Comparison of the Removal of Synthetic Wastewater Samples Containing Basic Blue 3 Dye Using Electrochemical and Adsorption Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Linden Leaf Adsorbent
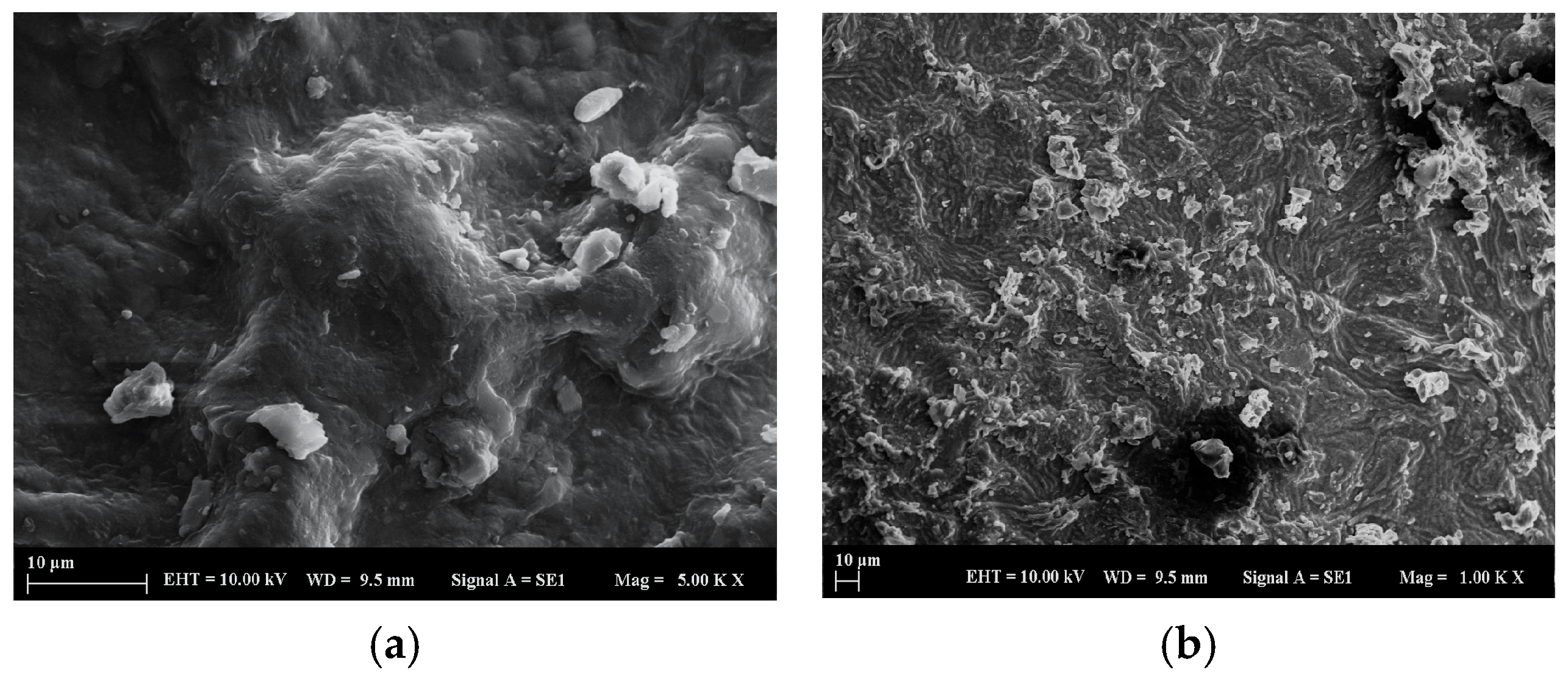
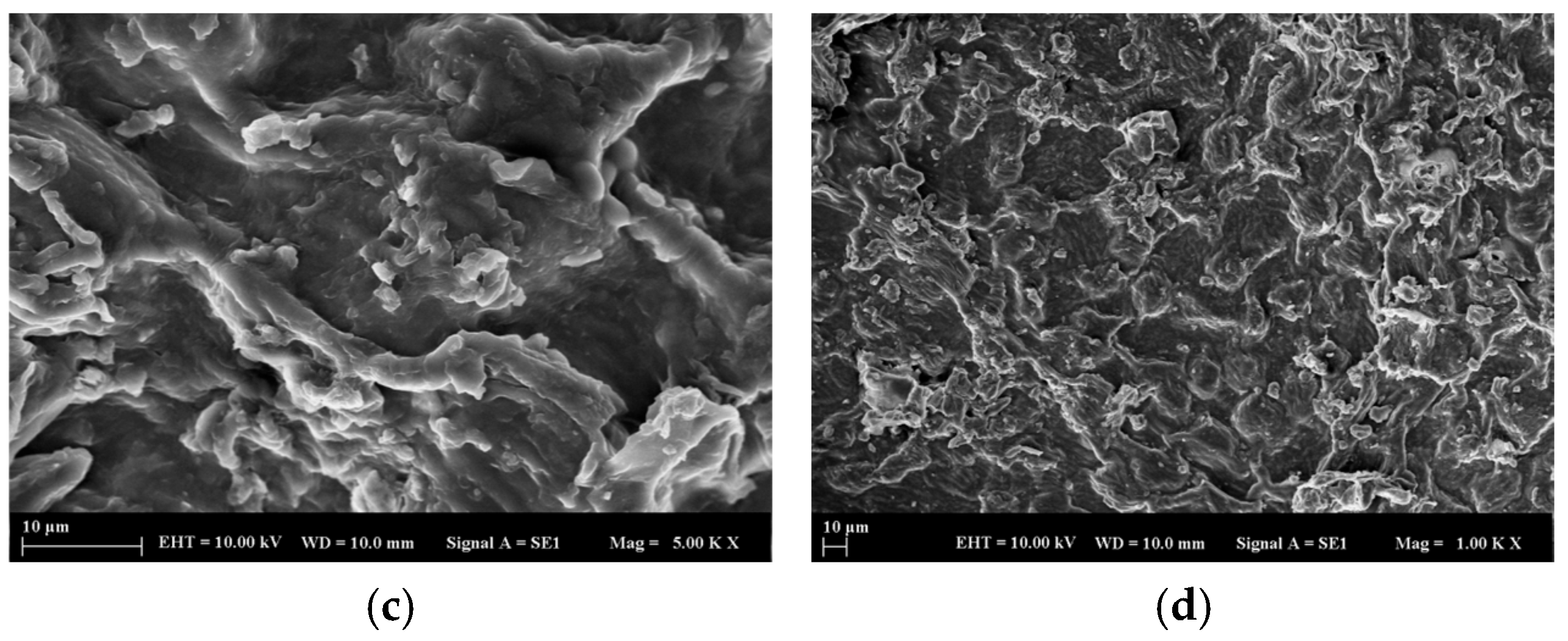
2.1.1. SEM Analysis of the Adsorbent Material
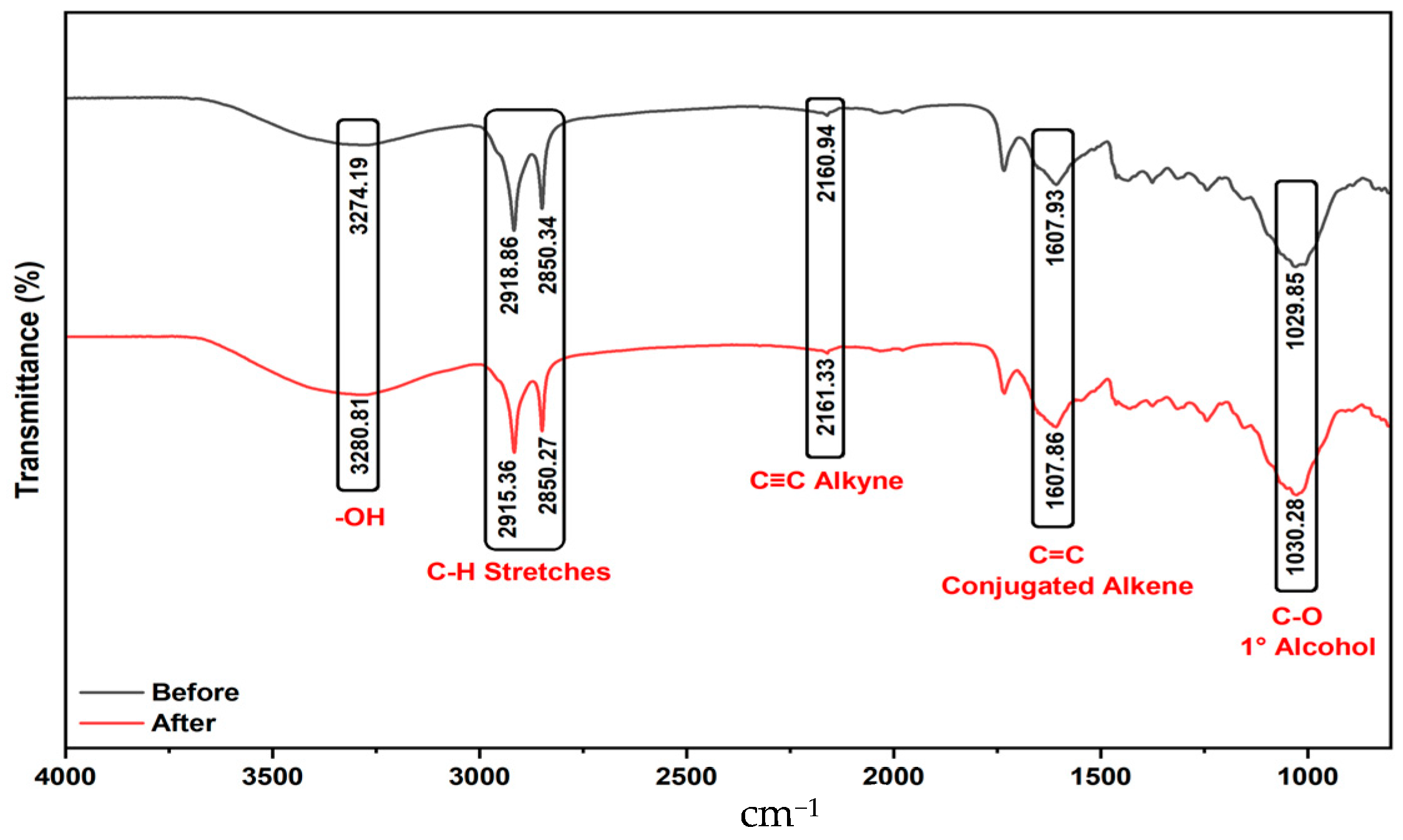
2.1.2. Analysis of FTIR Results
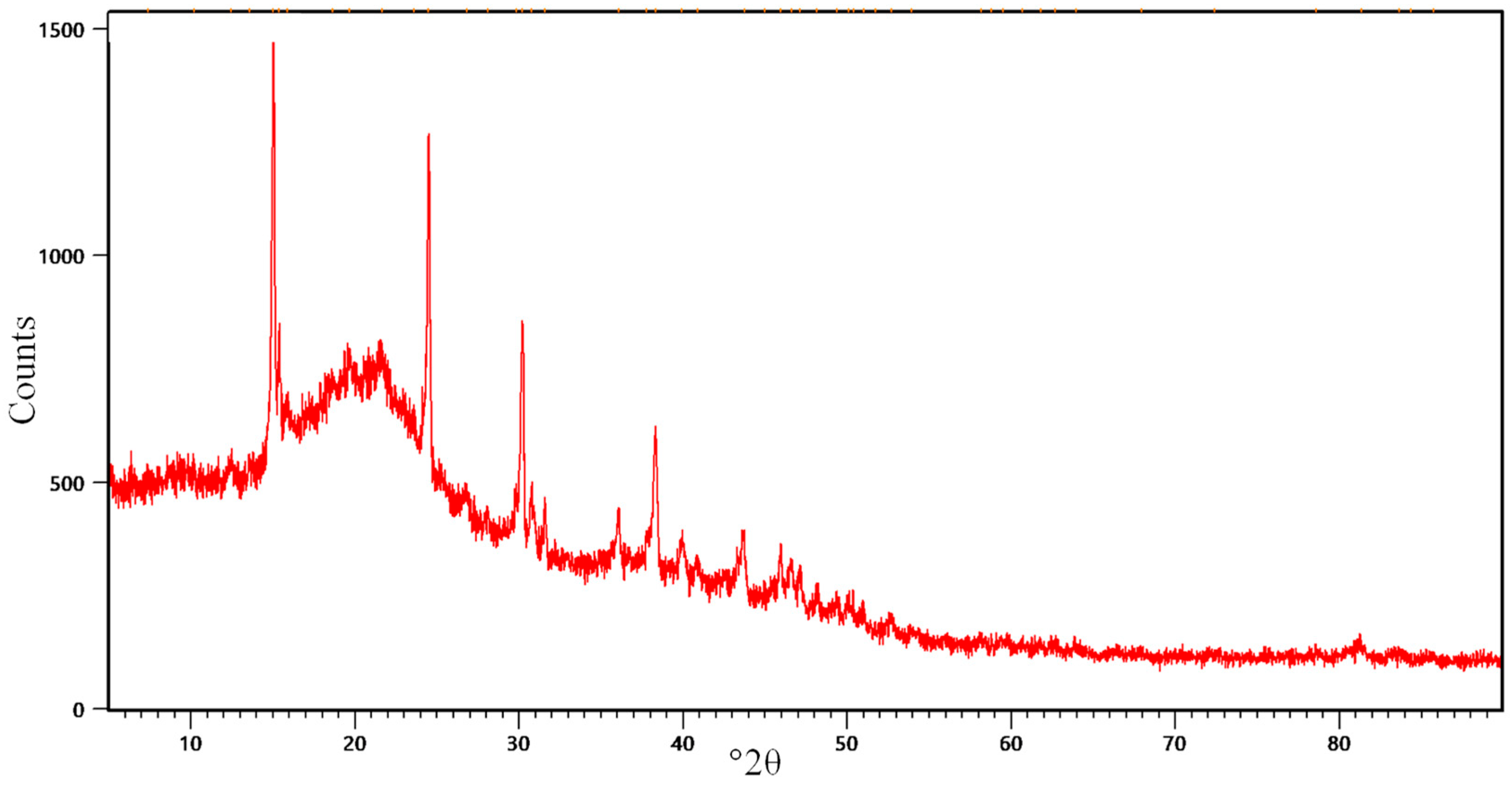
2.1.3. XRD Results
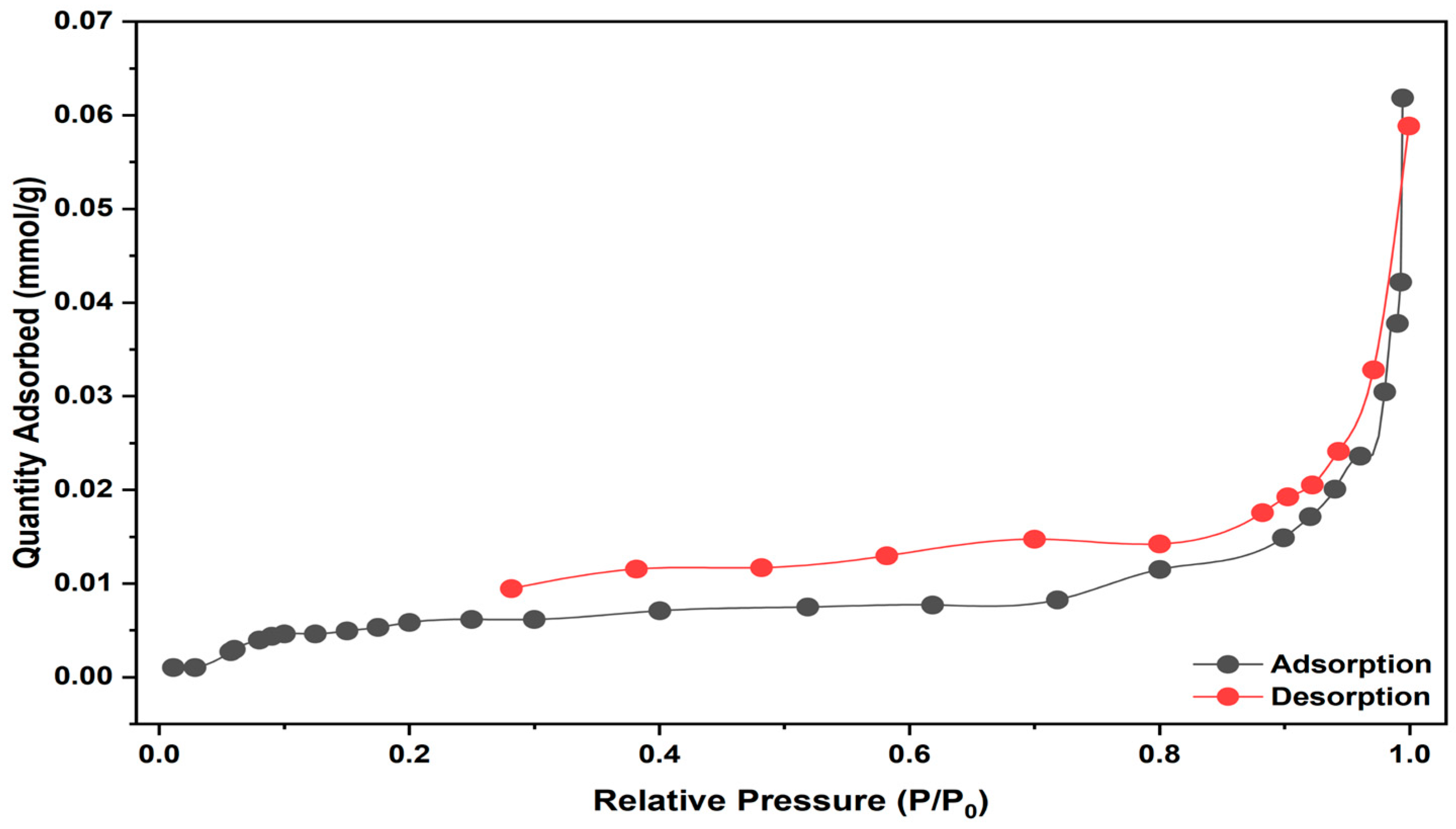
2.1.4. BET Analysis of Linden Leaf Adsorbent
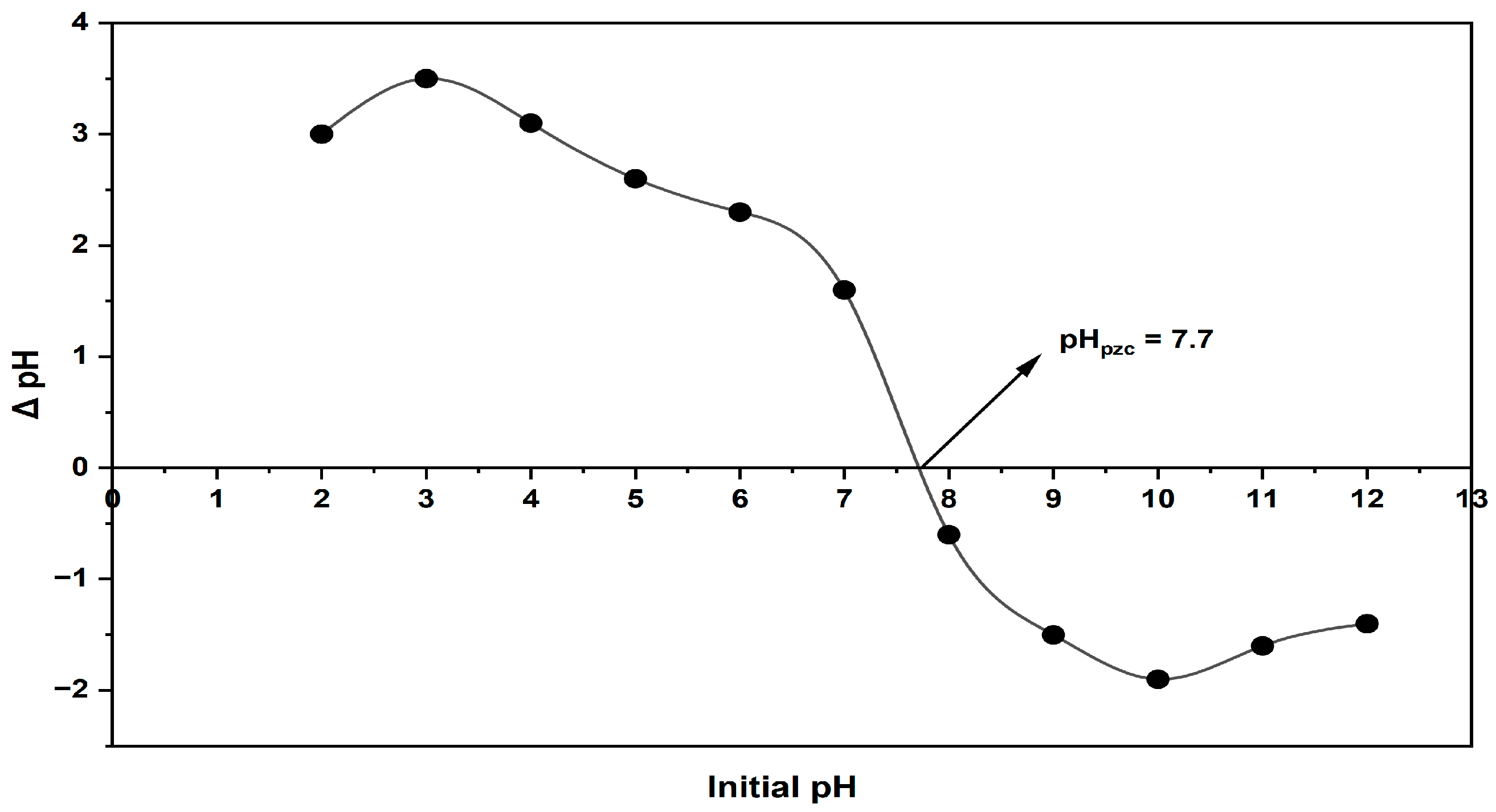
2.1.5. pHpzc (Point of Zero Charge) Determination
2.2. The Results of Adsorption Experiments
2.2.1. The Effect of Initial Dye Concentration on Adsorption of BB3
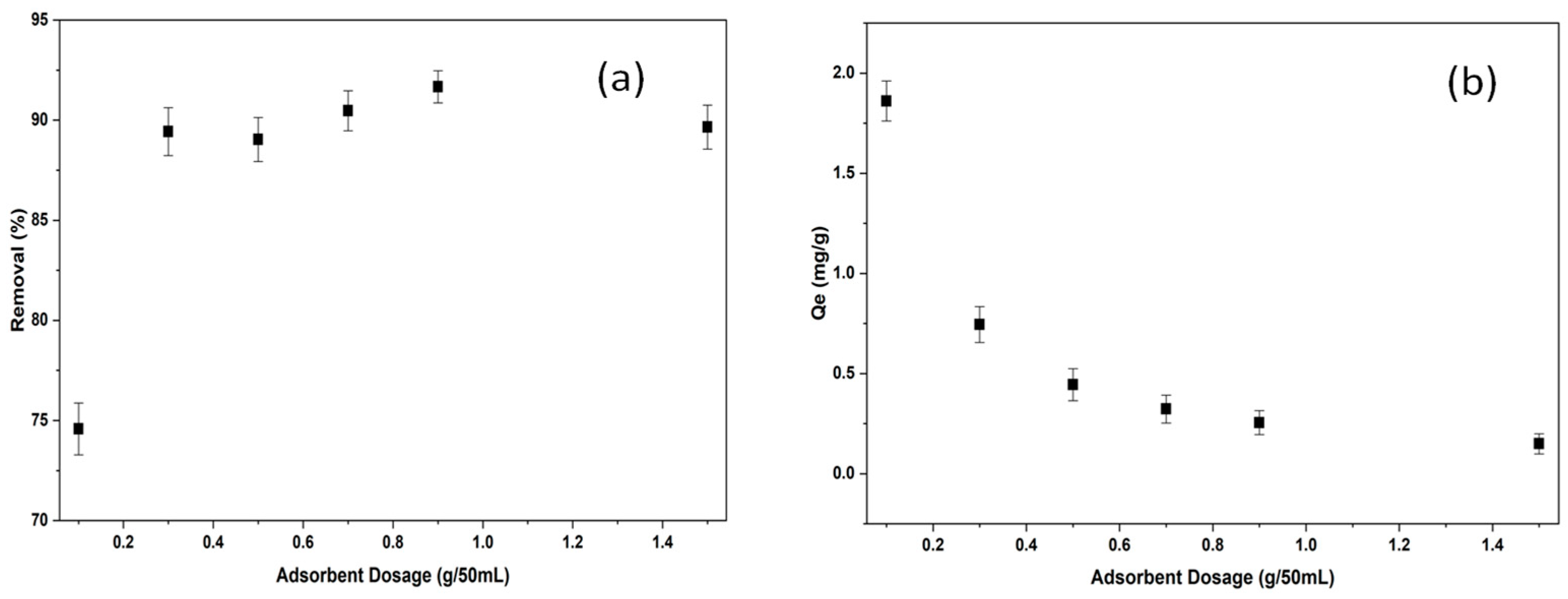
2.2.2. The Effect of Adsorbent Dosage on Adsorption of BB3
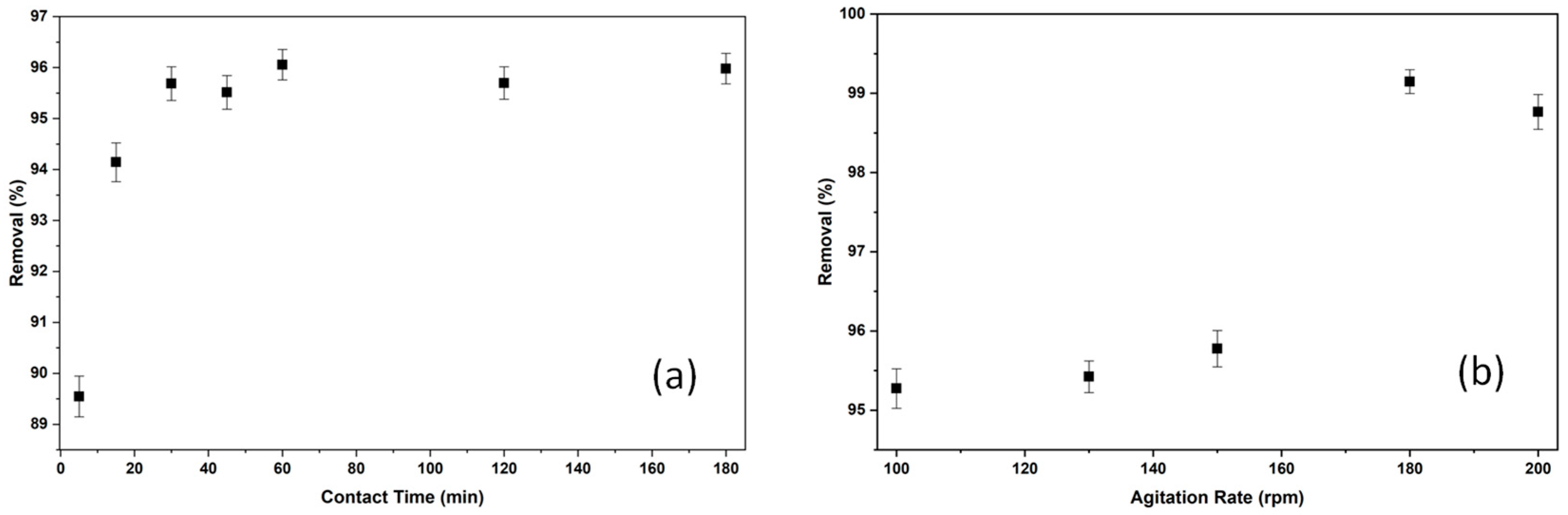
2.2.3. The Effect of Contact Time and Agitation Rate on Adsorption of BB3
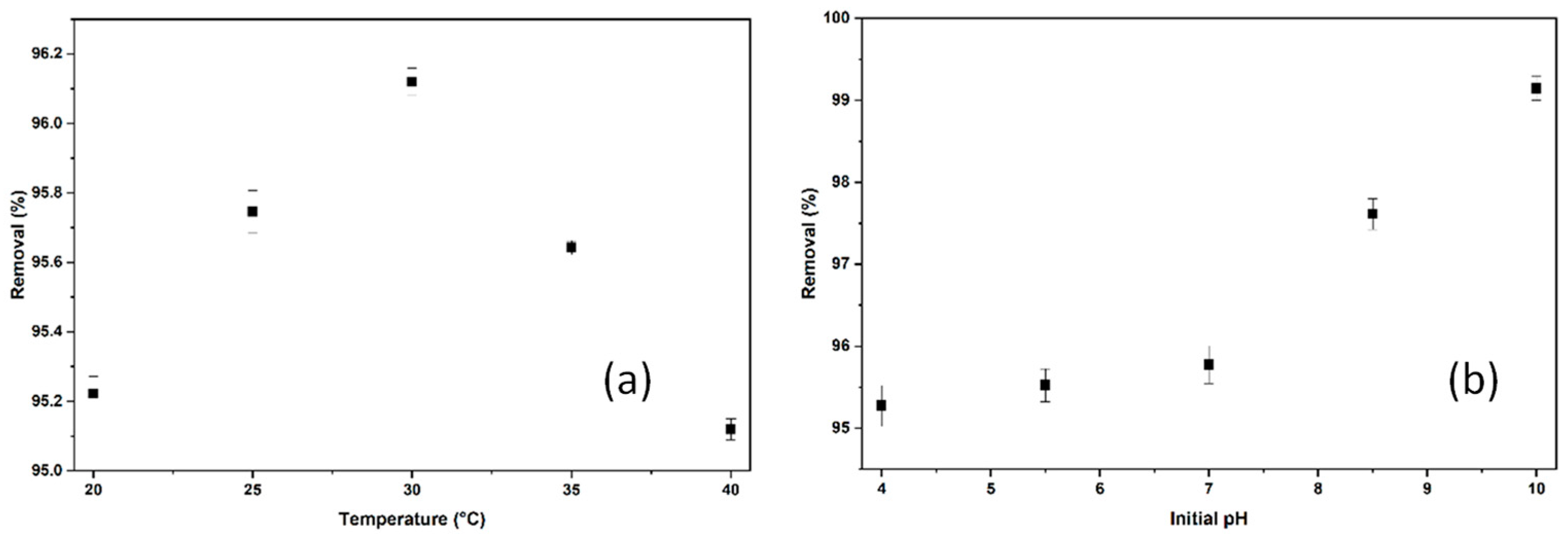
2.2.4. The Effect of Temperature and pH on the Adsorption of BB3
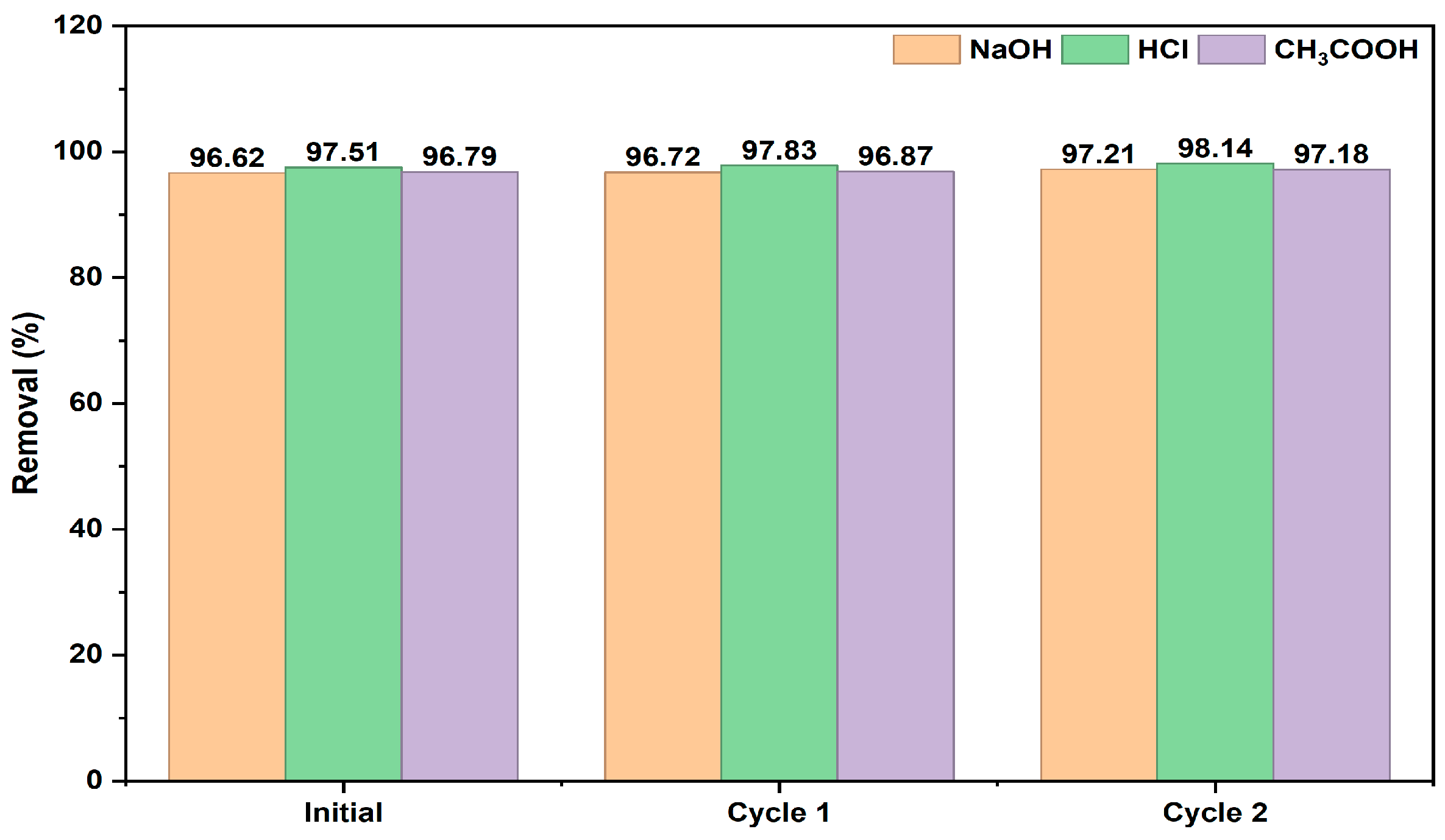
2.2.5. Regeneration of the Adsorbent
2.2.6. Adsorption Isotherms
2.2.7. Comparative Research of Adsorption Capacity for BB3
2.3. The Results of Electrocoagulation (EC) Experiments
2.3.1. The Effect of Different Concentrations of BB3 on % Removal
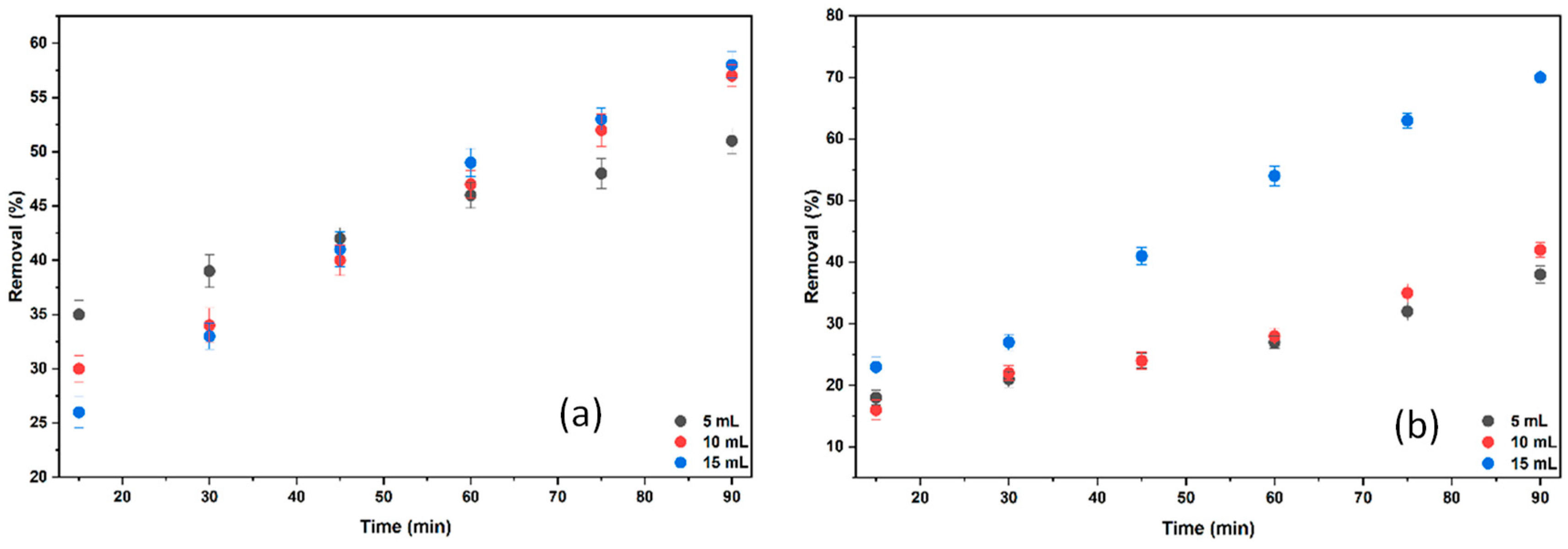
2.3.2. The Effect of Different KCl and NaCl Volumes on the % Removal of BB3
2.3.3. The Effect of Different Stirring Speed and pH on the % Removal of BB3
2.3.4. Different Electrode Studies in the Literature
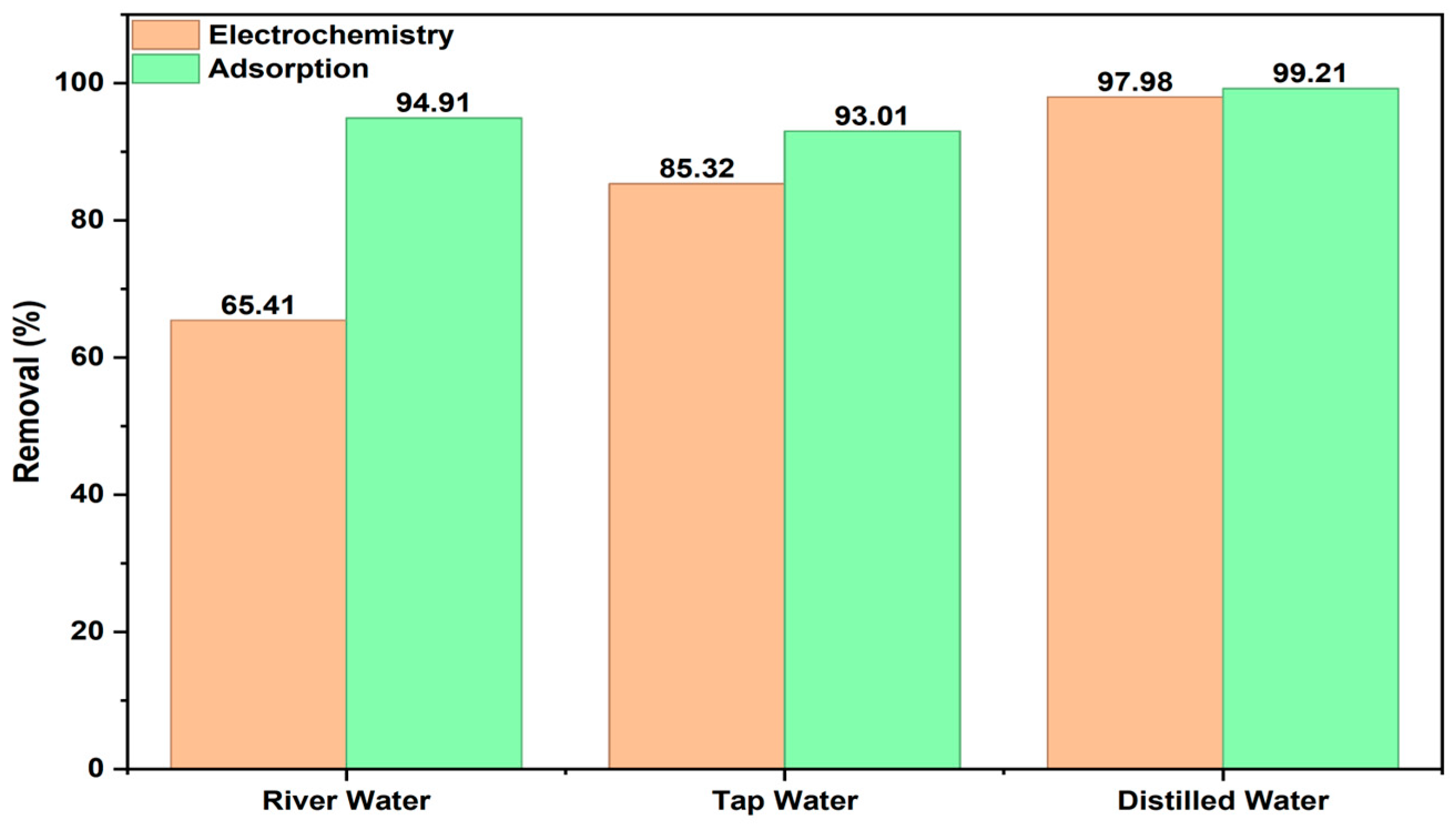
2.4. Experimental Studies by Using BB3 Solutions Prepared from Different Water Sources
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Preparation of Linden (Tilia) Tree Leaves as the Adsorbent
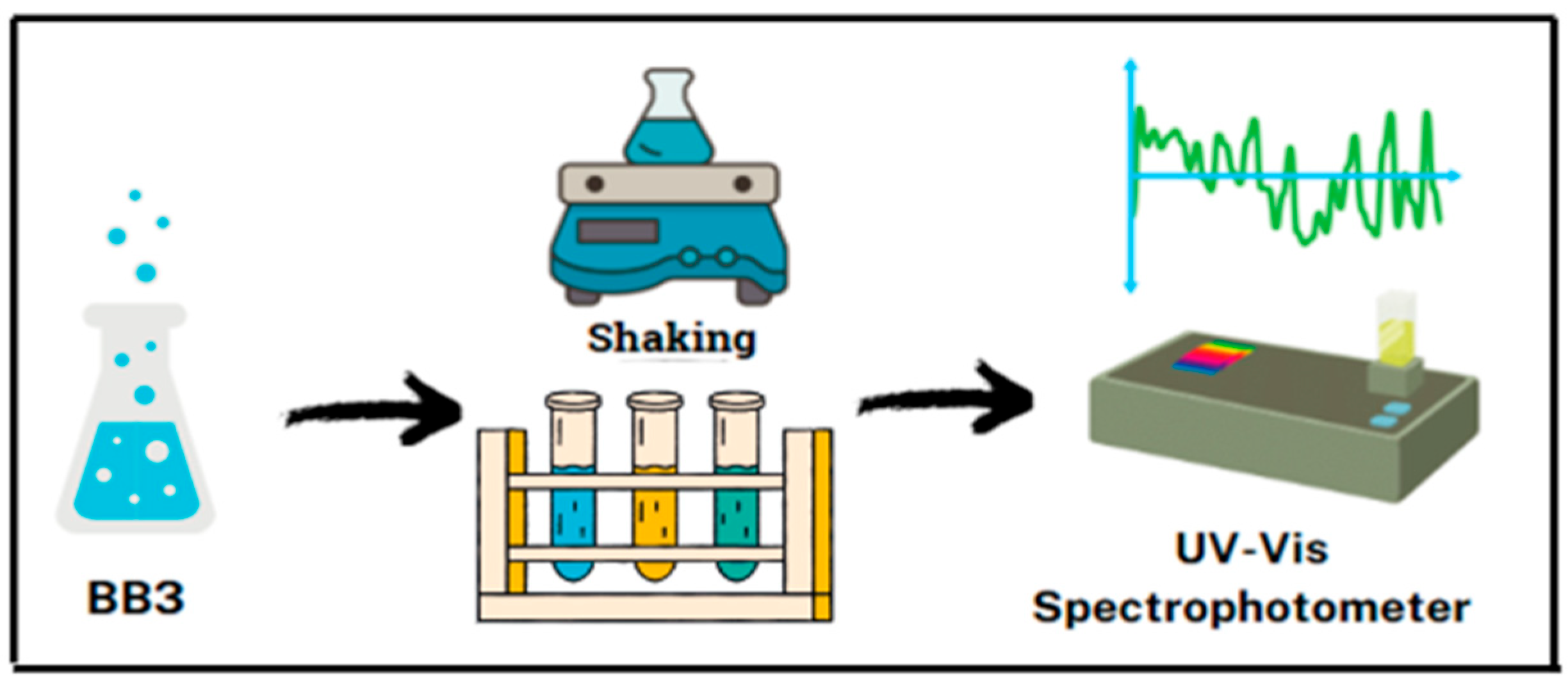
3.4. Adsorption Experiments
3.5. The Figureout Procedure of pHpzc (Point of Zero Charge)
3.6. The Isotherms of Adsorption
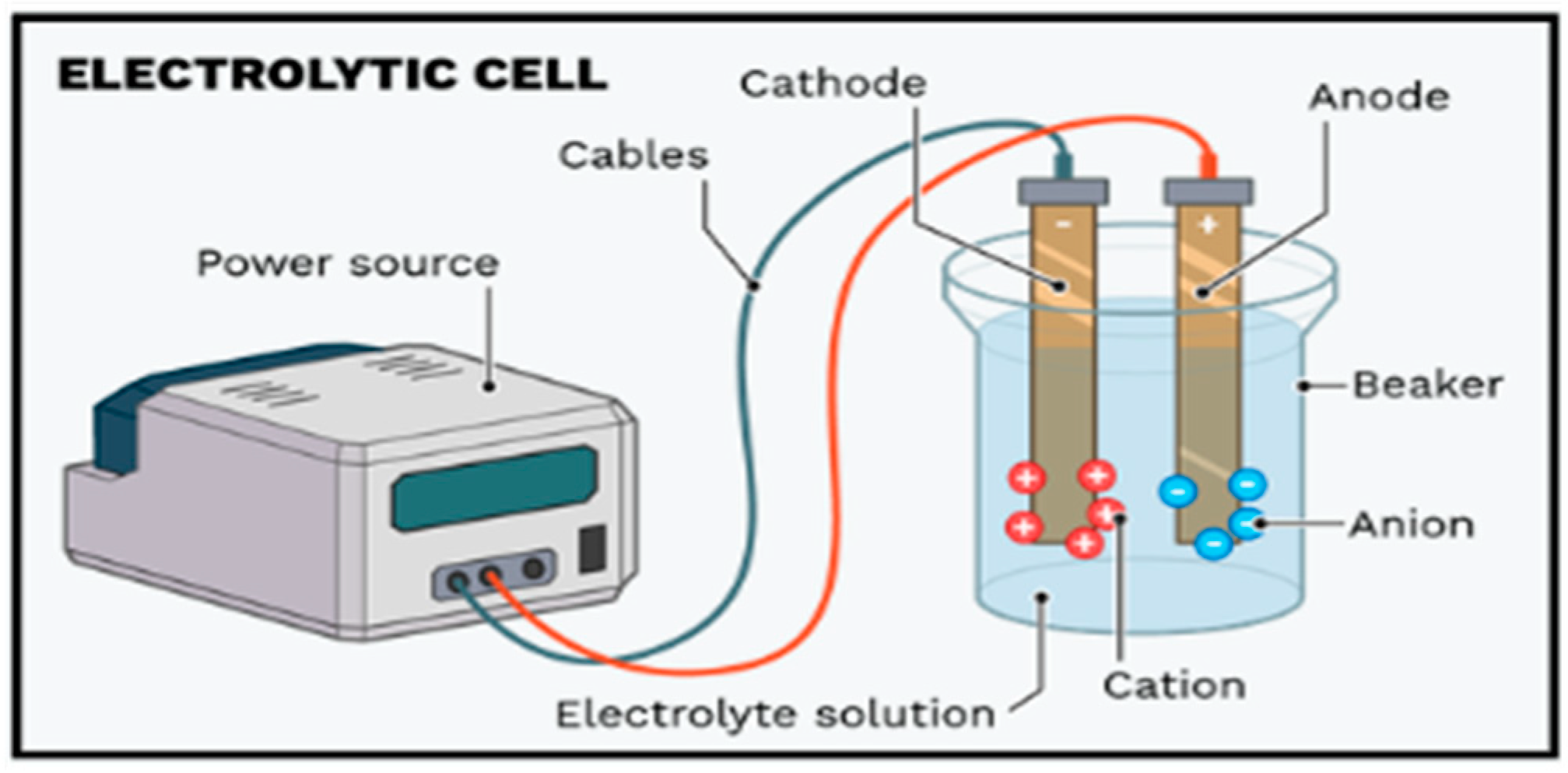
3.7. Electrocoagulation (EC) Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hisada, M.; Tomizawa, Y.; Kawase, Y. Removal kinetics of cationic azo-dye from aqueous solution by poly-γ-glutamic acid biosorbent: Contributions of adsorption and complexation/precipitation to Basic Orange 2 removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladimeji, T.; Oyedemi, M.; Emetere, M.; Agboola, O.; Adeoye, J.; Odunlami, O. Review on the impact of heavy metals from industrial wastewater effluent and removal technologies. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Viraraghavan, T. Removal of Congo Red from an aqueous solution by fungus Aspergillus niger. Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 7, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragaw, T.A.; Angerasa, F.T. Synthesis and characterization of Ethiopian kaolin for the removal of basic yellow (BY 28) dye from aqueous solution as a potential adsorbent. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Chang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Song, G.; Sun, Y.; Ding, G. A review on selective dye adsorption by different mechanisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragaw, T.A.; Alene, A.N. A comparative study of acidic, basic, and reactive dyes adsorption from aqueous solution onto kaolin adsorbent: Effect of operating parameters, isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Emerg. Contam. 2022, 8, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaari, I.; Fakhfakh, E.; Medhioub, M.; Jamoussi, F. Comparative study on adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes by smectite rich natural clays. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1179, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Antonini, G.; Al-Omari, A.; Muller, C.; Mathew, J.; Bell, K.; Pearce, J.M.; Santoro, D. Electrochemical Methods for Nutrient Removal in Wastewater: A Review of Advanced Electrode Materials, Processes, and Applications. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madi-Azegagh, K.; Yahiaoui, I.; Arfi, R.; Benkerrou, L.; Khenniche, L.; Lebik, H.; Assadi, A.A.; Khezami, L.; Kriaa, K.; Aissani-Benissad, F. Adsorption Combined with Electrocoagulation Process for Ketoprofen Removal from Aqueous Solution: Optimization Using Central Composite Design. Water 2025, 17, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvidović, N.V.; Vrsalović, L.; Svilović, S.; Gudić, S.; Čule, I. Sono- and Zeolite-Assisted Electrocoagulation for Compost Wastewater Treatment: Does Ultrasound Power Make a Difference? Minerals 2024, 14, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairungsi, N.; Jumpatong, K.; Phutdhawong, W.; Buddhasukh, D. Solvent Effects in Electrocoagulation of Selected Plant Pigments and Tannin. Molecules 2006, 11, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husein, S.; Slamet; Dewi, E.L. The Impact of Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Concentrations on Electrocoagulation for Simultaneous Tartrazine Dye Removal and Hydrogen Production. Eng. Proc. 2024, 67, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, Y.H.; Helal, R.H.; Radi, H.; El-Nemr, K.F.; Khozemy, E.E. Preparation and application of irradiated polyvinyl alcohol/starch/pumice composites for adsorption of basic dye: Isotherm and kinetics study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 249, 126106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janos, P. Sorption of dyes from aqueous solutions onto fly ash. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4938–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutunga, M.F.; Wanyonyi, W.C.; Ongera, G. Utilization of Macadamia seed husks as a low-cost sorbent for removing cationic dye (basic blue 3 dye) from aqueous solution. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2020, 2, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption isotherm models: Classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaddouz, M.; Azzaoui, K.; Akartasse, N.; Mejdoubi, E.; Hammouti, B.; Taleb, M.; Sabbahi, R.; Alshahateet, S. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption onto hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1288, 135807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-González, A.M.; Caldera-Villalobos, M.; Peláez-Cid, A.-A. Adsorption of textile dyes using an activated carbon and crosslinked polyvinyl phosphonic acid composite. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 234, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božić, D.; Stanković, V.; Gorgievski, M.; Bogdanović, G.; Kovačević, R. Adsorption of heavy metal ions by sawdust of deciduous trees. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toker, G.; Küpeli, E.; Memisoğlu, M.; Yesilada, E. Flavonoids with antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities from the leaves of Tilia argentea (silver linden). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 95, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Pan, M.; Shi, Y. Nano-Scale Pore Structure and Its Multi-Fractal Characteristics of Tight Sandstone by N2 Adsorption/Desorption Analyses: A Case Study of Shihezi Formation from the Sulige Gas Filed, Ordos Basin, China. Minerals 2020, 10, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jang, B.; Li, F.; Liu, J. Structure and fractal characteristic of micro- and meso-pores in low, middle-rank tectonic deformed coals by CO2 and N2 adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 253, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, T.B. Adsorption of Basic Yellow 28 and Basic Blue 3 Dyes from Aqueous Solution Using Silybum Marianum Stem as a Low-Cost Adsorbent. Molecules 2023, 28, 6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardieka, A.M.; Budak, T.B. Investigation of Removing Basic Yellow 28 and Basic Blue 3 Dyes from Water Using Mulberry Leaves (Morus nigra L.) and Assessment of Ultrasonic Effects. Molecules 2025, 30, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencheqroun, Z.; El Mrabet, I.; Nawdali, M.; Benali, M.; Zaitan, H. Adsorption removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by raw and chemically activated cedar sawdust. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 240, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.Y.; Tan, Y.P.; Abdullah, A.H.; Ong, S.T. Removal of basıc blue 3 and reactıve orange 16 by adsorptıon onto quartenızed sugar cane bagasse. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2009, 13, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Taşar, Ş.; Kaya, F.; Özer, A. Adsorption of CI Basic Blue 3 Dye Molecules from Aqueous Media by Sulfuric Acid-Activated Montmorillonite Mineral. J. Turk. Chem. Soc. Sect. B Chem. Eng. 2017, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, A.; Shah, A.-U.A.; Bilal, S.; Rahman, G. Basic Blue Dye Adsorption from Water Using Polyaniline/Magnetite (Fe3O4) Composites: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Aspects. Materials 2019, 12, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Gimbert, F.; Robert, C.; Martel, B.; Adam, O.; Morin-Crini, N.; De Giorgi, F.; Badot, P.-M. The removal of Basic Blue 3 from aqueous solutions by chitosan-based adsorbent: Batch studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, N.; Thakur, C. Continuous Treatment of Paper Mill Effluent by Electrocoagulation for Holding Time Analysis. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, N.; Thakur, C.; Ghosh, P.; Hiwarkar, A.D. Desirability Analysis of Multiple Responses for Electrocoagulation Remediation of Paper Mill Wastewater by Using a Central Composite Design. J. Inst. Eng. (India) Ser. E 2021, 102, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassyouni, D.; Ali, S.; Abdel-Aziz, M.; Elashtoukhy, E. Electrocoagulation technique and statistical analysis for treatment of real effluent from the pulp and paper industry. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2023, 18, 100389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, C.; Srivastava, V.C.; Mall, I.D.; Hiwarkar, A.D. Mechanistic Study and Multi-Response Optimization of the Electrochemical Treatment of Petroleum Refinery Wastewater. CLEAN—Soil Air Water 2018, 46, 1700624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katal, R.; Pahlavanzadeh, H. Influence of different combinations of aluminum and iron electrode on electrocoagulation efficiency: Application to the treatment of paper mill wastewater. Desalination 2011, 265, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Volpe, M.; Fiori, L.; Volpe, R.; Messineo, A.; Reza, M.T. Cationic Dye Adsorption on Hydrochars of Winery and Citrus Juice Industries Residues: Performance, Mechanism, and Thermodynamics. Energies 2020, 13, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Farooqui, M. Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions onto Morus nigra L. (mulberry tree) leaves powder and its biochar—Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 104, 4364–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

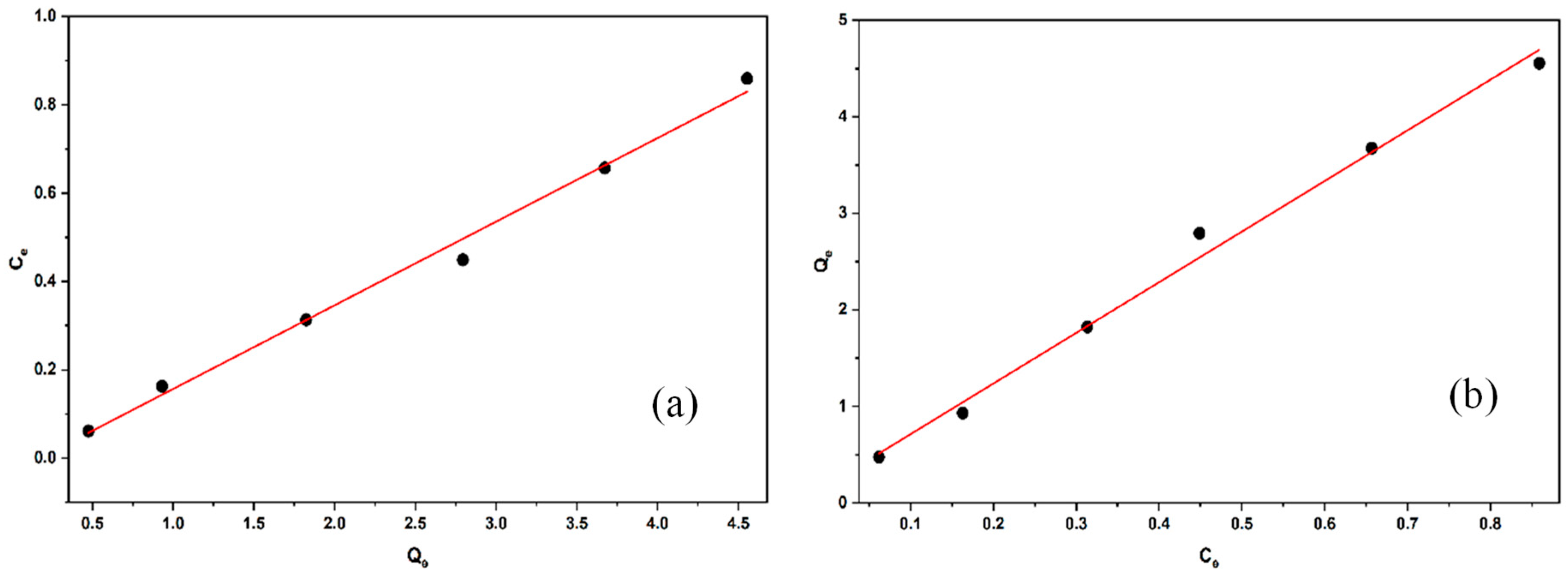


| Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL (mg/L) | qmax (mg/g) | r2 | Kf (mg/L) | 1/n | r2 | |
| Linear Non-Linear | −5.837 | 5.283 | 0.992 | 1.544 | 5.242 | 0.993 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorption Capacities (mg g−1) | Adsorption Model | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| BB3 | |||
| Linden Tree Leaves (Tilia L.) | 5.28 | Langmuir | This Study |
| Silybum marianum (SLM) Stem-Natural | 13.96 | Langmuir | [23] |
| Silybum marianum (SLM) Stem-800 °C | 36.80 | Langmuir | [23] |
| Mulberry leaves (Morus nigra L.) | 10.30 | Langmuir | [24] |
| Raw cedar sawdust | 47.62 | Langmuir | [25] |
| Quarternized sugarcane bagasse | 37.59 | Freundlich | [26] |
| Sulfuric acid-activated montmorillonit | 303–64.53 | Langmuir–Freundlich | [27] |
| PANI | 47.97 | Langmuir | [28] |
| Chitosan-based adsorbent | 166.5 | Langmuir | [29] |
| Wastewater | Removal Efficiency (%) | Electrode Material | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Textile Industry (BB3) | 97.98 | Al | This Study |
| Recycled fiber | 94.91 | Fe | [30] |
| Recycled fiber based | 75.03 | Al | [31] |
| Paper mill | 83.00 | Al | [32] |
| Petroleum refinery | 52.00 | Stainless Steel | [33] |
| Paper mill | >95.00 | Al/Fe | [34] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moralı, B.; Börklü Budak, T. Comparison of the Removal of Synthetic Wastewater Samples Containing Basic Blue 3 Dye Using Electrochemical and Adsorption Methods. Molecules 2025, 30, 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204039
Moralı B, Börklü Budak T. Comparison of the Removal of Synthetic Wastewater Samples Containing Basic Blue 3 Dye Using Electrochemical and Adsorption Methods. Molecules. 2025; 30(20):4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204039
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoralı, Beyza, and Türkan Börklü Budak. 2025. "Comparison of the Removal of Synthetic Wastewater Samples Containing Basic Blue 3 Dye Using Electrochemical and Adsorption Methods" Molecules 30, no. 20: 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204039
APA StyleMoralı, B., & Börklü Budak, T. (2025). Comparison of the Removal of Synthetic Wastewater Samples Containing Basic Blue 3 Dye Using Electrochemical and Adsorption Methods. Molecules, 30(20), 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204039






