Spectroscopic Characterization Using 1H and 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Computational Analysis of the Complex of Donepezil with 2,6-Methyl-β-Cyclodextrin and Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. NMR Analysis
2.1.1. NMR Characterization of Donepezil (DH)
2.1.2. NMR Characterization of 2,6-Methyl-β-Cyclodextrin (2,6-Me-β-CD)
2.1.3. NMR Characterization of Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC)
2.1.4. NMR Analysis of the Complex

Mixture of DH and HPMC
Mixture of Me-β-CD and DH
Mixture of Me-β-CD, HPMC and DH
2.2. DFT Calculations
2.3. Study of NOEs of Molecules in Complexed Phase
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Samples
3.3. NMR Experiments
3.4. Density Functional Theory (DFT) Calculations
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Birks, J.S.; Harvey, R.J. Donepezil for Dementia Due to Alzheimer’s Disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2018, CD001190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Day, C.M.; Abdella, S.; Garg, S. Alzheimer’s Disease Current Therapies, Novel Drug Delivery Systems and Future Directions for Better Disease Management. J. Control. Release 2024, 367, 402–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marucci, G.; Buccioni, M.; Ben, D.D.; Lambertucci, C.; Volpini, R.; Amenta, F. Efficacy of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuropharmacology 2021, 190, 108352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Maeng, H.; Yu, K.; Lee, K.; Tsuruo, T.; Kim, D.; Shim, C.; Chung, S. Evidence of Carrier-mediated Transport in the Penetration of Donepezil into the Rat Brain. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1548–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment ISSN. Donepezil in Alzheimer’s Disease: From Conventional Trials to Pharmacogenetics Ramón Cacabelos. 2022. Available online: www.tandfonline.com/journals/dndt20 (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Dong, H.; Yuede, C.M.; Coughlan, C.A.; Murphy, K.M.; Csernansky, J.G. Effects of Donepezil on Amyloid-β and Synapse Density in the Tg2576 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Res. 2009, 1303, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, R.T.; Abedinifar, F.; Mahmood, E.A.; Ebadi, A.G.; Rajabi, F.; Vessally, E. The Recent Development of Donepezil Structure-Based Hybrids as Potential Multifunctional Anti-Alzheimer’s Agents: Highlights from 2010 to 2020. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 30781–30797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Greunen, D.G.; Cordier, W.; Nell, M.; van der Westhuyzen, C.; Steenkamp, V.; Panayides, J.-L.; Riley, D.L. Targeting Alzheimer’s Disease by Investigating Previously Unexplored Chemical Space Surrounding the Cholinesterase Inhibitor Donepezil. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojanasthien, N.; Aunmuang, S.; Hanprasertpong, N.; Roongapinun, S.; Teekachunhatean, S. Bioequivalence Study of Donepezil Hydrochloride Tablets in Healthy Male Volunteers. ISRN Pharmacol. 2012, 2012, 527679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, C.F.; Kumar, D.; Cullen, E.I.; Bolton, W.K.; Marbury, T.C.; Gutierrez, M.J.; Hutman, H.W.; Pratt, R.D. Steady-state Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Donepezil HCl in Subjects with Moderately Impaired Renal Function. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 58, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, M.K.; Ismail, A.A.; Kamel, M.A. Combined Donepezil with Astaxanthin via Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Effective Delivery to Brain for Alzheimer’s Disease in Rat Model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 4193–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, L.C.; Silva-Abreu, M.; Clares, B.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Halbaut, L.; Cañas, M.-A.; Calpena, A.C. Formulation Strategies to Improve Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Donepezil. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, L.C.; Guaya, D.; Calpena, A.C.; Perotti, R.M.; Halbaut, L.; Sosa, L.; Brito-Llera, A.; Mallandrich, M. Comparative Study of Donepezil-Loaded Formulations for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease by Nasal Administration. Gels 2022, 8, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Balafas, E.; Colombo, G.; Rekkas, D.M.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Valsami, G. Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Donepezil Hydrochloride Following Administration of an HPMC-Me-β-CD-PEG400 Nasal Film in Mice. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 84, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, S.; Maggi, L.; Segale, L.; Ochoa Machiste, E.; Conte, U.; Grenier, P.; Vergnault, G. Matrices Containing NaCMC and HPMC. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 333, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tundisi, L.L.; Mostaço, G.B.; Carricondo, P.C.; Petri, D.F.S. Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose: Physicochemical Properties and Ocular Drug Delivery Formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 159, 105736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathbone, M.; Senel, S.; Pather, I. Oral Mucosal Drug Delivery and Therapy. Advances in Delivery Science and Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.Y.; Chan, L.W.; Heng, P.W.S. Influence of Partially Cross-Linked Alginate Used in the Production of Alginate Microspheres by Emulsification. J. Microencapsul. 2005, 22, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarabia-Vallejo, Á.; Caja, M.d.M.; Olives, A.I.; Martín, M.A.; Menéndez, J.C. Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Improved Drug Bioavailability and Activity: Synthetic and Analytical Aspects. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Rai, A. Cyclodextrins in Delivery Systems: Applications. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wan, X.; Luo, Z.; Liu, C.; Quan, P.; Cun, D.; Fang, L. A Donepezil/Cyclodextrin Complexation Orodispersible Film: Effect of Cyclodextrin on Taste-Masking Based on Dynamic Process and in Vivo Drug Absorption. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, W.; Cai, C.; Xu, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, T. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Novel Immediate Release Carbamazepine Tablets: Complexation with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin in the Presence of HPMC. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 409, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiassa, V.; Garnero, C.; Longhi, M.R.; Zoppi, A. Cyclodextrin Multicomponent Complexes: Pharmaceutical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cova, T.F.; Murtinho, D.; Pais, A.A.C.C.; Valente, A.J.M. Combining Cellulose and Cyclodextrins: Fascinating Designs for Materials and Pharmaceutics. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Rekkas, D.M.; Colombo, G.; Valsami, G. Development and In Vitro-Ex Vivo Evaluation of Novel Polymeric Nasal Donepezil Films for Potential Use in Alzheimer’s Disease Using Experimental Design. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna Reddy, K.V.S.R.; Moses Babu, J.; Kumar, P.A.; Chandrashekar, E.R.R.; Mathad, V.T.; Eswaraiah, S.; Reddy, M.S.; Vyas, K. Identification and Characterization of Potential Impurities of Donepezil. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 35, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, P.; He, W. Solubilization techniques used for poorly water-soluble drugs. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 4683–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupanc, A.; Petkovšek, M.; Zdovc, B.; Žagar, E.; Zupanc, M. Degradation of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) by Acoustic and Hydrodynamic Cavitation. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2024, 109, 107020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansare, V.J.; Rawal, A.; Goodwin, A.; Beyerinck, R.; Prud’homme, R.K.; Friesen, D.T.; Grass, M.; Muske-Dukes, A.; Vodak, D.T. Millisecond Self-Assembly of Stable Nanodispersed Drug Formulations. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullian, C.; Moyano, L.; Yanez, C.; Olea-Azar, C. Complexation of quercetin with three kinds of cyclodextrins: An antioxidant study. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2007, 67, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, N.; Kakava, M.G.; Routsi, E.A.; Petsas, E.; Stavridis, N.; Freris, C.; Zoupanou, N.; Moschovou, K.; Kiriakidi, S.; Mavromoustakos, T. Quercetin: A Potential Polydynamic Drug. Molecules 2023, 28, 8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. A New Mixing of Hartree–Fock and Local Density-Functional Theories. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti Correlation-Energy Formula into a Functional of the Electron Density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtiss, L.A.; McGrath, M.P.; Blaudeau, J.-P.; Davis, N.E.; Binning, R.C.; Radom, L. Extension of Gaussian-2 Theory to Molecules Containing Third-Row Atoms Ga–Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 6104–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeli, D.; Tsoungas, P.G.; Petsalakis, I.D.; Kozielewicz, P.; Zloh, M. Intramolecular Cyclization of β-Nitroso-o-Quinone Methides. A Theoretical Endoscopy of a Potentially Useful Innate ‘Reclusive’ Reaction. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghetti, G.S.; Lula, I.S.; Sinisterra, R.D.; Bassani, V.L. Quercetin/beta-cyclodextrin solid complexes prepared in aqueous solution followed by spray-drying or by physical mixture. AAPS Pharmscitech 2009, 10, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossi, M.; Scalmani, G.; Rega, N.; Barone, V. New Developments in the Polarizable Continuum Model for Quantum Mechanical and Classical Calculations on Molecules in Solution. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision B.01. In Gaussian 09; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
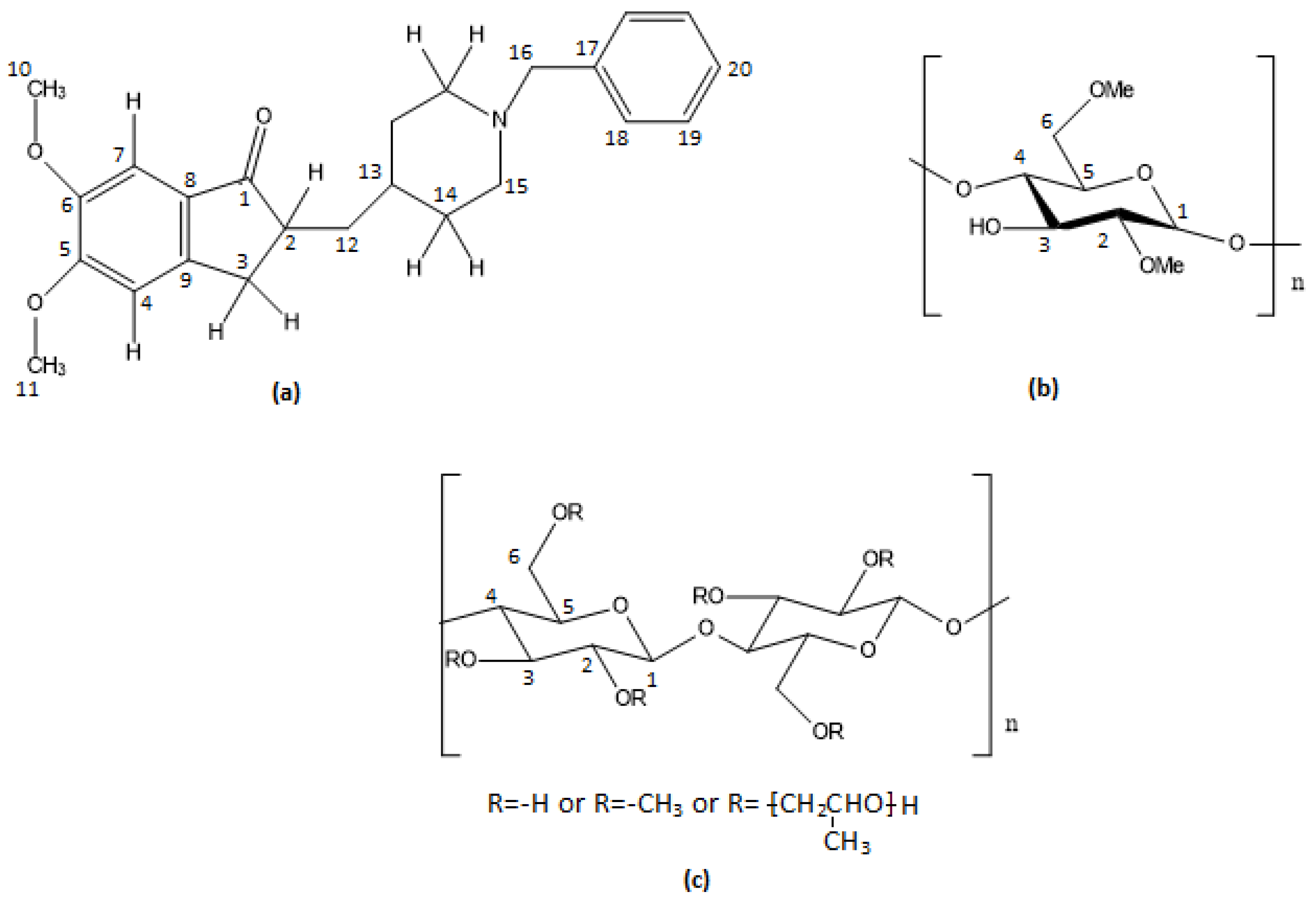
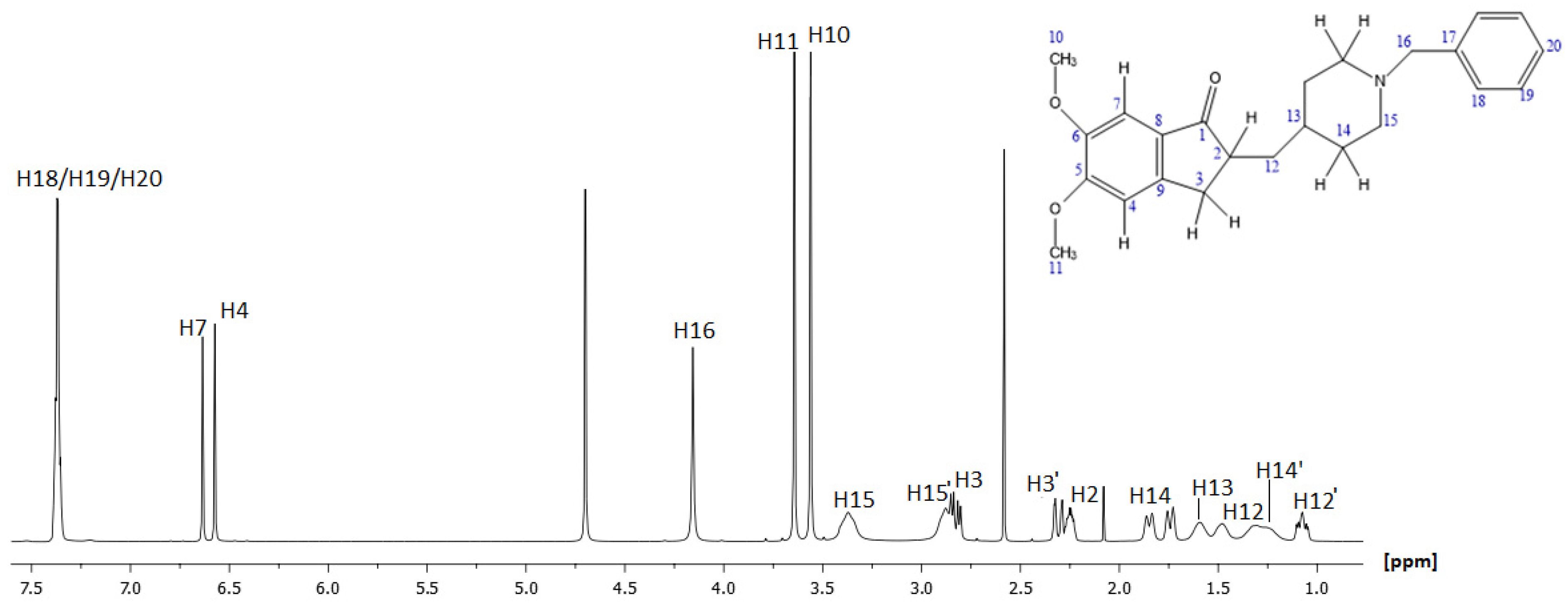

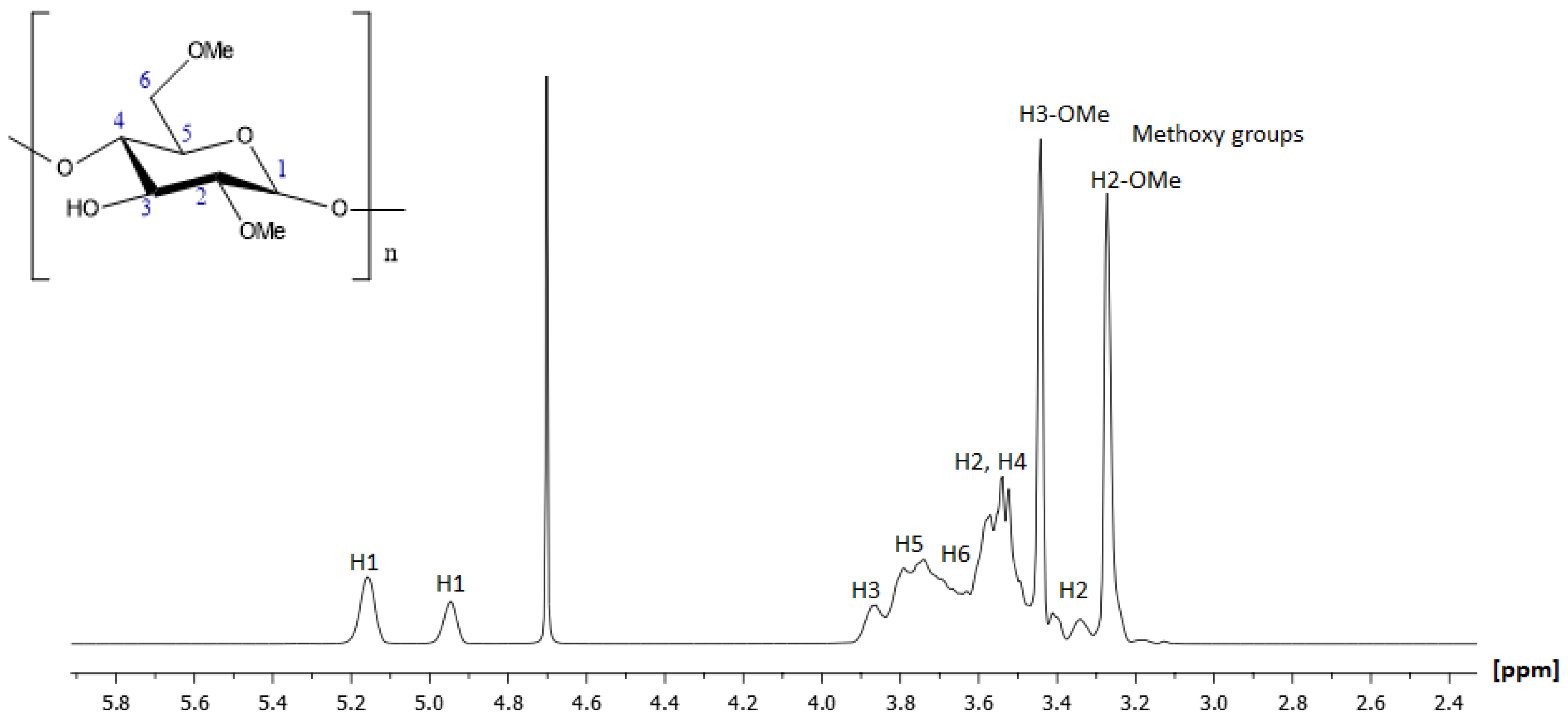
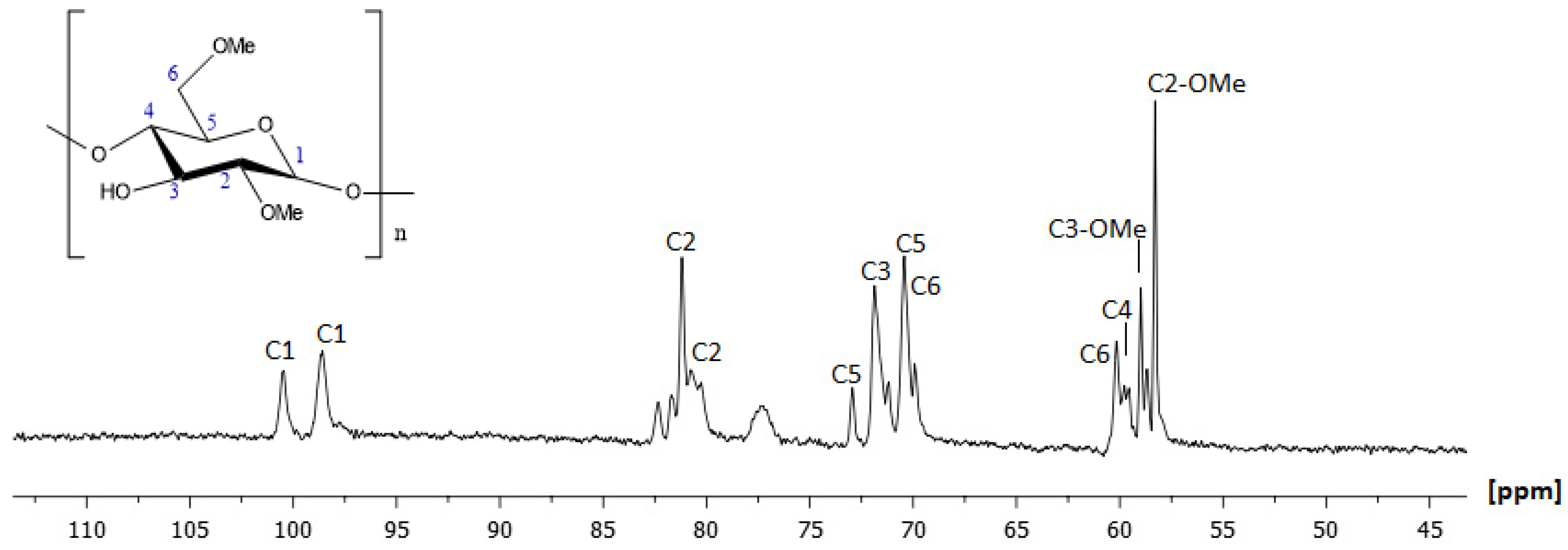
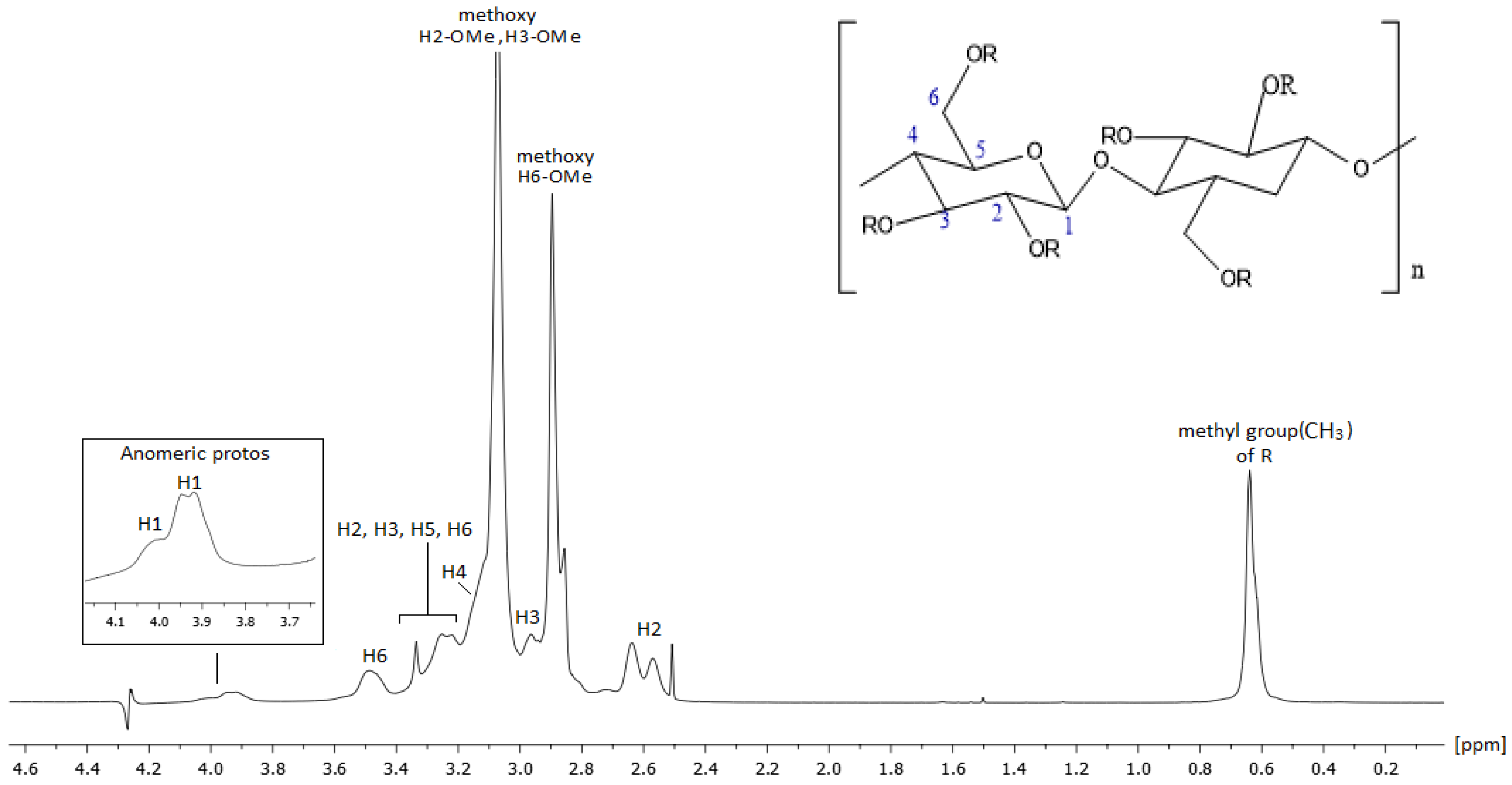

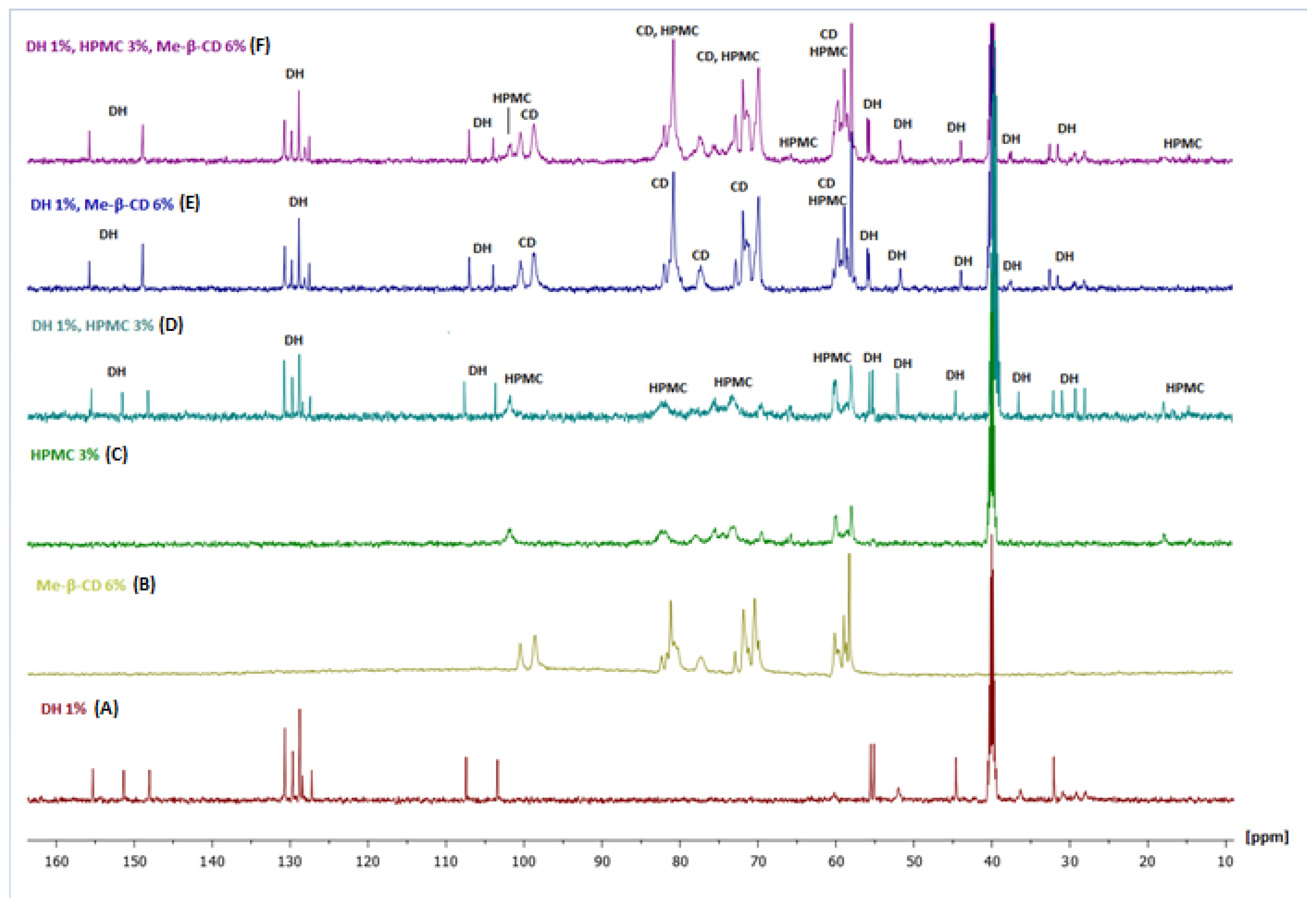
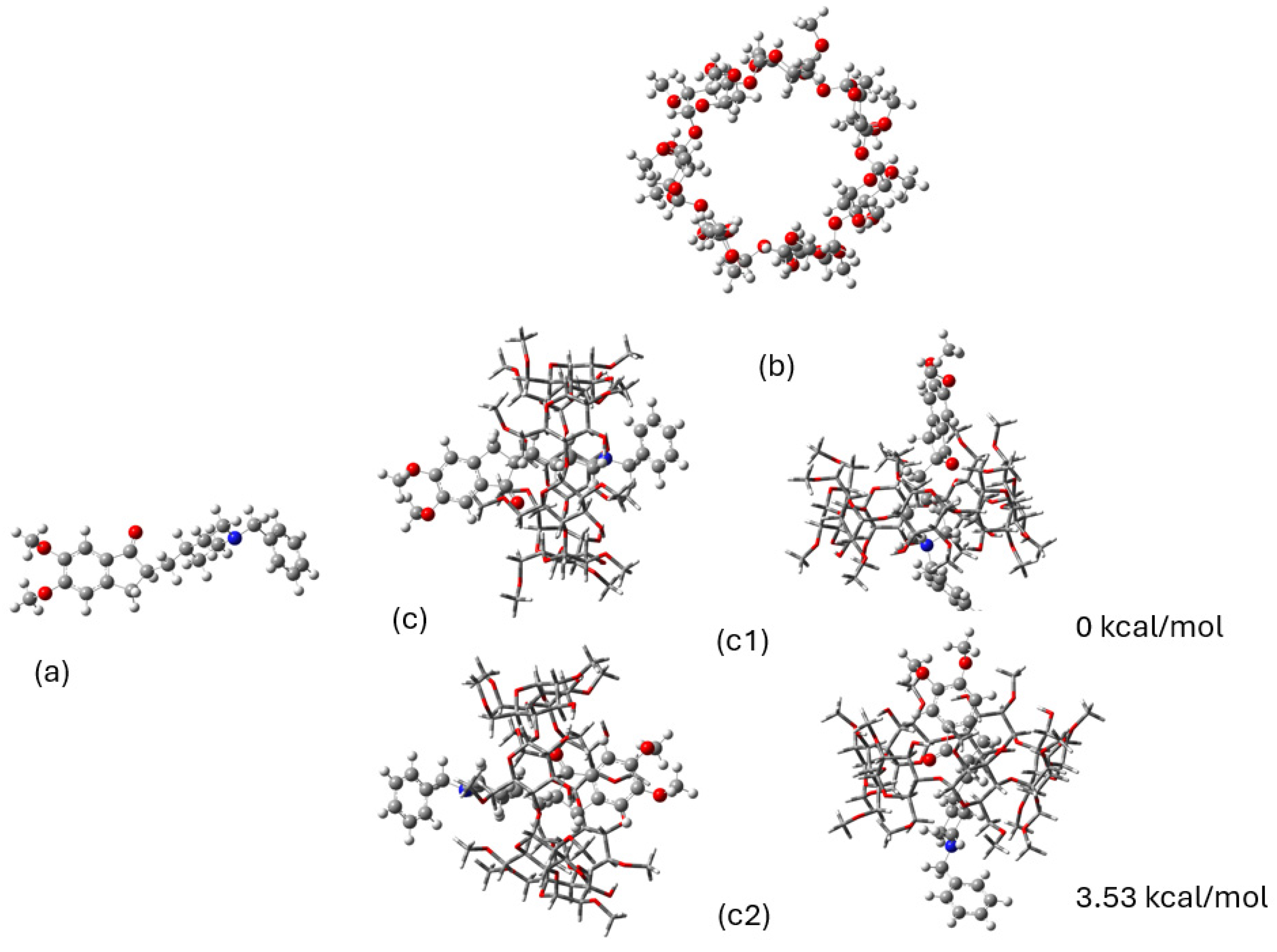
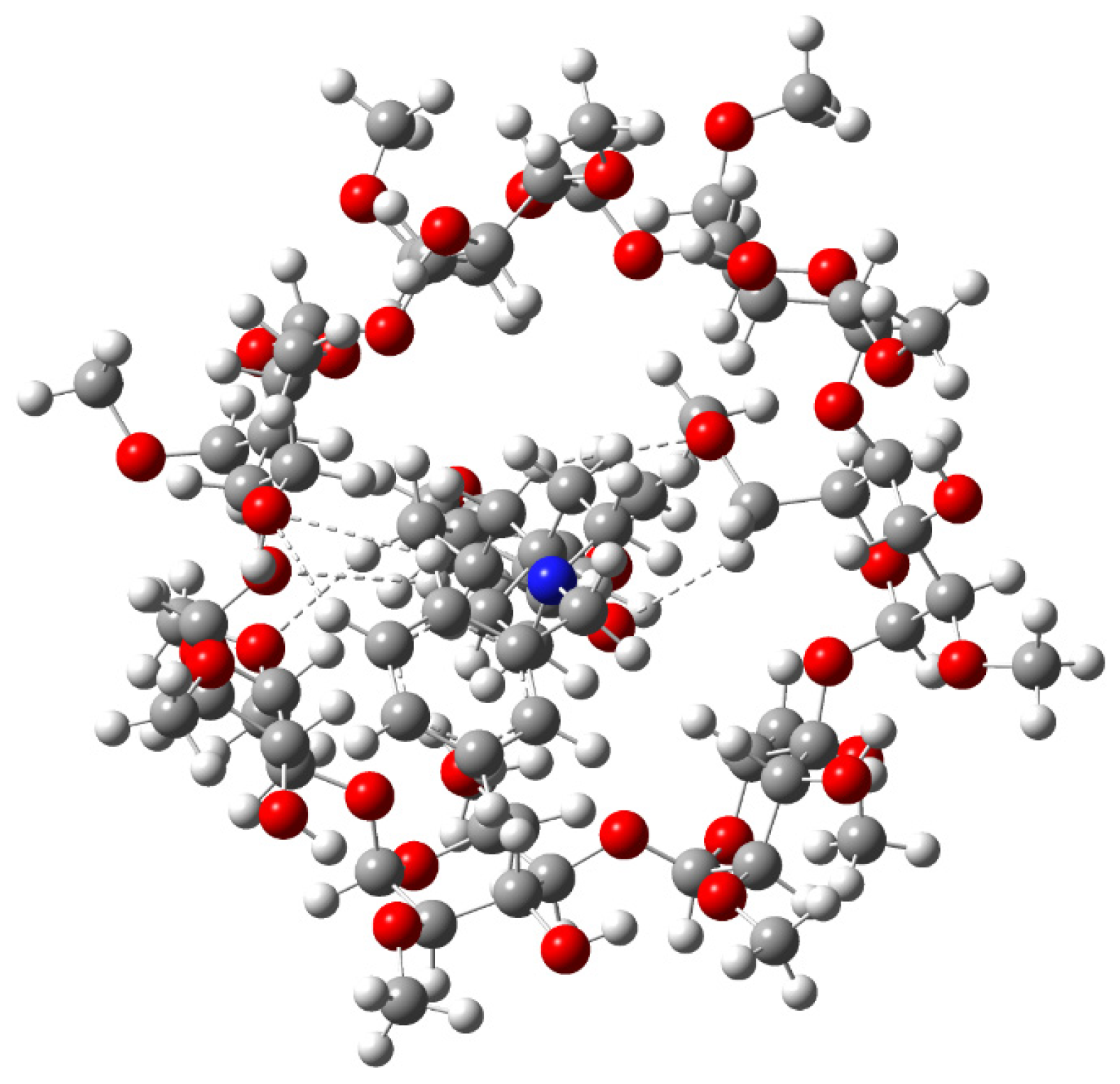

| Position | Protons (ppm) | Carbons (ppm) | Position | Protons (ppm) | Carbons (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | - | 211.33 | H11 | 3.64 | 55.24 |
| H2 | 2.25 | 44.82 | H12 | 1.49 | 36.63 |
| H3 | 2.84/2.81 | 32.42 | H12′ | 1.08 | 36.63 |
| H3′ | 2.33/2.29 | 32.42 | H13 | 1.58 | 31.29 |
| H4 | 6.57 | 103.22 | H14 | 1.85/1.74 | 29.58 |
| H5 | - | 148.15 | H14′ | 1.22/1.31 | 28.24 |
| H6 | - | 155.38 | H15 | 3.37 | 52.21 |
| H7 | 6.64 | 107.48 | H15′ | 2.88 | 52.21 |
| H8 | - | 151.38 | H16 | 4.16 | 60.63 |
| H9 | - | 127.24 | H17 | - | 128.42 |
| H10 | 3.56 | 55.79 | H18/H19/H20 | 7.35–7.39 | 131.05/129.15 |
| Position | Protons (ppm) | Carbons (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
| H1 | 5.16 | 98.67 |
| H1′ | 4.95 | 100.54 |
| H2 | 3.52 | 80.59 |
| H2 | 3.34 | 81.62 |
| H3 | 3.87 | 71.83 |
| H4 | 3.54 | 59.02 |
| H5 | 3.79 | 72.97 |
| H6a | 3.73 | 60.13 |
| H6b | 3.62 | 70.49 |
| H6-O-Me | 3.44 | 58.98 |
| H2-O-Me | 3.27 | 58.29 |
| Position | Protons (ppm) | Carbons (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
| H1 | 3.94 | 101.75 |
| H1 | 4.01 | 101.94 |
| H2 | 2.57 | 82.44 |
| H2 | 2.64 | 82.01 |
| H3 | 2.96 | 82.48 |
| H2, H3, H5, H6 | 3.24, 3.12, 3.03, 3.22, 3.14, 3.11 | 69.50, 73.22, 74.50, 75,49, 75.49, 78.04 |
| H4 | 3.12 | 78.08 |
| H4 | 3.14 | 77.63 |
| H6 | 3.44 | 66.27 |
| H6 | 3.49 | 65.82 |
| -H6-OCH3 | 2.86 | 55.03 |
| -H6-OCH3 | 2.90 | 58.00 |
| H2-OCH3/H3-OCH3 | 3.06 | 58.53 |
| H2-OCH3/H3-OCH3 | 3.07 | 60.05 |
| H2-OCH3/H3-OCH3 | 3.28 | 59.33 |
| H2-OCH3/H3-OCH3 | 3.45 | 59.43 |
| -OH | 4.91 | - |
| -OH | 5.04 | - |
| R(-CH3) | 0.62 | 14.60 |
| R(-CH3) | 0.62 | 16.48 |
| R(-CH3) | 0.64 | 17.90 |
| Position of P1 Protons | Chemical Shifts of P1 | Chemical Shifts of P5 | Chemical Shifts of P4 | Chemical Shifts of P7 | Δδ of DH (P1–P4) | Δδ of DH (P1–P5) | Δδ of DH (P1–P7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H18, H19, H20 | 7.35–7.39 | 6.98–7.01 | 6.97–6.99 | 6.97–7.01 | 0.38–0.36 | 0.38–0.36 | 0.38–0.36 |
| H7 | 6.64 | 6.53 | 6.45 | 6.53 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| H4 | 6.57 | 6.40 | 6.44 | 6.41 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.16 |
| H16 | 4.16 | 3.79 | 3.76 | 3.79 | 0.4 | 0.37 | 0.37 |
| H10 | 3.56 | 3.37 | 3.27 | 3.46 | 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.10 |
| H11 | 3.64 | 3.32 | 3.34 | 3.38 | 0.3 | 0.32 | 0.26 |
| H12 | 1.08 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 |
| 1.49 | 1.25 | 1.19 | 1.28 | 0.3 | 0.24 | 0.21 | |
| H14 | 1.74–1.85 | 1.45–1.51 | 1.35–1.51 | 1.44–1.52 | 0.29–0.33 | 0.29–0.34 | 0.3–0.08 |
| 1.26–1.32 | 1.03 | 0.92 | 1.02 | 0.24 | 0.23 | - | |
| H13 | 1.58 | 1.30 | 1.24 | 1.31 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.3 |
| H2 | 2.25 | 2.15 | 2.08 | 2.11 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.14 |
| H15 | 3.37 | - | 2.51 | 2.37 | 0.86 | - | 1 |
| 2.88 | 2.43 | - | - | - | 0.45 | - | |
| H3 | 2.84/2.81 | 2.80–2.77 | 2.62 | 2.37–2.49 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.47–0.32 |
| 2.33/2.29 | 2.15–2.18 | 2.12 | 2.14–2.18 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.19–1.1 |
| Position of P1 Protons | Chemical Shifts of P1 | Chemical Shifts of P5 | Chemical Shifts of P4 | Chemical Shifts of P7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 211.33 | 207.80 | 211.66 | 207.85 |
| C6 | 155.38 | 155.75 | 155.48 | 155.74 |
| C8 | 151.38 | - | 151.52 | - |
| C5 | 148.15 | 148.92 | 148.24 | 148.91 |
| C18 | 130.69 | 130.70 | 130.77 | 130.72 |
| C19 | 129.67 | 129.80 | 129.73 | 129.83 |
| C20 | 128.79 | 128.87 | 128.83 | 128.88 |
| C17 | 128.42 | 128.13 | 128.39 | 128.10 |
| C9 | 127.24 | 127.55 | 127.43 | 127.55 |
| C7 | 107.48 | 107.02 | 107.65 | 107.05 |
| C4 | 105.41 | 103.97 | 103.68 | 103.96 |
| C10 | 55.79 | 55.94 | 55.69 | 55.94 |
| C11 | 55.24 | 55.77 | 55.29 | 55.76 |
| C2 | 44.82 | 43.90 | 44.68 | 43.91 |
| C3 | 32.42 | 31.56 | 31.01 | 31.55 |
| C15 | 52.21 | 51.75 | 52.10 | 51.76 |
| C12 | 36.63 | 37.48 | 36.57 | 37.55 |
| C14 | 29.58 | 29.29 | 29.32 | 29.44 |
| C14′ | 28.24 | 28.22 | 28.11 | 28.09 |
| C16 | 60.63 | Overlappted peak | 60.17 | Overlappted peak |
| Donepezil@2,6Me-β-CD | c1 | c2 |
|---|---|---|
| BEr | −9.77 | −8.17 |
| BE | −2.00 | +4.59 |
| DefD | 0.48 | 0.38 |
| DefCD | 7.29 | 12.38 |
| Preparation | DH | HPMC | Me-β-CD |
|---|---|---|---|
| % w/w | % w/w | % w/w | |
| P1 | 1 | − | |
| P2 | − | 3 | − |
| P3 | - | 6 | |
| P4 | 1 | 3 | − |
| P5 | 1 | − | 6 |
| P6 | − | 3 | 6 |
| P7 | 1 | 3 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zoupanou, N.; Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Georgiou, N.; Cheilari, A.; Javornik, U.; Podbevsek, P.; Tzeli, D.; Valsami, G.; Mavromoustakos, T. Spectroscopic Characterization Using 1H and 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Computational Analysis of the Complex of Donepezil with 2,6-Methyl-β-Cyclodextrin and Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose. Molecules 2025, 30, 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051169
Zoupanou N, Papakyriakopoulou P, Georgiou N, Cheilari A, Javornik U, Podbevsek P, Tzeli D, Valsami G, Mavromoustakos T. Spectroscopic Characterization Using 1H and 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Computational Analysis of the Complex of Donepezil with 2,6-Methyl-β-Cyclodextrin and Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose. Molecules. 2025; 30(5):1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051169
Chicago/Turabian StyleZoupanou, Nikoletta, Paraskevi Papakyriakopoulou, Nikitas Georgiou, Antigoni Cheilari, Uroš Javornik, Peter Podbevsek, Demeter Tzeli, Georgia Valsami, and Thomas Mavromoustakos. 2025. "Spectroscopic Characterization Using 1H and 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Computational Analysis of the Complex of Donepezil with 2,6-Methyl-β-Cyclodextrin and Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose" Molecules 30, no. 5: 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051169
APA StyleZoupanou, N., Papakyriakopoulou, P., Georgiou, N., Cheilari, A., Javornik, U., Podbevsek, P., Tzeli, D., Valsami, G., & Mavromoustakos, T. (2025). Spectroscopic Characterization Using 1H and 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Computational Analysis of the Complex of Donepezil with 2,6-Methyl-β-Cyclodextrin and Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose. Molecules, 30(5), 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051169









