Ozone Saline Solution Polarizes Microglial Cells Towards an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype
Abstract
1. Introduction
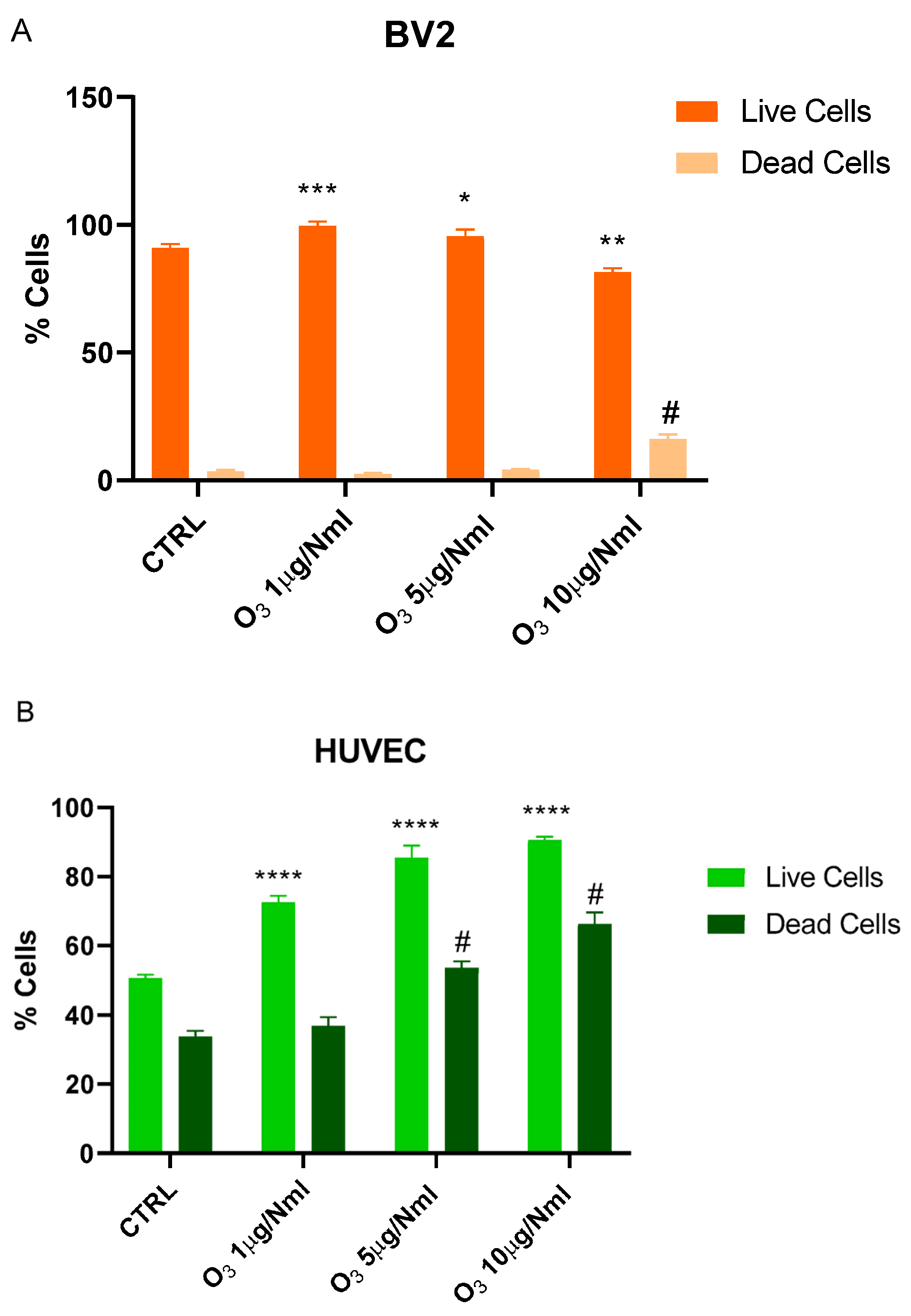
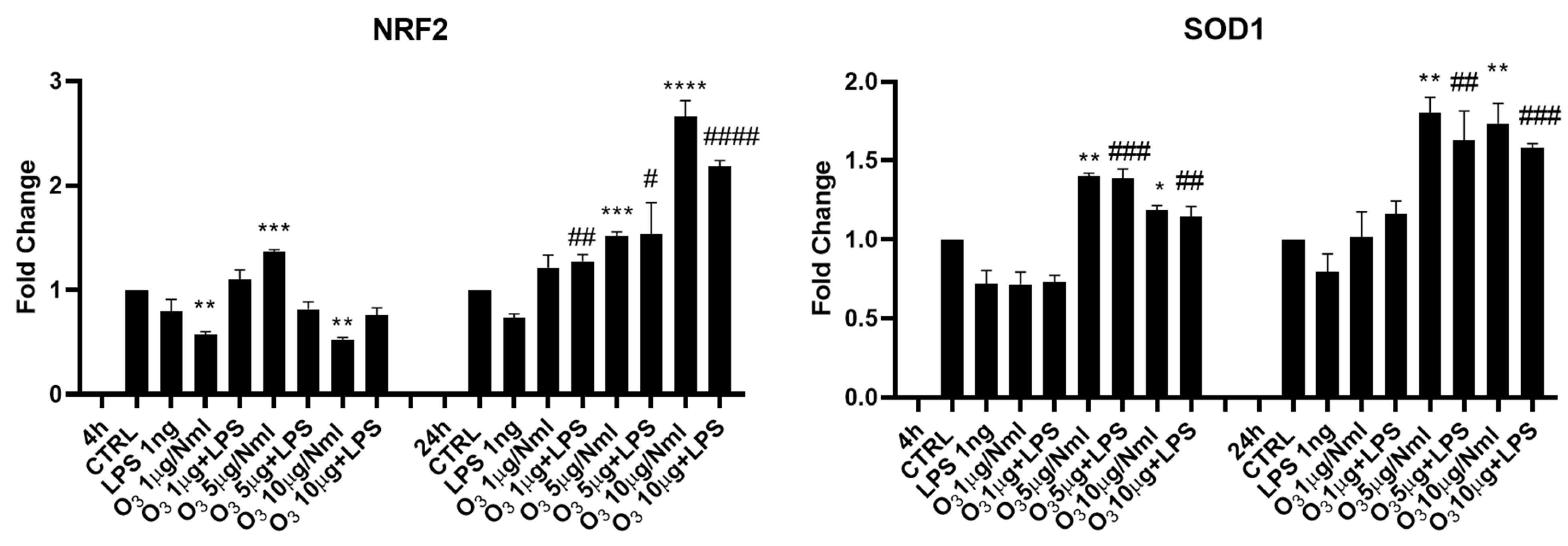
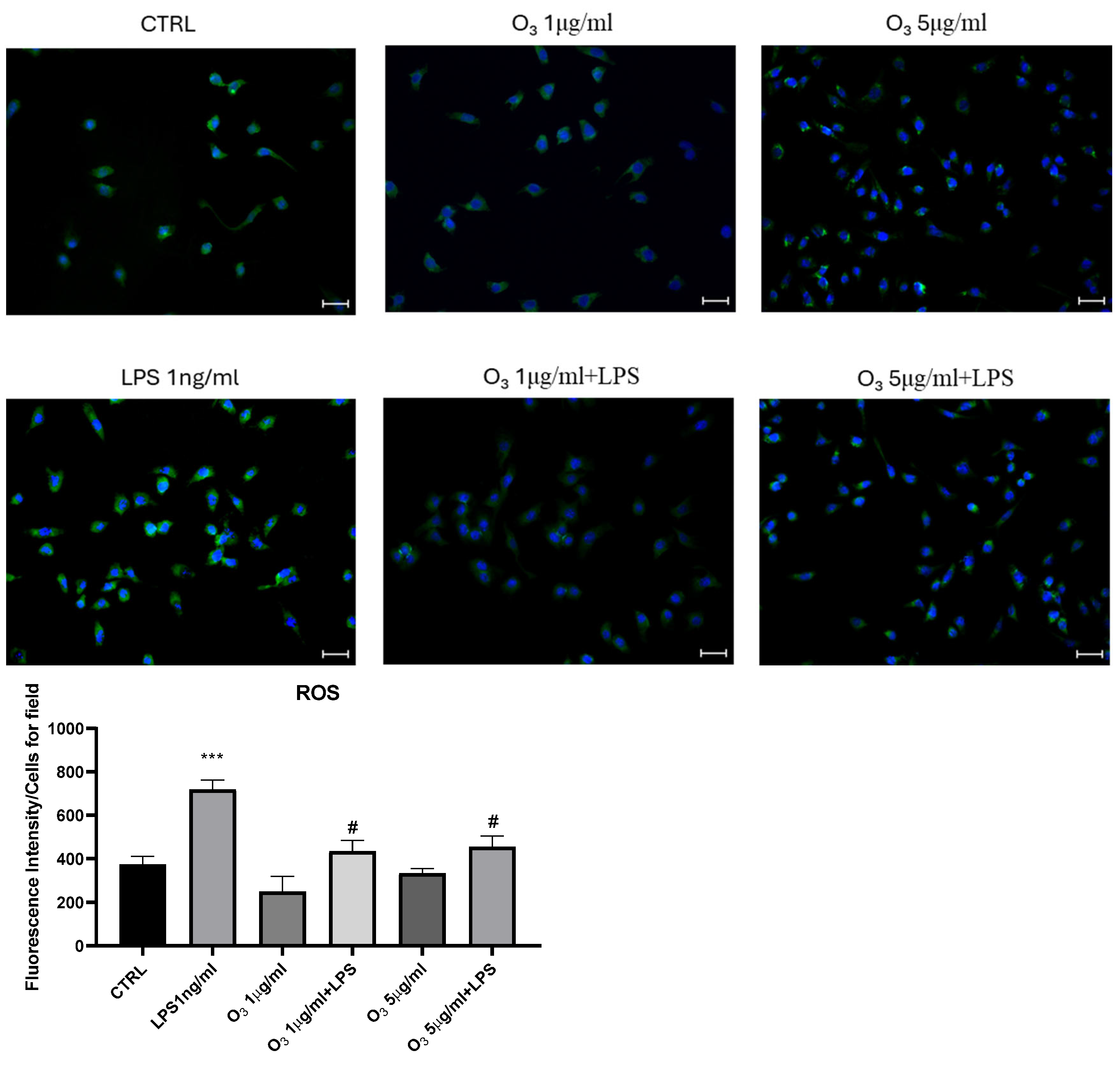
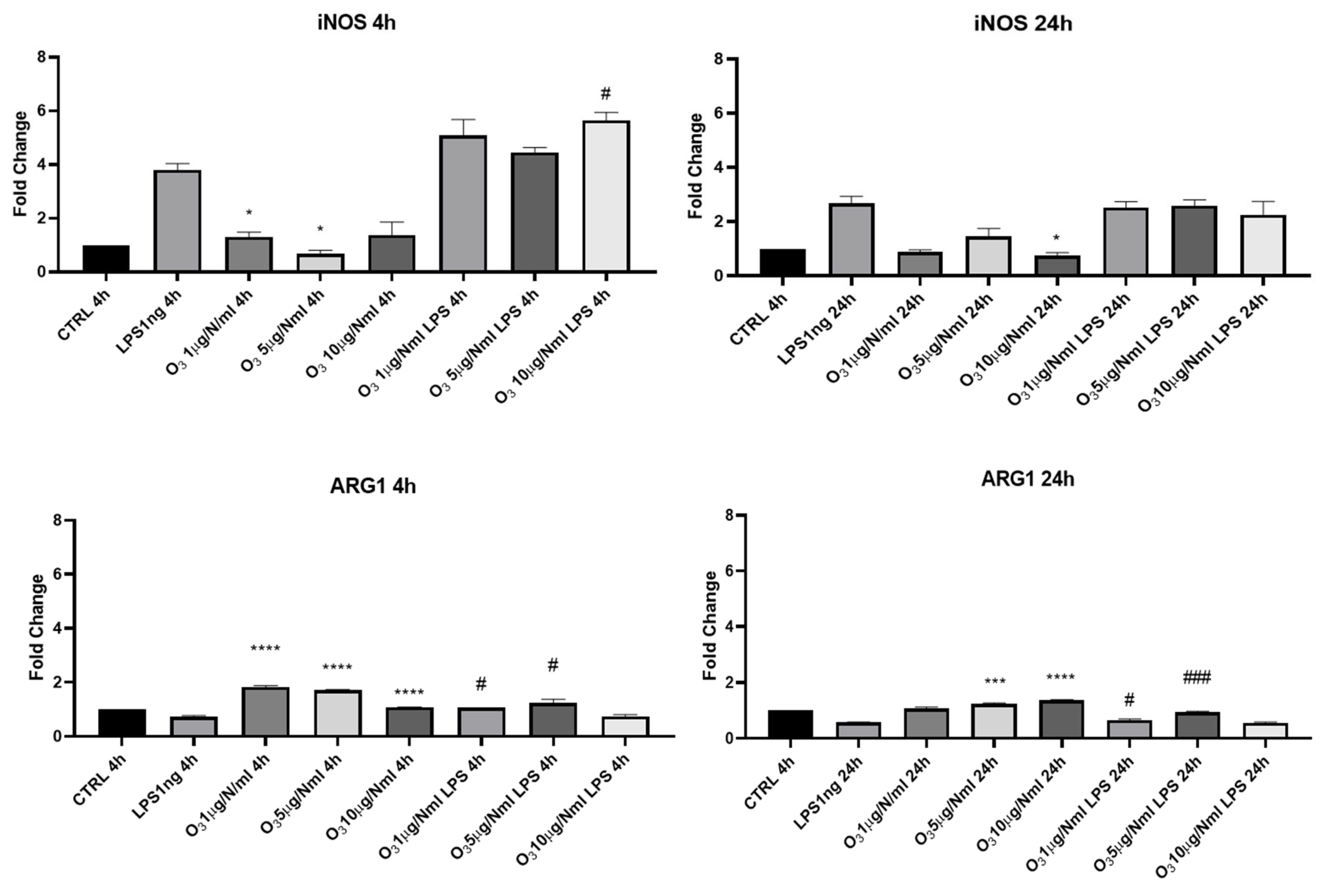
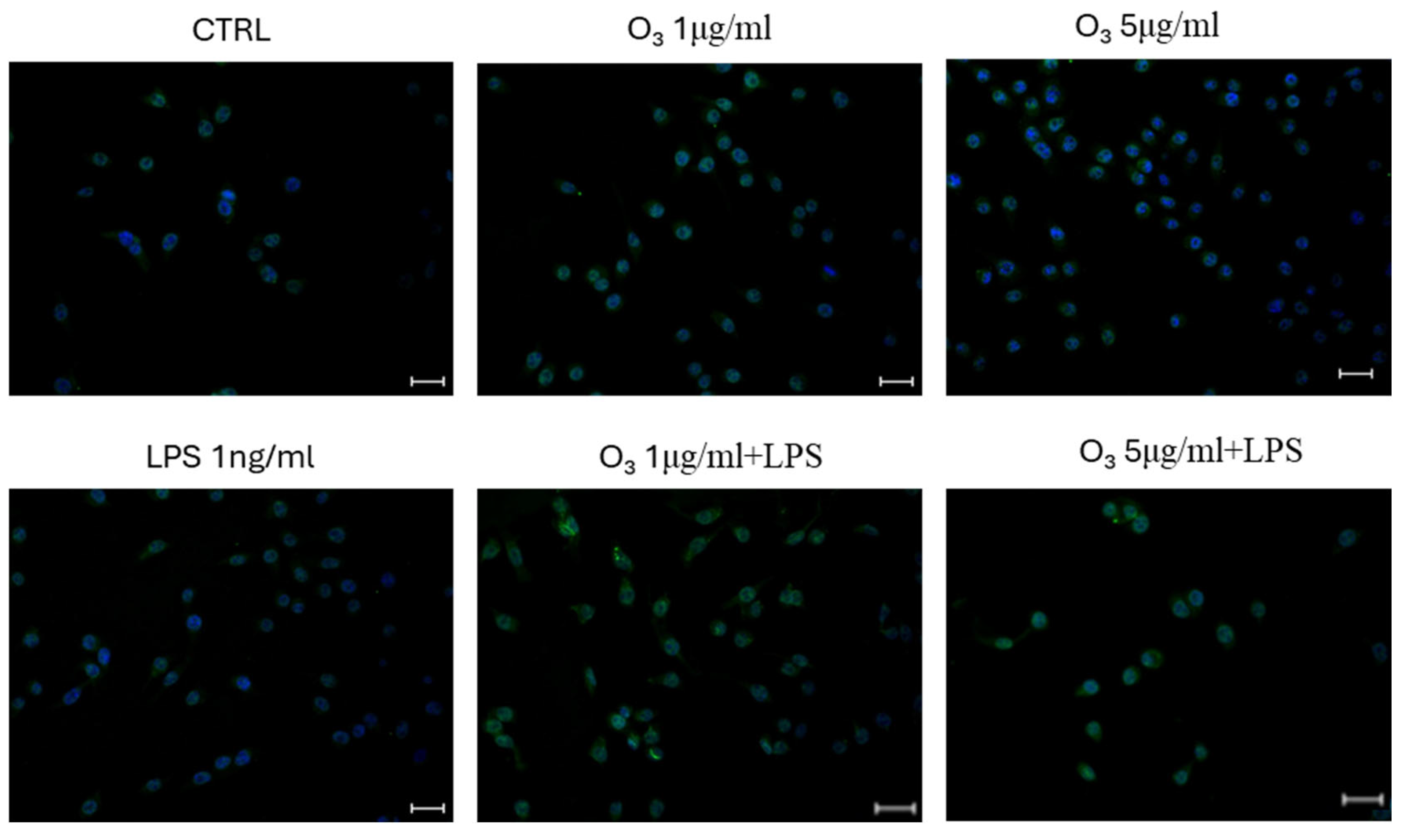
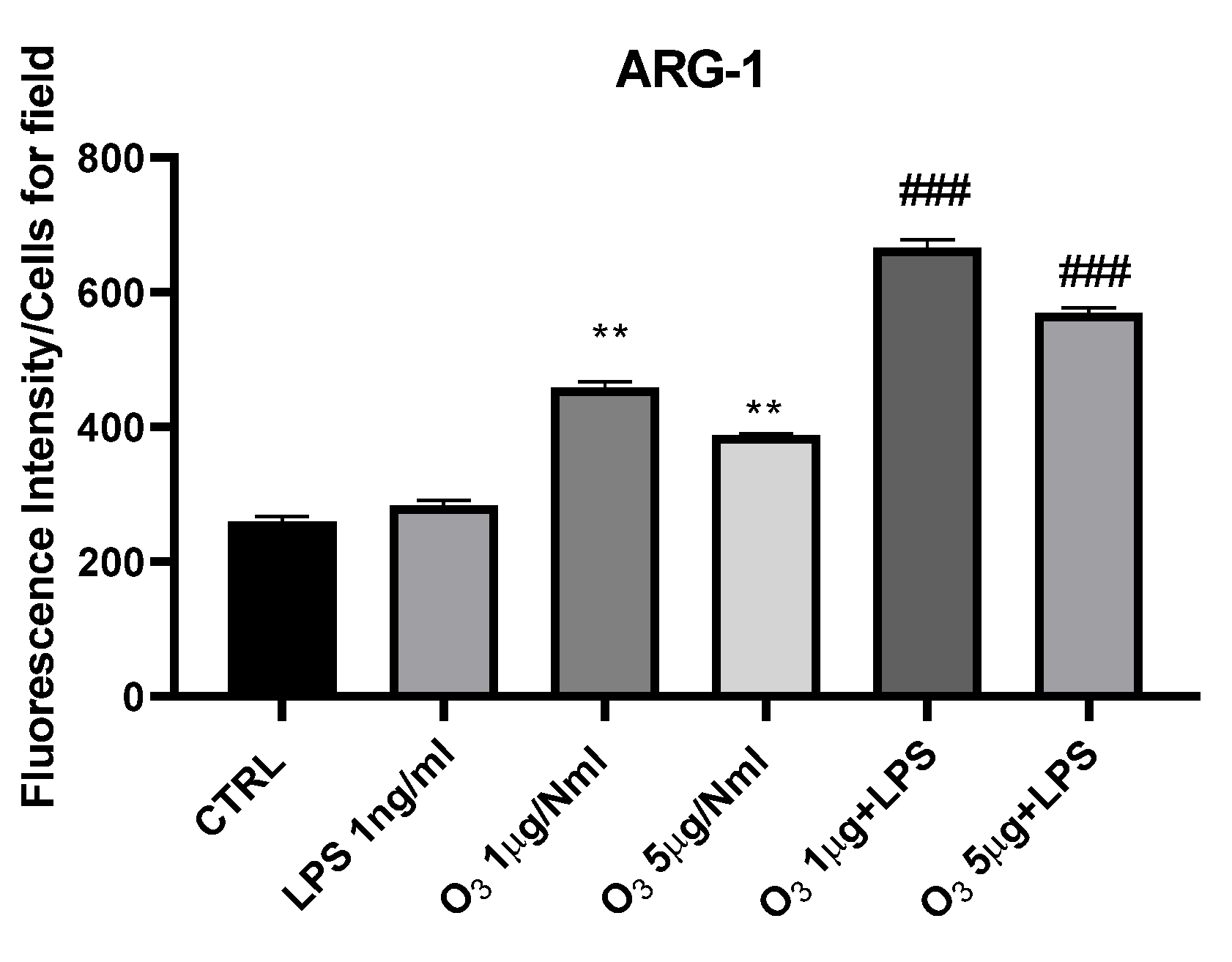
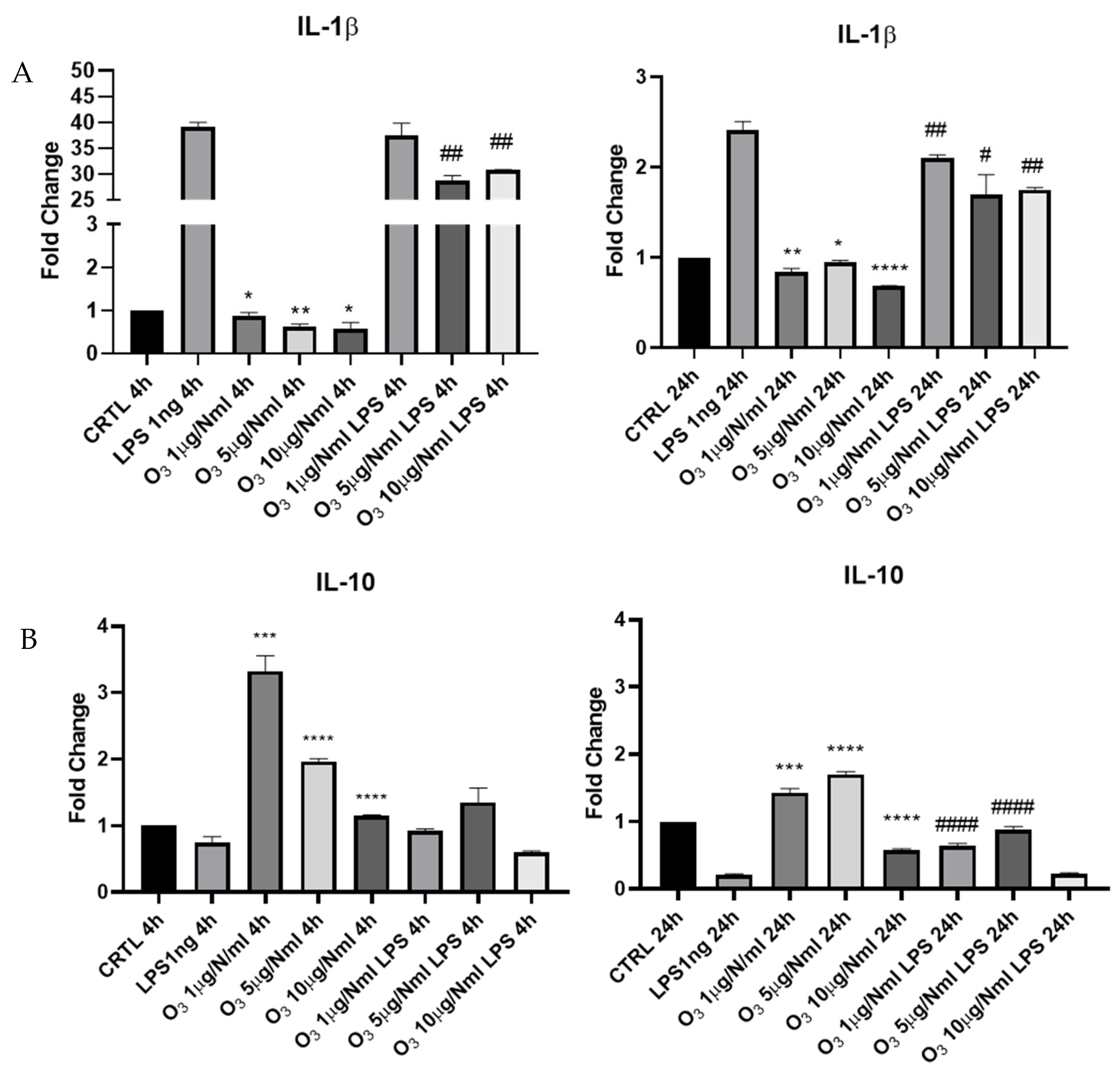
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.2. Trypan Blue Exclusion Assay
4.3. Real-Time Quantitative PRC Analysis
4.4. Immunofluorescence
4.5. Analysis Using the Cell-Permeable Probe 2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein Diacetate (H2DCFDA)
4.6. Detection of Reactive Chlorine Species (Hypochlorous Acid/Hypochlorite)
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Fang, Z. Ozone Pollution: A Major Health Hazard Worldwide. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stübinger, S.; Sader, R.; Filippi, A. The Use of Ozone in Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery: A Review. Quintessence Int. 2006, 37, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chirumbolo, S.; Tirelli, U.; Franzini, M.; Pandolfi, S.; Ricevuti, G.; Vaiano, F.; Valdenassi, L. Ozone in the Adjunct Medical Treatment. The Round Personality of a Molecule with Hormetic Properties. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2023, 42, 9603271231218926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, M.E.G.; Baeza-Noci, J.; Mendes Abdala, C.V.; Luvisotto, M.M.; Bertol, C.D.; Anzolin, A.P. The Role of Ozone Treatment as Integrative Medicine. An Evidence and Gap Map. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1112296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocci, V.; Di Paolo, N. Oxygen-Ozone Therapy in Medicine: An Update. Blood Purif. 2009, 28, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mauro, R.; Cantarella, G.; Bernardini, R.; Di Rosa, M.; Barbagallo, I.; Distefano, A.; Longhitano, L.; Vicario, N.; Nicolosi, D.; Lazzarino, G.; et al. The Biochemical and Pharmacological Properties of Ozone: The Smell of Protection in Acute and Chronic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viebahn-Haensler, R.; León Fernández, O.S. Ozone as Redox Bioregulator in Preventive Medicine: The Molecular and Pharmacological Basis of the Low-Dose Ozone Concept—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15747. [Google Scholar]
- Viebahn-Haensler, R.; León Fernández, O.S. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Its Oxidative Stress-Induced Pathologies and Redox Bioregulation through Low-Dose Medical Ozone: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masan, J.; Sramka, M.; Rabarova, D. The Possibilities of Using the Effects of Ozone Therapy in Neurology. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2021, 42, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz Tapia, A. ISCO3/MET/00/21 Ozonized Saline Solution (O3SS). ISCO3. 2025. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?q=https://isco3.org/officialdocs/&source=gmail-imap&ust=1759140325000000&usg=AOvVaw0ggJgEAstGR7guKAHarOq5 (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Cheng, H.; Lu, R.; Du, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhuang, Z. A Clinical Study on Ozone Autohemotherapy for the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1595568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Ding, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z. Ozone-Mediated Cerebral Protection: Unraveling the Mechanism through Ferroptosis and the NRF2/SLC7A11/GPX4 Signaling Pathway. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2024, 136, 102387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, S.-J.; Wan, S.-C.; Li, X.; Chen, G. Ozone: Complicated Effects in Central Nervous System Diseases. Med. Gas Res. 2025, 15, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi, S.; Qasim, M.T.; Krivenkova, M.V.; Zekiy, A.O.; Thangavelu, L.; Aravindhan, S.; Izadi, M.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Ghaebi, M.; Aslani, S.; et al. The Effects of Oxygen–Ozone Therapy on Regulatory T-cell Responses in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, L.; Di Benedetto, S.; Müller, V. The Dual Nature of Neuroinflammation in Networked Brain. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1659947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Sancheti, H.; Patil, I.; Cadenas, E. Energy Metabolism and Inflammation in Brain Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 100, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razumovskii, S.D.; Konstantinova, M.L.; Grinevich, T.V.; Korovina, G.V.; Zaitsev, V.Y. Mechanism and Kinetics of the Reaction of Ozone with Sodium Chloride in Aqueous Solutions. Kinet. Catal 2010, 51, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretiagin, S.P.; Struchkov, A.A.; Peretiagin, N.C.; Kulechina, N.B. Ozonization Method of Saline Solution. Russian Patent RU2289413. 10 February 2006. Available online: https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/b4/e7/c6/6a593e156466b9/RU2289413C2.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Ma, L.; Wen, S.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, D.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, S. Detection of Chlorite, Chlorate and Perchlorate in Ozonated Saline. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 2569–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, G.M. Practical Aspects in Ozone Therapy: Study of the Ozone Concentration in the Ozonized Saline Solution. Ozone Ther. Glob. J. 2020, 10, 56–68. [Google Scholar]
- De Vera, G.A.; Stalter, D.; Gernjak, W.; Weinberg, H.S.; Keller, J.; Farré, M.J. Towards Reducing DBP Formation Potential of Drinking Water by Favouring Direct Ozone over Hydroxyl Radical Reactions during Ozonation. Water Res. 2015, 87, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachay Agurto, J.U.; Huambo-Chávez, J.A.; Vásquez-Bravo, M.; Álvarez Ángeles, M.A.; Angulo Cornejo, H.H.; Garcia Terzo, L.; Martínez-Sánchez, G. Systemic Ozone Application and Its Impact on the Mobilization of CD34+ Cells. Preliminary Study. G. Ital. Ozono Ter. House Organ Nuova FIO 2024, 18, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Malatesta, M.; Tabaracci, G.; Pellicciari, C. Low-Dose Ozone as a Eustress Inducer: Experimental Evidence of the Molecular Mechanisms Accounting for Its Therapeutic Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricarico, G.; Travagli, V. The Relationship between Ozone and Human Blood in the Course of a Well-Controlled, Mild, and Transitory Oxidative Eustress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.Y.; Song, K.S.; Park, G.H.; Chang, S.H.; Kim, H.W.; Park, J.H.; Jin, H.; Eu, K.J.; Cho, H.S.; Kang, G.; et al. B6C3F1 Mice Exposed to Ozone with 4-(N-Methyl-N-Nitrosamino)-1-(3-Pyridyl)-1-Butanone and/or Dibutyl Phthalate Showed Toxicities through Alterations of NF-kappaB, AP-1, Nrf2, and Osteopontin. J. Vet. Sci. 2004, 5, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.-Y.; Gladwell, W.; Yamamoto, M.; Kleeberger, S.R. Exacerbated Airway Toxicity of Environmental Oxidant Ozone in Mice Deficient in Nrf2. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 254069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, D.; Peng, F.; Liu, L.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y. Effect of ozonized saline on signaling passway of Keap1-Nrf2-ARE in rat hepatocytes. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2011, 19, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xie, P.; Zhu, M.; Zhong, H.; Luo, S.; Tang, J.; Mo, G. Ozone Therapy Mitigates Parthanatos after Ischemic Stroke. Biol. Res. 2024, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, M.; Romanello, D. Systemic Ozone Therapy May Improve the Perception of Quality of Life: Ozonized Glucose Solution 5% Extends Reach to Patients Ineligible for Blood Infusion. Cureus 2024, 16, e64629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellan, G.; Iannarone, C.; Fegiz, A.; Baumgartner, I.; Maselli, A.M.; Fantera, A. Variation of Acid-Base Balance, Glycemia, Electrolytes and ETCO2 after Fast i.v. Infusion of 5% Fructose and/or Glucose. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 1997, 1, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Hessov, I.; Bojsen-Møller, M.; Melsen, F. Experimental Infusion Thrombophlebitis: A Comparison between Glucose and Fructose and 5% and 10% Glucose Solutions. Intensive Care Med. 1979, 5, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, I.V.; Shchukin, Y.V.; Lukashova, A.V. Effect of combined application of ozone therapy and gravitational therapy on the remote results of complex treatment of geriatric patients. Adv. Gerontol. 2017, 30, 558–562. [Google Scholar]
- Andryushchenko, V.V. Current Issues of Practical Application of Parenteral Ozone Therapy in Emergency Medicine. Emerg. Med. 2019, 8, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Dou, X.; Gu, D.; Shen, C.; Yao, T.; Nguyen, V.; Braunschweig, C.; Song, Z. 4-Hydroxynonenal Differentially Regulates Adiponectin Gene Expression and Secretion via Activating PPARγ and Accelerating Ubiquitin–Proteasome Degradation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 349, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion-Letellier, R.; Savoye, G.; Ghosh, S. Fatty Acids, Eicosanoids and PPAR Gamma. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 785, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhapola, R.; Hota, S.S.; Sarma, P.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Medhi, B.; Reddy, D.H. Recent Advances in Molecular Pathways and Therapeutic Implications Targeting Neuroinflammation for Alzheimer’s Disease. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 1669–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiè, M.; Costanzo, M.; Nodari, A.; Boschi, F.; Calderan, L.; Mannucci, S.; Covi, V.; Tabaracci, G.; Malatesta, M. Mild Ozonisation Activates Antioxidant Cell Response by the Keap1/Nrf2 Dependent Pathway. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 124, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacavalla, M.A.; Inguscio, C.R.; Cisterna, B.; Bernardi, P.; Costanzo, M.; Galiè, M.; Scambi, I.; Angelini, O.; Tabaracci, G.; Malatesta, M. Ozone at Low Concentration Modulates Microglial Activity in Vitro: A Multimodal Microscopy and Biomolecular Study. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2022, 85, 3777–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenci, A.; Macchia, I.; La Sorsa, V.; Sbarigia, C.; Di Donna, V.; Pietraforte, D. Mechanisms of Action of Ozone Therapy in Emerging Viral Diseases: Immunomodulatory Effects and Therapeutic Advantages With Reference to SARS-CoV-2. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 871645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, S.; Kumaragurubaran, R.; Giri, H.; Dixit, M. Isolation and Culture of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs). In Vascular Hyperpermeability; Tharakan, B., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2024; Volume 2711, pp. 147–162. ISBN 978-1-07-163428-8. [Google Scholar]
- Siow, R.C.M. Culture of Human Endothelial Cells from Umbilical Veins. In Human Cell Culture Protocols; Mitry, R.R., Hughes, R.D., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 806, pp. 265–274. ISBN 978-1-61779-366-0. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, N.; Krouwer, V.J.D.; Post, J.A. A New, Rapid and Reproducible Method to Obtain High Quality Endothelium in Vitro. Cytotechnology 2013, 65, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Peng, S.; Samuel, S.B.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.-F.; Liu, H. A Simple and Biosafe Method for Isolation of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 508, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śladowski, D.; Combes, R.; Van Der Valk, J.; Nawrot, I.; Gut, G. ESTIV Questionnaire on the Acquisition and Use of Primary Human Cells and Tissue in Toxicology. Toxicol. Vitr. 2005, 19, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISCO3. 2019. Available online: https://isco3.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/Generadores-ISCO3-SOP-DEV-01-01-2019.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Louis, K.S.; Siegel, A.C. Cell Viability Analysis Using Trypan Blue: Manual and Automated Methods. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 740, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, W.; Li, M.; Wu, C.; Shen, X.; Sun, Z. Proteomic Dissimilarities of Primary Microglia and BV2 Cells under Stimuli. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2022, 55, 1709–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rak, M.; Reiss, K. Double Labeling Fluorescent Immunocytochemistry. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 147–161. ISBN 978-1-07-161947-6. [Google Scholar]
| Gene | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) | Accession Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|
| mIL-1β | GAAATGCCACCTTTTGACAGTG | TGGATGCTCTCATCAGGACAG | NM_008361.4 |
| mIL-10 | GCCCTTTGCTATGGTGTCCTTTC | TCCCTGGTTTCTCTTCCCAAGAC | NM_010548.2 |
| mARG1 | ATGTGCCCTCTGTCTTTTAGGG | GGTCTCTCACGTCATACTCTGT | NM_007482.3 |
| miNOS | GGCAGCCTGTGAGACCTTTG | GCATTGGAAGTGAAGCGTTTC | AF427516.1 |
| mACT-β | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT | NM_007393.5 |
| mNRF2 | TCTGAGCCAGGACTACGACG | GAGGTGGTGGTGGTGTCTCTGC | NM_010902 |
| mSOD1 | GCCCGCTAAGTGCTGAGTC | AGCCCCAGAAGGATAACGGA | NM_017050 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Armeli, F.; Mengoni, B.; Menin, M.; Martínez-Sánchez, G.; Martinelli, M.; Maggiorotti, M.; Businaro, R. Ozone Saline Solution Polarizes Microglial Cells Towards an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype. Molecules 2025, 30, 3932. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193932
Armeli F, Mengoni B, Menin M, Martínez-Sánchez G, Martinelli M, Maggiorotti M, Businaro R. Ozone Saline Solution Polarizes Microglial Cells Towards an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype. Molecules. 2025; 30(19):3932. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193932
Chicago/Turabian StyleArmeli, Federica, Beatrice Mengoni, Martina Menin, Gregorio Martínez-Sánchez, Mauro Martinelli, Maurizio Maggiorotti, and Rita Businaro. 2025. "Ozone Saline Solution Polarizes Microglial Cells Towards an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype" Molecules 30, no. 19: 3932. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193932
APA StyleArmeli, F., Mengoni, B., Menin, M., Martínez-Sánchez, G., Martinelli, M., Maggiorotti, M., & Businaro, R. (2025). Ozone Saline Solution Polarizes Microglial Cells Towards an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype. Molecules, 30(19), 3932. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193932







