Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 5,8-Dimethyl Shikonin Oximes as SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthetic Studies
2.2. Enzymatic Inhibition Assay
2.3. Structure–Activity Relationship Studies
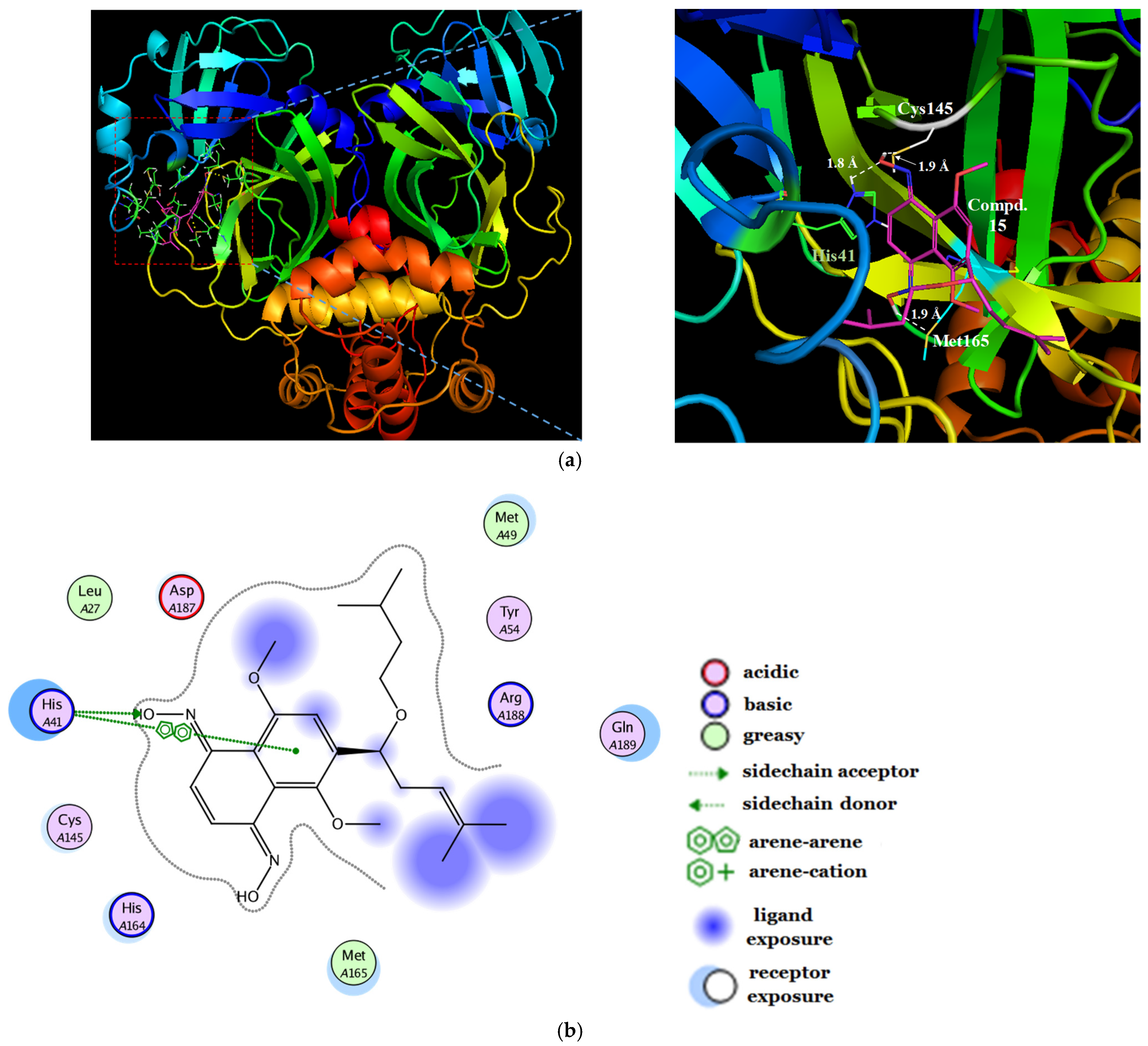
2.4. Molecular Docking Studies
2.5. Surface Plasmon Resonance Assay
2.6. Cytotoxicity Evaluations
2.7. In Vitro Antiviral Activity
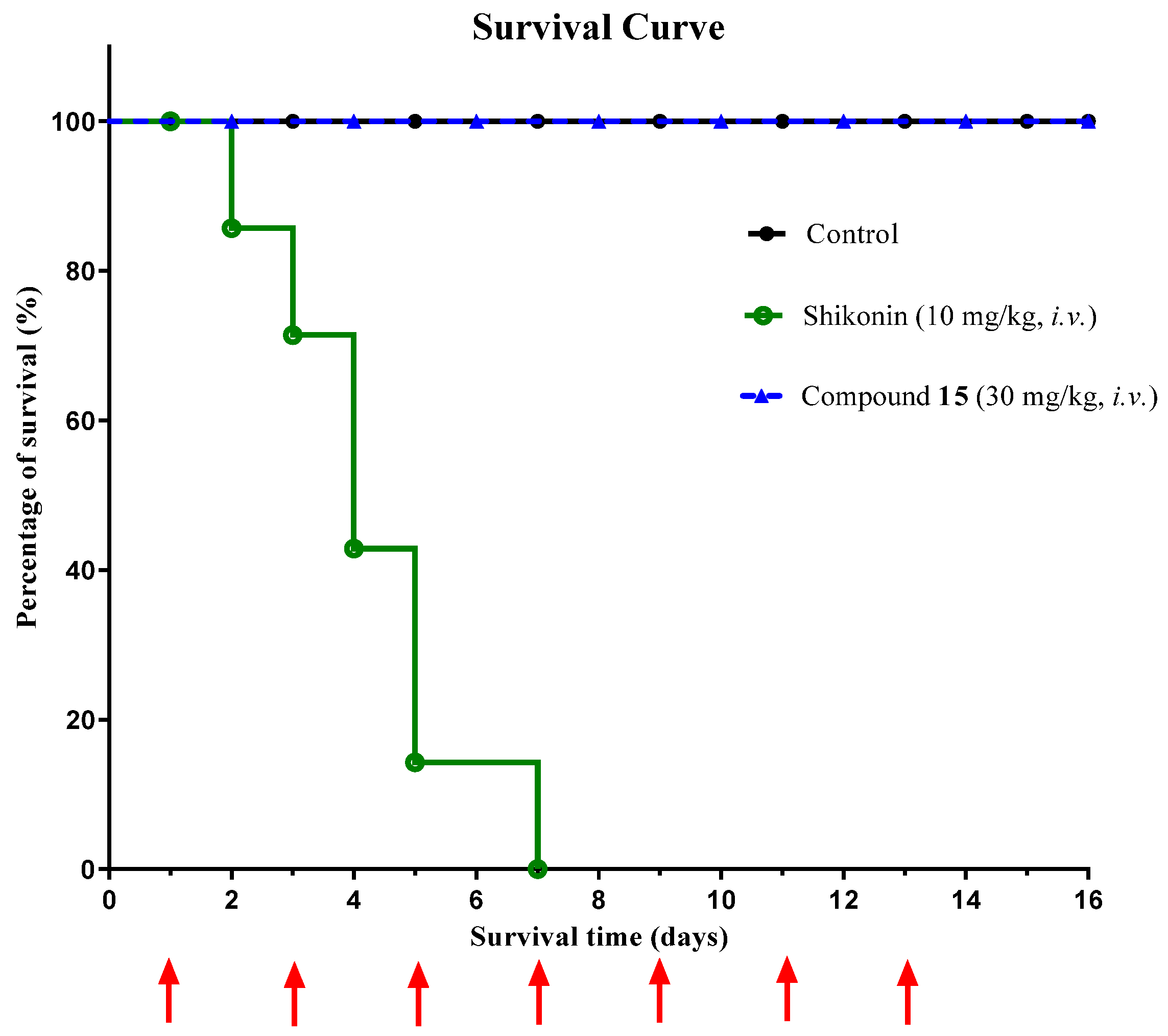
2.8. In Vivo Toxicity Evaluation of 5,8-Dimethyl Shikonin Oxime 15 and Shikonin in Balb/c Mice
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthesis of 2-(1-(Isopentyloxy)-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl)-1,4,5,8-tetramethoxy Naphthalene (3)
3.1.2. Synthesis of 6-(1-(Isopentyloxy)-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl)-5,8-dimethoxy Naphthalene-1,4-dione (4)
3.1.3. (1E,4E)-6-(1-(Isopentyloxy)-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl)-5,8-dimethoxynaphthal-ene-1,4-dione Dioxime (5)
3.1.4. (1E,4E)-6-((R)-1-(Isopentyloxy)-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl)-5,8-dimethoxy Naphthalene-1,4-dione Dioxime (14)
3.1.5. (1E,4E)-6-((S)-1-(Isopentyloxy)-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl)-5,8-dimethoxy Naphthalene-1,4-dione Dioxime (15)
3.1.6. (1E,4E)-6-(1-((5-Hydroxyhexyl)oxy)-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl)-5,8-dimethoxy Naphthalene-1,4-dione Dioxime (9)
3.1.7. (1E,4E)-6-(1-((8-Hydroxyoctyl)oxy)-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl)-5,8-dimethoxy Naphthalene-1,4-dione Dioxime (10)
3.1.8. 1-((5E,8E)-5,8-bis(Hydroxyimino)-1,4-dimethoxy-5,8-dihydronaphthalen-2-yl)-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl Cinnamate (12)
3.1.9. Synthesis of (1E,4E)-6-(1-(Isopentyloxy)-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl)-5,8-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,4-dione O,O-Dibenzoyl Dioxime (6)
3.1.10. Synthesis of 6-((4-Methyl-1-(1,4,5,8-tetramethoxynaphthalen-2-yl)pent-3-en-1-yl)oxy)hexan-2-ol (7) and 8-((4-Methyl-1-(1,4,5,8-tetramethoxynaphthalen-2-yl)pent-3-en-1-yl)oxy)octan-1-ol (8)
3.1.11. Synthesis of 4-Methyl-1-(1,4,5,8-tetramethoxynaphthalen-2-yl)pent-3-en-1-one (13)
3.1.12. Synthesis of (S)-4-Methyl-1-(1,4,5,8-tetramethoxynaphthalen-2-yl)pent-3-en-1-ol (2-S) and (R)-4-Methyl-1-(1,4,5,8-tetramethoxynaphthalen-2-yl)pent-3-en-1-ol (2-R)
3.2. Biological Activity Evaluations
3.2.1. Enzymatic Inhibition Assay
3.2.2. Molecular Docking
3.2.3. Surface Plasmon Resonance Analysis
3.2.4. Cell Lines
3.2.5. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
3.2.6. In Vitro Antiviral Activity Evaluation
3.2.7. In Vivo Toxicity Evaluation of Compound 15 in Balb/c Mice
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Weekly Epidemiological Update and Weekly Operational Update. 2024, 862, p. 478. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports (accessed on 24 December 2024).
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; St Denis, K.J.; Hoelzemer, A.; Lam, E.C.; Nitido, A.D.; Sheehan, M.L.; Berrios, C.; Ofoman, O.; Chang, C.C.; Hauser, B.M.; et al. mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine boosters induce neutralizing immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. Cell 2022, 185, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, N.; Lareau, C.A.; Keshishian, H.; Ganskih, S.; Schneider, C.; Hennig, T.; Melanson, R.; Werner, S.; Wei, Y.; Zimmer, M.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 RNA–protein interactome in infected human cells. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, D.; Sun, X.; Curth, U.; Drosten, C.; Sauerhering, L.; Becker, S.; Rox, K.; Hilgenfeld, R. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved α-ketoamide inhibitors. Science 2020, 368, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, X.-M.; Su, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, X.; Jin, Z.; Peng, J.; Liu, F.; et al. Structure-based design of antiviral drug candidates targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Science 2020, 368, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Du, X.; Xu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.; et al. Structure of Mpro from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors. Nature 2020, 582, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A.; Halilović-Alihodžić, M.; Vanwieren, A.R.; Smajkan, A.; Karić, A.; Djedović, H.; Šutković, J. A review on drug repurposing in COVID-19: From antiviral drugs to herbal alternatives. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Bhattacharya, M.; Lee, S.-S. A Detailed Overview of Immune Escape, Antibody Escape, Partial Vaccine Escape of SARS-CoV-2 and Their Emerging Variants with Escape Mutations. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 801522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Kmiec, D.; Koepke, L.; Zech, F.; Jacob, T.; Sparrer, K.M.J.; Kirchhoff, F. Omicron: What Makes the Latest SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern So Concerning? J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0207721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Jia, J. Discovery of juglone and its derivatives as potent SARS-CoV-2 main proteinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 225, 113789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Liu, L.; Qu, Z.-Y.; Wei, F.-X.; Wang, S.-Q.; Chen, G.; Qin, L.; Jiang, F.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Shang, L.; et al. Anti-adenovirus Activities of Shikonin, a Component of Chinese Herbal Medicine in Vitro. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Carr, M.J.; Xing, W.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, W. Effects of Acetylshikonin on the Infection and Replication of Coxsackievirus A16 in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cui, J.-H.; Meng, Q.-Q.; Li, S.-S.; Zhou, W.; Xiao, S. Advance in Anti-tumor Mechanisms of Shikonin, Alkannin and their Derivatives. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, F.; Lin, C.; McCormick, P.J.; Jiang, F.; Luo, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Q.; et al. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease in complex with the natural product inhibitor shikonin illuminates a unique binding mode. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.-M.; Xu, D.-F.; Zhou, W.; Li, S.-S. Concise Formal Synthesis of (±)-Shikonin Via a Highly α-Regioselective Prenylation of 1, 4, 5, 8-Tetramethoxynaphthalene-2-Carbaldehyde. Lett. Org. Chem. 2008, 5, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giagou, T.; Meyer, M.P. Kinetic Isotope Effects in Asymmetric Reactions. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 10616–10628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, S.E.; Meyer, M.P. Experimental transition state for the B-chlorodiisopinocampheylborane (DIP-Cl) reduction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 3027–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Hepworth, D. Concise and Efficient Total Syntheses of Alkannin and Shikonin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 839–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Hu, H.; Xu, D. A new synthetic method toward a key intermediate in the total synthesis of alkannin and shikonin. J. Chem. Res. 2021, 45, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cui, J.; Wang, R.; Li, S. Asymmetric synthesis of shikonin and alkannin. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2014, 31, 440–443. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Guo, H.; Cui, J.; Li, S. A novel and efficient total synthesis of shikonin. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 3977–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.-X.; Yao, S.; Zhao, W.-F.; Li, M.-J.; Liu, J.; Shang, W.-J.; Xie, H.; Ke, C.-Q.; Hu, H.-C.; Gao, M.-N.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities in vitro of Shuanghuanglian preparations and bioactive ingredients. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkadi, H.; Jbeily, R. Role of Chirality in Drugs: An Overview. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2018, 18, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.A.; He, H.; Pham-Huy, C. Chiral drugs: An overview. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2006, 2, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ordoudi, S.A.; Tsermentseli, S.K.; Nenadis, N.; Assimopoulou, A.N.; Tsimidou, M.Z.; Papageorgiou, V.P. Structure-radical scavenging activity relationship of alkannin/shikonin derivatives. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, L.; Ding, J.; Liu, Q.-H.; Li, S.-S. Semi-synthesis and antitumor activity of 6-isomers of 5, 8-O-dimethyl acylshikonin derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 3420–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Song, H.; Zhou, S.; Li, S. Synthesis and evaluation of novel alkannin and shikonin oxime derivatives as potent antitumor agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 4304–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Hu, Y.; Townsend, J.A.; Lagarias, P.I.; Marty, M.T.; Kolocouris, A.; Wang, J. Ebselen, Disulfiram, Carmofur, PX-12, Tideglusib, and Shikonin Are Nonspecific Promiscuous SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 1265–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| No. of Compd. | Enzymatic Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 4 | 10.6 |
| 5 | 35.8 |
| 6 | −6.9 |
| 9 | 10.7 |
| 10 | 11.3 |
| 12 | 28.0 |
| 1 | 51.4 |
| No. of Compd. | Chemical Structure | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| 14 |  | 22.75 ± 4.61 |
| 15 |  | 12.53 ± 3.59 |
| 1 |  | 11.26 ± 2.35 |
| Compd. | Molecular Formula | Lipinski’s Rule of Five | Calculated Binding Energy (Kcal/mol) | Binding Amino Acid Residues | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | C23H32N2O5 | Molecular weight (<500 DA) | 416.51 | −16.8006 | His41, Cys145, His164, Met165, Thr190, Arg188, Gln189 |
| LogP (<5) | 4.29 * | ||||
| H-bond donor (5) | 2 | ||||
| H-Bond acceptor (10) | 7 | ||||
| Shikonin | C16H16O5 | Molecular weight (<500 DA) | 288.30 | −16.0859 | His41, Cys145, His164, Met165, Tyr54, Arg188, Asp187, Gln189, Met49 |
| LogP (<5) | 0.92 *; 1.08 Δ | ||||
| H-bond donor (5) | 3 | ||||
| H-Bond acceptor (10) | 5 | ||||
| No. of Compd. | Chemical Structures | CC50 Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HFF-1 | Vero E6 | ||
| 15 |  | 85.6 ± 5.9 μM | 96.7 ± 8.3 μM |
| 1 |  | 1.31 ± 0.09 μM | 1.48 ± 0.06 μM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, J.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, S.; Yuan, G.; Liu, C.; Li, S. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 5,8-Dimethyl Shikonin Oximes as SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Inhibitors. Molecules 2025, 30, 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061321
Cui J, Xiang S, Zhang Q, Xiao S, Yuan G, Liu C, Li S. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 5,8-Dimethyl Shikonin Oximes as SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Inhibitors. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061321
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Jiahua, Shouyan Xiang, Qijing Zhang, Shangqing Xiao, Gaoyang Yuan, Chenwu Liu, and Shaoshun Li. 2025. "Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 5,8-Dimethyl Shikonin Oximes as SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Inhibitors" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061321
APA StyleCui, J., Xiang, S., Zhang, Q., Xiao, S., Yuan, G., Liu, C., & Li, S. (2025). Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 5,8-Dimethyl Shikonin Oximes as SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Inhibitors. Molecules, 30(6), 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061321





