Synthesis of FeOOH/Al2O3 Composites with Excellent Adsorption Performance and Regenerability for Phosphate Removal from Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Adsorbents
2.2. Adsorption Behavior
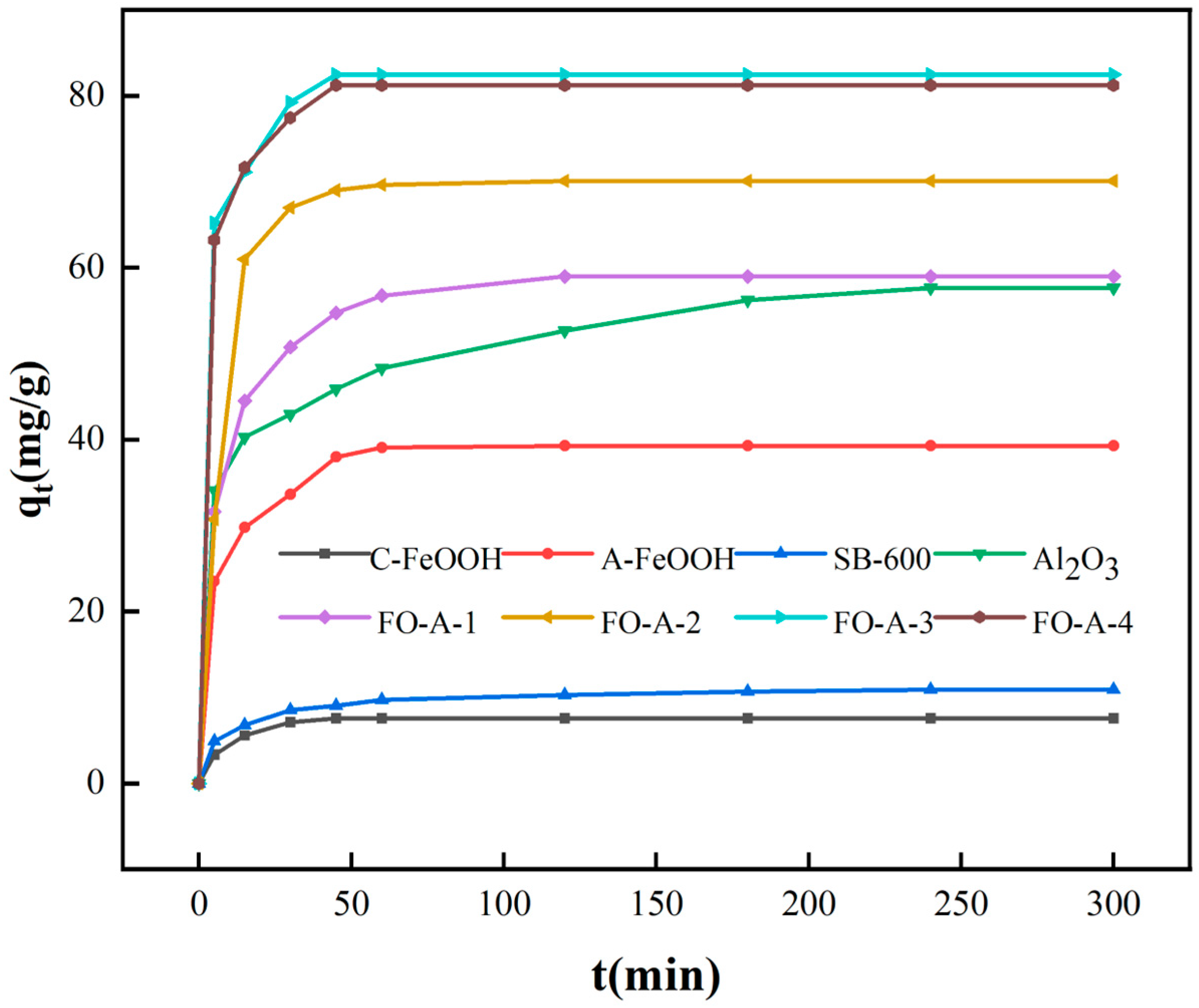
2.2.1. Study on Adsorption Kinetics
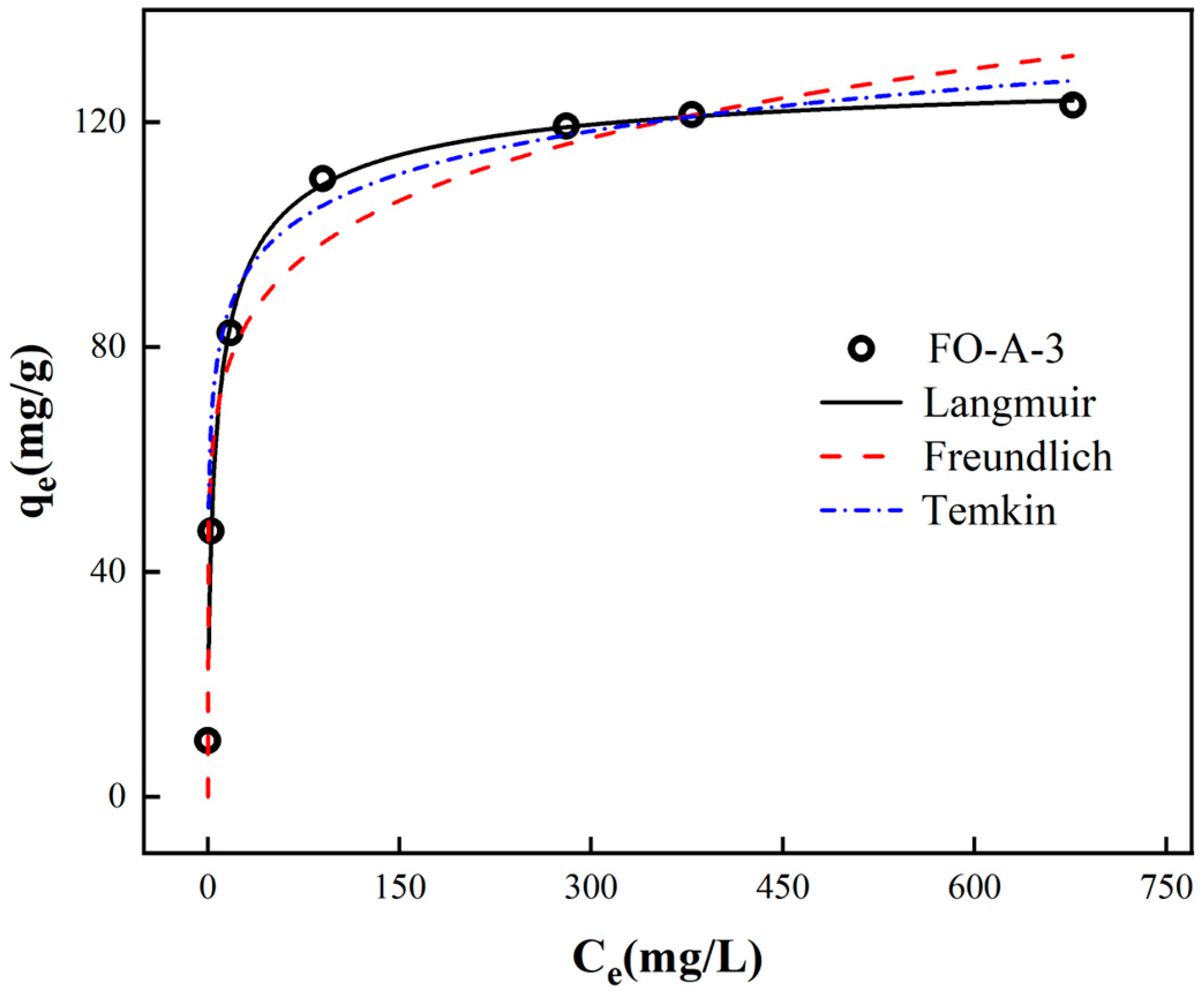
2.2.2. Adsorption Isotherm Models
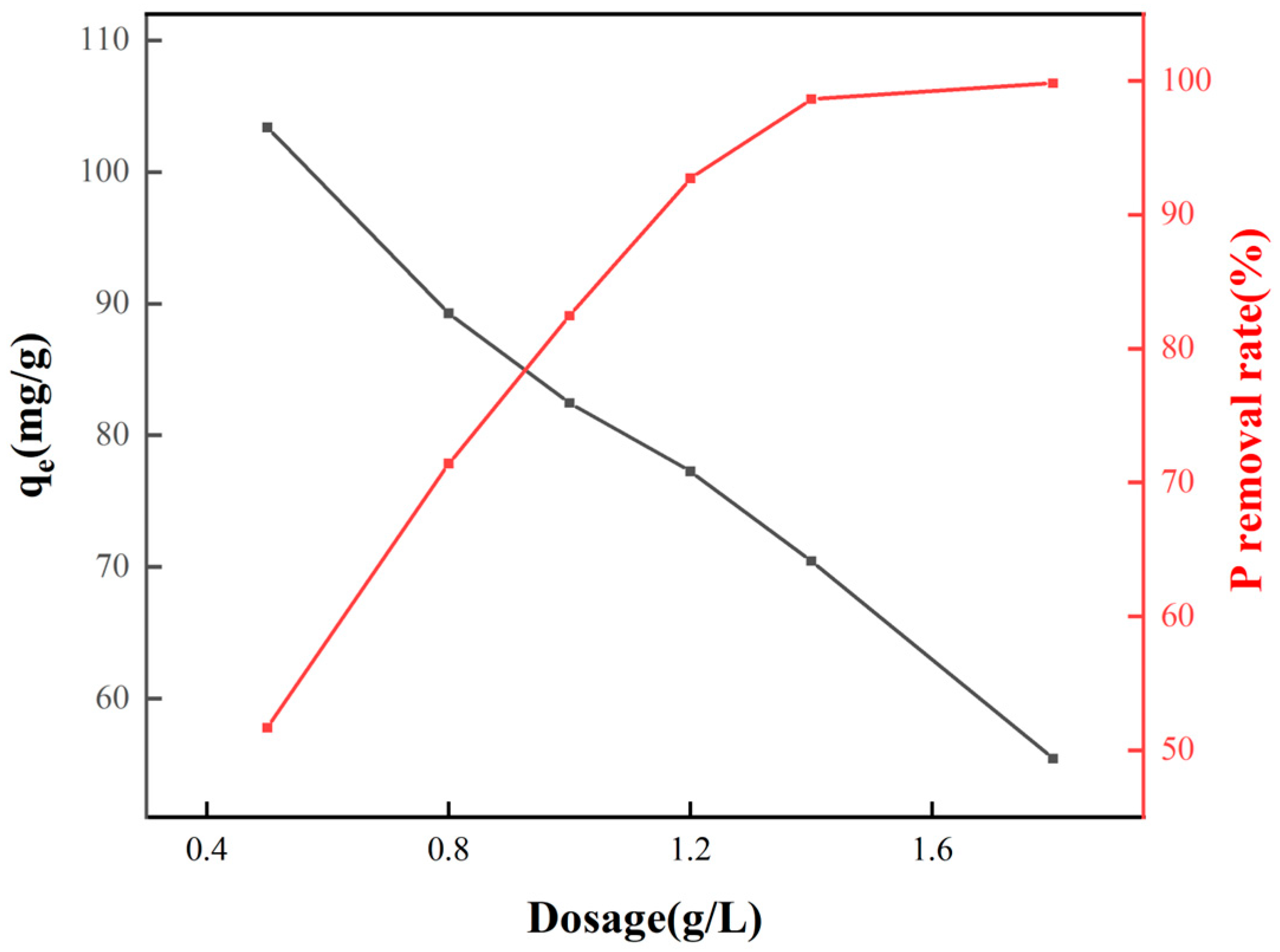
2.2.3. The Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
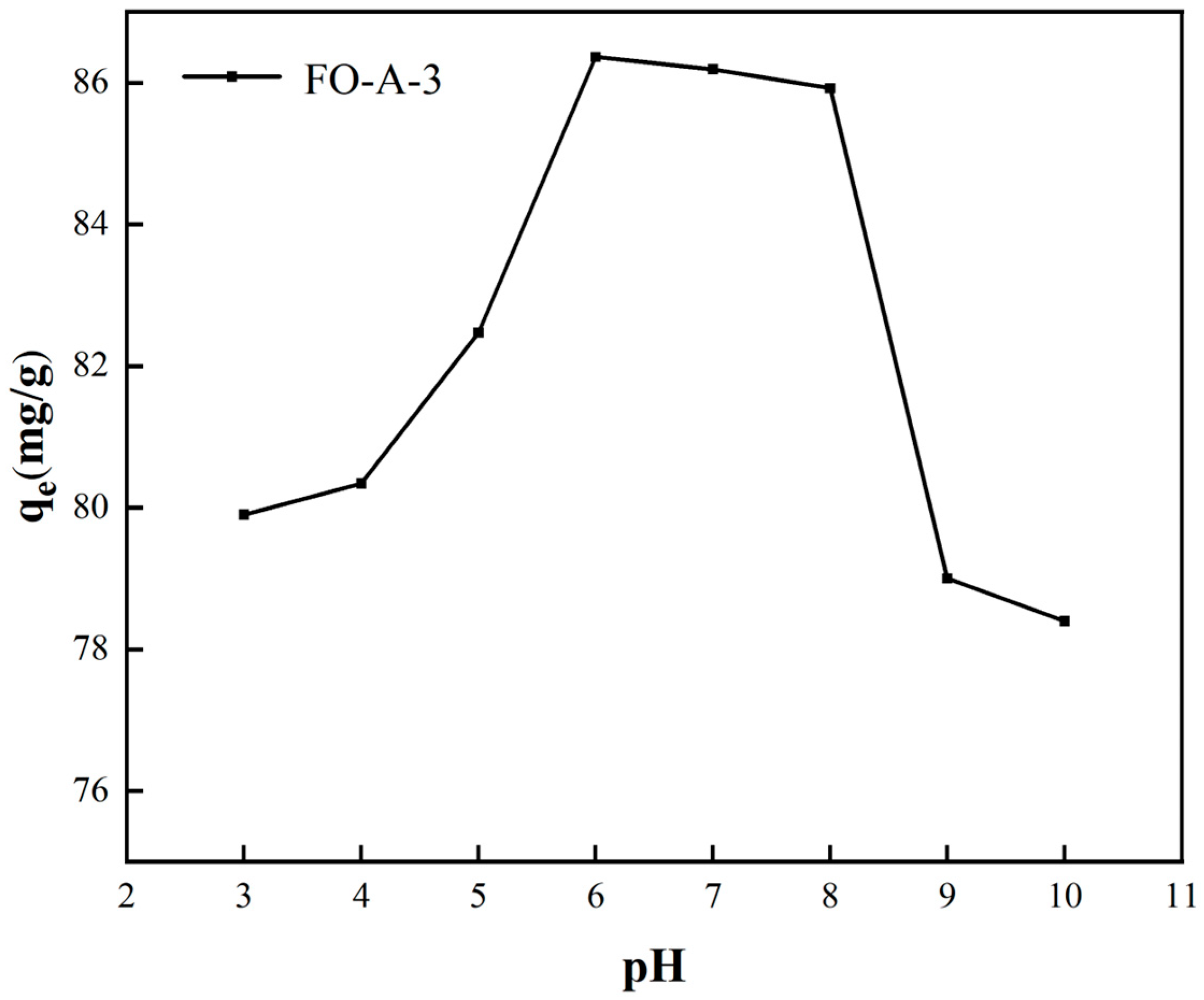
2.2.4. The Effect of Initial pH
2.3. Regeneration of FeOOH/Al2O3 Composites
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
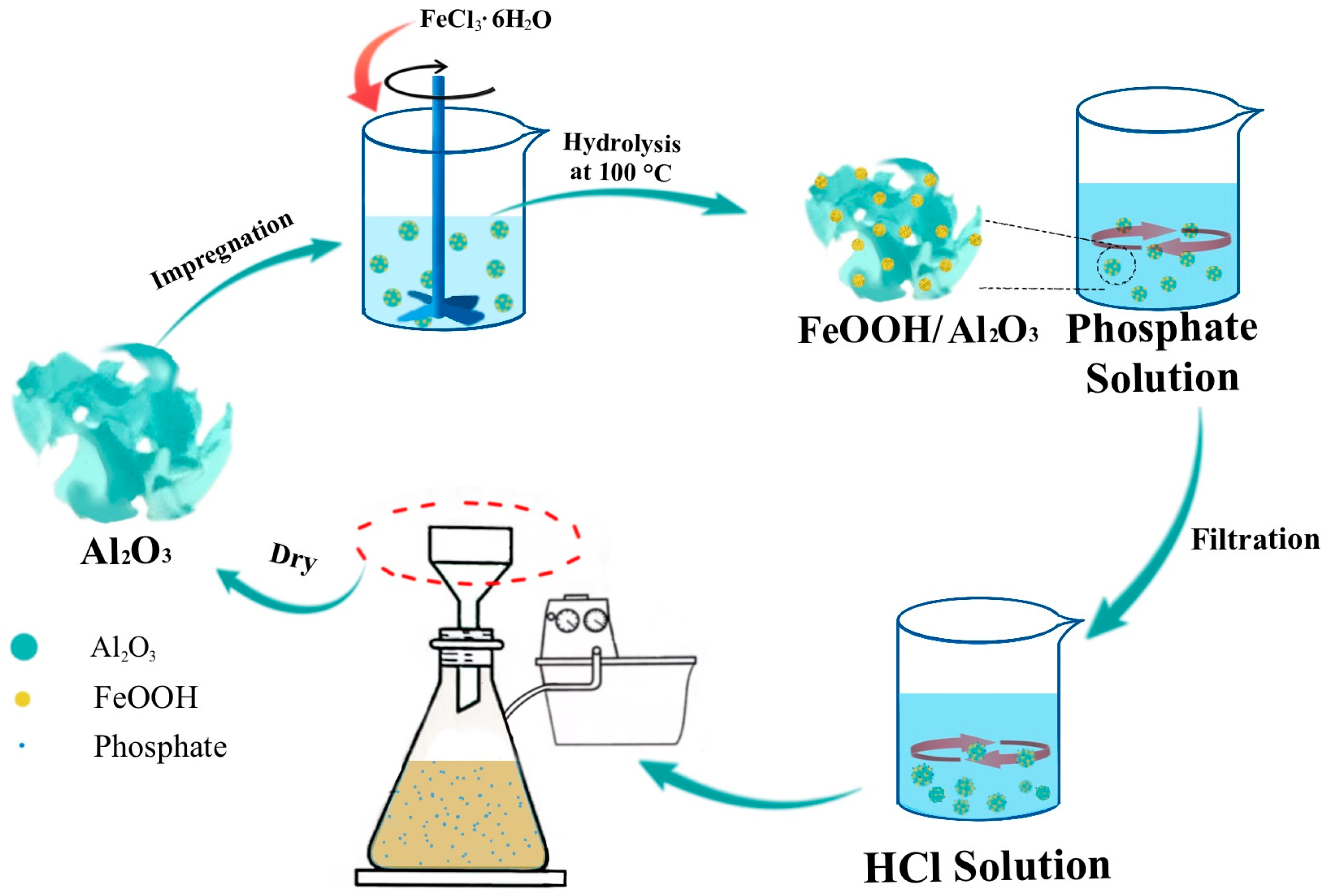
3.2. Synthesis
3.2.1. Preparation of Al2O3
3.2.2. Preparation of SB-600
3.2.3. Preparation of Amorphous FeOOH and Crystalline FeOOH
3.2.4. Preparation of FeOOH/Al2O3 Composites
3.3. Analytical Procedures
3.4. Adsorption and Desorption Studies
3.4.1. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherm
3.4.2. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage and the Initial pH
3.4.3. Regeneration Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bacelo, H.; Pintor, A.M.A.; Santos, S.C.R.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Performance and prospects of different adsorbents for phosphorus uptake and recovery from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, B.; Lo, I.M.C. Selective Phosphate Removal from Water and Wastewater using Sorption: Process Fundamentals and Removal Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, S.; Rubertelli, G.; Jefferson, B.; Soares, A. Demonstration of ion exchange technology for phosphorus removal and recovery from municipal wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Soares, A.; Jefferson, B. The impact of background wastewater constituents on the selectivity and capacity of a hybrid ion exchange resin for phosphorus removal from wastewater. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Gao, B. Recovery of phosphorus from wastewater: A review based on current phosphorous removal technologies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 1148–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jia, H. Insight into chemical phosphate recovery from municipal wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna Veni, D.; Kannan, P.; Jebakumar Immanuel Edison, T.N.; Senthilkumar, A. Biochar from green waste for phosphate removal with subsequent disposal. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, T.; Lu, D.; Soh, Y.N.A.; Webster, R.D.; Zhou, Y. Biotransformation of phosphorus in enhanced biological phosphorus removal sludge biochar. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; He, S.; Wu, F. Biochemical processes mediated by iron-based materials in water treatement: Enhancing nitrogen and phosphorus removal in low C/N ratio wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muisa, N.; Nhapi, I.; Ruziwa, W.; Manyuchi, M.M. Utilization of alum sludge as adsorbent for phosphorus removal in municipal wastewater: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, G.-J.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Jin, D.; Ali, Z.; Zhou, J.; Sun, R. Recent advances and challenges on removal and recycling of phosphate from wastewater using biomass-derived adsorbents. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Lin, Y.; Li, C.; Wu, D.; Kong, H. Removal and recovery of phosphate from water by activated aluminum oxide and lanthanum oxide. Powder Technol. 2015, 269, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Gao, A.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Song, J. Removal of Phosphorus from Wastewater by Different Morphological Alumina. Molecules 2020, 25, 3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Chu, W.; Ren, X.; Ma, F.; Chen, R.; Ning, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, C.; Shi, L.; Ren, L.; et al. Optimizing Coordinated Active Sites of Transition Metal Complexes: Exploring Metal–Molecule Interactions for Governing CO2-to-CO Conversion. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 17336–17346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lu, Y.; Eltohamy, K.M.; Liu, B.; Xin, H.; He, S.; Fang, Y.; Liang, X. Zr/Zn nanocomposites modified ceramsite enhances phosphorus removal from agricultural drainage water. Chemosphere 2023, 340, 139852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, B.; Shan, C.; Gao, X. Enhanced Phosphate Removal by Nanosized Hydrated La(III) Oxide Confined in Cross-linked Polystyrene Networks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, X.; Jing, M.; Li, C. Enhanced arsenic removal from drinking water by FeOOH/γ-Al2O3 granules. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Qian, G. Phosphate adsorption on metal oxides and metal hydroxides: A comparative review. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhang, M.; Mortimer, R.J.G.; Pan, G. Enhanced Phosphorus Locking by Novel Lanthanum/Aluminum–Hydroxide Composite: Implications for Eutrophication Control. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3418–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Feng, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Yan, W. Adsorption mechanism of phosphate by polyaniline/TiO2 composite from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.K.; Kim, D. Smart Design of Self-Assembled Mesoporous α-FeOOH Nanoparticles: High-Surface-Area Sorbent for Hg2+ from Wastewater. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockgreitens, J.W.; Heidari, F.; Abbas, A. Versatile Process for the Preparation of Nanocomposite Sorbents: Phosphorus and Arsenic Removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9034–9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ren, X.; Mo, S.; Cao, W.; Zhou, C.; Ma, F.; Chen, R.; Zeng, C.; Shi, L.; Liu, T.; et al. Modulating Fe/P ratios in Fe-P alloy through smelting reduction for long-term electrocatalytic overall water splitting. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 199, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, H.; Lei, X.; Lian, Q.; Roy, A.; Doucet, D.; Yan, H.; Zappi, M.E.; Gang, D.D. A comparative study for phosphate adsorption on amorphous FeOOH and goethite (α-FeOOH): An investigation of relationship between the surface chemistry and structure. Environ. Res. 2021, 199, 111223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoerr, R.; Brendlé, J.; Lebeau, B.; Demais, H. Preparation of ferric oxide modified diatomite and its application in the remediation of As(III) species from solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 169, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, H.; Li, X.; Chen, C.; Xu, L.; Fu, M.-L.; Sun, W.; Yuan, B. Immobilization of β-FeOOH nanomaterials on the basalt fiber as a novel porous composite to effectively remove phosphate from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 632, 127815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyngsie, G.; Katika, K.; Fabricius, I.L.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Borggaard, O.K. Phosphate removal by iron oxide-coated diatomite: Laboratory test of a new method for cleaning drainage water. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Adsorptive removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions using iron oxide tailings. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, Q.C.; Ko, S.-O.; Jang, A.; Kim, Y.; Kang, S. Incorporation of iron (oxyhydr)oxide nanoparticles with expanded graphite for phosphorus removal and recovery from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Qu, M.; Zhang, S.; Quan, F.; Zhang, M.; Shen, W.; Mei, Y. Preparation of FeOOH supported by melamine sponge and its application for efficient phosphate removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Guo, J.; Hossain, M.F.; Lu, J.; Lu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y. Recent advances in the removal and recovery of phosphorus from aqueous solution by metal-based adsorbents: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 204, 107464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Ye, Y.; Kang, J.; Liu, D.; Ren, Y.; Li, D.; Luo, C.; Xu, Z. Enhanced phosphate removal by zeolite loaded with Mg–Al–La ternary (hydr)oxides from aqueous solutions: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew Lin, K.-Y.; Chang, H.-A.; Chen, B.-J. Multi-functional MOF-derived magnetic carbon sponge. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13611–13625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Song, J. Synthesis of Mesoporous Alumina with High Specific Surface Area via Reverse Precipitation Method for Enhanced Adsorption and Regeneration of Congo Red. Materials 2025, 18, 2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Cai, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Fang, Y.; et al. Cobalt nanoparticles-embedded magnetic ordered mesoporous carbon for highly effective adsorption of rhodamine B. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 314, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Han, J.; Gu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, H.; Ni, S.; Cao, Y.; Yang, K. Characteristics and mechanisms of phosphorus adsorption by blue algae biochar modified with a polyaluminum chloride (PAC) dehydrating agent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, X.; Yan, L. Phosphate adsorption performance and mechanisms by nanoporous biochar–iron oxides from aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 28132–28145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Wang, J.J.; Zhou, B.; Awasthi, M.K.; Ali, A.; Zhang, Z.; Gaston, L.A.; Lahori, A.H.; Mahar, A. Enhancing phosphate adsorption by Mg/Al layered double hydroxide functionalized biochar with different Mg/Al ratios. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Han, W.; Marquina, C.; Kwan, J.K.C.; Ricardo Ibarra, M.; Yeung, K.L. Efficient adsorption of phosphate on magnetic Fe3O4@MOF@LDH superstructures: Kinetics, thermodynamics, and mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2025, 283, 122183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Lei, M.; Liu, D.; Guo, J.; Yan, L.; Chen, T.; Li, Y. Highly efficient and selective adsorption of phosphorus and mechanism study by La-Zr co-modified hydrogel beads with 3D network structure. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 708, 136010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, T.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. Preparation of Mg/Al-LDH@HC composite with low concentration hydrochloric acid modified for phosphate removal from aqueous solution: Synthesis, adsorption performance and mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ji, C.; Mo, H.; Jing, X.; Qian, J.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Z. One-pot synthesis of magnetic Mg-enriched MgFe2O4 composites for high recovery of phosphate from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 503, 158379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Liao, Y.; Gao, A.; Hu, Y.; Yang, T.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, J. Defluoridation of Water Using Active Alumina Derived from Single–Layer Boehmite. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin 2020, 36, 1911009. [Google Scholar]
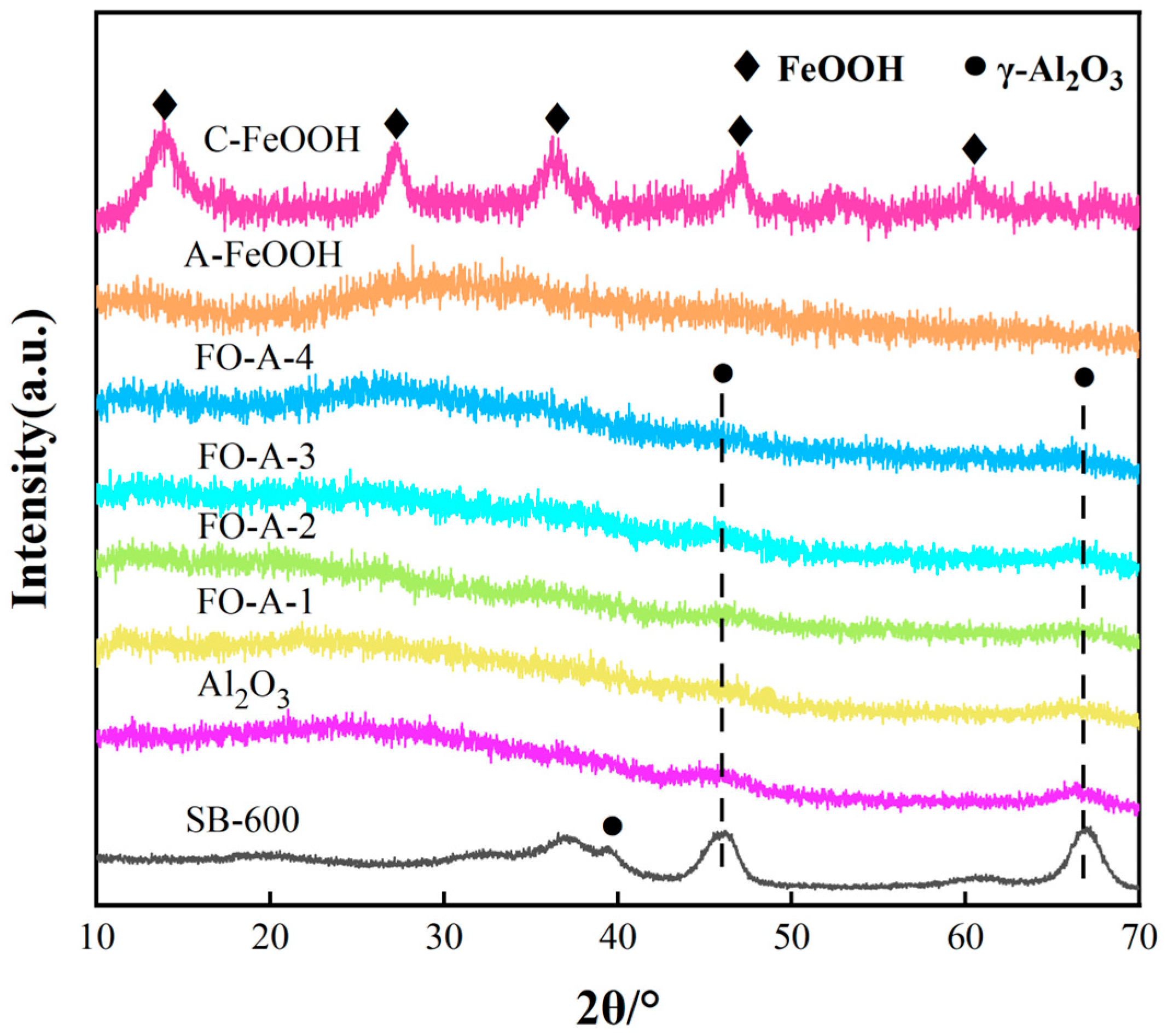
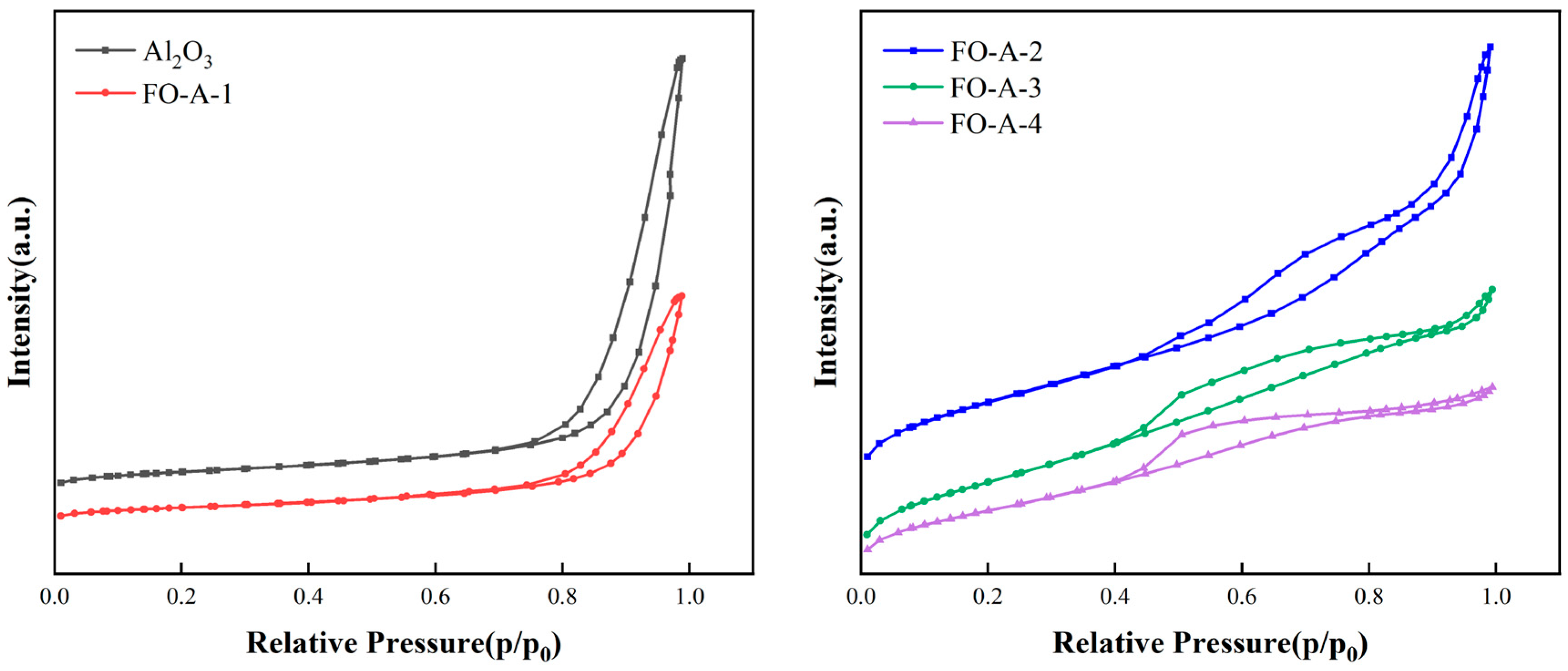
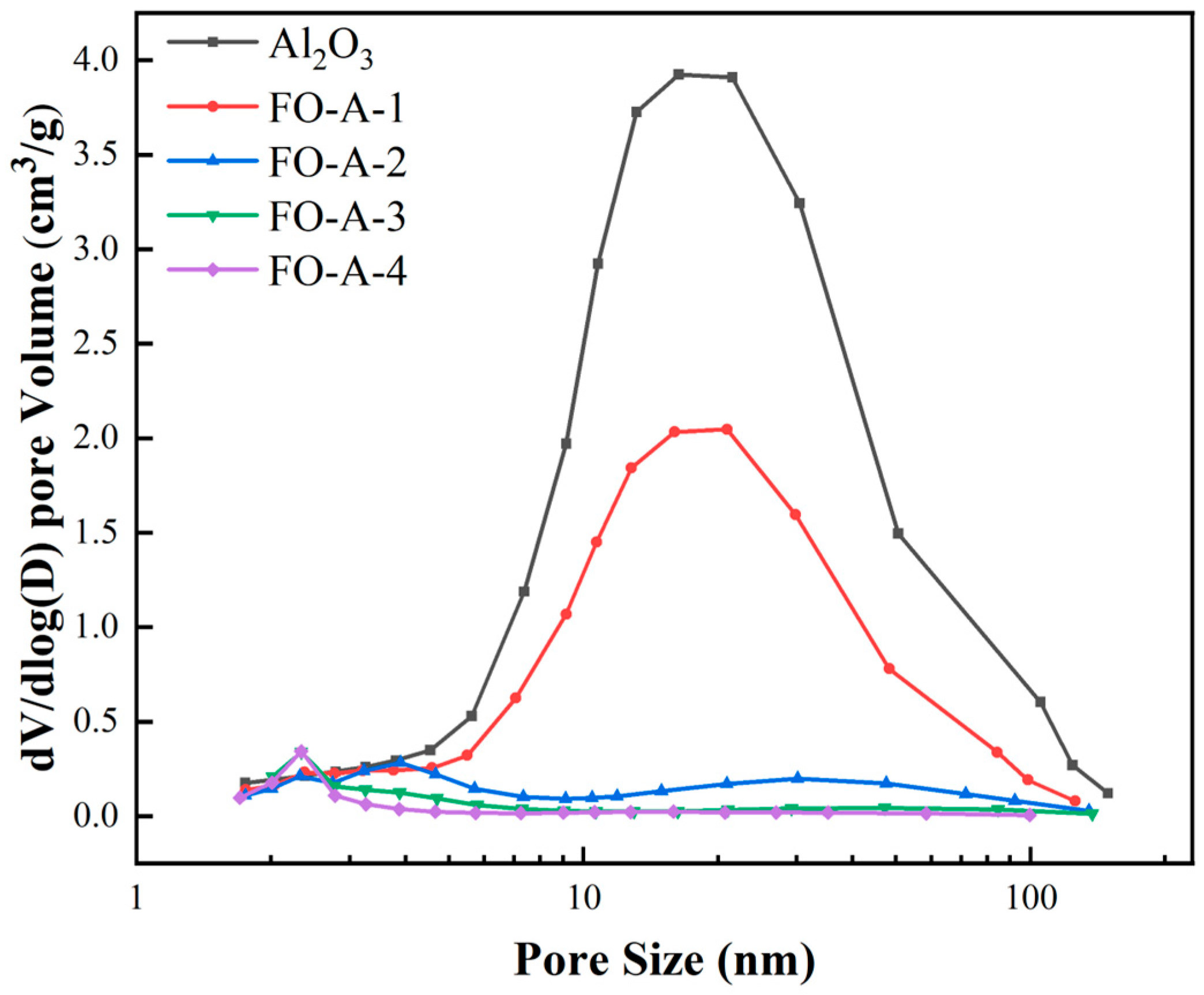
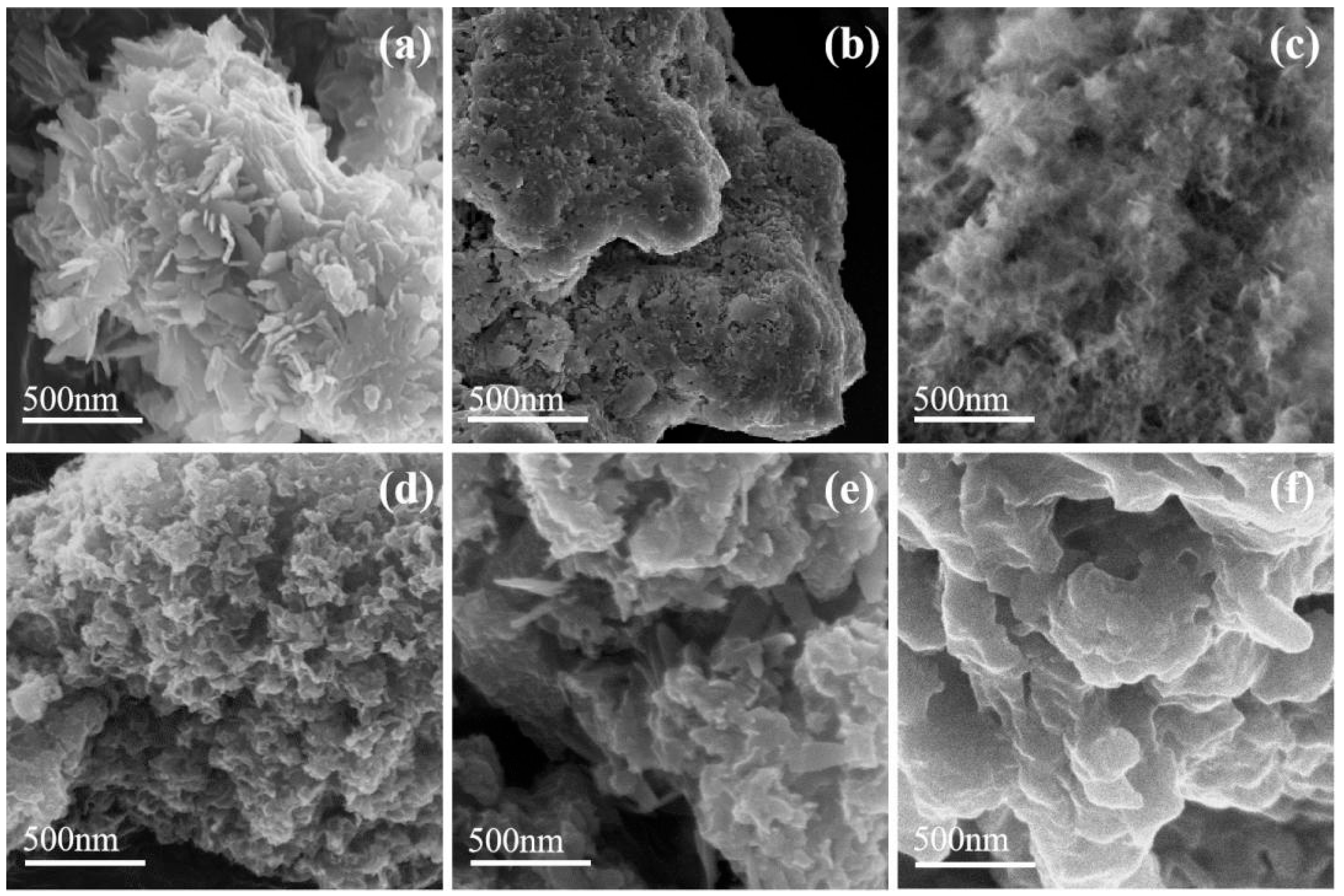



| Adsorbent | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | BET Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Most Probable Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 493.7 | 3.62 | 16.3 |
| FO-A-1 | 307.9 | 1.48 | 20.8 |
| FO-A-2 | 264.6 | 0.45 | 3.9 |
| FO-A-3 | 235.0 | 0.28 | 2.3 |
| FO-A-4 | 182.7 | 0.20 | 2.3 |
| Adsorbent | Fe Atomic Fraction (%) | Al Atomic Fraction (%) | nFe3+/nAl3+ EDS |
|---|---|---|---|
| FO-A-1 | 2.41 | 25.22 | 0.08 |
| FO-A-2 | 1.15 | 20.77 | 0.20 |
| FO-A-3 | 2.33 | 20.67 | 0.45 |
| FO-A-4 | 2.25 | 19.98 | 0.56 |
| Adsorbent | Qe,exp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg/g) | k1 (min−1) | R2 | qe (mg/g) | k2 (g/(mg∙min)) | R2 | ||
| C-FeOOH | 7.56 | 8.03 | 0.1641 | 0.9047 | 7.80 | 0.03197 | 0.9989 |
| A-FeOOH | 39.27 | 31.78 | 0.07623 | 0.9471 | 40.32 | 0.006276 | 0.9995 |
| Al2O3 | 57.75 | 57.64 | 0.01520 | 0.9835 | 59.52 | 0.001610 | 0.9987 |
| FO-A-1 | 59.98 | 31.30 | 0.04445 | 0.9950 | 60.98 | 0.003244 | 0.9998 |
| FO-A-2 | 70.11 | 39.93 | 0.07807 | 0.9743 | 71.94 | 0004342 | 0.9992 |
| FO-A-3 | 82.47 | 26.80 | 0.06840 | 0.9725 | 85.47 | 0.005265 | 0.9993 |
| FO-A-4 | 81.24 | 24.51 | 0.06241 | 0.9999 | 84.03 | 0.005510 | 0.9995 |
| Langmuir | Freundlich | Temkin | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent | qm,cal (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 | bT (J/mol) | KT (L/mg) | R2 |
| FO-A-3 | 131.00 | 0.2964 | 0.9987 | 51.4151 | 0.1445 | 0.9488 | 206.3171 | 157.03 | 0.9238 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorption Capacity mg/g | References |
|---|---|---|
| P500K1.5–500 | 58.72 | [36] |
| BC-G | 22.14 | [37] |
| 4:1 Mg/Al-LDHs | 81.83 | [38] |
| Amorphous FeOOH | 115.61 | [24] |
| MALZ | 80.80 | [32] |
| Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe)@Mg-Al LDH | 54.43 | [39] |
| La-Zr@SA/NIPAM | 105.26 | [40] |
| Mg/Al-LDH@HC-HCl | 143.03 | [41] |
| FeOOH/BF | 39.08 | [26] |
| FeOOH@MS | 115.50 | [30] |
| Activated aluminum oxide | 20.88 | [12] |
| FO-A-3 | 131.00 | This study |
| Adsorbent | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | BET Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Most Probable Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZJ-2 | 169.7 | 0.18 | 2.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, B.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Yan, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Song, J. Synthesis of FeOOH/Al2O3 Composites with Excellent Adsorption Performance and Regenerability for Phosphate Removal from Wastewater. Molecules 2025, 30, 4200. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214200
Jiang B, Chen S, Wang H, Yan J, Wang X, Xu X, Song J. Synthesis of FeOOH/Al2O3 Composites with Excellent Adsorption Performance and Regenerability for Phosphate Removal from Wastewater. Molecules. 2025; 30(21):4200. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214200
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Boning, Shuaiqi Chen, Haoran Wang, Jingwen Yan, Xuhui Wang, Xiangyu Xu, and Jiaqing Song. 2025. "Synthesis of FeOOH/Al2O3 Composites with Excellent Adsorption Performance and Regenerability for Phosphate Removal from Wastewater" Molecules 30, no. 21: 4200. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214200
APA StyleJiang, B., Chen, S., Wang, H., Yan, J., Wang, X., Xu, X., & Song, J. (2025). Synthesis of FeOOH/Al2O3 Composites with Excellent Adsorption Performance and Regenerability for Phosphate Removal from Wastewater. Molecules, 30(21), 4200. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214200






