Beef Traceability Between China and Argentina Based on Various Machine Learning Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
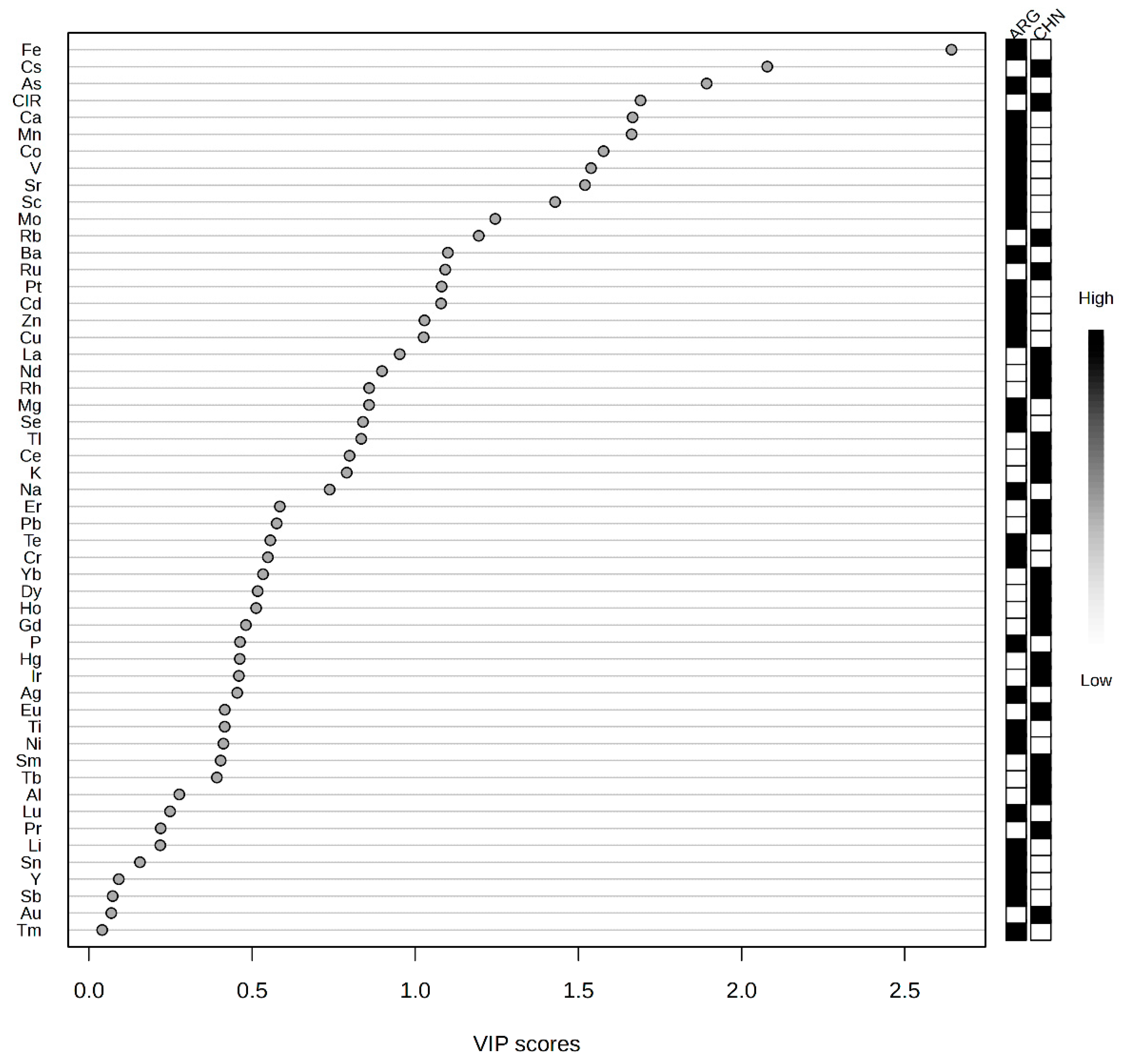
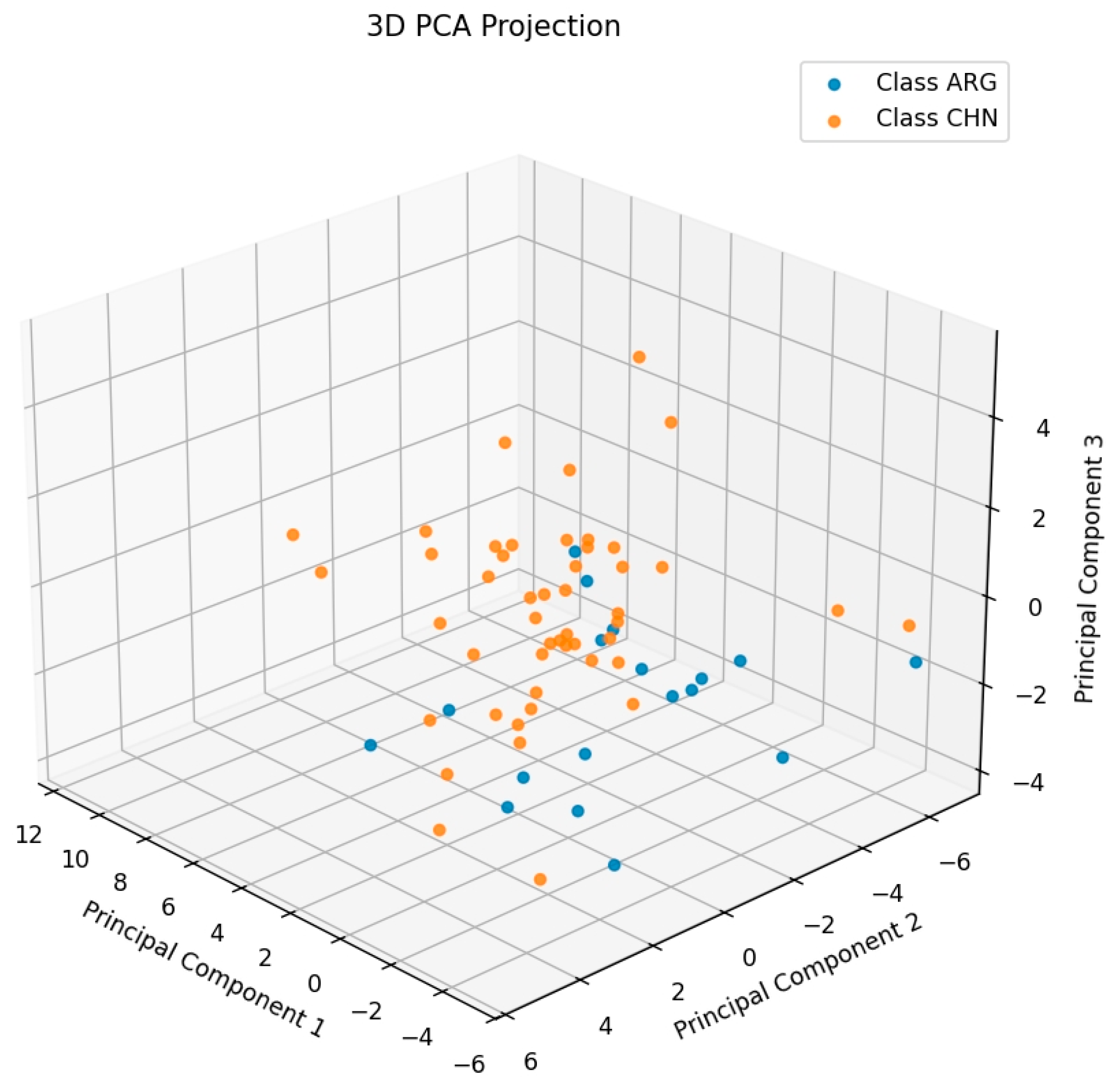
2.1. Analysis of Elemental Data
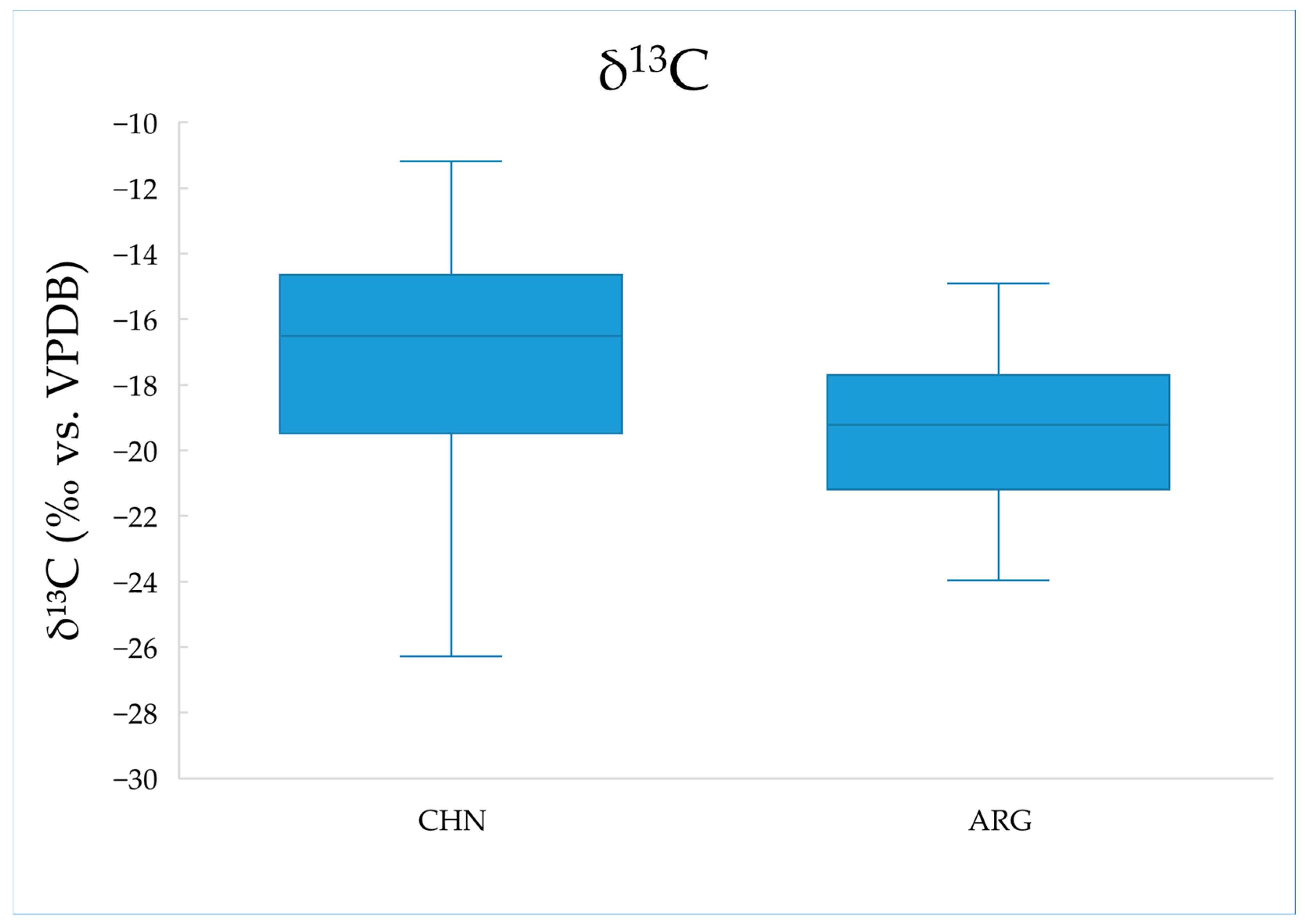
2.2. Analysis of Carbon Stable Isotope Ratios
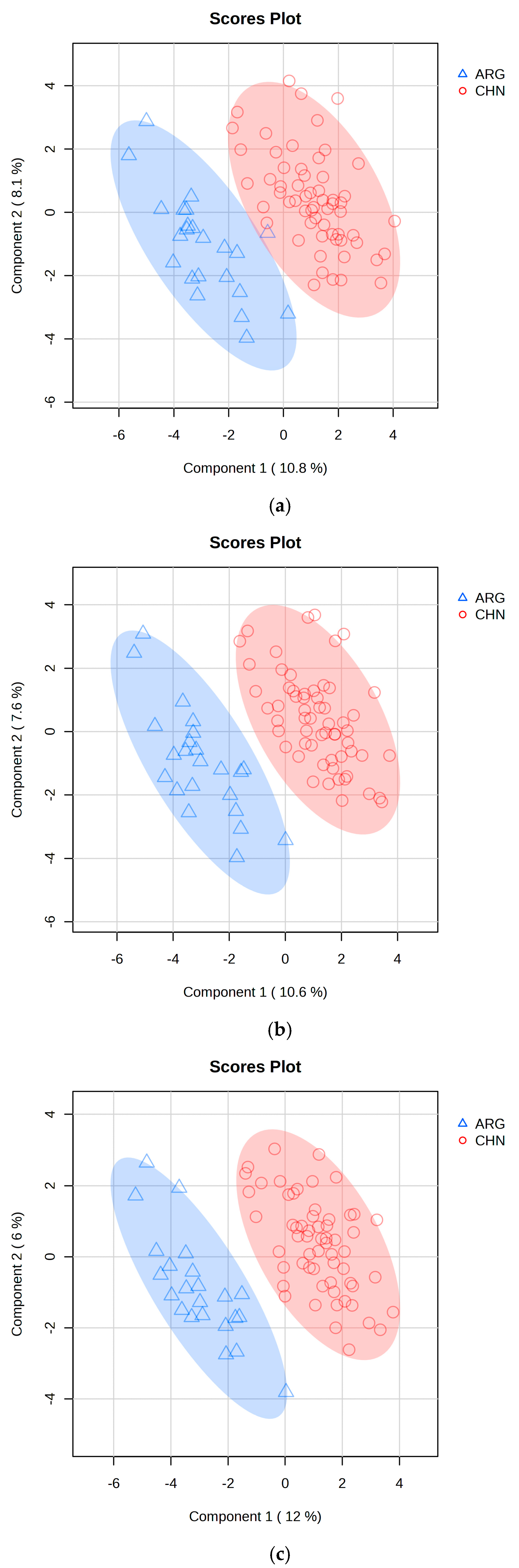
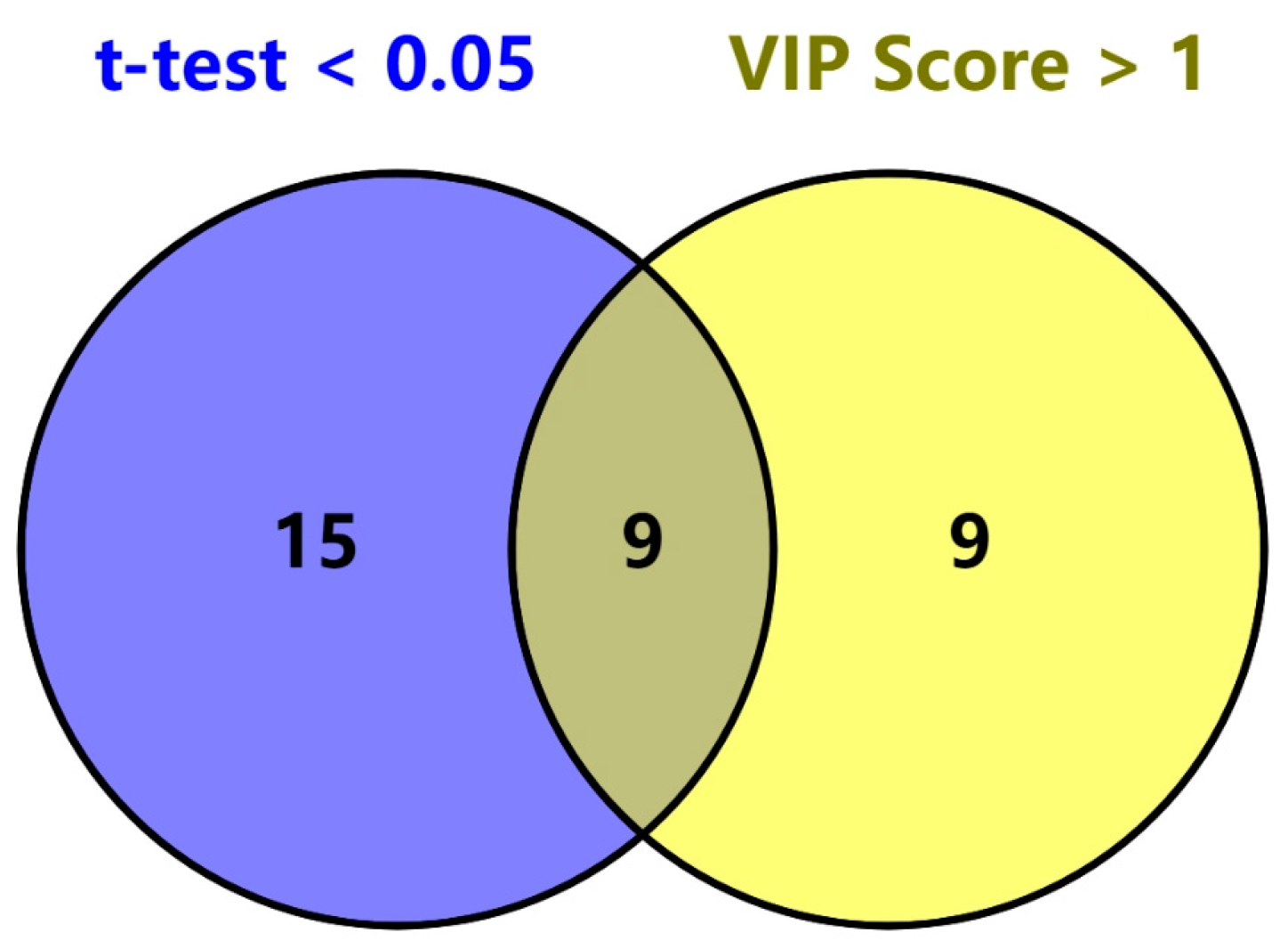
2.3. PLS-DA Classification Model
2.4. CNN Classification Model
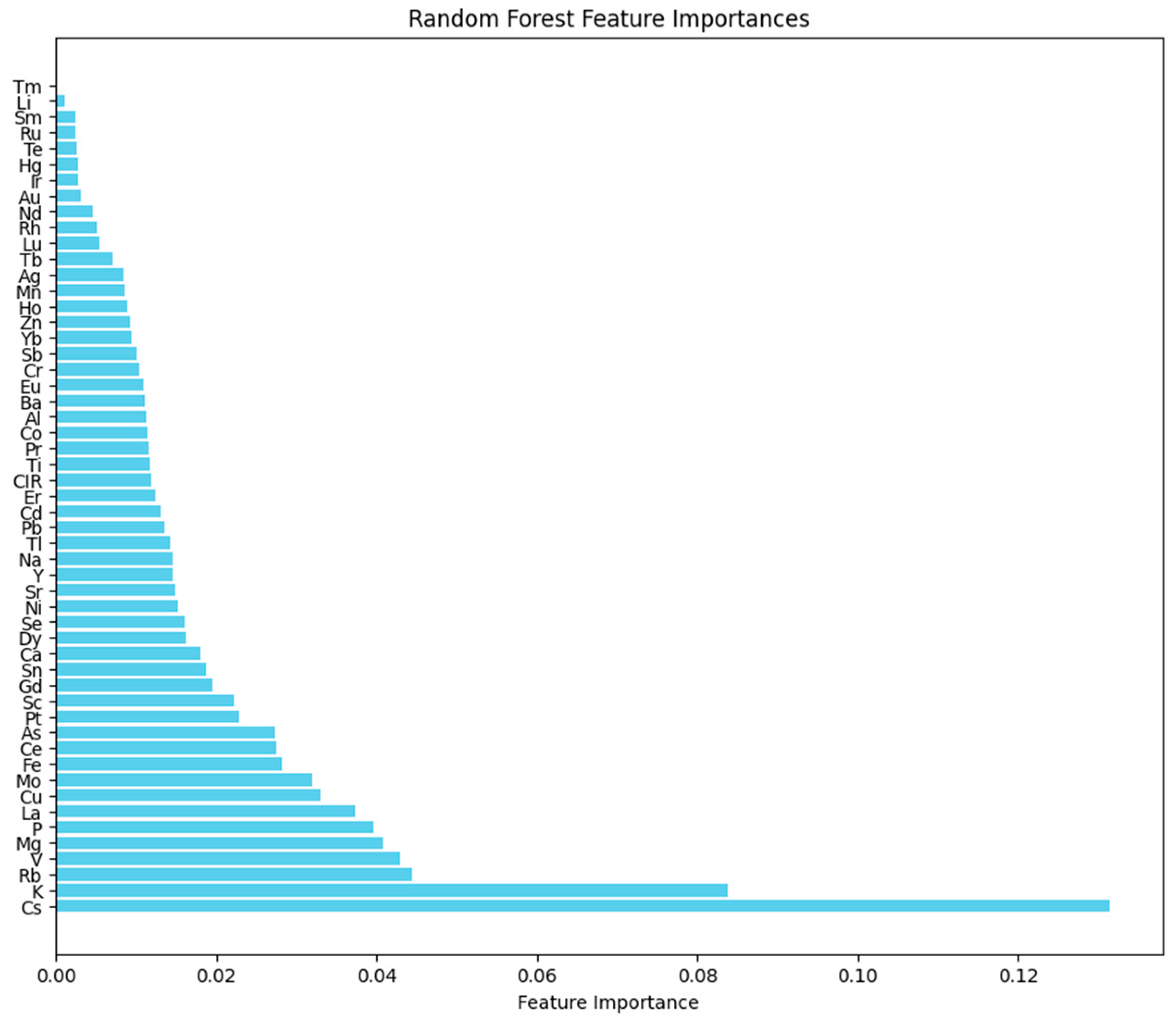
2.5. Random Forest Classification Model
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Sample Collection
3.2.2. Preparation for Elemental Determination
3.2.3. Preparation for Carbon Stable Isotope Ratio Determination
3.2.4. Elemental Measurements by ICP-OES and ICP-MS
3.2.5. δ13C Measurements by EA-IRMS
3.2.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greenwood, P.L. Review: An overview of beef production from pasture and feedlot globally, as demand for beef and the need for sustainable practices increase. Animal 2021, 15, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schor, A.; Cossu, M.E.; Picallo, A.; Ferrer, J.M.; Naón, J.J.G.; Colombatto, D. Nutritional and eating quality of Argentinean beef: A review. Meat Sci. 2008, 79, 408–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visciano, P.; Schirone, M. Food frauds: Global incidents and misleading situations. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 114, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoupá, K.; Šťastný, K.; Sládek, Z. Anabolic Steroids in Fattening Food-Producing Animals—A Review. Animals 2022, 12, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Cheng, X.; Ma, Y.; Chen, N. Foodborne doping and supervision in sports. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Zhao, S.; Qie, M.; Guo, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y. Research Progress on Traceability and Authenticity of Beef. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 1645–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, A.; Jin, X.; Pan, L. Technologies in individual animal identification and meat products traceability. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2020, 34, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccio, Z.; Jackson, G.P. Isotope ratio mass spectrometry. Analyst 2009, 134, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bontempo, L.; Perini, M.; Pianezze, S.; Horacek, M.; Roßmann, A.; Kelly, S.D.; Thomas, F.; Heinrich, K.; Schlicht, C.; Schellenberg, A.; et al. Characterization of Beef Coming from Different European Countries through Stable Isotope (H, C, N, and S) Ratio Analysis. Molecules 2023, 28, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H. International Evaluation of China’s Beef Cattle Industry Development Level and Lagging Points. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prache, S.; Martin, B.; Coppa, M. Review: Authentication of grass-fed meat and dairy products from cattle and sheep. Animal 2020, 14, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbie, E.A.; Werner, R.A. Intramolecular, compound-specific, and bulk carbon isotope patterns in C3 and C4 plants: A review and synthesis. New Phytol. 2004, 161, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaton, K.; Kelly, S.D.; Hoogewerff, J.; Woolfe, M. Verifying the geographical origin of beef: The application of multi-element isotope and trace element analysis. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumeliotis, K.I.; Tselikas, N.D. ChatGPT and Open-AI Models: A Preliminary Review. Future Internet 2023, 15, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Yang, J.; Xiao, G.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Bai, W.; Zeng, X.; Dong, H. A comprehensive overview of emerging techniques and chemometrics for authenticity and traceability of animal-derived food. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadood, S.A.; Boli, G.; Xiaowen, Z.; Hussain, I.; Yimin, W. Recent development in the application of analytical techniques for the traceability and authenticity of food of plant origin. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Domínguez, R.; Sayago, A.; Fernández-Recamales, Á. An Overview on the Application of Chemometrics Tools in Food Authenticity and Traceability. Foods 2022, 11, 3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhao, C.; Deng, X.; Zhang, R.; Qu, L.; Wang, M.; Ren, S.; Wu, H.; Yue, Z.; Niu, B. Determining the geographical origin of milk by multivariate analysis based on stable isotope ratios, elements and fatty acids. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 2537–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehelean, A.; Cristea, G.; Puscas, R.; Hategan, A.R.; Magdas, D.A. Assigning the Geographical Origin of Meat and Animal Rearing System Using Isotopic and Elemental Fingerprints. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, J. A Survey of Convolutional Neural Networks: Analysis, Applications, and Prospects. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 6999–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, S.; Guo, B.; Du, Y.; Wang, M.; Tang, P.; Zhao, J. Feasibility of Authenticating Mutton Geographical Origin and Breed Via Hyperspectral Imaging with Effective Variables of Multiple Features. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’ Sullivan, R.; Cama-Moncunill, R.; Salter-Townshend, M.; Schmidt, O.; Monahan, F.J. Verifying origin claims on dairy products using stable isotope ratio analysis and random forest classification. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nadai Fernandes, E.A.; Sarriés, G.A.; Bacchi, M.A.; Mazola, Y.T.; Gonzaga, C.L.; Sarriés, S.R.V. Trace elements and machine learning for Brazilian beef traceability. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doncel, B.; Puentes, J.D.; Caffarena, R.D.; Riet-Correa, F.; Costa, R.A.; Giannitti, F. Hypomagnesemia in beef cattle. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2021, 41, e06826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E.A.D.N.; Mazola, Y.T.; Sarriés, G.A.; Bacchi, M.A.; Bode, P.; Gonzaga, C.L.; Sarriés, S.R.V. Discriminating Beef Producing Countries by Multi-Element Analysis and Machine Learning. AAIML 2021, 01, 01–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, B.M.; Haldimann, M.; Gremaud, G.; Bosset, J.-O.; Hadorn, R.; Kreuzer, M. Element signature analysis: Its validation as a tool for geographic authentication of the origin of dried beef and poultry meat. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, E.M.; Aguiar, S.; González Fischer, C.; Cuchietti, A.; Cabrol, D.A.; González, A.D.; Jobbágy, E.G. Environmental footprints of meat, milk and egg production in Argentina. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 347, 131325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, E.M.; Cabrol, D.A.; Cuchietti, A.; González, A.D. Biomass consumption and environmental footprints of beef cattle production in Argentina. Agric. Syst. 2020, 185, 102944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Lan, X.; An, J.; Shen, W.; Wan, F. Recent advances in feed and nutrition of beef cattle in China—A review. Anim. Biosci. 2023, 36, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguita, D.; Ghelardoni, L.; Ghio, A.; Oneto, L.; Ridella, S. The ‘K’ in K-fold Cross Validation. In Proceedings of the ESANN 2012 proceedings, European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning, Bruges, Belgium, 25–27 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fushiki, T. Estimation of prediction error by using K-fold cross-validation. Stat. Comput. 2011, 21, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.-T.; Yang, N.-Y. Dependency Analysis of Accuracy Estimates in k-Fold Cross Validation. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2017, 29, 2417–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Perez, D.; Guan, H.; Madhivanan, P.; Mathee, K.; Narasimhan, G. So you think you can PLS-DA? BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.; Zhou, X.; Rogers, K.M.; Yi, B.; Bian, X.; Yan, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhou, H.; Xie, L.; Lin, G.; et al. A stable isotope and chemometric framework to distinguish fresh milk from reconstituted milk powder and detect potential extraneous nitrogen additives. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 108, 104441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, L.; Lei, W.; Deng, H.; Chen, M.; Xiang, P.; Su, M.; Di, B.; Chen, H. Stable isotope ratio analysis combined with likelihood ratio as a new tool for establishing ethanol origin. Forensic Chem. 2022, 31, 100451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussama, A.; Elabadi, F.; Platikanov, S.; Kzaiber, F.; Tauler, R. Detection of Olive Oil Adulteration Using FT-IR Spectroscopy and PLS with Variable Importance of Projection (VIP) Scores. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahieu, B.; Qannari, E.M.; Jaillais, B. Extension and significance testing of Variable Importance in Projection (VIP) indices in Partial Least Squares regression and Principal Components Analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2023, 242, 104986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Lin, S.; Li, X.; Li, D. Different stages of flavor variations among canned Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba): Based on GC-IMS and PLS-DA. Food Chem. 2024, 459, 140465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.; Lu, C.; Li, M.; Ye, Y.; Wei, X.; Tong, H. Identification of key aromatic compounds in Congou black tea by partial least-square regression with variable importance of projection scores and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry/gas chromatography–olfactometry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5278–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketkar, N.; Moolayil, J. Convolutional Neural Networks. Deep Learning with Python: Learn Best Practices of Deep Learning Models with PyTorch 197-242. 2021. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/350762343_Deep_Learning_with_Python_Learn_Best_Practices_of_Deep_Learning_Models_with_PyTorch (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- Zafar, I.; Tzanidou, G.; Burton, R.; Patel, N.; Araujo, L. Hands-on Convolutional Neural Networks with TensorFlow: Solve Computer Vision Problems with Modeling in TensorFlow and Python; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Deng, Z.; Lai, H.; Zhang, L.; Yun, Y.; Zhang, C. Application of stable isotope and mineral element fingerprint in identification of Hainan camellia oil producing area based on convolutional neural networks. Food Control 2023, 150, 109744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qian, J.; Chen, J.; Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Dong, C.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, P.; Zhao, Z. Recent advances of machine learning in the geographical origin traceability of food and agro-products: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2025, 24, e70082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Kong, F.; Peng, H.; Dong, S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, G. Combing machine learning and elemental profiling for geographical authentication of Chinese Geographical Indication (GI) rice. Npj Sci. Food 2021, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 5009.268-2016; Determination of Multi-Elements in Foods. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; Xu, Z.; Chen, A.; Zhao, Y. A rapid sample preparation method for the analysis of stable isotope ratios of beef samples from different countries. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 34, e8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Elements | Unit | CHN (n = 60) | ARG (n = 23) | CHN Max | CHN Min | ARG Max | ARG Min | t-Test Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | ||||||||
| Li | mg/kg | 0.796 ± 2.707 | 0.486 ± 0.870 | 16.533 | <0.000 | 2.778 | <0.000 | 0.4328 |
| Na | mg/100 g | 58.421 ± 44.472 | 50.555 ± 15.529 | 322.23 | 21.51 | 78.68 | 27.59 | 0.2362 |
| Mg * | mg/100 g | 18.293 ± 3.059 | 15.486 ± 3.563 | 23.31 | 7.48 | 21.37 | 8.32 | 0.002 |
| Al | mg/kg | 13.231 ± 32.063 | 5.630 ± 5.230 | 195.049 | <0.000 | 21.492 | <0.000 | 0.0803 |
| P * | mg/100 g | 156.554 ± 26.276 | 128.242 ± 30.410 | 209.93 | 62.84 | 169.33 | 64.08 | 0.0004 |
| K * | mg/100 g | 301.091 ± 53.428 | 229.876 ± 53.821 | 367.87 | 121.97 | 317.51 | 124.53 | <0.0000 |
| Ca | mg/100 g | 9.966 ± 5.063 | 10.850 ± 3.152 | 40.29 | 2.95 | 18.45 | 6.65 | 0.344 |
| Sc * | mg/kg | 0.165 ± 0.084 | 0.227 ± 0.124 | 0.496 | 0.016 | 0.446 | 0.019 | 0.0326 |
| Ti | mg/kg | 4.856 ± 2.333 | 4.267 ± 2.183 | 12.352 | <0.000 | 12.298 | 0.663 | 0.2866 |
| V * | μg/kg | 0.036 ± 0.020 | 0.105 ± 0.136 | 0.101 | <0.000 | 0.431 | 0.003 | 0.023 |
| Cr | mg/kg | 0.476 ± 0.433 | 0.435 ± 0.222 | 2.635 | 0.106 | 1.189 | <0.000 | 0.5739 |
| Mn | mg/100 g | 17.211 ± 5.139 | 18.787 ± 5.269 | 30.53 | 5.84 | 31.26 | 8.73 | 0.2268 |
| Fe * | mg/100 g | 1.979 ± 0.619 | 2.654 ± 0.721 | 3.46 | 0.69 | 4.69 | 1.01 | 0.0003 |
| Co * | μg/kg | 0.049 ± 0.028 | 0.065 ± 0.028 | 0.135 | <0.000 | 0.124 | 0.022 | 0.0292 |
| Ni | mg/kg | 0.125 ± 0.153 | 0.161 ± 0.337 | 0.618 | <0.000 | 1.671 | <0.000 | 0.6234 |
| Cu | mg/kg | 11.769 ± 3.182 | 12.870 ± 7.082 | 19.288 | 3.884 | 26.763 | <0.000 | 0.479 |
| Zn | mg/100 g | 4.214 ± 1.321 | 4.029 ± 1.424 | 7.05 | 1.12 | 7.8 | 1.33 | 0.5935 |
| As * | μg/kg | 0.209 ± 0.094 | 0.370 ± 0.272 | 0.558 | 0.071 | 1.124 | <0.000 | 0.0469 |
| Se | mg/kg | 2.362 ± 1.532 | 2.560 ± 1.394 | 9.421 | 0.607 | 6.734 | <0.000 | 0.5763 |
| Rb * | mg/kg | 8.053 ± 4.785 | 4.092 ± 2.510 | 22.382 | 1.903 | 9.652 | 1.422 | <0.0000 |
| Sr | mg/kg | 6.551 ± 2.804 | 7.477 ± 2.668 | 13.965 | 0.776 | 14.086 | 4.457 | 0.1706 |
| Y | μg/kg | 0.058 ± 0.055 | 0.042 ± 0.030 | 0.231 | <0.000 | 0.125 | <0.000 | 0.094 |
| Mo | mg/kg | 0.075 ± 0.056 | 0.119 ± 0.103 | 0.281 | <0.000 | 0.337 | 0.008 | 0.064 |
| Ru * | μg/kg | 0.014 ± 0.034 | 0.000 ± 0.000 a | 0.17 | <0.000 | 0.001 | <0.000 | 0.003 |
| Rh * | μg/kg | 0.002 ± 0.003 | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 0.012 | <0.000 | 0.005 | <0.000 | 0.0024 |
| Ag | μg/kg | 1.354 ± 1.233 | 1.262 ± 1.017 | 6.615 | 0.245 | 4.96 | 0.267 | 0.7289 |
| Cd | μg/kg | 0.017 ± 0.012 | 0.022 ± 0.017 | 0.05 | <0.000 | 0.082 | <0.000 | 0.1673 |
| Sn | μg/kg | 0.045 ± 0.030 | 0.039 ± 0.033 | 0.126 | <0.000 | 0.163 | <0.000 | 0.452188 |
| Sb | μg/kg | 0.048 ± 0.112 | 0.026 ± 0.012 | 0.848 | <0.000 | 0.053 | 0.01 | 0.1524 |
| Te | μg/kg | 0.003 ± 0.012 | 0.003 ± 0.010 | 0.07 | <0.000 | 0.037 | <0.000 | 0.998 |
| Cs * | mg/kg | 0.539 ± 0.562 | 0.097 ± 0.082 | 2.835 | 0.062 | 0.287 | 0.021 | <0.0000 |
| Ba | mg/kg | 2.087 ± 1.309 | 2.099 ± 0.665 | 10.467 | 0.124 | 3.734 | 1.298 | 0.9537 |
| La * | mg/kg | 0.321 ± 0.722 | 0.095 ± 0.168 | 4.729 | 0.003 | 0.682 | <0.000 | 0.0262 |
| Ce * | μg/kg | 0.126 ± 0.140 | 0.066 ± 0.053 | 0.831 | 0.001 | 0.22 | <0.000 | 0.0056 |
| Pr | μg/kg | 0.014 ± 0.014 | 0.011 ± 0.010 | 0.073 | <0.000 | 0.035 | <0.000 | 0.2524 |
| Nd * | μg/kg | 0.060 ± 0.048 | 0.034 ± 0.034 | 0.2 | <0.000 | 0.132 | <0.000 | 0.0074 |
| Sm * | μg/kg | 0.015 ± 0.019 | 0.008 ± 0.010 | 0.105 | <0.000 | 0.042 | <0.000 | 0.0469 |
| Eu * | μg/kg | 0.023 ± 0.027 | 0.014 ± 0.010 | 0.18 | 0.004 | 0.042 | 0.002 | 0.0288 |
| Gd * | μg/kg | 0.017 ± 0.022 | 0.009 ± 0.013 | 0.107 | <0.000 | 0.049 | <0.000 | 0.0491 |
| Tb * | μg/kg | 0.005 ± 0.005 | 0.003 ± 0.003 | 0.017 | <0.000 | 0.011 | <0.000 | 0.0128 |
| Dy * | μg/kg | 0.014 ± 0.012 | 0.009 ± 0.009 | 0.049 | <0.000 | 0.028 | <0.000 | 0.0231 |
| Ho | μg/kg | 0.003 ± 0.003 | 0.002 ± 0.003 | 0.015 | <0.000 | 0.012 | <0.000 | 0.1663 |
| Er | μg/kg | 0.011 ± 0.008 | 0.007 ± 0.007 | 0.034 | <0.000 | 0.024 | <0.000 | 0.0586 |
| Tm | μg/kg | 0.001 ± 0.002 | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 0.01 | <0.000 | 0.003 | <0.000 | 0.1684 |
| Yb * | μg/kg | 0.007 ± 0.007 | 0.004 ± 0.005 | 0.037 | <0.000 | 0.013 | <0.000 | 0.0464 |
| Lu | μg/kg | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 0.005 | <0.000 | 0.005 | <0.000 | 0.9613 |
| Ir | μg/kg | 0.016 ± 0.021 | 0.008 ± 0.015 | 0.109 | <0.000 | 0.036 | <0.000 | 0.061 |
| Pt | μg/kg | 0.047 ± 0.054 | 0.069 ± 0.066 | 0.262 | <0.000 | 0.238 | <0.000 | 0.1587 |
| Au | μg/kg | 0.035 ± 0.056 | 0.019 ± 0.038 | 0.182 | <0.000 | 0.097 | <0.000 | 0.1401 |
| Tl * | μg/kg | 0.007 ± 0.020 | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 0.125 | <0.000 | 0.004 | <0.000 | 0.0469 |
| Hg | μg/kg | 0.002 ± 0.008 | 0.000 ± 0.002 b | 0.038 | <0.000 | 0.011 | <0.000 | 0.0761 |
| Pb * | mg/kg | 0.448 ± 0.477 | 0.256 ± 0.177 | 2.559 | 0.066 | 0.844 | <0.000 | 0.009 |
| Location | δ13C AVG | δ13C STD | Max | Min | t-Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China (n = 60) | −17.52 | 3.81 | −11.18 | −27.23 | 0.005 |
| Argentina (n = 23) | −19.58 | 2.42 | −14.91 | −23.97 |
| Data Source | Accuracy | R2 | Q2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elements | 97.8% | 0.915 | 0.706 |
| Elements and δ13C | 97.5% | 0.924 | 0.743 |
| Elements and δ13C with redundant variables removed | 98.8% | 0.925 | 0.787 |
| Samples Number | Origin Class | Predicted Class | Confidence | Accuracy | Total Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CHN | CHN | 0.88 | 91.67% | 94.312% |
| 2 | CHN | CHN | 0.95 | ||
| 3 | CHN | CHN | 0.99 | ||
| 4 | CHN | CHN | 0.84 | ||
| 5 | CHN | CHN | 0.93 | ||
| 6 | CHN | CHN | 0.94 | ||
| 7 | CHN | CHN | 1 | ||
| 8 | CHN | CHN | 0.98 | ||
| 9 | CHN | CHN | 1 | ||
| 10 | CHN | ARG | 0.62 | ||
| 11 | CHN | CHN | 0.82 | ||
| 12 | CHN | CHN | 0.94 | ||
| 13 | ARG | ARG | 0.97 | 100% | |
| 14 | ARG | ARG | 0.99 | ||
| 15 | ARG | ARG | 0.98 | ||
| 16 | ARG | ARG | 0.97 | ||
| 17 | ARG | ARG | 0.92 |
| Samples Number | Origin Class | Predicted Class | Confidence | Accuracy | Total Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CHN | CHN | 0.86 | 100% | 82.35% |
| 2 | CHN | CHN | 0.9 | ||
| 3 | CHN | CHN | 0.83 | ||
| 4 | CHN | CHN | 0.53 | ||
| 5 | CHN | CHN | 0.84 | ||
| 6 | CHN | CHN | 0.86 | ||
| 7 | CHN | CHN | 0.87 | ||
| 8 | CHN | CHN | 0.98 | ||
| 9 | CHN | CHN | 0.79 | ||
| 10 | CHN | CHN | 0.72 | ||
| 11 | CHN | CHN | 0.85 | ||
| 12 | CHN | CHN | 0.9 | ||
| 13 | ARG | ARG | 0.71 | 60% | |
| 14 | ARG | ARG | 0.69 | ||
| 15 | ARG | ARG | 0.65 | ||
| 16 | ARG | CHN | 0.59 | ||
| 17 | ARG | CHN | 0.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Cristos, D.; Liu, B.; Xu, S.; Yi, X. Beef Traceability Between China and Argentina Based on Various Machine Learning Models. Molecules 2025, 30, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040880
Xiang X, Zhao C, Zhang R, Zeng J, Wang L, Zhang S, Cristos D, Liu B, Xu S, Yi X. Beef Traceability Between China and Argentina Based on Various Machine Learning Models. Molecules. 2025; 30(4):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040880
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Xiaomeng, Chaomin Zhao, Runhe Zhang, Jing Zeng, Liangzi Wang, Shuran Zhang, Diego Cristos, Bing Liu, Siyan Xu, and Xionghai Yi. 2025. "Beef Traceability Between China and Argentina Based on Various Machine Learning Models" Molecules 30, no. 4: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040880
APA StyleXiang, X., Zhao, C., Zhang, R., Zeng, J., Wang, L., Zhang, S., Cristos, D., Liu, B., Xu, S., & Yi, X. (2025). Beef Traceability Between China and Argentina Based on Various Machine Learning Models. Molecules, 30(4), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040880








