Study on the Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction Process of Anthocyanin from Purple Cabbage with Deep Eutectic Solvent
Abstract
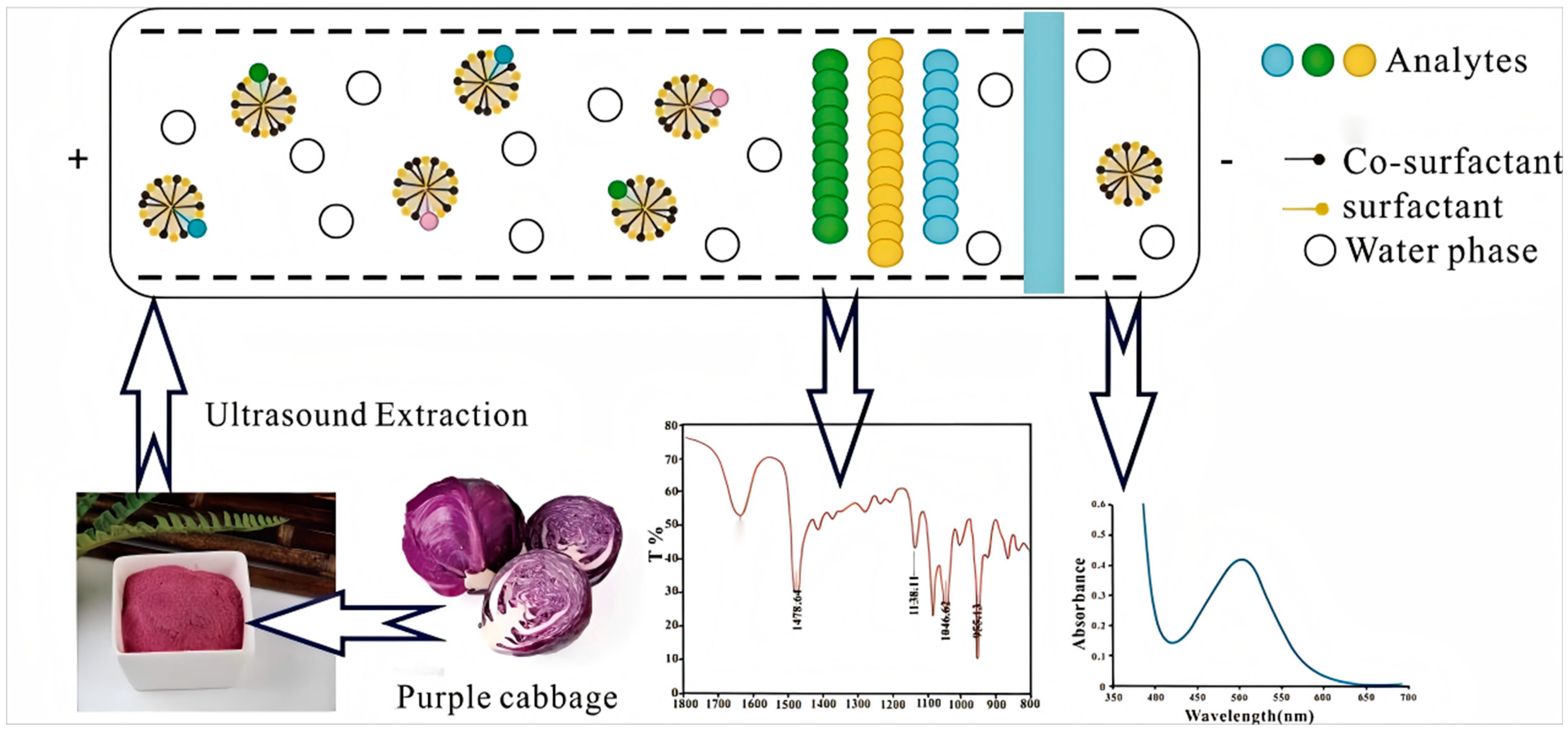
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
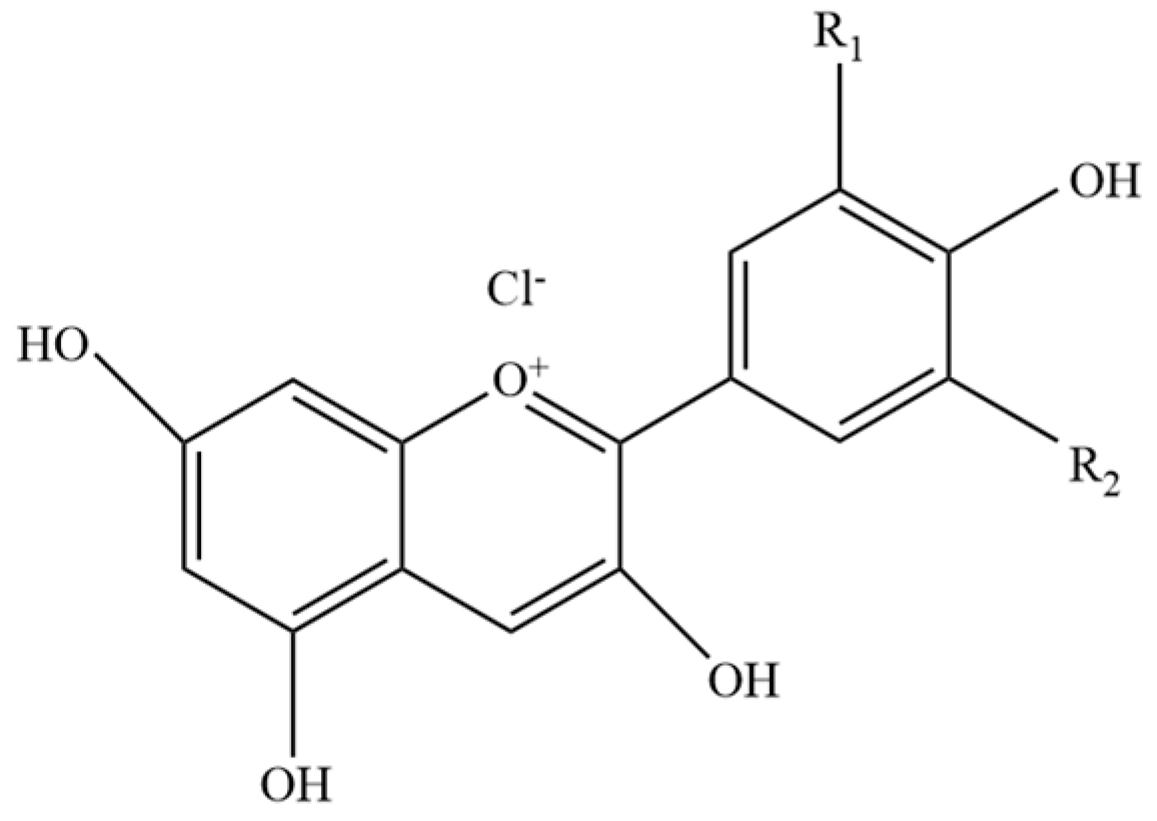
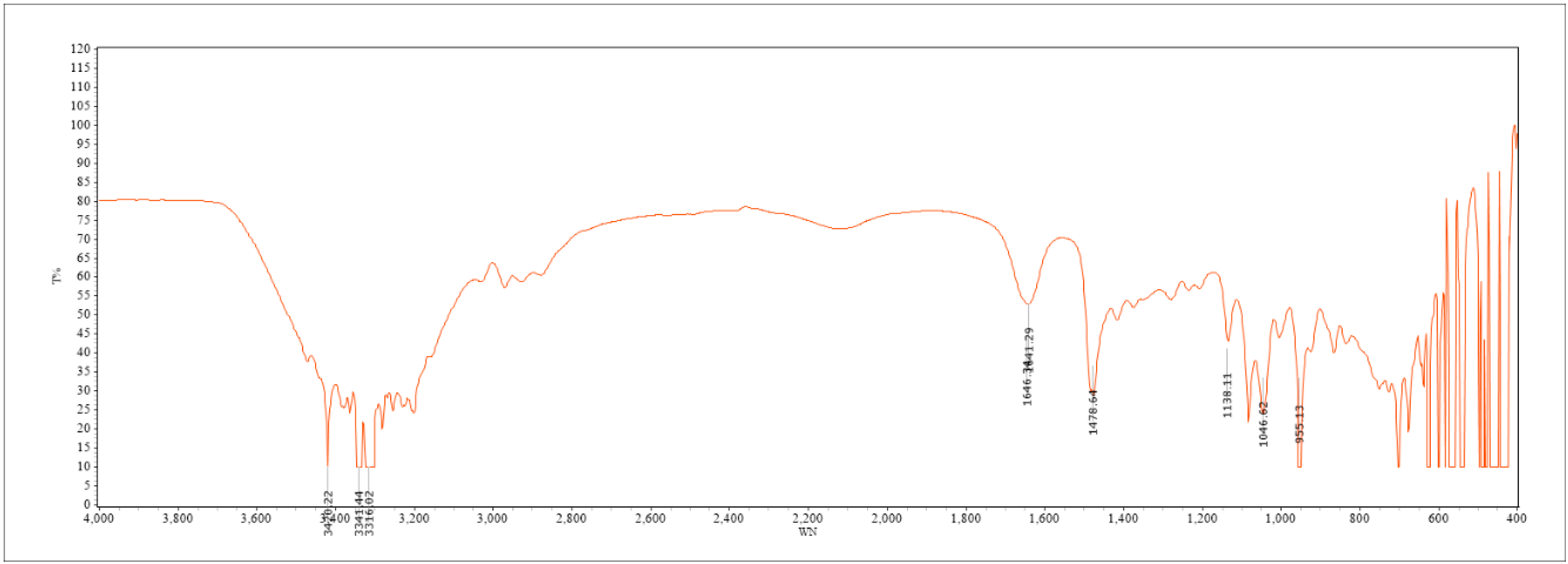
2.1. Results of Infrared Spectrum Characterization of DES
2.2. Results of Single Factor Test
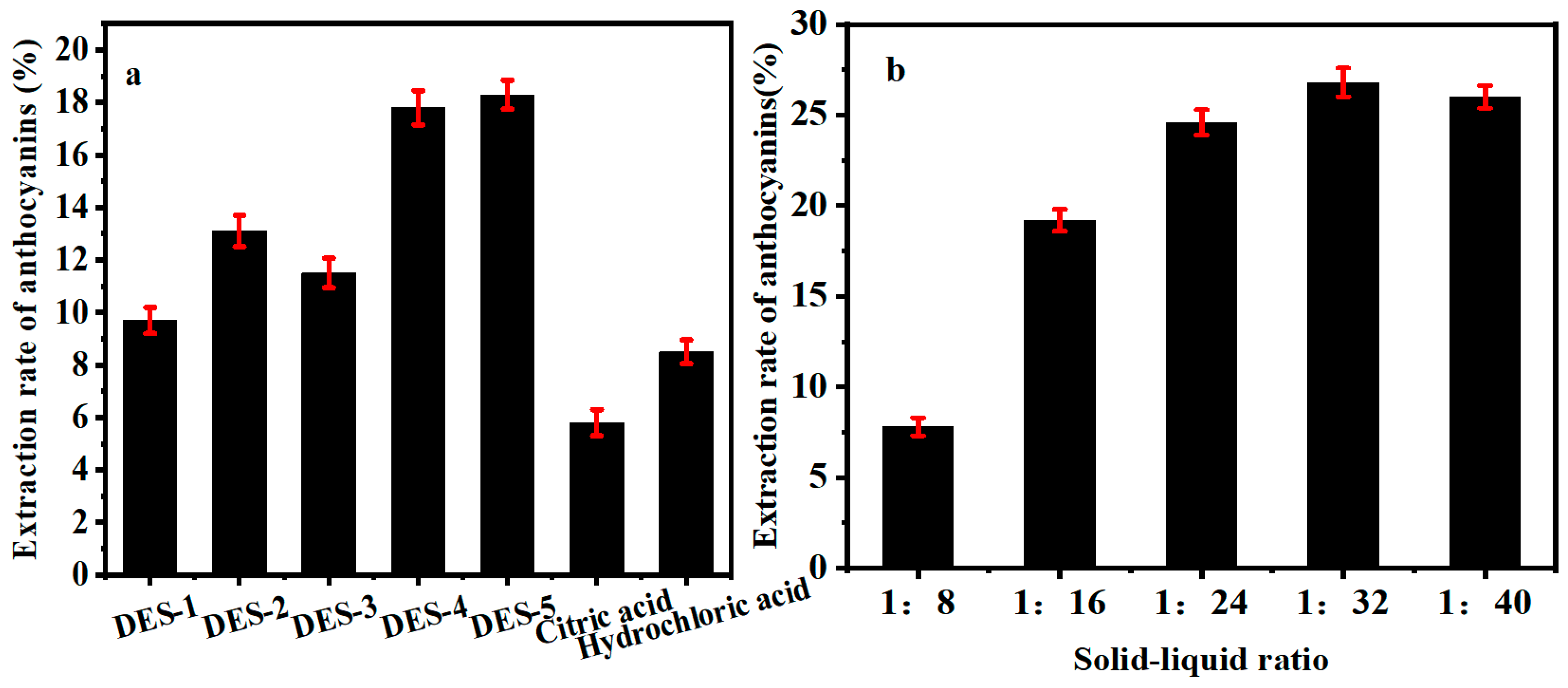
2.2.1. Effect of Extraction Solvent Type on the Yield of Anthocyanin
2.2.2. Effect of Solid–Liquid Ratio on the Yield of Anthocyanin
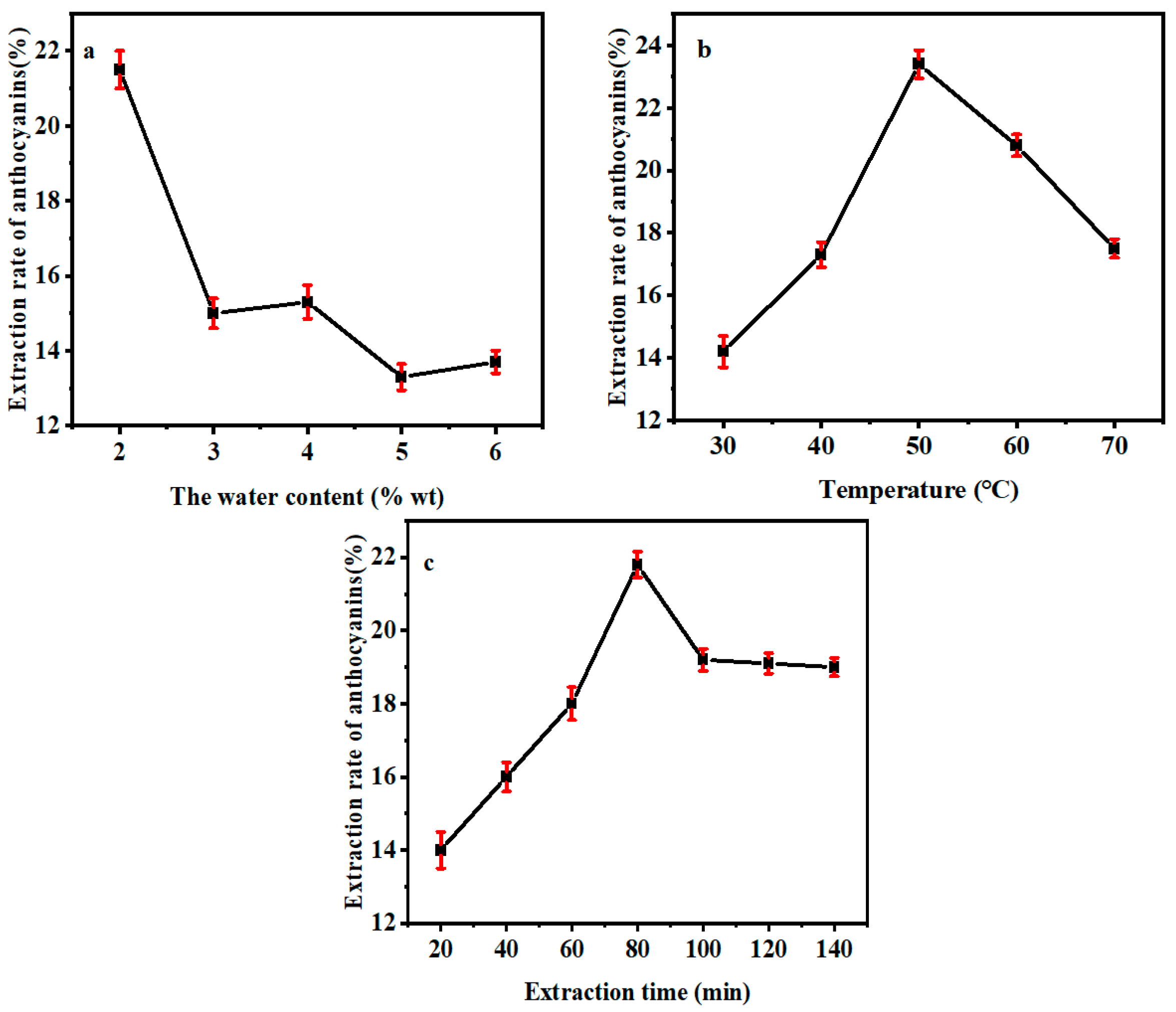
2.2.3. Effect of Water Content on the Yield of Anthocyanin
2.2.4. Effect of Extraction Temperature on the Yield of Anthocyanin
2.2.5. Effect of Extraction Time on the Yield of Anthocyanin
2.3. Results of Standard Addition Recovery Test
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Instruments
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Sample Treatment
3.2.2. Preparation of Extraction Solvent
3.2.3. Preparation of Conventional Solvents
3.3. Extraction Methods
3.3.1. Extraction Processes
3.3.2. Extraction of Anthocyanin
3.3.3. Extraction of Anthocyanin by Conventional Solvents
3.3.4. Calculation of Anthocyanin Production
3.4. Determination of Anthocyanin Content in Actual Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giampieri, F.; Cianciosi, D.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Quiles, J.L.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Navarro-Hortal, M.D.; Machì, M.; Casanova, R.D.J.P.; Espinosa, J.C.M.; Chen, X.; et al. Anthocyanins: What Do We Know until Now? J. Berry Res. 2023, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romera-Fernández, M.; Berrueta, L.A.; Garmón-Lobato, S.; Gallo, B.; Vicente, F.; Moreda, J.M. Feasibility Study of FT-MIR Spectroscopy and PLS-R for the Fast Determination of Anthocyanins in Wine. Talanta 2012, 88, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noypitak, S.; Jaitrong, N.; Terdwongworakul, A. Detection of Spongy Pulp in Guava Using Light Properties and Near Infrared Spectroscopy. Int. Food Res. J. 2022, 28, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales-Bueno, J.; Baca-Bocanegra, B.; Jara-Palacios, M.J.; Hernández-Hierro, J.M.; Heredia, F.J. Evaluation of the Influence of White Grape Seed Extracts as Copigment Sources on the Anthocyanin Extraction from Grape Skins Previously Classified by near Infrared Hyperspectral Tools. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1685–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuppner, S.; Mayr, S.; Beganovic, A.; Beć, K.; Grabska, J.; Aufschnaiter, U.; Groeneveld, M.; Rainer, M.; Jakschitz, T.; Bonn, G.K.; et al. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy as a Rapid Screening Method for the Determination of Total Anthocyanin Content in Sambucus Fructus. Sensors 2020, 20, 4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.D.; Liang, Y.Z.; Cao, D.S.; Xu, Q.S. Model-Population Analysis and Its Applications in Chemical and Biological Modeling. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 38, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, F.R.; Bedair, A.; Hamed, M.; Magdy, G.; Ali, I.; Locatelli, M. Applications of (Natural) Deep Eutectic Solvents in Liquid Phase Microextraction: A Review. Microchem. J. 2024, 198, 110178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zheng, C.; Xu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y.; Jing, C. Sequential Separation of Critical Metals from Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Deep Eutectic Solvent and Electrodeposition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, N.; Chen, P.; Sun, J.H.; Harnly, J.M.; Zhang, M. Study of UV-Vis Molar Absorptivity Variation and Quantitation of Anthocyanins Using Molar Relative Response Factor. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhamarnah, Y.; Qiblawey, H.; Nasser, M. A Review on Deep Eutectic Solvents as the Emerging Class of Green Solvents for Membrane Fabrication and Separations. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 398, 124250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarca, R.S.; Ferreira, S.D.S.; Paganini, E.R.; Ferreira, N.D.S.; Ayala-Durán, S.C.; Isquibola, G.; de Lima Gomes, P.C.F.; Amaral, C.D.B.; Magnani, M.; Franco, D.F.; et al. Sustainable Cadmium Extraction from Sewage Sludge Samples: A Novel Approach with Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents and Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (HDES-UAE) Prior to ICP-MS Analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 398, 124264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, C.; Xue, Z.; Kou, X. Investigation on the Biological Activity of Anthocyanins and Polyphenols in Blueberry. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusty, K.; Dash, K.K.; Giri, S.; Bhagya Raj, G.V.S.; Tiwari, A.; Shaikh, A.M.; Béla, K. Ultrasound Assisted Phytochemical Extraction of Red Cabbage by Using Deep Eutectic Solvent: Modelling Using ANFIS and Optimization by Genetic Algorithms. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 102, 106762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel Solvent Properties of Choline Chloride/Urea Mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 7, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tsao, R. Dietary Polyphenols, Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 8, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petreska Stanoeva, J.; Damjanovski, V.; Cichna-Markl, M.; Stefova, M. Anthocyanin Fingerprinting as an Authentication Testing Tool for Blueberry, Aronia, and Pomegranate Juices. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 250, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Shi, J.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; An, T.; Li, X.; Yan, P.; Dong, C. Detection of Anthocyanin Content in Fresh Zijuan Tea Leaves Based on Hyperspectral Imaging. Food Control. 2023, 152, 109839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiki, H.; Tobase, K.; Muguruma, H. Electrochemical Determination of the Procyanidins in Peanut Skin Using a Carbon Nanotube Electrode. Anal. Sci. Int. J. Jpn. Soc. Anal. Chem. 2024, 40, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Lu, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J. Deep Eutectic Solvents with Low Viscosity for the Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Environmental Water Samples by Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction. Microchem. J. 2024, 198, 110086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, M.; Toepfl, S.; Butz, P.; Knorr, D.; Tauscher, B. Extraction of Anthocyanins from Grape By-Products Assisted by Ultrasonics, High Hydrostatic Pressure or Pulsed Electric Fields: A Comparison. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2008, 9, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Wang, D.; Guo, H.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, X.; Liu, F.; Ling, W. Optimization of Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Anthocyanins from Mulberry and Identification of Anthocyanins in Extract Using HPLC-ESI-MS. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C46–C50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Syed, U.T.; Pinto, E.; Leonardo, I.C.; Romero, P.; Gaspar, F.B.; Barreto Crespo, M.T.; Sebastian, V.; Crespo, J.G.; Brazinha, C. Sustainable Production of Nanoemulsions by Membrane-Assisted Nanoemulsification Using Novel Aroma-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for Enhanced Antifungal Activities. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 444, 141167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Xun, C.; Yang, Y. A Green Deep Eutectic Solvents Microextraction Coupled with Acid-Base Induction for Extraction of Trace Phenolic Compounds in Large Volume Water Samples. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 178, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrochenko, A.A.; Orlova, A.; Frolova, N.; Serebryakov, E.B.; Soboleva, A.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Frolov, A.; Shikov, A.N. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extraction of Triterpene Saponins from Aralia elata var. mandshurica (Rupr. & Maxim.). J. Wen. Mol. 2023, 28, 3614. [Google Scholar]
- Velásquez, P.; Bustos, D.; Montenegro, G.; Giordano, A. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Anthocyanins Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Incorporation in Edible Films. Molecules 2021, 26, 4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendehdel, A.A.; Sorouraddin, S.M.; Farajzadeh, M.A. Development of Salt-Induced Homogeneous Liquid-Liquid Extraction Using a Deep Eutectic Solvent Performed in a Narrow-Bore Tube for the Extraction of Zn(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) Ions from Honey Samples. Anal. Methods Adv. Methods Appl. 2024, 16, 1593–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.Y.; Bulatov, A.V. Automated Microextraction Separation of Lead from Vegetable Oils for Determination by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. J. Anal. Chem. 2024, 79, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hunter, J.R.; Ullah, A.; Shao, Q.; Shi, J. Lignin Derived Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extraction of Nanoplastics from Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 467, 133695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktaş, H.; Kurek, M.A. Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extraction of Polyphenols from Food Plants. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Guo, X.; Xu, T.; Fan, L.; Zhou, X.; Wu, S. Ionic Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extraction and Separation of Natural Products. J. Chromatogr. A Incl. Electrophor. Other Sep. Methods 2019, 1598, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutani, Z.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R.; Ghasempour, Z.; Ghareaghajlou, N. Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Extraction of Anthocyanins: Stability, Bioavailability, and Antioxidant Property. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 144, 104324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Goswami, A.; Patil, R.; Mitra, A.; Kutty, N.N. An Eco-Friendly Approach to Extract Anthocyanins from Rose Flowers Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 210, 118059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | Measured of Sample (mg/mL) | Standard Addition (mg/mL) | Measured of Standard Addition Sample (mg/mL) | Recovery Rate % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purple cabbage | 0.0351 | 0.8 | 0.73 | 86.87 |
| 1.0 | 0.89 | 85.62 | ||
| 1.5 | 1.35 | 87.75 |
| DES | Composition | Mass Ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | Hydrogen Bond Donor | Water | ||
| DES-1 | ChCl | Citric acid | Water | 1:1:4 |
| DES-2 | - | Lactic acid | - | 1:1:4 |
| DES-3 | - | Glucose | - | 1:1:4 |
| DES-4 | - | Glycerol | - | 1:1:4 |
| DES-5 | - | 1,2-Propylene glycol | - | 1:1:4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, L.; Ding, P.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J. Study on the Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction Process of Anthocyanin from Purple Cabbage with Deep Eutectic Solvent. Molecules 2025, 30, 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061281
Meng L, Ding P, Tan Y, Zhang Y, Zhao J. Study on the Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction Process of Anthocyanin from Purple Cabbage with Deep Eutectic Solvent. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061281
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Lifen, Pengpeng Ding, Ye Tan, Yinying Zhang, and Jun Zhao. 2025. "Study on the Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction Process of Anthocyanin from Purple Cabbage with Deep Eutectic Solvent" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061281
APA StyleMeng, L., Ding, P., Tan, Y., Zhang, Y., & Zhao, J. (2025). Study on the Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction Process of Anthocyanin from Purple Cabbage with Deep Eutectic Solvent. Molecules, 30(6), 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061281






