Charge Regulation in Liquid Films Stabilized by Ionic Surfactants: Change in Adsorption with Film Thickness and Phase Transitions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Poisson–Boltzmann Equation
2.2. The Adsorption Isotherm
2.3. Disjoining Pressure
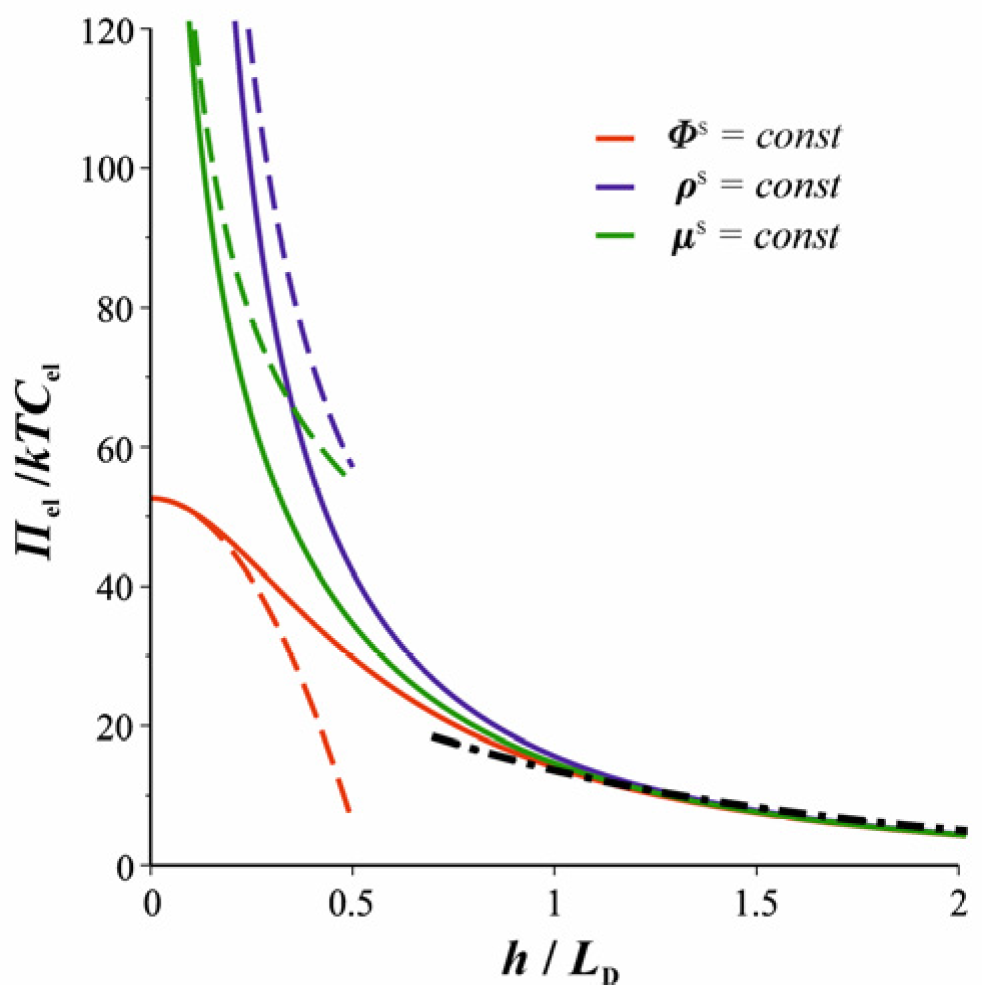
2.4. Charge Regulation According to the Davies Isotherm Versus Constant Charge or Potential
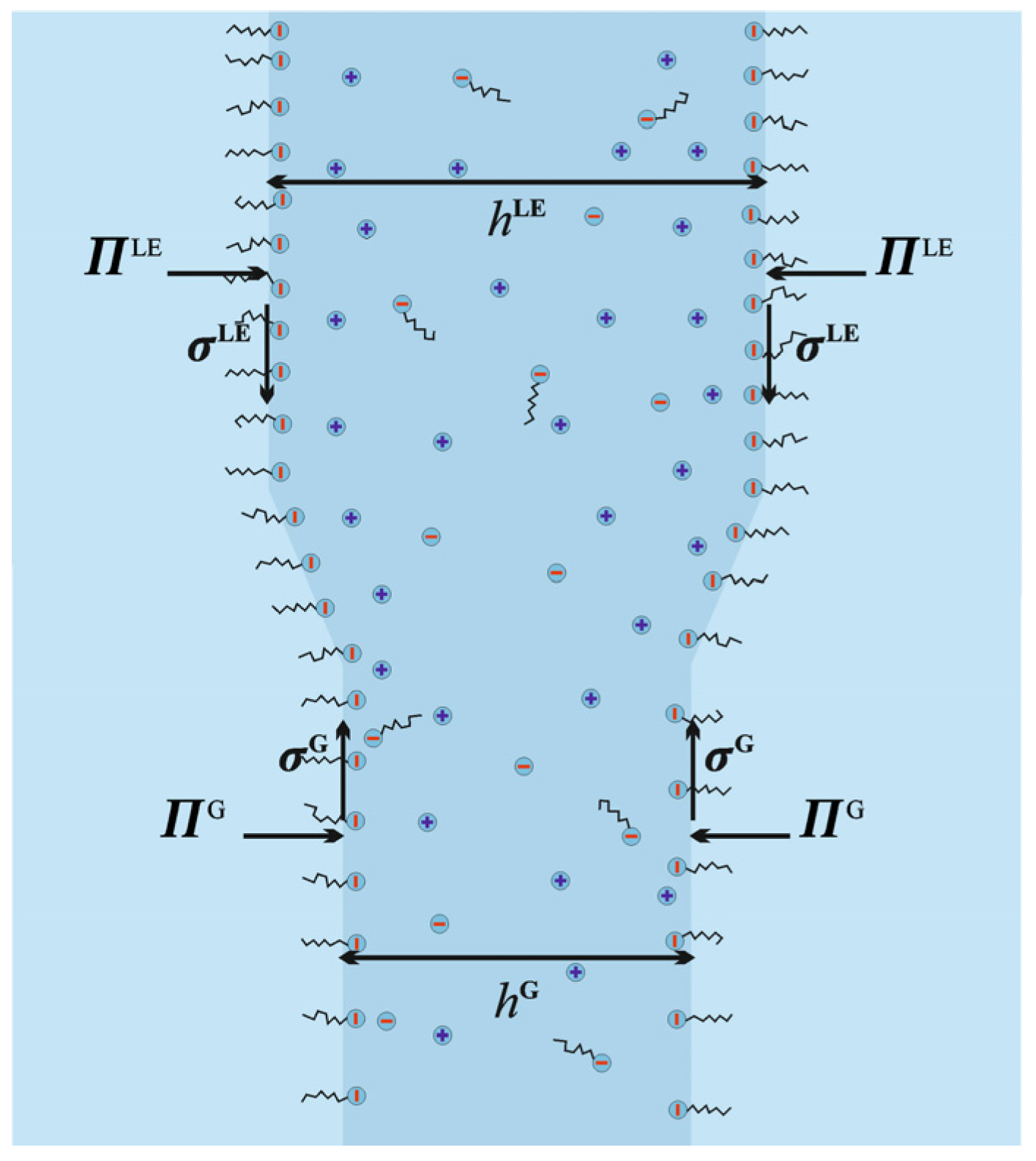
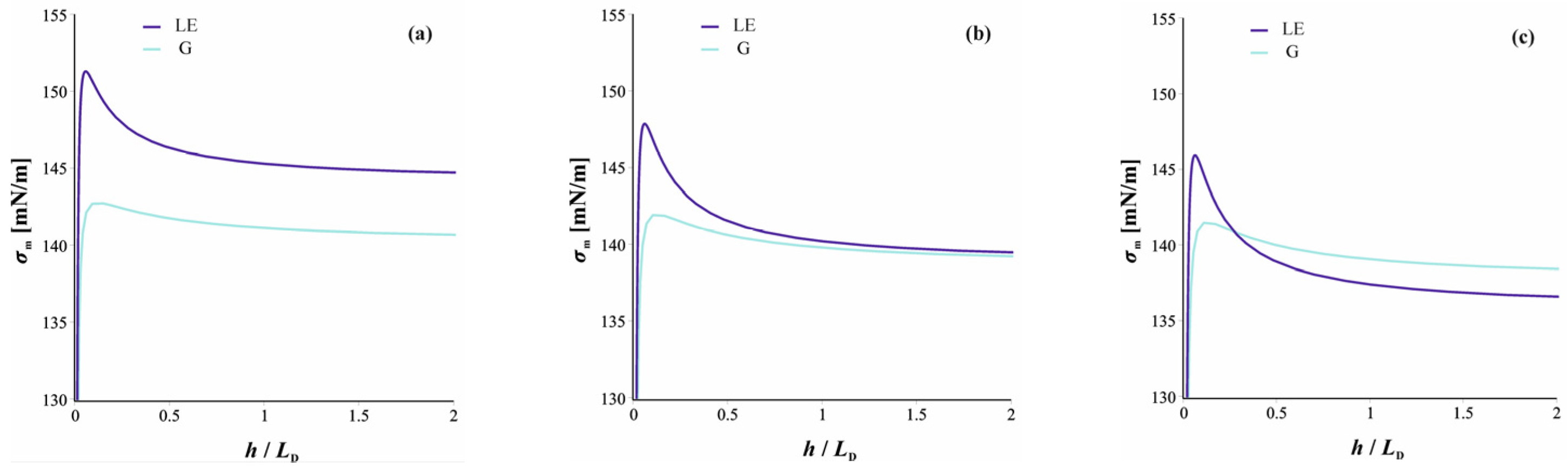
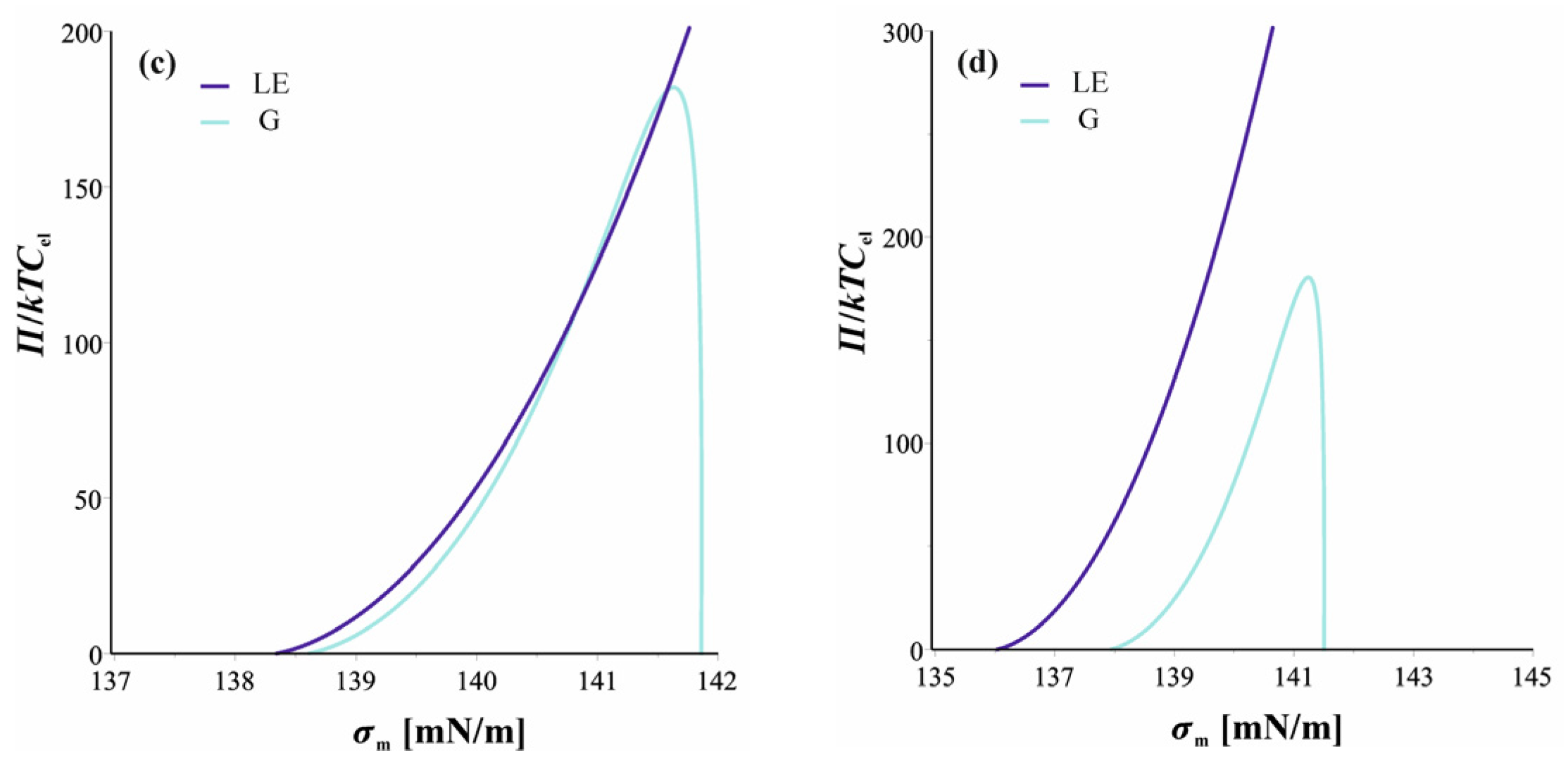
2.5. Phase Transition at W|A Interface Triggered by Film Thinning
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AH | Hamaker constant |
| Cel | total electrolyte concentration |
| Cs | surfactant concentration |
| Cs,pt∞ | phase transition concentration of an isolated surface |
| E | electric field |
| e | elementary electric charge |
| Ka | equilibrium adsorption constant (from the aqueous phase) |
| adsorption constant for gaseous phase | |
| adsorption constant for liquid expanded phase | |
| k | Boltzmann constant |
| LB | Bjerumm’s length (LB = e2/εkT) |
| LD | Debye’s length ( = εkT/2e2Cel) |
| P | pressure tensor (including the Maxwell tensor) |
| p | isotropic mechanical pressure |
| T | temperature |
| U | unit tensor |
| z | distance from the center of the film |
| Γ | adsorption of the surfactant |
| Γ G | surfactant adsorption for 2D gaseous phase |
| Γ LE | surfactant adsorption for liquid expanded phase |
| γS | surface activity coefficient of the surfactant |
| ε | absolute dielectric permittivity |
| μS | chemical potential of the surface active ion |
| Π | disjoining pressure |
| Πel | electrostatic disjoining pressure |
| π | surface pressure of the monolayer (π ≡ σ0 – σ) |
| πcoh | Langmuir’s cohesive pressure |
| πpt∞ | phase transition surface pressure of an isolated surface |
| πG | surface pressure for gaseous phase |
| πLE | surface pressure for liquid expanded phase |
| ρ | charge density |
| ρS | surface charge (ρS = −eΓ) for ionic 1:1 surfactant |
| σ | surface tension of the monolayer |
| σ0 | surface tension of the neat surface |
| σ AL | contribution of the adsorbed layer to the surface tension |
| σm | membrane tension |
| contribution of the electric double layer to the membrane tension | |
| Van der Waals contribution to the membrane tension | |
| Φ | Boltzmann factor for a cation (Φ = exp(−eϕ/kT)) |
| Φm | Boltzmann factor in the center of the film (Φm = exp(−eϕm/kT)) |
| ΦS | surface Boltzmann factor (ΦS = exp(−eϕS/kT)) |
| ϕ | electrostatic potential |
| ϕm | extremum of the electrostatic potential in the center of the film |
| ϕS | surface electric potential |
| 2D | two-dimensional |
| CMC | critical micelle concentration |
| EoS | equation of state |
| W|G | water–gas surface |
| W|O | water–oil interface |
References
- Rusanov, A.I. Phase Transitions and Surface Phenomena, 1st ed.; Scientific Research: Leningrad, Russia, 1967. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Derjaguin, B.V. Theory of the Stability of Colloids and Thin Films, 1st ed.; Scientific Research: Moscow, Russia, 1986. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bierman, A. Electrostatic forces between nonidentical colloidal particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1955, 10, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, J.B.; Smith, A.L. Interaction between silver iodide surfaces in the presence of specifically adsorbed ions. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 1974, 70, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paunov, V.N.; Dimova, R.I.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; Broze, G.; Mehreteab, A. The hydration repulsion between charged surfaces as an interplay of volume exclusion and dielectric saturation effects. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 182, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralchevsky, P.A.; Danov, K.D.; Basheva, E.S. Hydration force due to the reduced screening of the electrostatic repulsion in few-nanometer-thick films. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pericet-Camara, R.; Papastavrou, G.; Behrens, S.H.; Borkovec, M. Interaction between Charged Surfaces on the Poisson-Boltzmann Level: The Constant Regulation Approximation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 19467–19475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyklema, J.; Duval, J.F.L. Hetero-interaction between Gouy–Stern double layers: Charge and potential regulation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 114–115, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, S. Interaction between dissimilar double layers with like signs under charge regulation on the basis of the Gouy–Chapman–Stern–Grahame model. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 280, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.Y.C.; Healy, T.W.; Supasiti, T.; Usui, S. Electrical double layer interactions between dissimilar oxide surfaces with charge regulation and Stern–Grahame layers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 296, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa, I.; Sinha, P.; Finessi, M.; Maroni, P.; Papastavrou, G.; Borkovec, M. Importance of charge regulation in attractive double-layer forces between dissimilar surfaces. Physical. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 228301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnie, S.L.; Chan, D.Y.C. Interaction free energy between plates with charge regulation: A linearized model. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 161, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleharty, M.E.; van Swol, F.; Petsev, D.N. The effect of surface charge regulation on conductivity in fluidic nanochannels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 416, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilella, V.M.; Verdia-Baguena, C.; Alcaraz, A. Lipid charge regulation of non-specific biological ion channels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 3881–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Nap, R.J.; Lagzi, I.; Kowalczyk, B.; Han, S.; Grzybowski, B.A.; Szleifer, I. How and why nanoparticle’s curvature regulates the apparent pKa of the coating ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2192–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Komura, S.; Andelman, D.; Podgornik, R. Diffusive dynamics of charge regulated macro-ion solutions. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J. Intermolecular and Surface Forces; Academic Press: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ducker, W.A.; Senden, T.J.; Pashley, R.M. Direct measurement of colloidal forces using an atomic force microscope. Nature 1991, 353, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, H.J. Measuring electrostatic, van der Waals, and hydration forces in electrolyte solutions with an atomic force microscope. Biophys. J. 1991, 60, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheludko, A. Thin liquid films. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1967, 1, 391–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, J.; Khristov, K.; Masliyah, J.; Panchev, N.; Taylor, S.D.; Tchoukov, P. Application of Scheludko–Exerowa thin liquid film technique to studies of petroleum W/O emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 519, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Tchoukov, P.; Qiao, P.; Ma, X.; Pensini, E.; Dabros, T.; Czarnecki, J.; Xu, Z. Studying demulsification mechanisms of water-in-crude oil emulsions using a modified thin liquid film technique. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 540, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavchov, R.I.; Peychev, B.; Minkov, I. Electrolytes at uncharged liquid interfaces: Adsorption, potentials, surface tension, and the role of the surfactant monolayer. Langmuir 2024, 40, 17170–17189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrova, I.M.; Slavchov, R.I.; Ivanov, T.; Moshbach, T.S. A spherical cavity model for quadrupolar dielectics. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 114502–114519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.T.; Rideal, E.K. Interfacial Phenomena, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Gouy, L.G. Sur la constitution de la charge électrique à la surface d’un èlectrolyte. Le J. De Phys. Et Le Radium 1910, 9, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, E.S.; Radke, C.J. Double layer interactions between charge-regulated colloidal surfaces: Pair potentials for spherical particles bearing ionogenic surface groups. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 47, 59–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.T. Adsorption of long-chain ions I. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1958, 245, 417–428. [Google Scholar]
- Slavchov, R.I.; Karakashev, S.I.; Ivanov, I.B. Ionic surfactants and ion-specific effects: Adsorption, micellization, thin liquid films. In Surfactant Science and Technology: Retrospects and Prospects; Römsted, L., Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor&Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar]
- Tamm, I.E. Foundamentals of the Theory of Electricity, 10th ed.; Nauka: Tolyatti, Russia, 1989. (In Russian); 9th ed.; Mir Publishers: Moscow, Russia, 1979. (In English); Chapter 2 [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Nestler, B. Multi-component electro-hydro-thermodynamic model with phase-field method. I. Dielectric. J. Comput. Phys. 2024, 505, 112907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavchov, R.I.; Dimitrova, I.M.; Ivanov, T.I. The polarized interface between quadrupolar insulators: Maxwell stress tensor, surface tension, and potential. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143, 154707–154721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The role of attractive and repulsive forces in the formation of tactoids, thixotropic gels, protein crystals and coacervates. J. Chem. Phys. 1938, 6, 873–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. Oil lenses on water and the nature of monomolecular expanded films. J. Chem. Phys. 1933, 1, 756–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honig, E.P.; Mul, P.M. Tables and equations of the diffuse double layer repulsion at constant potential and at constant charge. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1971, 36, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.J. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Aratono, M.; Uryu, S.; Hayami, Y.; Motomura, K.; Matuura, R. Phase transition in the adsorbed films at water/air interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1984, 98, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurkov, T.D.; Dimitrova, T.D.; Marinova, K.G.; Bilke-Crause, C.; Gerber, C.; Ivanov, I.B. Ionic surfactants on fluid interfaces: Determination of the adsorption; role of the salt and the type of hydrophobic phase. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 261, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehfeld, S.J. Adsorption of sodium dodecyl sulfate at various hydrocarbon-water interfaces. J. Phys. Chem. 1967, 71, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, J.D. The preparation of surface chemically pure sodium n-dodecyl sulfate by foam fractionation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 180, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, V. Disjoining pressure and film stability of alkyltrimethylammonium bromide foam films. Langmuir 1997, 13, 3474–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aratono, M. (Kyushu University, Japan). Personal communication, 2010.
- Uryu, S.; Aratono, M.; Yamanaka, M.; Motomura, K.; Matuura, R. Adsorption of dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride-decylammonium chloride mixtures at water/air interface. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1983, 56, 3219–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exerowa, D.; Nikolov, A.; Zacharieva, M. Common black and Newton film formation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1981, 81, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anachkov, S.E.; Danov, K.D.; Basheva, E.S.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P. Determination of the aggregation number and charge of ionic surfactant micelles from the stepwise thinning of foam films. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 183–184, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Surfactant | Adsorption Parameters | Phase Transition for Isolated Surface (mM, mN/m) | Phase Transition in a Film | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ln(/m) | ln(/m) | πcoh [mN/m] | ||||
| hG [nm] | hLE [nm] | |||||
| C10H21OC2H4SO3Na | −10.31 | −7.42 | −3.1 | Cs,pt∞ = 1.18 mM πpt∞ = 1.9 mN/m | Cs = 1.20 mM | |
| 11.0 | 12.8 | |||||
| Cs = 1.25 mM | ||||||
| 5.2 | 6.9 | |||||
| C12H25SO4Na | −8.25 | −4.64 | −7.0 | Cs,pt∞ = 0.81 mM πpt∞ = 3.0 mN/m | Cs = 0.85 mM | |
| 4.9 | 6.2 | |||||
| Cs = 1.00 mM | ||||||
| - | - | |||||
| C10H21N(CH3)3Br | −11.62 | −8.63 | −3.5 | Cs,pt∞ = 2.51 mM πpt∞ = 2.1 mN/m | Cs = 2.53 mM | |
| 22.2 | 23.9 | |||||
| Cs = 2.60 mM | ||||||
| 7.3 | 8.9 | |||||
| C12H25N(CH3)3Br | −10.57 | −5.74 | −6.4 | Cs,pt∞ = 1.02 mM πpt∞ = 1.6 mN/m | Cs = 1.05 mM | |
| 7.2 | 9.9 | |||||
| Cs = 1.10 mM | ||||||
| - | - | |||||
| C12H25N(CH3)3Cl | −10.65 | −7.27 | −3.1 | Cs,pt∞ = 0.95 mM πpt∞ = 1.5 mN/m | Cs = 0.97 mM | |
| 15.2 | 17.6 | |||||
| Cs = 1.00 mM | ||||||
| 7.3 | 9.7 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimitrova, I.M.; Slavchov, R.I. Charge Regulation in Liquid Films Stabilized by Ionic Surfactants: Change in Adsorption with Film Thickness and Phase Transitions. Molecules 2025, 30, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030659
Dimitrova IM, Slavchov RI. Charge Regulation in Liquid Films Stabilized by Ionic Surfactants: Change in Adsorption with Film Thickness and Phase Transitions. Molecules. 2025; 30(3):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030659
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimitrova, Iglika M., and Radomir I. Slavchov. 2025. "Charge Regulation in Liquid Films Stabilized by Ionic Surfactants: Change in Adsorption with Film Thickness and Phase Transitions" Molecules 30, no. 3: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030659
APA StyleDimitrova, I. M., & Slavchov, R. I. (2025). Charge Regulation in Liquid Films Stabilized by Ionic Surfactants: Change in Adsorption with Film Thickness and Phase Transitions. Molecules, 30(3), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030659






