Discrimination of Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis Based on Raman and NIR Spectra Using Machine-Learning Algorithms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Spectra of Serum Lyophilizates
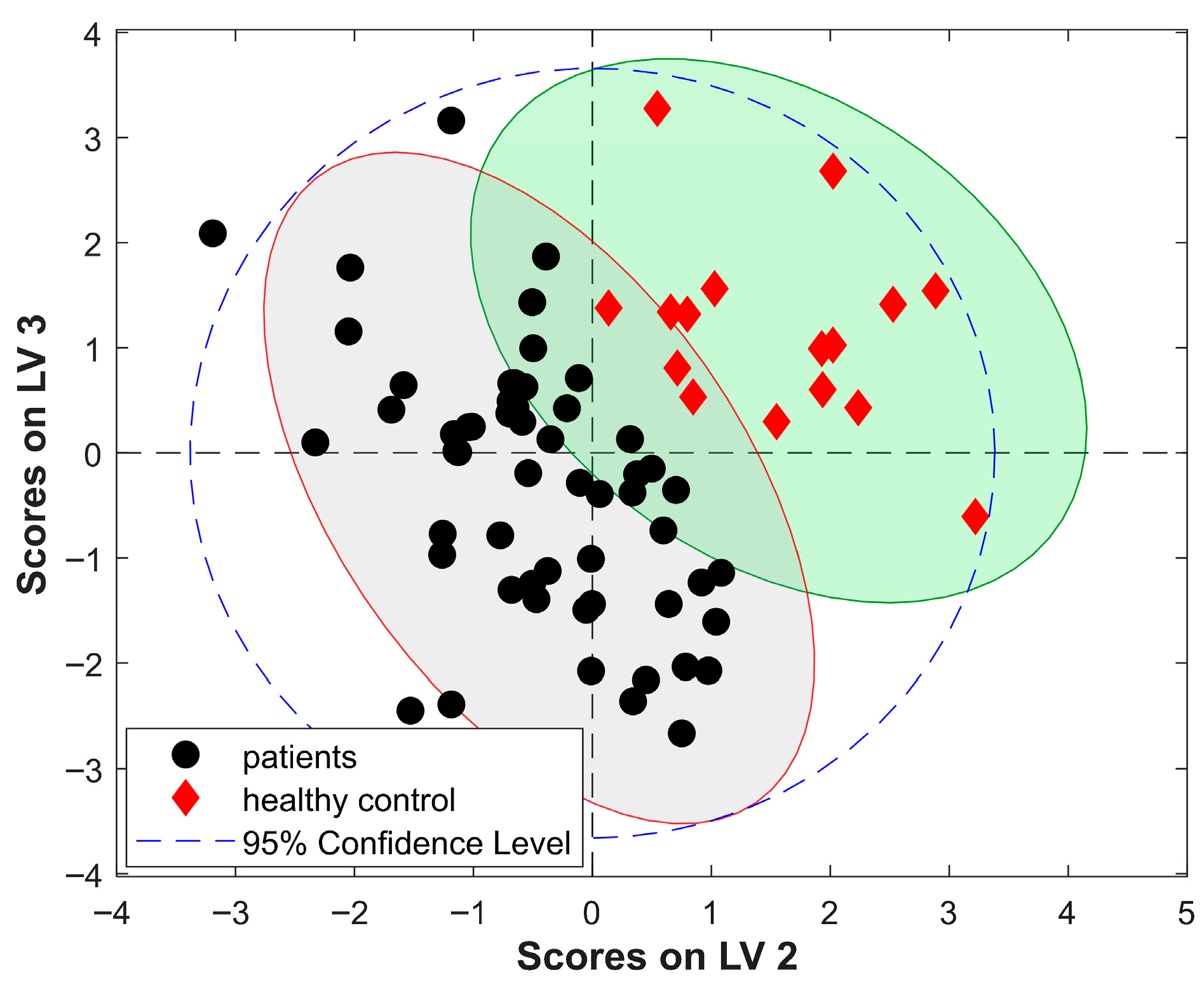
2.2. Discriminant Analysis
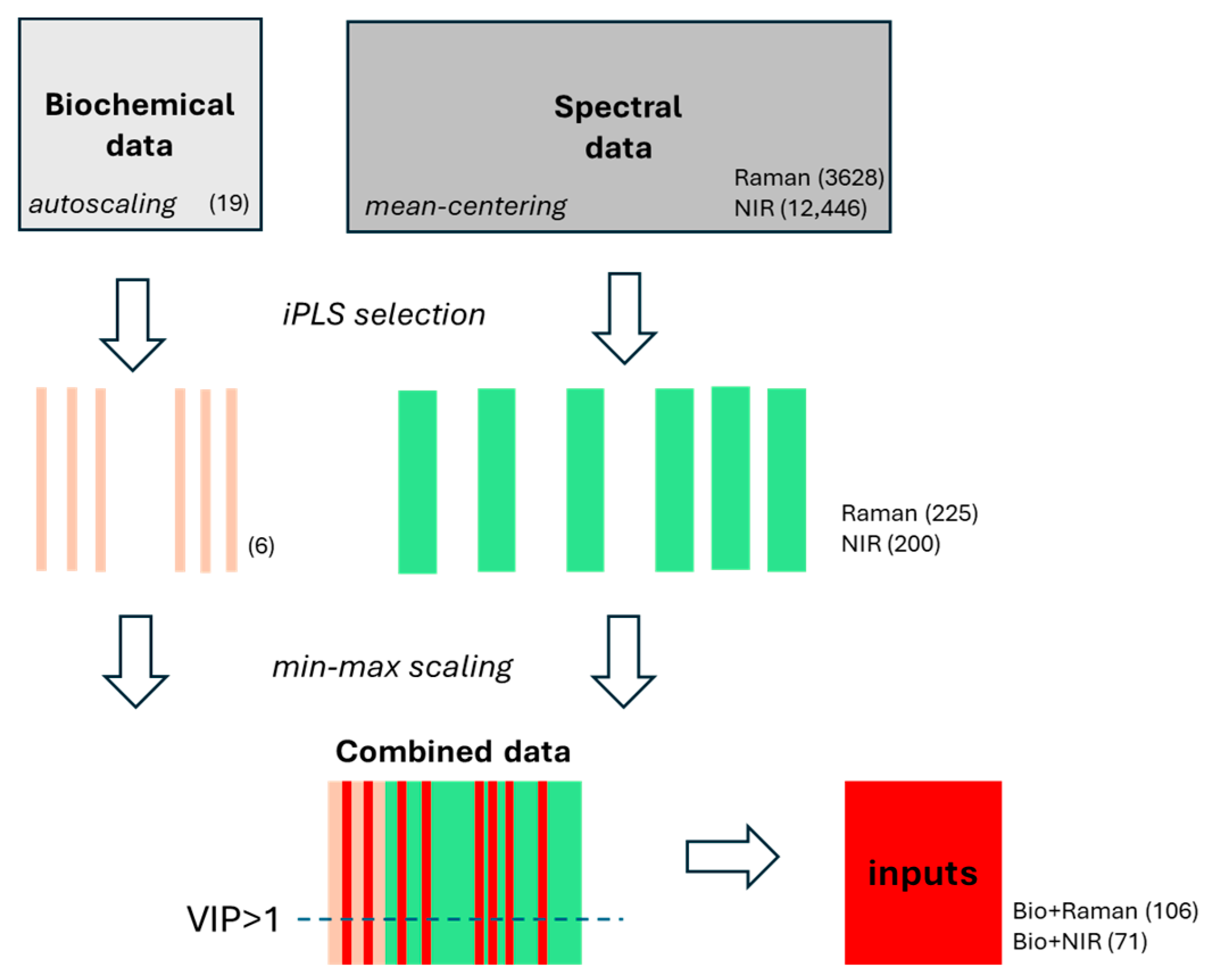
2.2.1. Selection of Spectral Features
2.2.2. Construction of Hybrid Models
2.2.3. PLS-DA Modeling
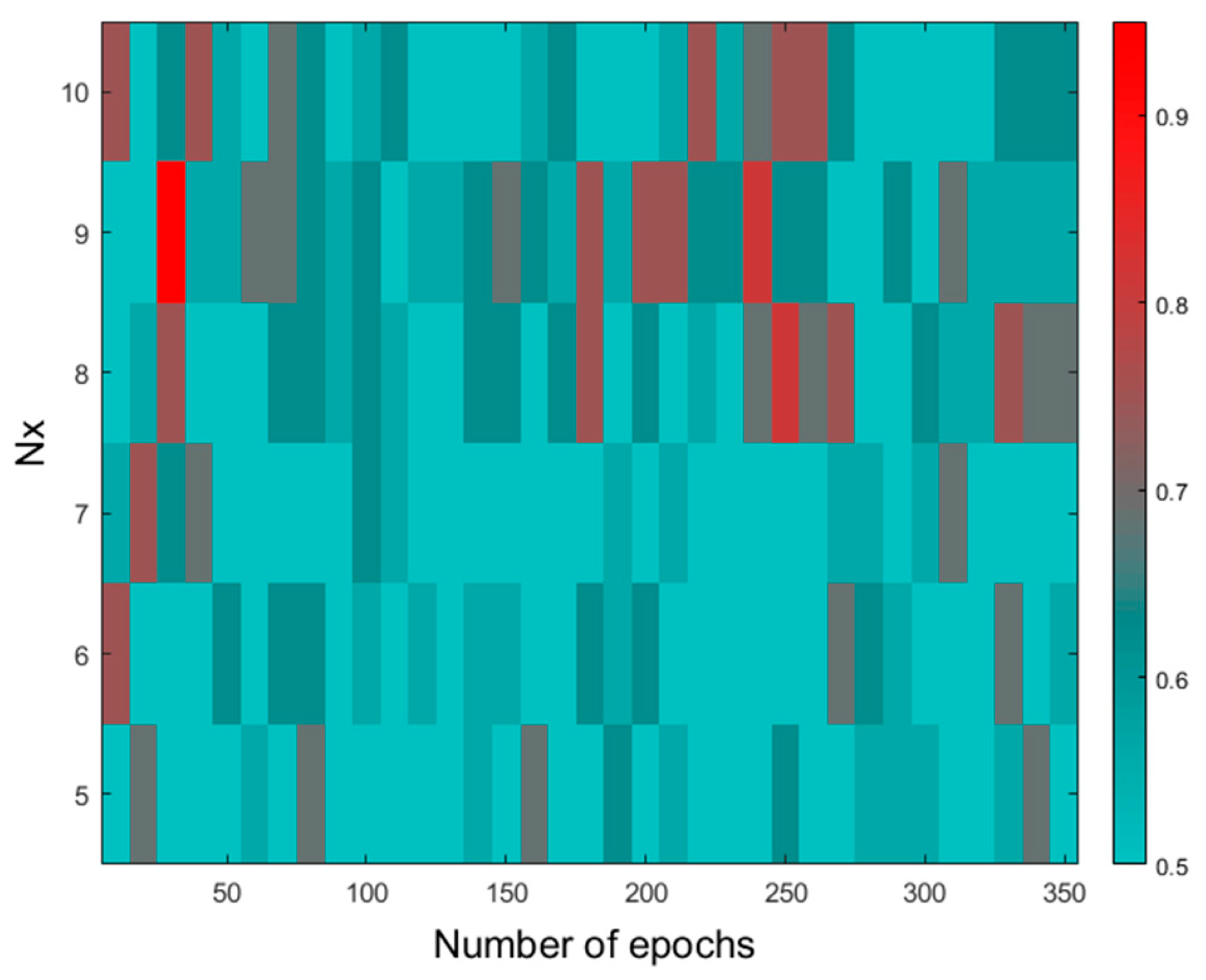
2.2.4. CP-ANN Modeling
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Biological Material
3.2. Spectroscopic Measurements
3.3. Computational Techniques
3.4. Data Treatment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACR-EULAR | American College of Rheumatology and European League Against Rheumatism |
| ATR | Attenuated Total Reflectance |
| CASPAR | Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis |
| CP-ANN | Counter-Propagation Artificial Neural Network |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CV | Cross-validation |
| DA | Discriminant Analysis |
| HC | Healthy control |
| iPLS | interval Partial Least Squares |
| IR | Infrared |
| LV | Latent Variable |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| OA | Overall Accuracy |
| PLS | Partial Least Squares |
| PsA | Psoriatic arthritis |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| RF | Rheumatoid Factor |
| VIP | Variability Importance in Projection |
References
- Merola, J.F.; Espinoza, L.R.; Fleischmann, R. Distinguishing Rheumatoid Arthritis from Psoriatic Arthritis. RMD Open 2018, 4, e000656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J.; Upchurch, K.S. ACR/EULAR 2010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria. Rheumatology 2012, 51, vi5–vi9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.; Gladman, D.; Helliwell, P.; Marchesoni, A.; Mease, P.; Mielants, H. Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis: Development of New Criteria from a Large International Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2665–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callery, E.L.; Rowbottom, A.W. Vibrational Spectroscopy and Multivariate Analysis Techniques in the Clinical Immunology Laboratory: A Review of Current Applications and Requirements for Diagnostic Use. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2022, 57, 411–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyne, S.; Speeckaert, M.M.; Delanghe, J.R. Applications of Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy in the Clinical Laboratory Setting. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 55, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigo, F.; Tozzi, A.; Disler, M.; Gisi, A.; Kavvadias, V.; Kavvadias, T. Vibrational Spectroscopy in Urine Samples as a Medical Tool: Review and Overview on the Current State-of-the-Art. Diagnostics 2022, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staib, A.; Dolenko, B.; Fink, D.J.; Früh, J.; Nikulin, A.E.; Otto, M.; Pessin-Minsley, M.S.; Quarder, O.; Somorjai, R.; Thienel, U.; et al. Disease Pattern Recognition Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Infrared Spectra of Human Serum. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 308, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, C.S.; Martin, A.A.; Santo, A.M.E.; Andrade, L.E.C.; Pinheiro, M.M.; Cardoso, M.A.G.; Raniero, L. A Rheumatoid Arthritis Study Using Raman Spectroscopy. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2011, 130, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canvin, J.M.G.; Bernatsky, S.; Hitchon, C.A.; Jackson, M.; Sowa, M.G.; Mansfield, J.R.; Eysel, H.H.; Mantsch, H.H.; El-Gabalawy, H.S. Infrared Spectroscopy: Shedding Light on Synovitis in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2003, 42, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokot, I.; Mazurek, S.; Piwowar, A.; Sokolik, R.; Rodak, K.; Kacperczyk, M.; Szostak, R.; Cuprych, P.; Korman, L.; Maria Kratz, E. Comparative Profiling of Serum Biomarkers and ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy for Differential Diagnosis of Patients with Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis—A Pilot Study. Spectrochim. Acta A 2024, 321, 124654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordechai, S.; Shufan, E.; Porat Katz, B.S.; Salman, A. Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Infrared Spectroscopy of Isolated Blood Samples Followed by Multivariate Analyses. Analyst 2017, 142, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, C.G.; Buckley, K.; Blades, M.W.; Turner, R.F.B. Raman Spectroscopy of Blood and Blood Components. Appl. Spectrosc. 2017, 71, 767–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movasaghi, Z.; Rehman, S.; Rehman, I.U. Raman Spectroscopy of Biological Tissues. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2007, 42, 493–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichardo-Molina, J.L.; Frausto-Reyes, C.; Barbosa-García, O.; Huerta-Franco, R.; González-Trujillo, J.L.; Ramírez-Alvarado, C.A.; Gutiérrez-Juárez, G.; Medina-Gutiérrez, C. Raman Spectroscopy and Multivariate Analysis of Serum Samples from Breast Cancer Patients. Lasers Med. Sci. 2007, 22, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, N.; Kendall, C.; Smith, J.; Crow, P.; Barr, H. Raman Spectroscopy for Identification of Epithelial Cancers. Faraday Discuss. 2004, 126, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; McWilliams, A.; Lui, H.; McLean, D.I.; Lam, S.; Zeng, H. Near-infrared Raman Spectroscopy for Optical Diagnosis of Lung Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 107, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notingher, I. Raman Spectroscopy Cell-Based Biosensors. Sensors 2007, 7, 1343–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faoláin, E.Ó.; Hunter, M.B.; Byrne, J.M.; Kelehan, P.; McNamara, M.; Byrne, H.J.; Lyng, F.M. A Study Examining the Effects of Tissue Processing on Human Tissue Sections Using Vibrational Spectroscopy. Vib. Spectrosc. 2005, 38, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.W.; Taylor, D.S.; Zwerdling, T.; Lane, S.M.; Ihara, K.; Huser, T. Micro-Raman Spectroscopy Detects Individual Neoplastic and Normal Hematopoietic Cells. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigurdsson, S.; Philipsen, P.A.; Hansen, L.K.; Larsen, J.; Gniadecka, M.; Wulf, H.C. Detection of Skin Cancer by Classification of Raman Spectra. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parachalil, D.R.; Brankin, B.; McIntyre, J.; Byrne, H.J. Raman spectroscopic analysis of high molecular weight proteins in solution—Considerations for sample analysis and data pre-processing. Analyst 2018, 143, 5987–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, J.; Nishimoto, N.; Yasuda, T.; Takeshita, H. Discrimination Between Infant and Adult Bloodstains Using Micro-Raman Spectroscopy: A Preliminary Study. J. Forensic Sci. 2019, 64, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westad, F.; Schmidt, A.; Kermit, M. Incorporating Chemical Band-Assignment in near Infrared Spectroscopy Regression Models. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2008, 16, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwanninger, M.; Rodrigues, J.C.; Fackler, K. A Review of Band Assignments in near Infrared Spectra of Wood and Wood Components. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2011, 19, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, K.; Yamada, K.; Tsenkova, R.; Wang, Y.; Ozaki, Y. Near-Infrared Spectra of Serum Albumin and γ-Globulin and Determination of Their Concentrations in Phosphate Buffer Solutions by Partial Least Squares Regression. Vib. Spectrosc. 1998, 18, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, Y.; Šašić, S.; Jiang, J.H. How Can We Unravel Complicated near Infrared Spectra?—Recent Progress in Spectral Analysis Methods for Resolution Enhancement and Band Assignments in the near Infrared Region. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2001, 9, 63–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourant, P.; Baeten, V.; Morales, M.T.; Meurens, M.; Aparicio, R. Oil and Fat Classification by Selected Bands of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2000, 54, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O.; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punzi, L.; Poswiadek, M.; Oliviero, F.; Lonigro, A.; Modesti, V.; Ramonda, R.; Todesco, S. Laboratory findings in psoriatic arthritis. Reumatismo 2011, 59, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olumuyiwa-Akeredolu, O.O.; Pretorius, E. Platelet and Red Blood Cell Interactions and Their Role in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingegnoli, F.; Castelli, R.; Gualtierotti, R. Rheumatoid Factors: Clinical Applications. Dis. Markers 2013, 35, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratz, E.M.; Kacperczyk, M.; Kokot, I.; Piwowar, A.; Konopska, B.; Sokolik, R.; Korman, L. Glycosylation Pattern of Serum Clusterin in Psoriatic Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis—The Search for New Diagnostic Glycomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geneva-Popova, M.; Popova-Belova, S.; Popova, V.; Chompalov, K.; Batalov, A. Assessment of Serum and Synovial Fluid MMP-3 and MPO as Biomarkers for Psoriatic Arthritis and Their Relation to Disease Activity Indices. Rheumatol. Int. 2022, 42, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, V.; Sandhu, A.; Gupta, N.; Dhawan, V.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, A. Low Serum Levels of Myeloid Progenitor Inhibitory Factor-1 Predict Good Response to Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis. ISRN Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 460469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haringman, J.J.; Smeets, T.J.M.; Reinders-Blankert, P.; Tak, P.P. Chemokine and Chemokine Receptor Expression in Paired Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells and Synovial Tissue of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis, and Reactive Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, E.; Bloom, G.D. Cyclic Nucleotide Involvement in Histamine Release from Mast Cells—A Reevaluation. Life Sci. 1982, 30, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Shen, Y.; Jin, K.; Qiu, J.; Hu, B.; Jadhav, R.R.; Sheth, K.; Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Arachidonic Acid-Regulated Calcium Signaling in T Cells from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Promotes Synovial Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wei, X.; Ma, G.; Ding, J.; Lu, C.; Zhou, R.; Hu, W. Immunomodulatory Functions of TRPM7 and Its Implications in Autoimmune Diseases. Immunology 2022, 165, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.C.; Liong, C.-Y.; Jemain, A.A. Partial Least Squares-Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA) for Classification of High-Dimensional (HD) Data: A Review of Contemporary Practice Strategies and Knowledge Gaps. Analyst 2018, 143, 3526–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Sjöström, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-Regression: A Basic Tool of Chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupan, J. Neural Networks with Counter-Propagation Learning Strategy Used for Modelling. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1995, 27, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupan, J.; Novič, M.; Ruisánchez, I. Kohonen and Counterpropagation Artificial Neural Networks in Analytical Chemistry. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1997, 38, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharwat, A. Classification Assessment Methods. Appl. Comput. Inform. 2021, 17, 168–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.J.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Lister, S.J. Standard Normal Variate Transformation and De-trending of Near-Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Spectra. Appl. Spectrosc. 1989, 43, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotelling, H. The generalization of Student’s ratio. Ann. Math. Stat. 1931, 2, 360–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saptoro, A.; Tadé, M.O.; Vuthaluru, H. A Modified Kennard-Stone Algorithm for Optimal Division of Data for Developing Artificial Neural Network Models. Chem. Prod. Process Model. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Johansson, A.; Cochi, M. PLS—Partial Least Squares Projections to Latent Structures; ESCOM Science Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 523–550. [Google Scholar]
- Nørgaard, L.; Saudland, A.; Wagner, J.; Nielsen, J.P.; Munck, L.; Engelsen, S.B. Interval Partial Least-Squares Regression (iPLS): A Comparative Chemometric Study with an Example from Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2000, 54, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, N.M.; Rajkó, R. How to Avoid Over-Fitting in Multivariate Calibration—The Conventional Validation Approach and an Alternative. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 595, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
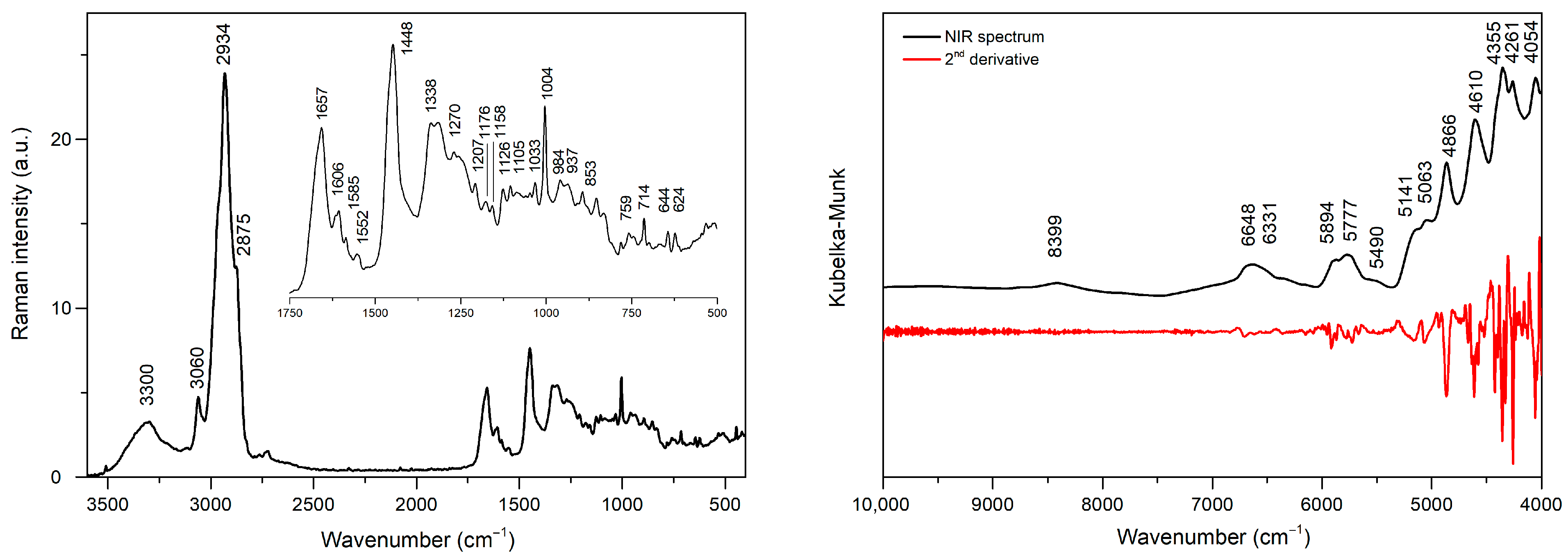

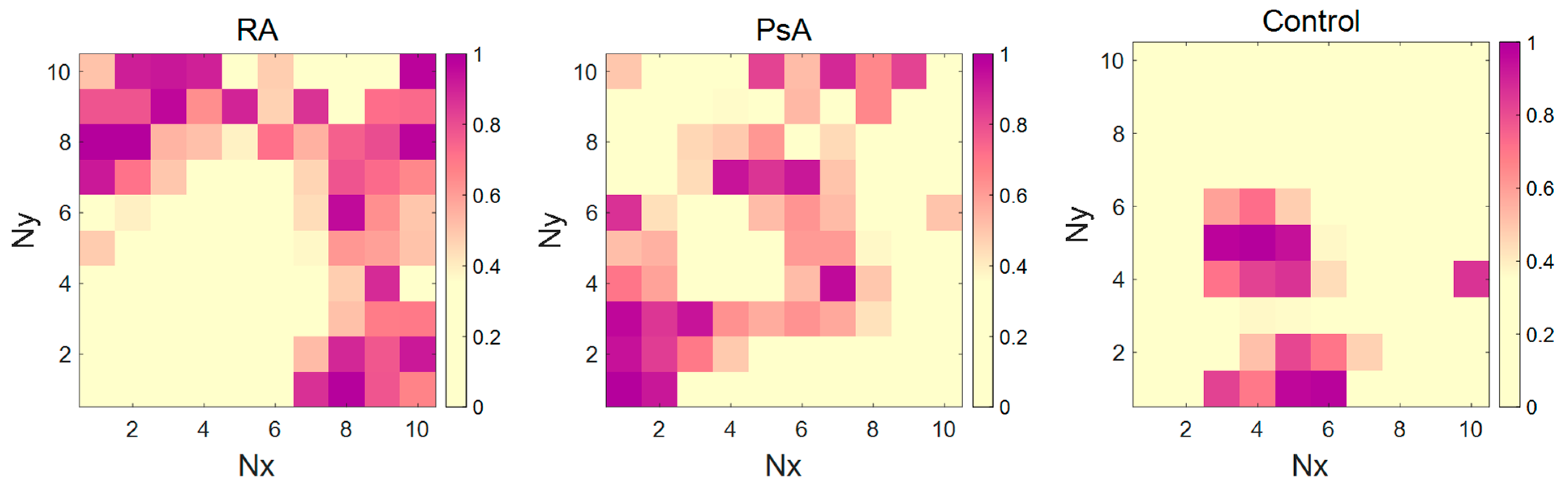
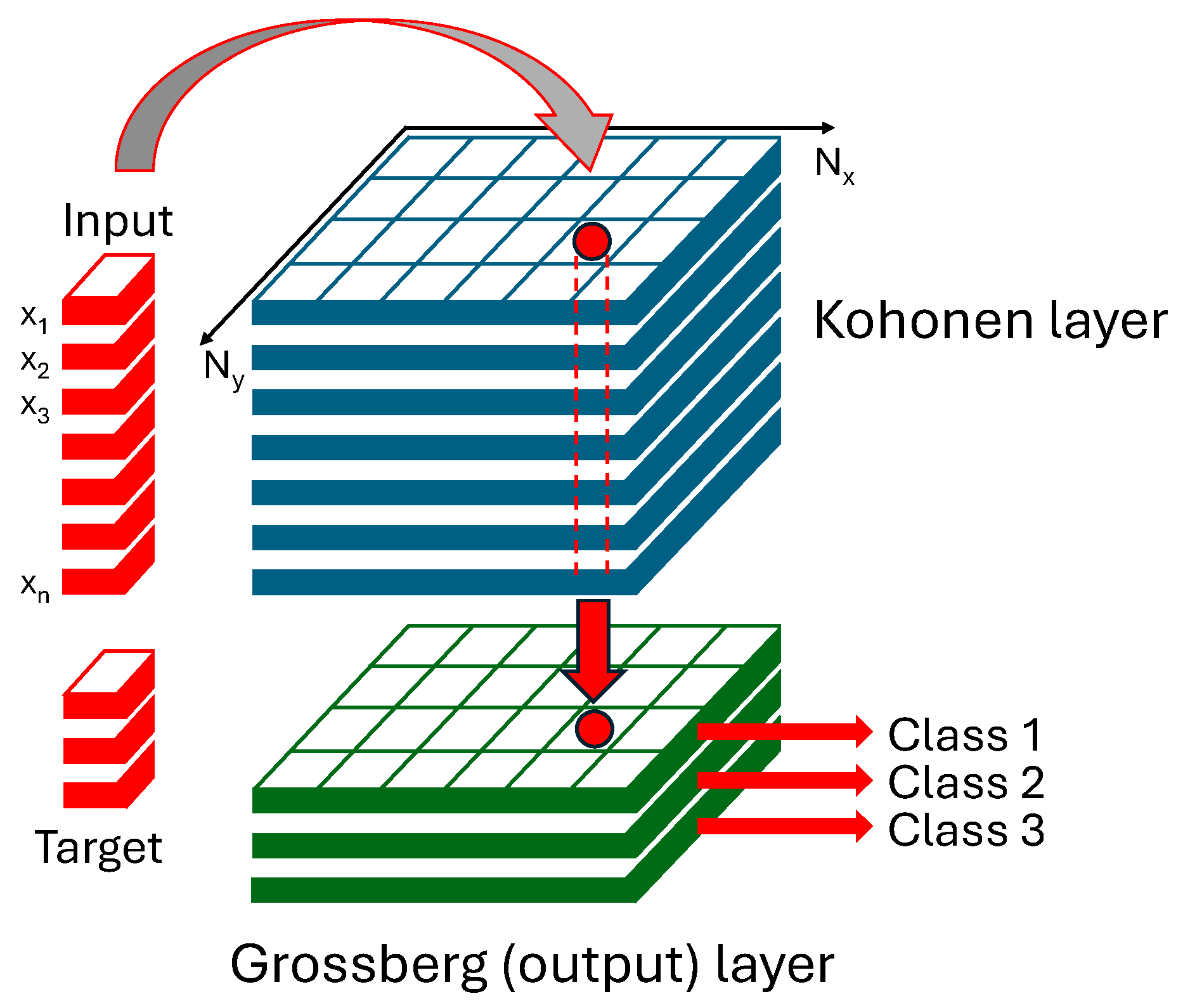
| Position [cm−1] | Modes | Molecules | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3300 | ν(N-H), ν(O-H) | [11] | |
| 3060 | aromatic ν(C-H) | [12] | |
| 2969 | νas(C-H) | methyl groups | [13] |
| 2932 | νas(C-H) | methylene groups | [13] |
| 2870 | νs(C-H) | methyl groups | [13] |
| 2853 | νs(C-H) | methylene groups | [13] |
| 1657 | amide I band ν(C=O) | proteins | [14,15,16] |
| 1606 | ν(C=C) | tyrosine, phenylalanine | [15,16,17] |
| 1585 | ν(C=C) | [18] | |
| 1552 | ν(C=C) | tryptophan | [16] |
| 1448 | δ(CH2) | phospholipids | [16] |
| 1338 | DNA purine bases | [14,15,19] | |
| 1270 | amide III band ν(C-N) | proteins | [15,20] |
| 1207 | ν(C-C6H5) | tryptophan, phenylalanine | [15] |
| 1176 | δ(C-H) | tyrosine | [16] |
| 1158 | ν(C-N), ν(C-C) | proteins | [15,16,17] |
| 1126 | νs (C-N) | proteins | [15,17] |
| 1105 | ν(C-N) | proteins | [21] |
| 1033 | C−H in-plane | phenylalanine | [22] |
| 1004 | benzene ring breathing mode | phenylalanine | [14,16,19] |
| 937 | ν(C-C) in α-helix structure | proteins | [14,16,17] |
| 894 | ν(C-C) backbone | [14,15,16,17] | |
| 853 | ring breathing mode | tyrosine | [19] |
| 759 | ring breathing mode | tryptophan | [15,17,19] |
| 714 | polysaccharides | [15,17] | |
| 644 | C-C twisting | tyrosine | [14] |
| 624 | C-C twisting | phenylalanine | [15,17] |
| Position [cm−1] | Position [nm] | Band Assignment | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8399 | 1191 | 2nd overtone ν(C-H) | [23,24] |
| 6648 | 1504 | 1st overtone ν(O-H), ν(N-H) | [24,25,26] |
| 6331 | 1580 | 1st overtone ν(N-H) | [25] |
| 5893 | 1697 | 1st overtone νas(C-H) | [25] |
| 5777 | 1731 | 1st overtone νs(C-H) | [25,26] |
| 5141 | 1945 | combinatorial ν(O-H) | [23,24] |
| 5063 | 1975 | combinational ν(O-H) | [24] |
| 4866 | 2055 | combinational ν(N-H) | [26] |
| 4610 | 2169 | combinational ν(N-H) | [26] |
| 4355 | 2296 | combinational ν(C-H) | [26] |
| 4261 | 2347 | combinational ν(C-H) | [26,27] |
| 4054 | 2467 | combinational ν(C-H) | [27] |
| Parameter | Unit | Description | RA | PsA | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESR | mm/h | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate | 2.0–87.0 | 2.0–64.0 | 2.0–24.0 |
| RBC | mln/mm3 | Red blood cells | 3.7–5.0 | 3.9–5.4 | 4.0–5.6 |
| Ca2+ | mg/dL | Calcium ions | 6.9–10.2 | 8.9–10.4 | 8.8–9.9 |
| MMP-3 | ng/mL | matrix metalloproteinase-3 | 5.0–64.9 | 7.1–48.9 | 5.6–19.0 |
| TIMP-1 | pg/mL | Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase | 141.0–340.2 | 127.8–275.7 | 65.3–175.1 |
| RF | IU/mL | Rheumatoid factor | 1.0–413.2 | 1.5–194.6 | 0.7–54.5 |
| MPIF-1 | pg/mL | Myeloid progenitor inhibitory factor 1 | 2.0–260.3 | 2.0–219.2 | 2.0–113.8 |
| HCC-4 | pg/mL | Liver-expressed chemokine | 80.8–2204.1 | 174.3–1236.9 | 407.5–986.8 |
| Method | Parameter | Data Type (Number of Variables) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raman Spectra | NIR Spectra | Biochemical Parameters + Raman Spectra | Biochemical Parameters + NIR Spectra | ||
| (225) | (200) | (106) | (71) | ||
| LVs | 6 | 8 | 7 | 4 | |
| OACAL (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| PLS-DA | OACV (%) | 72.7 | 79.1 | 90.9 | 88.6 |
| OATEST (%) | 87.5 | 87.5 | 93.8 | 93.8 | |
| architecture | TRI/0.8/9 × 9/30 * | TRI/0.8/9 × 9/100 | TRI/0.5/10 × 10/140 | TRI/0.3/8 × 8/270 | |
| OACAL (%) | 93.2 | 90.7 | 97.7 | 95.4 | |
| CP-ANN | OACV (%) | 93.2 | 90.7 | 97.7 | 95.4 |
| OATEST (%) | 93.8 | 81.3 | 87.5 | 87.5 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuprych, P.; Kokot, I.; Szostak, R.; Kratz, E.M.; Mazurek, S. Discrimination of Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis Based on Raman and NIR Spectra Using Machine-Learning Algorithms. Molecules 2025, 30, 4513. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234513
Cuprych P, Kokot I, Szostak R, Kratz EM, Mazurek S. Discrimination of Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis Based on Raman and NIR Spectra Using Machine-Learning Algorithms. Molecules. 2025; 30(23):4513. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234513
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuprych, Przemysław, Izabela Kokot, Roman Szostak, Ewa Maria Kratz, and Sylwester Mazurek. 2025. "Discrimination of Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis Based on Raman and NIR Spectra Using Machine-Learning Algorithms" Molecules 30, no. 23: 4513. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234513
APA StyleCuprych, P., Kokot, I., Szostak, R., Kratz, E. M., & Mazurek, S. (2025). Discrimination of Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis Based on Raman and NIR Spectra Using Machine-Learning Algorithms. Molecules, 30(23), 4513. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234513







