S- and N-Co-Doped Carbon-Nanoplate-Encased Ni Nanoparticles Derived from Dual-Ligand-Assembled Ni-MOFs as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
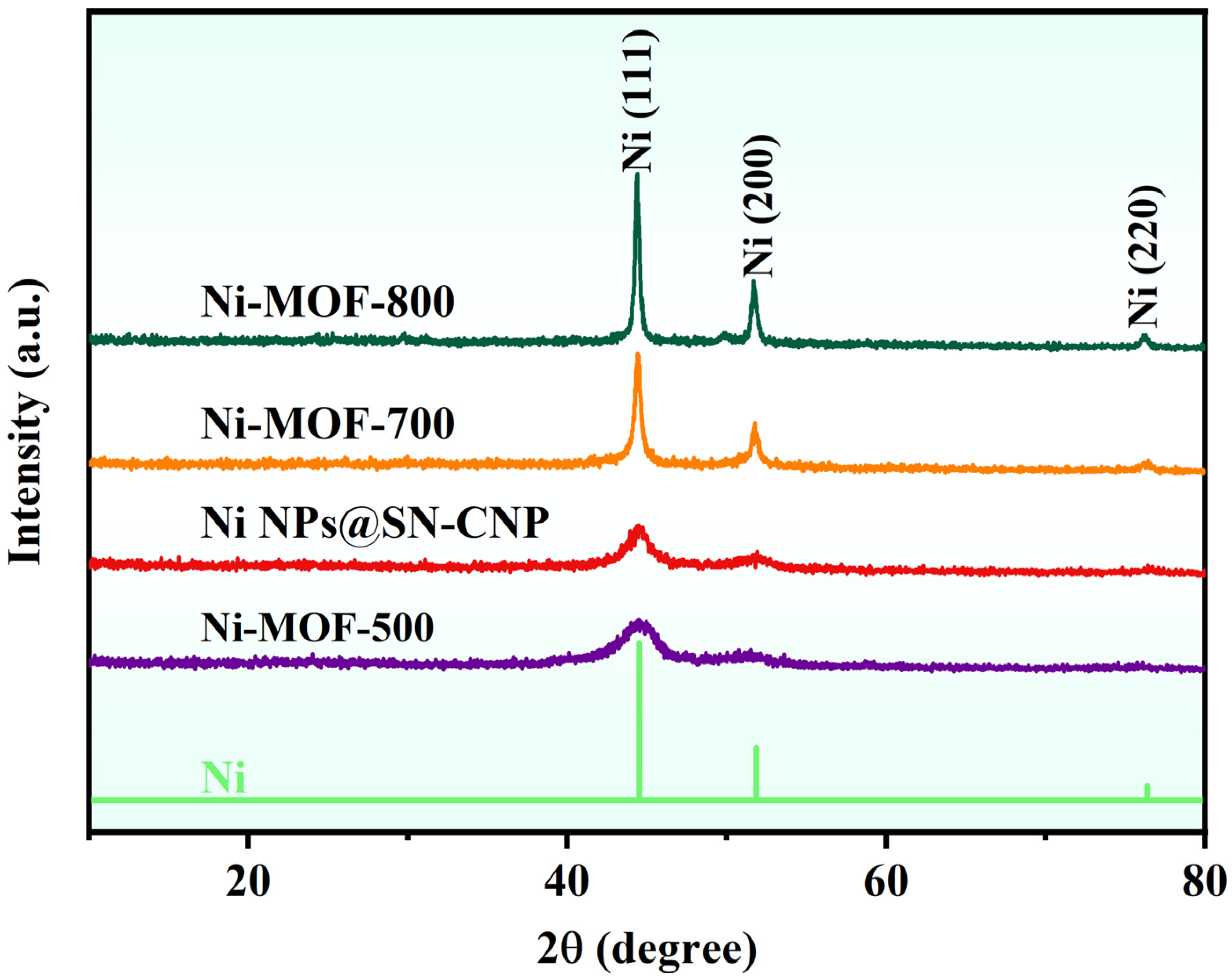
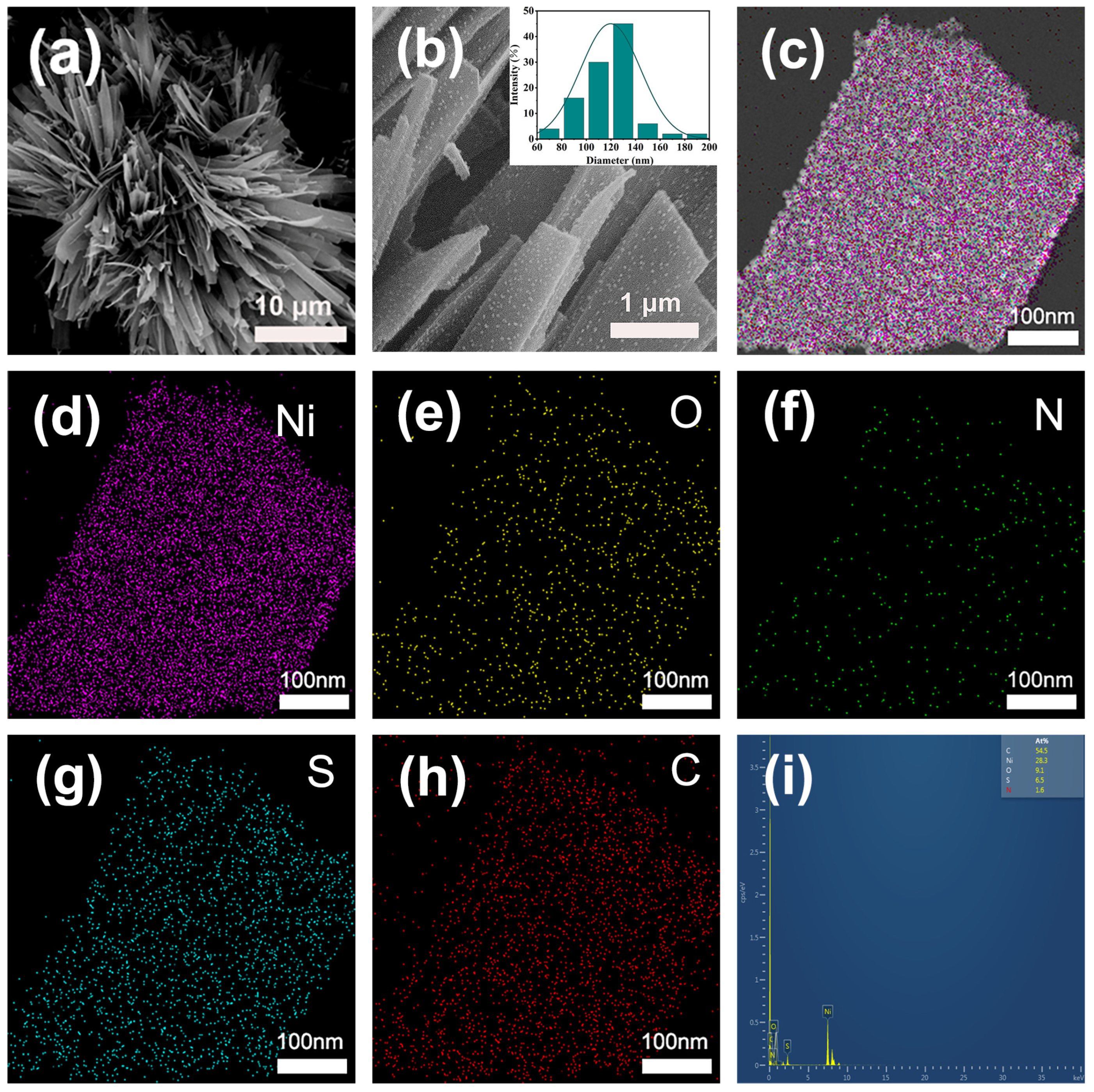
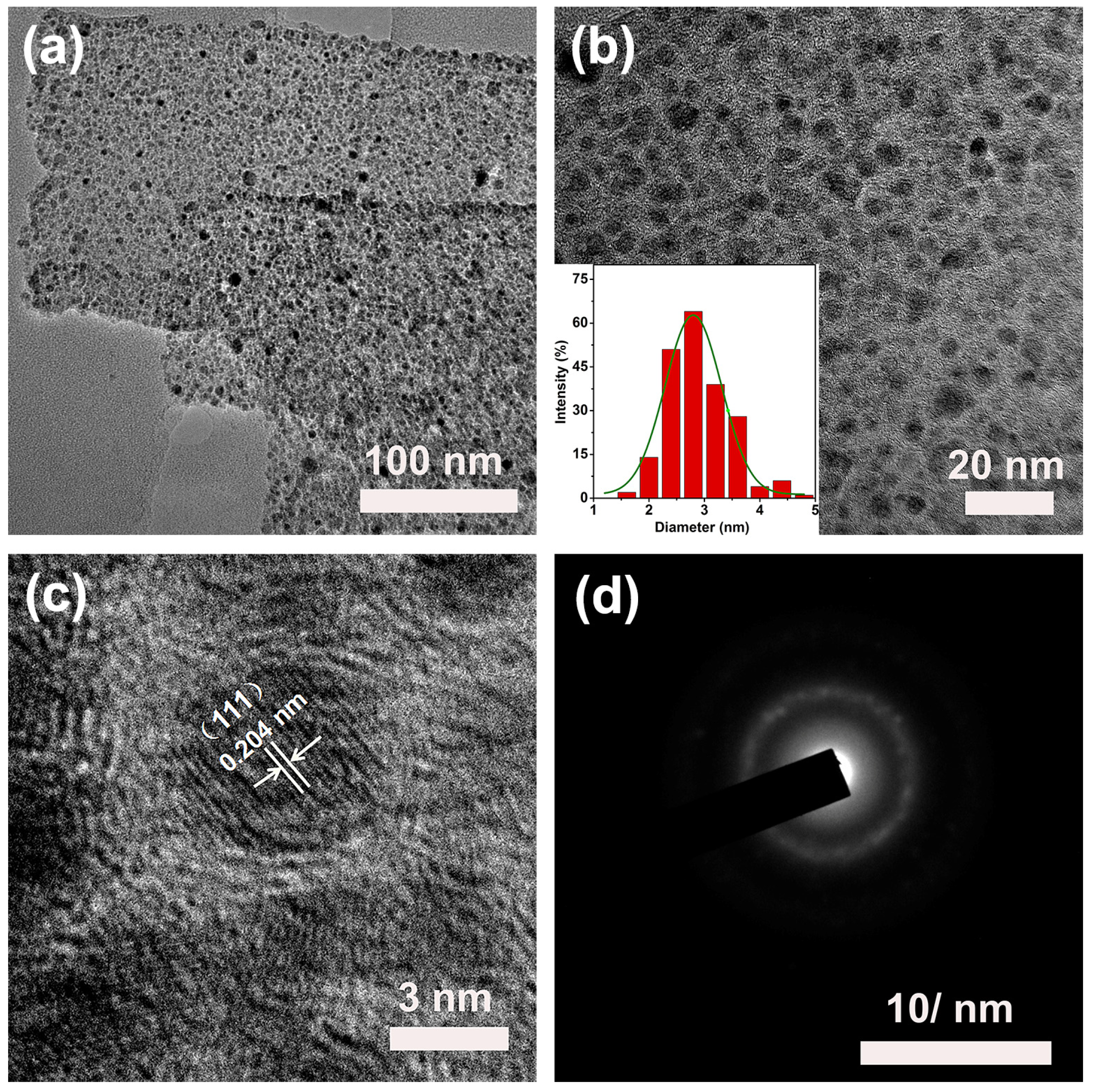
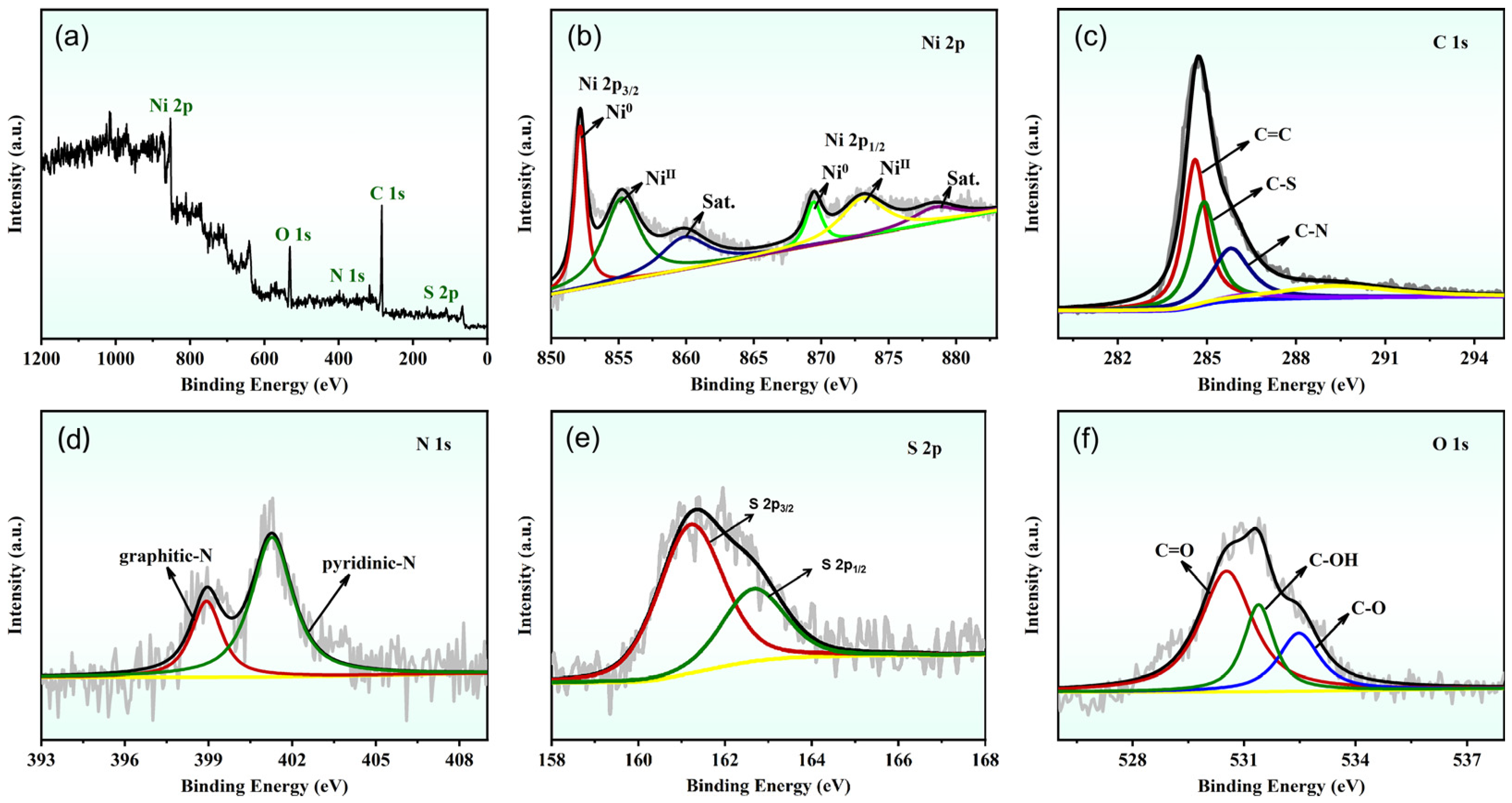
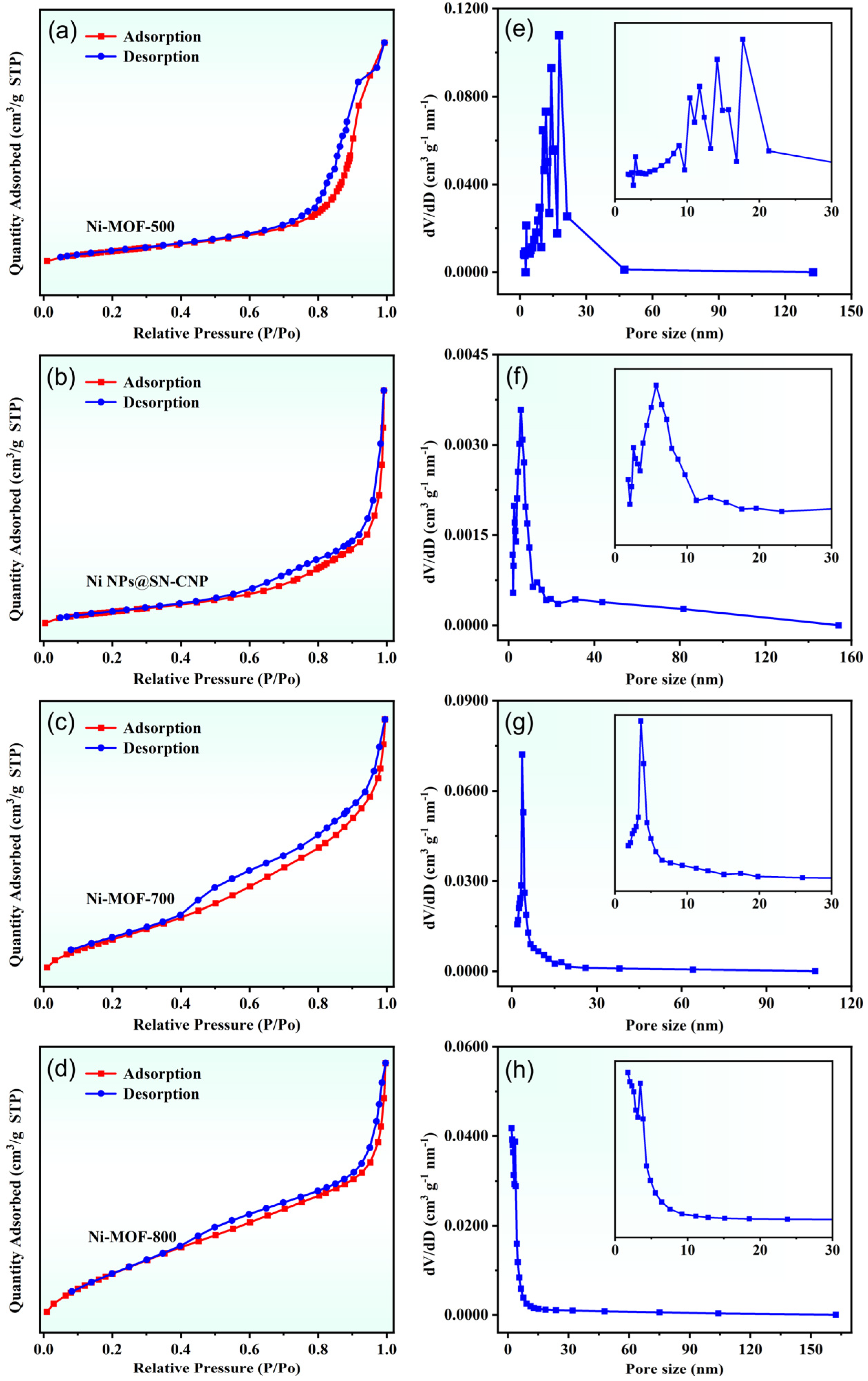
2.1. Structure and Morphology of the Ni NPs@SN-CNP
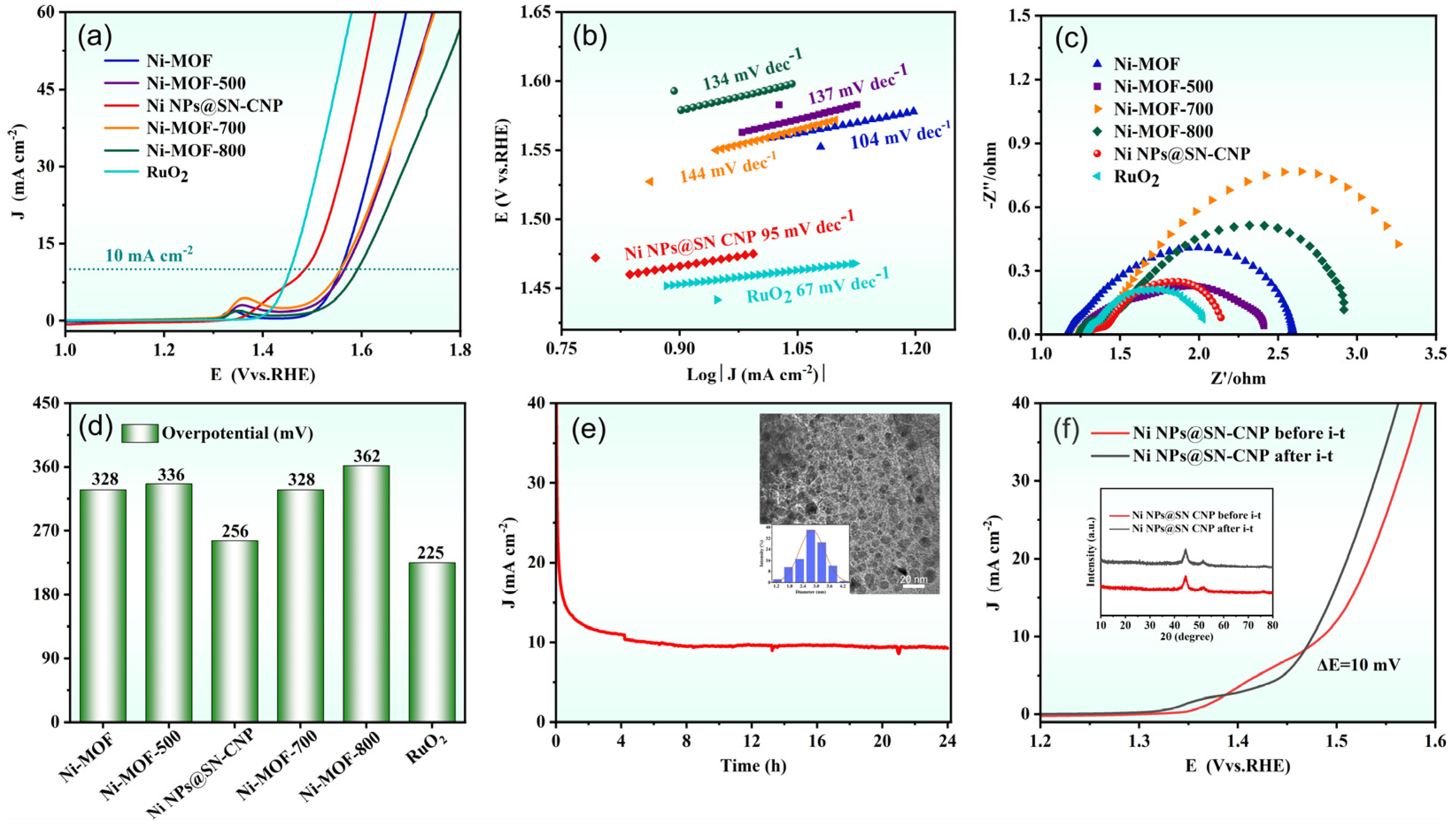
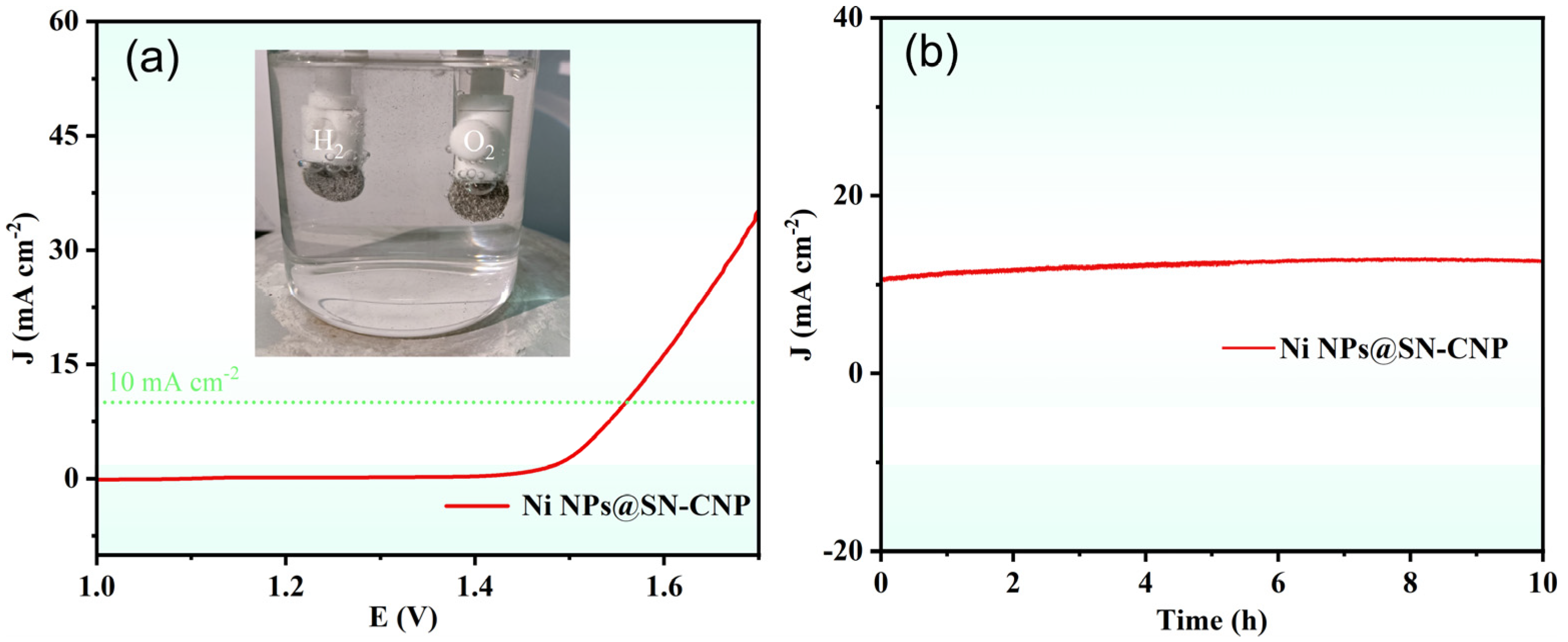
2.2. OER Performance
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Material
3.2. Synthesis of Ni-MOFs
3.3. Synthesis of Ni NPs@SN-CNP
3.4. Characterizations
3.5. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Qiao, Z. Robust Ru-VO2 bifunctional catalysts for all-pH overall water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2310690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, T. Designing MOF nanoarchitectures for electrochemical water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, G.M.; Belchior, F.N.; Villena, J.E.N. Hybrid electrical energy generation from hydropower, solar photovoltaic and hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 53, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.C.; Ting, Y.C.; Yen, F.Y. Synergistic Mo and W single atoms co-doped surface hydroxylated NiFe oxide as bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2024, 358, 124356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Y. Construction of Co3O4/Fe2O3 nanosheets on nickel foam as efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 148, 109680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, R. CuO@CoFe layered double hydroxide core–shell heterostructure as an efficient water oxidation electrocatalyst under mild alkaline conditions. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 9491–9495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, J. Engineering ruthenium-based electrocatalysts for effective hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanomicro Lett. 2021, 13, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Chen, D.; Qiu, X. Lignin-metal supramolecular framework strategy of self-healing carbon-coated CoRu alloy nanocatalyst for efficient overall water splitting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2303442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lu, Z.A.; Li, S. In situ growth of amorphous Fe(OH)3 on nickel nitrate hydroxide nanoarrays for enhanced electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. ACS. Appl. Mater. 2020, 12, 12668–12676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Rafiq, K.; Najam, T. Metal-organic frameworks for electrocatalytic water-splitting: Beyond the pyrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 35075–35111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Luo, W.; Wang, S. Discharge-induced enhancement of the oxygen evolution reaction. Angew. Chew. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20042–20048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuvanendran, N.; Park, C.W.; Su, H. Multifunctional Pt3Rh–Co3O4 alloy nanoparticles with Pt-enriched surface and induced synergistic effect for improved performance in ORR, OER, and HER. Environ. Res. 2023, 229, 115950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, J.S.; Rittiruam, M.; Saelee, T. Ru tailored hydrous cobalt phosphate as a rational approach for high-performance alkaline oxygen evolution reaction. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Wu, D.; Si, D. Monolayer NiIr-layered double hydroxide as a long-lived efficient oxygen evolution catalyst for seawater splitting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 9254–9263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, J.; Meng, F. Ru nanoparticles modified Ni3Se4/Ni(OH)2 heterostructure nanosheets: A fast kinetics boosted bifunctional overall water splitting electrocatalyst. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 663, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, P.; Li, H. Spin-state reconfiguration induced by alternating magnetic field for efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Ambient fast synthesis and active sites deciphering of hierarchical foam-like trimetal–organic framework nanostructures as a platform for highly efficient oxygen evolution electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Sheng, H.; Ross, R.D. Modifying redox properties and local bonding of Co3O4 by CeO2 enhances oxygen evolution catalysis in acid. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Ma, Z.; Yang, W. Magnesium incorporation activates perovskite cobaltites toward efficient and stable electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Mater. Rep. Energy 2023, 3, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Xu, X.; Fei, L. Electrochemical oxidation of small molecules for energy-saving hydrogen production. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2401242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.P.; Lu, X.F.; Zang, S.Q. Non-noble-metal-based electrocatalysts toward the oxygen evolution reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Chang, X.; Li, L. Synthesis of CoMoO4 nanofibers by electrospinning as efficient electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Molecules 2023, 29, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. An advanced flower-like Co-Ni/PI-CNT film electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 729, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ji, S.; Kannan, P. Hydrophilic Ni(OH)2@CoB nano-chains with shell-core structure as an efficient catalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 844, 156129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Guo, X.; Jiang, J. Modulating nickel-iron active species via dealloying to boost the oxygen evolution reaction. Dalton Trans. 2024, 53, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.D.; Mou, C.L.; Ma, W.L. Nano-TiO2 anchored onto 2D Cu–Ni bimetallic MOF as a heterojunction for highly-efficient OER overpotential reduction. New J. Chem. 2024, 48, 2979–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Wang, D.P.; Rui, X. In-situ formation of hollow hybrids composed of cobalt sulfides embedded within porous carbon polyhedra/carbon nanotubes for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3038–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zou, R.; Xia, W. Facile synthesis of ultrasmall CoS2 nanoparticles within thin N-doped porous carbon shell for high performance lithium-ion batteries. Small 2015, 11, 2511–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, R.; Ma, G. Cobalt sulfide/N, S codoped porous carbon core–shell nanocomposites as superior bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 20674–20684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Sun, H.; Jiang, S.P. Modulating metal–organic frameworks for catalyzing acidic oxygen evolution for proton exchange membrane water electrolysis. SusMat 2021, 1, 460–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Ma, G.; Kong, D. Atomically homogeneous dispersed ZnO/N-doped nanoporous carbon composites with enhanced CO2 uptake capacities and high efficient organic pollutants removal from water. Carbon 2015, 95, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Wang, J.; Su, D. In situ cobalt–cobalt oxide/N-doped carbon hybrids as superior bifunctional electrocatalysts for hydrogen and oxygen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2688–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torad, N.L.; Hu, M.; Ishihara, S. Direct synthesis of MOF-derived nanoporous carbon with magnetic Co nanoparticles toward efficient water treatment. Small 2014, 10, 2096–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Ma, G.; Zhu, Y. Metal-organic-framework-derived bi-metallic sulfide on N, S-codoped porous carbon nanocomposites as multifunctional electrocatalysts. J. Power Sources 2016, 334, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ding, S.; Xu, S. Metallic two-dimensional metal-organic framework arrays for ultrafast water splitting. J. Power Sources 2021, 494, 229733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, G.; Wan, H. 2D free-standing nitrogen-doped Ni-Ni3S2@ carbon nanoplates derived from metal–organic frameworks for enhanced oxygen evolution reaction. Small 2019, 15, 1900348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, P. Structural investigation of metallic Ni nanoparticles with N-doped carbon for efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, S.; Xiao, Y.X.; Dietrich, D. Nickel nanoparticles supported on a covalent triazine framework as electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction and oxygen reduction reactions. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.C.; Shown, I.; Chang, S.T. Pyrolyzed cobalt corrole as a potential non-precious catalyst for fuel cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 3500–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Xu, L.; Ding, L. Using pyridine as nitrogen-rich precursor to synthesize Co-NS/C non-noble metal electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Appl. Catal. 2012, 125, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Kamiya, K. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials as non-metal electrocatalysts for water oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, J. Onion-like graphitic nanoshell structured Fe–N/C nanofibers derived from electrospinning for oxygen reduction reaction in acid media. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 30, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, W.; Luo, Z.; Jiang, J. Nitrogen and sulfur codoped graphene: Multifunctional electrode materials for high-performance Li-ion batteries and oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6186–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Wu, D.; Feng, X. Nitrogen-doped ordered mesoporous graphitic arrays with high electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 14, 2565–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathankumar, M.; Karthick, K. In situ decorated Ni metallic layer with CoS2-layered thin films via a layer-by-layer strategy using pulsed laser deposition for enhanced electrocatalytic OER. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 8946–8957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shreyanka, S.N.; Theerthagiri, J.; Lee, S.J. Multiscale design of 3D metal–organic frameworks (M−BTC, M: Cu, Co, Ni) via PLAL enabling bifunctional electrocatalysts for robust overall water splitting. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Liu, Z.; Huang, M. 2D iron-doped nickel MOF nanosheets grown on nickel foam for highly efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 529, 147201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Wei, Z.; Ma, C. MXene boosted CoNi-ZIF-67 as highly efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, K.; Zhao, G.; Chen, Y. Hybrid 2D dual-metal–organic frameworks for enhanced water oxidation catalysis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Cheng, K.; Xie, J. Construction of core-shell NiFe LDH/Co(OH)F amorphous/crystalline heterostructure for synergistically enhanced electrocatalytic water oxidation. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1010, 177889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M. Interface engineering of Ni3S2@NiFe-LDH core-shell heterostructure to achieve energy-saving hydrogen production. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1010, 177855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.; Qin, H.; Zou, Y. In-situ decoration of NiCo-thiophene based metal-organic framework on nickel foam as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. J. Power Sources 2025, 629, 235942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, M.; Yang, F. Size controllable CoNiP nanoparticle supported on porous carbon for highly-efficient electrocatalytic overall water splitting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 105, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yun, H.; Kang, Y.; Du, K.; Wang, J.; Chao, S.; Wang, J. S- and N-Co-Doped Carbon-Nanoplate-Encased Ni Nanoparticles Derived from Dual-Ligand-Assembled Ni-MOFs as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Molecules 2025, 30, 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040820
Han H, Zhang Y, Zhou C, Yun H, Kang Y, Du K, Wang J, Chao S, Wang J. S- and N-Co-Doped Carbon-Nanoplate-Encased Ni Nanoparticles Derived from Dual-Ligand-Assembled Ni-MOFs as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Molecules. 2025; 30(4):820. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040820
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Huijuan, Yalei Zhang, Chunrui Zhou, Haixin Yun, Yiwen Kang, Kexin Du, Jianying Wang, Shujun Chao, and Jichao Wang. 2025. "S- and N-Co-Doped Carbon-Nanoplate-Encased Ni Nanoparticles Derived from Dual-Ligand-Assembled Ni-MOFs as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction" Molecules 30, no. 4: 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040820
APA StyleHan, H., Zhang, Y., Zhou, C., Yun, H., Kang, Y., Du, K., Wang, J., Chao, S., & Wang, J. (2025). S- and N-Co-Doped Carbon-Nanoplate-Encased Ni Nanoparticles Derived from Dual-Ligand-Assembled Ni-MOFs as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Molecules, 30(4), 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040820





