A Novel Sesquiterpene from Callistephus chinensis Improves Alcohol-Induced Liver Disease by Regulating the AMPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Gut Flora
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
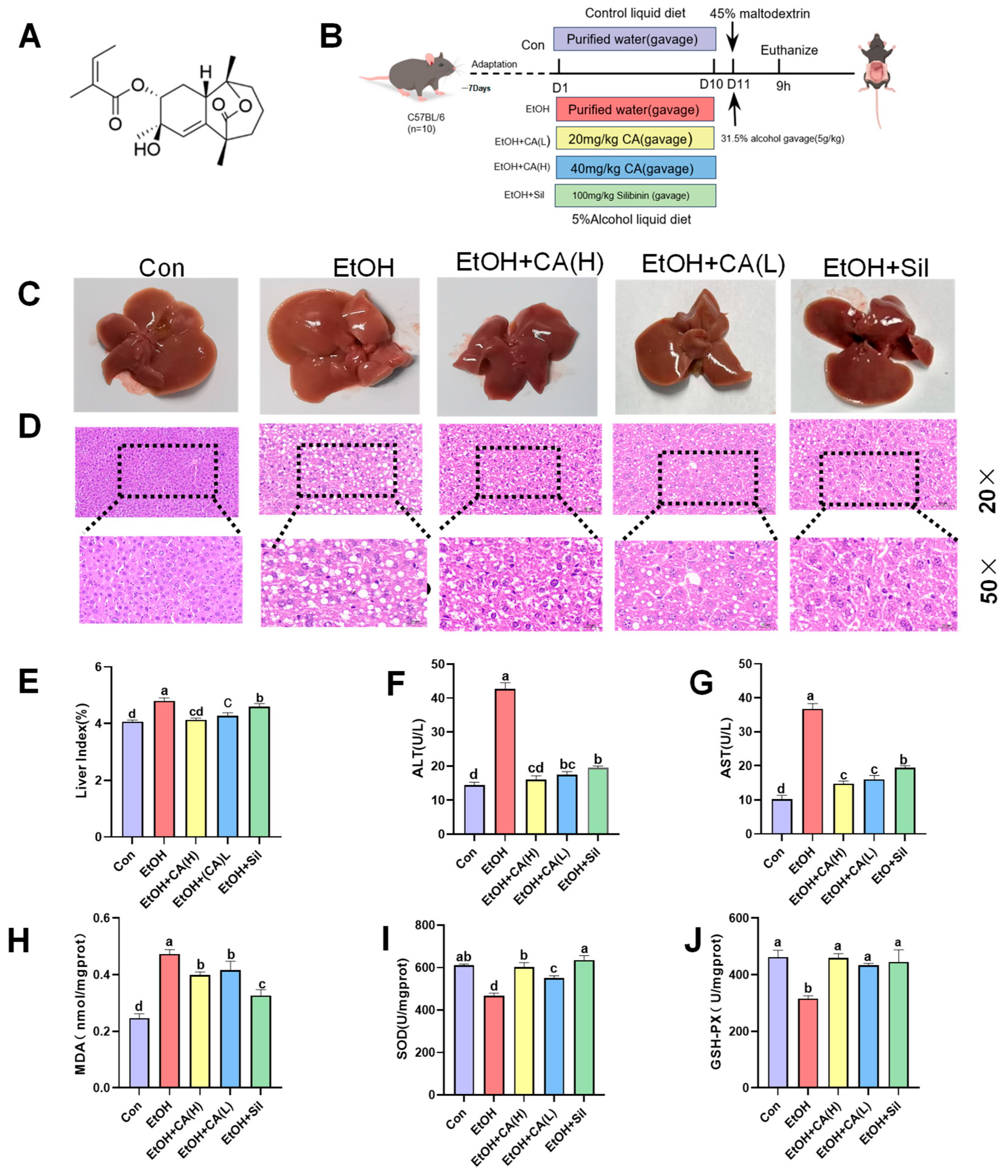
2.1. CA Ameliorated Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury
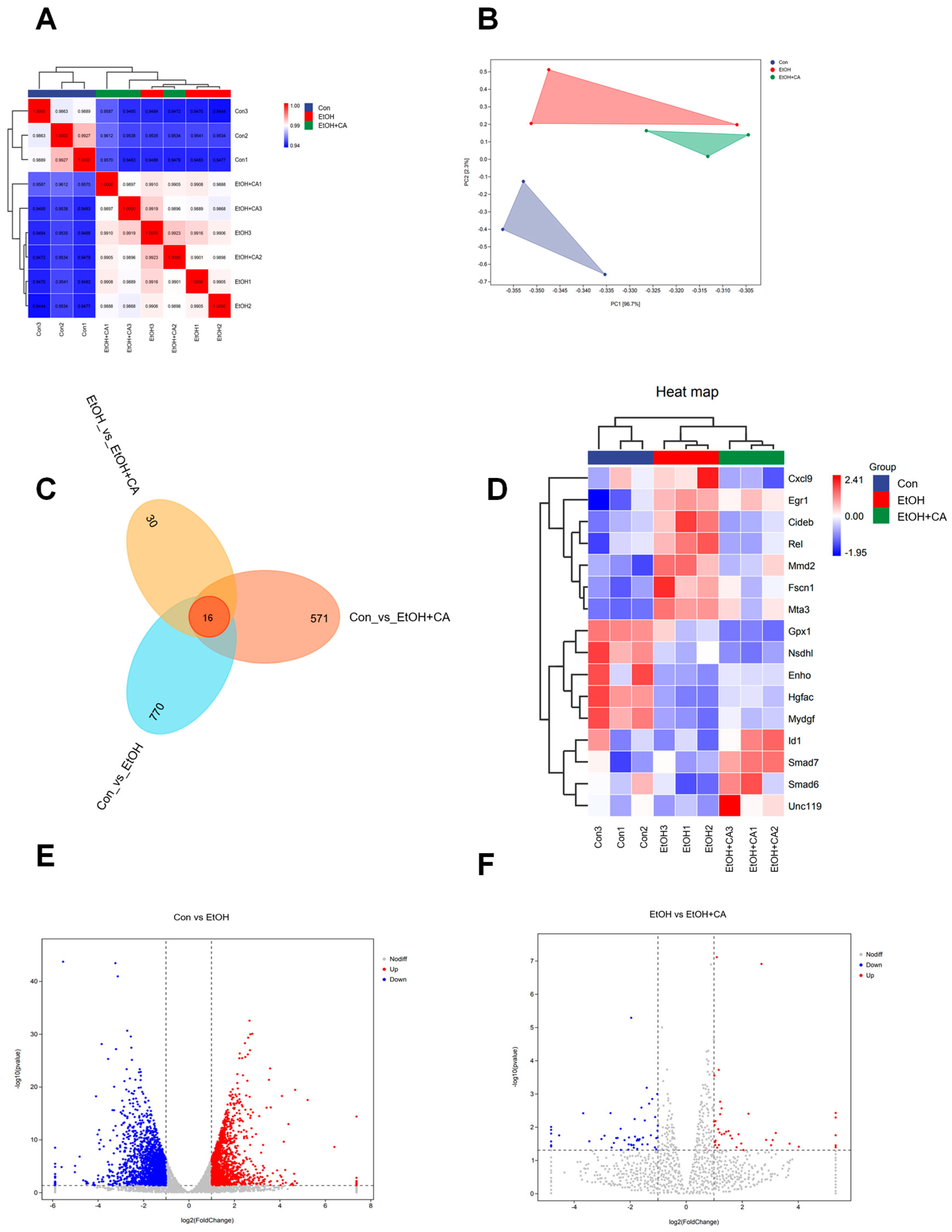
2.2. Effect of CA on the Liver Transcriptome
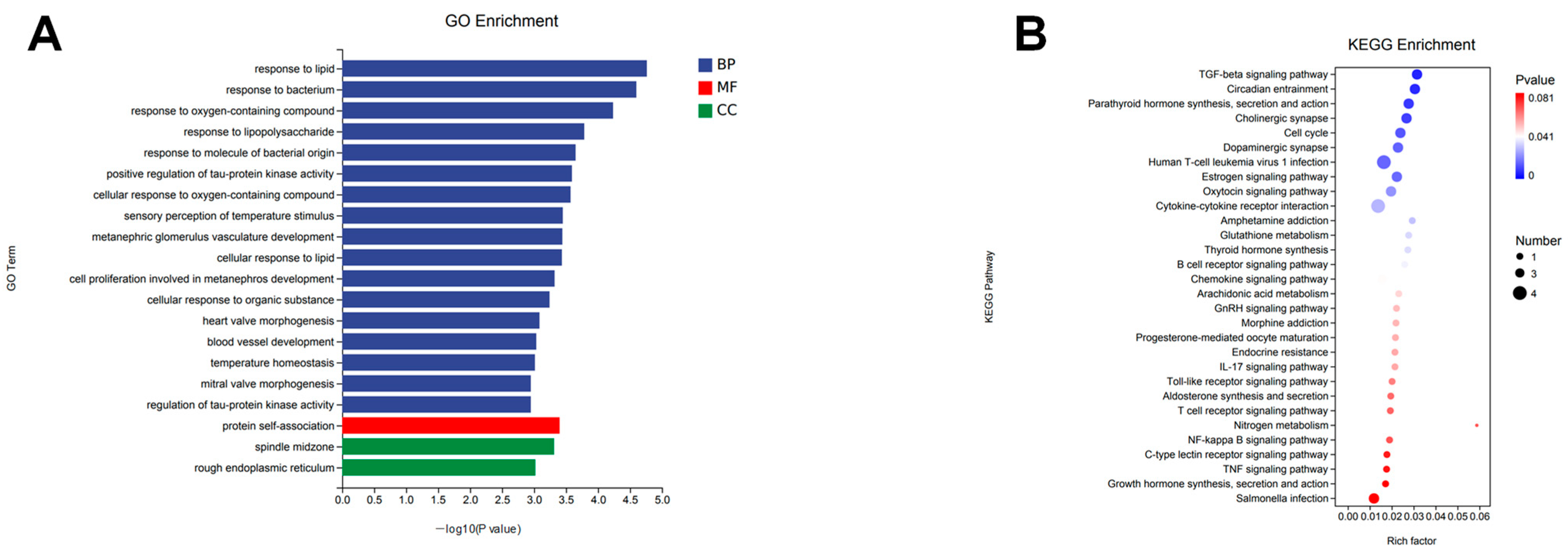
2.3. Functional Annotation and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
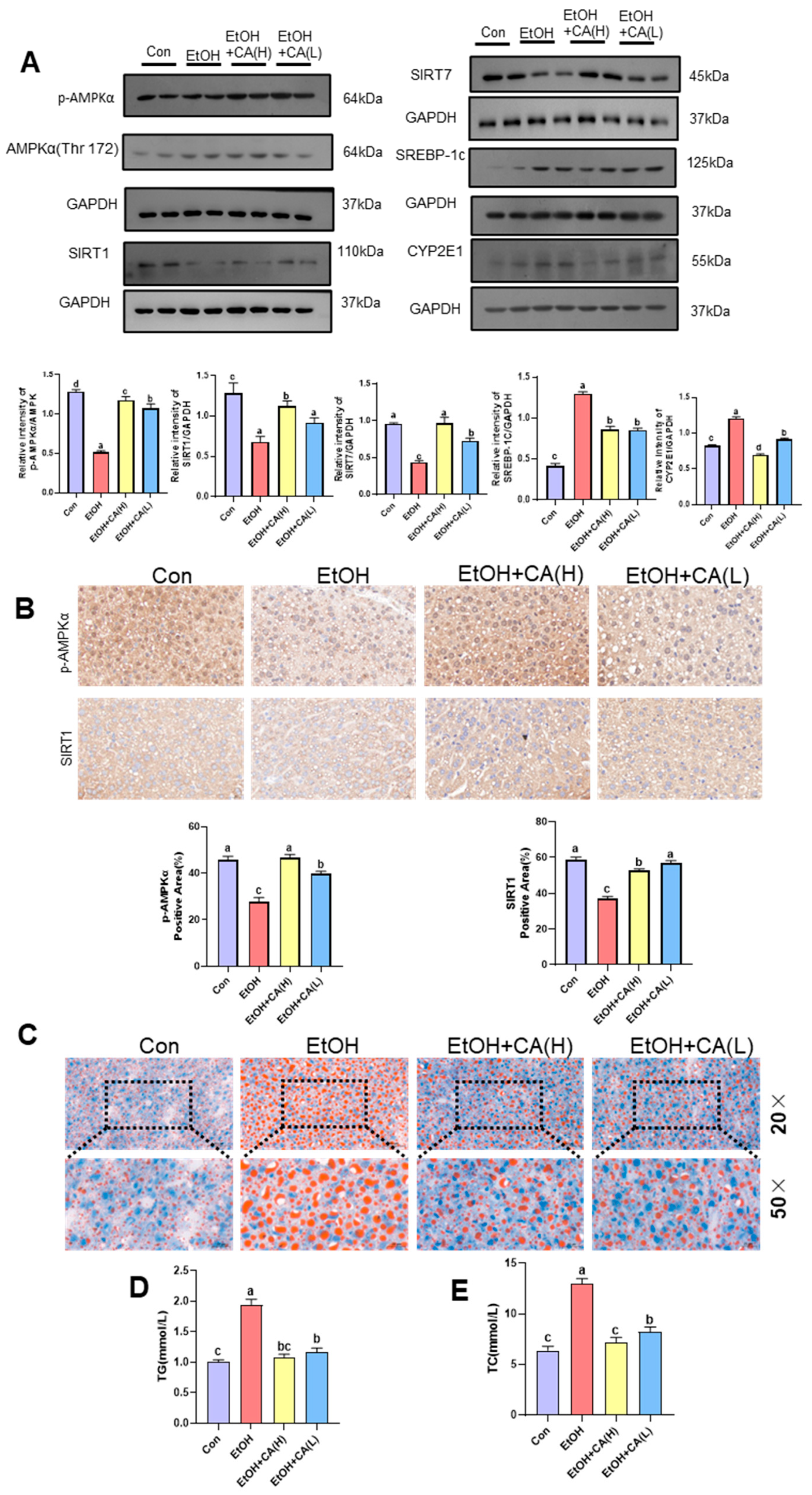
2.4. CA Improved Alcohol-Induced Hepatic Lipid Accumulation
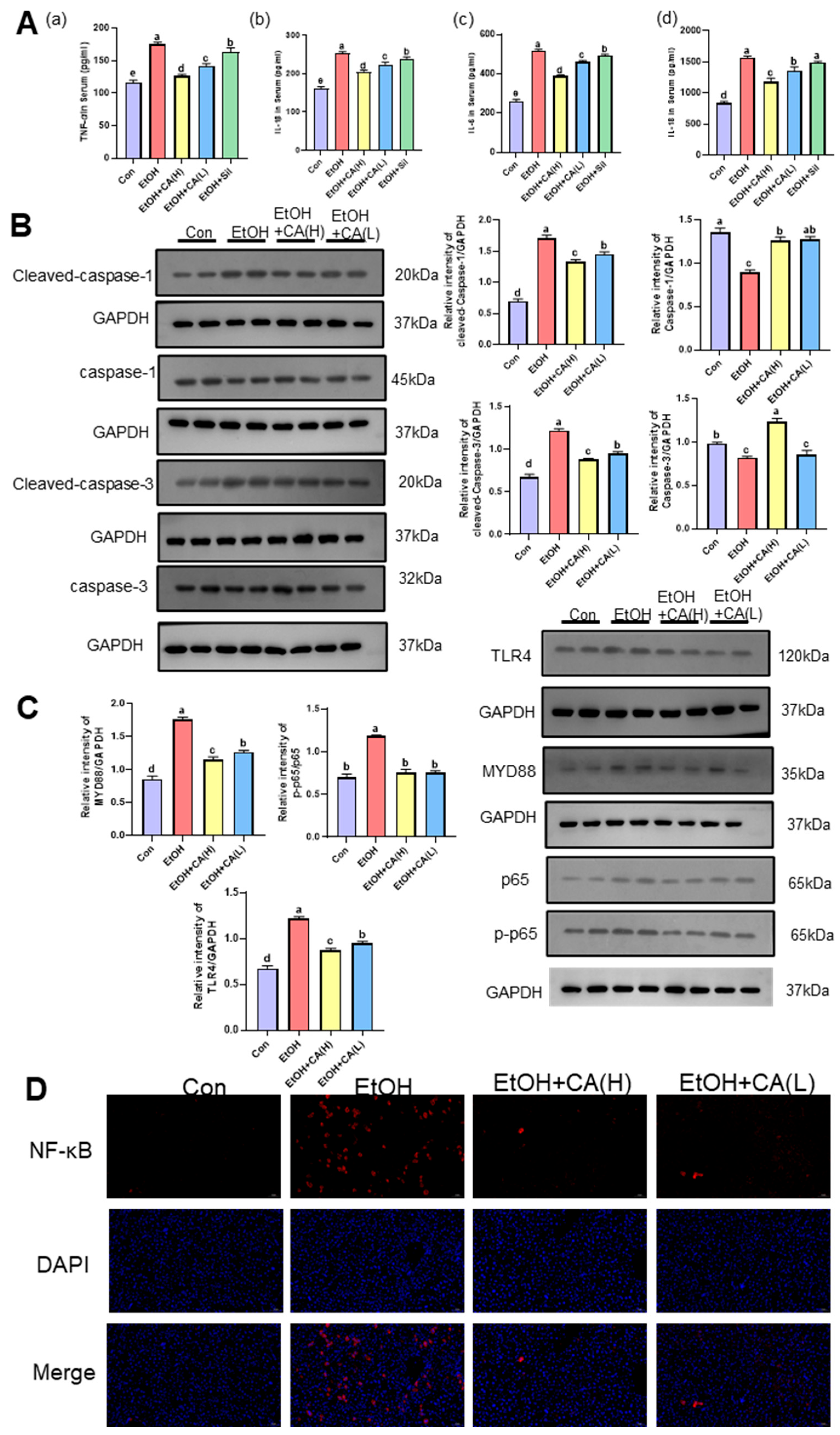
2.5. CA Improved Inflammatory Response
2.6. Molecular Docking Suggested That CA Interacts with Several Key Proteins in the NF-κB/AMPK Signaling Pathway
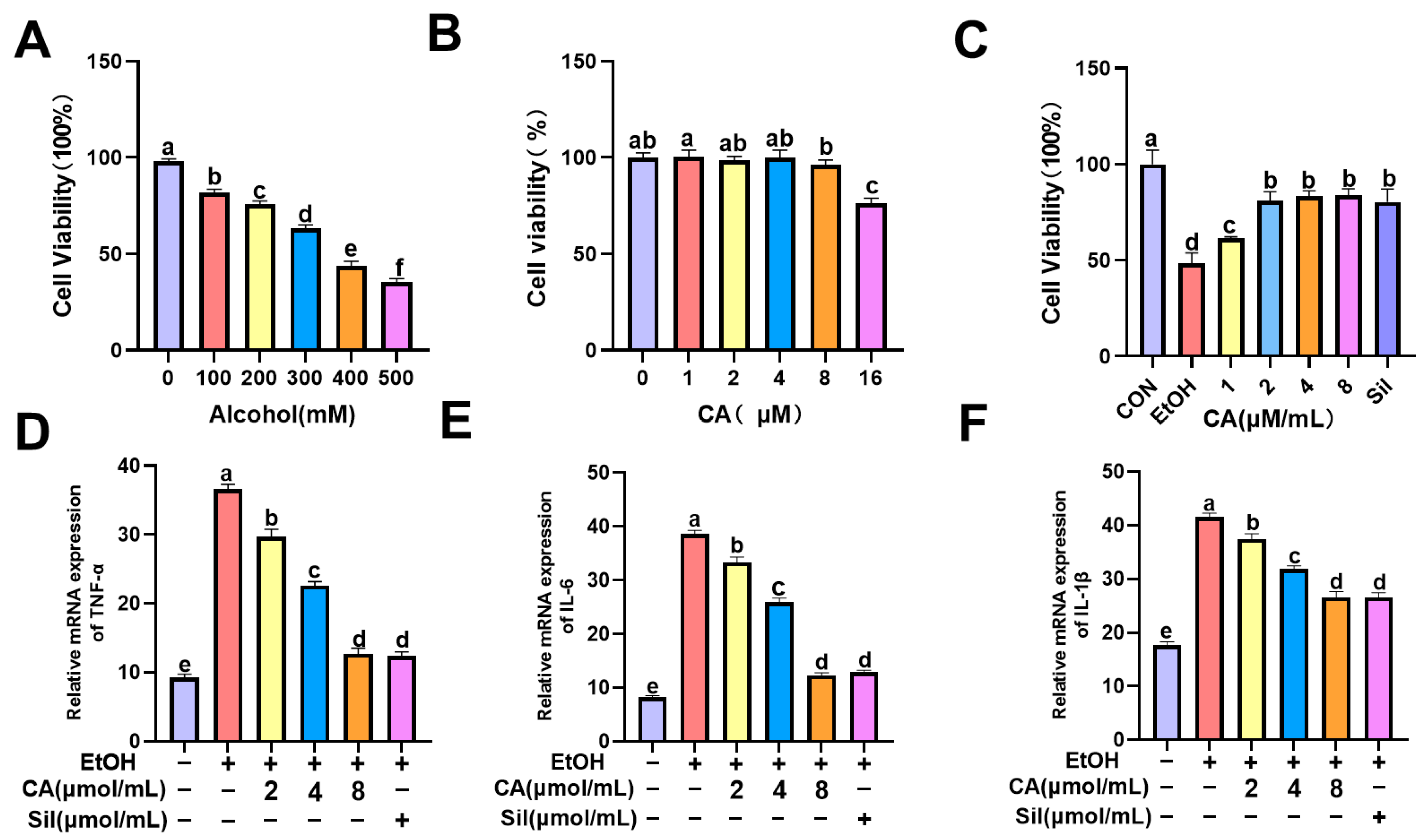
2.7. Effect of CA on Alcohol-Induced AML-12 Cell Survival and Associated Levels of Inflammation
2.8. Effect of CA on Alcohol-Induced Inflammatory Pathway-Related Proteins in AML-12 Cells
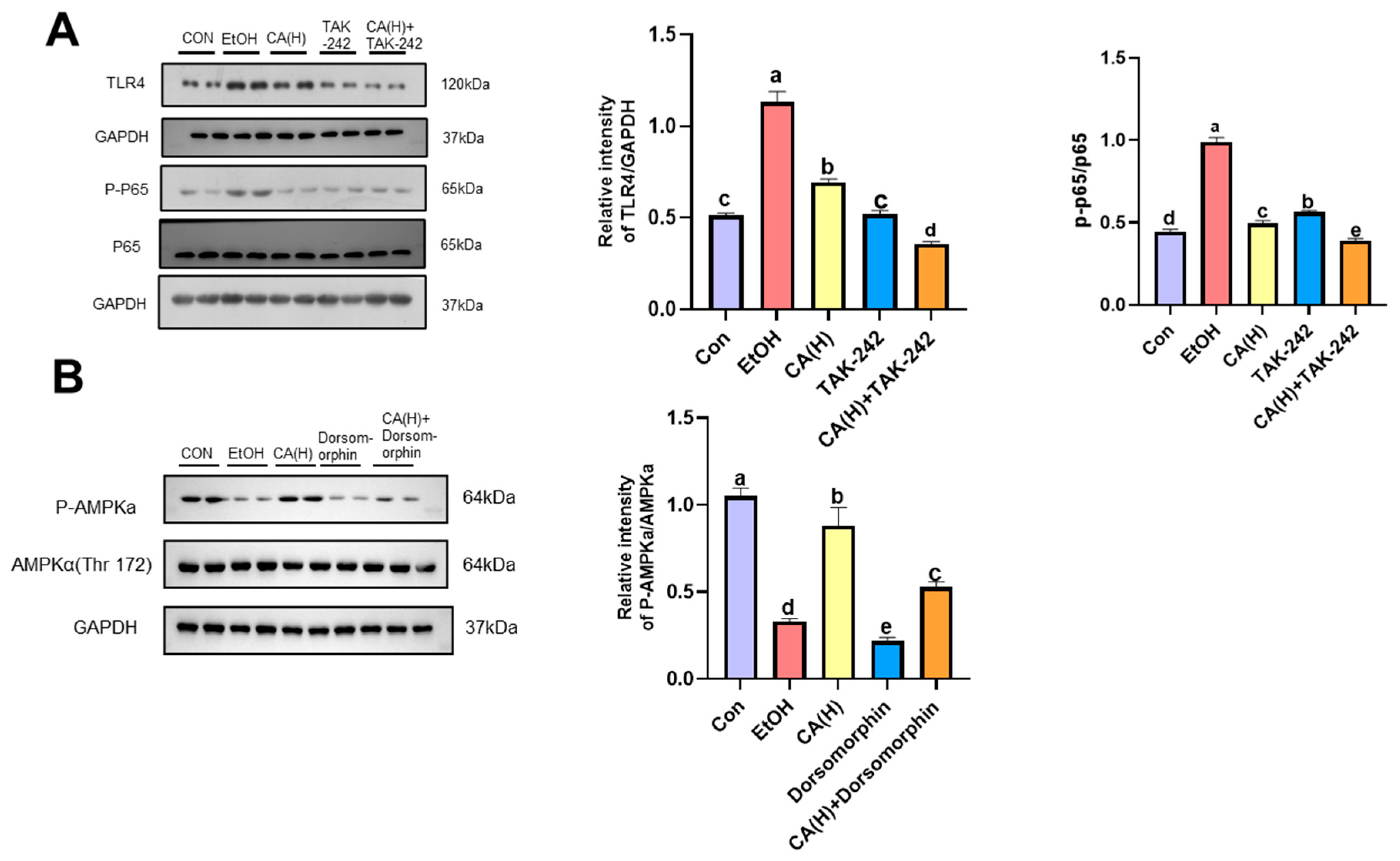
2.9. CA Alleviates Alcoholic Liver Injury by Activating AMPK
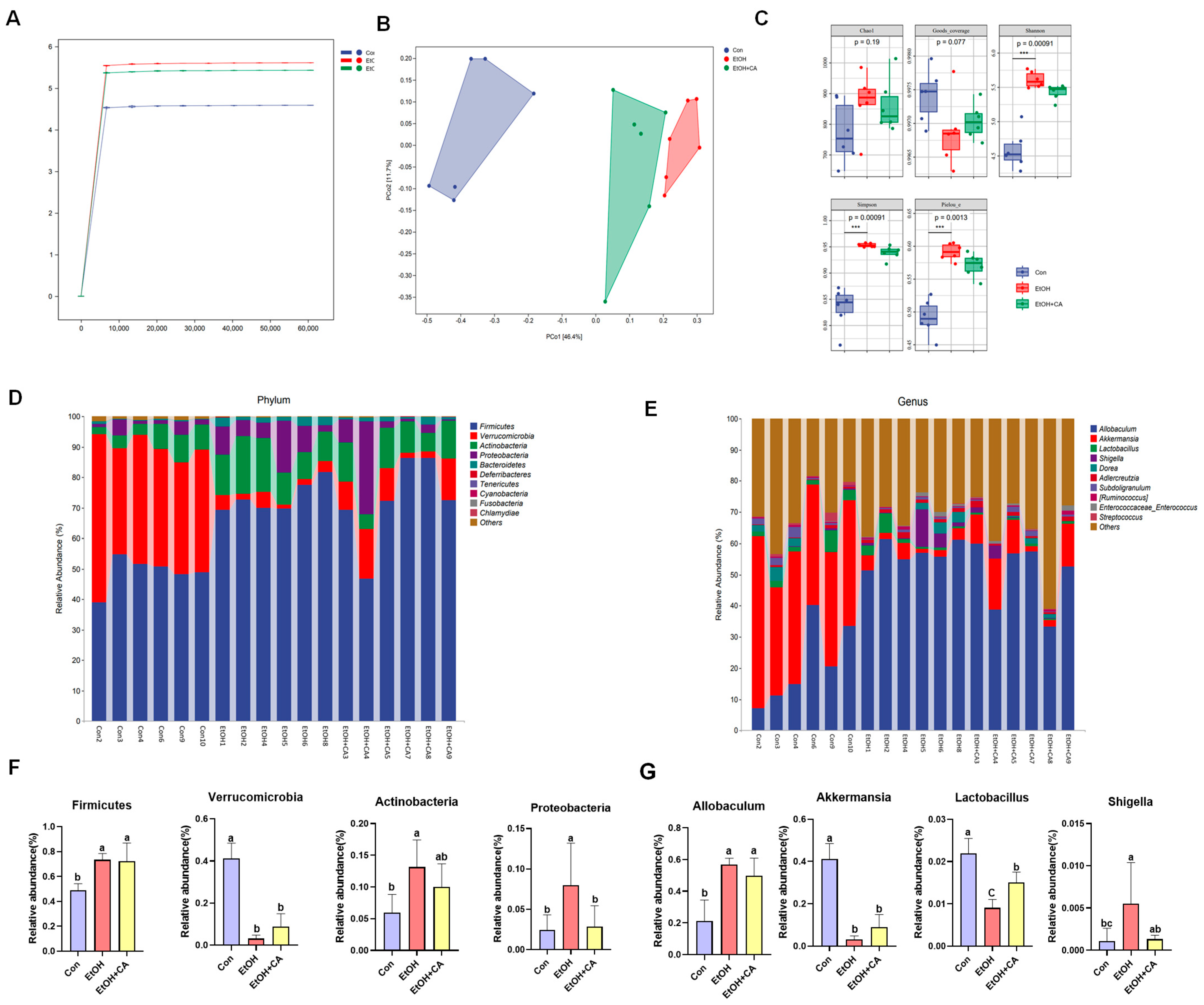
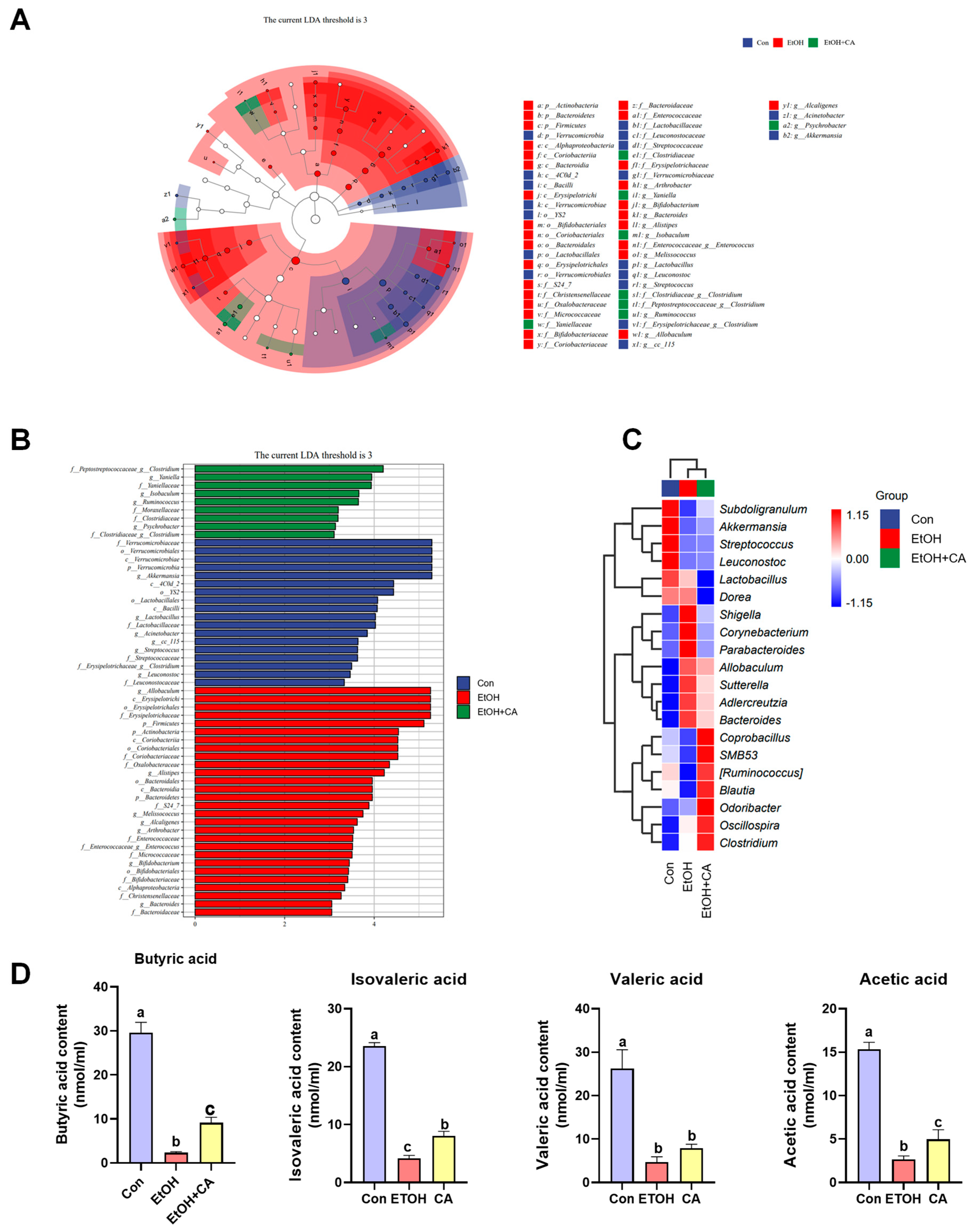
2.10. CA Regulated Gut Microbiota
2.11. Effect of CA on the Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animal Experiments
4.3. Serum and Liver Biochemical Markers
4.4. Histopathological
4.5. Transcriptomic
4.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent
4.7. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.8. Molecular Docking
4.9. Cell Culture
4.10. Determination of Cell Viability
4.11. Immunofluorescence (IF)
4.12. Western Blot (WB)
4.13. 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing of Gut Microbiota
4.14. Measurement of Intestinal Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
4.15. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hyun, J.; Han, J.; Lee, C.; Yoon, M.; Jung, Y. Pathophysiological Aspects of Alcohol Metabolism in the Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Syed, F.; Xia, Y.; Sanyal, A.J.; Shah, V.H.; Chalasani, N.; Zheng, X.; Yu, Q.; Lou, Y.; Li, W. Blood Biomarkers of Intestinal Epithelium Damage Regenerating Islet-derived Protein 3α and Trefoil Factor 3 Are Persistently Elevated in Patients with Alcoholic Hepatitis. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 45, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, X.; Yang, L.; Chu, H. The Role of Gut Bacteria and Fungi in Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 840752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S. Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcondes-de-Castro, I.A.; Reis-Barbosa, P.H.; Marinho, T.S.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-de-Lacerda, C.A. AMPK/mTOR pathway significance in healthy liver and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its progression. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 38, 1868–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, S.; Matsushita, Y.; Kurosaki, S.; Tange, M.; Fujiwara, N.; Hayata, Y.; Hayakawa, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Hata, M.; Tsuboi, M.; et al. Inhibiting SCAP/SREBP exacerbates liver injury and carcinogenesis in murine nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e151895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Chen, N.; Jiang, X.L.; Zhan, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zuo, R.M.; Wang, H.; Lan, X.Q.; Ren, J.; et al. Inhibition of HMGB1/TLR4 Signaling Pathway by Digitoflavone: A Potential Therapeutic Role in Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2968–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.N.; Tan, Y.; Xiao, X.C.; Li, Q.; Wu, Q.; Peng, Y.Y.; Ren, J.; Dong, M.L. Deletion of TLR4 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Lu, L.; Bo, N.; Chaoyue, Y.; Haiyang, Y. Allicin Ameliorates Intestinal Barrier Damage via Microbiota-Regulated Short-Chain Fatty Acids-TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Cascade Response in Acrylamide-Induced Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 12837–12852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.F.; Chen, Q.C.; Ni, Q.; Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; Yi, Y.K.; Jiang, C.P.; Shen, C.Y. p-Synephrine ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating liver-adipose axis via AMPK/NF-kappa B pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 348, 119890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Wang, T.; Liu, T.; Guo, Y.; Granato, D. Green tea polyphenols mitigate the plant lectins-induced liver inflammation and immunological reaction in C57BL/6 mice via NLRP3 and Nrf2 signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2020, 144, 111576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Song, S.; Chen, N.; Bian, Y.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, W.; Duan, H.; Shi, Y. NQO1 alleviates renal fibrosis by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy. Cell. Signal. 2023, 108, 110712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.Y.; Lim, S.S.; Park, J.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, H.J.; Yoon Park, J.H.; Kim, J.S. Protection by Chrysanthemum zawadskii extract from liver damage of mice caused by carbon tetrachloride is maybe mediated by modulation of QR activity. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2010, 4, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Liu, W.; Xia, X.; Chen, L.; Mu, T.; Liu, J.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Callistephus chinensis flower polyphones on improving metabolic disorders in high-fat diet-induced mice. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 3304–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, M.; Jiang, Z.; Zafar, S.; Xie, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, H.; Jian, Y.; Wang, W. Chemistry and Pharmacological Activity of Sesquiterpenoids from the Chrysanthemum Genus. Molecules 2021, 26, 3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, K.; Yuan, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. A new derivative with 6/7 ring skeleton obtained from Callistephus chinensis flowers with anti-hepatic fibrosis activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2025, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackowiak, B.; Fu, Y.; Maccioni, L.; Gao, B. Alcohol-associated liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e176345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Tapias, E.; Pose, E.; Gratacós-Ginès, J.; Clemente-Sánchez, A.; López-Pelayo, H.; Bataller, R. Alcohol-associated liver disease: Natural history, management and novel targeted therapies. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2025, 31, S112–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Bian, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Echinacoside: A potential therapeutic approach for alcohol-related liver disease by alleviating intestinal microbial dysbiosis, intestinal barrier dysfunction, and liver inflammation mediated by the endotoxin-TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 1005, 178027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Cheng, M.; Chen, Z.; Sun, L.; Huang, C.; Xu, Y.; Li, J. BRD2 promotes inflammation and lipid accumulation through the NF-κB pathway in alcoholic liver injury. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2025, 243, 117442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ding, Q.; Qian, Q.; Feng, L.; Zhu, Q.; Si, C.; Dou, X.; Li, S. AMPK-Regulated Autophagy Contributes to Ursolic Acid Supplementation-Alleviated Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury in Chronic Alcohol-Fed Mice. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, J. Protective Effects of Isostrictiniin Against High-Fat, High-Sugar Diet-Induced Steatosis in MASLD Mice via Regulation of the AMPK/SREBP-1c/ACC Pathway. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Zheng, H.; Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhi, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, B.; Wu, J.; Zhang, K.; Gao, Y. Bergenin inhibits hepatic fat deposition by activating the AMPK signaling pathway, thereby attenuating alcoholic liver disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 142, 113169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagappan, A.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, D.Y.; Jung, M.H. Cryptotanshinone from the Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge Attenuates Ethanol-Induced Liver Injury by Activation of AMPK/SIRT1 and Nrf2 Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, H.; Song, J.; Song, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Man Hoi, M.P.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Q. Dimeric guaianolide sesquiterpenoids from the flowers of Chrysanthemum indicum ameliorate hepatic steatosis through mitigating SIRT1-mediated lipid accumulation and ferroptosis. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 76, 345–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cai, T.; Cheng, Y.; Bai, J.; Li, M.; Gu, B.; Huang, M.; Fu, W. Postbiotics Prepared Using Lactobacillus reuteri Ameliorates Ethanol-Induced Liver Injury by Regulating the FXR/SHP/SREBP-1c Axis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, e2300927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.U.; Yoon, J.H. High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Levels in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD), Metabolic Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease (MetALD), and Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD) with Metabolic Dysfunction. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Hu, C.; Yin, L.; Tao, X.; Xu, L.; Qi, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Dioscin reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory liver injury via regulating TLR4/MyD88 signal pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 36, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuge, A.; Li, S.; Han, S.; Yuan, Y.; Shen, J.; Wu, W.; Wang, K.; Xia, J.; Wang, Q.; Gu, Y.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila-derived acetate activates the hepatic AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α axis to alleviate ferroptosis in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. Acta Pharm. Sinica. B 2025, 15, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Kounatidis, D.; Tsilingiris, D.; Panagopoulos, F.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Evangelopoulos, A.; Karampela, I.; Dalamaga, M. The Role of Next-Generation Probiotics in Obesity and Obesity-Associated Disorders: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aja, E.; Zeng, A.; Gray, W.; Connelley, K.; Chaganti, A.; Jacobs, J.P. Health Effects and Therapeutic Potential of the Gut Microbe Akkermansia muciniphila. Nutrients 2025, 17, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaja, M.D.; Chokshi, H.A.; Jansari, J.J.; Dixit, O.S.; Savaliya, S.S.; Patel, D.P.; Patel, F.S. Study of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) in Shigella spp. in India. Recent Adv. Anti-Infect. Drug Discov. 2024, 19, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Guan, F.; Sagratini, G.; Yan, J.; Xie, J.; Jin, Z.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, J. Ginsenoside Rd attenuated hyperglycemia via Akt pathway and modulated gut microbiota in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiippala, K.; Barreto, G.; Burrello, C.; Diaz-Basabe, A.; Suutarinen, M.; Kainulainen, V.; Bowers, J.R.; Lemmer, D.; Engelthaler, D.M.; Eklund, K.K.; et al. Novel Odoribacter splanchnicus Strain and Its Outer Membrane Vesicles Exert Immunoregulatory Effects in vitro. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 575455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Chan, J.Y.H.; Wu, K.L.H.; Yu, H.R.; Lee, W.C.; Hou, C.Y.; Tain, Y.L. Altered Gut Microbiota and Its Metabolites in Hypertension of Developmental Origins: Exploring Differences between Fructose and Antibiotics Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Ding, X.; Li, X.; Jing, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, G.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, C.; et al. Inulin supplementation ameliorates hyperuricemia and modulates gut microbiota in Uox-knockout mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 2217–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziętek, M.; Celewicz, Z.; Szczuko, M. Short-Chain Fatty Acids, Maternal Microbiota and Metabolism in Pregnancy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Mu, Y.; Song, Y.; Hao, N.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Q.; Mackay, C.R. Propionate Ameliorates Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via the Gut-Liver Axis: Focus on the Improvement of Intestinal Permeability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6084–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Jin, D.; Huang, S.; Wu, J.; Xu, M.; Liu, T.; Dong, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Zhong, W.; et al. Clostridium butyricum, a butyrate-producing probiotic, inhibits intestinal tumor development through modulating Wnt signaling and gut microbiota. Cancer Lett. 2020, 469, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeFort, K.R.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Song, B.J. Contributing roles of mitochondrial dysfunction and hepatocyte apoptosis in liver diseases through oxidative stress, post-translational modifications, inflammation, and intestinal barrier dysfunction. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2024, 81, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, D.; Ma, K.; Wang, T.; Shi, G.; Shao, J.; Wang, C.; Yan, G. Paeonol ameliorates murine alcohol liver disease via mycobiota-mediated Dectin-1/IL-1β signaling pathway. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Lai, C.H.; Yang, W.; Yue, P.; Ye, Q.; Xiao, J. TAK242 suppresses the TLR4 signaling pathway and ameliorates DCD liver IRI in rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, D.; Liu, S.; Zhong, Y.; Wen, Y.; Chen, L. Ginsenoside Rh1 attenuates chondrocyte senescence and osteoarthritis via AMPK/PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 159, 114911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, X.; Yuan, M.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X. Callistephus A from Callistephus chinensis Nees alleviates concanavalin A-induced immunological liver injury in mice by inhibiting the activation of JAK/STAT1 and MAPK signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 148, 114153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
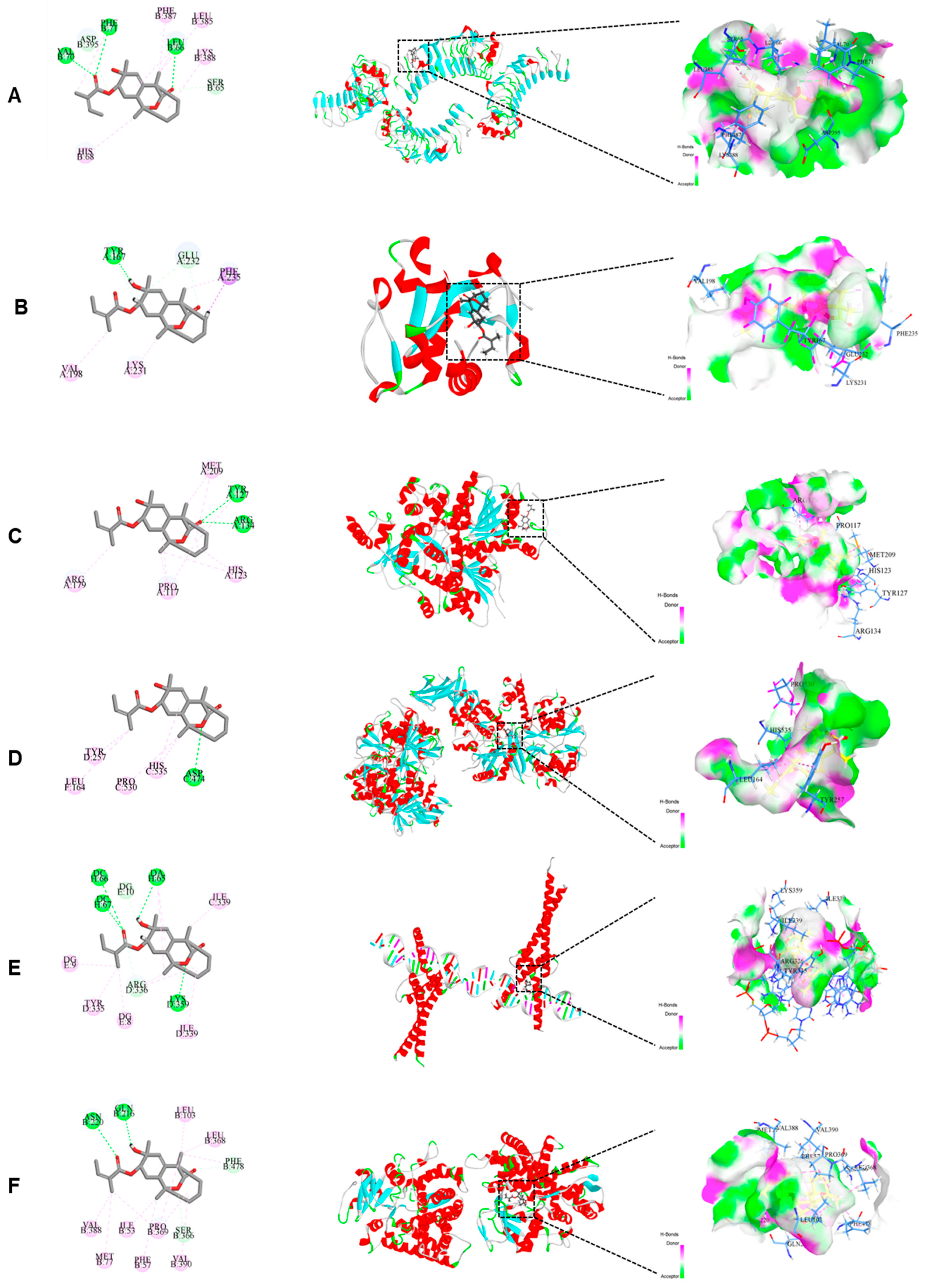
| Number | Protein | PDB ID | LibDock Score | H-Bonds Number | H-Bonds Residues |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TLR4 | 2Z66 | 106.344 | 3 | VALB70, PHEB71, LEUB66 |
| 2 | MYD88 | 4DOM | 100.359 | 1 | TYRA167 |
| 3 | NF-κB | 6SH6 | 105.696 | 2 | TYRA127, ARGA134 |
| 4 | AMPK | 7YMJ | 109.448 | 1 | ASPC474 |
| 5 | SREBP-1c | 1AM9 | 116.711 | 4 | DCH66, DCH67, DAH65, LYSD359 |
| 6 | CYP2E1 | 3E6I | 104.621 | 2 | ASNB220, GLNB216 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, X.; Yang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X. A Novel Sesquiterpene from Callistephus chinensis Improves Alcohol-Induced Liver Disease by Regulating the AMPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Gut Flora. Molecules 2025, 30, 4371. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224371
Zhang B, Wang N, Chen X, Yang N, Zhao Y, Zhang X. A Novel Sesquiterpene from Callistephus chinensis Improves Alcohol-Induced Liver Disease by Regulating the AMPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Gut Flora. Molecules. 2025; 30(22):4371. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224371
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bingxin, Ning Wang, Xiaoxu Chen, Nan Yang, Ying Zhao, and Xiaoshu Zhang. 2025. "A Novel Sesquiterpene from Callistephus chinensis Improves Alcohol-Induced Liver Disease by Regulating the AMPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Gut Flora" Molecules 30, no. 22: 4371. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224371
APA StyleZhang, B., Wang, N., Chen, X., Yang, N., Zhao, Y., & Zhang, X. (2025). A Novel Sesquiterpene from Callistephus chinensis Improves Alcohol-Induced Liver Disease by Regulating the AMPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Gut Flora. Molecules, 30(22), 4371. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224371





