An Insight on Ellagic Acid Formulations for the Management of Skin Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Ellagic Acid
2.1. Extraction Techniques for Ellagic Acid from Natural Sources and Detection Methods
2.2. Chemistry
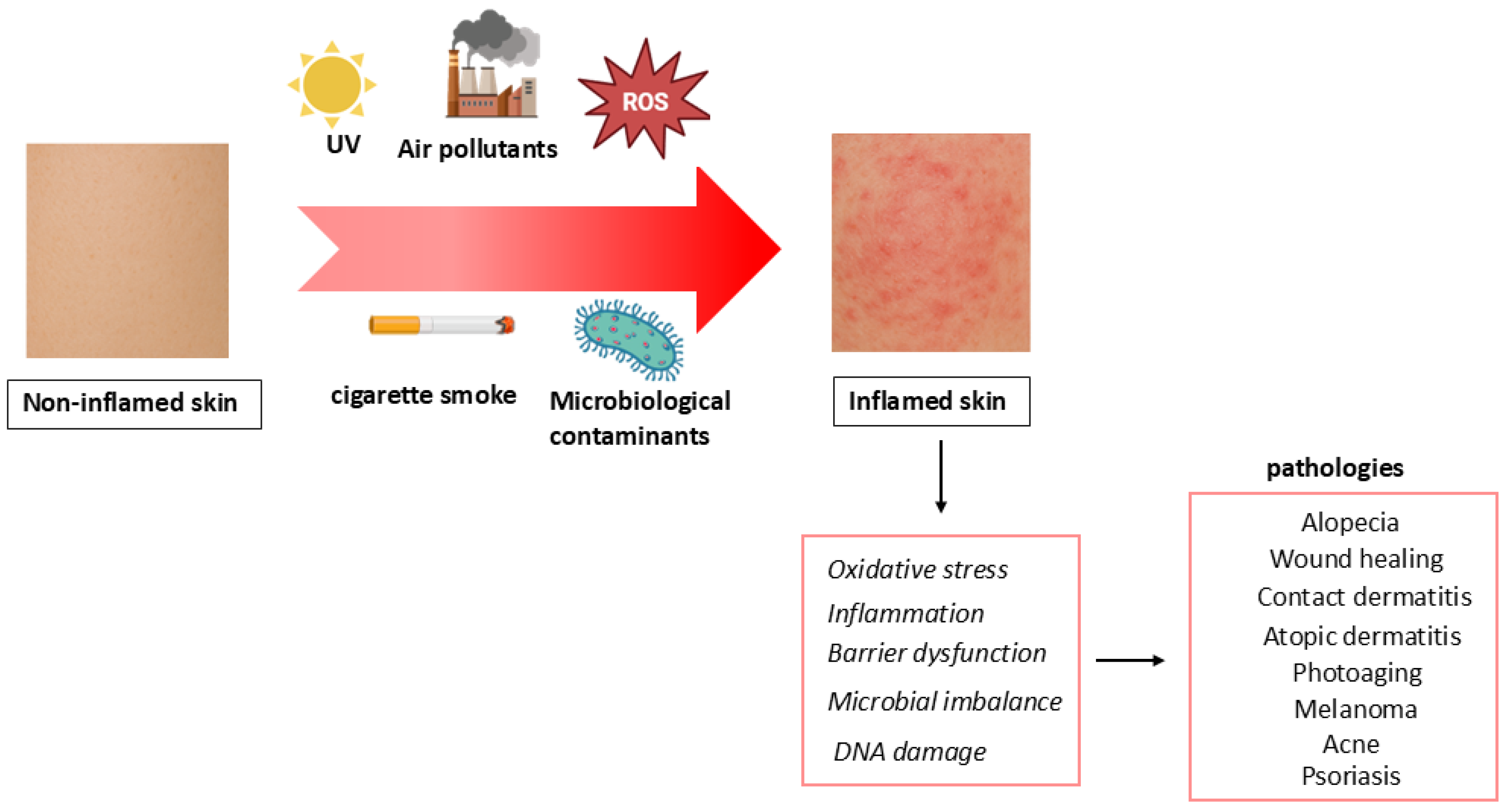
3. EA and Skin
3.1. Anti-Aging and Photoprotection Activity
3.2. Wound Healing and Anti-Fibrotic Activity
3.3. Melanoma and Hyperpigmentation
3.4. Acne
3.5. Psoriasis
3.6. Androgenic Alopecia
3.7. Antifungal Infections
3.8. Potential Risks Associated with the Topical Use of EA
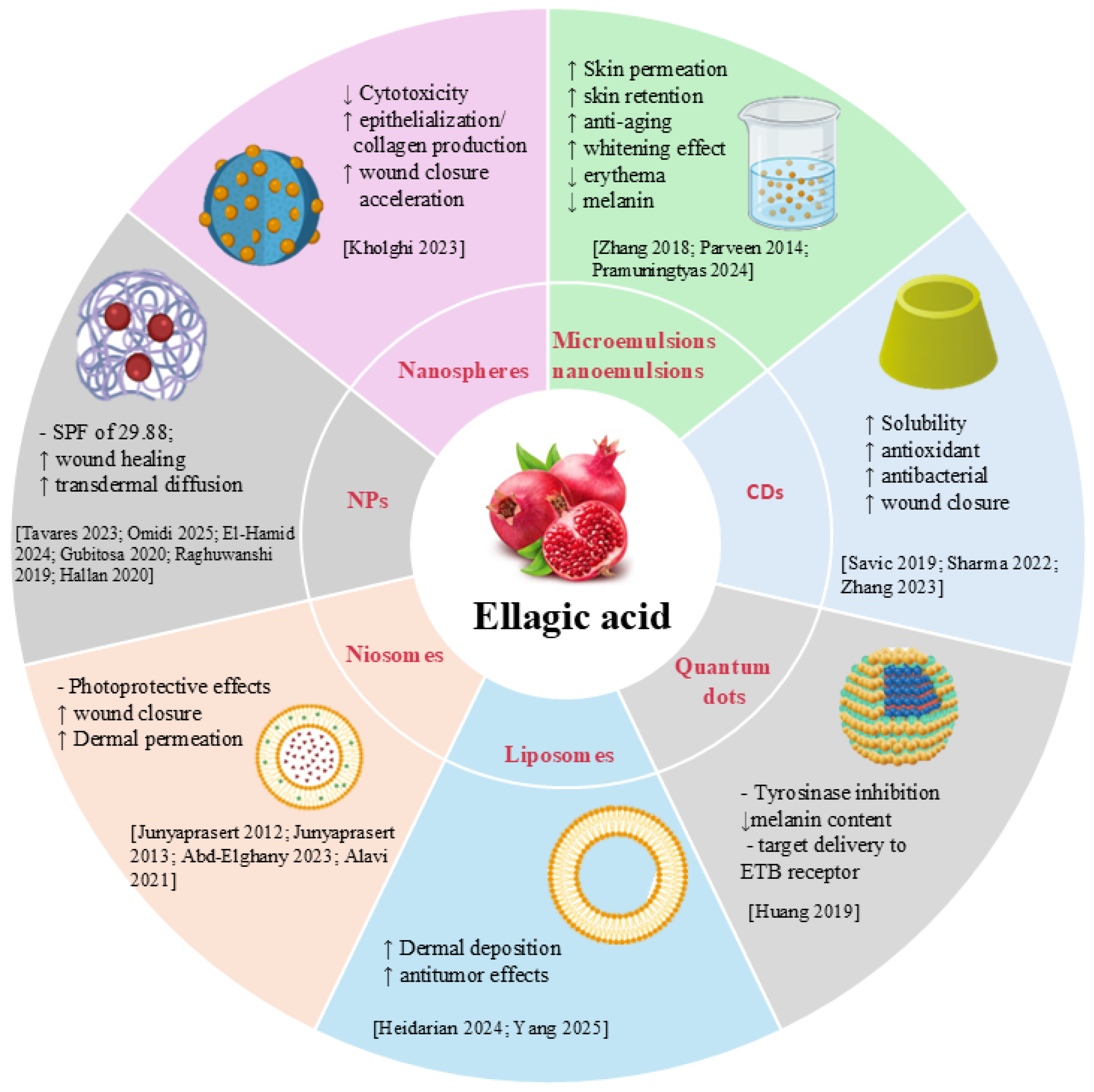
4. Nanotechnology-Based Delivery Systems for Ellagic Acid in Skin Disorders
4.1. Nanoemulsions and Microemulsions
4.2. Liposomes, Niosomes, and Extracellular Vesicles
4.3. Nanoparticles, Nanospheres, and Quantum Dots
4.4. Ciclodextrins
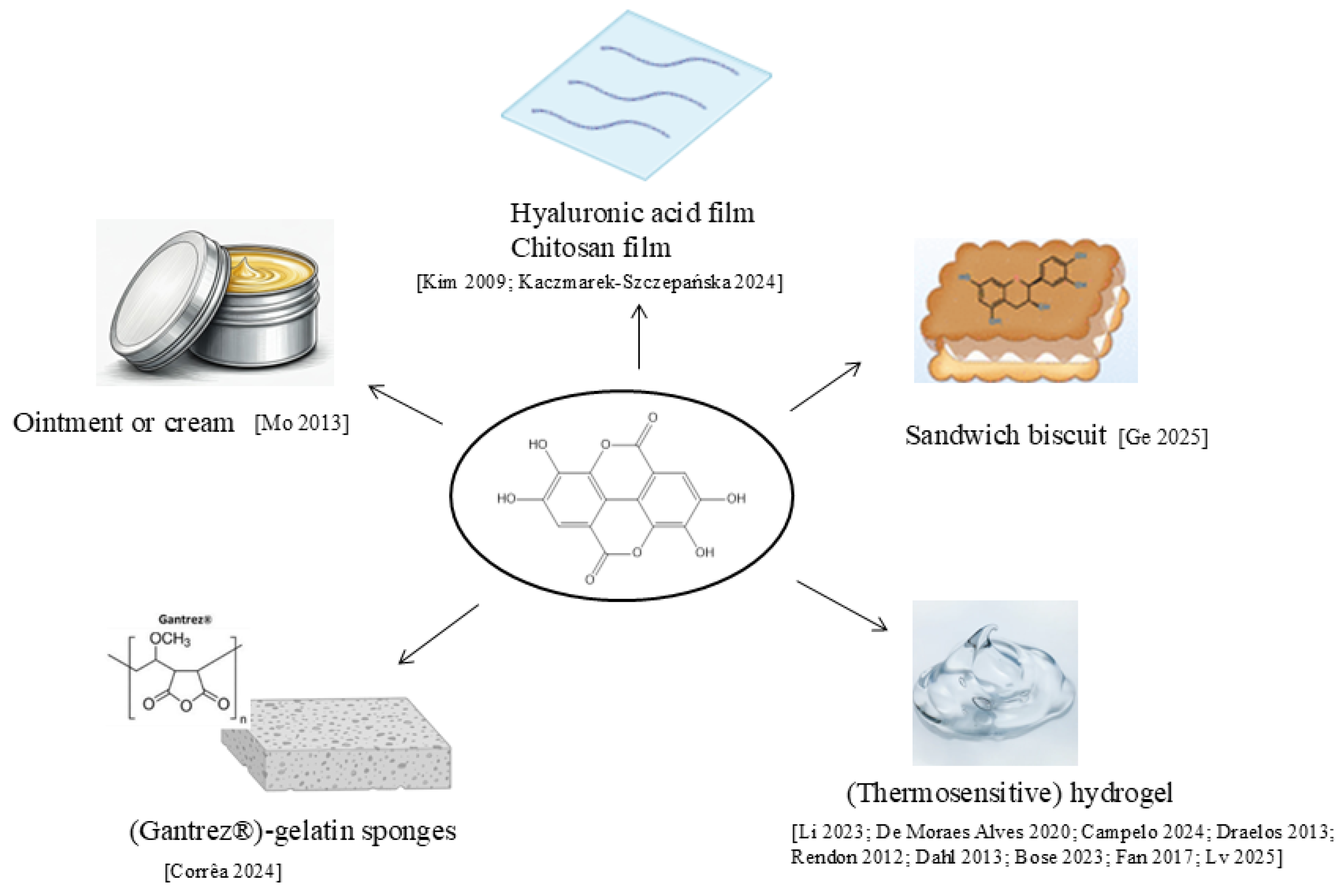
4.5. Other Formulations
4.6. Comparative Evaluation and Challenges
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrara, F.; Pambianchi, E.; Woodby, B.; Messano, N.; Therrien, J.P.; Pecorelli, A.; Canella, R.; Valacchi, G. Evaluating the Effect of Ozone in UV Induced Skin Damage. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 338, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valacchi, G.; Sticozzi, C.; Pecorelli, A.; Cervellati, F.; Cervellati, C.; Maioli, E. Cutaneous Responses to Environmental Stressors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1271, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Ye, D.; Qian, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; Ying, J.; Wang, M.; Lin, H.; Guo, J.; Sun, X.; et al. Long-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and the Incidence of Systemic Lupus erythematosus. Chemosphere 2025, 370, 143974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, W. Air Pollution and Skin Disorders. Int. J. Womens Dermatol. 2020, 7, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkhoff, I.M.; Drasler, B.; Karakocak, B.B.; Petri-Fink, A.; Valacchi, G.; Eeman, M.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Impact of Airborne Particulate Matter on Skin: A Systematic Review from Epidemiology to In Vitro Studies. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Li, Z.; Su, J. Air Pollution and Skin Diseases: A Comprehensive Evaluation of the Associated Mechanism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holme, J.A.; Vondráček, J.; Machala, M.; Lagadic-Gossmann, D.; Vogel, C.F.A.; Le Ferrec, E.; Sparfel, L.; Øvrevik, J. Lung Cancer Associated with Combustion Particles and Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5)—The Roles of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR). Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 216, 115801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, J.L.; Giner, R.M.; Marín, M.; Recio, M.C. A Pharmacological Update of Ellagic Acid. Planta Medica 2018, 84, 1068–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamba, I.; Lechanteur, A.; Semdé, R.; Evrard, B. Physical Formulation Approaches for Improving Aqueous Solubility and Bioavailability of Ellagic Acid: A Review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 159, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccari, G.; Baldassari, S.; Ailuno, G.; Turrini, F.; Alfei, S.; Caviglioli, G. Formulation Strategies to Improve Oral Bioavailability of Ellagic Acid. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.G.; Neves, M.A.; Antunes, M.D. Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.): A Medicinal Plant with Myriad Biological Properties—A Short Review. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 2836–2847. [Google Scholar]
- Ceci, C.; Graziani, G.; Faraoni, I.; Cacciotti, I. Nanotechnology Strategies to Improve Ellagic Acid Bioavailability: From Natural or Semisynthetic Derivatives to Nanotechnological Approaches Based on Innovative Carriers. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 382001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hseu, Y.C.; Chou, C.W.; Senthil Kumar, K.J.; Fu, K.T.; Wang, H.M.; Hsu, L.S.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wu, C.R.; Chen, S.C.; Yang, H.L. Ellagic Acid Protects Human Keratinocyte (HaCaT) Cells Against UVA-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis Through the Upregulation of the HO-1 and Nrf-2 Antioxidant Genes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Määttä-Riihinen, K.R.; Kamal-Eldin, A.; Törrönen, A.R. Identification and Quantification of Phenolic Compounds in Berries of Fragaria and Rubus Species (Family Rosaceae). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6178–6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.J.; Edwards, D.; Pun, S.; Chaliha, M.; Sultanbawa, Y. Profiling Ellagic Acid Content: The Importance of Form and Ascorbic Acid Levels. Food Res. Int. 2014, 66, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, L.; Ou, B. Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Content of Oregon Caneberries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3495–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häkkinen, S.H.; Kärenlampi, S.O.; Mykkänen, H.M.; Heinonen, I.M.; Törrönen, A.R. Ellagic Acid Content in Berries: Influence of Domestic Processing and Storage. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2000, 212, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, Y.Y.; Barlow, P.J. Quantification of Gallic Acid and Ellagic Acid from Longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) Seed and Mango (Mangifera indica L.) Kernel and Their Effects on Antioxidant Activity. Food Chem. 2006, 97, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Talcott, S.T. Fruit Maturity and Juice Extraction Influences Ellagic Acid Derivatives and Other Antioxidant Polyphenolics in Muscadine Grapes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 52, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansky, E.P. Beware of Pomegranates Bearing 40% Ellagic Acid. J. Med. Food 2006, 9, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmagara, A.; Krzyszczak, A.; Sadok, I.; Karczmarz, K.; Staniszewska, M.M.; Stefaniak, E.A. Determination of Ellagic Acid in Rose Matrix by Spectrofluorimetry. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 78, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, E.M.; Krupnick, A.S.; Heur, Y.H.; Blinzler, J.A.; Nims, R.W.; Stoner, G.D. Extraction, Stability, and Quantitation of Ellagic Acid in Various Fruits and Nuts. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1989, 2, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koponen, J.M.; Happonen, A.M.; Mattila, P.H.; Törrönen, A.R. Contents of Anthocyanins and Ellagitannins in Selected Foods Consumed in Finland. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, W.N.L.; da Silva Sauthier, M.C.; dos Santos, A.M.P.; de Andrade Santana, D.; Almeida Azevedo, R.S.; da Cruz Caldas, J. Simultaneous Determination of 13 Phenolic Bioactive Compounds in Guava (Psidium guajava L.) by HPLC-PAD with Evaluation Using PCA and Neural Network Analysis (NNA). Microchem. J. 2017, 133, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.Y.; Chan, C.L.; Yang, Q.Q.; Li, H.B.; Zhang, D.; Ge, Y.Y.; Gunaratne, A.; Ge, J.; Corke, H. Bioactive compounds and beneficial functions of sprouted grains. In Sprouted Grains: Nutritional Value, Production, and Applications; Woodhead Publishing and AACC International Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 191–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kähkönen, M.P.; Hopia, A.I.; Heinonen, M. Berry Phenolics and Their Antioxidant Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4076–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Pratibha; Neeraj; Sami, R.; Khojah, E.; Aljahani, A.H.; Al-Mushhin, A.A.M. Effects of drying methods and solvent extraction on quantification of major bioactive compounds in pomegranate peel waste using HPLC. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, A.; Campo, M.; Pinelli, P. HPLC/DAD/ESI-MS Analyses and Anti-Radical Activity of Hydrolyzable Tannins from Different Vegetal Species. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, L.M.; Porte, A.; de Oliveira Godoy, R.L.; da Costa Souza, M.; Pacheco, S.; de Araujo Santiago, M.C.P.; Gouvêa, A.C.M.S.; da Silva de Mattos do Nascimento, L.; Borguini, R.G. Chemical Characterization of Myrciaria floribunda (H. West Ex Willd) Fruit. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.S.A.; Perez, J.L.; Lombardini, L.; Cornacchia, R.; Cisneros-Zevallosb, L.; Braforda, J. Phenolic Compounds and Fatty Acid Composition of Organic and Conventional Grown Pecan Kernels. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 2207–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glabasnia, A.; Hofmann, T. Sensory-Directed Identification of Taste-Active Ellagitannins in American (Quercus alba L.) and European Oak Wood (Quercus robur L.) and Quantitative Analysis in Bourbon Whiskey and Oak-Matured Red Wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3380–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafsa, J.; Hammi, K.M.; Ben Khedher, M.R.; Smach, M.A.; Charfeddine, B.; Limem, K.; Majdoub, H. Inhibition of Protein Glycation, Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Activities of Carpobrotus edulis Extracts. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.A.O.; Freire, C.S.R.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Neto, C.P. Characterization of Phenolic Components in Polar Extracts of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Bark by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 9386–9393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, E.; Ghorbani Nohooji, M.; Habibi, M.; Ebrahimi, M.; Mehrafarin, A.; Khalighi-Sigaroodi, F. Antioxidant Potential Assessment of Phenolic and Flavonoid Rich Fractions of Clematis orientalis and Clematis ispahanica (Ranunculaceae). Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1991–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, G.S.; Marques, A.S.F.; Machado, M.T.C.; Silva, V.M.; Hubinger, M.D. Determination of Anthocyanins and Non-Anthocyanin Polyphenols by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography/Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (UPLC/ESI-MS) in Jussara (Euterpe edulis) Extracts. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2135–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.A.O.; Vilela, C.; Domingues, R.M.A.; Oliveira, C.S.D.; Villaverde, J.J.; Freire, C.S.R.; Neto, C.P.; Silvestre, A.J.D. Secondary Metabolites from Eucalyptus grandis Wood Cultivated in Portugal, Brazil and South Africa. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 95, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajera, H.P.; Gevariya, S.N.; Hirpara, D.G.; Patel, S.V.; Golakiya, B.A. Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Functionality Associated with Phenolic Constituents from Fruit Parts of Indigenous Black Jamun (Syzygium cumini L.) Landraces. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3180–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.M.; Romanini, E.B.; Silva, E.; Pilau, E.J.; da Costa, S.C.; Madrona, G.S. Camu-Camu Bioactive Compounds Extraction by Ecofriendly Sequential Processes (Ultrasound Assisted Extraction and Reverse Osmosis). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 64, 105017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çam, M.; Hişil, Y. Pressurised Water Extraction of Polyphenols from Pomegranate Peels. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawoosa, S.; Chakradhar, J.V.U.S.; Shafi, H.; Yadav, P.; Tripathi, S.; Fazili, A.A.; Bashir, R.; Ali, T.; Nazir, S.; Raza, S.N.; et al. Analytical Method Development for Ellagic Acid by RP-HPLC: Comparative Solubility and Stress Stability Assessment of Pure Drug and Its Solid Dispersion Formulation. Microchem. J. 2025, 215, 114456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard-Dazeur, C.; Jacolot, P.; Niquet-Léridon, C.; Goethals, L.; Barbezier, N.; Anton, P.M. HPLC-DAD Optimization of Quantification of Vescalagin, Gallic and Ellagic Acid in Chestnut Tannins. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moccia, F.; Liberti, D.; Giovando, S.; Caddeo, C.; Monti, D.M.; Panzella, L.; Napolitano, A. Chestnut Wood Mud as a Source of Ellagic Acid for Dermo-Cosmetic Applications. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Umesh Patel, H.; Akabari, A.H.; Chem, E. Eco-Friendly HPTLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Gallic Acid, Ellagic Acid, and Curcumin Biomarker in Herbal Formulation. Essent. Chem. 2024, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiyal, S.; Laddha, K. Validated High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatographic Method for Quantification of Gallic Acid and Ellagic Acid in Fruits of Terminalia chebula, Phyllanthus emblica, and Quercus infectoria. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, 2200991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Xu, L.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Nong, L.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Cen, S. Serum Metabolomics Based on GC-MS Reveals the Antipyretic Mechanism of Ellagic Acid in a Rat Model. Metabolites 2022, 12, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto Araujo, N.M.; Arruda, H.S.; dos Santos, F.N.; de Morais, D.R.; Pereira, G.A.; Pastore, G.M. LC-MS/MS Screening and Identification of Bioactive Compounds in Leaves, Pulp and Seed from Eugenia calycina Cambess. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Seeram, N.P. Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Time-of-Flight Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Comprehensive Phenolic Characterization of Pomegranate Fruit and Flower Extracts Used as Ingredients in Botanical Dietary Supplements. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 3022–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.V.; Lima, D.L.D.; Evtyugin, D.V.; Esteves, V.I. Development and Application of a Capillary Electrophoresis Method for the Determination of Ellagic Acid in E. globulus Wood and in Filtrates from E. globulus Kraft Pulp. Wood Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spisso, A.; Gomez, F.J.V.; Fernanda Silva, M. Determination of Ellagic Acid by Capillary Electrophoresis in Argentinian Wines. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemetz, R.; Gross, G.G. Enzymology of Gallotannin and Ellagitannin Biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 2001–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landete, J.M. Ellagitannins, Ellagic Acid and Their Derived Metabolites: A Review about Source, Metabolism, Functions and Health. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzourani, C.; Kakouri, E.; Palikaras, K.; Tarantilis, P.A.; Kokotou, M.G. Urolithins and Their Precursors Ellagic Acid and Ellagitannins: Natural Sources, Extraction and Methods for Their Determination. Separations 2024, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, I.; Bhardwaj, V.; Hariharan, S.; Kumar, M.N.V.R. Analytical Methods for Assay of Ellagic Acid and Its Solubility Studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoner, G.D.; Sardo, C.; Apseloff, G.; Mullet, D.; Wargo, W.; Pound, V.; Singh, A.; Sanders, J.; Aziz, R.; Casto, B.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of Anthocyanins and Ellagic Acid in Healthy Volunteers Fed Freeze-Dried Black Raspberries Daily for 7 Days. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadhanam, M.V.; Aqil, F.; Ravoori, S.; Gupta, R.C. Bioavailability of Ellagic Acid/Ellagitannins from Black Raspberry and Pomegranate. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtunik-Kulesza, K.; Niziński, P.; Krajewska, A.; Oniszczuk, T.; Combrzyński, M.; Oniszczuk, A. Therapeutic Potential of Ellagic Acid in Liver Diseases. Molecules 2025, 30, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espín, J.C.; Larrosa, M.; García-Conesa, M.T.; Tomás-Barberán, F. Biological Significance of Urolithins, the Gut Microbial Ellagic Acid-Derived Metabolites: The Evidence So Far. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 270418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liao, R.; Zhang, S.; Weng, H.; Liu, Y.; Tao, T.; Yu, F.; Li, G.; Wu, J. Promising Remedies for Cardiovascular Disease: Natural Polyphenol Ellagic Acid and Its Metabolite Urolithins. Phytomedicine 2023, 116, 154867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.J.; Chung, H.S.; Hwang, H.S. Ellagic Acid Suppresses β-Defensin2 Antimicrobial Peptide and CCL20 Chemokine in Psoriasis-like HaCaT Human Keratinocyte. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2024, 25, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellagic Acid Benefits for Skin|SkinCeuticals. Available online: https://www.skinceuticals.com/ellagic-acid.html (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Bae, J.Y.; Choi, J.S.; Kang, S.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, J.; Kang, Y.H. Dietary Compound Ellagic Acid Alleviates Skin Wrinkle and Inflammation Induced by UV-B Irradiation. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, e182–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lembo, S.; Balato, A.; Di Caprio, R.; Cirillo, T.; Giannini, V.; Gasparri, F.; Monfrecola, G. The Modulatory Effect of Ellagic Acid and Rosmarinic Acid on Ultraviolet-B-Induced Cytokine/Chemokine Gene Expression in Skin Keratinocyte (HaCaT) Cells. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 346793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, C.; Stutts, J.; Clatterbuck, K.; Nosoudi, N. Effect of Ellagic Acid and Retinoic Acid on Collagen and Elastin Production by Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2023, 34, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Du, J.; Zheng, Y.; Fang, Y.; Huang, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Nie, T. Zinc Ions Coordinated Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel Doped with Ellagic Acid for Accelerative Diabetic Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 327, 147372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Gao, X.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Chen, X.; Meng, X.; Yu, J. Ellagic Acid Exerts Anti-Fibrotic Effects on Hypertrophic Scar Fibroblasts via Inhibition of TGF-Β1/Smad2/3 Pathway. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illescas-Montes, R.; González-Acedo, A.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; García-Recio, E.; Ruiz, C.; García-Martínez, O.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J. Modulation of Gene Expression in Human Fibroblasts by Punicalagin and Ellagic Acid: An In Vitro Study. In Molecular Nutrition & Food Research; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025; p. e70237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primarizky, H.; Yuniarti, W.M.; Lukiswanto, B.S. Ellagic Acid Activity in Healing Process of Incision Wound on Male Albino Rats (Rattus norvegicus). KnE Life Sci. 2017, 3, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürsoy, E.N.; Balabanli, K.B.; Tuğcu Demiröz, F.N.; Coşkun Cevher, Ş. The Cumulative Effect of Ellagic Acid and Carnosic Acid Attenuates Oxidative Events During Diabetic Wound Healing: In Different Applications and on Different Days. Turk. J. Biol. 2024, 48, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, T.Y.; Hong, C.H.; An, H.J. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ellagic Acid on Keratinocytes via MAPK and STAT Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, P.; Sun, Y.; Yu, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Ellagic Acid Mediates the Delay of Dermal Fibroblast Senescence via CSNK2A1. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2025, 18, 1971–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Chai, W.M.; Ma, Z.Y.; Deng, W.L.; Wei, Q.M.; Song, S.; Zou, Z.R.; Peng, Y.Y. Antityrosinase Mechanism of Ellagic Acid In Vitro and Its Effect on Mouse Melanoma Cells. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimogaki, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Tamai, H.; Masuda, M. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Ellagic Acid on Melanogenesis Inhibition. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2000, 22, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.D.; Dunn, J.H.; Luo, Y.; Liu, W.; Fujita, M.; Dellavalle, R.P. Ellagic Acid Inhibits Melanoma Growth In Vitro. Dermatol. Rep. 2011, 3, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.H.; Shudo, T.; Yoshida, T.; Sugiyama, Y.; Si, J.Y.; Tsukano, C.; Takemoto, Y.; Kakizuka, A. Ellagic Acid, Extracted from Sanguisorba Officinalis, Induces G1 Arrest by Modulating PTEN Activity in B16F10 Melanoma Cells. Genes Cells 2019, 24, 688–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Chen, J.; Xiang, D.; Lian, X.; Wu, C.; Quan, J. Ellagic Acid Inhibits Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Melanoma via EGFR Pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 2295–2304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K. A Convenient Screening Method to Differentiate Phenolic Skin Whitening Tyrosinase Inhibitors from Leukoderma-Inducing Phenols. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 80, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, K.; Yoshimura, M.; Koga, T.; Arii, M.; Kawasaki, S. Effects of Oral Administration of Ellagic Acid-Rich Pomegranate Extract on Ultraviolet-Induced Pigmentation in the Human Skin. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2006, 52, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertam, I.; Mutlu, B.; Unal, I.; Alper, S.; Kivçak, B.; Ozer, O. Efficiency of Ellagic Acid and Arbutin in Melasma: A Randomized, Prospective, Open-Label Study. J. Dermatol. 2008, 35, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, N.; Hernandez, L.E.; Martin, M.R.; Does, A.V.; Nouri, K. Acne Treatment Review and Future Perspectives. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.C.; Dellavalle, R.P.; Garner, S. Acne Vulgaris. Lancet 2012, 379, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muddathir, A.M.; Yamauchi, K.; Mitsunaga, T. Anti-Acne Activity of Tannin-Related Compounds Isolated from Terminalia laxiflora. J. Wood Sci. 2013, 59, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankar, C.; Maruthupandiyan, S.; Balamurugan, K.; James, P.B.; Krishnan, V.; Pandian, S.K. A Combination of Ellagic Acid and Tetracycline Inhibits Biofilm Formation and the Associated Virulence of Propionibacterium acnes In Vitro and In Vivo. Biofouling 2016, 32, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Ji, H.; Roh, K.B.; Cho, E.; Chajra, H.; Frechet, M.; Park, D.; Jung, E. Anti-Acne Effects of Castanea crenata Bur Extract and Identification of Active Compound. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2022, 65, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, R.G.; Cano, A.; Ortiz, A.; Espina, M.; Prat, J.; Muñoz, M.; Severino, P.; Souto, E.B.; García, M.L.; Pujol, M.; et al. Psoriasis: From Pathogenesis to Pharmacological and Nano-Technological-Based Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulqader, E.H.; Kadhim, H.M. Evaluation of Anti-Psoriatic Effects of Ellagic Acid on Imiquimod Induced Psoriatic-like Dermatitis in Mice. Ann. Trop. Med. Public Health 2021, 24, 24216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, J.N.; Babu, A.N.; Nadendla, R.R.; Lakshmi, J.N.; Babu, A.N.; Nadendla, R.R. Evaluation of Anti-Psoriatic Activity of Selected Phytochemicals on UV-Induced Psoriasis in Mouse Tail Model. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 64, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Fu, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Qu, Q.; Li, K.; Fan, Z.; Hu, Z.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals an Inhibitory Effect of Dihydrotestosterone-Treated 2D- and 3D-Cultured Dermal Papilla Cells on Hair Follicle Growth. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 724310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adil, A.; Godwin, M. The Effectiveness of Treatments for Androgenetic Alopecia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Tang, Q.; Weng, Z.; Zhu, L.; Ding, B. Ellagic Acid Inhibits Dihydrotestosterone-Induced Ferroptosis and Promotes Hair Regeneration by Activating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 330, 118227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, J.; Ortega, Á.; Pérez, J.L.; Garrido, B.; Santeliz, R.; Galbán, N.; Díaz, M.P.; Cano, R.; Cano, G.; Contreras-Velasquez, J.C.; et al. Role of Polyphenols in Dermatological Diseases: Exploring Pharmacotherapeutic Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Guo, X.; Dawuti, G.; Aibai, S. Antifungal Activity of Ellagic Acid In Vitro and In Vivo. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenção Brighenti, F.; Salvador, M.J.; Gontijo, A.V.L.; Delbem, A.C.B.; Delbem, Á.C.B.; Soares, C.P.; De Oliveira, M.A.C.; Girondi, C.M.; Koga-Ito, C.Y. Plant Extracts: Initial Screening, Identification of Bioactive Compounds and Effect Against Candida albicans Biofilms. Future Microbiol. 2017, 12, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejatbakhsh, S.; Ilkhanizadeh-Qomi, M.; Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M.; Jahanshiri, Z. The Effects of Ellagic Acid on Growth and Biofilm Formation of Candida albicans. J. Med. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 8, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossatto, F.C.P.; Tharmalingam, N.; Escobar, I.E.; D’azevedo, P.A.; Zimmer, K.R.; Mylonakis, E. Antifungal Activity of the Phenolic Compounds Ellagic Acid (Ea) and Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (Cape) Against Drug-Resistant Candida auris. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, A.G.G.; Campos, C.D.L.; Pereira-Filho, J.L.; Pereira, A.P.A.; Reis, G.S.A.; Araújo, Á.W.d.M.S.; Monteiro, P.d.M.; Vidal, F.C.B.; Monteiro, S.G.; Figueiredo, I.F.d.S.; et al. Ellagic Acid Potentiates the Inhibitory Effects of Fluconazole Against Candida albicans. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athukuri, B.L.; Neerati, P. Enhanced Oral Bioavailability of Metoprolol with Gallic Acid and Ellagic Acid in Male Wistar Rats: Involvement of CYP2D6 Inhibition. Drug Metab. Pers. Ther. 2016, 31, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumpa-Ngern, P.; Plengsuriyakarn, T.; Mahavorasirikul, W.; Na-Bangchang, K. Potential Inhibitory and Inducing Effects of Triphala Formulation on Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. Trends Sci. 2022, 19, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghizadeh, B.; Mansouri, M.T.; Ghorbanzadeh, B. Ellagic Acid Enhances the Antinociceptive Action of Carbamazepine in the Acetic Acid Writhing Test with Mice. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellagic Acid: Overview, Uses, Side Effects, Precautions, Interactions, Dosing and Reviews. Available online: https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-1074/ellagic-acid#sideeffects (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Arora, P.; Magner, E.T.; Bigliardi, P.L. Honey Flower Dermatitis: Contact Allergy to Ellagic Acid in Melianthus comosus. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 179, 113956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, C.; Landucci, E.; Mazzantini, C.; Castellacci, R.; Bergonzi, M.C. Vitamin D Nanoliposomes to Improve Solubility, Stability, and Uptake Across Intestinal Barrier. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilia, A.R.; Piazzini, V.; Asprea, M.; Risaliti, L.; Vanti, G.; Bergonzi, M.C. Plants Extracts Loaded in Nanocarriers: An Emergent Formulating Approach. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellacci, R.; Sacco, C.; Donato, R.; Salvatici, M.C.; Bilia, A.R.; Bergonzi, M.C. Nanocomposite Gel Containing Usnic Acid: Characterization and evaluation of the Antibacterial Efficacy on Staphylococcus epidermidis. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 671, 125232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaifi, M.Y.; Elbehairi, S.I.; Shati, A.A.; Fahmy, U.A.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Md, S. Ellagic Acid Loaded TPGS Micelles for Enhanced Anticancer Activities in Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 16, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigal-Carballo, S.; Lim, S.; Rodriguez, G.; Vila, A.O.; Krueger, C.G.; Gunasekaran, S.; Reed, J.D. Biopolymer Coating of Soybean Lecithin Liposomes via Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly as Novel Delivery System for Ellagic Acid. J. Funct. Foods 2010, 2, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, A.; Azam, M.; Allemailem, K.S.; Alrumaihi, F.; Almatroudi, A.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Azam, F.; Khan, S.H.; Zofair, S.F.F.; et al. Liposomal Ellagic Acid Alleviates Cyclophosphamide-Induced Toxicity and Eliminates the Systemic Cryptococcus neoformans Infection in Leukopenic Mice. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarian, F.; Alavizadeh, S.H.; Kalantari, M.R.; Hoseini, S.J.; Farshchi, H.K.; Jaafari, M.R.; Doagooyan, M.; Bemidinezhad, A.; Kesharwani, P.; Sahebkar, A.; et al. Ellagic Acid Nanoliposomes Potentiate Therapeutic Effects of PEGylated Liposomal Doxorubicin in Melanoma: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 93, 105396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, W.d.S.; Pena, G.R.; Martin-Pastor, M.; de Sousa, F.F.O. Design and Characterization of Ellagic Acid-Loaded Zein Nanoparticles and Their Effect on the Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 341, 116915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Thanki, A.; Kapoor, D.U.; Prajapati, B.G. QbD Decorated Ellagic Acid Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles: Factors Influencing Desolvation Method and Preliminary Evaluations. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2024, 40, 8611–8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Ghosh, S.; Kumar, P.; Basu, B.; Nagpal, K. Ellagic Acid-Loaded, Tween 80-Coated, Chitosan Nanoparticles as a Promising Therapeutic Approach Against Breast Cancer: In-Vitro and In-Vivo Study. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulmozhi, V.; Pandian, K.; Mirunalini, S. Ellagic Acid Encapsulated Chitosan Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery System in Human Oral Cancer Cell Line (KB). Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 110, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ying, X.; Peng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Yao, X.; Chen, W. Ellagic Acid Nanoemulsion in Cosmetics: The Preparation and Evaluation of a New Nanoemulsion Method as a Whitening and Antiaging Agent. IEEE Nanotechnol. Mag. 2018, 12, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, R.; Akhtar, N.; Mahmood, T. Topical Microemulsion Containing Punica granatum Extract: Its Control over Skin Erythema and Melanin in Healthy Asian Subjects. Postepy. Dermatol. Alergol. 2014, 31, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramuningtyas, R.; Prakoeswa, F.R.S.; Wahyuni, S. Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Peel-Based Topical Nanoemulgel for Skin Infection: Formulation and Antibacterial Activity Against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Med. Plants 2024, 23, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junyaprasert, V.B.; Singhsa, P.; Suksiriworapong, J.; Chantasart, D. Physicochemical Properties and Skin Permeation of Span 60/Tween 60 Niosomes of Ellagic Acid. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junyaprasert, V.B.; Singhsa, P.; Jintapattanakit, A. Influence of Chemical Penetration Enhancers on Skin Permeability of Ellagic Acid-Loaded Niosomes. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 8, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elghany, A.A.; Mohamad, E.A. Chitosan-Coated Niosomes Loaded with Ellagic Acid Present Antiaging Activity in a Skin Cell Line. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 16620–16629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Miao, K.; Chen, Z.; Meng, Y.; Xiang, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Shi, Z. Oligomeric Hyaluronic Acid-Modified Liposomes Effectively Improved Skin Permeability and Anti-Ageing Activity of Ellagic Acid. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 27183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, S.S.; Razavi, S.H.; Khodaiyan, F.; Cardia, M.C.; Lai, F.; Valenti, D.; Pini, E.; Rosa, A.; Nieddu, M.; Fadda, A.M. Proniosomal Formulation Encapsulating Pomegranate Peel Extract for Nutraceutical Applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 21, 2907–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, W.d.S.; Pastor, M.M.; Pérez, L.; Morán, M.d.C.; de Sousa, F.F.O. Skin Repairing Potential of Ellagic Acid-Loaded Zein Nanoparticles: Chemical and Biopharmaceutical Characterization, Enzymatic Inhibition and Cytotoxicity over Keratinocytes. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 384, 122198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidi, M.; Saeedi, M.; Zahiri, M.A.; Azimi, S.; Mohammadian, E.; Mohammad, S.; Hashemi, H. Green Arbutin-Chitosan Nanoparticles Gel as an Eco-Friendly and Promising Product for Skin Lightening: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessment. Nanomed. J. 2025, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hamid, M.I.A.; Ibrahim, D.; Abdelfattah-Hassan, A.; Mohammed, O.B.; Pet, I.; Khalil, S.S.; El-Badry, S.M.; Metwally, A.S.; Azouz, A.A.; Elnegiry, A.A.; et al. Silver Nanoparticles Loaded with Pomegranate Peel Extract and Hyaluronic Acid Mediate Recovery of Cutaneous Wounds Infected with Candida albicans. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1469493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubitosa, J.; Rizzi, V.; Fini, P.; Del Sole, R.; Lopedota, A.; Laquintana, V.; Denora, N.; Agostiano, A.; Cosma, P. Multifunctional Green Synthetized Gold Nanoparticles/Chitosan/Ellagic Acid Self-Assembly: Antioxidant, Sun Filter and Tyrosinase-Inhibitor Properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 106, 110170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuwanshi, N.; Yadav, T.C.; Srivastava, A.K.; Raj, U.; Varadwaj, P.; Pruthi, V. Structure-Based Drug Designing and Identification of Woodfordia fruticosa Inhibitors Targeted against Heat Shock Protein (HSP70-1) as Suppressor for Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis Like Skin Inflammation in Mice Model. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 95, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallan, S.S.; Sguizzato, M.; Pavoni, G.; Baldisserotto, A.; Drechsler, M.; Mariani, P.; Esposito, E.; Cortesi, R. Ellagic Acid Containing Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Topical Application: A Preliminary Study. Molecules 2020, 25, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, C.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, S.; Gong, X.; Xiao, Z.; Jiang, N.; Yu, C.; Yi, C. Transdermal BQ-788/EA@ZnO Quantum Dots as Targeting and Smart Tyrosinase Inhibitors in Melanocytes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholghi, K.K.; Tamri, P.; Haddadi, R.; Pourmoslemi, S. Ellagic Acid Loaded Nanospheres/Biodegradable PVA-Sodium Alginate Hydrogel for Wound Healing Application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e54406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, I.M.; Jocic, E.; Nikolic, V.D.; Popsavin, M.M.; Rakic, S.J.; Savic-Gajic, I.M. The Effect of Complexation with Cyclodextrins on the Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Ellagic Acid. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Kadian, V.; Kumar, A.; Mahant, S.; Rao, R. Evaluation of Solubility, Photostability and Antioxidant Activity of Ellagic Acid Cyclodextrin Nanosponges Fabricated by Melt Method and Microwave-Assisted Synthesis. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Guo, L.; Li, R.; Shao, J.; Lu, L.; Yang, P.; Zhao, A.; Liu, Y. Ellagic Acid-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex-Loaded Thiol-Ene Hydrogel with Antioxidant, Antibacterial, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties for Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 4959–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccarin, T.; Lemos-Senna, E. Potential Application of Nanoemulsions for Skin Delivery of Pomegranate Peel Polyphenols. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 3307–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Guo, K.; Hao, Y.; Ma, L.; Ma, K.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; et al. Ellagic Acid-Loaded SEVs Encapsulated in GelMA Hydrogel Accelerate Diabetic Wound Healing by Activating EGFR on Skin Repair Cells. Cell Prolif. 2025, 58, e70064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokton, N.; Ounaroon, A.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Tiyaboonchai, W. Development of Ellagic Acid Rich Pomegranate Peel Extract Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs). Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 259–265. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, A.; Park, D.W.; Kwon, J.E.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kim, T.; Kim, I.; Kang, S.C.; Chi, K.W. Investigation of the Biological and Anti-Cancer Properties of Ellagic Acid-Encapsulated Nano-Sized Metalla-Cages. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein-al-ali, S.H.; Abudoleh, S.M.; Hussein, M.Z.; Bullo, S.; Palanisamy, A. Graphene Oxide-Ellagic Acid Nanocomposite as Effective Anticancer and Antimicrobial Agent. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 15, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Jiang, X. Effect of Solubilization with Surfactant on the Antioxidant Activity of Ellagic Acid. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2024, 61, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Kaewnopparat, N.; Nitiruangjaras, A.; Reanmongkol, W. Topical Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activities of Standardized Pomegranate Rind Extract in Comparison with Its Marker Compound Ellagic Acid In Vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Kaewnopparat, N.; Songkro, S.; Reanmongkol, W. Topical Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Standardized Pomegranate Rind Extract and Ellagic Acid in Contact Dermatitis. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Liu, Y.; Gaber, M.W.; Bumgardner, J.D.; Haggard, W.O.; Yang, Y. Development of Chitosan–Ellagic Acid Films as a Local Drug Delivery System to Induce Apoptotic Death of Human Melanoma Cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 90B, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarek-Szczepańska, B.; Kleszczyński, K.; Zasada, L.; Chmielniak, D.; Hollerung, M.B.; Dembińska, K.; Pałubicka, K.; Steinbrink, K.; Brzezinska, M.S.; Grabska-Zielińska, S. Hyaluronic Acid/Ellagic Acid as Materials for Potential Medical Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes Alves, M.M.; Arcanjo, D.D.R.; Figueiredo, K.A.; de Sousa Macêdo Oliveira, J.S.; Viana, F.J.C.; de Sousa Coelho, E.; Lopes, G.L.N.; Gonçalves, J.C.R.; Carvalho, A.L.M.; dos Santos Rizzo, M.; et al. Gallic and Ellagic Acids Are Promising Adjuvants to Conventional Amphotericin B for the Treatment of Cutaneous leishmaniasis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00807-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campelo, J.E.S.; Nascimento, M.O.D.; Carvalho, A.L.M.; Santos, H.S.P.; de Almeida, J.O.C.S.; Alves, M.M.d.M.; Arcanjo, D.D.R.; Neto, J.M.T.; Muratori, M.C.S.; Costa, A.P.R. Evaluation of the Acute Toxicity of Ellagic Acid and Gallic Acid Incorporated in Poloxamer407® Gel, in Zophobas morio Larvae. Toxicol. Vitr. 2024, 95, 105727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draelos, Z.; Dahl, A.; Yatskayer, M.; Chen, N.; Krol, Y.; Oresajo, C. Dyspigmentation, Skin Physiology, and a Novel Approach to Skin Lightening. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2013, 12, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon, M.; Horwitz, S. Topical Treatment of Hyperpigmentation Disorders. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 139, S153–S158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, A.; Yatskayer, M.; Raab, S.; Oresajo, C. Tolerance and Efficacy of a Product Containing Ellagic and Salicylic Acids in Reducing Hyperpigmentation and Dark Spots in Comparison with 4% Hydroquinone. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2013, 12, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa, T.O.; Tavares, W.S.; Sousa, F.F.O. Ellagic Acid-Loaded Poly-Methyl Vinyl Ether-Co-Maleic Anhydride (Gantrez®)—Gelatin Sponges for Wound Bandaging: Preparation, Characterization and Ex-Vivo Antibiofilm Activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 102, 106403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, V.B.S.C.; Balaganesan, V.; Govindaraj, G.; Veerichetty, V. Cellular Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activity of Astaxanthin and Ellagic Acid on UV Irradiated Skin Melanoma Cells and Gel Formulation. Mater. Today Proc. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X. Preparation of Pomegranate Ellagic Acid Inclusion Complex Gel and Its Transdermal Permeation In Vitro. Procedia Eng. 2017, 174, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Liu, D.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Guan, Z.; Yu, K.; Chu, L.; et al. Double Crosslinked Hydrogels Loaded with Zinc-Ellagic Acid Metal-Organic Frameworks Combined with a Mild Heat Stimulation Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 519, 165454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Wei, X.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, X.; Lin, J.; Li, M.; Tian, Y.; Fan, S.; Ye, T.; et al. Natural Ellagic Acid-Polyphenol “Sandwich Biscuit” Self-Assembled Solubilizing System for Formation Mechanism and Antibacterial Synergia. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 27772–27787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castellacci, R.; Bergonzi, M.C. An Insight on Ellagic Acid Formulations for the Management of Skin Diseases. Molecules 2025, 30, 4493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234493
Castellacci R, Bergonzi MC. An Insight on Ellagic Acid Formulations for the Management of Skin Diseases. Molecules. 2025; 30(23):4493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234493
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastellacci, Rebecca, and Maria Camilla Bergonzi. 2025. "An Insight on Ellagic Acid Formulations for the Management of Skin Diseases" Molecules 30, no. 23: 4493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234493
APA StyleCastellacci, R., & Bergonzi, M. C. (2025). An Insight on Ellagic Acid Formulations for the Management of Skin Diseases. Molecules, 30(23), 4493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234493