Utilizing Some Indole Derivatives to Control Mild Steel Corrosion in Acidic Environments: Electrochemical and Theoretical Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
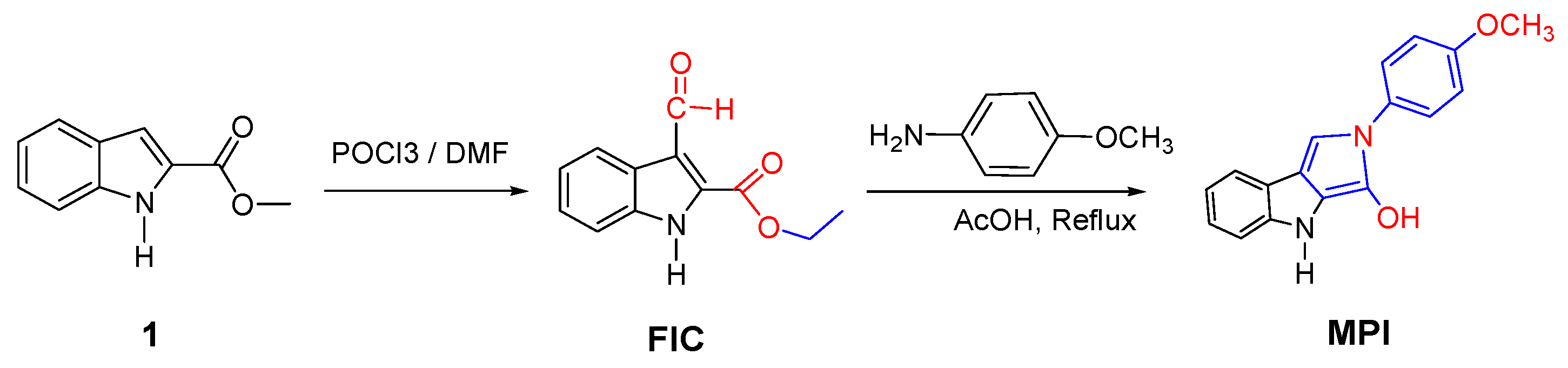
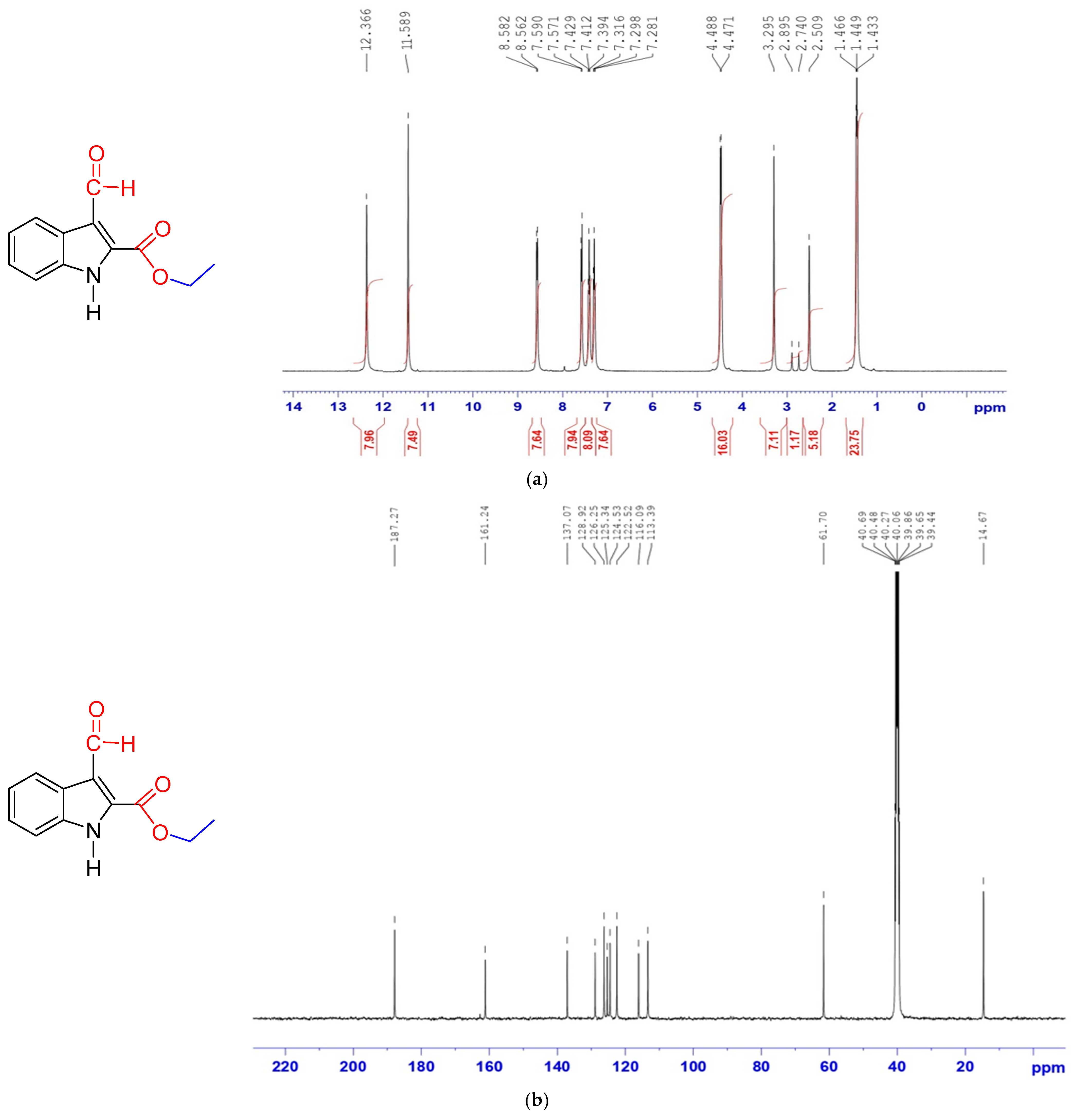
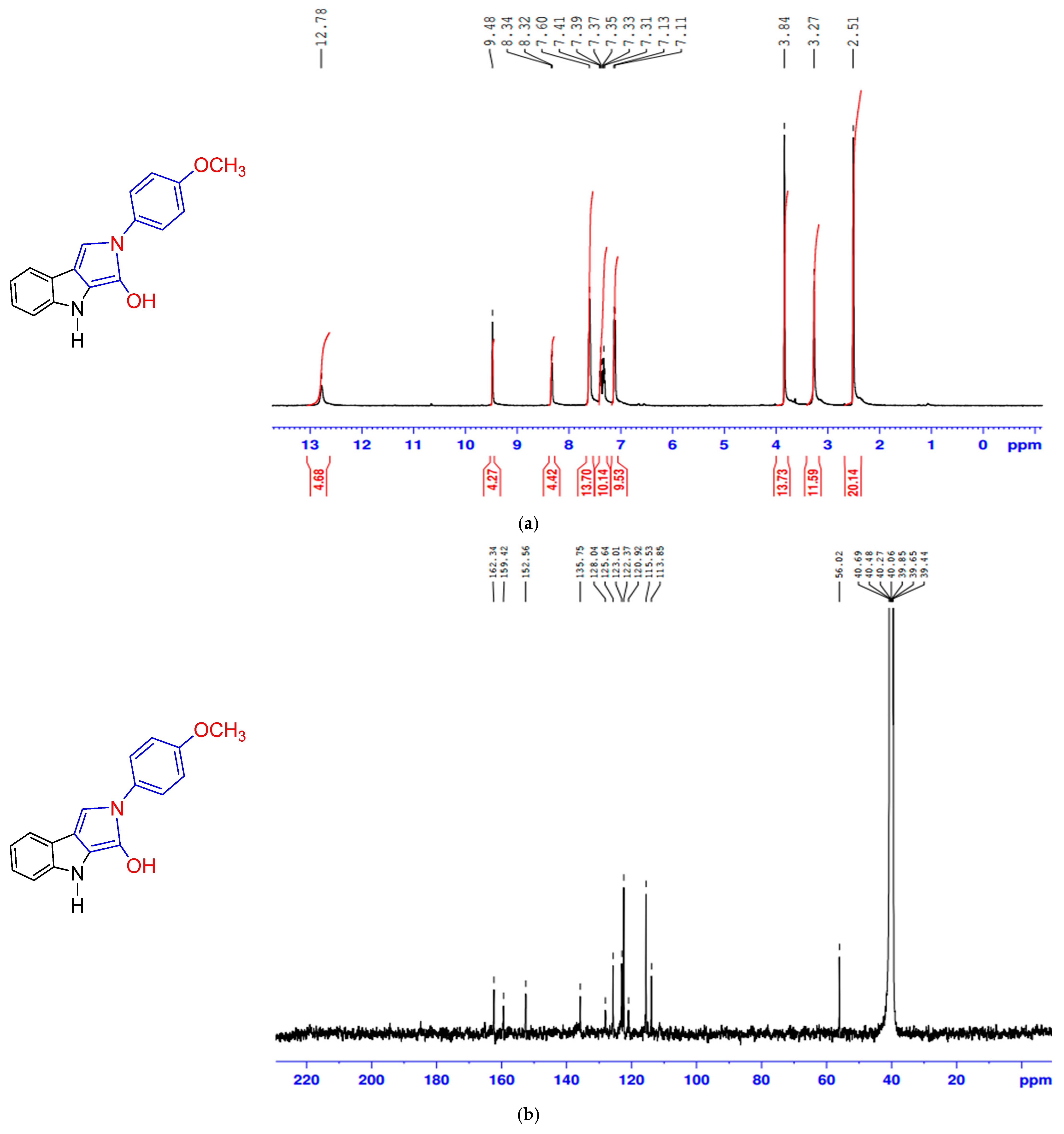
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization
2.2. Electrochemical Results
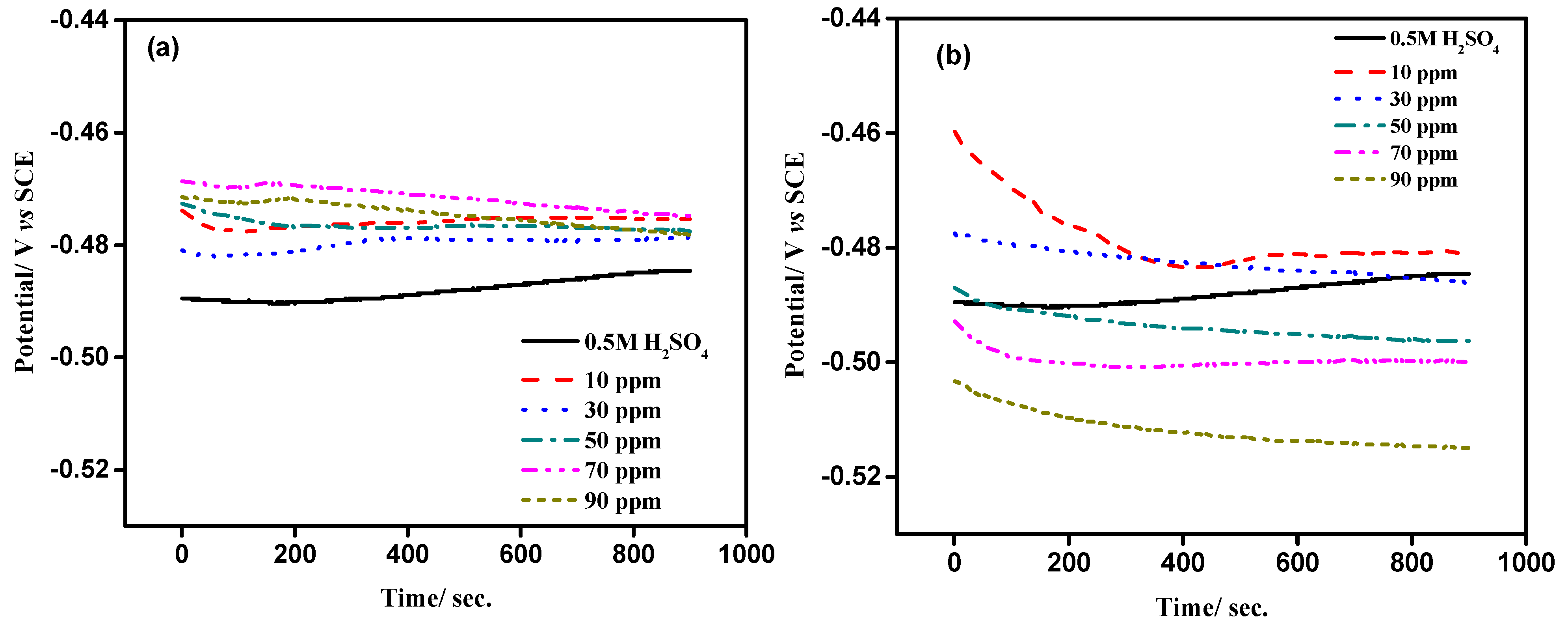
2.2.1. OCP Measurements
2.2.2. EIS Outcomes
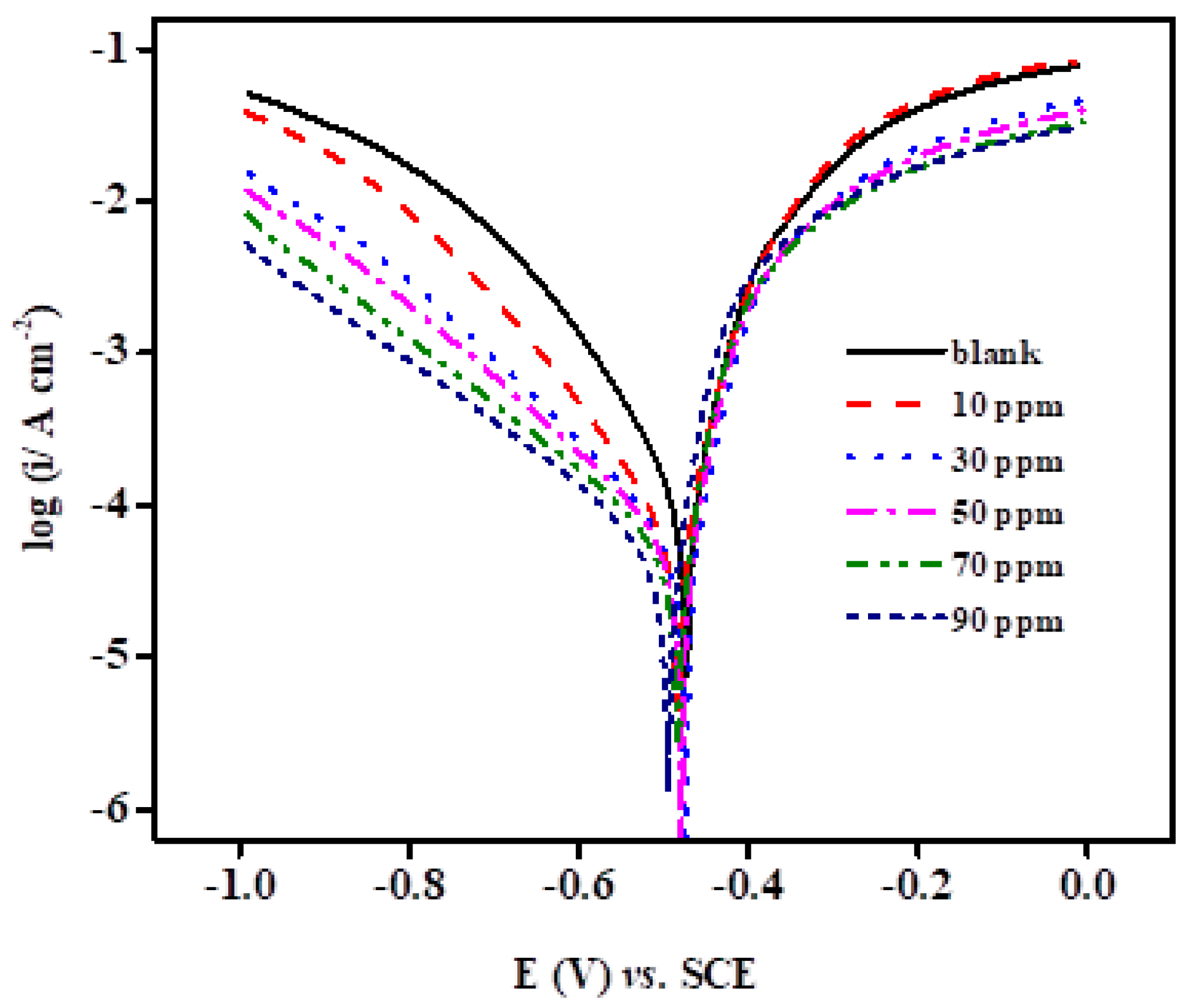
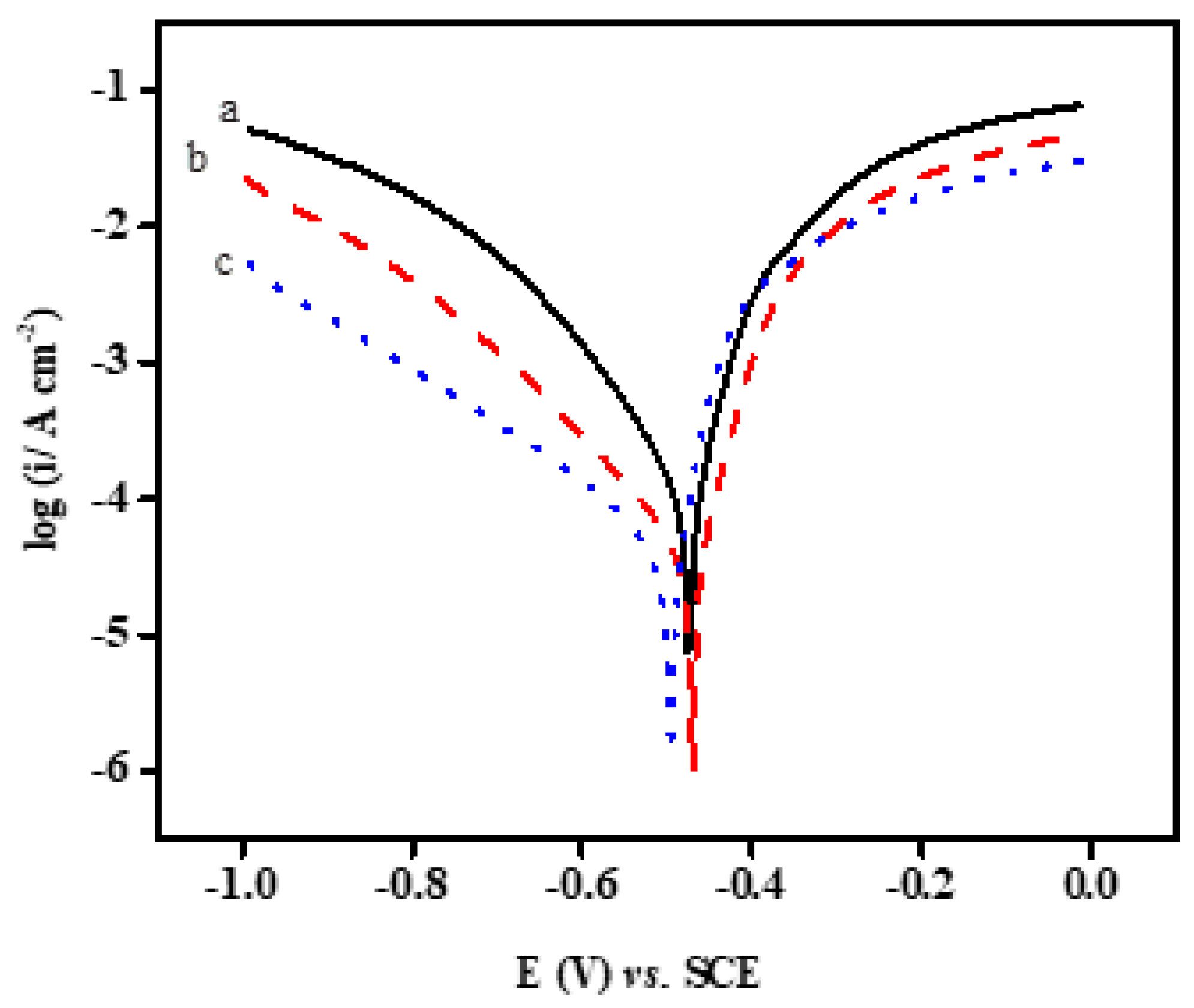
2.2.3. PDP Measurements
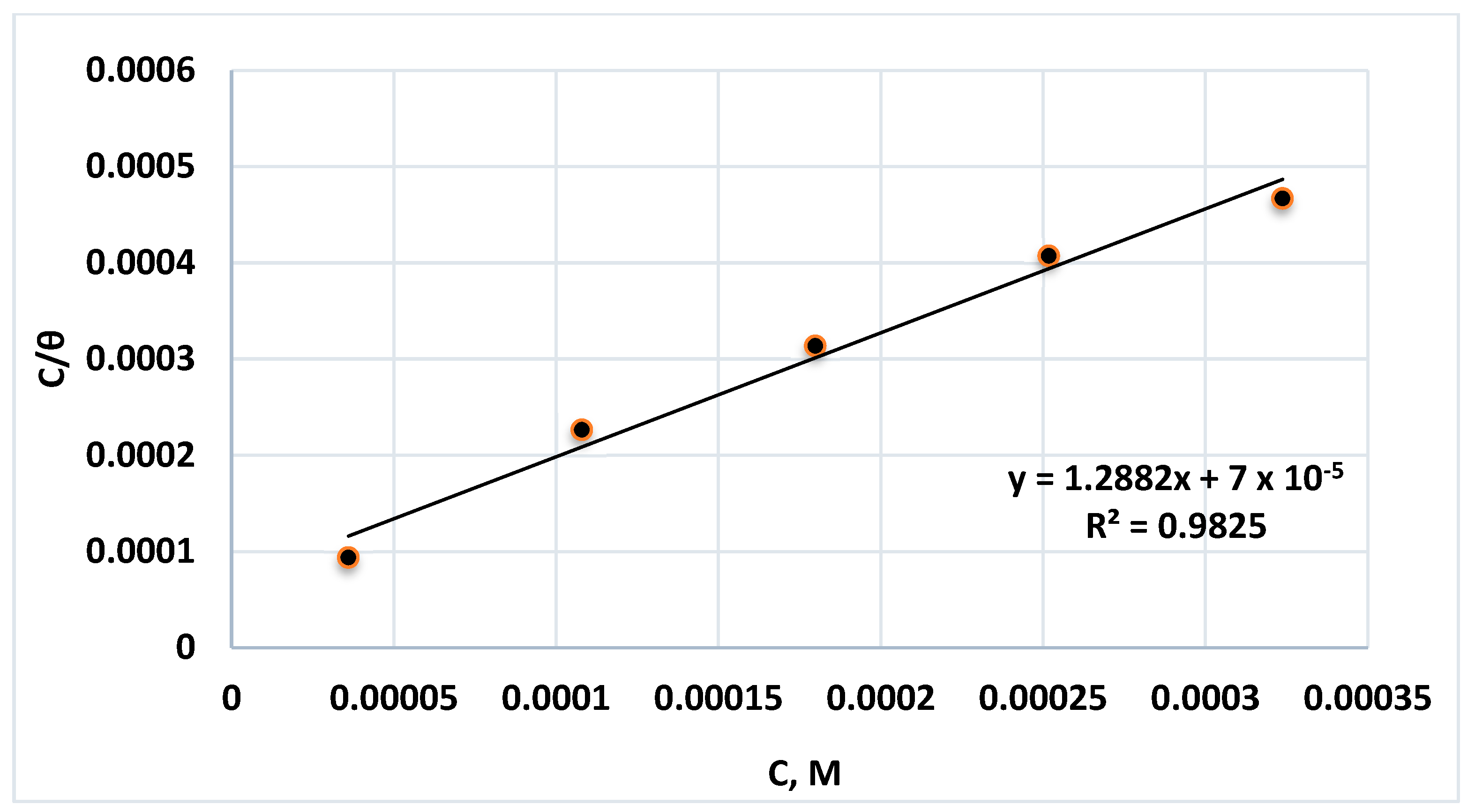
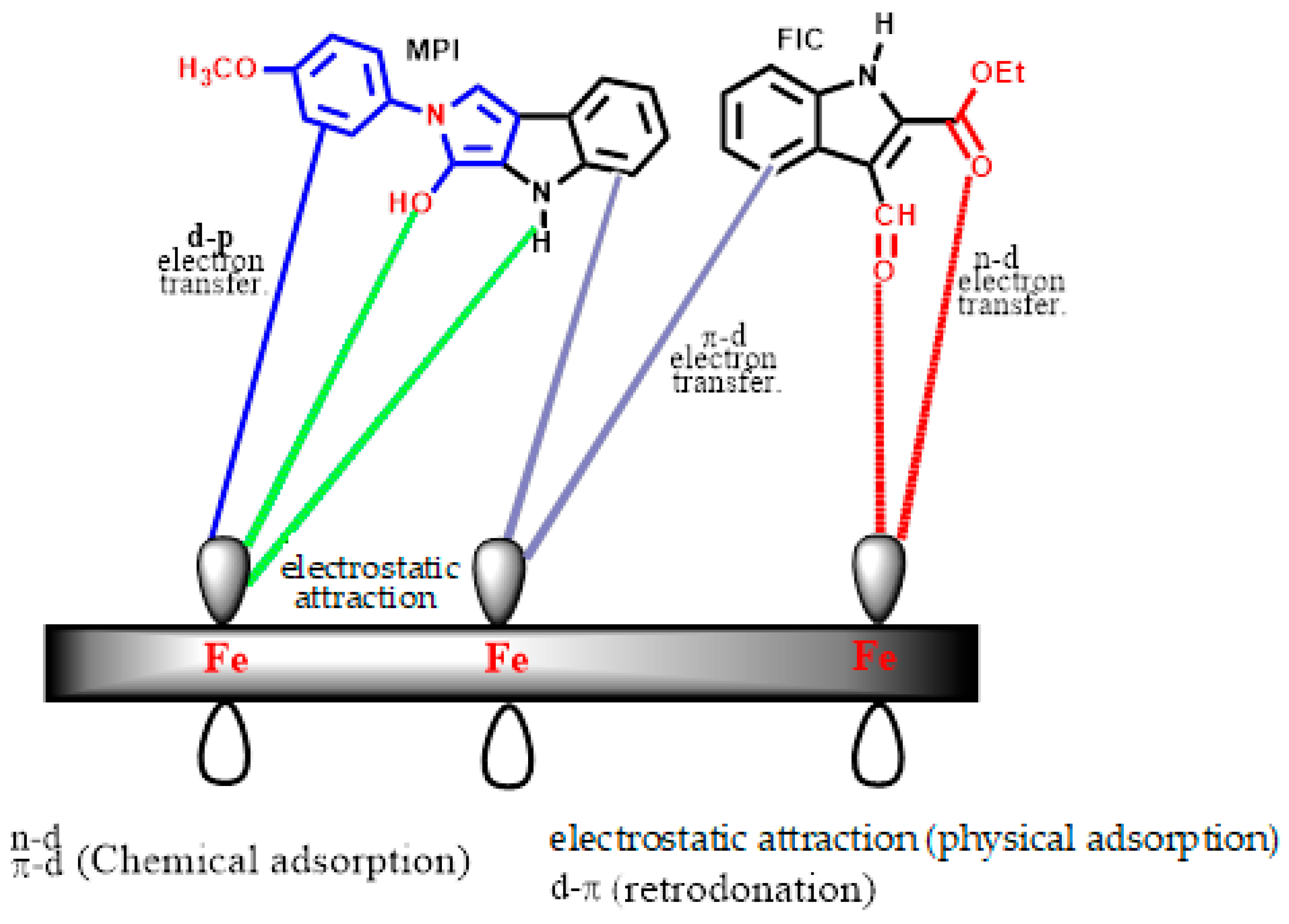
2.2.4. Adsorption Isotherm Calculations
2.3. Quantum Chemical Studies of FIC and MPI
2.3.1. Molecular Orbital Analysis of Corrosion Inhibitors FIC and MPI
2.3.2. MD Simulations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Apparatus
3.3. Preparation of Indole Derivatives
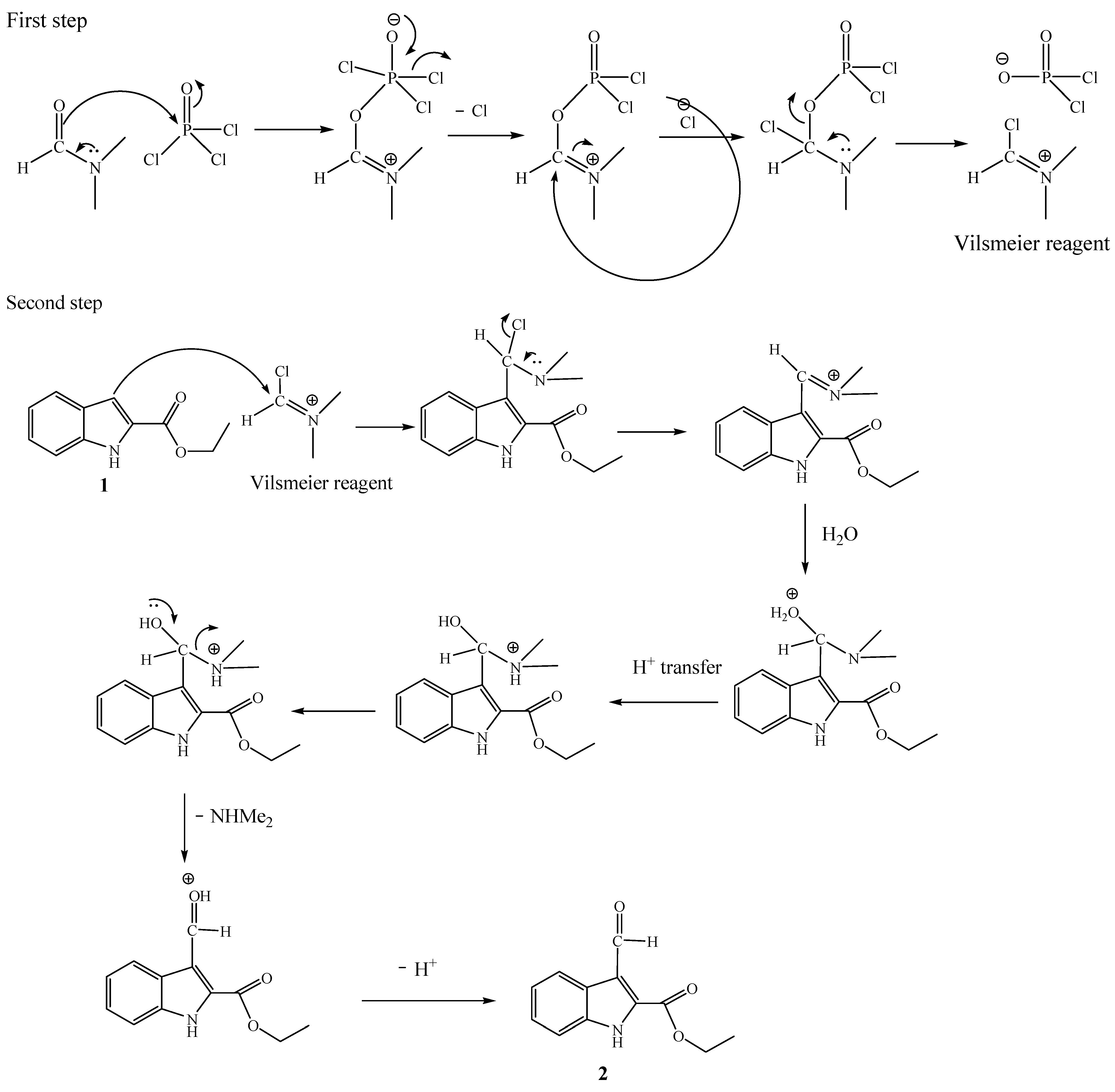
3.3.1. Preparation of Ethyl 3-Formyl-1H-indole-2-carboxylate (FIC)
3.3.2. Formation of 2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-2,4-dihydropyrrolo [3,4-b]indol-3-ol (MPI)
3.4. Electrochemical Measurements
3.5. Computational Model
3.6. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alharthi, N.H.; El-Hashemy, M.A.; Derafa, W.M.; Althobaiti, I.O.; Altaleb, H.A. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel by highly stable polydentate schiff base derived from 1,3-propanediamine in aqueous acidic solution. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2022, 26, 101501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haddad, M.A.M.; Radwan, A.B.; Sliem, M.H.; Hassan, W.M.I.; Abdullah, A.M. Highly efficient eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 5 M HCl at elevated temperatures: Experimental & molecular dynamics study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, M.; Zahari, A.; Awang, K.; Hussin, H. Corrosion inhibition on mild steel in 1 M HCl solution by Cryptocarya nigra extracts and three of its constituents (alkaloids). RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 6547–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manh, T.D.; Huynh, T.L.; Thi, B.V.; Lee, S.; Yi, J.; Dang, N.N. Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Environments Containing Sonneratia caseolaris Leaf Extract. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 8874–8886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoola, A.A.; Babalola, R.; Durodola, B.M.; Alagbe, E.E.; Agboola, O.; Adegbile, E.O. Corrosion inhibition of A36 mild steel in 0.5 M acid medium using waste citrus limonum peels. Results Eng. 2022, 15, 100490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.-L.; Shao, J.-J.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Lai, Y.-M.; Zhao, Z.-N. Adsorption and corrosion of renewable inhibitor of Pomelo peel extract for mild steel in phosphoric acid solution. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faydy, M.E.; Benhiba, F.; Warad, I.; Saoiabi, S.; Alharbi, A.; Alluhaybi, A.; Lakhrissi, B.; Abdallah, M.; Zarrouk, A. Bisquinoline analogs as corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in acidic electrolyte: Experimental, DFT, and molecular dynamics simulation approaches. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1265, 133389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonijevic, M.M.; Petrovic, M.B. Copper corrosion Inhibitors. A review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2008, 3, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, J.; Sowmiya, M.; Sounthari, P.; Parameswari, K.; Chitra, S.; Senthilkumar, K. N-heterocycles as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acid medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 216, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düdükcü, M.; Yazici, B.; Erbil, M. The effect of indole on the corrosion behaviour of stainless steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 87, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.A.; Ebenso, E.E.; Obot, I.B.; Assyry, A.E. 3-Amino alkylated indoles as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in 1M HCl: Experimental and theoretical studies. Mol. Liq. 2016, 219, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrini, M.; Robert, F.; Roos, C. Adsorption properties and inhibition of C38 steel corrosion in hydrochloric solution by some indole derivates: Temperature effect, activation energies, and thermodynamics of adsorption. Int. J. Corros. 2013, 2013, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, G. Corrosion inhibition of indole-3-acetic acid on mild steel in 0.5 M HCl. Colloids Surf. 2008, 317, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, F.K.; Adejoro, I.A.; Lori, J.A.; Oyeneyin, O.E.; Akpomie, K.G. Indole derivatives as organic corrosion inhibitors of low carbon steel in HCl medium-experimental and theoretical approach. Chem. Afr. 2022, 5, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, D.; Kumari, P.; Shetty, P.; Rao, S.A. Indole hydrazide derivatives as potential corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in HCl acid medium: Experimental study and theoretical calculations. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2021, 75, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.E.-A.S.; Rashwan, S.M.; Kamel, M.M.; Atef, M.; El-Hossiany, A. Eco-friendly impact of a novel green Melilotus officinalis extract as a sustainable inhibitor to reduce acid corrosion of copper. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 37240–37251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.S.; Migahed, M.A.; Atia, A.A.; Mousa, I.M. Corrosion Inhibition and Adsorption Behavior of Some Cationic Surfactants on Carbon Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution. J. Bio Tribo Corros. 2016, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, P. Hydrazide derivatives: An overview of their inhibition activity against acid corrosion of mild steel. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 71, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Shetty, P.; Suma, R. Corrosion Inhibition Effect of 4-Hydroxy-N′-[(E)-(1H-indole-2-ylmethylidene)] Benzohydrazide on Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution. Int. J. Corros. 2014, 2014, 256424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartarone, G.; Bonaldo, L.; Tortato, C. Inhibitive action of indole-5-carboxylic acid towards corrosion of mild steel in deaerated 0.5 M sulfuric acid solutssions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.A.; Ebenso, E.E.; Obot, I.B.; Assyry, A.E. Ionic Liquids as Green Corrosion Inhibitors for Industrial Metals and Alloys. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 219, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartarone, G.; Zingales, A.; Bellomi, T.; Bortolato, D.; Capobianco, G. Study of inhibition mechanism and efficiency of indole-5-carboxylic acid on corrosion of copper in aerated 0.5 M H2SO4. Br. Corros. J. 2013, 35, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damous, M.; Allal, H.; Belhocine, Y.; Maza, S.; Merazig, H. Quantum chemical exploration on the inhibition performance of indole and some of its derivatives against copper corrosion. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 340, 117136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrini, M.; Robert, F.; Vezin, H.; Roos, C. Electrochemical and quantum chemical studies of some indole derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for C38 steel in molar hydrochloric acid. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 3367–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Huan, Z.; Yang, J.-D.; Cheng, J.-P. Catalytic Vilsmeier–Haack Reactions for C1-Deuterated Formylation of Indoles. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 15539–15546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, E.E.; Althobaiti, I.O.; Haukka, M.; Boraei, A.T.A. Synthesis, X-ray Single-Crystal Analysis, and Anticancer Activity Evaluation of New Alkylsulfanyl-Pyridazino[4,5-b]indole Compounds as Multitarget Inhibitors of EGFR and Its Downstream PI3K-AKT Pathway. Crystals 2022, 12, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakše, R.; Bevk, D.; Golobič, A.; Svete, J.; Stanovnik, B. Synthesis and Transformations of Ethyl 3-Formyl-1H-indole-2-carboxylate. Z. Naturforsch. 2006, 61, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Young, E.H.P. The synthesis of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) and related tryptamines. J. Chem. Soc. 1958, 3493–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabica, A.C.; Howe, E.E.; Ziegler, J.B.; Tishler, M. Improved Syntheses of Indole-3-aldehyde. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1946, 68, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Malviya, M.; Verma, C.; Quraishi, M. Aminoazobenzene and diaminoazobenzene functionalized graphene oxides as novel class of corrosion inhibitors for mild steel: Experimental and DFT studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 198, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.A. Novel cationic surfactant based on triazole as a corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in phosphoric acid produced by dihydrate wet process. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 208, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Hernandez, A.; Barreda-Serrano, M.C.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.A.; López-Sesenes, R.; González-Rodríguez, J.G.; Mejía-Sánchez, E.; Ramírez-Cano, J.A.; Orozco-Cruz, R.; Galván-Martínez, R. Insight into the Corrosion Inhibition Performance of Pistia stratiotes Leaf Extract as a Novel Eco-Friendly Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in 1 M HCl Solution. Molecules 2024, 29, 5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, C.; Rüther, T.; Jahn, L.; Schamel, M.; Schmidt, J.P.; Ciucci, F.; Danzer, M.A. A review on the distribution of relaxation times analysis: A powerful tool for process identification of electrochemical systems. J. Power Sources 2024, 594, 233845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, K.R.; Quraishi, M.A. Bis-Schiff bases of isatin as new and environmentally benign corrosion inhibitor for mild steel. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2819–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Z.; Guo, X. Carbon dots as effective corrosion inhibitor for 5052 aluminium alloy in 0.1 M HCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2019, 161, 108197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasia, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Its Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Yang, D.; Chen, H.; Guo, S.; Yang, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L. A high-efficiency corrosion inhibitor of N-doped citric acid-based carbon dots for mild steel in hydrochloric acid environment. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 223, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.; Sobhi, M.; Altass, H.M. Corrosion inhibition of aluminum in hydrochloric acid by pyrazinamide derivatives. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 223, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.K.; Zhang, J.-T.; Hu, J.-M.; Zhang, J.-Q. Improved corrosion performance of electrophoretic coatings by silane addition. Corros. Sci. 2012, 56, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Luo, Z.; Wan, S.; Chen, L. Insight into the anti-corrosion performance of Acanthopanax senticosus leaf extract as eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in acidic medium. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 117, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkacz, J.; Minda, J.; Fintová, S.; Wasserbauer, J. Comparison of Electrochemical Methods for the Evaluation of Cast AZ91 Magnesium Alloy. Materials 2016, 9, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Rehim, S.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Khalid, K. The inhibition of 4-(2′-amino-5′-methylphenylazo) antipyrine on corrosion of mild steel in HCl solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 70, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, M.; Bataillon, C.; Gwinner, B.; Miserque, F.; Orazem, M.E.; Sánchez-Sánchez, C.M.; Tribollet, B.; Vivier, V. Comparison of different methods for measuring the passive film thickness on metals. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 201, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, A.A.; El-Din, M.R.N. The adsorption and corrosion inhibition of some nonionic surfactants on API X65 steel surface in hydrochloric acid. Corros. Sci. 2012, 64, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunleye, O.O.; Arinkoola, A.O.; Eletta, O.A.; Agbede, O.O.; Osho, Y.A.; Morakinyo, A.F.; Hamed, J.O. Green corrosion inhibition and adsorption characteristics of Luffa cylindrica leaf extract on mild steel in hydrochloric acid environment. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, M.; Sarkar, T.K.; Purkait, T. Studies on Adsorption and Corrosion Inhibitive Properties of Indoline Compounds on N80 Steel in Hydrochloric Acid. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 4975–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Lateef, H.M.A.; Tantawy, A.H.; Soliman, K.A.; Eid, S.; Abo-Riya, M.A. Novel Imine-Tethering Cationic Surfactants: Synthesis, Surface Activity, and Investigation of the Corrosion Mitigation Impact on Carbon Steel in Acidic Chloride Medium via Various Techniques. Molecules 2023, 28, 4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sabbah, M.M.B.; Bedair, M.A.; Abbas, M.A.; Fahmy, A.; Hassaballa, S.; Moustafa, A.A. Synergistic Effect between Natural Honey and 0.1 M KI as Green Corrosion Inhibitor for Steel in Acid Medium. Z. Phys. Chem. 2019, 233, 627–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althobaiti, I.O.; Eid, S.; El-Nasser, K.S.; Hashem, N.; Salama, E.E. Evaluation of the Impact of Two Thiadiazole Derivatives on the Dissolution Behavior of Mild Steel in Acidic Environments. Molecules 2023, 28, 3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syam, S.M.; Elhenawy, A.A.; Gad, E.; Nady, H.; Eid, S. Combination of practical and theoretical measurements of albumin egg as an eco-friendly inhibitossr for copper corrosion in alkaline solutions. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 33929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Vazquez, A.; Rodr, F.J.; Vergara-Arenas, B.I.; Lomas-Romero, L.; Angeles-Beltran, D.; Negron-Silva, G.E.; Morales-Serna, J.A. Synthesis of 1,2,3-triazoles in the presence of mixed Mg/Fe oxides and their evaluation as corrosion inhibitors of API 5L X70 steel submerged in HCl. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 24736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khowdiary, M.M.; Taha, N.A.; Saleh, N.M.; Elhenawy, A.A. Synthesis of novel nano-sulfonamide metal-based corrosion inhibitor surfactants. Materials 2022, 15, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khowdiary, M.M.; Taha, N.A.; Barqawi, A.A.; Elhenawy, A.A.; Sheta, M.; Hassan, N. Theoretical and experimental evaluation of the anticorrosion properties of new Coumarin’s derivatives. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 6937–6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, N.I.N.; Sobri, S.; Yusof, Y.A.; Kassim, N.K. An Overview of Molecular Dynamic Simulation for Corrosion Inhibition of Ferrous Metals. Metals 2021, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Jin, Z.; Yang, C.; Akkermans, R.L.; Robertson, S.H.; Spenley, N.A.; Miller, S.; Todd, S.M. COMPASS II: Extended coverage for polymer and drug-like molecule databases. J. Mol. Model. 2016, 22, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Conc., ppm | Rs/Ω | CPE/S·sn·cm−2 | n | Rct/Ω cm2 | %EF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3.523 | 41.77 × 10−5 | 0.8387 | 279.6 | - |
| 10 | 4.177 | 3.717 × 10−5 | 0.8485 | 454.1 | 38.43 |
| 30 | 7.281 | 3.189 × 10−5 | 0.8459 | 534.5 | 47.69 |
| 50 | 8.729 | 2.842 × 10−5 | 0.8483 | 655.8 | 57.37 |
| 70 | 11.26 | 3.217 × 10−5 | 0.8228 | 733.2 | 61.87 |
| 90 | 12.74 | 25.24 × 10−5 | 0.822 | 913.1 | 69.38 |
| Inhibitor | Rs/Ω | CPE/S·sn·cm−2 | n | Rct/Ω cm2 | %EF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 M H2SO4 | 3.523 | 41.77 × 10−5 | 0.8387 | 279.6 | - |
| 0.5 M H2SO4 + MPI | 12.74 | 25.24 × 10−5 | 0.822 | 913.1 | 69.38 |
| 0.5 M H2SO4 + FIC | 6.414 | 3.303 × 10−5 | 0.8595 | 591.1 | 52.70 |
| Inh. Conc. | Ecorr/mV(SCE) | icorr/μA cm−2 | βa/mV dec−1 | βc/mV dec−1 | EF % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIC | Free inh. | −480.8 | 171.7 | 70.5 | −136.4 | - |
| 10 ppm | −477.2 | 52.9 | 58.9 | −173.3 | 69.2 | |
| 30 ppm | −470 | 49.5 | 52.1 | −162.6 | 71.1 | |
| 50 ppm | −487.8 | 47.0 | 74.0 | −171.5 | 72.6 | |
| 70 ppm | −464.1 | 42.9 | 48.2 | −154.7 | 75.0 | |
| 90 ppm | −470.4 | 40.8 | 53.4 | −152.9 | 76.2 | |
| MPI | 10 ppm | −476.9 | 54.5 | 56.0 | −168.3 | 68.3 |
| 30 ppm | −475.7 | 50.9 | 51.2 | −174.5 | 70.4 | |
| 50 ppm | −480.0 | 47.7 | 46.6 | −179.9 | 72.2 | |
| 70 ppm | −480.9 | 40.8 | 38.5 | −194.1 | 76.2 | |
| 90 ppm | −492.8 | 32.2 | 34.2 | −169.8 | 81.2 | |
| Inhibitor | Metal Surface | Medium | Efficiency (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present Inhibitors (MPI, FIC) | Mild Steel | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 81.5% | The present work |
| Indole-3-Acetic Acid | Mild Steel | 0.5 M HCl | 92% | [13] |
| Indole Hydrazide Derivatives | Mild Steel | 1 M HCl | 80.4% | [15] |
| Indoline Compounds | N80 Steel | 15% HCl | 82.3% | [46] |
| EHOMO | ELUMO | Ɛ | IP | EA | η | σ | χ | ω | ΔƐ | ΔN110 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIC | −6.081 | −1.832 | 3.882 | 8.088 | −0.827 | 3.630 | 0.275 | 3.630 | 1.478 | −1.114 | 0.164 |
| MPI | −6.543 | −2.993 | 4.139 | 6.543 | −2.993 | 1.775 | 0.563 | 1.775 | 0.330 | −1.192 | 0.858 |
| E | Eads | Erig | Edef | dEad/dNi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIC | 23.70935 | −433.11 | −12.8313 | −420.279 | −433.11 |
| MPI | 15.45956 | −651.189 | −9.97061 | −641.219 | −651.189 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salama, E.E.; Alrashdi, S.; Boraei, A.T.A.; Eid, S.; Gomaa, I.; Gad, E.S.; Elhenawy, A.A.; Nady, H. Utilizing Some Indole Derivatives to Control Mild Steel Corrosion in Acidic Environments: Electrochemical and Theoretical Methods. Molecules 2025, 30, 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061235
Salama EE, Alrashdi S, Boraei ATA, Eid S, Gomaa I, Gad ES, Elhenawy AA, Nady H. Utilizing Some Indole Derivatives to Control Mild Steel Corrosion in Acidic Environments: Electrochemical and Theoretical Methods. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061235
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalama, Eid E., Saad Alrashdi, Ahmed T. A. Boraei, Salah Eid, Islam Gomaa, Ehab S. Gad, Ahmed A. Elhenawy, and Hashem Nady. 2025. "Utilizing Some Indole Derivatives to Control Mild Steel Corrosion in Acidic Environments: Electrochemical and Theoretical Methods" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061235
APA StyleSalama, E. E., Alrashdi, S., Boraei, A. T. A., Eid, S., Gomaa, I., Gad, E. S., Elhenawy, A. A., & Nady, H. (2025). Utilizing Some Indole Derivatives to Control Mild Steel Corrosion in Acidic Environments: Electrochemical and Theoretical Methods. Molecules, 30(6), 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061235








