.0 | 84.7 | 6.0 | 5.6 | Cad | 2.0 | 112 | 7.0 | 5.9 |
| 10.0 | 85.5 | 6.3 | 6.2 | 10.0 | 95.2 | 6.0 | 4.2 | ||
| 50.0 | 91.6 | 7.2 | 5.8 | 50.0 | 93.5 | 4.9 | 2.2 | ||
| 2-phe | 2.0 | 88.3 | 5.7 | 6.7 | Tyr | 2.0 | 90.7 | 5.3 | 3.6 |
| 10.0 | 91.5 | 4.9 | 5.9 | 10.0 | 89.6 | 6.8 | 4.7 | ||
| 50.0 | 85.2 | 6.1 | 7.7 | 50.0 | 91.5 | 6.9 | 3.9 | ||
| Trp | 2.0 | 88.7 | 3.7 | 5.9 | Put | 2.0 | 92.8 | 7.1 | 4.0 |
| 10.0 | 89.2 | 5.4 | 4.3 | 10.0 | 93.0 | 5.2 | 5.9 | ||
| 50.0 | 90.1 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 50.0 | 115 | 5.9 | 5.2 | ||
| Spm | 2.0 | 88.9 | 6.9 | 5.3 | Spd | 2.0 | 92.4 | 6.6 | 4.3 |
| 10.0 | 91.1 | 7.0 | 6.2 | 10.0 | 97.3 | 7.5 | 5.7 | ||
| 50.0 | 90.7 | 5.7 | 5.3 | 50.0 | 88.1 | 6.2 | 4.1 |
| BAs mg/100 g | Storage Time/d | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | |
| Spd | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Spm | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Cad | 0.284 ± 0.018 | 1.24 ± 0.0275 | 1.70 ± 0.1785 | 4.40 ± 0.121 | 8.80 ± 0.43 | 11.9 ± 0.2875 | 16.5 ± 0.3485 | 22.9 ± 0.346 |
| His | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Put | 0.306 ± 0.0045 | 0.876 ± 0.0125 | 1.35 ± 0.01 | 2.37 ± 0.37 | 5.36 ± 0.35 | 9.85 ± 0.7825 | 17.5 ± 0.065 | 20.1 ± 0.450 |
| Tyr | 0.976 ± 0.00115 | 1.36 ± 0.0115 | 2.47 ± 0.254 | 5.98 ± 0.1495 | 7.42 ± 0.94 | 18.3 ± 0.25 | 22.1 ± 0.25 | 29.0 ± 0.560 |
| 2-Phe | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Trp | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Bas mg/100 g | Storage Time/h | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 12 | 24 | 32 | 48 | 60 | 72 | 84 | 96 | |
| Spd | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Spm | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Cad | 0.117 ± 0.0105 | 0.42 ± 0.0015 | 1.09 ± 0.0205 | 1.48 ± 0.10 | 3.71 ± 0.515 | 15.6 ± 0.3575 | 22.5 ± 0.8555 | 40.8 ± 1.871 | 47.1 ± 0.4855 |
| His | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Put | 0.180 ± 0.0015 | 0.572 ± 0.0095 | 1.23 ± 0.01 | 2.30 ± 0.04 | 5.37 ± 0.17 | 19.9 ± 0.16 | 28.7 ± 1.28 | 38.1 ± 0.49 | 52.3 ± 1.595 |
| Tyr | 0.214 ± 0.0205 | 1.50 ± 0.0215 | 3.13 ± 0.0925 | 5.71 ± 0.0625 | 10.3 ± 0.4475 | 24.3 ± 0.408 | 31.7 ± 1.009 | 49.65 ± 0.8595 | 72.0 ± 0.566 |
| β-Phe | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Trp | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Chen, Y.; Bai, J.; Yang, H.; He, P.; Zeng, J. The Determination of Eight Biogenic Amines Using MSPE-UHPLC-MS/MS and Their Application in Regard to Changes in These Biogenic Amines in Traditional Chinese Dish-Pickled Swimming Crabs. Molecules 2025, 30, 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061353
Li P, Chen Y, Bai J, Yang H, He P, Zeng J. The Determination of Eight Biogenic Amines Using MSPE-UHPLC-MS/MS and Their Application in Regard to Changes in These Biogenic Amines in Traditional Chinese Dish-Pickled Swimming Crabs. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061353
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Peipei, Yu Chen, Junlu Bai, Huicheng Yang, Pengfei He, and Junjie Zeng. 2025. "The Determination of Eight Biogenic Amines Using MSPE-UHPLC-MS/MS and Their Application in Regard to Changes in These Biogenic Amines in Traditional Chinese Dish-Pickled Swimming Crabs" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061353
APA StyleLi, P., Chen, Y., Bai, J., Yang, H., He, P., & Zeng, J. (2025). The Determination of Eight Biogenic Amines Using MSPE-UHPLC-MS/MS and Their Application in Regard to Changes in These Biogenic Amines in Traditional Chinese Dish-Pickled Swimming Crabs. Molecules, 30(6), 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061353




