Redox-Active Quinazolinone Thioamide Ag(I) Complexes with Potent Antibacterial Activity: Mechanistic Insights and Hydrogel-Enhanced Efficacy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
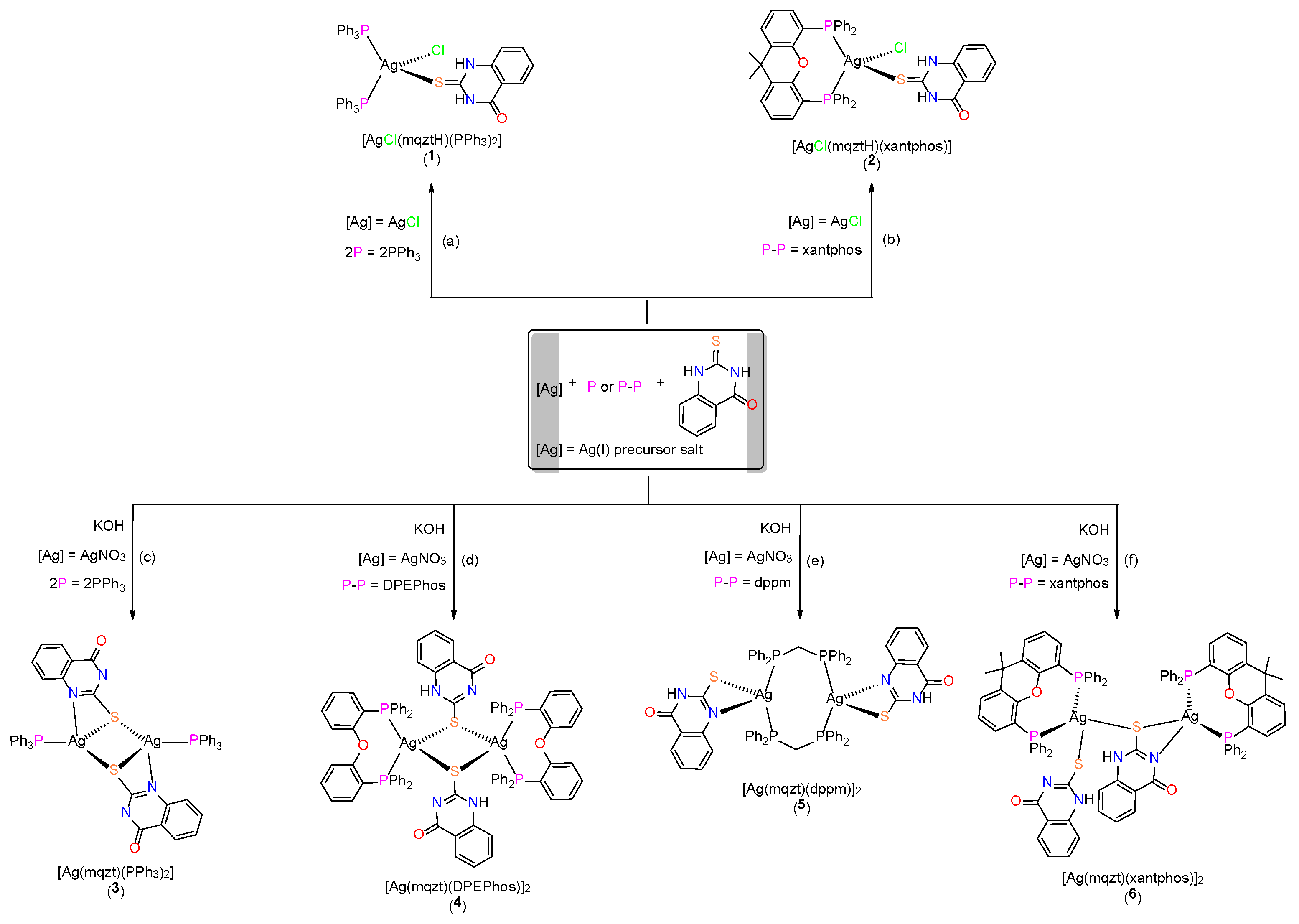
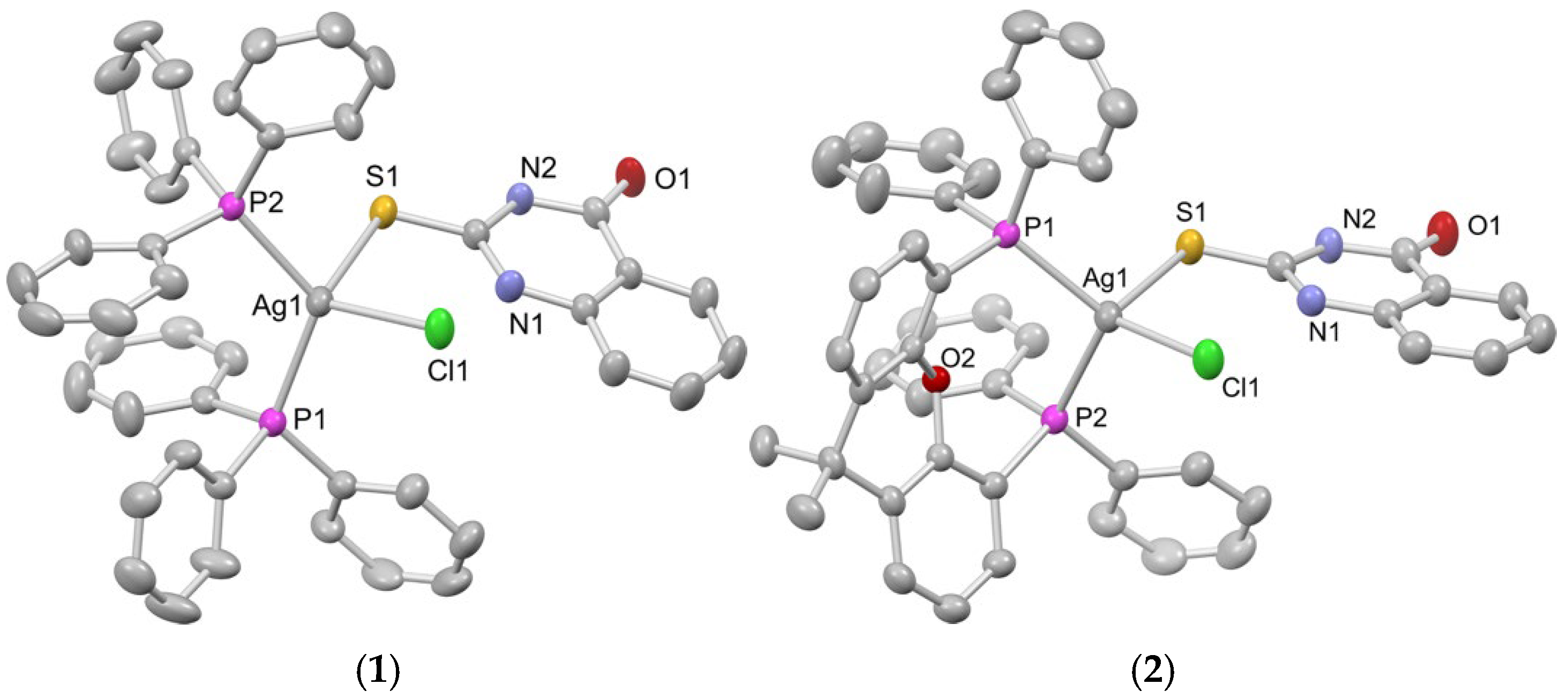
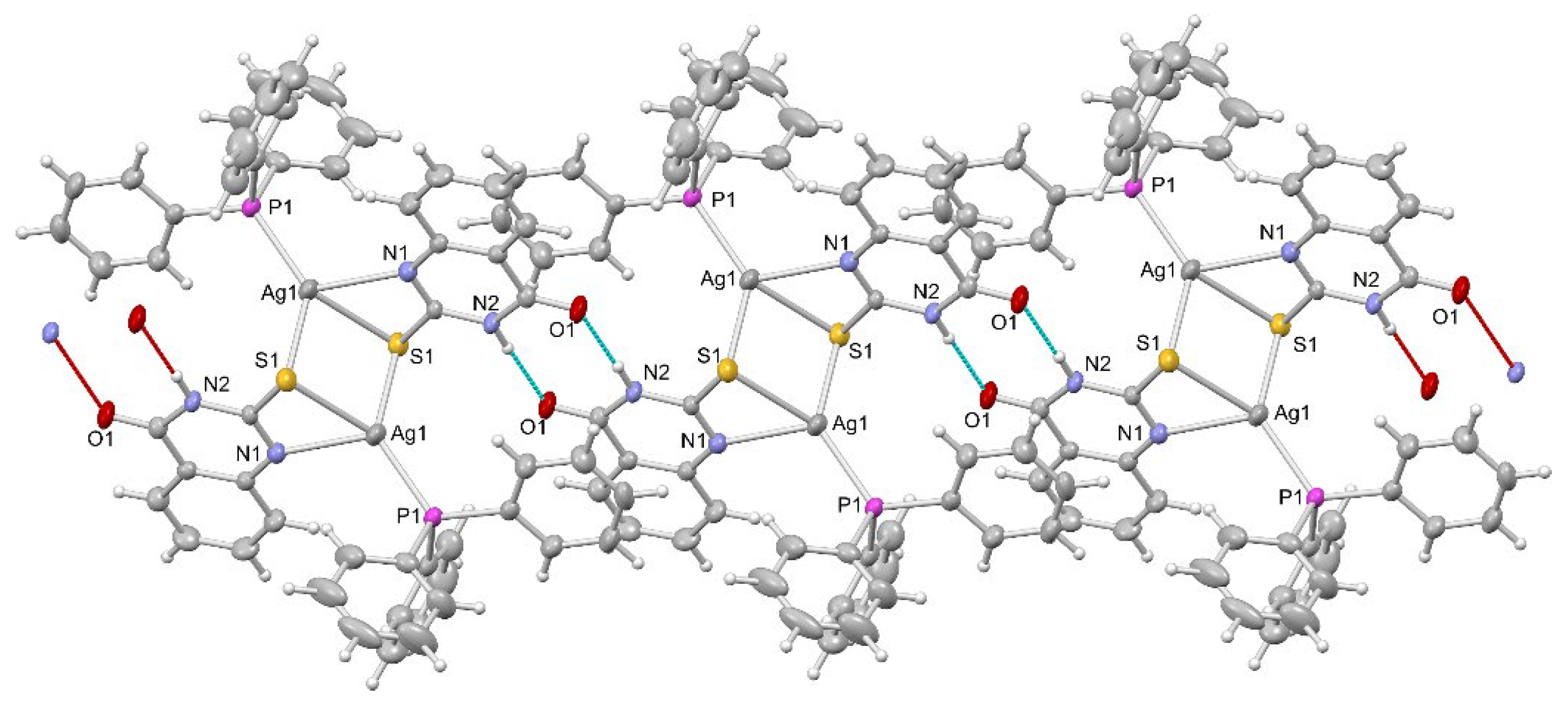
2.1. Synthesis, Crystal Structures and Characterization of Complexes 1–6
2.2. Photophysical Properties of Complexes 1–6
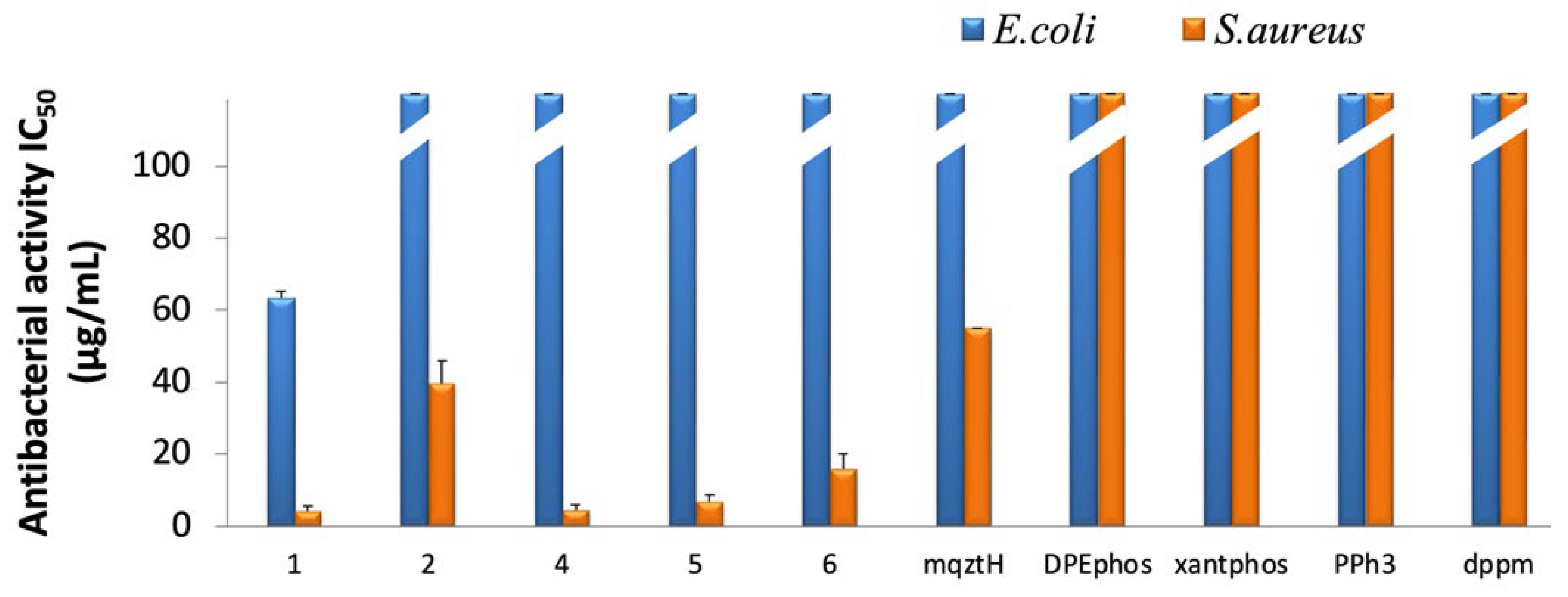
2.3. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Complexes 1–6
2.4. Synthesis, Characterization and Properties of Hydrogels of Complex 1
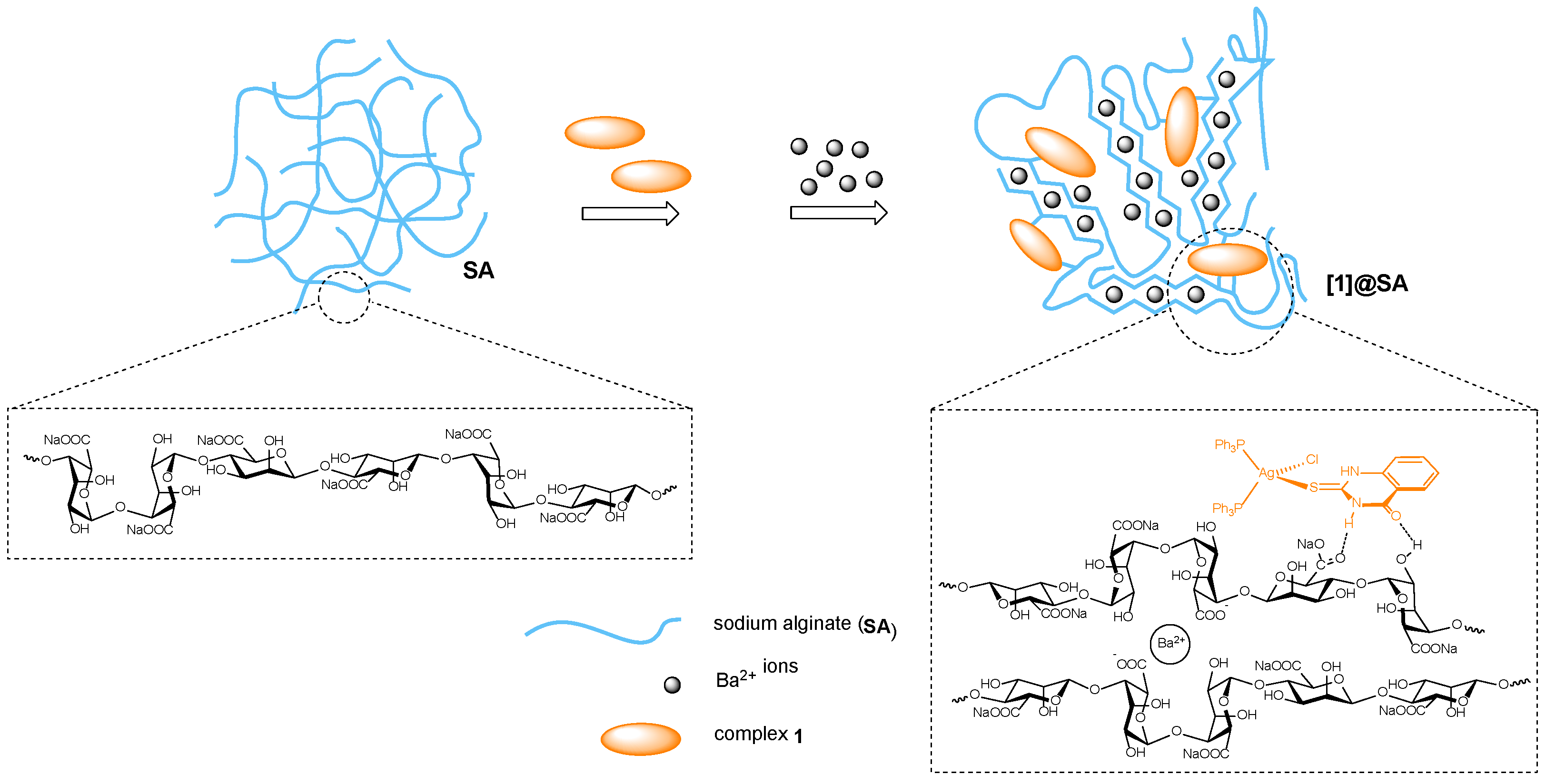
2.4.1. Synthesis and Characterization
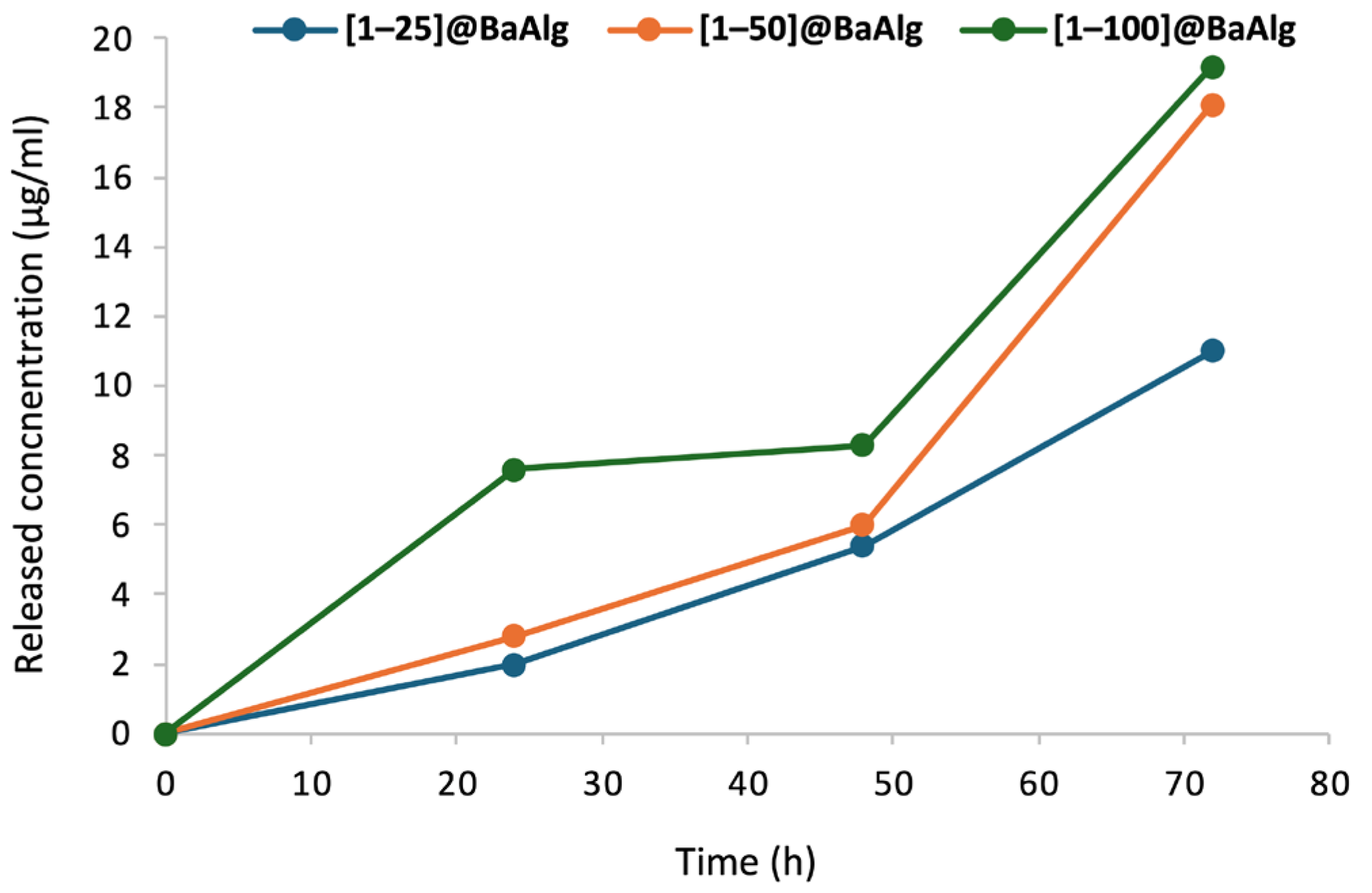
2.4.2. In Vitro Release Studies
2.5. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity Studies of Hydrogels of Complex 1
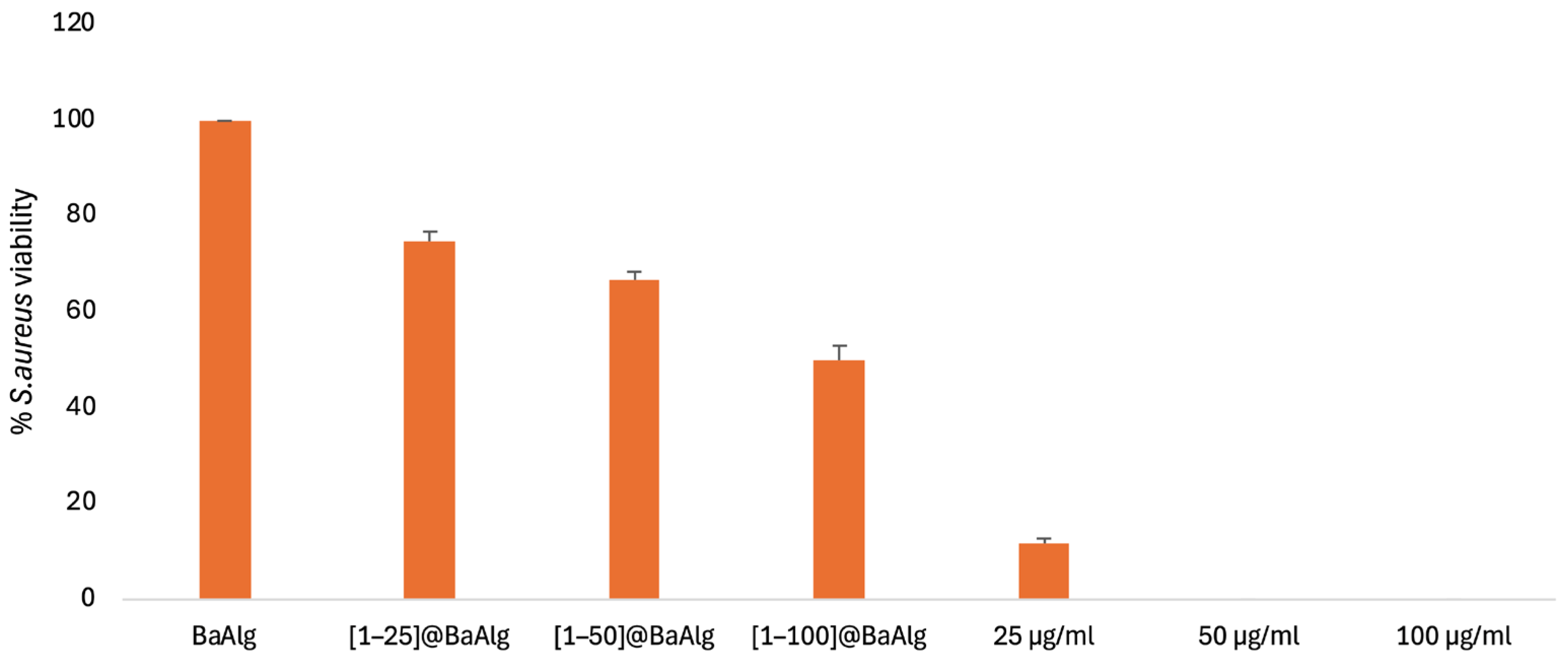
2.5.1. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity Studies
2.5.2. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies
2.6. Mechanistic Investigations
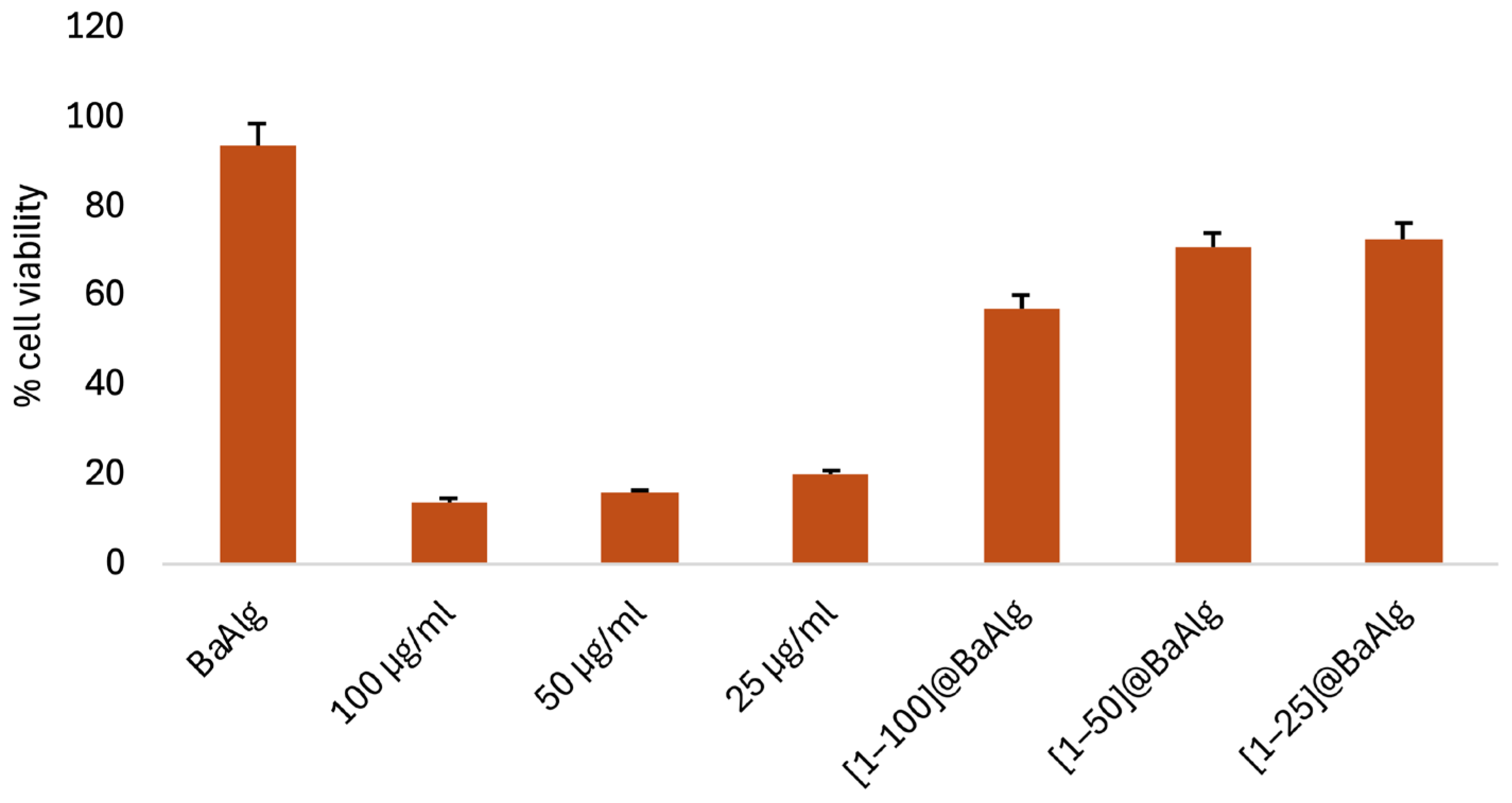
2.6.1. In Vitro Effect of Complex 1 on L929 Normal Cell Line
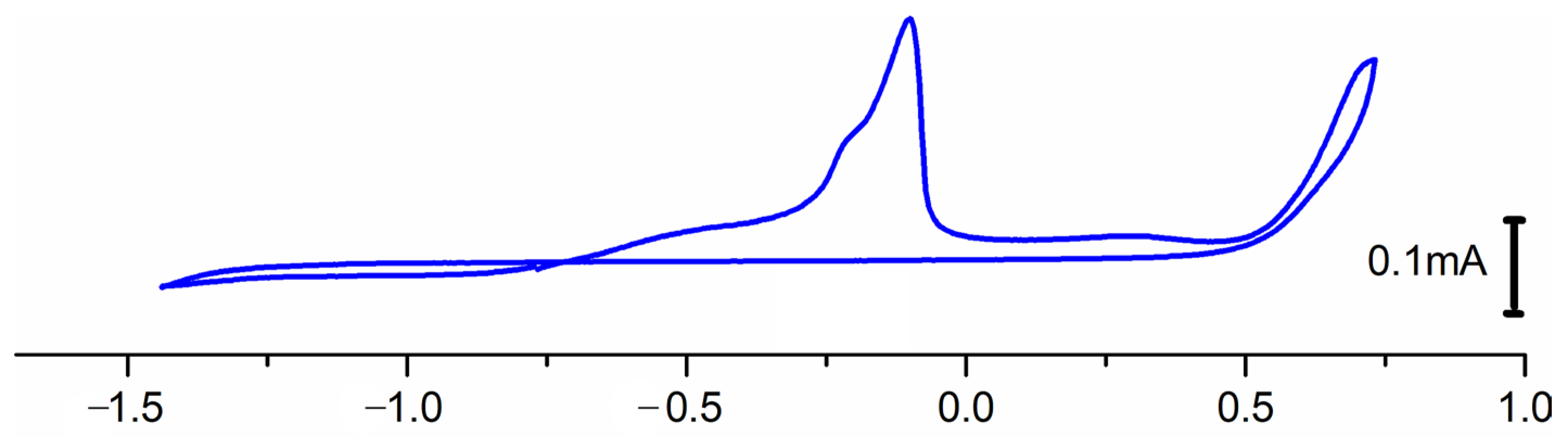
2.6.2. Redox Behavior of Complex 1
2.6.3. Inhibition of Bacterial GR and TrxR by Complex 1
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 10325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations, The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. 2016. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.5555/20173071720 (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Duse, A.; Wattal, C.; Zaidi, A.K.M.; Wertheim, H.F.L.; Sumpradit, N.; Vlieghe, E.; Hara, G.L.; Gould, I.M.; Goossens, H.; et al. Antibiotic resistance–the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 1057–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.D.; Wright, E.D. Antibacterial drug discovery in the resistance era. Nature 2016, 529, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Lu, T.K. Development and Challenges of Antimicrobial Peptides for Therapeutic Applications. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibstu, Z.; Belew, H.; Akelew, Y.; Mengist, H.M. Phage Therapy: A different approach to fight bacterial infections. Biol. Targets Ther. 2022, 16, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junaid, M.; Thirapanmethee, K.; Khuntayaporn, P.; Chomnawang, M.T. CRISPR-Based Gene Editing in Acinetobacter baumannii to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, A.; Pati, S.; Samal, S.K. Bacteriophage as a potential biotherapeutics to combat present-day crisis of multi-drug-resistant pathogens. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37489. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Guo, H.; Gao, S.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Yang, D. Nanotechnology-driven strategies to enhance the treatment of drug-resistant bacterial infections. Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 16, e1968. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wei, X.; Zhong, L.; Chan, C.L.; Li, H.; Sun, H. Metal-Based Approaches for the Fight against Antimicrobial Resistance: Mechanisms, Opportunities, and Challenges. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 12361–12380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromm, K.M. Give silver a shine. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, G.; Russell, A.D. Antiseptics and disinfectants: Activity, action, and resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 147–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.L.; Modak, S.M. Mechanism of Silver Sulfadiazine Action on Burn Wound Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1974, 5, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.; Willcox, M.D.P.; Stapleton, F. In vivo efficacy of silver-impregnated barrel contact lens storage cases. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2021, 44, 101357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banti, C.; Hadjikakou, S. Silver and gold compounds as antibiotics. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijboom, R.; Iroegbu, A.O.C.; Ray, S.S. Advancing cancer therapy: The role of silver(I) phosphine complexes in overcoming resistance and toxicity. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, S. Bacterial silver resistance: Molecular biology and uses and misuses of silver compounds. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, P.L.; Hazelwood, K.J. Exposure-related health effects of silver and silver compounds: A review. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2005, 49, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindi, K.M.; Siciliano, T.J.; Durmus, S.; Panzner, M.J.; Medvetz, D.A.; Reddy, D.V.; Hogue, L.A.; Hovis, C.E.; Hilliard, J.K.; Mallet, R.J.; et al. Synthesis, stability, and antimicrobial studies of electronically tuned silver acetate N-heterocyclic carbenes. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngs, W.J.; Knapp, A.R.; Wagers, P.O.; Tessier, C.A. Nanoparticle encapsulated silver carbene complexes and their antimicrobial and anticancer properties: A perspective. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzner, M.J.; Deeraksa, A.; Smith, A.; Wright, B.D.; Hindi, K.M.; Nebioglu, A.K.; Torres, A.G.; Judy, B.M.; Hovis, C.E.; Hilliard, J.K.; et al. Synthesis and in vitro efficacy studies of silver carbene complexes on biosafety level 3 bacteria. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 13, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbel, S.R.; Patil, S.A.; Bugarin, A. NHCs silver complexes as potential antimicrobial agents. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2024, 563, 121899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varna, D.; Geromichalou, E.; Papachristou, E.; Papi, R.; Hatzidimitriou, A.G.; Panteris, E.; Psomas, G.; Geromichalos, G.D.; Aslanidis, P.; Choli-Papadopoulou, T.; et al. Biocompatible silver(I) complexes with heterocyclic thioamide ligands for selective killing of cancer cells and high antimicrobial activity—A combined in vitro and in silico study. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2022, 28, 111695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzein, A.; Al Jomeh, G.A.S.; Tizzard, G.J.; Coles, S.J.; Banti, C.N.; Hadjikakou, S.K.; Kostakis, G.E. Investigating the antimicrobial activity of 1-heteroaryl benzotriazole silver compounds. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 11431–11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mather, J.C.; Wyllie, J.A.; Hamilton, A.; de Costa, T.P.S.; Barnard, P.J. Antibacterial silver and gold complexes of imidazole and 1,2,4-triazole derived N-heterocyclic carbenes. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 12056–12070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aulakh, J.K.; Lobana, T.S.; Sood, H.; Arora, D.S.; Garcia-Santos, I.; Kaur, M.; Jasinski, J.P. Synthesis, structures, and novel antimicrobial activity of silver (I) halide complexes of imidazolidine-2-thiones. Polyhedron 2020, 175, 114235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varna, D.; Geromichalos, G.D.; Dalezis, P.; Hatzidimitriou, A.G.; Psomas, G.; Zachariadis, G.; Psatha, K.; Aivaliotis, M.; Papi, R.; Trafalis, D.; et al. Amine-substituted heterocyclic thioamide Cu(I) and Ag(I) complexes as effective anticancer and antibacterial agents targeting the periplasm of E. coli bacteria. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 277, 116746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esarev, I.V.; Ott, I. Modulation of the mechanism of action of antibacterial silver N-heterocyclic carbene complexes by variation of the halide ligand. RSC Adv. 2025, 25, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varna, D.; Geromichalou, E.; Hatzidimitriou, A.G.; Papi, R.; Psomas, G.; Dalezis, P.; Aslanidis, P.; Choli-Papadopoulou, T.; Trafalis, D.T.; Angaridis, P.A. Silver (I) complexes bearing heterocyclic thioamide ligands with NH2 and CF3 substituents: Effect of ligand group substitution on antibacterial and anticancer properties. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 9412–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Crisponi, G.; Nurchi, V.M.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Remelli, M.; Zoroddu, M.A. Silver coordination compounds: A new horizon in medicine. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 327–328, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cong, H.; Yu, B.; Shen, Y. A review on the synthesis and development of alginate hydrogels for wound therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varna, D.; Christodoulou, E.; Gounari, E.; Apostolidou, C.P.; Landrou, G.; Papi, R.; Koliakos, G.; Coutsolelos, A.G.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Angaridis, P.A. Pegylated-polycaprolactone nano-sized drug delivery platforms loaded with biocompatible silver(I) complexes for anticancer therapeutics. RSC Med. Chem. 2022, 13, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.S. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Jia, R.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Qin, Z. Preparation and Application of Sustained-Release Antibacterial Alginate Hydrogels by Loading Plant-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 1388–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y. A review of sodium alginate-based hydrogels: Structure, mechanisms, applications, and perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 292, 139151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, N.S.; Hashem, A.H.; Khattab, T.A.; Kamel, S. New antibacterial hydrogels based on sodium alginate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, D.; Ray, P.C.; Bayliss, T.; Prosser, G.A.; Harrison, J.R.; Green, K.; de Melo, C.S.; Feng, T.-S.; Street, L.J.; Chibale, K.; et al. 2-Mercapto-quinazolinones as inhibitors of type II NADH dehydrogenase and Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Structure–activity relationships, mechanism of action and absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion characterization. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 954–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Bueler, S.A.; Cook, G.M.; Rubinstein, J.L. Structure of mycobacterial NDH-2 bound to a 2-mercapto-quinazolinone inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 68, 7579–7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatadi, S.; Lakshmi, T.V.; Nanduri, S. 4(3H)-Quinazolinone derivatives: Promising antibacterial drug leads. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 170, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halappanavar, V.; Teli, S.; Sannakki, H.B.; Teli, D. Quinazoline scaffold as a target for combating microbial resistance: Synthesis and antimicrobial profiling of quinazoline derivatives. Results Chem. 2025, 13, 101955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadou, D.; Geromichalou, E.; Tsavea, E.; Psomas, G.; Hatzidimitriou, A.G.; Kalogiannis, S.; Geromichalos, G.; Trafalis, D.; Dalezis, P.; Aslanidis, P. Silver complexes with heterocyclic thioamide and tertiary arylphosphane ligands: Synthesis, crystal structures, in vitro and in silico antibacterial and cytotoxic activity, and interaction with DNA. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 210, 111167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, J.K.; Lobana, T.S.; Sood, H.; Arora, D.S.; Kaur, R.; Singh, J.; Garcia-Santos, I.; Kaur, M.; Jasinski, J.P. Silver derivatives of multi-donor heterocyclic thioamides as antimicrobial/anticancer agents: Unusual bioactivity against methicillin resistant S. aureus, S. epidermidis, and E. faecalis and human bone cancer MG63 cell line. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15470–15487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.-H.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.-P.; Qiu, Q.-M.; Liu, M.; Li, Z.-F.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Zhang, C.-L. Polynuclear silver(I) complexes of diphosphine ligands and isoquinoline: Synthesis, structural characterization and spectroscopic properties. Polyhedron 2015, 101, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, K.; Ganguly, K.; More, U.A.; Reddy, K.R.; Dugge, T.; Naik, B.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Noolvi, M.N. Chapter 3—Sodium alginate in drug delivery and biomedical areas. In Natural Polysaccharides in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications; Hasnain, M.S., Nayak, A.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 59–100. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, R.I.; Morales-Quintana, L.; Alvarado, N.; Guzmán, L.; Forero-Doria, O.; Valenzuela-Riffo, F.; Laurie, V.F. Design and Optimization of a Self-Assembling Complex Based on Microencapsulated Calcium Alginate and Glutathione (CAG) Using Response Surface Methodology. Polymers 2021, 13, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergonzi, C.; Bianchera, A.; Remaggi, G.; Ossiprandi, M.C.; Bettini, R.; Elviri, L. 3D Printed Chitosan/Alginate hydrogels for the controlled release of silver sulfadiazine in wound healing applications: Design, characterization and antimicrobial activity. Micromachines 2023, 14, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohseni, M.; Shamloo, A.; Aghababaie, Z.; Afjoul, H.; Abdi, S.; Moravvej, H.; Vossoughi, M. A comparative study of wound dressings loaded with silver sulfadiazine and silver nanoparticles: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 564, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanello, P.; Connelly, N.G. Inorganic Electrochemistry; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2003; Available online: https://books.rsc.org/books/monograph/439/Inorganic-Electrochemistry (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Mohamed, A.; Bruce, A.E.; Bruce, M.R.M. The Electrochemistry of Gold and Silver Complexes, Organic Derivatives of Gold and Silver; Chapter 9; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VHC: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.M.; Hu, L.G.; Yan, X.T.; Zhao, X.C.; Zhou, Q.F.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, G.B. Surface ligand controls silver ion release of nanosilver and its antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3193–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loginova, N.V.; Koval’chuk, T.V.; Gres, A.T.; Osipovich, N.P.; Polozov, G.I.; Halauko, Y.S.; Faletrov, Y.V.; Harbatsevich, H.I.; Hlushko, A.V.; Azarko, I.I.; et al. Redox-active metal complexes of sterically hindered phenolic ligands: Antibacterial activity and reduction of cytochrome c. Part IV. Silver(I) complexes with hydrazone and thiosemicarbazone derivatives of 4,6-di-tert-butyl-2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde. Polyhedron 2015, 88, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Y.; Mei, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Glutathione reductase modulates endogenous oxidative stress and affects growth and virulence in Avibacterium paragallinarum. Vet. Res. 2025, 56, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagah, O.M.A.; Silaa, B.B.; Zhu, M.; Pan, Q.; Qi, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Peng, W.; Ullah, Z.; Yudas, A.F.; et al. Exploring Immune Redox Modulation in Bacterial Infections: Insights into Thioredoxin-Mediated Interactions and Implications for Understanding Host-Pathogen Dynamics. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEsarev, V.; Karge, B.; Zeng, H.; Lippmann, P.; Jones, P.G.; Schrey, H.; Brönstrup, M.; Ott, I. Silver Organometallics that are Highly Potent Thioredoxin and Glutathione Reductase Inhibitors: Exploring the Correlations of Solution Chemistry with the Strong Antibacterial Effects. ACS Infect. Dis. 2024, 10, 1753–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, P.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, L. Synergistic therapeutic efficacy of ebselen and silver ions against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii-induced urinary tract infections. Metallomics 2020, 12, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Loughlin, J.; Napolitano, S.; Alkhathami, F.; O’Beirne, C.; Marhöfer, D.; O’Shaughnessy, M.; Howe, O.; Tacke, M.; Rubini, M. The antibacterial drug candidate SBC3 is a potent inhibitor of bacterial thioredoxin reductase. ChemBioChem 2021, 22, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruker Analytical X-ray Systems, Inc. Apex2, Version 2 User Manual, M86-E01078; Bruker Analytical X-ray Systems, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Betteridge, P.W.; Carruthers, J.R.; Cooper, R.I.; Prout, K.; Watkin, D.J. Software for guided crystal structure analysis. J. Appl. Cryst. 2003, 36, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrae, C.F.; Edgington, P.R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Shields, G.P.; Taylor, R.; Towler, M.; van de Streek, J. Mercury: Visualization and analysis of crystal structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 2006, 39, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falivene, L.; Credendino, R.; Poater, A.; Petta, A.; Serra, L.; Oliva, R.; Scarano, V.; Cavallo, L. SambVca 2. A Web Tool for Analyzing Catalytic Pockets with Topographic Steric Maps. Organometallics 2016, 35, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.M. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 48, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiaggali, M.A.; Andreadou, E.G.; Hatzidimitriou, A.G.; Pantazaki, A.A.; Aslanidis, P. Copper (I) halide complexes of N-methylbenzothiazole-2-thione: Synthesis, structure, luminescence, antibacterial activity and interaction with DNA. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2013, 121, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Karge, B.; Misgeld, R.; Prokop, A.; Franke, R.; Brönstrup, M.; Ott, I. Gold(I) NHC Complexes: Antiproliferative Activity, Cellular Uptake, Inhibition of Mammalian and Bacterial Thioredoxin Reductases, and Gram-Positive Directed Antibacterial Effects. Chemistry 2017, 23, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Vlamis-Gardikas, A.; Kandasamy, K.; Zhao, R.; Gustafsson, T.N.; Engstrand, L.; Hoffner, S.; Engman, L.; Holmgren, A. Inhibition of bacterial thioredoxin reductase: An antibiotic mechanism targeting bacteria lacking glutathione. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

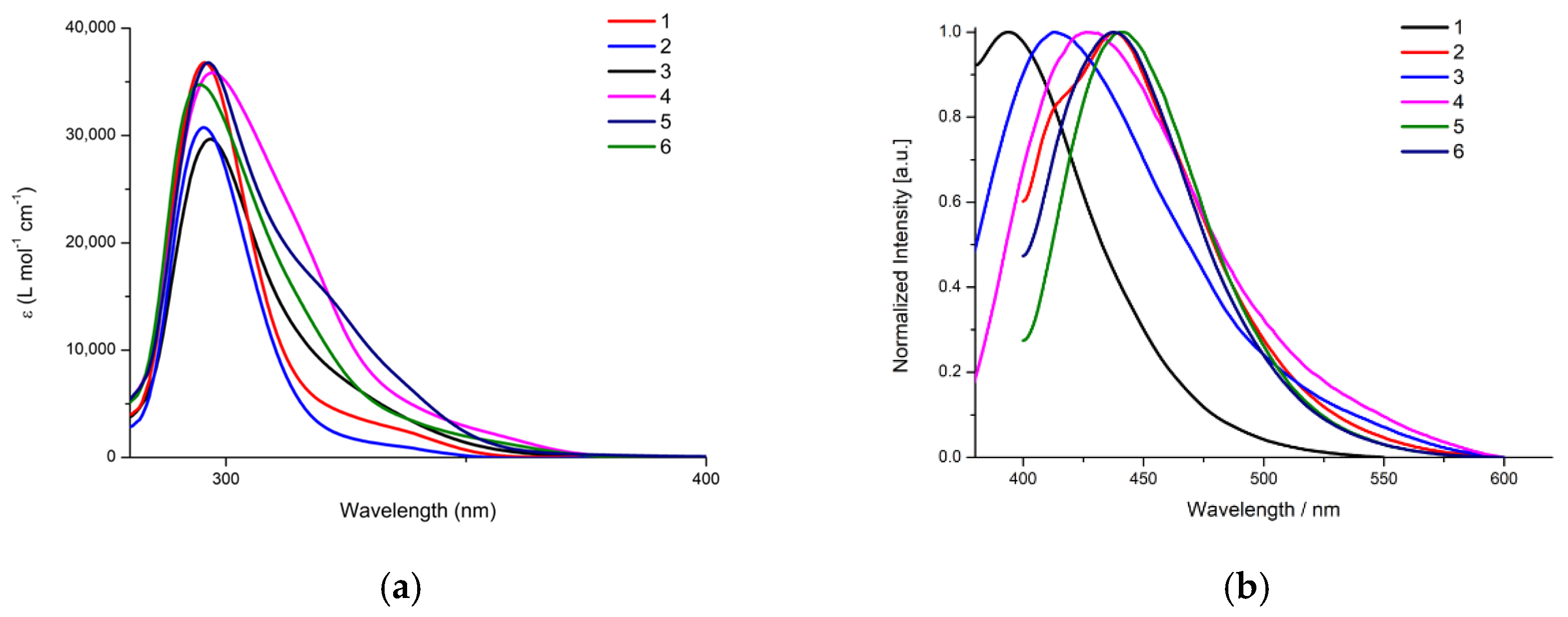



| λmax(abs)/nm (ε/M−1 cm−1) | λmax(em)/nm | |
|---|---|---|
| [AgCl(mqztH)(PPh3)2] (1) | 295 (37,000), 337 (2500) | 394 |
| [AgCl(mqztH)(xantphos)] (2) | 295 (31,000), 337 (1000) | 440 |
| [Ag(mqzt)(PPh3)]2 (3) | 297 (30,000) | 437 |
| [Ag(mqzt)(dppm)]2 (4) | 297 (35,000), 317 (20,000), 356 (2000) | 428 |
| [Ag(mqzt)(DPEPhos)]2 (5) | 296 (37,000), 319 (16,000), 340 (6000) | 442 |
| [Ag(mqzt)(xantphos)]2 (6) | 295 (35,000), 356 (1500) | 438 |
| %LC | %EE | |
|---|---|---|
| [1–25]@BaAlg | 0.010 | 99 |
| [1–50]@BaAlg | 0.037 | 99 |
| [1–100]@BaAlg | 0.050 | 99 |
| Actual Concentration of Complex 1 (μg mL−1) | % Viability of S. aureus Bacteria | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 μg mL−1 | 12 |
| 50 μg mL−1 | 0 | |
| 100 μg mL−1 | 0 | |
| [1–25]@BaAlg | 2.0 | 75 |
| [1–50]@BaAlg | 2.8 | 67 |
| [1–100]@BaAlg | 7.6 | 50 |
| Actual Concentration of Complex 1 (μg mL−1) | % Viability of L929 Normal Cells | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 20 |
| 50 | 16 | |
| 100 | 14 | |
| [1–25]@BaAlg | 5.4 | 75 |
| [1–50]@BaAlg | 6.0 | 71 |
| [1–100]@BaAlg | 8.3 | 60 |
| E. coli GR | E. coli TrxR | |
|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μΜ) | ||
| [AgCl(mqztH)(PPh3)2] (1) | 0.065 (±0.013) | 0.215 (±0.043) |
| AgNO3 | 0.031 (±0.001) | 0.061 (±0.008) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tzaferi, E.I.; Varna, D.; Esarev, I.V.; Kavaratzi, K.; Hatzidimitriou, A.G.; Papi, R.; Ott, I.; Angaridis, P.A. Redox-Active Quinazolinone Thioamide Ag(I) Complexes with Potent Antibacterial Activity: Mechanistic Insights and Hydrogel-Enhanced Efficacy. Molecules 2025, 30, 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204071
Tzaferi EI, Varna D, Esarev IV, Kavaratzi K, Hatzidimitriou AG, Papi R, Ott I, Angaridis PA. Redox-Active Quinazolinone Thioamide Ag(I) Complexes with Potent Antibacterial Activity: Mechanistic Insights and Hydrogel-Enhanced Efficacy. Molecules. 2025; 30(20):4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204071
Chicago/Turabian StyleTzaferi, Eleni Ioanna, Despoina Varna, Igor V. Esarev, Konstantina Kavaratzi, Antonios G. Hatzidimitriou, Rigini Papi, Ingo Ott, and Panagiotis A. Angaridis. 2025. "Redox-Active Quinazolinone Thioamide Ag(I) Complexes with Potent Antibacterial Activity: Mechanistic Insights and Hydrogel-Enhanced Efficacy" Molecules 30, no. 20: 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204071
APA StyleTzaferi, E. I., Varna, D., Esarev, I. V., Kavaratzi, K., Hatzidimitriou, A. G., Papi, R., Ott, I., & Angaridis, P. A. (2025). Redox-Active Quinazolinone Thioamide Ag(I) Complexes with Potent Antibacterial Activity: Mechanistic Insights and Hydrogel-Enhanced Efficacy. Molecules, 30(20), 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204071








