Characteristics of Hydrogels as a Coating for Microneedle Transdermal Delivery Systems with Agomelatine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Particle Size Measurement
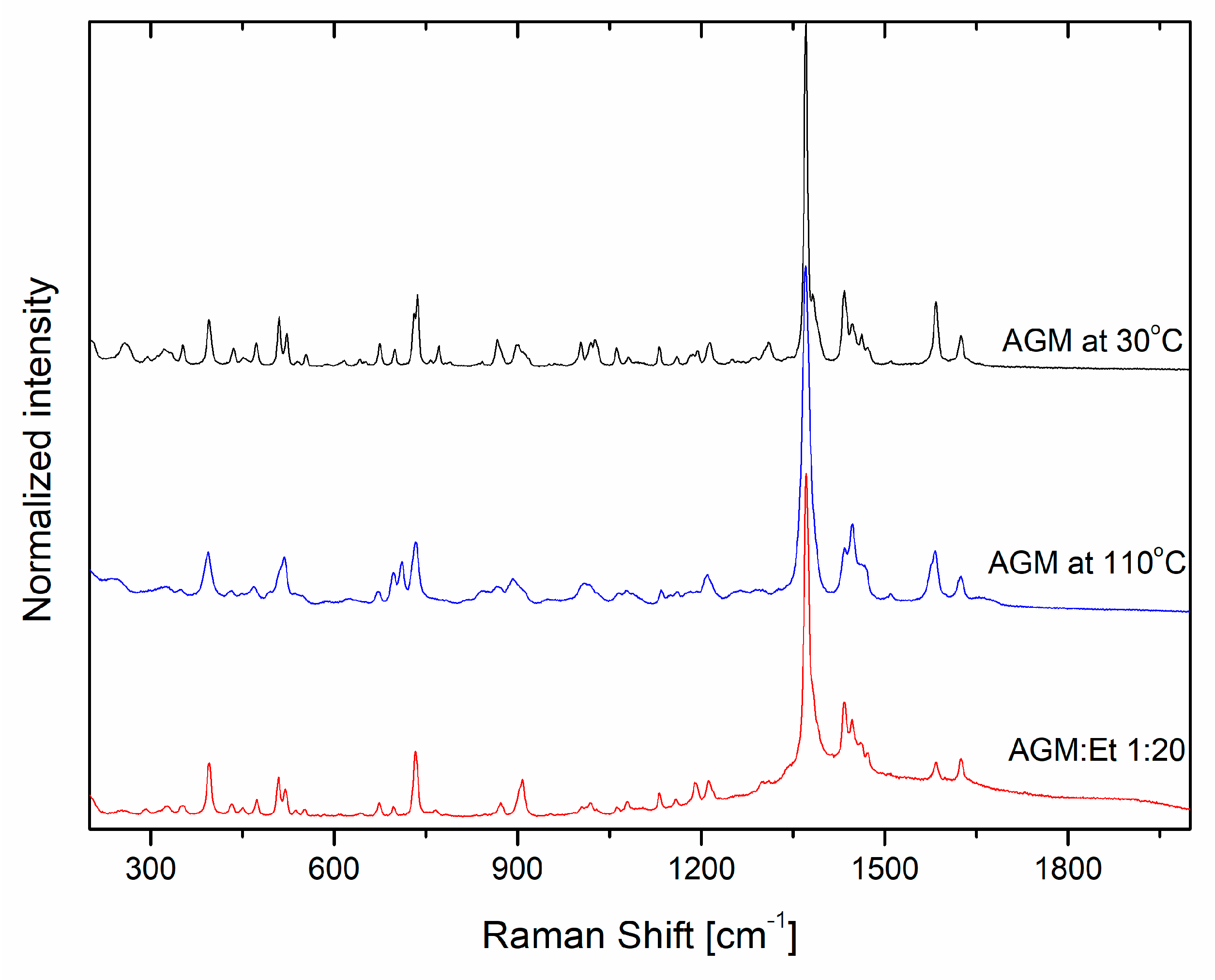
2.2. Raman Analysis
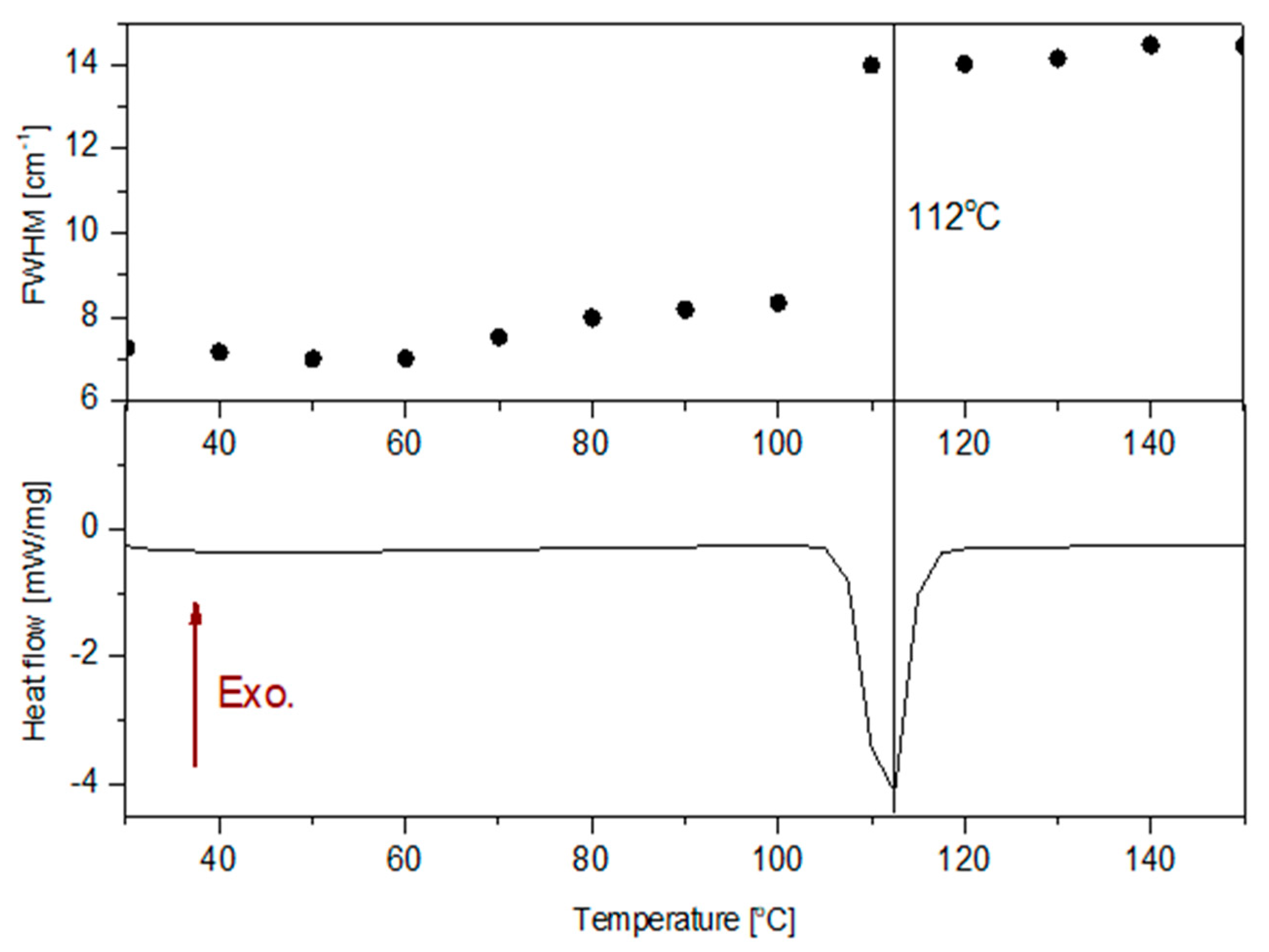
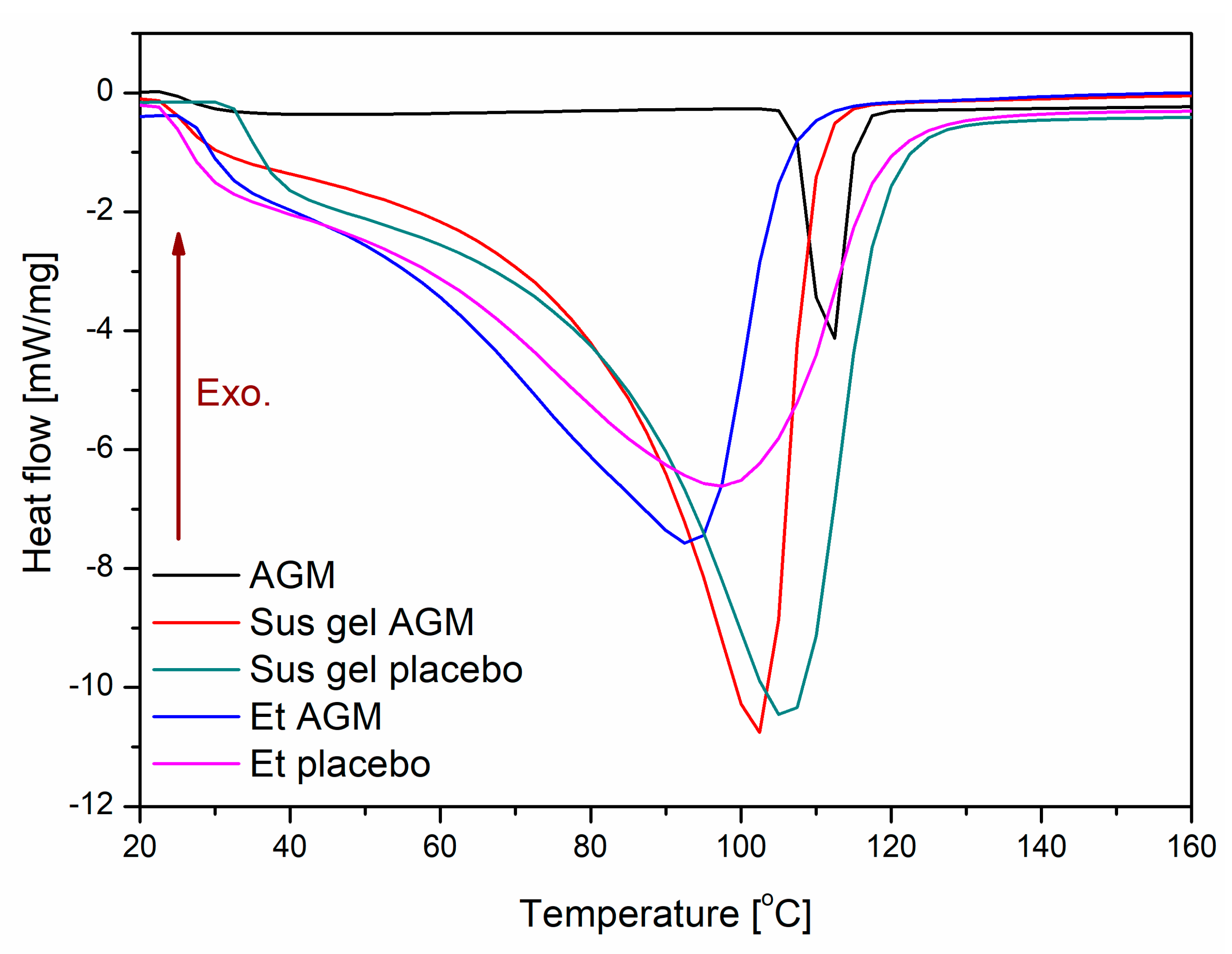
2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
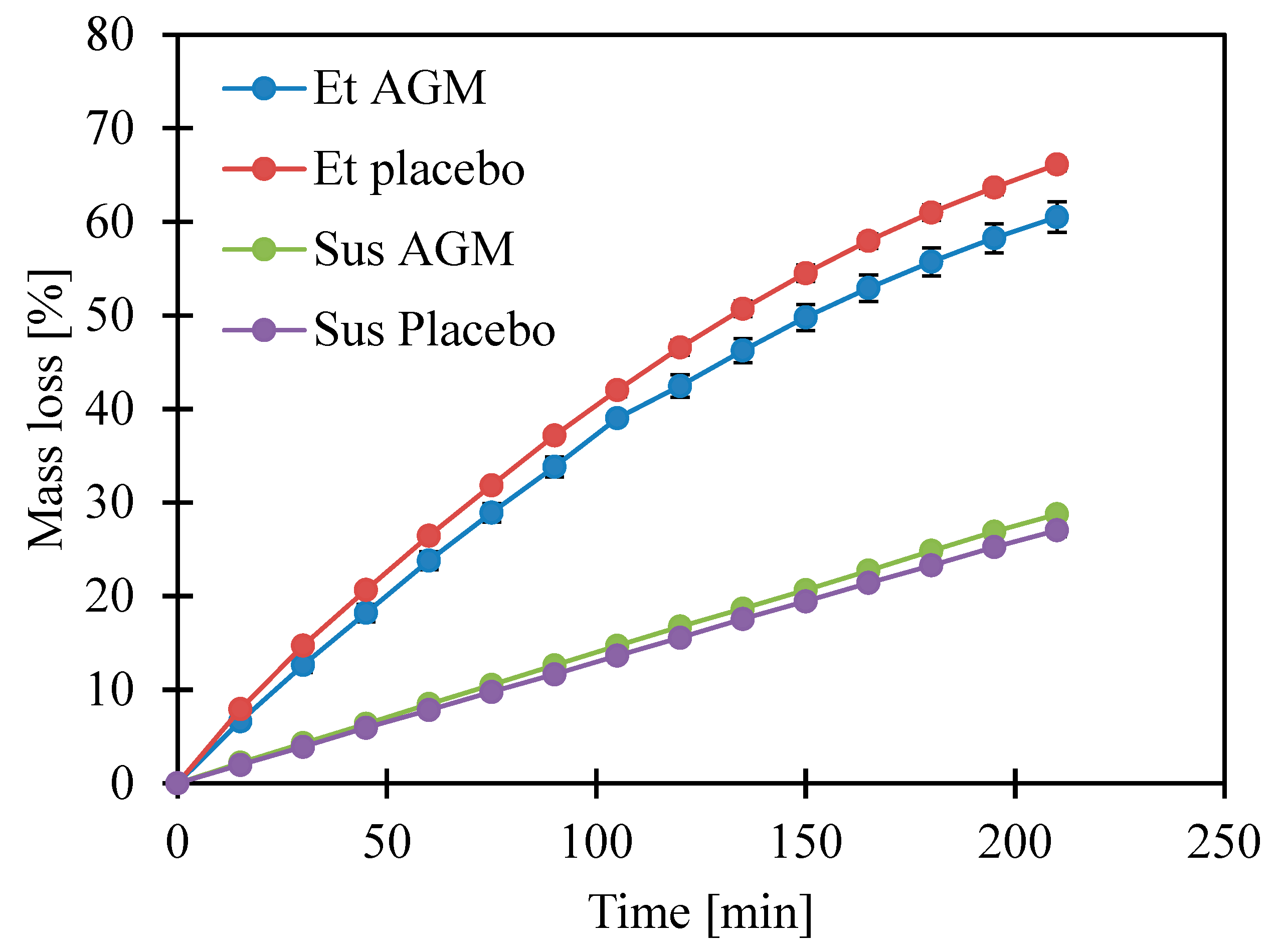
2.4. Loss of Volatile Components
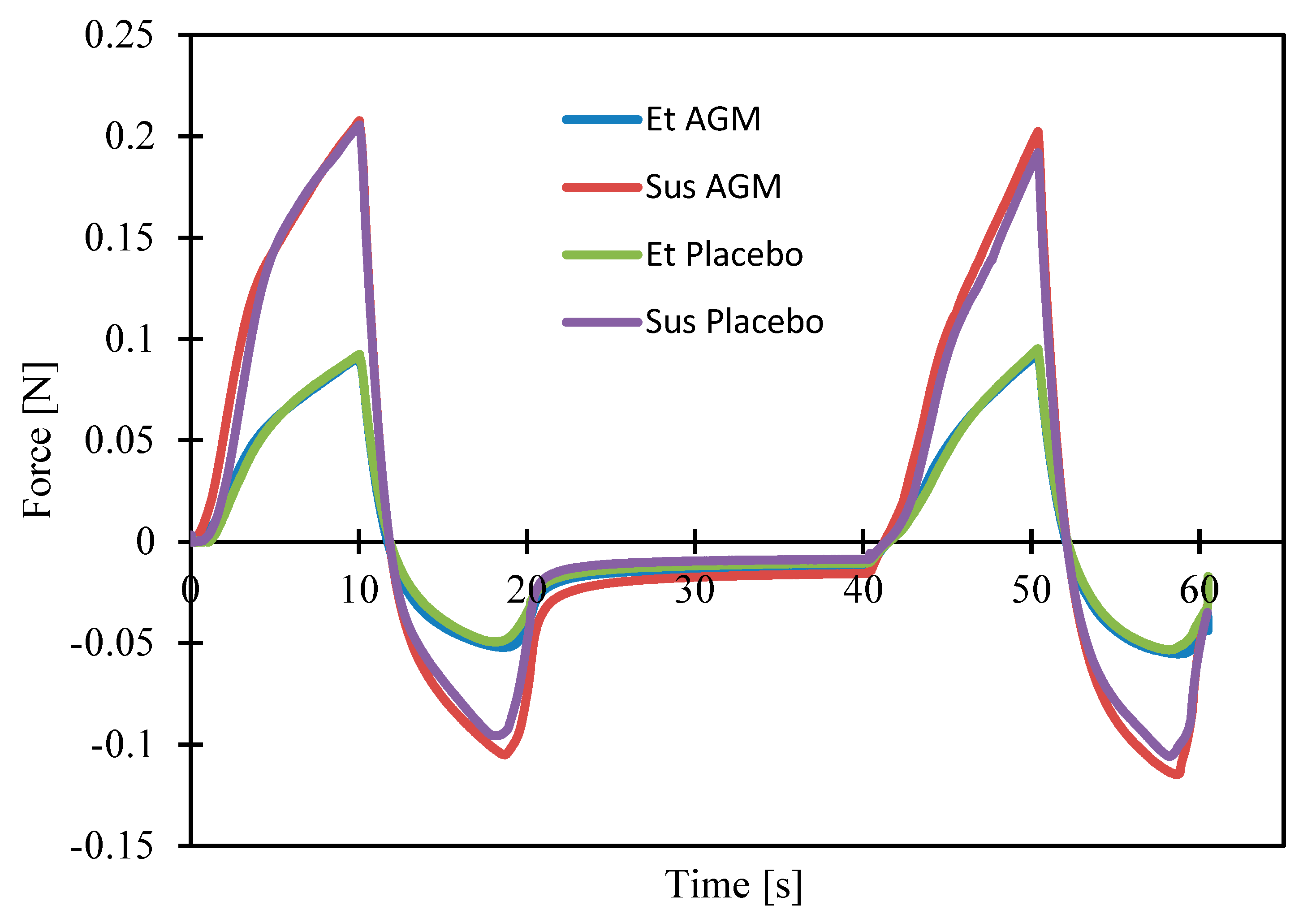
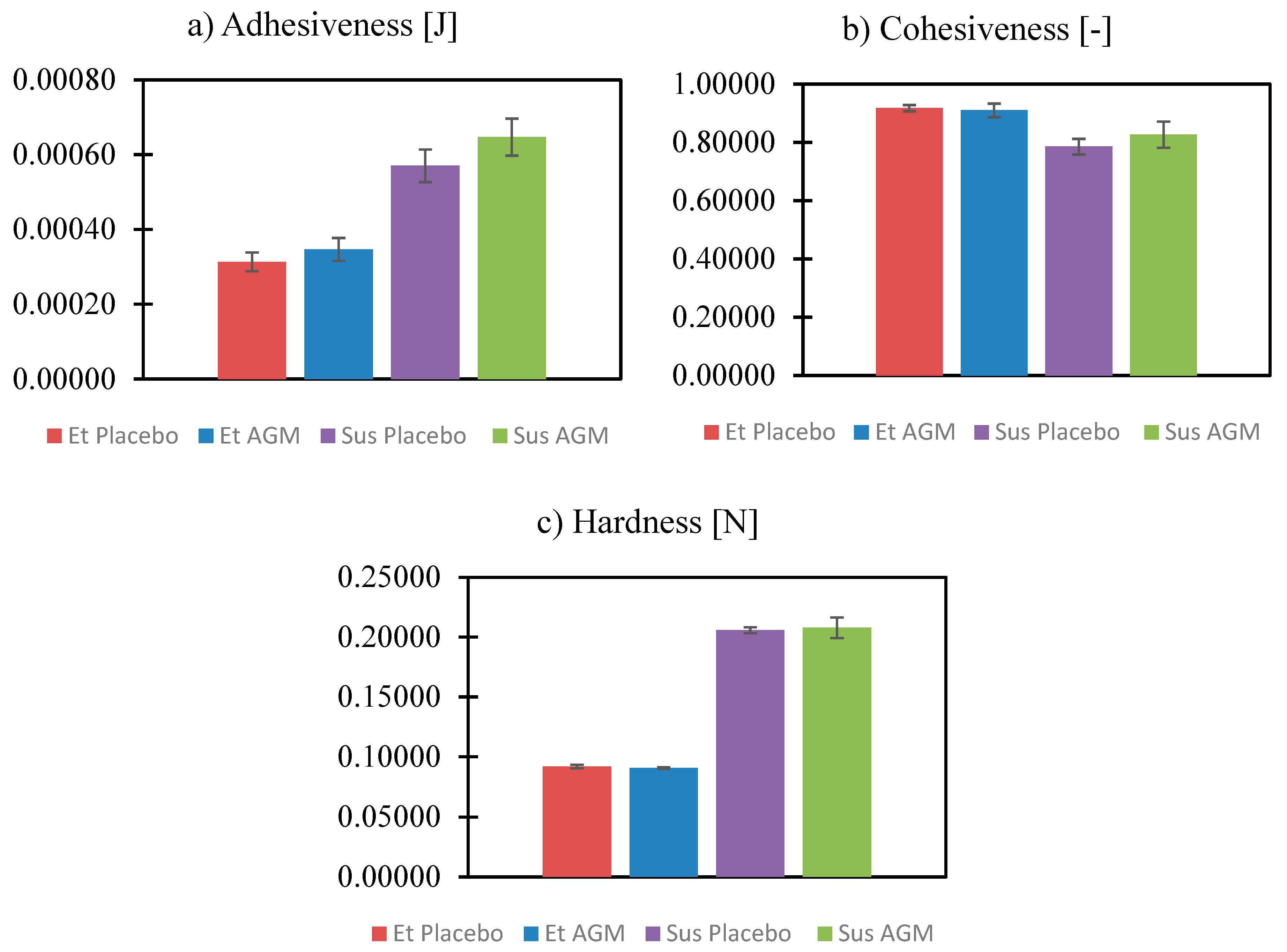
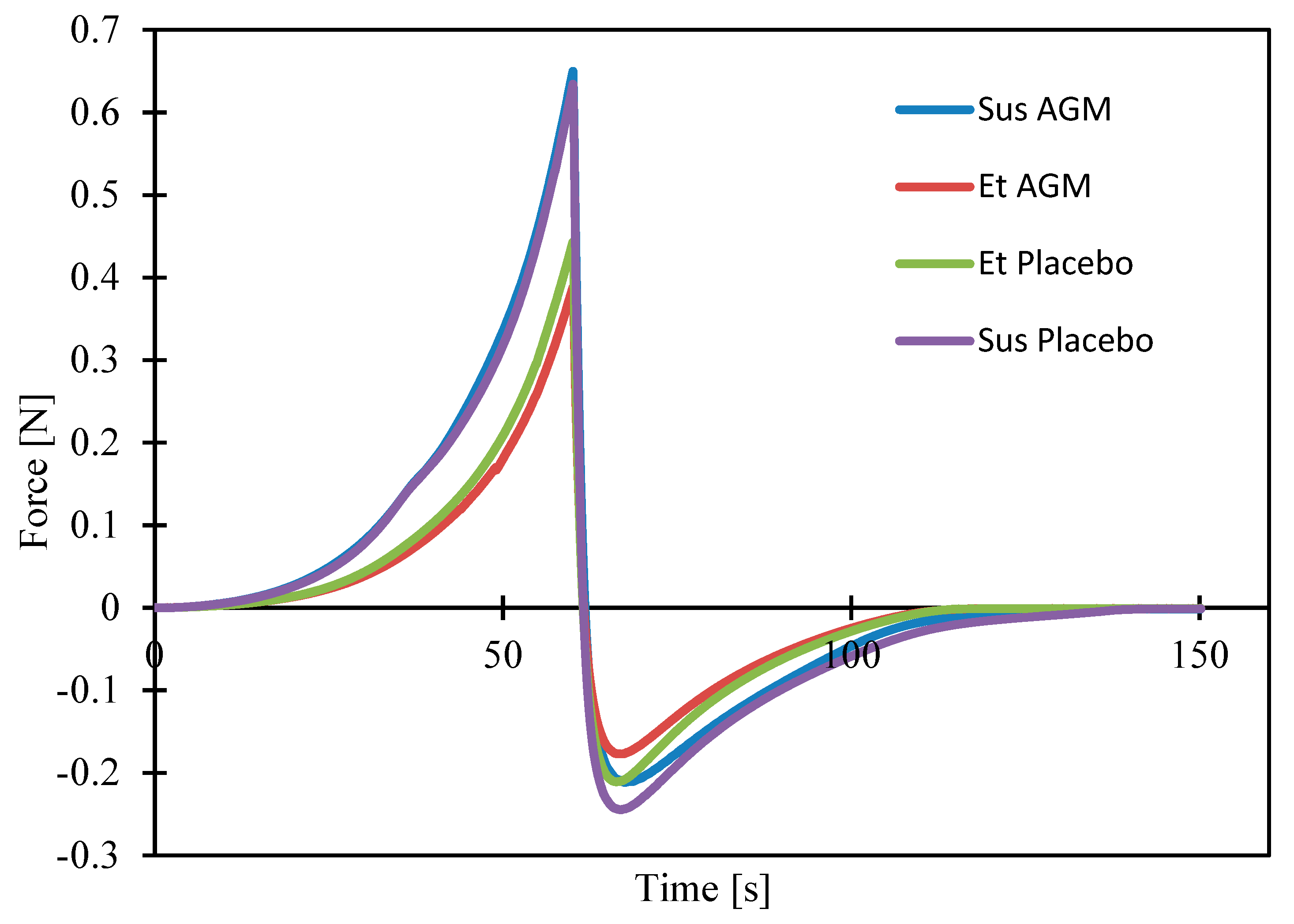
2.5. Texture Profile Analysis and Spreadability Study
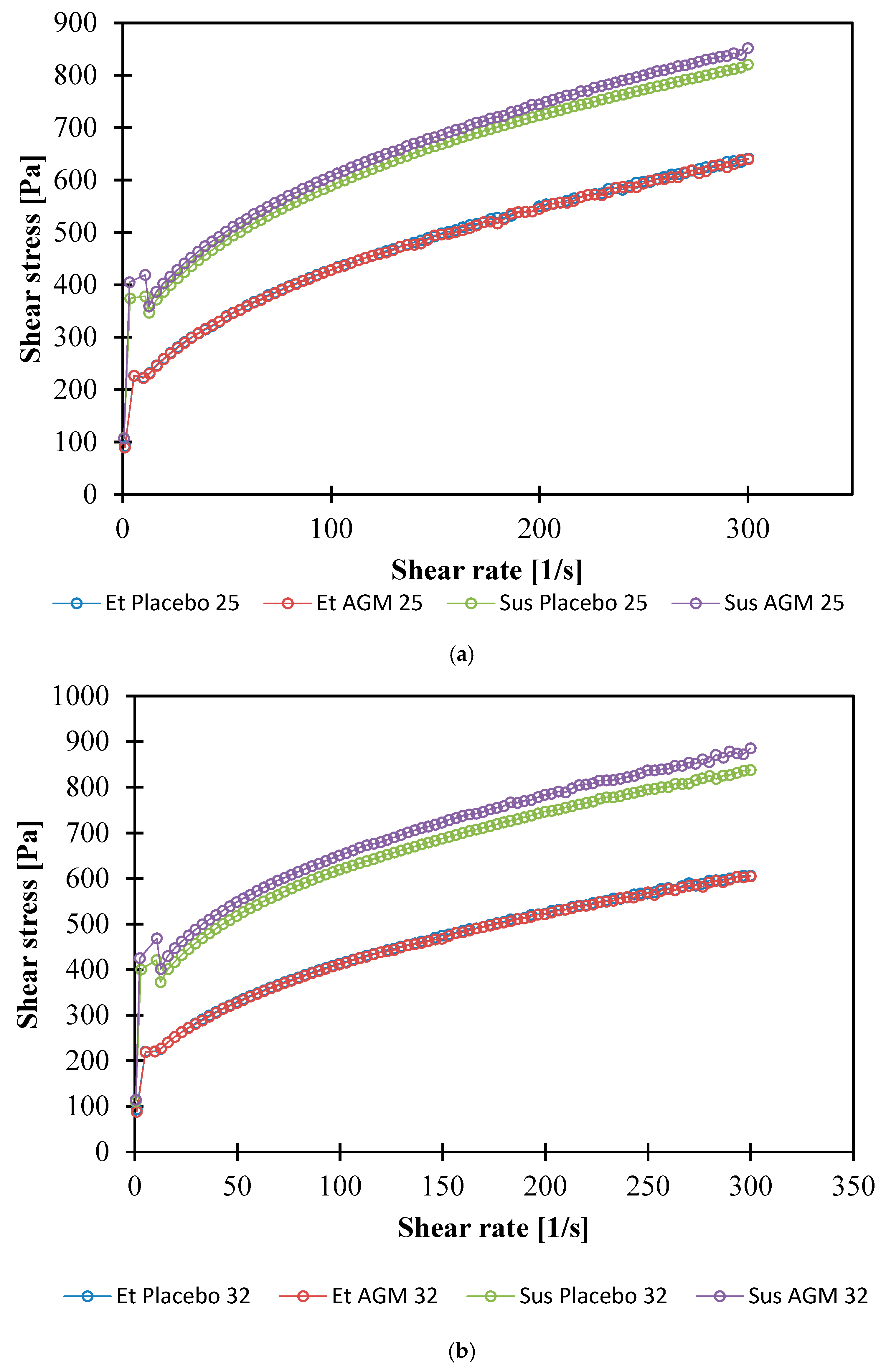
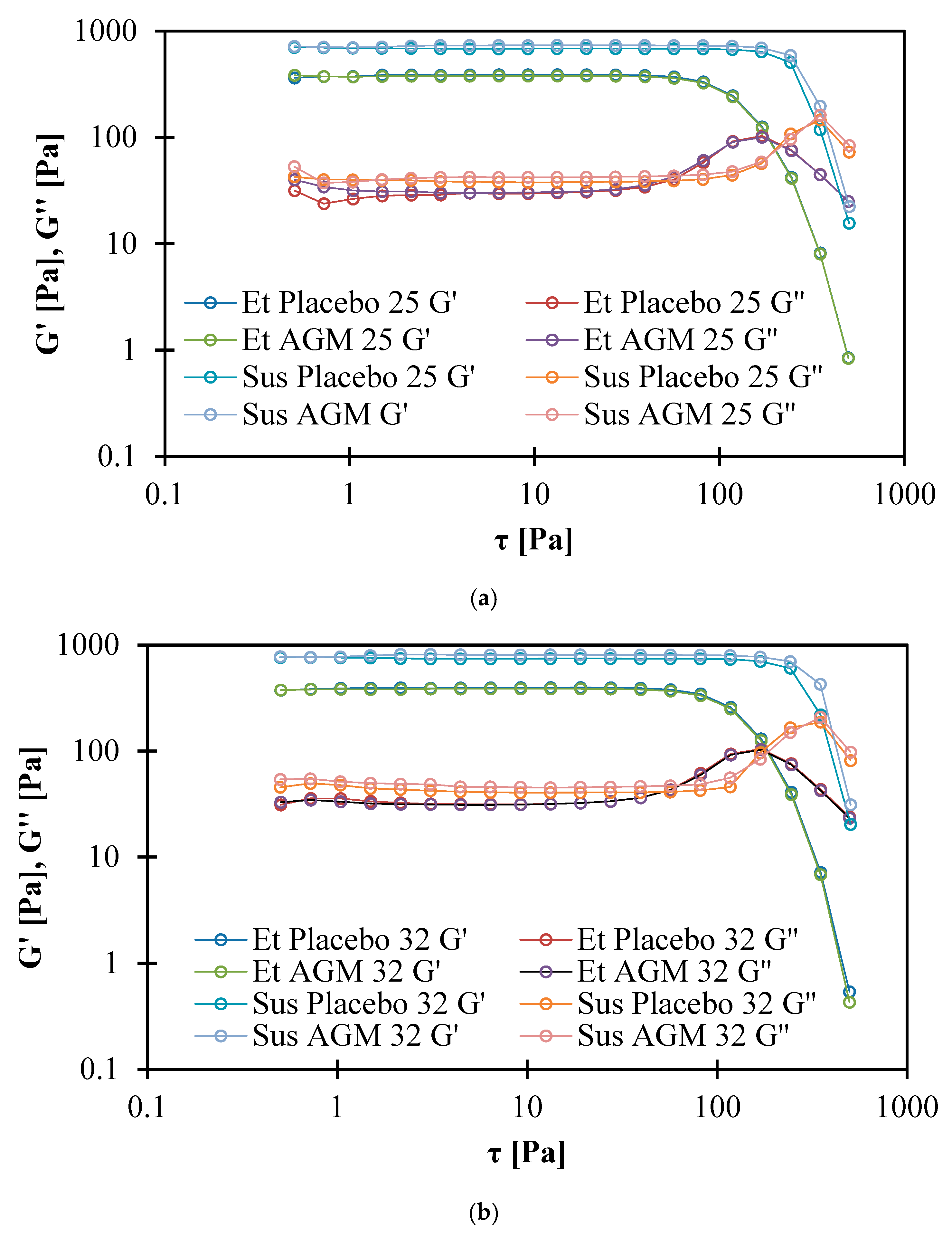
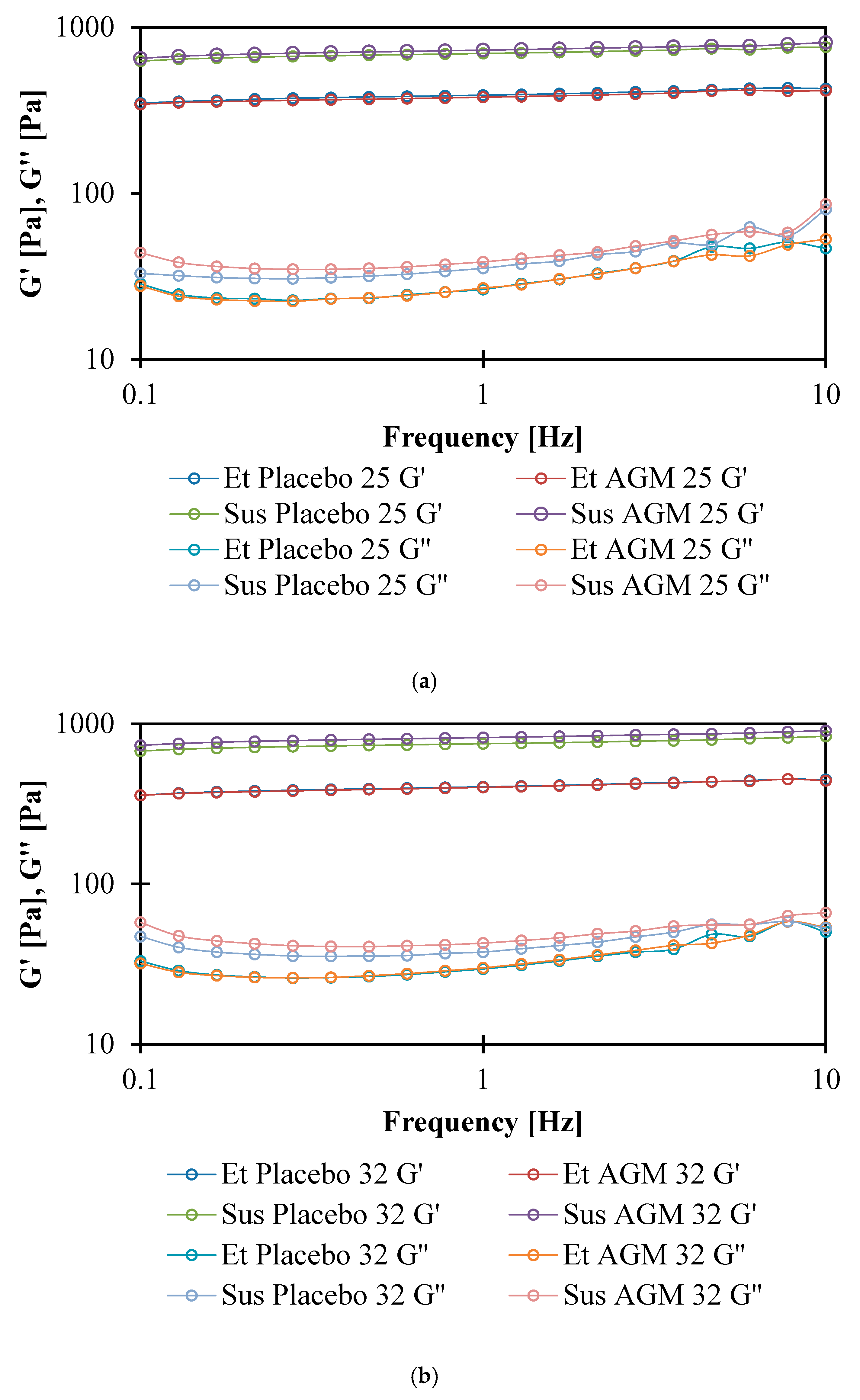
2.6. Rheological Studies
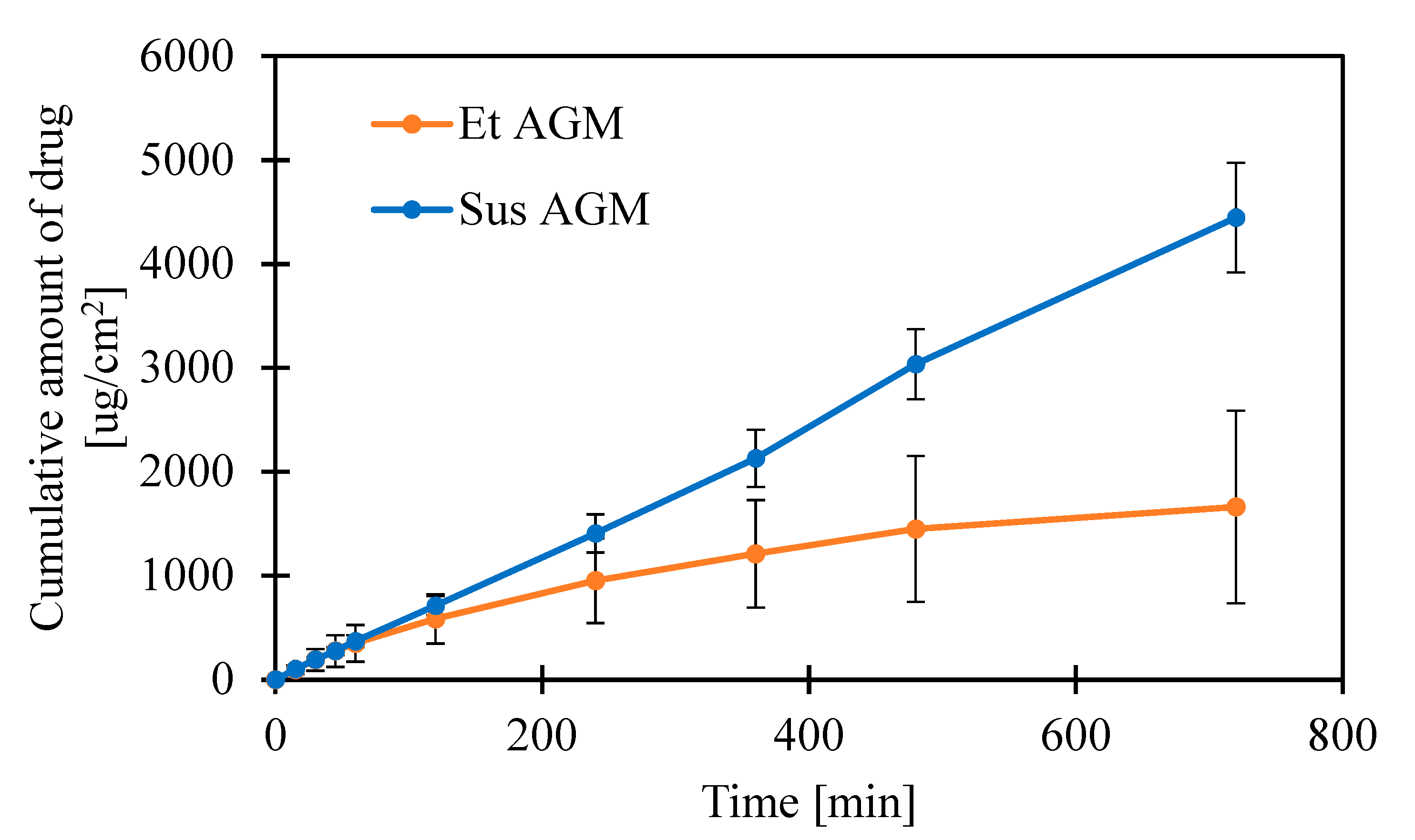
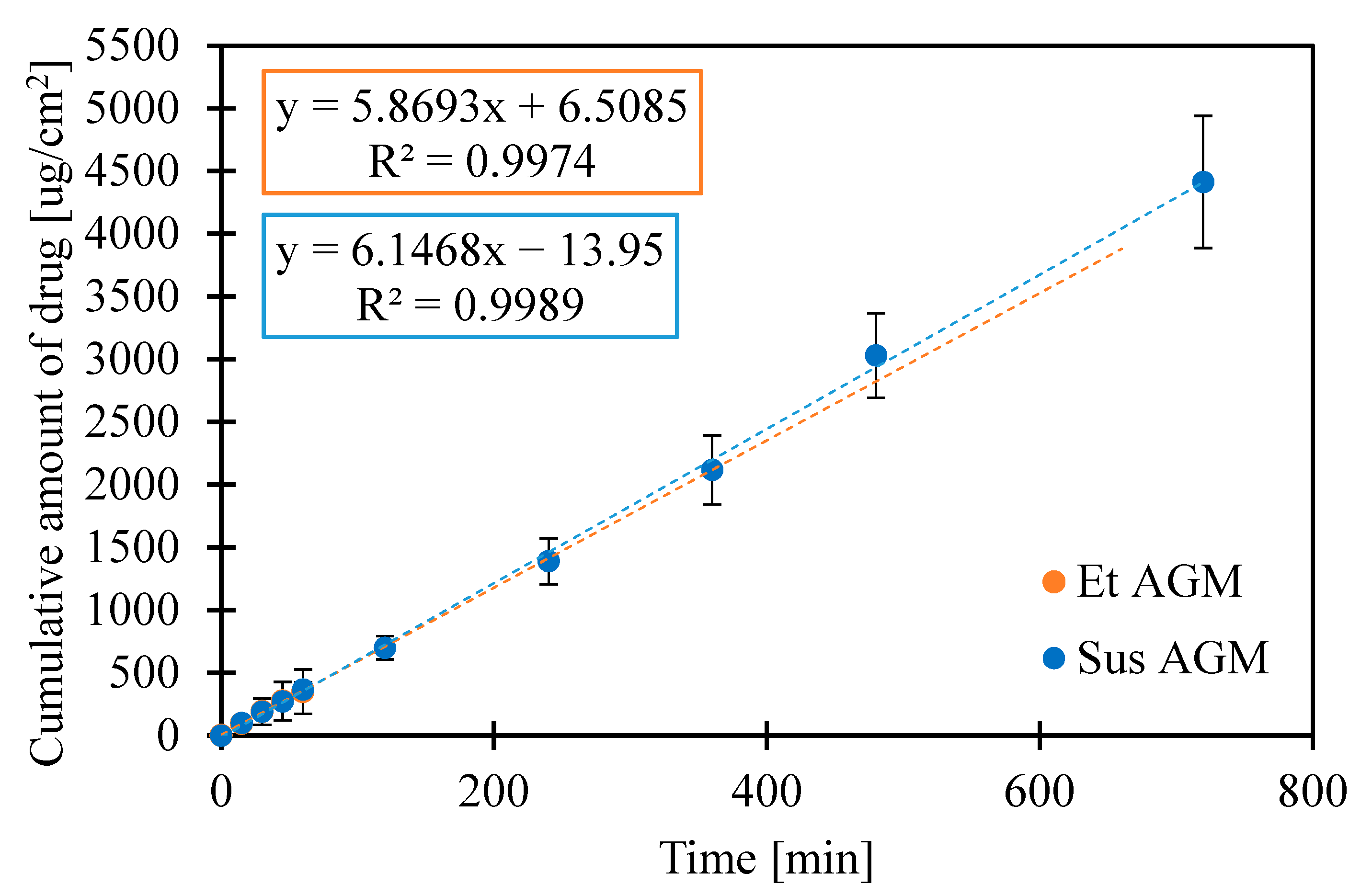
2.7. Release Studies
2.8. Ex Vivo Permeation Studies on Human Cadaver Skin
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Gels
3.3. Particle Size Measurement
3.4. Raman Analysis
3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
3.6. Loss of Volatile Components
3.7. Texture Profile Analysis and Spreadability
3.7.1. Texture Profile
3.7.2. Spreadability
3.8. Rheological Measurements
- Measurement of the shear stress at a shear rate of 0–300 [1/s].
- Measurement of deformation depending on the shear stress. Determination of the yield point by defining the cross point of two curves.
- Oscillatory measurement: Amplitude sweep. Determination of the cross point of storage modulus G′ and loss modulus G″ and sections of elastoviscosity at 1 Hz frequency.
- Oscillatory measurement: Frequency sweep. Measurement of storage modulus G′ and loss modulus G″ in a variable frequency of oscillation.
3.9. Release Studies
3.10. Ex Vivo Permeation Studies on Human Cadaver Skin
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konstantakopoulos, G.; Dimitrakopoulos, S.; Michalopoulou, P.G. The preclinical discovery and development of agomelatine for the treatment of depression. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, R.; Polito, A.N.; Marsala, G.; Ventriglio, A.; Di Salvatore, M.; De Stefano, M.I.; Valenzano, A.; Marinaccio, L.; Bellomo, A.; Cibelli, G.; et al. Agomelatine: A Potential Multitarget Compound for Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan, M.J. Agomelatine for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: Focus on its distinctive mechanism of action. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 12, 20451253221105128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, T.R. Agomelatine, melatonin and depressive disorder. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2013, 22, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pescosolido, N.; Gatto, V.; Stefanucci, A.; Rusciano, D. Oral treatment with the melatonin agonist agomelatine lowers the intraocular pressure of glaucoma patients. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2015, 35, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B. Focus on agomelatine. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2011, 27, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Vermeulen, A.; Colin, P.; Cheng, Z. A semiphysiological population pharmacokinetic model of agomelatine and its metabolites in Chinese healthy volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajapati, J.B.; Verma, S.D.; Patel, A.A. Oral bioavailability enhancement of agomelatine by loading into nanostructured lipid carriers: Peyer’s patch targeting approach. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, P.; Vanza, J.; Pandya, N.; Tandel, H. Formulation of Polymeric Nanoparticles of Antidepressant Drug for Intranasal Delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2019, 10, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukr, M.H.; Farid, O.A.A. Brain targeting of agomelatine egg lecithin based chitosan coated nanoemulsion. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Pu, C.; Wang, Q.; Tan, X.; Gou, J.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, T.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X. Physicochemical Characterization and Pharmacokinetics of Agomelatine-Loaded PLGA Microspheres for Intramuscular Injection. Pharm. Res. 2018, 36, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, M.; Elsayed, I.; Aboelwafa, A.A.; Elshafeey, A.H. Transdermal agomelatine microemulsion gel: Pyramidal screening, statistical optimization and in vivo bioavailability. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfik, M.A.; Tadros, M.I.; Mohamed, M.I.; El-Helaly, S.N. Low-Frequency versus High-Frequency Ultrasound-Mediated Transdermal Delivery of Agomelatine-Loaded Invasomes: Development, Optimization and in-vivo Pharmacokinetic Assessment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, ume 15, 8893–8910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, M.; Bali, N.; Rathod, S.; Karemore, M.; Salve, P. Effect of binary combinations of solvent systems on permeability profiling of pure agomelatine across rat skin: A comparative study with statistically optimized polymeric nanoparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 826–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Mahmood, S.; Ansari, M.D.; Gull, A.; Sharma, N.; Sultana, Y. Nanostructured lipid carrier to overcome stratum corneum barrier for the delivery of agomelatine in rat brain; formula optimization, characterization and brain distribution study. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 121006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.; Elsayed, I.; Aboelwafa, A.A.; Elshafeey, A.H. A novel concept of overcoming the skin barrier using augmented liquid nanocrystals: Box-Behnken optimization, ex vivo and in vivo evaluation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemr, A.A.; El-Mahrouk, G.M.; Badie, H.A. Hyaluronic acid-enriched bilosomes: An approach to enhance ocular delivery of agomelatine via D-optimal design: Formulation, in vitro characterization, and in vivo pharmacodynamic evaluation in rabbits. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 2343–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadon, D.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Courtenay, A.J.; Donnelly, R.F. Enhancement strategies for transdermal drug delivery systems: Current trends and applications. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 758–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.; Yang, F.; Qian, Z. Microneedles-Based Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghule, T.; Singhvi, G.; Dubey, S.K.; Pandey, M.M.; Gupta, G.; Singh, M.; Dua, K. Microneedles: A smart approach and increasing potential for transdermal drug delivery system. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 109, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarbox, T.N.; Watts, A.B.; Cui, Z.; Williams, R.O. An update on coating/manufacturing techniques of microneedles. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 8, 1828–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patzelt, A.; Knorr, F.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Hair follicles, their disorders and their opportunities. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2008, 5, e173–e181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moribe, K.; Shibata, M.; Furuishi, T.; Higashi, K.; Tomono, K.; Yamamoto, K. Effect of Particle Size on Skin Permeation and Retention of Piroxicam in Aqueous Suspension. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1096–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bułaś, L.; Szulc-Musioł, B.; Siemiradzka, W.; Dolińska, B. Influence of Technological Parameters on the Size of Benzocaine Particles in Ointments Formulated on Selected Bases. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M.E. Drug crystallization—Implications for topical and transdermal delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Mourik, T.; Bühl, M.; Gaigeot, M.-P. Density functional theory across chemistry, physics and biology. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2014, 372, 20120488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barmpalexis, P.; Grypioti, A.; Vardaka, E.; Karagianni, A.; Kachrimanis, K. Development of a Novel Amorphous Agomelatine Formulation With Improved Storage Stability and Enhanced Bioavailability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, A.P.; Radom, L. Harmonic Vibrational Frequencies: An Evaluation of Hartree—Fock, Møller—Plesset, Quadratic Configuration Interaction, Density Functional Theory, and Semiempirical Scale Factors. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 16502–16513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdyr, M. Fityk: A general-purpose peak fitting program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2010, 43, 1126–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelovici, E.; Frost, R.L.; Kloprogge, T. Cryogenic Raman Spectroscopy of Glycerol. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2000, 31, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrou, A.N.; McGilvreay, T.M.; Burgos, G. Steady Herschel–Bulkley fluid flow in three-dimensional expansions. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2001, 100, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saasen, A.; Ytrehus, J.D. Viscosity Models for Drilling Fluids—Herschel-Bulkley Parameters and Their Use. Energies 2020, 13, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.; Kalyon, D.M. Parallel-Disk Viscometry of a Viscoplastic Hydrogel: Yield Stress and Other Parameters of Shear Viscosity and Wall Slip. Gels 2022, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishinari, K. Some Thoughts on The Definition of a Gel. In Gels: Structures, Properties, and Functions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 87–94. ISBN 978-3-642-01070-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Gull, A.; Alam, M.; Aqil, M.; Sultana, Y. Ultrasonically tailored, chemically engineered and “QbD” enabled fabrication of agomelatine nanoemulsion; optimization, characterization, ex-vivo permeation and stability study. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyja, R.; Jankowski, A. The effect of additives on release and in vitro skin retention of flavonoids from emulsion and gel semisolid formulations. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrole, R.S.; Gill, H.S. Microneedle Coating Methods: A Review with a Perspective. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haj-Ahmad, R.; Khan, H.; Arshad, M.S.; Rasekh, M.; Hussain, A.; Walsh, S.; Li, X.; Chang, M.-W.; Ahmad, Z. Microneedle Coating Techniques for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-O.; Knutson, G.P.; David, M.M. Method of Contact Coating a Microneedle Array. U.S. Patent 8057842B2, 15 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Trautman, J.C.; Wright, C.T.; Cormier, M.J.N. Method and Apparatus for Coating Skin Piercing Microprojections. U.S. Patent 6855372B2, 15 February 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.L.; Zhang, X.P.; Liu, J.L.; Shen, C.B.; Cui, Y.; Guo, X.D. Optimization of dip-coating methods for the fabrication of coated microneedles for drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 101464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancu, A.I.; Oprea, E.; Dițu, L.M.; Ficai, A.; Ilie, C.-I.; Badea, I.A.; Buleandra, M.; Brîncoveanu, O.; Ghica, M.V.; Avram, I.; et al. Development, Optimization, and Evaluation of New Gel Formulations with Cyclodextrin Complexes and Volatile Oils with Antimicrobial Activity. Gels 2024, 10, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giuseppe, E.; Corbi, F.; Funiciello, F.; Massmeyer, A.; Santimano, T.; Rosenau, M.; Davaille, A. Characterization of Carbopol® hydrogel rheology for experimental tectonics and geodynamics. Tectonophysics 2015, 642, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neutralizing Carbopol®* and PemulenTM* Polymers in Aqueous and Hydroalcoholic Systems 2009. Available online: https://www.lubrizol.com/-/media/Lubrizol/Health/TDS/TDS-237_Neutralizing_Carbopol_Pemulen_in_Aqueous_Hydroalcoholic_Systems--PH.pdf (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Gupta, R.; Badhe, Y.; Rai, B.; Mitragotri, S. Molecular mechanism of the skin permeation enhancing effect of ethanol: A molecular dynamics study. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 12234–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, C. Recent Advances in the Application of Characterization Techniques for Studying Physical Stability of Amorphous Pharmaceutical Solids. Crystals 2021, 11, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wu, H.; Yi, D.; Liu, W.; Yao, X.; Li, T.; Ren, B. Analysis of agomelatine (Form II) dissolution behavior in different mono-solvents: Solubility, solvation thermodynamics as well as inter-molecular interactions. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2023, 190, 107209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, J.-M.; Geng, N.; Lu, T.-B. Improving the Solubility of Agomelatine via Cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 2226–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhao, C. Investigation of physicochemical properties and in-vitro in-vivo evaluation of agomelatine polymorphs. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 8, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Holaň, J.; Skořepová, E.; Heraud, L.; Baltes, D.; Rohlíček, J.; Dammer, O.; Ridvan, L.; Štěpánek, F. Polymorphic Crystallization and Structural Aspects of Agomelatine Metastable Form X Prepared by Combined Antisolvent/Cooling Process. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2015, 20, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Coating Formulations for Microneedles. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.S.; Lawlor, M.S.; Woolfson, A.D. Examination of the flow rheological and textural properties of polymer gels composed of poly(methylvinylether-co-maleic anhydride) and poly(vinylpyrrolidone): Rheological and mathematical interpretation of textural parameters. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 2090–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevher, E.; Taha, M.A.; Orlu, M.; Araman, A. Evaluation of Mechanical and Mucoadhesive Properties of Clomiphene Citrate Gel Formulations Containing Carbomers and Their Thiolated Derivatives. Drug Deliv. 2008, 15, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvamme, B. Small Alcohols as Surfactants and Hydrate Promotors. Fluids 2021, 6, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Rodríguez-Hornedo, N.; Ciotti, S.; Ackermann, C. Rheological Characterization of Topical Carbomer Gels Neutralized to Different pH. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, M.F.; Diéguez, A.R.; Soriano, M.J. Rheological characterization of hydroalcoholic gels—15% ethanol—of Carbopol® Ultrez™ 10. Il Farm. 2001, 56, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walicka, A.; Falicki, J.; Iwanowska-Chomiak, B. Rheology of Drugs For Topical and Transdermal Delivery. Int. J. Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 24, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, K.; Koshiba, T.; Mori, N. Effects of Rheological Property of Coating Liquid and Withdrawal Velocity on Dip Coating Process in Manufacturing of Capsules. Nihon Reoroji Gakkaishi 2004, 32, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Horita, D.; Todo, H.; Sugibayashi, K. Effect of Ethanol Pretreatment on Skin Permeation of Drugs. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadach, B.; Nowak, A.; Długaszewska, J.; Kordyl, O.; Budnik, I.; Osmałek, T. Coated Microneedle System for Delivery of Clotrimazole in Deep-Skin Mycoses. Gels 2024, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, D.W.; Dahl, K.; Parikh, H. Determination of Particle Size and Microstructure in Topical Pharmaceuticals. In The Role of Microstructure in Topical Drug Product Development; Langley, N., Michniak-Kohn, B., Osborne, D.W., Eds.; AAPS Advances in the Pharmaceutical Sciences Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 36, pp. 89–106. ISBN 978-3-030-17354-8. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision A.02. 2016. Available online: https://gaussian.com/g09citation/ (accessed on 8 December 2024).
- Zheng, S.-L.; Chen, J.-M.; Zhang, W.-X.; Lu, T.-B. CCDC 835469: Experimental Crystal Structure Determination 2011. Available online: https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/Search?Compound=agomelatine&DatabaseToSearch=Published (accessed on 8 December 2024).
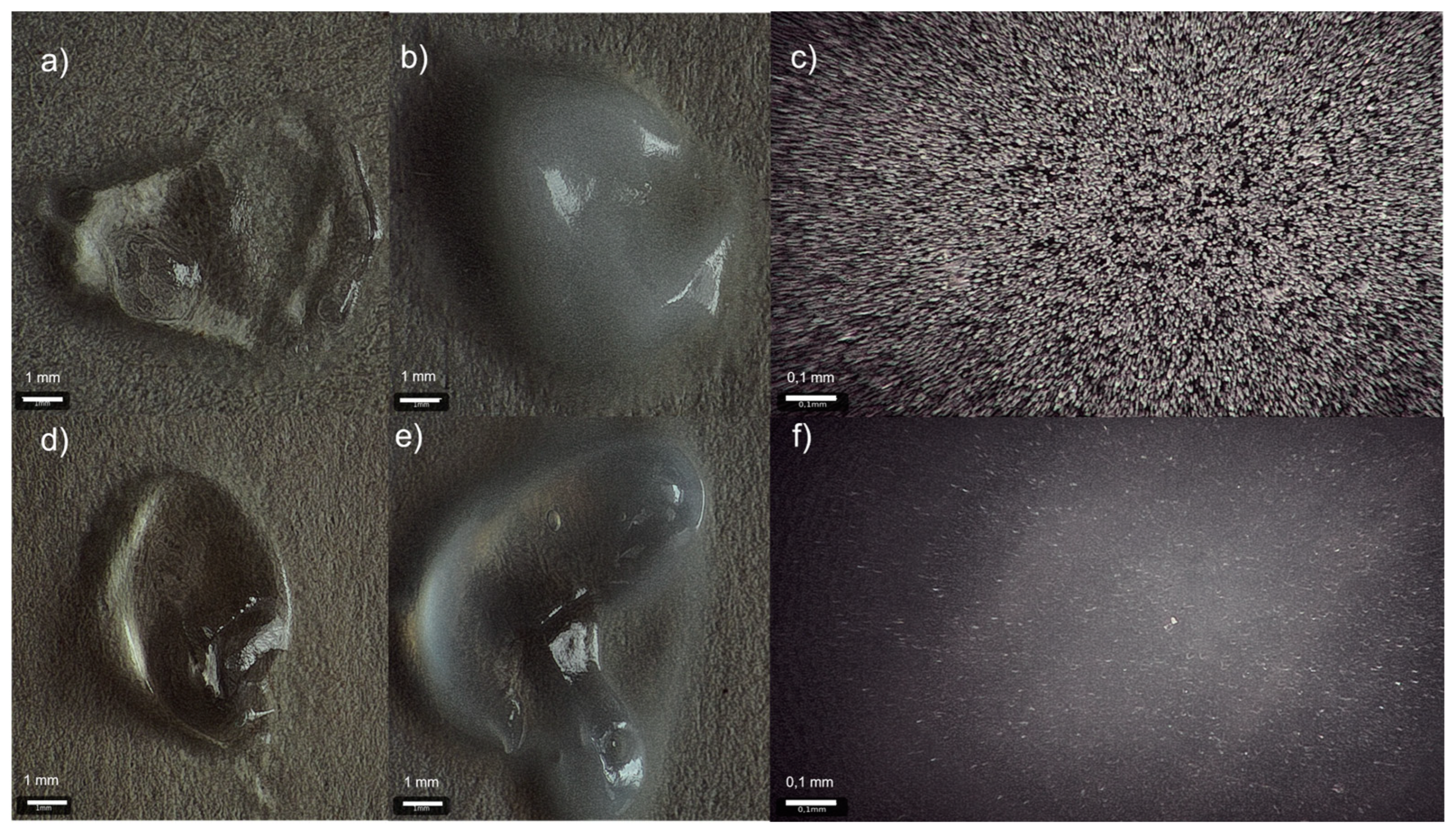
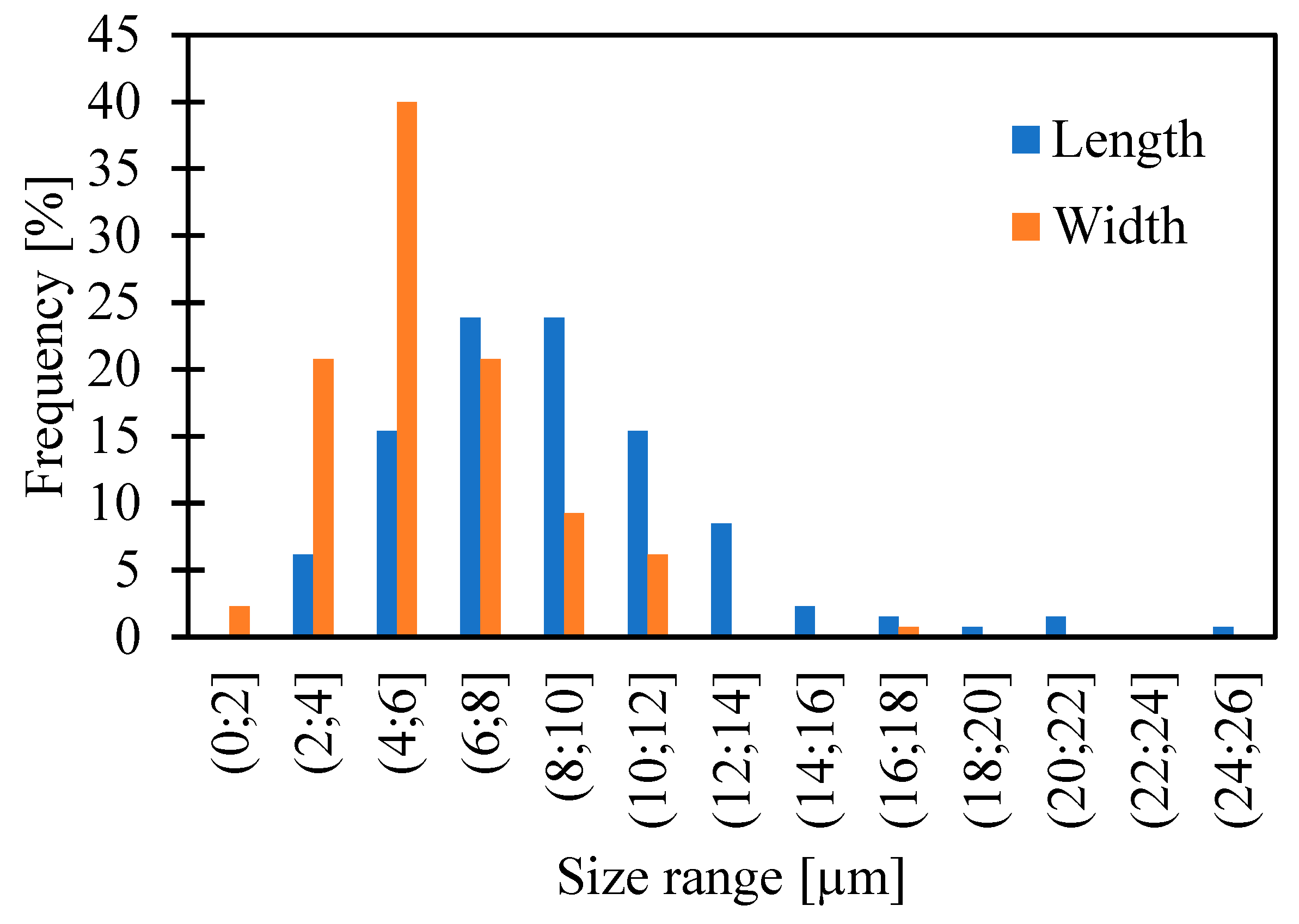
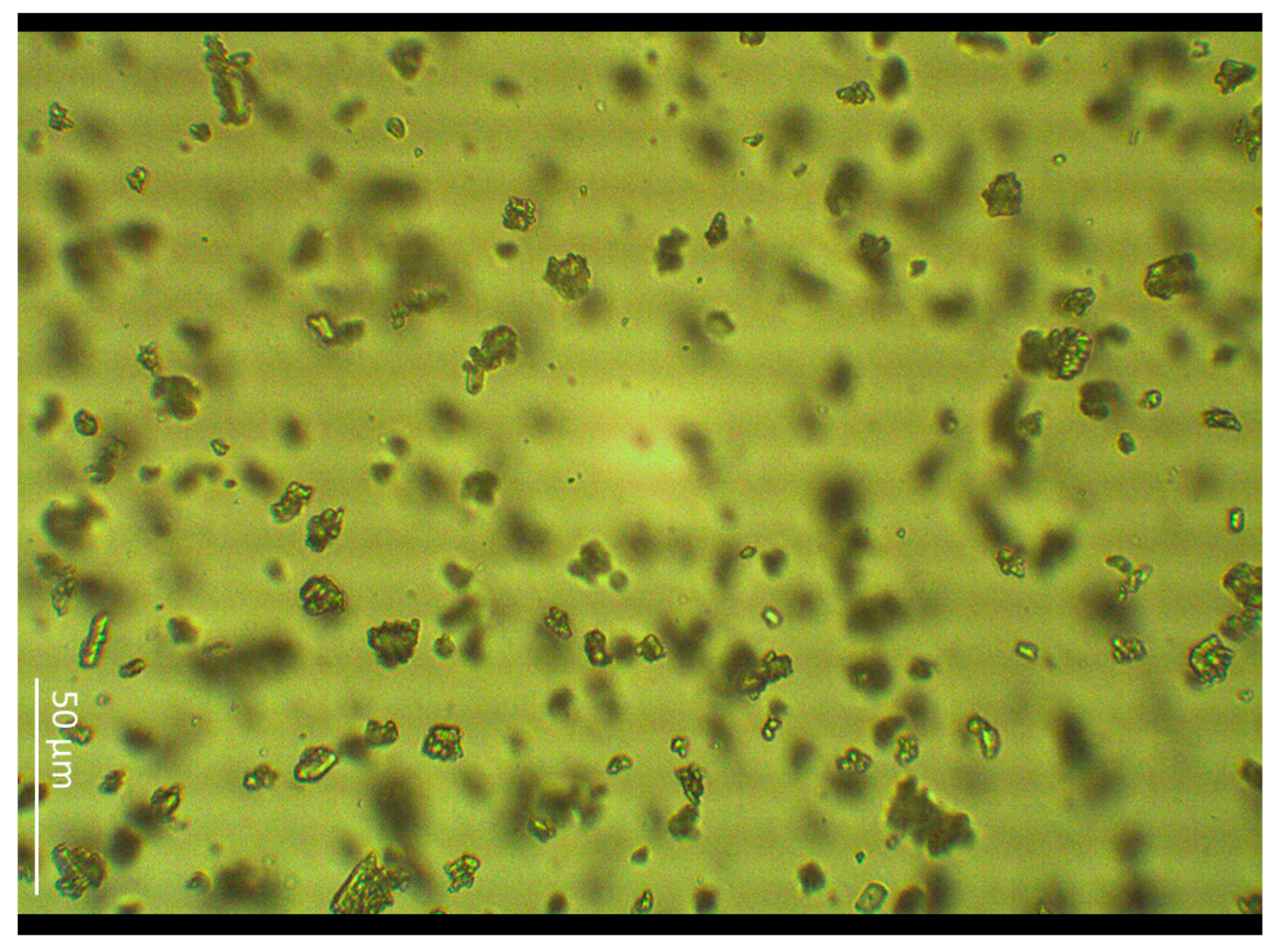

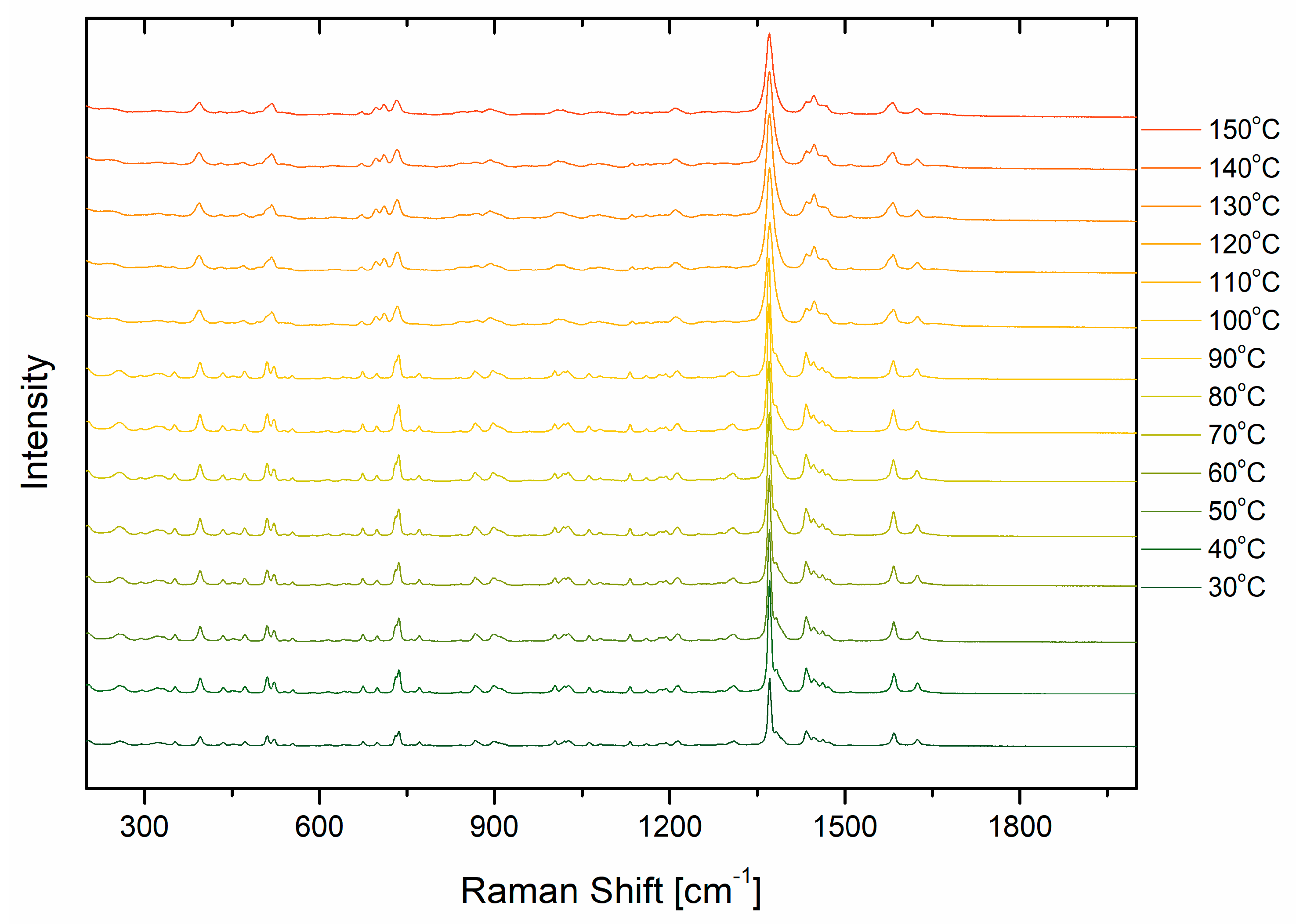



| Values [µm] | Length | Width |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 2.5 | 1.6 |
| Quartile 1 (Q1) | 6.3 | 4.1 |
| Median | 8.3 | 5.4 |
| Quartile 3 (Q3) | 10.6 | 6.9 |
| Maximum | 24.2 | 17.9 |
| Theory with Calculation Factor/cm−1 [28] | Experimental Data/cm−1 | Assignment |
|---|---|---|
| 315 | deformation of all molecules | |
|
380 383 | 395 | NH b, CH3 ab |
| 420 | 435 | CH b oop in benzene ring |
| 430 | 451 | deformation of all molecules |
| 454 | 472 | deformation of methoxy and naphthalene group |
| 498 | 509 | deformation of methoxy and naphthalene group |
| 510 | 522 | deformation of methoxy and naphthalene group |
| 540 | 555 | deformation of all molecules |
| 658 | 674 | b oop of naphthalene group |
| 685 | 698 | deformation of methoxy and naphthalene group oop, CH2-CH2 t |
| 714 | deformation of methoxy and naphthalene group ip | |
| 733 | 735 | CH b oop in benzene ring, t CH2 r |
| 743 | 737 | CH ab oop in naphthalene group, CH2 r |
| 768 | CH ab oop in naphthalene group, CH2 r | |
| 819 | CH syb oop in naphthalene group | |
| 845 | 868 | b of naphthalene group, b of acetamide group |
| 886 | 898 | CH b oop in benzene ring |
| 959 | 1003 | CH3 w in acetamide group, NH bending |
| 983 | 1018 | CC s, CH2 t |
| 993 | 1028 | CCs in ethylene group |
|
1032 1047 | 1060 |
CH2-CH2 t CO s in methoxy group, benzene ring r |
|
1062 1074 | 1080 |
CN s, CH3 sb, CH b in benzene ring CH b ip in benzene ring, CH2-CH2 t |
| 1120 | 1130 | CH b ip in benzene ring |
| 1145 | 1182 | CH b ip in benzene ring |
| 1164 | 1187 | CH3 sb, CH2 t, CH b ip in benzene ring |
| 1174 | 1193 | CH2 t, CH3 ab |
|
1196 1202 | 1213 |
CC s, CH3 sb, CH b ip in benzene ring, CH3-O-C b, CH b ip in benzene ring, CH2 t, NH b ip |
| 1226 | 1250 | NH b ip, CH b in CH2 |
| 1235 | 1260 | CH2 w, CH b ip, CH2 w in CH3, CH b in benzene ring |
| 1247 | 1268 | CO s in methoxy group, CH b ip |
| 1266 |
1283 1288 | CH2 w |
| 1289 |
1304 1311 | CH2 t |
|
1349 1353 | 1374 | CH2 w, CH3 symb (umbrella) C=C s between benzene rings, CH2 twisting, CH b in benzene ring |
| 1356 |
C=C as in benzene ring, CH2 twisting | |
| 1374 | 1384 |
C=C as in benzene ring, CH2 t |
| 1420 | CH3 syb (umbrella), CH2 sc, CH r in benzene ring | |
|
1427 1428 1433 | 1434 |
CH2 sc, CH3 ab, CH2 sc, CH3 ab, CH2 sc, CH3 ab, CH b in benzene ring |
|
1442 1444 | 1446 |
CH3 ab, NH b ip CH3 ab, HCCH r in benzene ring |
| 1455 | 1462 | CH3 ab, CH r in benzene ring |
|
1460 1462 | 1472 | CH2 sc, CH3 ab |
| 1486 | NH b ip, CH2 t, CH3 ab | |
| 1571 | 1584 | C=C sys in benzene ring |
| 1592 | C=C s in benzene ring, CH r in benzene ring | |
| 1615 | 1625 | C=C s in benzene ring, CH b ip in benzene ring |
| 1711 | C=O s, CH2 sc |
| Raman Shift /cm−1 | Integral Intensity | Intensity at Point | FWHM /cm−1 | Raman Shift /cm−1 | Integral Intensity | Intensity at Point | FWHM /cm−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 °C | 110 °C | ||||||
| 737 | 39,700 | 6996 | 5.33 | 733 | 99,254 | 8226 | 11.33 |
| 1213 | 20,615 | 2028 | 9.55 | 1210 | 35,081 | 2845 | 11.58 |
| 1371 | 255,992 | 33,876 | 7.11 | 1371 | 779,001 | 50,547 | 14.48 |
| 1383 | 105,843 | 5682 | 17.49 | 1384 | 80,204 | 5914 | 12.74 |
| 1584 | 56,494 | 6106 | 8.69 | 1583 | 80,519 | 6959 | 10.86 |
| Et Placebo 25 | Et AGM 25 | Sus Placebo 25 | Sus AGM 25 | Et Placebo 32 | Et AGM 32 | Sus Placebo 32 | Sus AGM 32 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 48.56 ± 1.76 | 49.23 ± 1.68 | 98.40 ± 6.26 | 84.11 ± 1.80 | 49.90 ± 1.99 | 50.78 ± 4.11 | 127.67 ± 9.82 | 121.30 ± 2.54 |
| n | 0.4270 ± 0.0035 | 0.4242 ± 0.0040 | 0.3453 ± 0.0085 | 0.3701 ± 0.0049 | 0.4132 ± 0.0079 | 0.4105 ± 0.0095 | 0.3062 ± 0.0128 | 0.3166 ± 0.0039 |
| Et Placebo 25 | Et AGM 25 | Sus Placebo 25 | Sus AGM 25 | Et Placebo 32 | Et AGM 32 | Sus Placebo 32 | Sus AGM 32 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| τ0 [Pa] | 105.2 ± 2.7 | 106.2 ± 2.0 | 279.0 ± 5.9 | 238.6 ± 22.4 | 98.0 ± 6.8 | 100.6 ± 6.4 | 199.2 ± 10.6 | 175.0 ± 25.4 |
| Et Placebo 25 | Et AGM 25 | Sus Placebo 25 | Sus AGM 25 | Et Placebo 32 | Et AGM 32 | Sus Placebo 32 | Sus AGM 32 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| τ [Pa] for G′ = G″ | 189.5 ± 9.3 | 189.9 ± 4.8 | 334.4 ± 1.8 | 372.1 ± 16.0 | 190.8 ± 0.4 | 188.6 ± 0.9 | 369.6 ± 6.3 | 412.9 ± 6.2 |
| Slope [µg/cm2/h] | Linear Part Correlation Efficient R2 | Cumulative Amount of Drug Released in 720 min [µg/cm2] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Et AGM | 5.8693 | 0.9974 | 1661.74 ± 927.32 |
| Sus AGM | 6.1468 | 0.9989 | 4413.87 ± 527.52 |
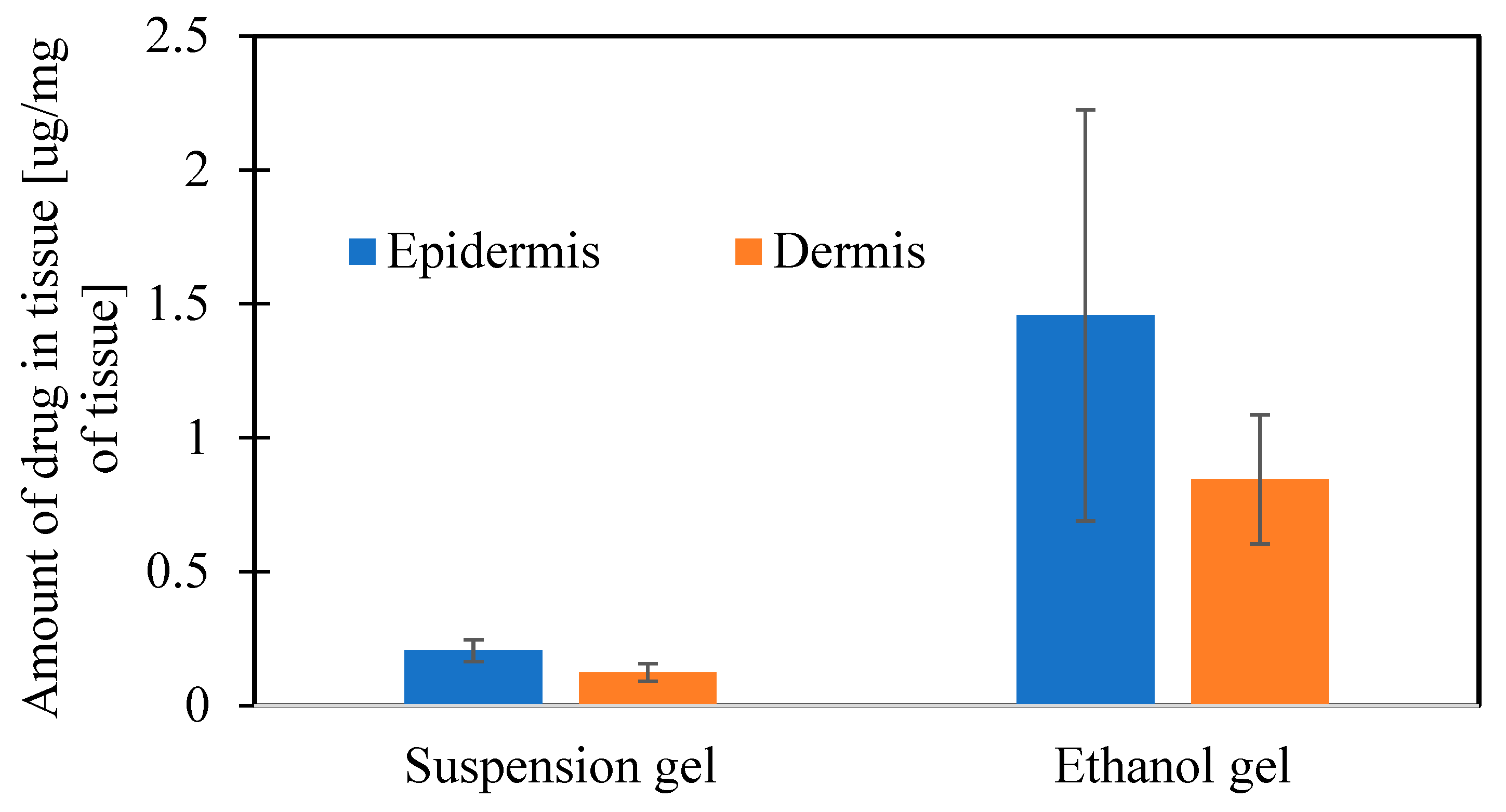
| Jss [µg/cm2/h] | Linear Correlation Efficient R2 | Lag Time [h] | Cumulative Amount of Drug Permeated in 102 h [µg/cm2] | Amount of Drug in Epidermis [µg/mg of Tissue] | Amount of Drug in Dermis [µg/mg of Tissue] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Et AGM | 30.386 | 0.9939 | 37.56 | 1955.23 ± 247.72 | 1.457 ± 0.768 | 0.845 ± 0.241 |
| Sus AGM | 2.7491 | 0.9997 | 2.48 | 271.90 ± 43.98 | 0.205 ± 0.041 | 0.123 ± 0.032 |
| Et AGM | Et Placebo | Sus AGM | Sus Placebo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agomelatine | 0.5 | - | 0.5 | - |
| Ethanol 96% v/v | 25.18 | 25.18 | - | - |
| Glycerol | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Carbopol® EZ-3 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Triisopropanolamine | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Water | 18.07 | 18.57 | 43.25 | 43.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wojtyłko, M.; Nowicka, A.B.; Froelich, A.; Szybowicz, M.; Banaszek, T.; Tomczak, D.; Kuczko, W.; Wichniarek, R.; Budnik, I.; Jadach, B.; et al. Characteristics of Hydrogels as a Coating for Microneedle Transdermal Delivery Systems with Agomelatine. Molecules 2025, 30, 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020322
Wojtyłko M, Nowicka AB, Froelich A, Szybowicz M, Banaszek T, Tomczak D, Kuczko W, Wichniarek R, Budnik I, Jadach B, et al. Characteristics of Hydrogels as a Coating for Microneedle Transdermal Delivery Systems with Agomelatine. Molecules. 2025; 30(2):322. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020322
Chicago/Turabian StyleWojtyłko, Monika, Ariadna B. Nowicka, Anna Froelich, Mirosław Szybowicz, Tobiasz Banaszek, Dorota Tomczak, Wiesław Kuczko, Radosław Wichniarek, Irena Budnik, Barbara Jadach, and et al. 2025. "Characteristics of Hydrogels as a Coating for Microneedle Transdermal Delivery Systems with Agomelatine" Molecules 30, no. 2: 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020322
APA StyleWojtyłko, M., Nowicka, A. B., Froelich, A., Szybowicz, M., Banaszek, T., Tomczak, D., Kuczko, W., Wichniarek, R., Budnik, I., Jadach, B., Kordyl, O., Białek, A., Krysztofiak, J., Osmałek, T., & Lamprou, D. A. (2025). Characteristics of Hydrogels as a Coating for Microneedle Transdermal Delivery Systems with Agomelatine. Molecules, 30(2), 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020322










