Advances in Synergistic Corrosion Mechanisms of and Management Strategies for Impurity Gases During Supercritical CO2 Pipeline Transportation
Abstract
1. Introduction
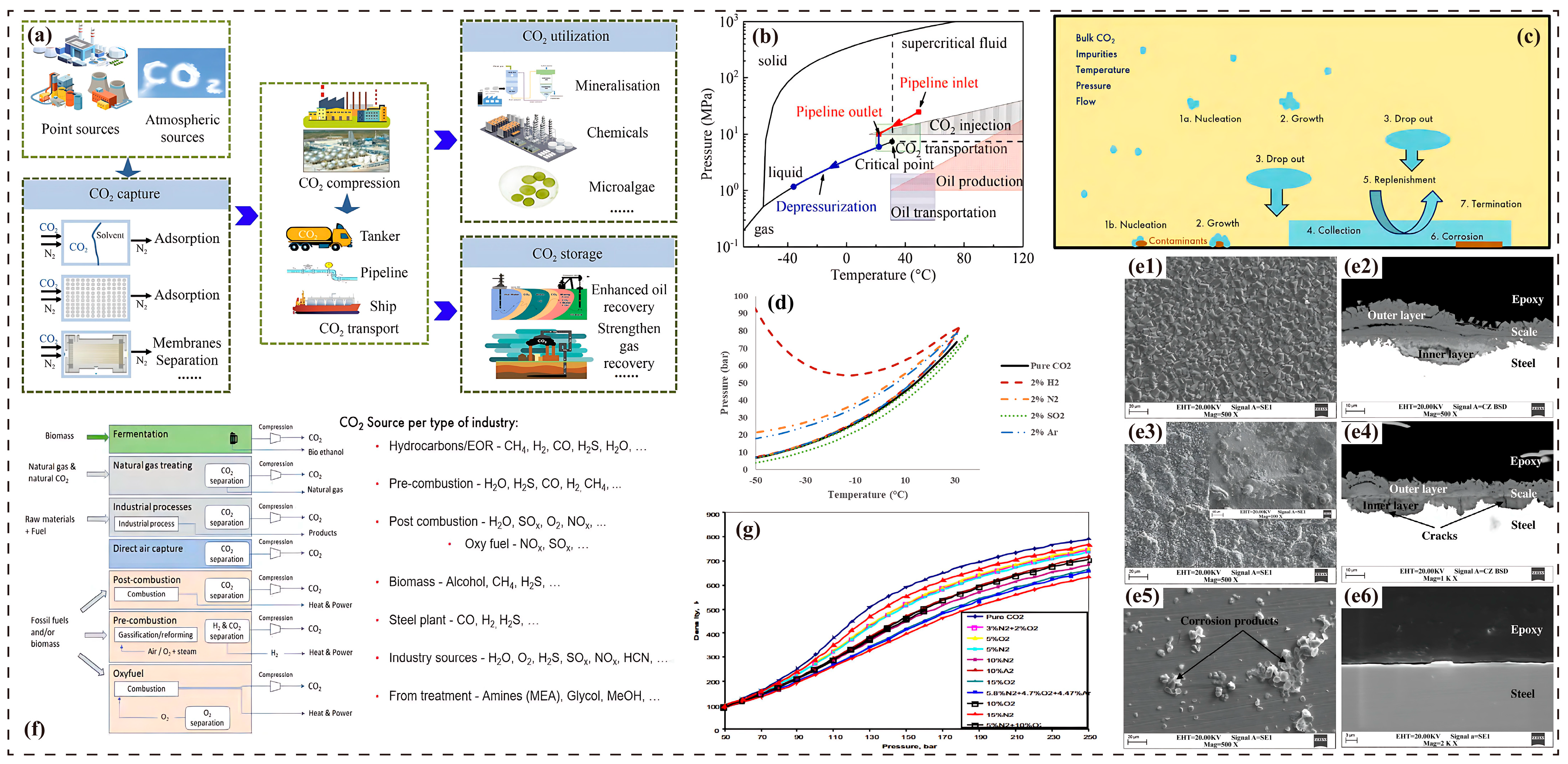
2. Impact of Impurities on Pipeline Fluid Properties
2.1. Key Changes in Phase Behavior and Density
2.2. Fluidity and Transportation Energy Consumption
3. Threats of Impurities to Pipeline Integrity
3.1. Core Role of H2O
3.2. Impact of O2
- (1)
- Corrosion Promotion by Low-Concentration O2
- (2)
- Corrosion Inhibition and Passivation Effect at High O2 Concentrations
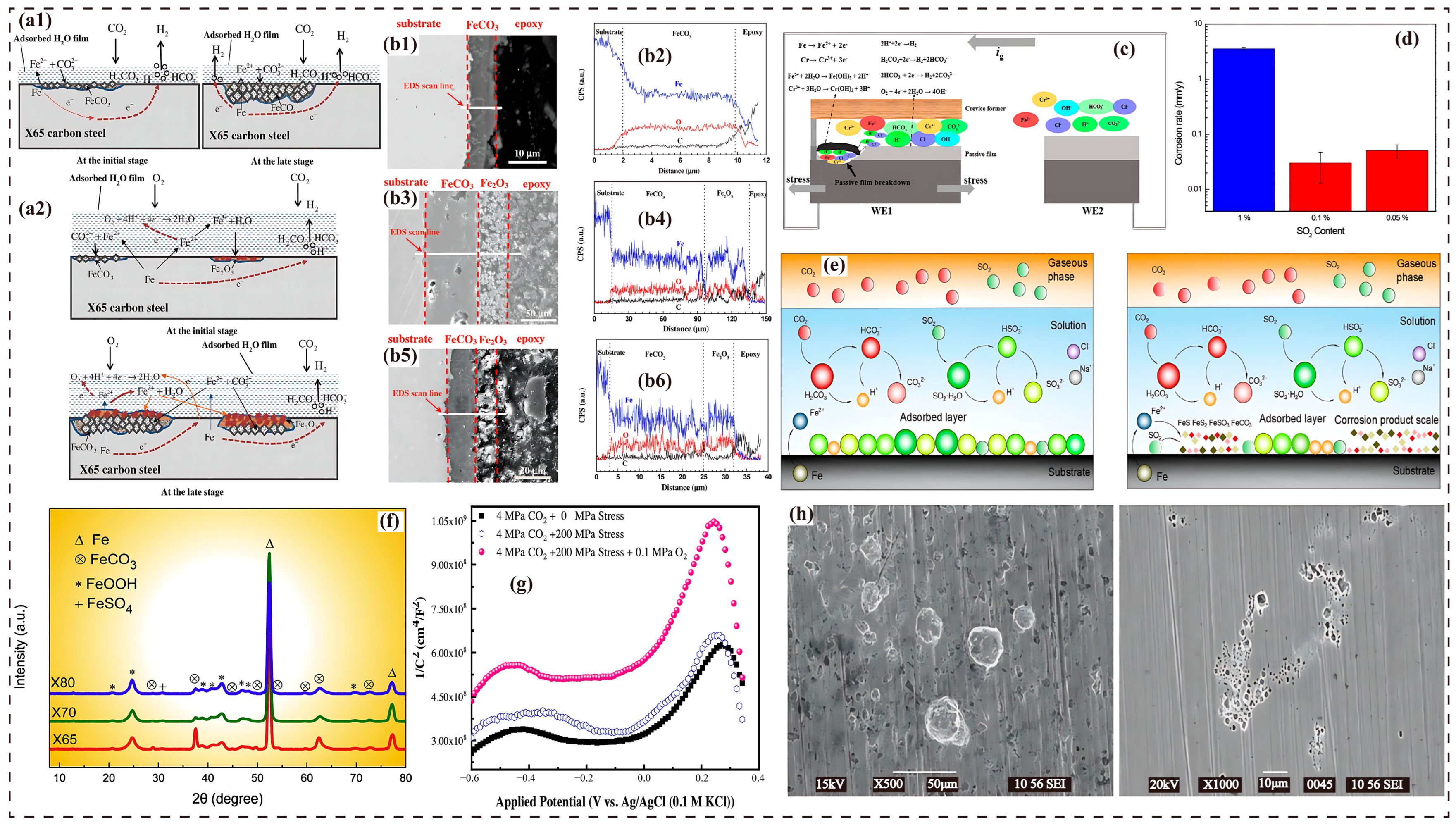
3.3. Impact of SO2
3.4. Impact of H2S
3.5. Impact of NO2
3.6. Impact of Non-Condensable Gases
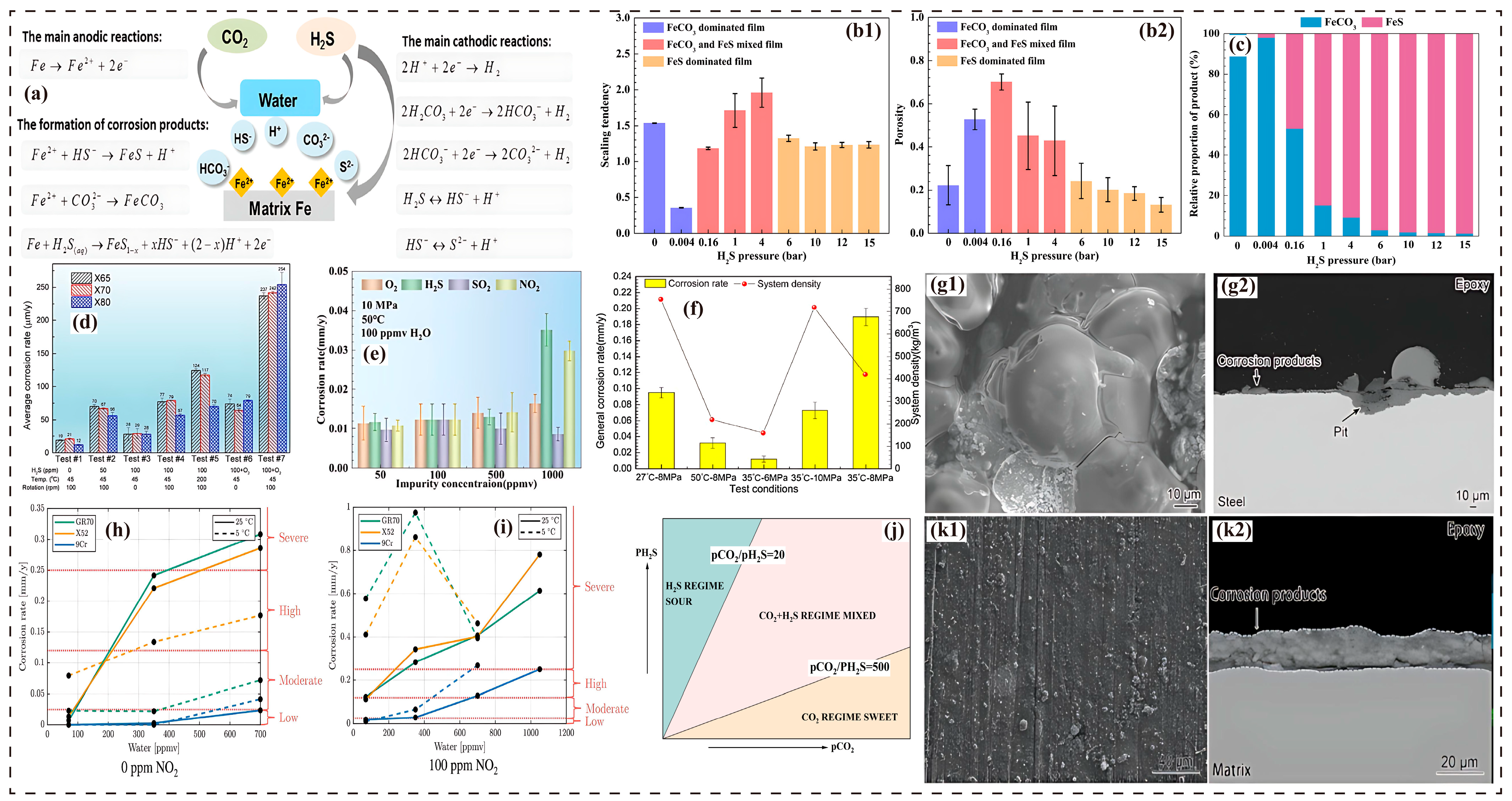
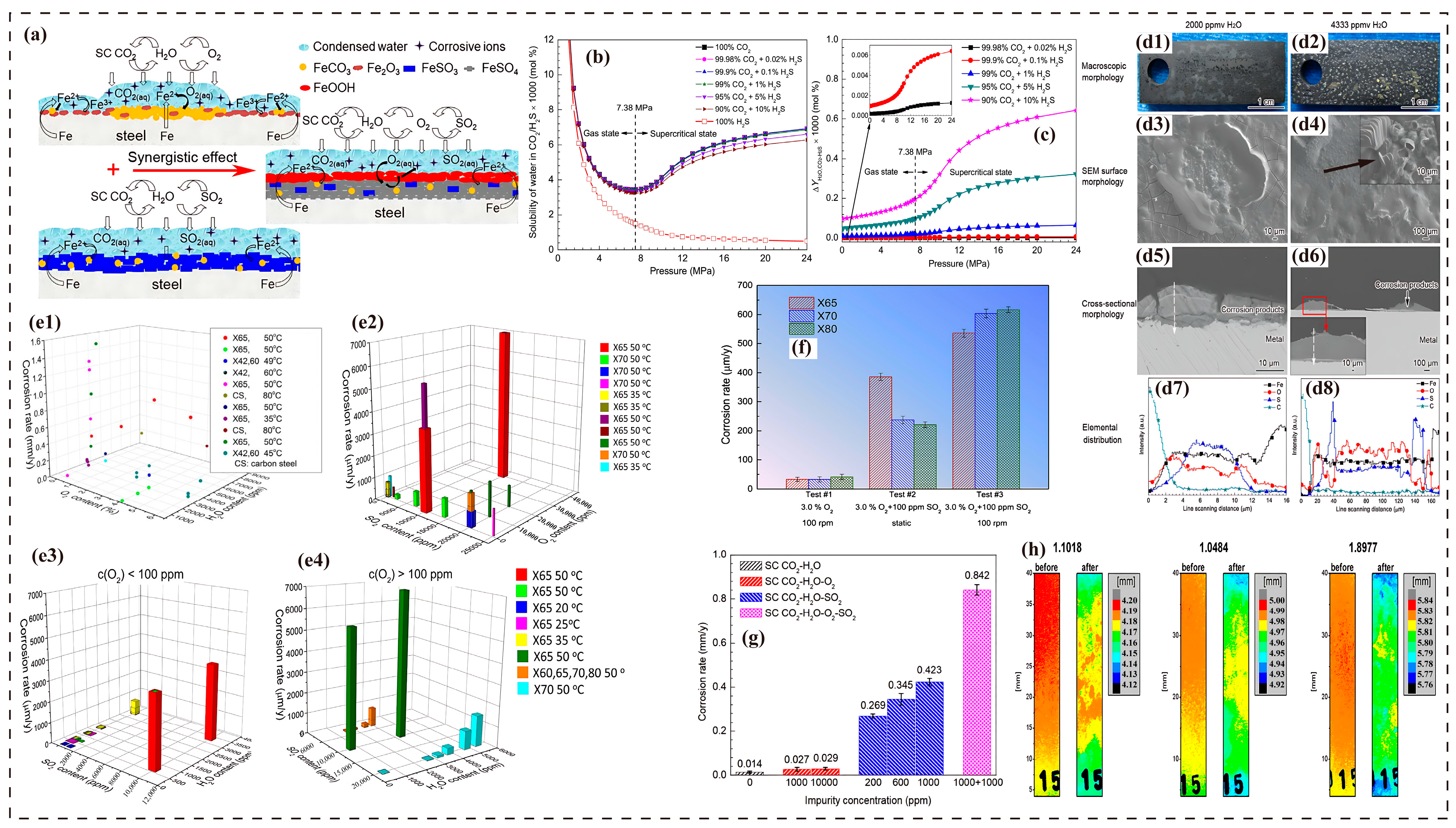
3.7. Corrosion Synergistic Effects
4. Engineering Standards for Impurity Control
4.1. Industry Specifications and Thresholds
4.2. Synergistic Impurity Control Strategies
5. Future Perspectives
5.1. In-Depth Quantification and Prediction of Synergistic Effects of Impurities
5.2. Long-Term Dynamic Corrosion Behavior and Product Layer Stability
5.3. Standardized Experimental Systems and Interdisciplinary Integration
5.4. Engineering-Oriented Optimization of Impurity Control
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calvin, K.; Dasgupta, D.; Krinner, G.; Mukherji, A.; Thorne, P.W.; Trisos, C.; Romero, J.; Aldunce, P.; Barrett, K.; Blanco, G.; et al. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, T.; Gao, M.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yu, H.; Ji, Z.; Lyu, W.; et al. Progress in CO2 flooding and storage techniques for lacustrine oil reservoirs in China and development directions of their large-scale application. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2025, 52, 1086–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, A.; Tavangar, R.; Verbeken, K.; Depover, T. A review of corrosion in flowing conditions during dense phase CO2 transport for carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS). Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 181, 109905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Ren, Z.; Si, W.; Ma, Q.; Huang, W.; Liao, K.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, P. Research progress on CO2 capture and utilization technology. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 66, 102260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhao, G.-B.; Adidharma, H.; Towler, B.; Radosz, M. Effect of Oxygen on Minimum Miscibility Pressure in Carbon Dioxide Flooding. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, J.; Davison, J. Transmission of CO2—Safety and economic considerations. Energy 2004, 29, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavchov, R.I.; Iqbal, M.H.; Faraji, S.; Madden, D.; Sonke, J.; Clarke, S.M. Corrosion maps: Stability and composition diagrams for corrosion problems in CO2 transport. Corros. Sci. 2024, 236, 112204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, C.; Néel, G.; Lima, L.; Rodriguez Barrera, D. Material Selection for Anthropogenic CO2 Injection: Mechanical and Corrosion Performances of Steels Under Dense CO2 with Impurities. In Proceedings of the CONFERENCE 2023, Denver, CO, USA, 19–23 March 2023; AMPP: Denver, CO, USA, 2023; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Vitali, M.; Corvaro, F.; Marchetti, B.; Terenzi, A. Thermodynamic challenges for CO2 pipelines design: A critical review on the effects of impurities, water content, and low temperature. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2022, 114, 103605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, K.; Helle, K.; Røneid, S.; Holt, H. DNV recommended practice: Design and operation of CO2 pipelines. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 3032–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, C.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Huang, M.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Zhou, H.; Ma, H.; et al. Recent advances, challenges, and perspectives on carbon capture. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2024, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, J. Corrosion challenges in supercritical CO2 transportation, storage, and utilization—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 179, 113292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SONKE, J.; Morland, B.H.; Moulie, G.; Franke, M.S. Corrosion and chemical reactions in impure CO2. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2024, 133, 104075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ryan, D.; Anthony, E.J.; Wildgust, N.; Aiken, T. Effects of impurities on CO2 transport, injection and storage. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 3071–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Pang, X.; Gao, K. Corrosion of low alloy steel and stainless steel in supercritical CO2/H2O/H2S systems. Corros. Sci. 2016, 111, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Ortiz, E.; Szklarczyk-Marshall, K.; Winter, M.; McAllister-Fognini, E. Impact of Hydrogen as Impurity in the Physical and Transport Properties of CO2 Streams in CCS/CCUS Transport Systems: A Technical Discussion. In Proceedings of the 15th Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies Conference, Virtual, 15–18 March 2021; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, A.; Solgaard, A.O.S.; Pease, B.J.; Geiker, M.R.; Stang, H.; Olesen, J.F. Experimental investigation of the relation between damage at the concrete-steel interface and initiation of reinforcement corrosion in plain and fibre reinforced concrete. Corros. Sci. 2013, 77, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, P.; Sun, J.; Hua, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Effect of temperature and pressure on corrosion behavior of X65 carbon steel in water-saturated CO2 transport environments mixed with H2S. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2018, 73, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallaert, E.; Depover, T.; De Graeve, I.; Verbeken, K. FeS Corrosion Products Formation and Hydrogen Uptake in a Sour Environment for Quenched & Tempered Steel. Metals 2018, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Barker, R.; Neville, A. The effect of O2 content on the corrosion behaviour of X65 and 5Cr in water-containing supercritical CO2 environments. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z. Study on Corrosion Law of Tubing and Casing in EOR-CCUS System. Master’s Thesis, China University of Petroleum, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Onyebuchi, V.E.; Kolios, A.; Hanak, D.P.; Biliyok, C.; Manovic, V. A systematic review of key challenges of CO2 transport via pipelines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2563–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Neville, A.; Barker, R. Corrosion Behaviour of X65 Steels in Water-Containing Supercritical CO2 Environments with NO2/O2. In Proceedings of the NACE CORROSION 2018 Conference and Expo, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 15–19 April 2018; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, I.S.; Paterson, D.A.; Corrigan, P.; Sim, S.; Birbilis, N. State of the aqueous phase in liquid and supercritical CO2 as relevant to CCS pipelines. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2012, 7, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sun, C.; Wang, Y. Effects of O2 and SO2 on Water Chemistry Characteristics and Corrosion Behavior of X70 Pipeline Steel in Supercritical CO2 Transport System. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 2365–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ryan, D.; Anthony, E.J.; Wigston, A.; Basava-Reddi, L.; Wildgust, N. The effect of impurities in oxyfuel flue gas on CO2 storage capacity. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2012, 11, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.R.; Leahy-Dios, A.; Teletzke, G.F.; Dickson, J.L. Use of CO2 containing impurities for miscible enhanced oil recovery. In Proceedings of the International Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition, Beijing, China, 8–10 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mallon, W.; Buit, L.; van Wingerden, J.; Lemmens, H.; Eldrup, N.H. Costs of CO2 Transportation Infrastructures. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 2969–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H. Cost Analysis of Offshore Carbon Dioxide Pipeline. Chem. Eng. Des. Commun. 2023, 49, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- McKaskle, R.; Beitler, C.; Dombrowski, K.; Fisher, K. The Engineer’s Guide to CO2 Transportation Options. In Proceedings of the 16th Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies Conference (GHGT-16), Lyon, France, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Luo, J.-L.; Li, K.; Arafin, M. Impacts of Impurities on Corrosion of Supercritical CO2 Transportation Pipeline Steels. In Proceedings of the AMPP CORROSION 2018, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 15–19 April 2018; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Peletiri, S.P.; Mujtaba, I.M.; Rahmanian, N. Process simulation of impurity impacts on CO2 fluids flowing in pipelines. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 118145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahak, M.Z.M.; Zain, M.M.; Alias, A.; Zulkifli, M.Y.; Rohani, S.N.; Rostani, K. Establishing Key Process Design Considerations for Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) Towards Decarbonization of Existing Assets Operations. In Proceedings of the ADIPEC, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 4–7 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Guo, X.P.; Zhang, G.A. Corrosion behaviour of X65 carbon steel in supercritical-CO2 containing H2O and O2 in carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology. Corros. Sci. 2017, 118, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farelas, F.; Choi, Y.S.; Nesic, S. Effects of CO2 Phase Change, SO2 Content and Flow on the Corrosion of CO2 Transmission Pipeline Steel. In Proceedings of the AMPP CORROSION 2012, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 11–15 March 2012; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Hou, B.S.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhang, G.A. Corrosion behavior of 13Cr stainless steel under stress and crevice in high pressure CO2/O2 environment. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 88, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thodla, R.; Francois, A.; Sridhar, N. Materials Performance in Supercritical CO2 Environments. In Proceedings of the AMPP CORROSION 2009, Atlanta, GA, USA, 22–26 March 2009; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Fan, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Meng, L.; Hu, Q.; Li, Y. Effect of Phase Change on corrosion behavior of X65 Steel in CO2 transportation pipeline environment. J. Pipeline Sci. Eng. 2025, 100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zeng, Y. Advancing the mechanistic understanding of corrosion in supercritical CO2 with H2O and O2 impurities. Corros. Sci. 2023, 213, 110981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugstad, A.; Halseid, M.; Morland, B.; Sivertsen, A.O. Dense Phase CO2 Corrosion and the Impact of Depressurization and Accumulation of Impurities. In Proceedings of the CORROSION 2013, Orlando, FL, USA, 17–21 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Sun, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y. Effect of water content on the corrosion behavior of X65 pipeline steel in supercritical CO2-H2O-O2-H2S-SO2 environment as relevant to CCS application. Corros. Sci. 2018, 137, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. Corrosion Mechanism of octg carbon steel in supercritical CO2/Oil/Water system. ACTA Metall. Sin. 2014, 50, 811–820. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ju, X.; Pang, X.; Gao, K. Effect of O2 Concentration on Corrosion Rate of Steels in Supercritical CO2. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2015, 35, 220–226. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, S.; Cole, I.S.; Bocher, F.; Corrigan, P.; Gamage, R.P.; Ukwattage, N.; Birbilis, N. Investigating the effect of salt and acid impurities in supercritical CO2 as relevant to the corrosion of carbon capture and storage pipelines. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2013, 17, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayello, F.; Evans, K.; Sridhar, N.; Thodla, R. Effect of Liquid Impurities on Corrosion of Carbon Steel in Supercritical CO2. In Proceedings of the 2010 8th International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 27 September–1 October 2010; ASME: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2010; Volume 1, pp. 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.-S.; Nesic, S.; Young, D. Effect of Impurities on the Corrosion Behavior of CO2 Transmission Pipeline Steel in Supercritical CO2−Water Environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9233–9238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Barker, R.; Neville, A. The influence of SO2 on the tolerable water content to avoid pipeline corrosion during the transportation of supercritical CO2. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2015, 37, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrini, M.; Lorenzi, S.; Pastore, T.; Radaelli, M. Corrosion rate of high CO2 pressure pipeline steel for carbon capture transport and storage. Metall. Ital. 2014, 106, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, X.; Cheng, X.; Liu, H. Synergistic effect of O2, H2S and SO2 impurities on the corrosion behavior of X65 steel in water-saturated supercritical CO2 system. Corros. Sci. 2016, 107, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairy, S.K.; Zhou, S.; Turnbull, A.; Hinds, G. Corrosion of pipeline steel in dense phase CO2 containing impurities: A critical review of test methodologies. Corros. Sci. 2023, 214, 110986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarenko, V.D.; Shatilo, S.P.; Gumerskii, K.K.; Belyaev, V.A. Effect of oxygen and hydrogen sulfide on carbon dioxide corrosion of welded structures of oil and gas installations. Chem. Pet. Eng. 2000, 36, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaperdas, G.T.; Uhlig, H.H. Corrosion of Steel by Dissolved Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1942, 34, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, K.; Tang, S.; Shen, R.; Parker, T.; Wang, Q. Synergistic effect of O2 and SO2 gas impurities on X70 steel corrosion in water-saturated supercritical CO2. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 130, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugstad, A.; Morland, B.; Clausen, S. Corrosion of transport pipelines for CO2–Effect of water ingress. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 3063–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zeng, Y. Long-term corrosion and stress corrosion cracking of X65 steel in H2O-saturated supercritical CO2 with SO2 and O2 impurities. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 362, 129746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Jiang, Z.N.; Zhang, Q.H.; Lei, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.A. Unveiling the influential mechanism of O2 on the corrosion of N80 carbon steel under dynamic supercritical CO2 conditions. Corros. Sci. 2022, 205, 110436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Pang, X.; Gao, K. Effect of small amount of H2S on the corrosion behavior of carbon steel in the dynamic supercritical CO2 environments. Corros. Sci. 2016, 103, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Jiang, T.; Liu, H.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Y. Effect of O2 and H2S impurities on the corrosion behavior of X65 steel in water-saturated supercritical CO2 system. Corros. Sci. 2016, 107, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiang, Y.; Li, W. Initial corrosion mechanism for API 5L X80 steel in CO2/SO2-saturated aqueous solution within a CCUS system: Inhibition effect of SO2 impurity. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 321, 134663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Li, K. Influence of SO2 on the corrosion and stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of supercritical CO2 transportation pipelines. Corros. Sci. 2020, 165, 108404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Ni, W.D. Effect of temperature on corrosion behaviour of X70 steel in high pressure CO2/SO2/O2/H2O environments. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morland, B.H.; Norby, T.; Tjelta, M.; Svenningsen, G. Effect of SO2, O2, NO2, and H2O Concentrations on Chemical Reactions and Corrosion of Carbon Steel in Dense Phase CO2. Corrosion 2019, 75, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S. Thermally Sprayed Corrosion Resistant Alloy Coatings on Carbon Steel for use in Supercritical CO2 Environments. In Proceedings of the CORROSION 2015, Dallas, TX, USA, 15–19 March 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, R.; Hua, Y.; Neville, A. Internal corrosion of carbon steel pipelines for dense-phase CO2 transport in carbon capture and storage (CCS)—A review. Int. Mater. Rev. 2017, 62, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finšgar, M.; Jackson, J. Application of corrosion inhibitors for steels in acidic media for the oil and gas industry: A review. Corros. Sci. 2014, 86, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva de Sá, J.; Ma, W.; Owen, J.; Hua, Y.; Neville, A.; Ponciano Gomes, J.A.C.; Barker, R. Effect of Flow Rate on the Corrosion Behavior of API 5L X80 Steel in Water-Saturated Supercritical CO2 Environments. Corrosion 2021, 78, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Xiang, Y.; Lu, W.; Yan, K.; Ren, J.; Yan, W.; Yao, E.; Zhao, X. Selective adsorption and corrosion mechanism of SO2 and its hydrates on X65 welded joints steel in CO2-saturated aqueous solution. Corros. Sci. 2024, 238, 112373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Qin, X.; Zhang, R.; Sun, J.; Sun, C.; Xu, X.; Lin, X. Coupling effect of H2S and SO2 on the corrosion behavior of X65 pipeline steel in high-pressure CO2 transport environments. Corros. Sci. 2025, 256, 113163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugstad, A. Fundamental Aspects of CO2 Metal Loss Corrosion, Part I: Mechanism. In Proceedings of the CORROSION 2015, Dallas, TX, USA, 15–19 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dugstad, A.; Halseid, M.; Morland, B. Effect of SO2 and NO2 on Corrosion and Solid Formation in Dense Phase CO2 Pipelines. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhl, A.S.; Kranzmann, A. Investigation of corrosive effects of sulphur dioxide, oxygen and water vapour on pipeline steels. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2013, 13, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Zhou, C.; Li, Z.; Ni, W. Impact of SO2 concentration on the corrosion rate of X70 steel and iron in water-saturated supercritical CO2 mixed with SO2. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2011, 58, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Li, C.; Long, Z.; Guan, C.; Wang, W.; Hesitao, W. Electrochemical behavior of valve steel in a CO2/sulfurous acid solution. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 258, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Yan, X.; Sun, J.; Pang, J.; Zhao, W.; Lin, X. Unraveling the effect of O2, NO2 and SO2 impurities on the stress corrosion behavior of X65 steel in water-saturated supercritical CO2 streams. Corros. Sci. 2022, 209, 110729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Sun, C.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, W.; Lin, X. A mechanistic model for the corrosion prediction of bare carbon steel in supercritical CO2-H2S-Cl- environments. Corros. Sci. 2025, 256, 113161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Tebbal, S. Critical Factors in Predicting CO2/H2S Corrosion in Multiphase Systems (Conference)|OSTI.GOV. In Nace Corrosion; NACE: Houston, TX, USA, 1998; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, J.-L. Influence of H2S on the general corrosion and sulfide stress cracking of pipelines steels for supercritical CO2 transportation. Corros. Sci. 2021, 190, 109639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-S.; Hassani, S.; Vu, T.N.; Nešić, S.; B Abas, A.Z.; Nor, A.M.; Suhor, M.F. Strategies for Corrosion Inhibition of Carbon Steel Pipelines Under Supercritical CO2/H2S Environments. Corrosion 2019, 75, 1156–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R. Stress Corrosion Cracking Behavior and Prevention of High Strength Tubing Steels in Typical H2S/CO2 Annulus Environments. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Ding, T.; Sun, J.; Lin, X.; Zhao, W.; Chen, H. Insights into the effect of H2S on the corrosion behavior of N80 steel in supercritical CO2 environment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 5462–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Deng, J.; Dong, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Li, X. Corrosion Products and Corrosion Behavior of Tubing Steel in CO2/H2S Environmen. Corros. Prot. 2011, 32, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Masamura, K.; Hashizume, S.; Sakai, J.; Matsushima, I. Polarization Behavior of High-Alloy OCTG in CO2 Environment as Affected by Chlorides and Sulfides. Corrosion 1987, 43, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.N.; Rihan, R.; Al-Hadhrami, L. Evaluation of the corrosion resistance of SA-543 and X65 steels in emulsions containing H2S and CO2 using a novel emulsion flow loop. Corros. Sci. 2015, 94, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Duan, H.; Jiang, R. Synergistic corrosion inhibition effect of quinoline quaternary ammonium salt and Gemini surfactant in H2S and CO2 saturated brine solution. Corros. Sci. 2015, 91, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-S.; Hassani, S.; Vu, T.N.; Nešić, S.; Abas, A.Z.B. Effect of H2S on the Corrosion Behavior of Pipeline Steels in Supercritical and Liquid CO2 Environments. Corrosion 2016, 72, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonke, J.; Paterson, S.J. Guidance for Materials Selection and Corrosion Control in CO2 Transport and Injection for Carbon Capture and Storage. In Proceedings of the CONFERENCE 2022, San Antonio, TX, USA, 6–10 March 2022; AMPP: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2022; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ruhl, A.S.; Kranzmann, A. Investigation of Pipeline Corrosion in Pressurized CO2 Containing Impurities. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 3131–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayello, F.; Evans, K.; Thodla, R.; Sridhar, N. Effect of impurities on corrosion of steel in supercritical CO2. In Proceedings of the CORROSION 2010, San Antonio, TX, USA, 14–18 March 2010; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Castaño, J.G.; de la Fuente, D.; Morcillo, M. A laboratory study of the effect of NO2 on the atmospheric corrosion of zinc. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8681–8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, K.R.; Goebel, J.; Hansen, D.S.; Pedersen, S. The influence of temperature, H2O, and NO2 on corrosion in CO2 transportation pipelines. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 198, 107190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. A comprehensive review of metal corrosion in a supercritical CO2 environment. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2019, 90, 102814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhi, S.; Liu, X.; Chai, C.; Wang, C.; Xinran, Y.; Qihui, H.; Shiduo, R. Research progress on internal corrosion of supercritical/dense-phase CO2 pipelines for CCUS. Oil Gas Storage Transp. 2024, 43, 510–523. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Jiang, X. Numerical investigation of the partitioning phenomenon of carbon dioxide and multiple impurities in deep saline aquifers. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, B.; Araujo de Itriago, Y.C.; Herrera, G. Effect of Impurities Present in the CO2 Stream on Injectivity and Seal Performance in Carbon Capture and Storage. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 5–8 May 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Han, Z.; Lin, B.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Tang, J. Research Progress on Corrosion Behavior and Mechanism of Supercritical CO2 Transport Pipeline. Surf. Technol. 2024, 53, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Chen, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, J.; Li, G. Corrosion dominant factor and corrosion prediction model for X52 pipeline steel in high-pressure CO2 streams with multiple impurities of H2O, O2, SO2, H2S and NO2. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 179, 109789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pots, B.F.M.; Kapusta, S.D.; John, R.C.; Thomas, M.J.J.S.; Rippon, I.J.; Whitham, T.S.; Girgis, M. Improvements on de Waard-Milliams Corrosion Prediction and Applications to Corrosion Management. In Proceedings of the CORROSION 2002, Denver, CO, USA, 7–12 April 2002; AMPP: Denver, CO, USA, 2002; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Xiang, Y.; Song, C.; Ji, Z. Assessing the corrosion product scale formation characteristics of X80 steel in supercritical CO2-H2O binary systems with flue gas and NaCl impurities relevant to CCUS technology. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 146, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y. ReaxFF molecular dynamics investigation on the oxidation mechanism of Fe surface in supercritical CO2 mixed with O2. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 65, 102224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Pang, X.; Liu, C.; Gao, K. Formation mechanism and protective property of corrosion product scale on X70 steel under supercritical CO2 environment. Corros. Sci. 2015, 100, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Jiang, J.; Ye, B.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, C. Comparative life cycle assessment of CO2 onshore transport in China: Pipeline or tanker truck? J. CO2 Util. 2025, 94, 103057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeri, M.; Haghighi, H.; Mckay, C.; Erickson, D.; Zhai, S. Impact of CO2 Specifications on Design and Operation Challenges of CO2 Transport and Storage Systems in CCUS. In Proceedings of the SPE Offshore Europe Conference & Exhibition, Virtual, 7–10 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, I.; Wang, H. Evaluating the likelihood of pipeline failures for future offshore CO2 sequestration projects. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2014, 24, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Wong, H.; Wang, G. CCUS global progress and China’s policy suggestions. Pet. Geol. Recovery Effic. 2020, 27, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterkamp, A.; Ramsen, J. State-of-the-Art Overview of CO2 Pipeline Transport with Relevance to Offshore Pipelines; POYTEC: Haugesund, Norway, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Yang, W.; Sun, J.; Yan, X.; Lin, X.; Xu, X. Hydrogen permeation and SCC susceptibility of X70 pipeline steel in CO2-saturated water environment containing acidic impurity. Corros. Sci. 2024, 236, 112259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.; Millet, C.; Barrera, D.R.; Néel, G.; Conder, R.; Fathi, N. Material Selection for CCUS Injection Well: A Case Study in North Sea. In Proceedings of the AMPP Annual Conference + Expo, New Orleans, LA, USA, 3–7 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Watt, J. Carbon dioxide transport infrastructure: Key learning and critical issues. J. Pipeline Eng. 2010, 9, 213–222. [Google Scholar]
| Gas | Primary Impact Mechanism | Critical Concentration Thresholds and Corrosion Rate Data |
|---|---|---|
| H2O | Initiates the corrosion process, forms an acidic water film, causes minor uniform corrosion at low concentrations, and accelerates pitting and general corrosion at high concentrations. | <50 ppm initiates mild corrosion (hazardous with SO2), 100–1000 ppm initiates pitting (1.2 mm/y), >1000 ppm yields general corrosion (19 mm/y), and the corrosion rate of X65 steel increases sharply at water content > 1500 mg/L. |
| O2 | Accelerates corrosion at low concentrations (disrupts FeCO3 film), may inhibit corrosion at high concentrations (forms dense oxides), and synergistically exacerbates corrosion with SO2. | 1.5 ppm can increase the corrosion rate to >100 mm/y, 200 ppm raises the corrosion rate of X70 steel to 0.09 mm/y, the recommended concentration is <1000 ppm, and the corrosion rate reaches 20.47 mm/y when coexisting with 500 ppm SO2. |
| SO2 | May inhibit corrosion at low concentrations, accelerates corrosion at high concentrations (generates strong acids), and synergistically forms H2SO4 with O2, significantly increasing the corrosion rate. | 0.05% SO2 in liquid CO2 causes a corrosion rate of 2.4 mm/y, 500 ppm increases the corrosion rate of X70 steel to 1.10 mm/y, the recommended concentration is <100 ppm, and corrosion products on X65 steel become porous when coexisting with 3% O2. |
| H2S | Accelerates uniform corrosion at low concentrations, may mitigate corrosion via FeS film at medium–high concentrations, and corrosion products are regulated by the CO2/H2S pressure ratio. | <500 ppm accelerates corrosion, 0.0004 MPa H2S increases the corrosion rate of N80 steel to 4.61 mm/y, >0.4 MPa reduces it to 0.72 mm/y, and the recommended concentration is <200 ppm. |
| NO2 | Generates HNO3, significantly reduces pH, accelerates uniform and localized corrosion, the effect is intensified at low temperatures, and the risk is amplified synergistically with O2/SO2. | 100 ppm leads to a corrosion rate of 11.6 mm/y, the rate at 5 °C is 3–4 times higher than at 25 °C; <1.5 ppm is recommended, and the localized corrosion rate reaches 6.8 mm/y when coexisting with 1000 ppm O2. |
| N2/H2/CH4 | Reduces water solubility, promotes free water separation, H2 may cause hydrogen embrittlement, CH4 alters phase behavior, and the total volumetric fraction should be <4%. | 10% N2 reduces the water solubility by 30%, 4% H2 triples the corrosion rate, 20% CH4 decreases the water solubility, and corrosion intensifies with water separation when non-condensable gases >5%. |
| Medium Component | DYNAMIS Project | Northern Lights Project | Porthos Project | Ecofys Company | Pace CCS Company | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content Limit Values | Content Limit Values (ppm/mol) | Content Limit Values (ppm/mol) | Content Limit Values | Content Limit Values (ppm/mol) | ||
| Saline Aquifer Storage | CO2-EOR Project | |||||
| CO2 | >95.5% | >99% | ≥95% | >95% | ≥95% | |
| H2O | 0.05% | ≤30 | ≤70 | <4% | 50 | |
| Ar | <4% | -- | ≤4% | <4% | 4% | |
| N2 | -- | <4% | 4% | |||
| H2 | ≤50 | <4% | 1% | |||
| CH4 | <4% | <2% | -- | <4% | 4% | |
| O2 | <4% | 0.01%~0.1% | ≤10 | <4% | 10 | |
| CO | 0.2% | ≤100 | -- | 0.2% | ||
| COS | -- | -- | ≤20 | -- | 5 | |
| H2S | 0.02% | ≤9 | -- | |||
| SOX | 0.01% | ≤10 | -- | 50 | ||
| NOX | 0.01% | ≤10 | ≤5 | -- | 50 | |
| Amines | -- | ≤20 | ≤1 | -- | 100 | |
| C2+ | -- | -- | 1200 | -- | 4.15% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Lyu, W.; Yu, H.; Lv, W.; Wei, K.; Jiang, L. Advances in Synergistic Corrosion Mechanisms of and Management Strategies for Impurity Gases During Supercritical CO2 Pipeline Transportation. Molecules 2025, 30, 4094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204094
Yan Y, Lyu W, Yu H, Lv W, Wei K, Jiang L. Advances in Synergistic Corrosion Mechanisms of and Management Strategies for Impurity Gases During Supercritical CO2 Pipeline Transportation. Molecules. 2025; 30(20):4094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204094
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yutong, Weifeng Lyu, Hongwei Yu, Wenfeng Lv, Keqiang Wei, and Lichan Jiang. 2025. "Advances in Synergistic Corrosion Mechanisms of and Management Strategies for Impurity Gases During Supercritical CO2 Pipeline Transportation" Molecules 30, no. 20: 4094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204094
APA StyleYan, Y., Lyu, W., Yu, H., Lv, W., Wei, K., & Jiang, L. (2025). Advances in Synergistic Corrosion Mechanisms of and Management Strategies for Impurity Gases During Supercritical CO2 Pipeline Transportation. Molecules, 30(20), 4094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204094





