New Horizon in Selective Tocols Extraction from Deodorizer Distillates Under Mild Conditions by Using Deep Eutectic Solvents
Abstract
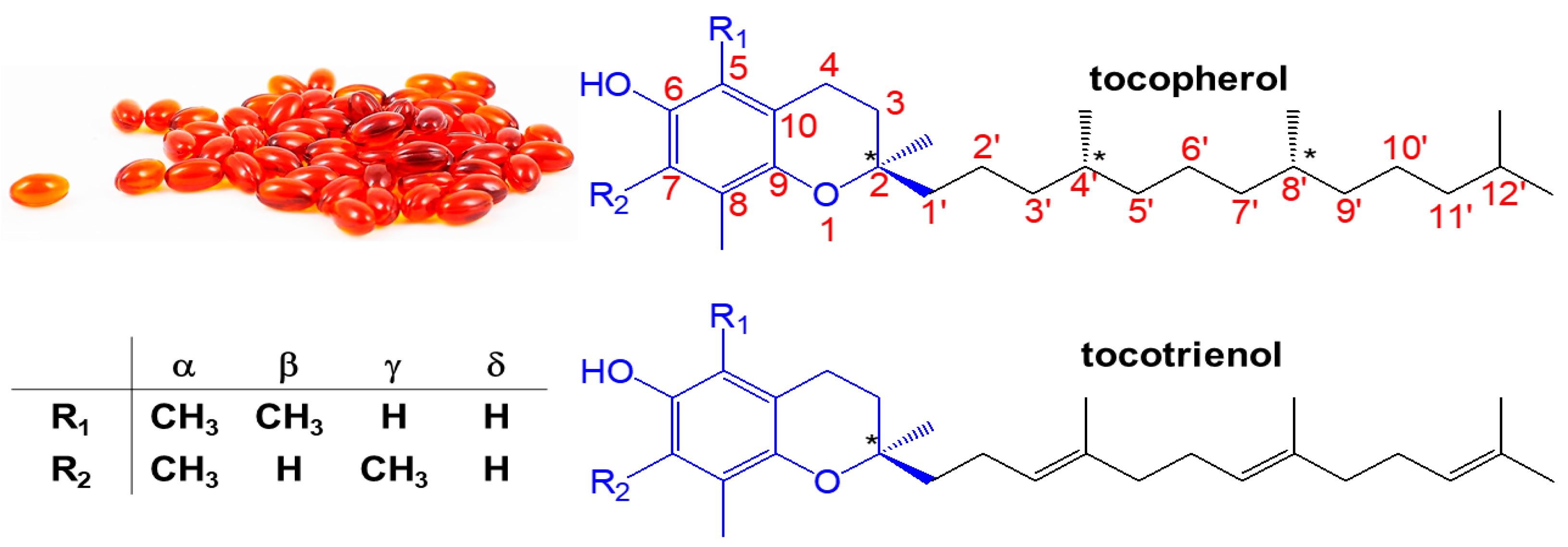
1. Introduction
| Tocols | Solubility (mg L−1) * | m.p. (°C) ** | b.p. (°C) ** | Log P | H-Bond Donor | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-tocopherol | Miscible with chloroform, vegetable oils, ether, acetone and alcohol. Immiscible with water. | 2.5–3.5 | 235.0 | 10.7 | 1 | [28] |
| β-tocopherol | Chloroform (Sparingly), Ethanol (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Methanol (Sparingly) | <25 | 474.9 | 10.3 | 1 | [29] |
| γ-tocopherol | Chloroform (Sparingly), Ethanol (Slightly), Methanol (Sparingly) | <25 | 518.0 | 10.3 | 1 | [30] |
| δ-tocopherol | Chloroform (Sparingly), Ethanol (Slightly, Sonicated), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), | <25 | 464.7 | 10.0 | 1 | [31] |
| α-tocotrienol | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) | <25 | 541.7 | 9.3 | 1 | [32] |
| β-tocotrienol | Soluble in ether, ethyl acetate, hexanes, and does not mix well water. | <25 | 507.5 | 8.9 | 1 | [33] |
| γ-tocotrienol | Chloroform (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) | <25 | 530.8 | 8.9 | 1 | [34] |
| δ-tocotrienol | Chloroform (Sparingly), Methanol (Slightly) | <25 | 541.7 | 8.6 | 1 | [35] |
2. Tocols Extraction Using Deep Eutectic Solvents
2.1. Mono-Phasic Solvent System
2.2. In Situ Dess Formation
2.3. Bi-Phasic Solvent System
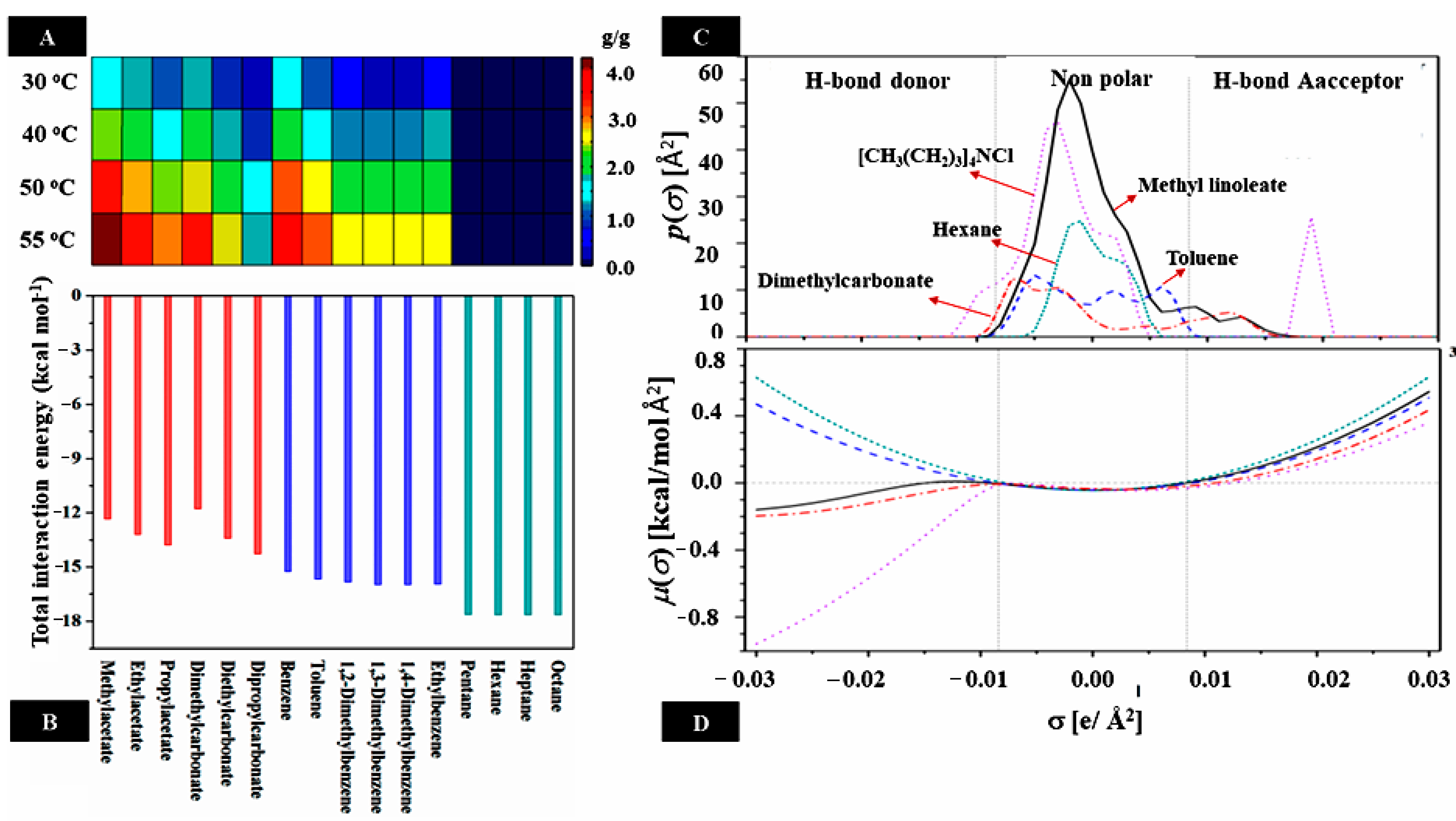
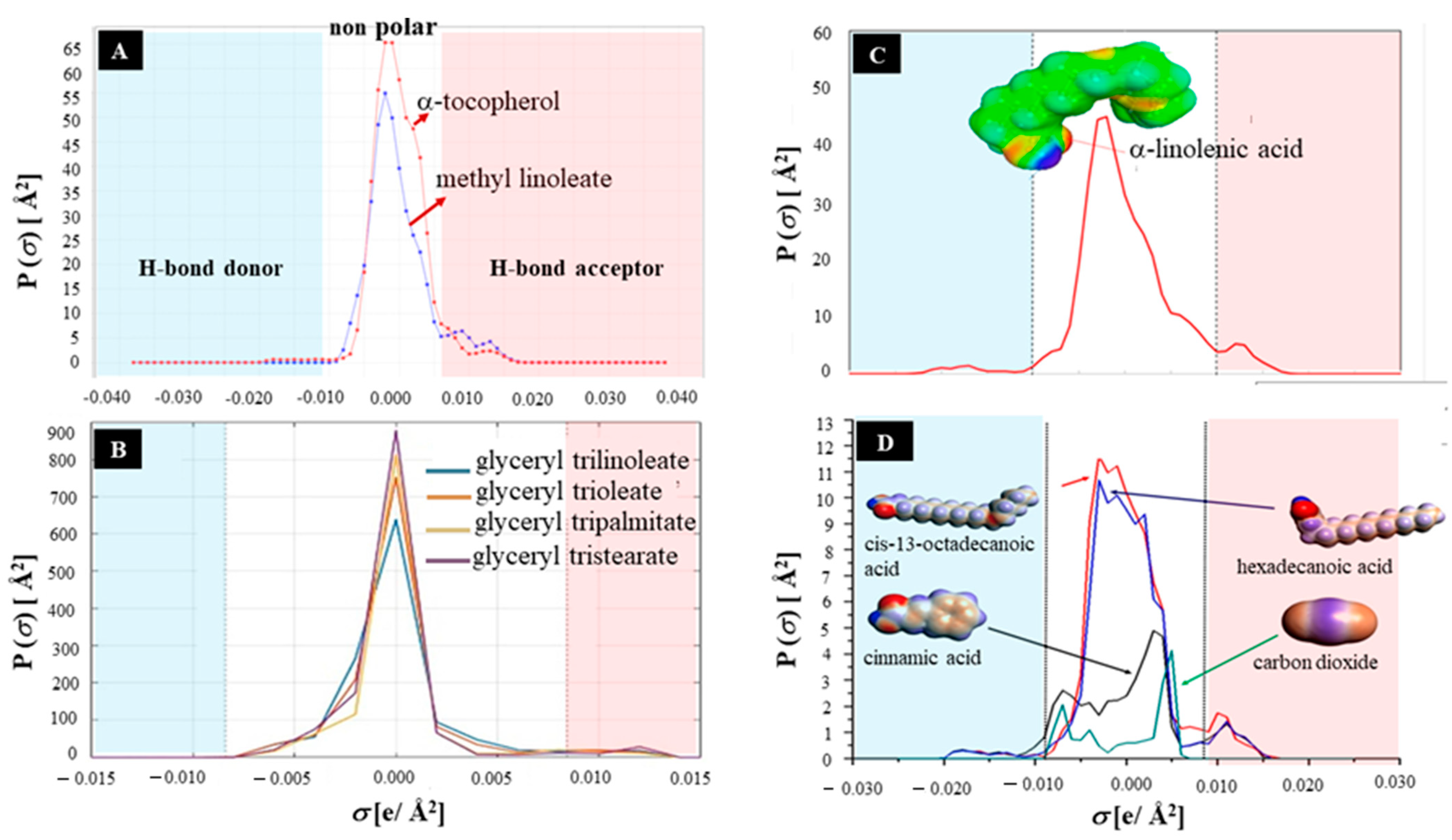
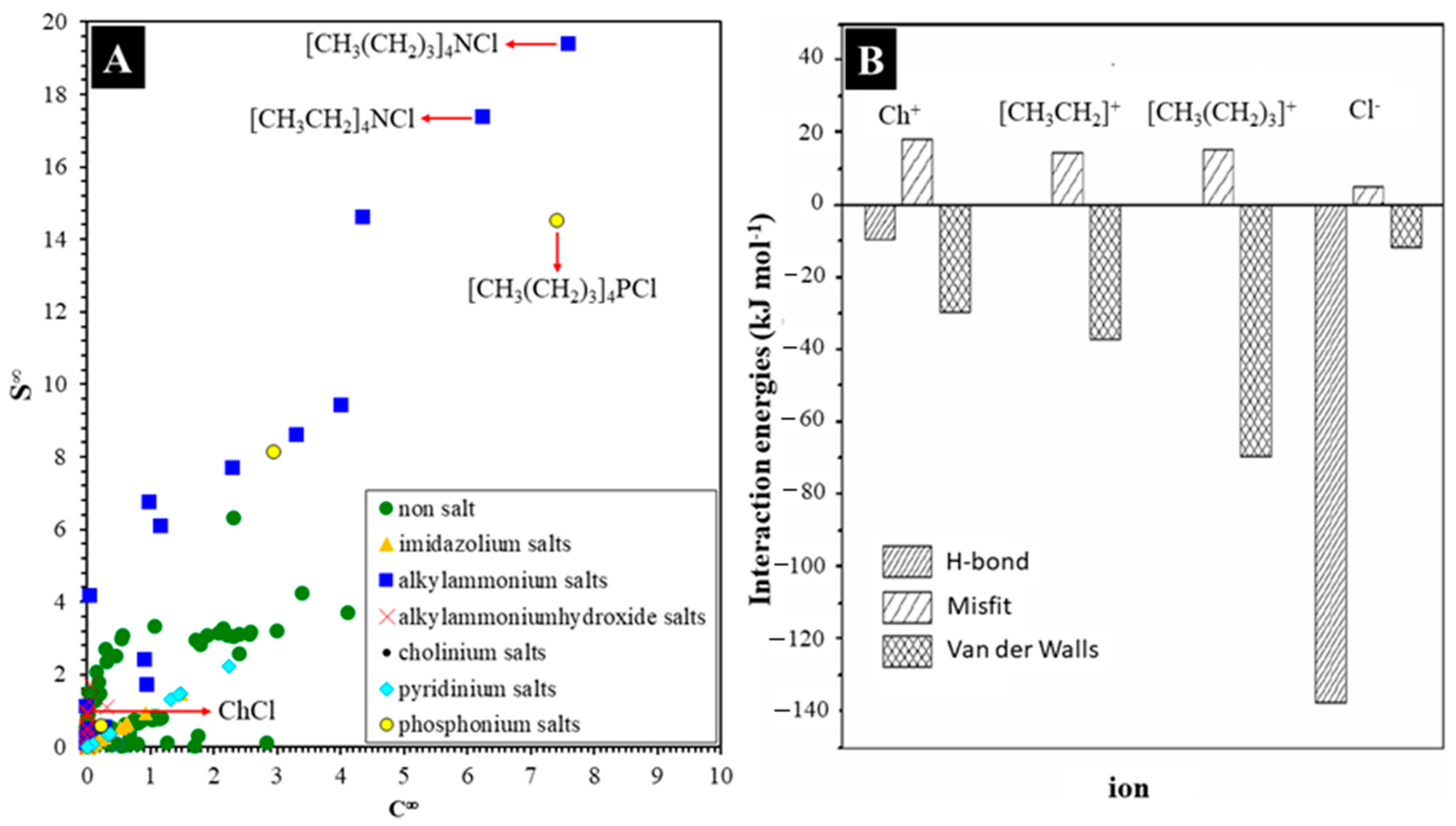
3. Tocols—Deep Eutectic Solvents Interaction
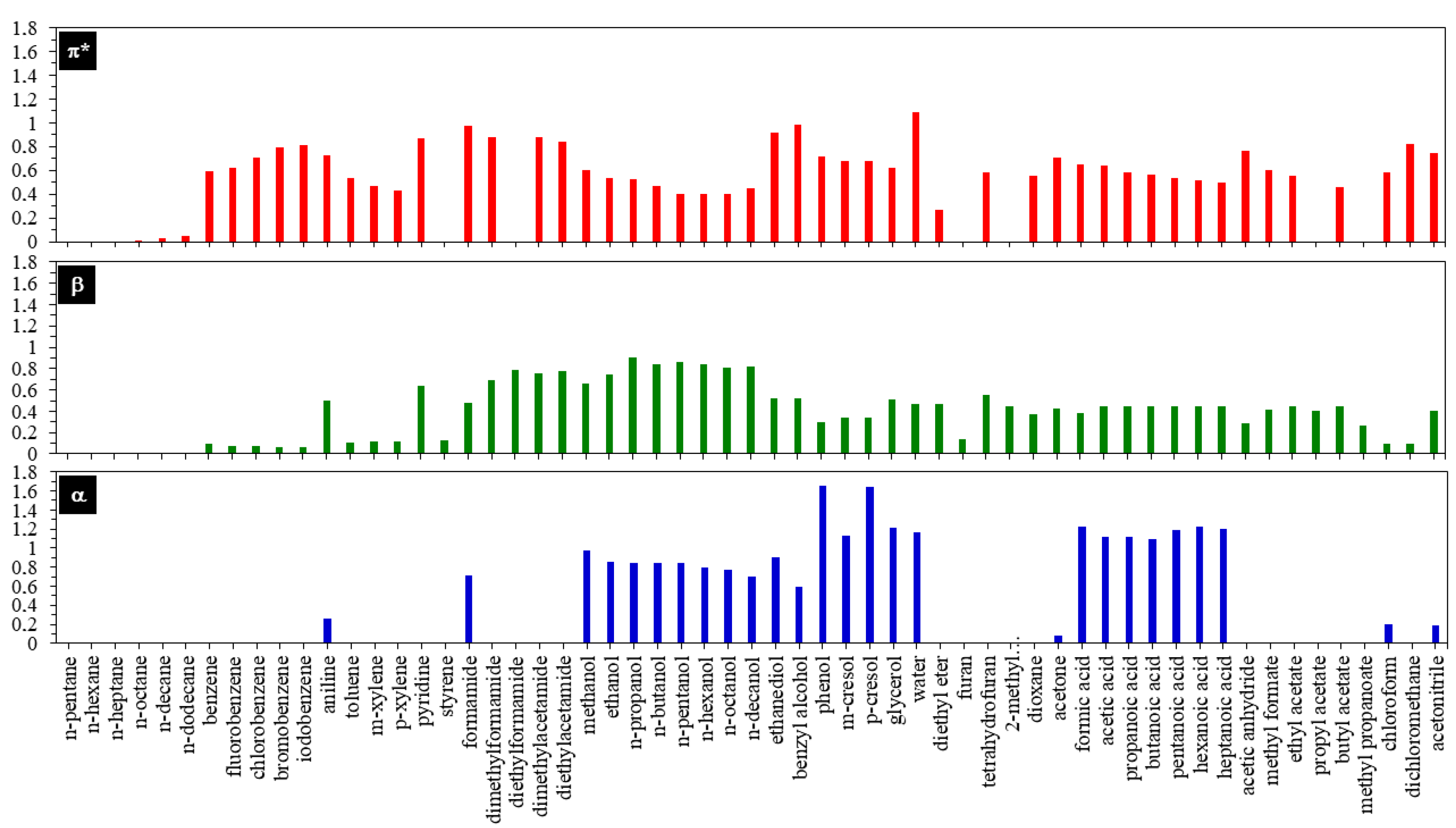
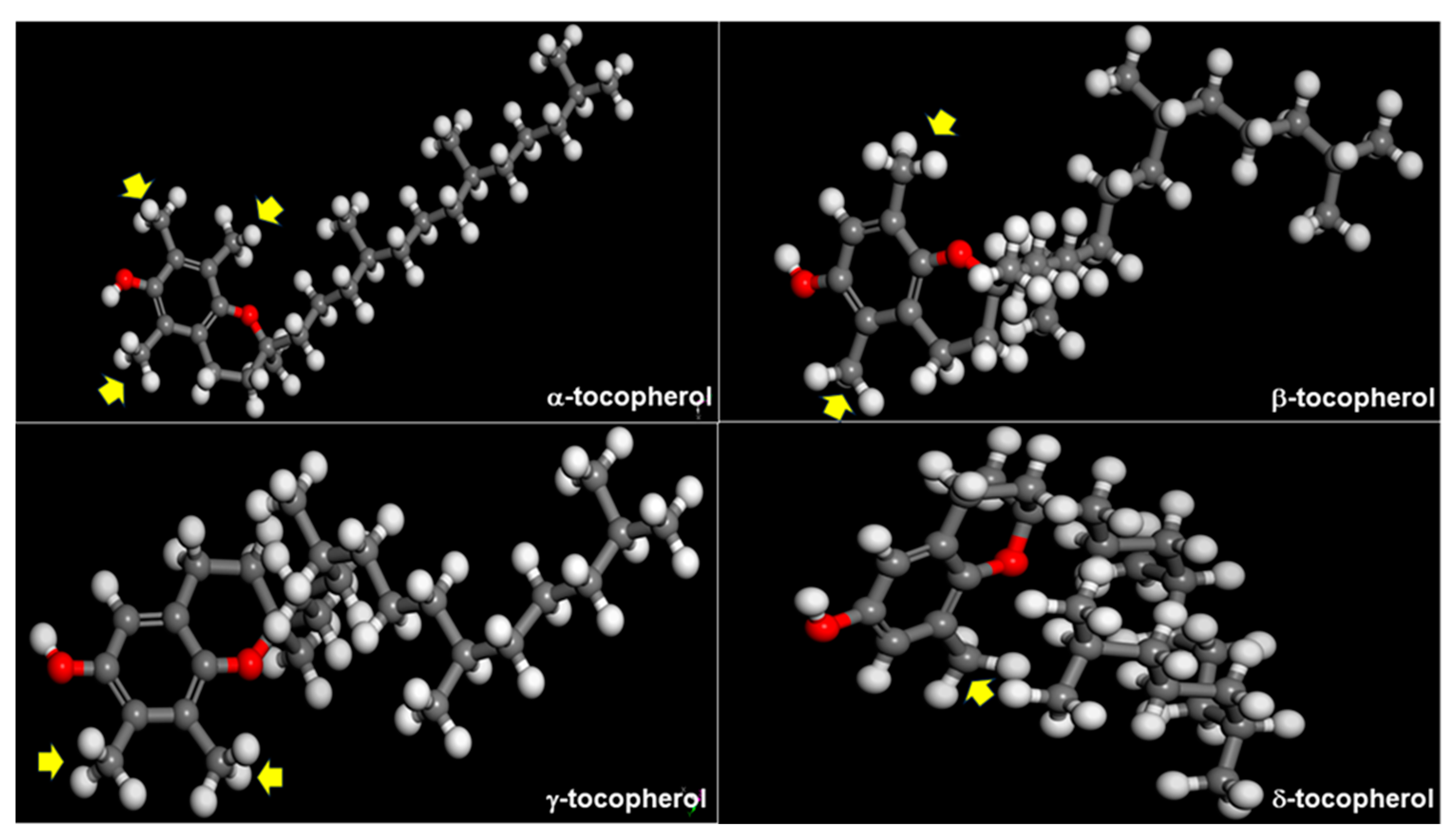
3.1. Intrinsic Factors
3.2. Extrinsic Factors
4. Toxicity of DESs
5. Summary and Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| α-TTP | alpha-Tocopherol Transfer Protein |
| ChCl | Choline Chloride |
| CODD | corn oil deodorizer distillate |
| CPO | Crude Palm Oil |
| DDs | Deodorizer Distillates |
| DESs | Deep eutectic solvents |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared |
| HBA | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor |
| HBD | Hydrogen Bond Donor |
| HESs | Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents |
| ILs | Ionic Liquids |
| MODD | Methylated Oil Deodorizer Distillates |
| NOESY | Nuclear Overhauser Effect |
| SODD | Soybean Oil Deodorizer Distillate |
| S | Selectivity |
| T | Tocopherol |
| T3 | Tocotrienol |
References
- Niki, E.; Abe, K. Chapter 1:Vitamin E: Structure, Properties and Functions. Food Chem. Funct. Anal. 2019, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bartosińska, E.; Buszewska-Forajta, M.; Siluk, D. GC–MS and LC–MS Approaches for Determination of Tocopherols and Tocotrienols in Biological and Food Matrices. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 127, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, H.; Ahad, A.; Iqbal, J.; Siddiqui, W.A. Pharmacological Potential of Tocotrienols: A Review. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, S.; Parinandi, N.L.; Kotha, S.R.; Roy, S.; Rink, C.; Bibus, D.; Sen, C.K. Nanomolar Vitamin E α-Tocotrienol Inhibits Glutamate-Induced Activation of Phospholipase A2 and Causes Neuroprotection. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.L. An Update on Vitamin E, Tocopherol and Tocotrienol-Perspectives. Molecules 2010, 15, 2103–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocchegiani, E.; Costarelli, L.; Giacconi, R.; Malavolta, M.; Basso, A.; Piacenza, F.; Ostan, R.; Cevenini, E.; Gonos, E.S.; Franceschi, C.; et al. Vitamin E–gene Interactions in Aging and Inflammatory Age-Related Diseases: Implications for Treatment. A Systematic Review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2014, 14, 81–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, R.; Nowicka, B.; Kruk, J. Vitamin E-Occurrence, Biosynthesis by Plants and Functions in Human Nutrition. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbinova, E.A.; Packer, L. Antioxidant Properties of α-Tocopherol and α-Tocotrienol.” Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994; Volume 234. [Google Scholar]
- Constantinou, C.; Papas, A.; Constantinou, A.I. Vitamin E and Cancer: An Insight into the Anticancer Activities of Vitamin E Isomers and Analogs. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koba, K.; Abe, K.; Ikeda, I.; Sugano, M. Effects of α-Tocopherol and Tocotrienols on Blood Pressure and Linoleic Acid Metabolism in the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat (SHR). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1992, 56, 1420–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.K.; Khanna, S.; Roy, S.; Packer, L. Molecular Basis of Vitamin E Action. Tocotrienol Potently Inhibits Glutamate-Induced Pp(60c-Src) Kinase Activation and Death of HT4 Neuronal Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 13049–13055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, S.; Roy, S.; Slivka, A.; Craft, T.K.S.; Chaki, S.; Rink, C.; Notestine, M.A.; DeVries, A.C.; Parinandi, N.L.; Sen, C.K. Neuroprotective Properties of the Natural Vitamin E α-Tocotrienol. Stroke 2005, 36, 2258–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F. Vitamin E as an Essential Micronutrient for Human Health: Common, Novel, and Unexplored Dietary Sources. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 176, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngoc Doan, P.A.; Tan, T.H.; Siow, L.F.; Tey, B.T.; Chan, E.S.; Tang, T.K.; Abdul Karim, N.A.; Phuah, E.T.; Lee, Y.Y. Dry Fractionation Approach in Concentrating Tocopherols and Tocotrienols from Palm Fatty Acid Distillate: A Green Pretreatment Process for Vitamin E Extraction. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, S.Y.; Chu, B.S.; Baharin, B.S. Commercial Extraction of Vitamin E from Food Sources. In The Encyclopedia of Vitamin E; Preedy, V., Watson, R., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2007; Volume 962. [Google Scholar]
- Netscher, T. Synthesis of Vitamin E. Vitam. Horm. 2007, 76, 155–202. [Google Scholar]
- Ranard, K.M.; Erdman, J.W. Effects of Dietary RRR α-Tocopherol vs All-Racemic α-Tocopherol on Health Outcomes. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, J.K. Vitamin E Bioavailability in Humans. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 162, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerald, F.; Combs, J.; McClung, J.P. The Vitamins: Fundamental Aspects in Nutrition and Health; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Irías-Mata, A.; Stuetz, W. Tocopherols, Tocomonoenols, and Tocotrienols in Oils of Costa Rican Palm Fruits: A Comparison between Six Varieties and Chemical versus Mechanical Extraction. ACS Publ. 2017, 65, 7476–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.-Y.; Maniam, G.; Wong, F.-S.; Tan, D.M.-Y.; Meganathan, P.; Chuah, L.-H. Tocotrienols: From Bench to Bedside. In Vitamin E: Chemistry and Nutritional Benefits; Niki, E., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2019; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Traber, M.G.; Burton, G.W.; Ingold, K.U.; Kayden, H.J. RRR- and SRR-α-Tocopherols Are Secreted without Discrimination in Human Chylomicrons, but RRR-α-Tocopherol Is Preferentially Secreted in Very Low Density Lipoproteins. J. Lipid Res. 1990, 31, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Jia, L.; Park, S.K.; Li, J.; Gopalan, A.; Simmons-Menchaca, M.; Sanders, B.G.; Kline, K. Anticancer Actions of Natural and Synthetic Vitamin E Forms: RRR-α-Tocopherol Blocks the Anticancer Actions of γ-Tocopherol. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, R.K.; Bhagavan, H.N. Relative Bioavailabilities of Natural and Synthetic Vitamin E Formulations Containing Mixed Tocopherols in Human Subjects. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1999, 69, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leth, T.; Sondergaard, H. Biological Activity of Vitamin E Compounds and Natural Materials by the Resorption-Gestation Test, and Chemical Determination of the Vitamin E Activity in Foods and Feeds. J. Nutr. 1977, 107, 2236–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, S.U.; Rimbach, G. Biological Activity of Tocotrienols. Handbook of Antioxidants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Blatt, D.H.; Pryor, W.A.; Mata, J.E.; Rodriguez-Proteau, R. Re-Evaluation of the Relative Potency of Synthetic and Natural α-Tocopherol: Experimental and Clinical Observations. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2004, 15, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 14985, Alpha-Tocopherol. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/alpha-tocopherol (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 6857447, Beta-Tocopherol. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/beta-tocopherol (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 92729, Gamma-Tocopherol. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/gamma-tocopherol (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 92094, Delta-Tocopherol. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/delta-tocopherol (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 5282347, Alpha-Tocotrienol. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/alpha-tocotrienol (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 5282348, Beta-Tocotrienol. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/beta-tocotrienol (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 5282349, Gamma-Tocotrienol. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/gamma-tocotrienol (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 5282350, Delta-Tocotrienol. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/delta-tocotrienol (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Ahsan, H.; Ahad, A.; Siddiqui, W.A. A Review of Characterization of Tocotrienols from Plant Oils and Foods. J. Chem. Biol. 2015, 8, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Shi, J.; Posada, L.R.; Kakuda, Y.; Xue, S.J. Separating Tocotrienols from Palm Oil by Molecular Distillation Separating Tocotrienols from Palm. Food Rev. Inter. 2008, 24, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yort, L.; Singanusong, R.; Yuenyong, J.; Sookwong, P.; Jiamyangyuen, S. Optimization of Vitamin E Extraction from Rice Bran Oil Deodorizer Distillate Using Response Surface Methodology. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 10, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estiasih, T.; Ahmadi, K. Bioactive Compounds from Palm Fatty Acid Distillate and Crude Palm Oil. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 131, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güçlü-Üstündağ, Ö.; Temelli, F. Column Fractionation of Canola Oil Deodorizer Distillate Using Supercritical Carbon Dioxide. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2007, 84, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarian Asl, P.; Niazmand, R.; Yahyavi, F. Extraction of Phytosterols and Tocopherols from Rapeseed Oil Waste by Supercritical CO2 plus Co-Solvent: A Comparison with Conventional Solvent Extraction. Heliyon 2020, 6, 3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Sherazi, S.T.H.; Talpur, F.N. Changes of Total Tocopherol and Tocopherol Species during Sunflower Oil Processing. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Fu, X.; Li, Z. Extraction of Tocopherol from Soybean Oil Deodorizer Distillate by Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarhan, İ.; Kara, H. A New HPLC Method for Simultaneous Analysis of Sterols, Tocopherols, Tocotrienols, and Squalene in Olive Oil Deodorizer Distillates Using a Monolithic Column with Chemometric Techniques. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 4681–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleyen, T.; Verhé, R.; Garcia, L.; Dewettinck, K.; Huyghebaert, A.; De Greyt, W. Gas Chromatographic Characterization of Vegetable Oil Deodorization Distillate. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 9, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Top, A.G.M.; Leong, L.W.; Ong, A.S.H.; Kawada, T.; Watanabe, H.; Tsuchiya, N. Production of High Concentration Tocopherols and Tocotrienols from Palm-Oil by-Products. US5190618A, 2 March 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Batistella, C.B.; Moraes, E.B.; Filho, R.M.; Maciel, M.W. Molecular Distillation: Rigorous Modeling and Simulation for Recovering Vitamin E from Vegetal Oils. In Proceedings of the Biotechnology for Fuels and Chemicals: The Twenty–Third Symposium; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 38, pp. 1187–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Choong, T.S.Y.; Chuah, T.G. Comment on “Separation of Vitamin E from Palm Fatty Acid Distillate Using Silica: I. Equilibrium of Batch Adsorption by B.S. Chu et al. [Journal of Food Engineering 62 (2004) 97-103].”. J. Food Eng. 2005, 67, 379. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, X.; Xing, H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; Su, B.; Bao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Q. Selective Liquid−Liquid Extraction of Natural Phenolic Compounds Using Amino Acid Ionic Liquids: A Case of α-Tocopherol and Methyl Linoleate Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 6480–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, A.J.; Bhagwat, S.S. Separation of Tocol (Tocopherol & Tocotrienol) and Phytosterols from Palm Fatty Acid Distillate by Saponification and Purification by Low Temperature Solvent Crystallization. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 2962–2971. [Google Scholar]
- Posada, L.R.; Shi, J.; Kakuda, Y.; Xue, S.J. Extraction of Tocotrienols from Palm Fatty Acid Distillates Using Molecular Distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 57, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as New Potential Media for Green Technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Namieśnik, J. Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Mixtures: Sustainable Solvents for Extraction Processes. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 1784–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xing, H.; Cao, Y.; Su, B.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Q. Selective Separation of Tocopherol Homologues by Liquid-Liquid Extraction Using Ionic Liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 6417–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z.; Yuan, W. Selection of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids for Vitamin e Extraction from Deodorizer Distillate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z. Integrated Process for Extracting Vitamin E with High Purity from the Methylated Oil Deodorizer Distillate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 196, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulfa, D.M.; Munim, A.; Rahmawati, S.I.; Putra, M.Y.; Bayu, A. Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids for the Selective Separation of Tocotrienol Homologues From Palm Fatty Acid Distillate Via Liquid-Liquid Extraction. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2024, 16, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Qin, H.; Cheng, H.; Song, Z.; Qi, Z.; Sundmacher, K. Rational Screening of Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Direct Extraction of α-Tocopherol from Deodorized Distillates. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 8216–8227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadid, A.; Mokrushina, L.; Minceva, M. Design of Deep Eutectic Systems: A Simple Approach for Preselecting Eutectic Mixture Constituents. Molecules 2020, 25, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Syntheses, Properties and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.; Wijffels, R.H.; Eppink, M.H.M. Lipid Recovery from Deep Eutectic Solvents by Polar Antisolvents. Food Bioprod. Process. 2024, 143, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Redha, A. Review on Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Natural Sources Using Green Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 878–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgxadeni, N.; Kabane, B.; Bahadur, I.; Varma, R.S.; Singh, S.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Sustainable Solvents for Industrial Separation Problems: A Recent Update. J. Ion. Liq. 2023, 3, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.J.; Zhang, J.B.; Zou, Y.T.; Peng, H.L.; Huang, K. Manufacturing Acidities of Hydrogen-Bond Donors in Deep Eutectic Solvents for Effective and Reversible NH3Capture. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 13408–13417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlić, B.; Mrkonjić, Ž.; Teslić, N.; Kljakić, A.C.; Pojić, M.; Mandić, A.; Stupar, A.; Santos, F.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Mišan, A. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent (NADES) Extraction Improves Polyphenol Yield and Antioxidant Activity of Wild Thyme (Thymus serpyllum L.) Extracts. Molecules 2022, 27, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Gui, C.; Dai, C.; Yu, G.; Lei, Z. Molecular Insights into SO2 Absorption by [EMIM][Cl] -Based Deep. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 13831–13841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z. Enhanced Vitamin E Extraction Selectivity from Deodorizer Distillate by a Biphasic System: A COSMO-RS and Experimental Study. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5547–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, I.D. A Critical Review of Emerging Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents’ Applications in Food Chemistry: Trends and Opportunities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11860–11879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bosco, C.; Di Lisio, V.; D’Angelo, P.; Gentili, A. Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvent with Antioxidant Properties: Application for the Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction of Fat-Soluble Micronutrients from Fruit Juices. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 8170–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonský, M.; Škulcová, A.; Malvis, A.; Šima, J. Extraction of Value-Added Components from Food Industry Based and Agro-Forest Biowastes by Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 282, 46–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizki, I.F.; Panjaitan, F.R.; Mulyono, M.E.; Bajra, B.D. The Utilization of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent Composition in Tocotrienol and Tocopherol Extraction from Crude Palm Oil and Its Acylglycerol Products. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numan, A.H.; Ng, M.H. Selective Separation of Tocol Homologues by Liquid-Liquid Extraction Using Choline-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Trends Sci. 2023, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
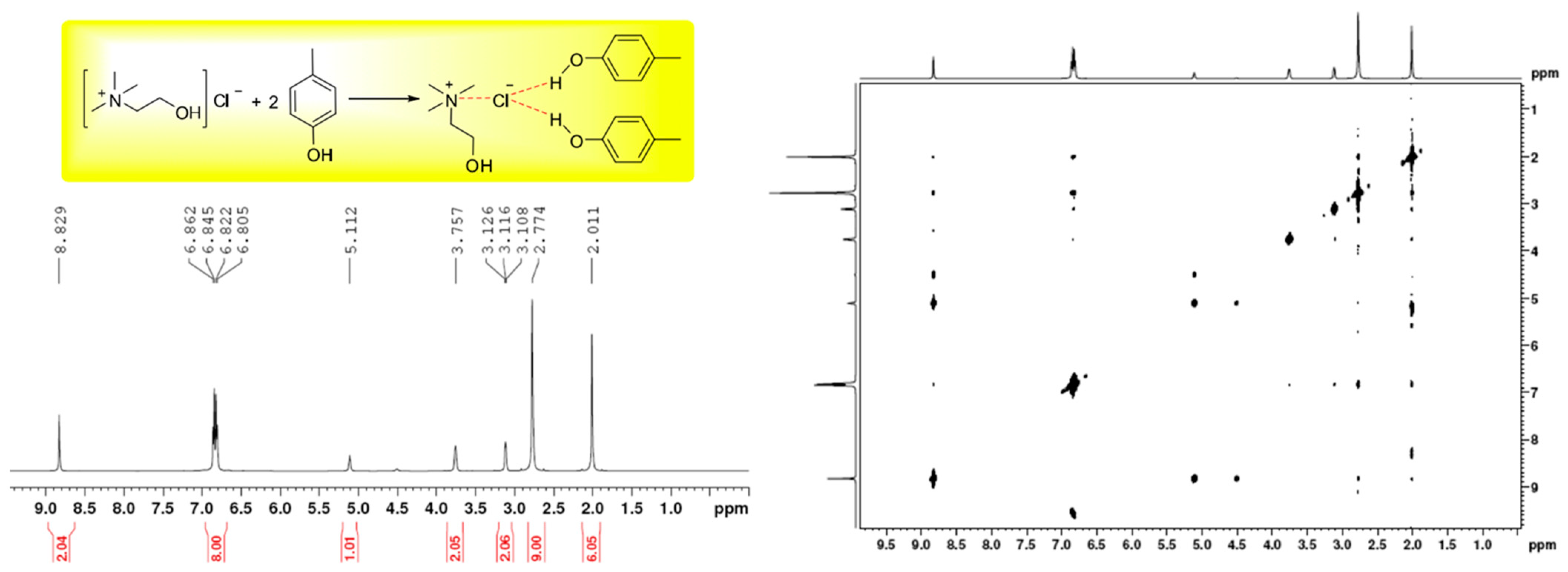
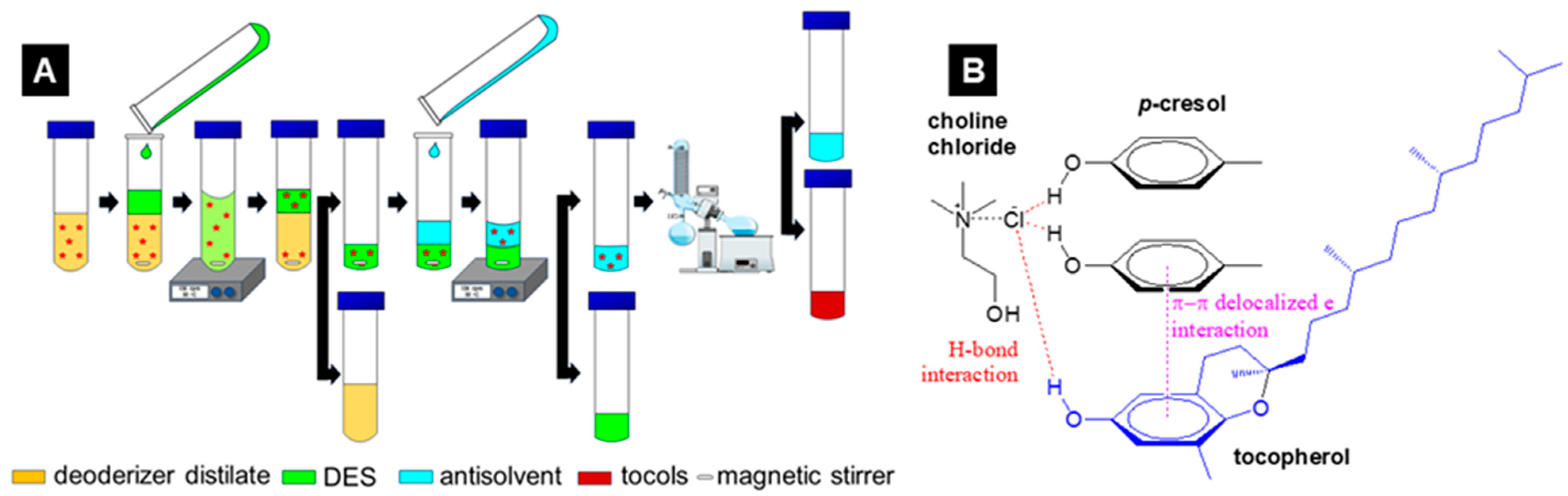
- Liu, W.; Zhang, K.; Yang, G.; Yu, J. A Highly Efficient Microextraction Technique Based on Deep Eutectic Solvent Formed by Choline Chloride and P-Cresol for Simultaneous Determination of Lignans in Sesame Oils. Food Chem. 2019, 281, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Li, J.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z.; Yuan, W. Association Extraction for Vitamin E Recovery from Deodorizer Distillate by In-Situ Formation of Deep Eutectic Solvent. AIChE J. 2016, 59, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Ye, W.; Pan, C.; Medical, A.; Zhang, C. Effective Extraction of Tocopherols from Soybean Oil Deodorizer Distillate Methyl Esters Using Phenolic Deep Eutectic Solvents. SSRN 2006, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Manurung, R.; Hutauruk, G.R.; Arief, A. Vitamin e Extraction from Red Palm Biodiesel by Using K2CO3 Based Deep Eutectic Solvent with Glycerol as Hydrogen Bond Donor. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1977, 20011. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Hadi, N.; Ng, M.H.; Choo, Y.M.; Hashim, M.A.; Jayakumar, N.S. Performance of Choline-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Extraction of Tocols from Crude Palm Oil. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2015, 92, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, B.; Shekaari, H.; Zafarani-Moattar, M.T. Selective Separation of α-Tocopherol Using Eco-Friendly Choline Chloride—Based Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) via Liquid-Liquid Extraction. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 617, 126317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Freitas, L.; Jacques, R.A.; Richter, M.F.; da Silva, A.L.; Caramão, E.B. Pressurized Liquid Extraction of Vitamin E from Brazilian Grape Seed Oil. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1200, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, A.R.R.; Capela, E.V.; Carmo, R.S.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, M.G. Solvatochromic Parameters of Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by Ammonium-Based Salts and Carboxylic Acids. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 448, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Vidović, S.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Jokić, S. New Perspective in Extraction of Plant Biologically Active Compounds by Green Solvents. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 109, 52–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y. The Properties of Organic Liquids That Are Relevant to Their Use as Solvating Solvents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1993, 22, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamt, A.; Jonas, V.; Bürger, T.; Lohrenz, J.C.W. Refinement and Parametrization of COSMO-RS. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 5074–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparetto, H.; Vieira, Y.; Paula Gonçalves Salau, N. The Role of Quantum-Chemical Descriptors and Sigma-Profile Overlapping of Different Co-Solvents on Tuning Ethanolic Extraction of Soybean Oil. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 384, 122306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Song, Z.; Qi, Z.; Sundmacher, K. Comparative Screening of Organic Solvents, Ionic Liquids, and Their Binary Mixtures for Vitamin E Extraction from Deodorizer Distillate. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2022, 171, 108711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spange, S.; Lungwitz, R.; Schade, A. Correlation of Molecular Structure and Polarity of Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 192, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J. The Essential Role of Hydrogen-Bonding Interaction in the Extractive Separation of Phenolic Compounds by Ionic Liquid. AIChE J. 2012, 59, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSID:2032. Available online: http://www.chemspider.com/chemical-structure.2032.html (accessed on 17 December 2023).
- CSID:5256784. Available online: http://www.chemspider.com/chemical-structure.5256784.html (accessed on 17 December 2023).
- CSID:83708. Available online: http://www.chemspider.com/chemical-structure.83708.html (accessed on 17 December 2023).
- Martínez, G.M.; Townley, G.G.; Martínez-Espinosa, R.M. Controversy on the Toxic Nature of Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Potential Contribution to Environmental Pollution. Heliyon 2022, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Rai, R.; Pal, M.; Pandey, S. How Polar Are Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Yu, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Li, F.; Tan, Z. Green Extraction of Cannabidiol from Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Coupled with Further Enrichment and Recovery by Macroporous Resin. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 287, 110957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungwitz, R.; Strehmel, V.; Spange, S. The Dipolarity/Polarisability of 1-Alkyl-3-Methylimidazolium Ionic Liquids as Function of Anion Structure and the Alkyl Chain Length. New J. Chem. 2010, 34, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radošević, K.; Železnjak, J.; Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Slivac, I.; Gaurina Srček, V. Comparative in Vitro Study of Cholinium-Based Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents toward Fish Cell Line. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 131, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shan, S.; Lu, Y.; Luo, J.; Li, Y.; Hao, R. Tuning Toxic Properties of Polyethylene Glycol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents for Achieving Greener Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 369, 120879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radošević, K.; Čanak, I.; Panić, M.; Markov, K.; Bubalo, M.C.; Frece, J.; Srček, V.G.; Redovniković, I.R. Antimicrobial, Cytotoxic and Antioxidative Evaluation of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14188–14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macário, I.P.E.; Oliveira, H.; Menezes, A.C.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Pereira, J.L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Gonçalves, F.J.M. Cytotoxicity Profiling of Deep Eutectic Solvents to Human Skin Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbous, Y.P.; Hayyan, M.; Wong, W.F.; Hayyan, A.; Looi, C.Y.; Hashim, M.A. Simulation of Deep Eutectic Solvents’ Interaction with Membranes of Cancer Cells Using COSMO-RS. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 9086–9094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Juan, E.; López, S.; Abia, R.; Muriana, F.J.; Muriana, F.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.; García-Borrego, A. Antimicrobial Activity on Phytopathogenic Bacteria and Yeast, Cytotoxicity and Solubilizing Capacity of Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 337, 116343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneidi, I.; Hayyan, M.; Hashim, M.A. Evaluation of Toxicity and Biodegradability for Cholinium-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 83636–83647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radošević, K.; Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Gaurina Srček, V.; Grgas, D.; Landeka Dragičević, T.; Redovniković, R.I. Evaluation of Toxicity and Biodegradability of Choline Chloride Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 112, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Morais, P.; Gonçalves, F.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Ventura, S.P.M. Ecotoxicity of Cholinium-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3398–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, M.; Looi, C.Y.; Hayyan, A.; Wong, W.F.; Hashim, M.A. In Vitro and in Vivo Toxicity Profiling of Ammonium-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Oil Source [References] | Tocopherols | Tocotrienols | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α- | β- | γ- | δ- | α- | β- | γ- | δ- | |
| Rice Bran [38] | 1.95 | 0.19 | 2.58 | 1.02 | 1.56 | nd | 4.46 | 0.11 |
| Palm [39] | 0.8 | nd | nd | nd | 0.19 | nd | 0.49 | 0.06 |
| Canola [40] | 1.44 | nd | 3.88 | 2.78 | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Rapeseed [41] | 5.50 | 1.00 | 6.40 | 1.70 | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Sunflower [42] | 17.08 | nd | 29.18 | 16.20 | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Soybean [43] | 0.83 | nd | 6.84 | 5.69 | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Olive [44] | 1.54 | nd | 1.67 | 0.03 | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Corn [45] | 0.15 | 0.06 | 1.09 | 0.12 | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Type | Analytes | DESs | Method of Extraction | Result | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SODD | α, γ and δ-T | ChCl: Acetic acid/Malonic acid/Ethylene glycol/Glycerol/Phenol/o/m/p-cresol | DES Preparation: heated and stirred at 60 °C Extraction: vortex for 5 min then centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 3 min, RT Recovery Tocol: n-hexane and water | extraction efficiency 77.6% | [43] |
| SODD and CODD | α-T | [N4,4,4,4]Cl | Extraction: stirrer at 1000 rpm/min, 2 h, 65 °C Recovery Tocol: hexane and water | Cβ-/γ-, and δ-tocopherol SODD (2.65% and 2.48%) | [75] |
| CODD (0.84% and 0.71%) | |||||
| MODD | α-T | ([N4,4,4,4]Cl | Extraction: stirred at 1000 rpm for 3 h, 55 °C, mixture settled for another 3 h at 35 °C | extraction ratio of α-tocopherol 91.2% | [38] |
| MODD SODD | α-T α, γ, δ -T | tetrabutylphosphonium chloride−ethanolamine (2:1) 12 kind TBAC-DES Based | DES Preparation: vigorously stirred for 3 h at 60−80 °C Extraction: stirred for 3 h, settled for another 3 h, RT Extraction: Sample dissolved in hexana add DES, vortex 5 min, centrifugated 4000 rpm 5 min, | β of 2.43 and S of 9.36 Max Extraction efficiency α, γ, δ -T: 85.0; 99.1; 98.0, Total Tocol: 97.5% | [58] [76] |
| Matrix | Analytes | DESs | Method of Extraction | Result | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Palm Biodiesel | T and T3 | K2CO3: glycerol (1:5, 1:6 and 1:7) | Preparation: DES in methanol) mixed with Biodiesel in hexane Extraction: 400 rpm for 3, RT Recovery Tocol: water-hexane mixture (4:1, v/v) | Ctokol 801.23 ppm | [77] |
| Crude Palm Oil (CPO) | T and T3 | ChCl: acetic acid (1:2) ChCl: malonic acid (1:1) ChCl: citric acid (3:2) | Preparation: DES in methanol) mixed with CPO in hexane (1/1–5/1) Extraction: 200 rpm, 25 °C for 3 h Recovery Tocol: water-hexane mixture (4:1, v/v) | Cextract 8671 mg/kg, Control 3285 mg/kg) | [78] |
| Crude Palm Oil (CPO) | T and T3 | ChCl and acetic acid glacial (1:2) ChCl and oxalic acid (1:2) ChCl and citric acid (1:2) | Preparation: DES in ethanol) mixed with CPO in hexane Extraction: 200 rpm, for 3 h, RT Recovery Tocol: water-hexane mixture (1:1, v/v) | Ctokol 4439 mg/kg extraction efficiency 74.98% | [72] |
| Crude Palm Oil (CPO) | T and T3 | ChCl and malonic acid (1:1) choline chloride and citric acid (1.5:1) | Preparation: DES in methanol) mixed with CPO in hexane (2/1–5/1) Extraction: 200 rpm, 25 °C for 3 h Recovery Tocol: water-hexane mixture (4:1, v/v) | Distribution coefficients for α-T, -, β, γ-, δ and δ-T3: 7.8, 13.1, 19.8, 22.1 and 29.6 | [73] |
| Ternary mixtures of {n-hexane tocopherol} | T | ChCl and (mono-, di- and tri-ethylene glycol/triethanolamine/sucrose (1:5) | Extraction: 550 rpm for 12 h, 25–35 °C | β (0.5118) and S (1.1679) for sucrose | [79] |
| No | HBA | HBD | Cells/Species | Level Toxicity | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Choline Chloride | glucose, glycerol, and oxalic acid | fish and human cell line | chloride:oxalic acid moderate cytotoxicity (EC50: 1.64 mM and 4.19) | [103] |
| 2 | Cholinium Chloride | acetic, citric, lactic, and glycolic acids | marine bacteria V. f ischeri | intermediate toxicity | [104] |
| 3 | Ammonium | glycerine (Gl), ethylene glycol (EG), triethylene glycol (TEG) and urea (U) | In vitro: OKF6, MCF-7, A375, HT29, and H413 In vivo: ICR mice | DES did not cause DNA damage, but it could enhance ROS production and induce apoptosis in treated cancer cells | [105] |
| 4 | Choline Chloride | malic acid, citric acid, lactic acid, fructose, xylose, mannose | Channel Catfish Ovary (CCO) cell line | low cytotoxicity | [96] |
| 5 | Polyethylene Glycol | lactic axid, Propanoic acid, urea, acetamide | lung cancer cell (A549) | DESs are more toxic than their individual components | [97] |
| 6 | Choline chloride, Betaine, Citric acid | oxalic acid, urea, xylitol, sorbitol, glucose, proline | HeLa, MCF-7, and HEK293T | formation of calcium oxalate crystals inside the cells induced detrimental effects on both tumor and normal cells | [98] |
| 7 | [Chol]Cl, [N1111]Cl, and [N4444]Cl | hexanoic and butanoic acid, ethylene glycol, 1-propanol and urea | keratinocytes (HaCaT) and tumor melanocytes (MNT-1) | [N4444]Cl-based DES, showed cytotoxicity for both cell lines | [99] |
| 8 | ChCl and N,N-diethylammonium chloride (DAC), | urea, glycerol, ethylene glycol, malonic acid and zinc chloride | HelaS3, AGS, MCF-7, and WRL-68 | ChCl-based DESs (279 ≤ IC50 ≥ 1260 mM) were less toxic than DAC-based DESs (37 ≤ IC50 ≥ 109 mM) | [100] |
| 9 | ChCl and Betaine | sucrose, 1,4-butanediol, xylitol (2:1), 1,2-propanediol, Fructose | Caco-2, HeLa and HepG2 cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) | DESs at concentrations below 1%, affected tumor cells; however, healthy PBMCs were unaffected | [101] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ulfa, D.M.; Bayu, A.; Rahmawati, S.I.; Ahmadi, P.; Putra, M.Y.; Karnjanakom, S.; Guan, G.; Mun’im, A. New Horizon in Selective Tocols Extraction from Deodorizer Distillates Under Mild Conditions by Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2025, 30, 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061217
Ulfa DM, Bayu A, Rahmawati SI, Ahmadi P, Putra MY, Karnjanakom S, Guan G, Mun’im A. New Horizon in Selective Tocols Extraction from Deodorizer Distillates Under Mild Conditions by Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061217
Chicago/Turabian StyleUlfa, Dian Maria, Asep Bayu, Siti Irma Rahmawati, Peni Ahmadi, Masteria Yunovilsa Putra, Surachai Karnjanakom, Guoqing Guan, and Abdul Mun’im. 2025. "New Horizon in Selective Tocols Extraction from Deodorizer Distillates Under Mild Conditions by Using Deep Eutectic Solvents" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061217
APA StyleUlfa, D. M., Bayu, A., Rahmawati, S. I., Ahmadi, P., Putra, M. Y., Karnjanakom, S., Guan, G., & Mun’im, A. (2025). New Horizon in Selective Tocols Extraction from Deodorizer Distillates Under Mild Conditions by Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules, 30(6), 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061217








