Cytotoxic Cytochalasans from Sponge-Derived Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41044
Abstract
1. Introduction
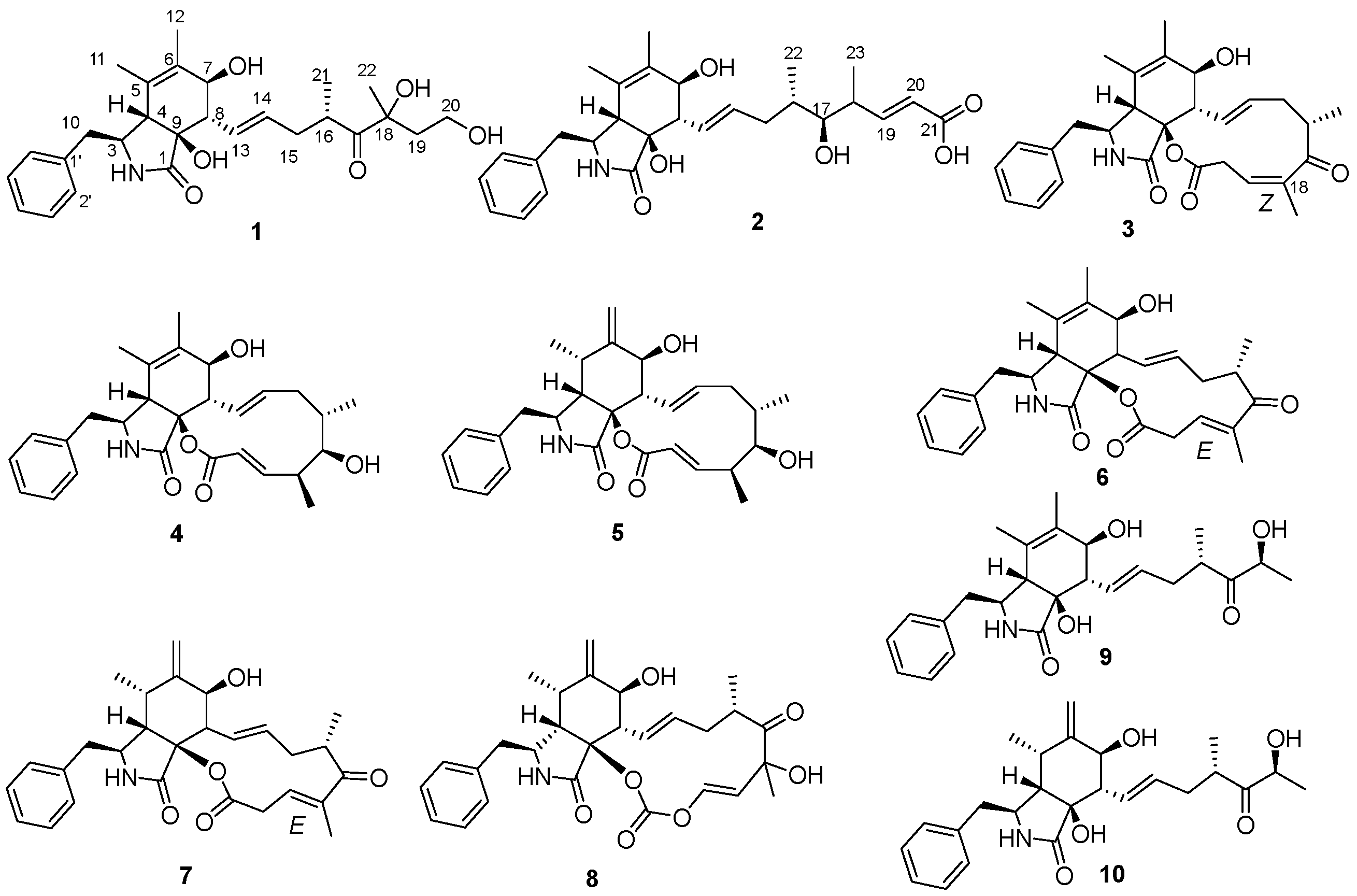
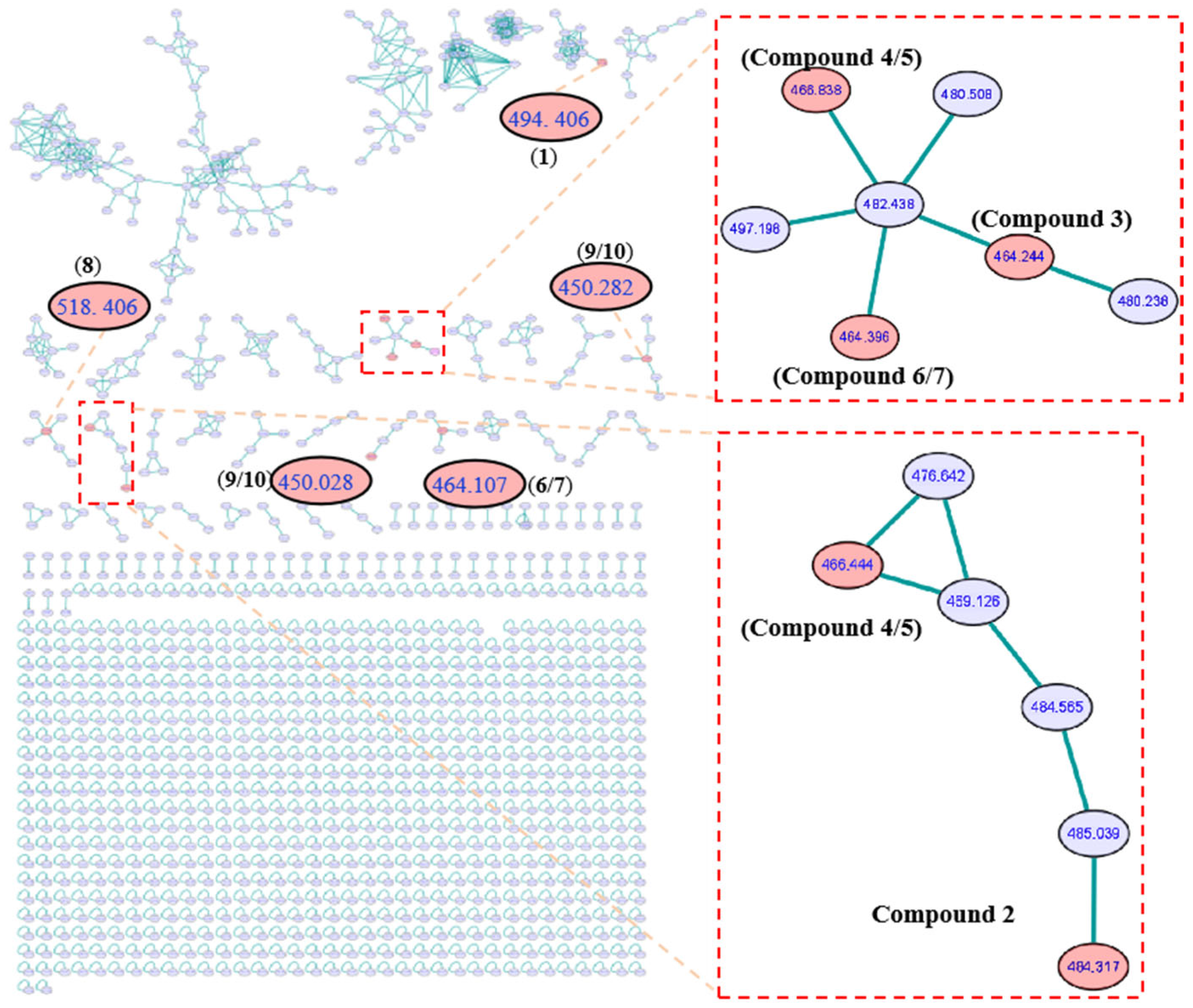
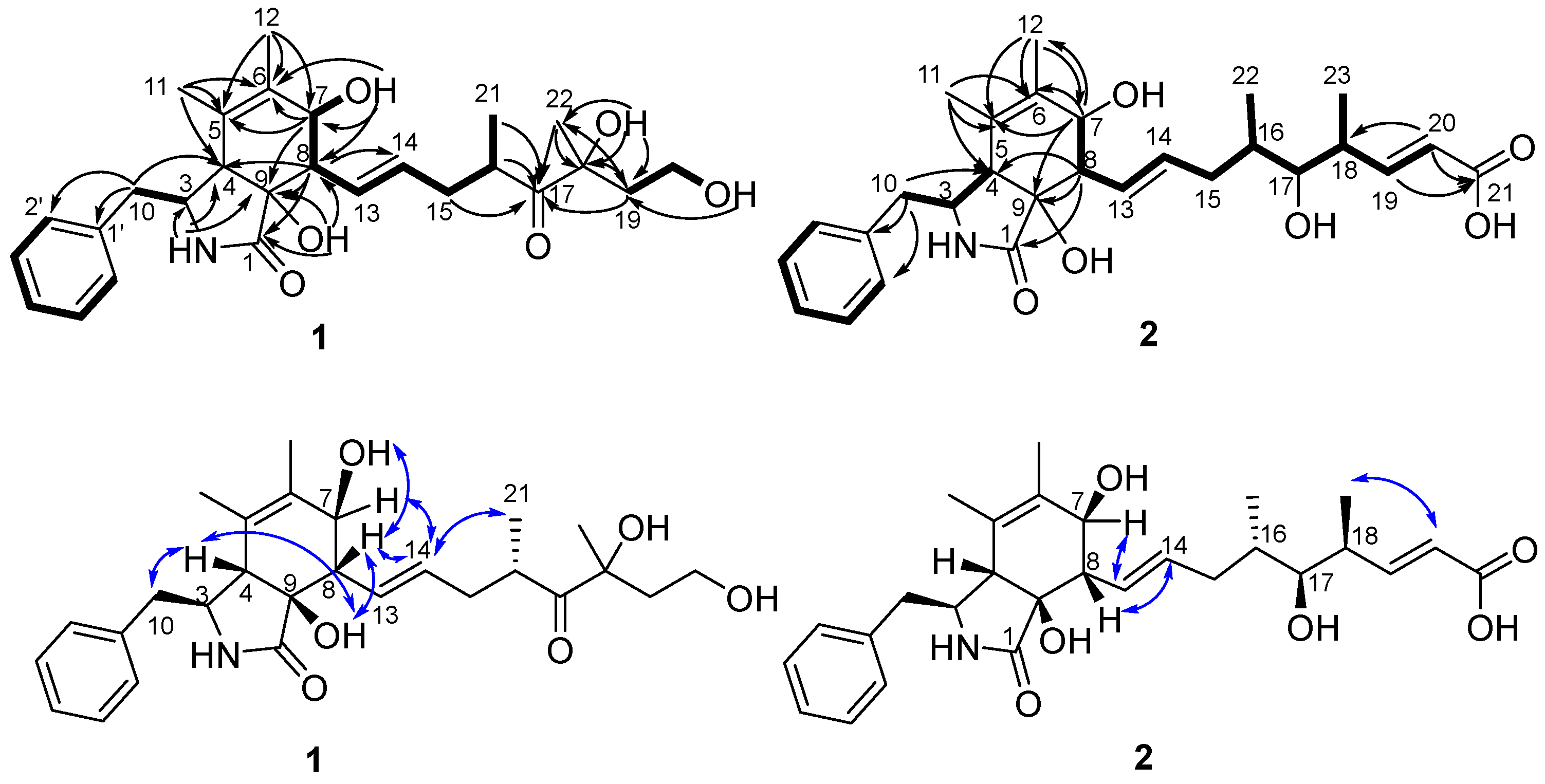
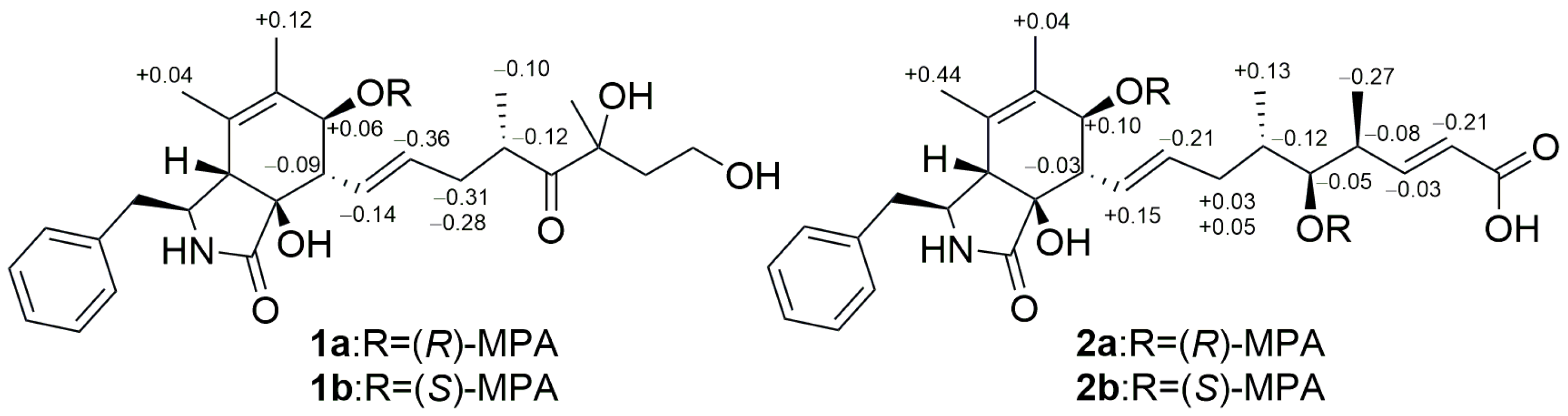
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Material
3.3. Fermentation, Extraction, and Isolation
3.4. Structural Characterizations of 1, 2 and 3
3.5. Preparation of the (S)- and (R)-MPA Esters of Cytochalasins Z29 and Z30 Using the Modified Mosher’s Method
3.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, B.; Zheng, R.; Zeng, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, K.; Chen, R.; Li, L.; Wei, W.; He, J. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2024, 4, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, A.M.; Laversanne, M.; Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Parkin, D.M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. The GLOBOCAN 2022 cancer estimates: Data sources, methods, and a snapshot of the cancer burden worldwide. Int. J. Cancer 2025, 156, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudin, C.M.; Brambilla, E.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Sage, J. Small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Liang, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, P.; Cai, M.; Xie, D.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Metabolism characterization and toxicity of N-hydap, a marine candidate drug for lung cancer therapy by LC-MS method. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2024, 14, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Scherlach, K.; Boettger, D.; Remme, N.; Hertweck, C. The chemistry and biology of cytochalasans. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 869–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammam, M.A.; Pereira, F.; Skellam, E.; Bidula, S.; Ganesan, A.; El-Demerdash, A. The cytochalasans: Potent fungal natural products with application from bench to bedside. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2025, 42, 788–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.L.; Dong, S.H.; Li, H.Y.; Wei, W.J.; Tu, Y.Q.; Gao, K. Cytochalasins from Xylaria sp. CFL5, an endophytic fungus of Cephalotaxus fortunei. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2021, 11, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, X.M.; Yang, S.Q.; Li, X.; Wang, B.G.; Si, S.Y.; Meng, L.H. Cytochalasin Derivatives from the endozoic Curvularia verruculosa CS-129, a fungus isolated from the deep-sea squat lobster Shinkaia crosnieri living in the cold seep environment. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 3122–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mao, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Hou, C.; Han, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, J. Discovery of highly oxygenated cytochalasans with antiproliferative activity from an endophytic fungus Boeremia exigua. Bioorg. Chem. 2025, 156, 108198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.M.; Tang, X.L.; Sun, Y.T.; Song, D.Y.; Cheng, Y.J.; Liu, H.; Li, P.L.; Li, G.Q. Biological and chemical diversity of marine sponge-derived microorganisms over the last two decades from 1998 to 2017. Molecules 2020, 25, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; She, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, J.; Ye, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Tao, H. Advances in natural products from the marine-sponge-associated microorganisms with antimicrobial activity in the last decade. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, G.; Lang, G.; Gulder, T.A.M.; Tsuruta, H.; Mühlbacher, J.; Maksimenka, K.; Steffens, S.; Schaumann, K.; Stöhr, R.; Wiese, J.; et al. The first sorbicillinoid alkaloids, the antileukemic sorbicillactones A and B, from a sponge-derived Penicillium chrysogenum strain. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 7252–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, T.; Fang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W. Novel open-chain cytochalsins from the marine-derived fungus Spicaria elegans. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.W.; Zhang, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhu, C.J.; Ng, S.W.; Tan, R.X. Ardeemins and cytochalasins from Aspergillus terreus residing in Artemisia annua. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Liu, M.; Qi, S.; Wu, Y.; Sun, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, K.; Cai, G.; Gong, K. Cytochalasins from coastal saline soil-derived fungus Aspergillus flavipes RD-13 and their cytotoxicities. J. Antibiot. 2022, 75, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seco, J.M.; Quinoa, E.; Riguera, R. The assignment of absolute configuration by NMR. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 17–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Meng, Q.; Niu, S.; Liu, J.; Guo, X.; Sun, Z.; Liu, D.; Gu, Y.; Huang, J.; Fan, A.; et al. Epigenetic manipulation to trigger production of guaiane-type sesquiterpenes from a marine-derived Spiromastix sp. fungus with antineuroinflammatory effects. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 1993–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Cui, C.; Fa, G.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Liu, H. 10-Phenyl-[12]-cytochalasins Z7,Z8, and Z9 from the marine-derived fungus Spicaria elegans. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.L.; Li, X.M.; Wang, Y.R.; Meng, L.H.; Wang, B.G. Antibacterial and cytotoxic methylthioether-containing cytochalasins from Chaetomium globosum AS-506, an endozoic fungus associated with deep-sea sponge of Magellan Seamounts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.J.; Zhang, G.J.; Zhu, T.J.; Liu, R.; Wei, H.J.; Gu, Q.Q. Bioactive cytochalasins from Aspergillus flavipes, an endophytic fungus associated with the mangrove plant Acanthus ilicifolius. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Schrader, K.K.; Elsohly, H.N.; Walker, L.A. Characterization of mycotypha metabolites found to be inhibitors of cell adhesion molecules. J. Antibiot. 2002, 55, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.; Xu, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Du, N.N.; Liu, D.F.; Yao, G.D.; Lin, B.; Song, S.J.; Huang, X.X. HSQC-based small molecule accurate recognition technology discovery of diverse cytotoxic sesquiterpenoids from Elephantopus tomentosus L. and structural revision of molephantins A and B. Phytochemistry 2023, 206, 113562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wu, X.; Huang, W.; Wang, Q.; Cai, G.; Wang, H.; Ou, T.; et al. Therapeutic targeting RORgamma with natural product N-hydroxyapiosporamide for small cell lung cancer by reprogramming neuroendocrine fate. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 178, 106160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Ma, S.; Pang, X.; Cong, M.; Liu, Q.; Han, F.; Wang, J.; Feng, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Cytotoxic pyridine alkaloids from a marine-derived fungus Arthrinium arundinis exhibiting apoptosis-inducing activities against small cell lung cancer. Phytochemistry 2023, 213, 113765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Position | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, type | δH, mult, J | δC, type | δH, mult, J | |
| 1 | 174.8 C | 174.8 C | ||
| 2 (NH) | 7.80, s | 7.77, s | ||
| 3 | 56.8 CH | 3.29–3.34, m | 56.7 CH | 3.30–3.34, m |
| 4 | 51.9 CH | 2.33, m | 51.9 CH | 2.30–2.35, m |
| 5 | 125.0 C | 125.0 C | ||
| 6 | 131.3 C | 131.3 C | ||
| 7 | 70.7 CH | 3.62, t, 7.0 | 70.9 CH | 3.63, brd, 6.5 |
| 8 | 52.4 CH | 2.29, dd, 9.0, 7.0 | 52.3 CH | 2.30–2.35, m |
| 9 | 75.9 C | 76.0 C | ||
| 10 | 42.2 CH2 | 3.01, dd, 13.0, 7.0 2.88, dd, 13.5, 5.5 | 42.2 CH2 | 3.02, dd, 13.0, 7.0 2.88, dd, 13.0, 5.0 |
| 11 | 17.4 CH3 | 1.39, s | 17.4 CH3 | 1.41, s |
| 12 | 15.9 CH3 | 1.61, s | 16.0 CH3 | 1.62, s |
| 13 | 129.0 CH | 5.65, dd, 15.5, 9.5 | 128.2 CH | 5.61, dd, 15.5, 9.0 |
| 14 | 131.4 CH | 5.31, dt, 15.5, 7.0 | 132.4 CH | 5.37, dt, 15.5, 7.0 |
| 15 | 36.0 CH2 | 2.22, brdt, 13.5, 5.5 1.88, dt, 13.5, 8.0 | 36.8 CH2 | 2.04, dt, 13.5, 5.5 1.83, dt, 14.0, 8.0 |
| 16 | 38.8 CH | 3.25, dq, 13.5, 6.5 | 35.9 CH | 1.47–1.55, m |
| 17 | 218.6 C | 75.9 CH | 3.13–3.18, m | |
| 18 | 77.9 C | 39.5 CH | 2.42, dt, 14.0, 7.0 | |
| 19 | 41.8 CH2 | 1.83, ddd, 14.0,8.0, 6.5 1.65, ddd, 8.0, 6.0 | 151.8 CH | 6.88, dd, 15.5, 8.0 |
| 20 | 56.8 CH2 | 3.37–3.50, m | 121.8 CH | 5.73, d, 15.5 |
| 21 | 16.8 CH3 | 0.96, d, 7.0 | 167.8 C | |
| 22 | 25.8 CH3 | 1.18, s | 13.7 CH3 | 0.80, d, 7.0 |
| 23 | 17.0 CH3 | 0.95, d, 6.5 | ||
| 1′ | 137.8 C | 137.7 C | ||
| 2′,6′ | 129.8 CH | 7.21–7.27, m | 129.8 CH | 7.20–7.27, m |
| 3′,5′ | 128.3 CH | 7.29–7.34, m | 128.3 CH | 7.29–7.34, m |
| 4’ | 126.4 CH | 7.21–7.27, m | 126.4 CH | 7.20–7.27, m |
| OH-7 | 4.61, d, 7.0 | |||
| OH-9 | 5.08, s | |||
| OH-18 | 5.18, s | |||
| OH-20 | 4.46, t, 5.0 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, X.; Wong, I.; Cao, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Cytotoxic Cytochalasans from Sponge-Derived Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41044. Molecules 2025, 30, 4483. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224483
Pang X, Wong I, Cao Q, Wang J, Zhou X, Yang B, Wang J, Wang H, Liu Y. Cytotoxic Cytochalasans from Sponge-Derived Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41044. Molecules. 2025; 30(22):4483. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224483
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Xiaoyan, Ini Wong, Qinlin Cao, Junfeng Wang, Xuefeng Zhou, Bin Yang, Junjian Wang, Hong Wang, and Yonghong Liu. 2025. "Cytotoxic Cytochalasans from Sponge-Derived Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41044" Molecules 30, no. 22: 4483. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224483
APA StylePang, X., Wong, I., Cao, Q., Wang, J., Zhou, X., Yang, B., Wang, J., Wang, H., & Liu, Y. (2025). Cytotoxic Cytochalasans from Sponge-Derived Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41044. Molecules, 30(22), 4483. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224483









