The Application of Poly(2-(hydroxymethyl)acrylic Acid as a Functional Nanomaterial to Ensure the Biosafety of Herbal Decoctions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
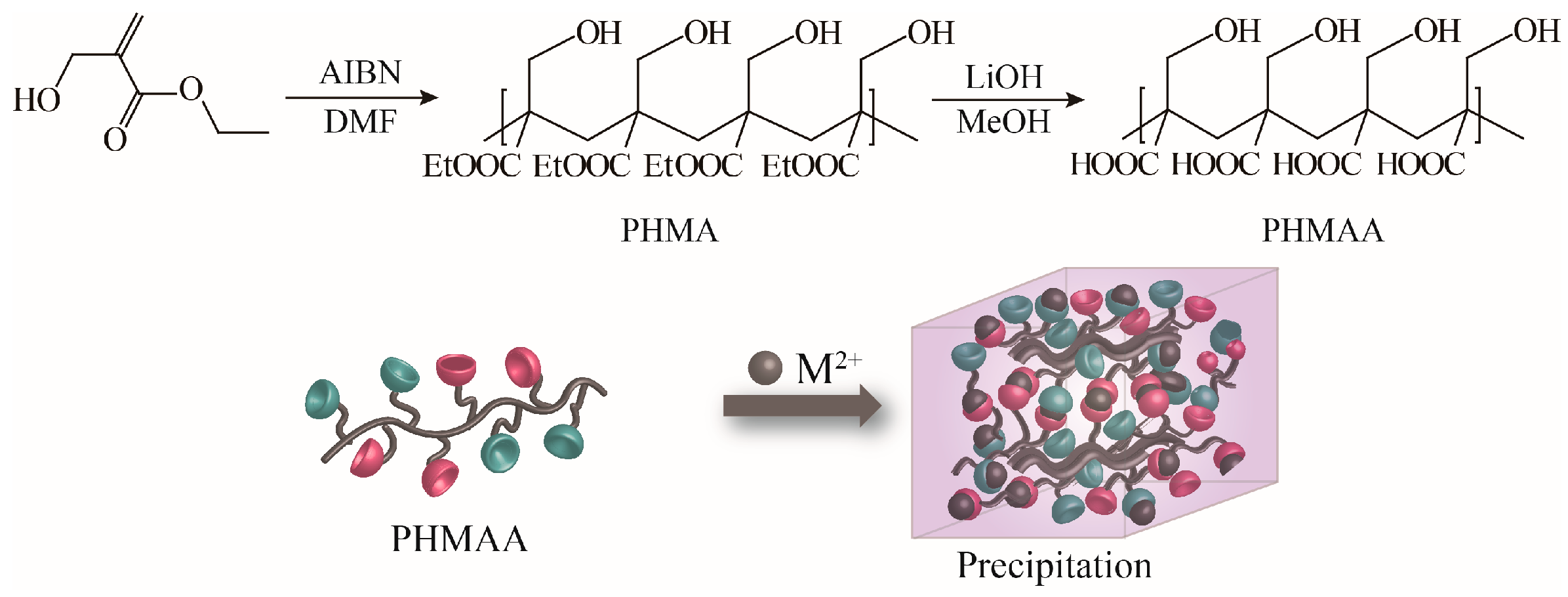
2.1. Synthesis of Nanoadsorbent PHMAE
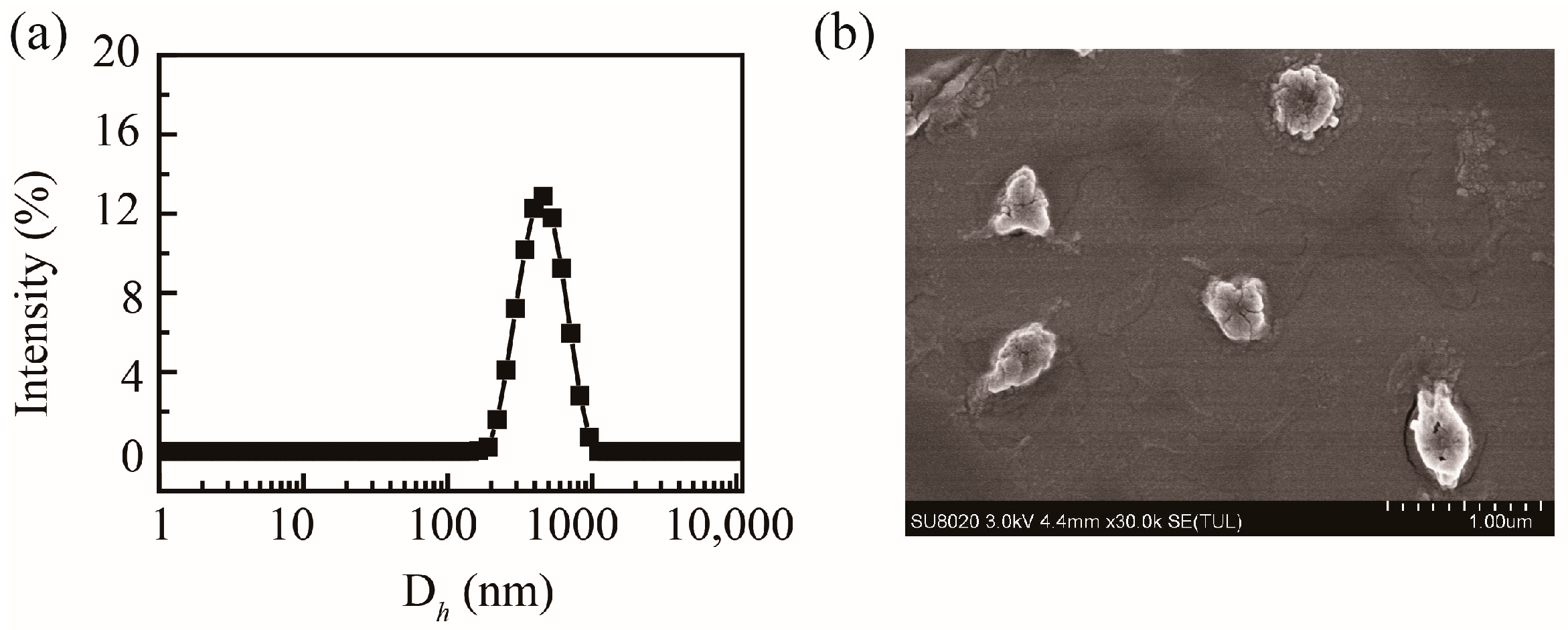
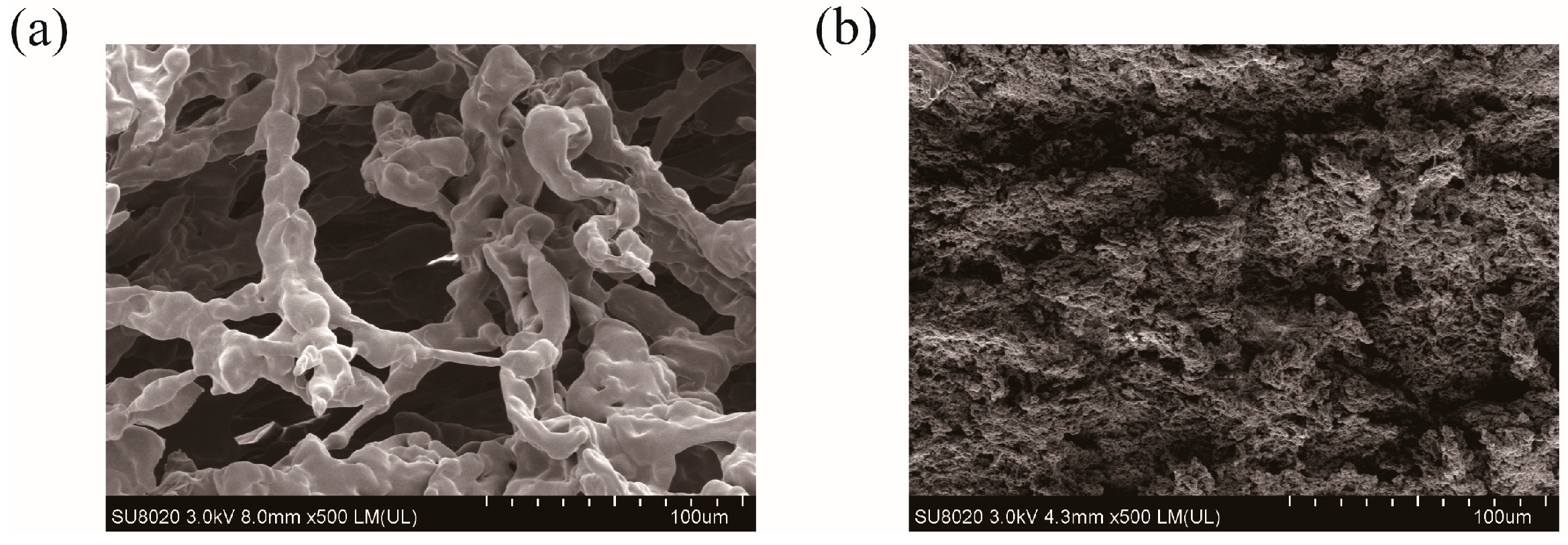
2.2. Particle Size and Morphology of PHMAA
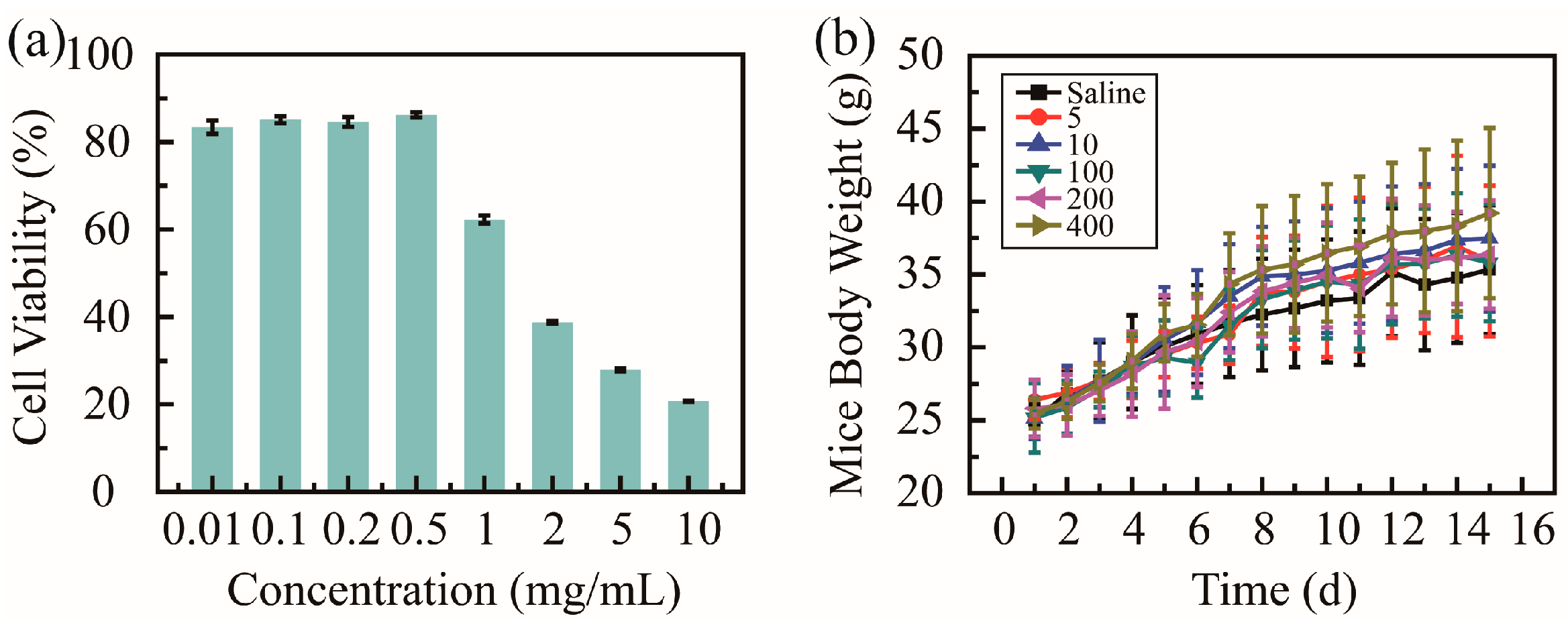
2.3. Biosafety Test
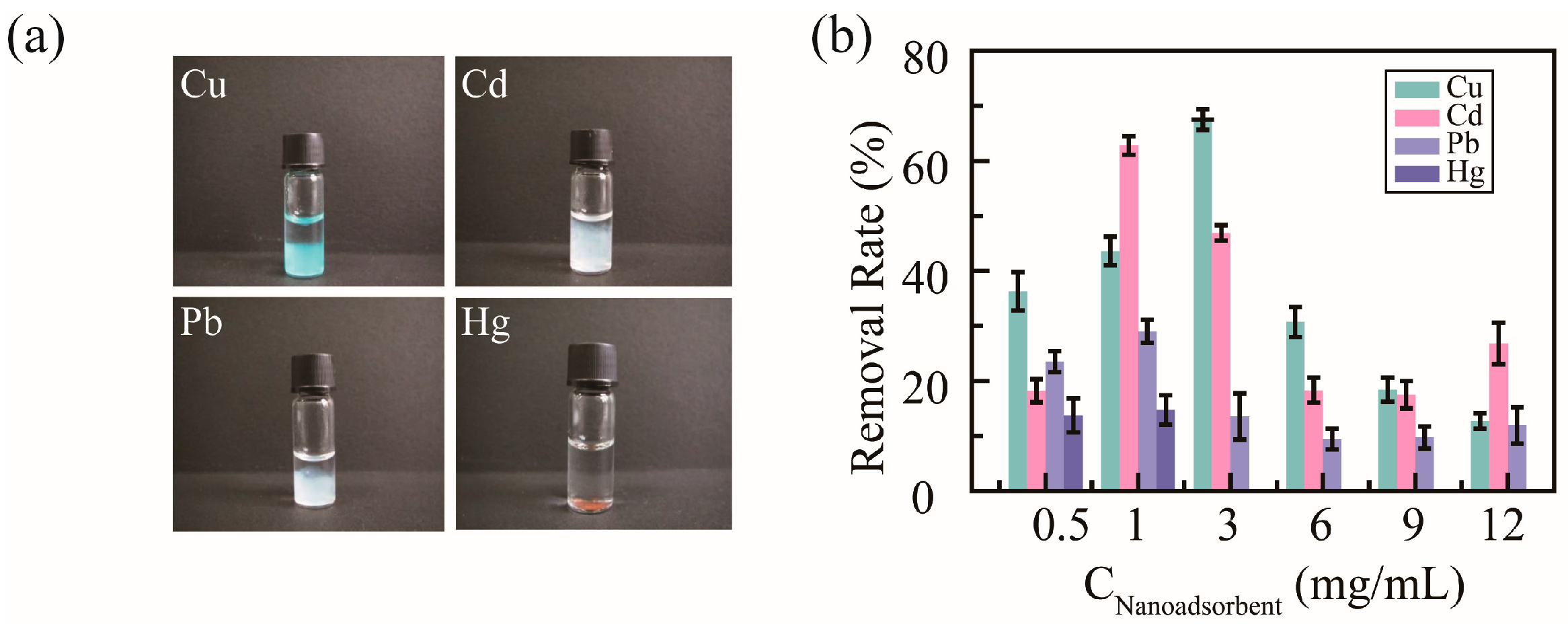
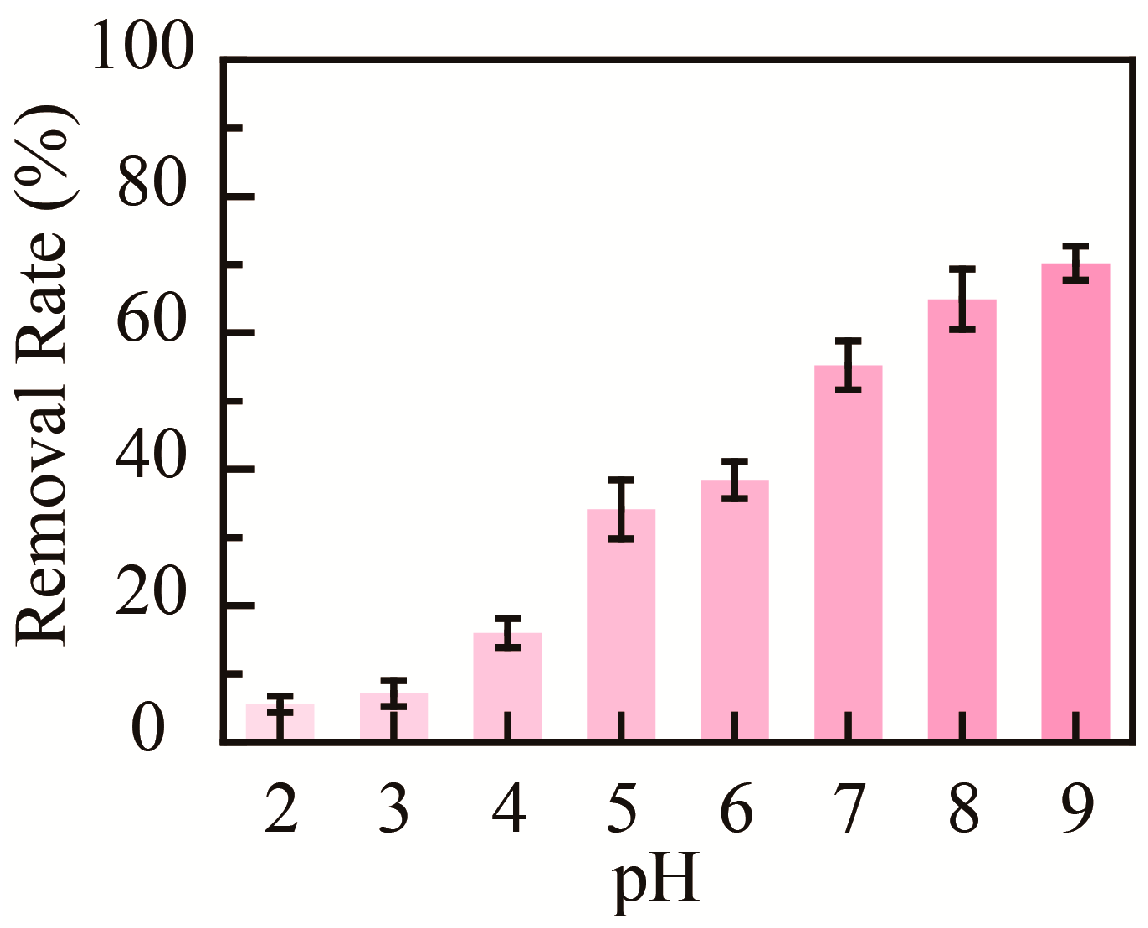
2.4. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution
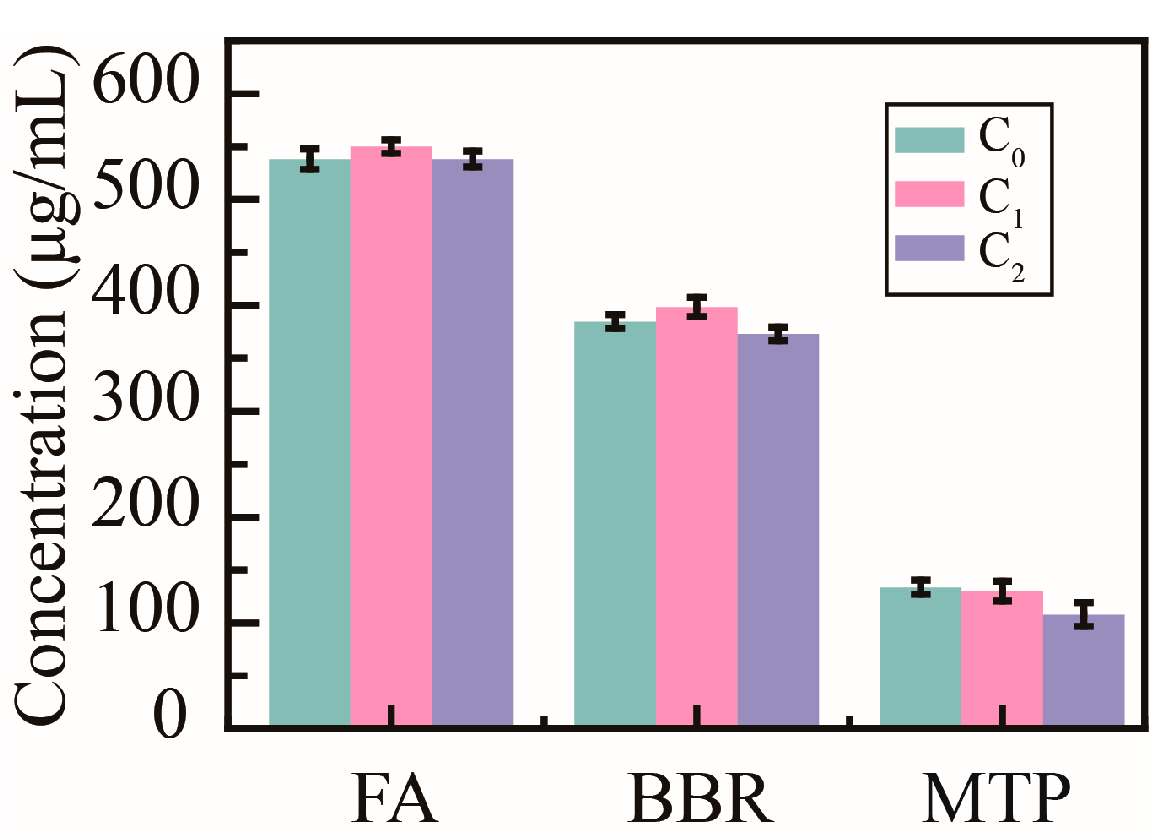
2.5. Removal of Cd2+ Ions in Herbal Decoctions
2.6. Removal of Cd2+ Ions at Low Concentration in Herbal Decoctions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Cells and Animals
3.3. Synthesis of PHMAE
3.4. Hydrolysis of PHMAA
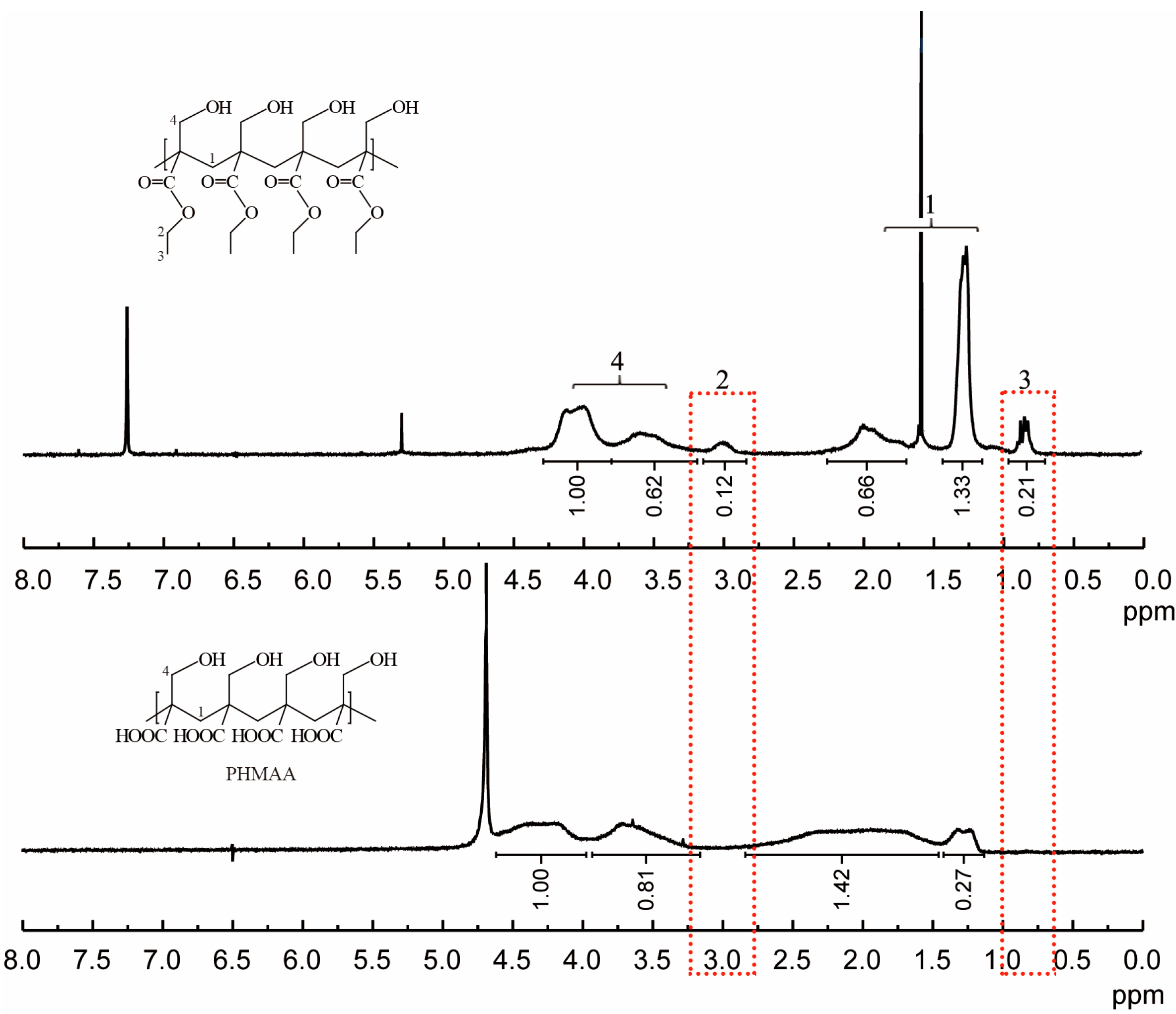
3.5. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Characterization
3.6. Molecular Weight
3.7. Dynamic Light Scattering Measurements
3.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.9. In Vitro and In Vivo Test
3.10. Adsorption Measurement
3.11. Adsorption Measurement in Chinese Herbal Decoctions
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jomova, K.; Makova, M.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Rhodes, C.J.; Valko, M. Essential metals in health and disease. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 367, 110173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. npj Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Xi, S. The effects of heavy metals on human metabolism. Toxicol. Mech. Method. 2020, 30, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghori, N.H.; Ghori, T.; Hayat, M.Q.; Imadi, S.R.; Gul, A.; Altay, V.; Ozturk, M. Heavy metal stress and responses in plants. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1807–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Lopez, M.L.; Narayan, M.; Saupe, G.; Gardea-Torresdey, J. The biochemistry of environmental heavy metal uptake by plants: Implications for the food chain. Int. J. Biochem. Cell B. 2009, 41, 1665–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, H.; Deka, S.; Deka, H.; Saikia, R.R. Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Selected Medicinal Plants. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Whitacre, D.M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 63–86. [Google Scholar]
- Chunilall, V.; Kindness, A.; Jonnalagadda, S.B. Heavy Metal Uptake by Two Edible Amaranthus Herbs Grown on Soils Contaminated with Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, and Nickel. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2005, 40, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, B.; Jiang, J.; Fitzgerald, M.; Huang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Wei, J.; Yang, C.; et al. Heavy Metal Contaminations in Herbal Medicines: Determination, Comprehensive Risk Assessments, and Solutions. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 595335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-G.; He, X.-L.-S.; Huang, J.-H.; Luo, R.; Ge, H.-Z.; Wołowicz, A.; Wawrzkiewicz, M.; Gładysz-Płaska, A.; Li, B.; Yu, Q.-X.; et al. Impacts of heavy metals and medicinal crops on ecological systems, environmental pollution, cultivation, and production processes in China. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 219, 112336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Ban, S.; Devkota, S.; Sharma, S.; Joshi, R.; Tiwari, A.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Joshi, M.K. Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Z. Comparison of heavy metal removals from aqueous solutions by chemical precipitation and characteristics of precipitates. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 26, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ray, A.K. Removal of toxic metal ions from wastewater by semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-K.; Leu, H.-J.; Chiu, K.-F.; Lin, C.-Y. Electrochemical Treatment of Heavy Metal-containing Wastewater with the Removal of COD and Heavy Metal Ions. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2017, 64, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjhi, F.A.; Janwery, D.; Chandio, I.; Ullah, S.; Rehman, F.; Memon, A.A.; Hakami, J.; Khan, F.; Boczkaj, G.; Thebo, K.H. Recent Advances in Graphene Oxide-Based Membranes for Heavy Metal Ions Separation. ChemBioEng Rev. 2022, 9, 574–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.; Malik, L.A.; Ahad, S.; Manzoor, T.; Bhat, M.A.; Dar, G.N.; Pandith, A.H. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous system by ion-exchange and biosorption methods. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 729–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, S.; Pan, S.-Y.; Zhu, S.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, H. Performance evaluation and optimization of flocculation process for removing heavy metal. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, W.; Ge, Q. Novel Multicharge Hydroacid Complexes That Effectively Remove Heavy Metal Ions from Water in Forward Osmosis Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4464–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, A.P.; Aris, A.Z. A review on economically adsorbents on heavy metals removal in water and wastewater. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2014, 13, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, R.; Shafiq, I.; Akhter, P.; Iqbal, M.J.; Hussain, M. A state-of-the-art review on wastewater treatment techniques: The effectiveness of adsorption method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9050–9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Huang, X.; Tang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Niu, F.; Wang, X. Polymer-based nanocomposites for heavy metal ions removal from aqueous solution: A review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 3562–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, E.N.; Motahari, A.; Sillanpää, M. Nanoadsorbents based on conducting polymer nanocomposites with main focus on polyaniline and its derivatives for removal of heavy metal ions/dyes: A review. Environ. Res. 2018, 162, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guibal, E. Interactions of metal ions with chitosan-based sorbents: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 38, 43–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.J.; Deshpande, S.V.; Kennedy, J.F. Metal complexation by chitosan and its derivatives: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 55, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhre, N.A.; Ibrahim, B.M. The use of new chemically modified cellulose for heavy metal ion adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhu, H.; Xue, F.; He, H.; Wang, S. Cellulose-based amphoteric adsorbent for the complete removal of low-level heavy metal ions via a specialization and cooperation mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, G.; Tan, Q.; Gao, M.; Chen, G.; Huang, X.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Polysaccharide-based biopolymer hydrogels for heavy metal detection and adsorption. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 44, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.N.K.; Ismail, A.F.; Beg, M.D.H.; Hegde, G.; Gohari, R.J. Polyvinyl alcohol/polysaccharide hydrogel graft materials for arsenic and heavy metal removal. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 5823–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Fan, W.; Yi, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.; Gu, H. Dithiocarbamate-modified starch derivatives with high heavy metal adsorption performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Anderson, D.P.; Chang, P.R. Modification of porous starch for the adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xiao, C.; Chen, B. A novel starch-based adsorbent for removing toxic Hg(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Han, J.; Jiang, C.; Luo, M.; Zhang, Q.; He, Z.; Hu, J.; Wang, G. Novel Fusion Protein Consisting of Metallothionein, Cellulose Binding Module, and Superfolder GFP for Lead Removal from the Water Decoction of Traditional Chinese Medicine. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 2893–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Liu, F.; Wang, C.; Tang, Z.; Peng, C.; Tan, Y. Polyethylene glycol functionalized Fe3O4@MIL-101(Cr) for the efficient removal of heavy metals from Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Qiu, H.; Kong, D.; Han, M.; Guo, Y. Poly(methacrylate citric acid) with good biosafety as nanoadsorbents of heavy metal ions. Colloid Surf. B 2020, 187, 110656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Qiu, H.; Sun, X.; Han, M.; Guo, Y. Nanoadsorbents preparing from oligoethylene glycol dendron and citric acid: Enhanced adsorption effect for the removal of heavy metal ions. Colloid Surf. B 2020, 189, 110876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.; Gong, G.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Liao, X.; Shi, B. Natural polyphenol-based nanoengineering of collagen-constructed hemoperfusion adsorbent for the excretion of heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 428, 128145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Li, S.; Feng, S.; Gao, J.; Fang, H.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Z. Efficient removal of radioactive Cs+ from contaminated water by PBA-modified Cu-MOF nanofiber three-dimensional porous aerogel: Selectivity, kinetics and biosafety evaluation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 379, 134920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavian, A.R.; Mirrahimi, M.A.-S. Efficient separation of heavy metal cations by anchoring polyacrylic acid on superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles through surface modification. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 159, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.-B.; Zhao, G.-X.; Wang, X.-K.; Yu, S.-H. Synthesis of Polyacrylic Acid Stabilized Amorphous Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticles and Their Application for Removal of Toxic Heavy Metal Ions in Water. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 12948–12954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, S.; He, F.; Liu, Y.; Mao, W.; Guan, Y. Highly efficient and selective capture of heavy metals by poly(acrylic acid) grafted chitosan and biochar composite for wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahat, A.; Awual, M.R.; Khaleque, M.A.; Alam, M.Z.; Naushad, M.; Chowdhury, A.M.S. Large-pore diameter nano-adsorbent and its application for rapid lead(II) detection and removal from aqueous media. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfanjani, L.; Farhadyar, N.; Shahbazi, H.R.; Fathi, F. Development of a method for cadmium ion removal from the water using nano γ-alumina/β-cyclodextrin. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 1877–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Bi, L.; Liu, J.; Huang, B.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, C.; Pan, G.; Song, M. Microalgae-derived carbon quantum dots mediated formation of metal sulfide nano-adsorbents with exceptional cadmium removal performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 629, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badvi Loulic, F.; Haji Seyed Mohammad Shirazi, R.; Miralinaghi, M.; Ahmad Panahi, H.; Moniri, E. Highly efficient removal of toxic As(V), Cd (II), and Pb(II) ions from water samples using MnFe2O4@SBA-15-(CH2)3-adenine as a recyclable bio-nanoadsorbent. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2023, 356, 112567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N.P. Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
| Entry | CPHMAA (mg/mL) | Ligusticum wallichii (%) | Coptidis rhizome (%) | Morindae officinalis (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 56.6 ± 3.9 | 72.4 ± 2.5 | 21.9 ± 3.5 |
| 2 | 1 | 61.3 ± 5.4 | 84.9 ± 6.1 | 25.6 ± 2.1 |
| 3 | 3 | 74.0 ± 4.7 | 87.9 ± 4.4 | 61.9 ± 5.8 |
| 4 | 6 | 83.9 ± 5.0 | 88.6 ± 3.6 | 61.5 ± 3.9 |
| 5 | 9 | 61.2 ± 4.6 | 88.9 ± 2.9 | 62.0 ± 5.6 |
| Entry | CCd (μg/mL) | Ligusticum wallichii | Coptidis rhizome | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 a (μg/mL) | C1 b (μg/mL) | RR c (%) | C0 a (μg/mL) | C1 b (μg/mL) | RR c (%) | ||
| 1 | 5 | 5.63 | 1.73 | 69.3 | 5.12 | 1.21 | 76.4 |
| 2 | 10 | 11.45 | 3.53 | 69.2 | 10.89 | 2.75 | 74.7 |
| 3 | 20 | 24.04 | 7.39 | 69.2 | 21.41 | 5.98 | 72.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Han, M.; Dong, Z. The Application of Poly(2-(hydroxymethyl)acrylic Acid as a Functional Nanomaterial to Ensure the Biosafety of Herbal Decoctions. Molecules 2025, 30, 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214276
Guo Y, Sun X, Zhao X, Wang X, Han M, Dong Z. The Application of Poly(2-(hydroxymethyl)acrylic Acid as a Functional Nanomaterial to Ensure the Biosafety of Herbal Decoctions. Molecules. 2025; 30(21):4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214276
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yifei, Xueqing Sun, Xiangsheng Zhao, Xiangtao Wang, Meihua Han, and Zhengqi Dong. 2025. "The Application of Poly(2-(hydroxymethyl)acrylic Acid as a Functional Nanomaterial to Ensure the Biosafety of Herbal Decoctions" Molecules 30, no. 21: 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214276
APA StyleGuo, Y., Sun, X., Zhao, X., Wang, X., Han, M., & Dong, Z. (2025). The Application of Poly(2-(hydroxymethyl)acrylic Acid as a Functional Nanomaterial to Ensure the Biosafety of Herbal Decoctions. Molecules, 30(21), 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214276




