Liquid Gold with a Dark Side—A Toxicological Overview of Bioactive Components in Honey
Abstract
1. Honey
2. Mechanism of Toxin Transfer to Honey
3. Phytotoxins in Honey
3.1. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids
3.2. Grayanotoxins
3.3. Triptolide
3.4. Celastrol
3.5. Gelsedine-Type Alkaloids
3.6. Tropane Alkaloids
3.7. Tutin
3.8. Coumarins
4. Other Hazardous Factors in Honey
4.1. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural
4.2. Trace Metals and Metalloids
4.3. Pesticides
4.4. Clostridium botulinum
4.5. Allergens
4.6. Miscellaneous (PAHs, PCBs, PFAS, Mycotoxins, Veterinary Drug Residues)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cianciosi, D.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Afrin, S.; Gasparrini, M.; Reboredo-Rodriguez, P.; Manna, P.P.; Zhang, J.; Lamas, L.B.; Flórez, S.M.; Toyos, P.A.; et al. Phenolic Compounds in Honey and Their Associated Health Benefits: A Review. Molecules 2018, 23, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squadrone, S.; Brizio, P.; Stella, C.; Pederiva, S.; Brusa, F.; Mogliotti, P.; Garrone, A.; Abete, M.C. Trace and Rare Earth Elements in Monofloral and Multifloral Honeys from Northwestern Italy; A First Attempt of Characterization by a Multi-Elemental Profile. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 61, 126556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.U.; Naz, S.; Abudabos, A.M. Towards a Better Understanding of the Therapeutic Applications and Corresponding Mechanisms of Action of Honey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27755–27766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasicka-Misiak, I.; Makowicz, E.; Stanek, N. Chromatographic Fingerprint, Antioxidant Activity, and Colour Characteristic of Polish Goldenrod (Solidago virgaurea L.) Honey and Flower. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 1169–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiegbuna, J.; Obiegbuna, J.E.; Osajiele, B.O.; Ishiwu, C.N. Quality Evaluation of Awka Market Honey and Honey from Beekeepers in Two Floral Regions of Anambra State, Nigeria. Am. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 5, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, G.A.; Nicolson, S.W.; Shafir, S. Nutritional Physiology and Ecology of Honey Bees. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2025, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolson, S.W.; Human, H.; Pirk, C.W.W. Honey Bees Save Energy in Honey Processing by Dehydrating Nectar before Returning to the Nest. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyer, M.; Neumann, P.; Dietemann, V. A Look into the Cell: Honey Storage in Honey Bees, Apis Mellifera. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, S.W.; Human, H. Bees Get a Head Start on Honey Production. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Inaudi, P.; Garzino, M.; Abollino, O.; Malandrino, M.; Giacomino, A. Honey: Inorganic Composition as Possible Marker for Botanical and Geological Assignment. Molecules 2025, 30, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciulu, M.; Spano, N.; Pilo, M.I.; Sanna, G. Recent Advances in the Analysis of Phenolic Compounds in Unifloral Honeys. Molecules 2016, 21, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloš, M.M.Ž.; Popov, N.S.; Radulović, J.Z.P.; Stojanov, I.M.; Jakšić, S.M. Sugar Profile of Different Floral Origin Honeys from Serbia. J. Apic. Res. 2020, 59, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcza, L.; Simms, C.; Chopra, M. Honey and Cancer: Current Status and Future Directions. Diseases 2016, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma-Morales, M.; Huertas, J.R.; Rodríguez-Pérez, C. A Comprehensive Review of the Effect of Honey on Human Health. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodor, Z.; Benedek, C.; Urbin, Á.; Szabó, D.; Sipos, L. Colour of Honey: Can We Trust the Pfund Scale?—An Alternative Graphical Tool Covering the Whole Visible Spectra. LWT 2021, 149, 111859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Gu, H.W.; Liu, R.J.; Qing, X.D.; Nie, J.F. A Comprehensive Review of the Current Trends and Recent Advancements on the Authenticity of Honey. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhlaei, R.; Selamat, J.; Khatib, A.; Razi, A.F.A.; Sukor, R.; Ahmad, S.; Babadi, A.A. The Toxic Impact of Honey Adulteration: A Review. Foods 2020, 9, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza Tette, P.A.; Guidi, L.R.; De Abreu Glória, M.B.; Fernandes, C. Pesticides in Honey: A Review on Chromatographic Analytical Methods. Talanta 2016, 149, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olas, B. Honey and Its Phenolic Compounds as an Effective Natural Medicine for Cardiovascular Diseases in Humans? Nutrients 2020, 12, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlak Gajger, I.; Dar, S.A.; Ahmed, M.M.M.; Aly, M.M.; Vlainić, J. Antioxidant Capacity and Therapeutic Applications of Honey: Health Benefits, Antimicrobial Activity and Food Processing Roles. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, R.; Ghojoghi, A.; Ghajarbeygi, P. Honey Safety Hazards and Public Health. J. Chem. Health Risks 2016, 6, 249–267. [Google Scholar]
- Pecoraro, L.; Flore, A.I.; Dalle Carbonare, L.; Piacentini, G.; Pietrobelli, A. Honey and Children: Only a Grandma’s Panacea or a Real Useful Tool? Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 72, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduwole, O.; Udoh, E.E.; Oyo-Ita, A.; Meremikwu, M.M. Honey for Acute Cough in Children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2018, CD007094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waris, A.; Macharia, W.; Njeru, E.K.; Essajee, F. Randomised double blind study to compare effectiveness of honey, salbutamol and placebo in treatment of cough in children with common cold. East. Afr. Med. J. 2014, 91, 50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shadkam, M.N.; Mozaffari-Khosravi, H.; Mozayan, M.R. A Comparison of the Effect of Honey, Dextromethorphan, and Diphenhydramine on Nightly Cough and Sleep Quality in Children and Their Parents. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2010, 16, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, H.A.; Rozen, J.; Kristal, H.; Laks, Y.; Berkovitch, M.; Uziel, Y.; Kozer, E.; Pomeranz, A.; Efrat, H. Effect of Honey on Nocturnal Cough and Sleep Quality: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Pediatrics 2012, 130, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaid, S.S.M.; Ruslee, S.S.; Mokhtar, M.H. Protective Roles of Honey in Reproductive Health: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosoghi, M.; Yousefi, S.; Honarvar, M. Physicochemical and Sensory Properties of Honey Powder from Different Climatic Regions. Appl. Food Res. 2025, 5, 100843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CXS 12-1981; Standard for Honey. Codex Alimentarius Commission: Rome, Italy, 2019.
- Faustino, C.; Pinheiro, L. Analytical Rheology of Honey: A State-of-the-Art Review. Foods 2021, 10, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sohaimy, S.A.; Masry, S.H.D.; Shehata, M.G. Physicochemical Characteristics of Honey from Different Origins. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2015, 60, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, P.; Bielawska-Pohl, A.; Dzimitrowicz, A.; Jamroz, P.; Welna, M.; Lesniewicz, A.; Szymczycha-Madeja, A. Recent Achievements in Element Analysis of Bee Honeys by Atomic and Mass Spectrometry Methods. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 93, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapla, U.M.; Solayman, M.; Alam, N.; Khalil, M.I.; Gan, S.H. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) Levels in Honey and Other Food Products: Effects on Bees and Human Health. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morariu, I.D.; Avasilcai, L.; Vieriu, M.; Lupu, V.V.; Ioniuc, I.; Morariu, B.A.; Lupu, A.; Morariu, P.C.; Pop, O.L.; Burduloi, V.M.; et al. A Comprehensive Narrative Review on the Hazards of Bee Honey Adulteration and Contamination. J. Food Qual. 2024, 2024, 3512676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, L.M.; Labella, G.F.; Giorgi, A.; Panseri, S.; Pavlovic, R.; Bonacci, S.; Arioli, F. The Occurrence of Pesticides and Persistent Organic Pollutants in Italian Organic Honeys from Different Productive Areas in Relation to Potential Environmental Pollution. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiotis, K.M.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Anastasiadou, P.; Machera, K. Pesticide Residues in Honeybees, Honey and Bee Pollen by LC–MS/MS Screening: Reported Death Incidents in Honeybees. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485–486, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasheras, R.J.; Lázaro, R.; Burillo, J.C.; Bayarri, S. Occurrence of Pesticide Residues in Spanish Honey Measured by QuEChERS Method Followed by Liquid and Gas Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2021, 10, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonerba, E.; Panseri, S.; Arioli, F.; Nobile, M.; Terio, V.; Di Cesare, F.; Tantillo, G.; Maria Chiesa, L. Determination of Antibiotic Residues in Honey in Relation to Different Potential Sources and Relevance for Food Inspection. Food Chem. 2021, 334, 12757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Waili, N.; Salom, K.; Al-Ghamdi, A.; Ansari, M.J. Antibiotic, Pesticide, and Microbial Contaminants of Honey: Human Health Hazards. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 930849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Alvarado, Y.; Clark, D.R.; Vega-Melendez, C.J.; Flores-Cruz, Z.; Domingez-Bello, M.G.; Giray, T. Antibiotics in Hives and Their Effects on Honey Bee Physiology and Behavioral Development. Biol. Open 2020, 9, bio053884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungerford, N.L.; Carter, S.J.; Anuj, S.R.; Tan, B.L.L.; Hnatko, D.; Martin, C.L.; Sharma, E.; Yin, M.; Nguyen, T.T.P.; Melksham, K.J.; et al. Analysis of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Queensland Honey: Using Low Temperature Chromatography to Resolve Stereoisomers and Identify Botanical Sources by Uhplc-Ms/Ms. Toxins 2019, 11, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, E.; Kwiatek, K. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Honey: Determination with Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Method. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugnerotto, P.; Silva, B.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Costa, A.C.O. Comprehensive Review of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Bee Products: Occurrence, Extraction, and Analytical Methods. Food Chem. 2025, 483, 144211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, A.; Gallina, A.; Benetti, C.; Mutinelli, F. Residues of Antibacterial Drugs in Honey from the Italian Market. Food Addit. Contam. Part B Surveill. 2009, 2, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Han, M.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qian, L.; Huang, M.; Luo, B.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Antibiotic Residues in Honey in the Chinese Market and Human Health Risk Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Arora, P.; Gupta, G. Contaminants in Honey: Safeguarding Quality and Consumer Health. Uttar Pradesh J. Zool. 2024, 45, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugnerotto, P.; Seraglio, S.K.T.; Schulz, M.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Fett, R.; Costa, A.C.O. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids and Beehive Products: A Review. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lis-Cieplak, A.; Trześniowska, K.; Stolarczyk, K.; Stolarczyk, E.U. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids as Hazardous Toxins in Natural Products: Current Analytical Methods and Latest Legal Regulations. Molecules 2024, 29, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, R.; Pereira, D.M.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids: Chemistry, Pharmacology, Toxicology and Food Safety. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.S.; Qiu, J.; Mu, X.Y.; Qian, Y.Z.; Chen, L. Levels, Toxic Effects, and Risk Assessment of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Foods: A Review. Foods 2024, 13, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Shi, M.; Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Ng, K.T.P.; Xia, Q.; Zhu, L.; Fu, P.P.C.; Man, K.; Tsui, S.K.W.; et al. Mutational Signature Analysis Reveals Widespread Contribution of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloid Exposure to Human Liver Cancer. Hepatology 2021, 74, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.L.; Ton, T.V.; Devereux, T.R.; Moomaw, C.; Clayton, N.; Chan, P.; Dunnick, J.K.; Sills, R.C. Chemical-Specific Alterations in Ras, P53, and β-Catenin Genes in Hemangiosarcomas from B6C3F1 Mice Exposed to o-Nitrotoluene or Riddelliine for 2 Years. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 191, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.P. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids: Metabolic Activation Pathways Leading to Liver Tumor Initiation. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, 30, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncada, P.; Isani, G.; Peloso, M.; Dalmonte, T.; Bonan, S.; Caprai, E. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids from Monofloral and Multifloral Italian Honey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Frandsen, H.L.; Christiansson, N.R.; Rosendal, S.E.; Pedersen, M.; Smedsgaard, J. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Honey: Quantification with and without Standards. Food Control 2019, 98, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tábuas, B.; Cruz Barros, S.; Diogo, C.; Cavaleiro, C.; Sanches Silva, A. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Foods, Herbal Drugs, and Food Supplements: Chemistry, Metabolism, Toxicological Significance, Analytical Methods, Occurrence, and Challenges for Future. Toxins 2024, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doğanyiğit, Z.; Silici, S.; Demirtaş, A.; Kaya, E.; Kaymak, E. Determination of Histological, Immunohistochemical and Biochemical Effects of Acute and Chronic Grayanotoxin III Administration in Different Doses in Rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenler, A.K. Cardiac Effects of Mad Honey Poisoning and Its Management in Emergency Department: A Review from Turkey. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2016, 16, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, S.A.; Kleerekooper, I.; Hofman, Z.L.M.; Kappen, I.F.P.M.; Stary-Weinzinger, A.; Van Der Heyden, M.A.G. Grayanotoxin Poisoning: ‘Mad Honey Disease’ and Beyond. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2012, 12, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doǧanyiǧit, Z.; Kaymak, E.; Silici, S. The Cardiotoxic Effects of Acute and Chronic Grayanotoxin-III in Rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2020, 39, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraslan, G.; Kanbur, M.; Karabacak, M.; Arslan, K.; Siliğ, Y.; Soyer Sarica, Z.; Tekeli, M.Y.; Taş, A. Effect on Oxidative Stress, Hepatic Chemical Metabolizing Parameters, and Genotoxic Damage of Mad Honey Intake in Rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtoglu, A.B.; Yavuz, R.; Evrendilek, G.A. Characterisation and Fate of Grayanatoxins in Mad Honey Produced from Rhododendron Ponticum Nectar. Food Chem. 2014, 161, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, A.; Turedi, S.; Russell, R.M.; Ayaz, F.A. Clinical Review of Grayanotoxin/Mad Honey Poisoning Past and Present. Clin. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Khan, S.U.; Saleh, T.A.; Fahad, S. Mad Honey: Uses, Intoxicating/Poisoning Effects, Diagnosis, and Treatment. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 18635–18646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Cho, H. Determination of Grayanotoxin I and Grayanotoxin III in Mad Honey from Nepal Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 35, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, A.; Keleş, A.; Bildik, F.; Aygencel, G.; Doǧan, N.Ö.; Gómez, H.F. Mad Honey Sex: Therapeutic Misadventures From an Ancient Biological Weapon. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2009, 54, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silici, S.; Atayoglu, A.T. Mad Honey Intoxication: A Systematic Review on the 1199 Cases. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 86, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.C.; Nebbia, C.S.; et al. Risks for Human Health Related to the Presence of Grayanotoxins in Certain Honey. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e07866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhao, L.; Wang, K.; Han, L.; Shan, J.; Wu, L.; Xue, X. Rapid Identification of “Mad Honey” from Tripterygium Wilfordii Hook. f. and Macleaya Cordata (Willd) R. Br Using UHPLC/Q-TOF-MS. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Wan, R.; Li, J. Fatal Honey Poisoning Caused by Tripterygium Wilfordii Hook F in Southwest China: A Case Series. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2016, 27, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Peng, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, J. Toxicity of Triptolide and the Molecular Mechanisms Involved. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Yang, L.; Yang, F.; Nie, G.; Jin, X.; Peng, X.; Zhong, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Traceability of Chemicals from Tripterygium Wilfordii Hook. f. in Raw Honey and the Potential Synergistic Effects of Honey on Acute Toxicity Induced by Celastrol and Triptolide. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 139044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Coghi, P. Exploring Medicinal Potential and Drug Delivery Solutions of Celastrol from the Chinese “Thunder of God Vine”. Eur. J. Chem. 2024, 15, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Luo, R.; Zhang, C.; Gao, F.; Zhang, J.; Fu, C. Celastrol: A Review of Useful Strategies Overcoming Its Limitation in Anticancer Application. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 558741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; He, G.N.; Dai, L. A Comprehensive Review on Celastrol, Triptolide and Triptonide: Insights on Their Pharmacological Activity, Toxicity, Combination Therapy, New Dosage Form and Novel Drug Delivery Routes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Lu, J.; Wang, M. Recent Advances in Drug Delivery of Celastrol for Enhancing Efficiency and Reducing the Toxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1137289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Dai, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, L.; Fu, K.; Ma, C.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Celastrol as an Emerging Anticancer Agent: Current Status, Challenges and Therapeutic Strategies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroni, L.; Dorne, J.L.C.M.; Dall’Asta, C.; Dellafiora, L. An in Silico Insight on the Mechanistic Aspects of Gelsenicine Toxicity: A Reverse Screening Study Pointing to the Possible Involvement of Acetylcholine Binding Receptor. Toxicol. Lett. 2023, 386, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gao, Y.; Ma, D. Divergent Entry to Gelsedine-Type Alkaloids: Total Syntheses of (-)-Gelsedilam, (-)-Gelsenicine, (-)-Gelsedine, and (-)-Gelsemoxonine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 11608–11612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Zuo, M.T.; Qi, X.J.; Gong, M.D.; Xu, W.B.; Meng, S.Y.; Long, J.Y.; Li, P.S.; Sun, Z.L.; Zheng, X.F.; et al. Hypoxia Tolerance Determine Differential Gelsenicine-Induced Neurotoxicity between Pig and Mouse. BMC Med. 2025, 23, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, K. Gelsedine-Type Alkaloids: Discovery of Natural Neurotoxins Presented in Toxic Honey. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zuo, M.T.; Qi, X.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.Y. Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography Method for the Determination of Gelsemium Alkaloids in Honey. Foods 2022, 11, 2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gómez, L.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Sierra, I. Occurrence and Chemistry of Tropane Alkaloids in Foods, with a Focus on Sample Analysis Methods: A Review on Recent Trends and Technological Advances. Foods 2022, 11, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Gómez, L.; Gañán, J.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Sierra, I. Atropine and Scopolamine Occurrence in Spices and Fennel Infusions. Food Control 2023, 146, 109555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamp, J.; Knappstein, K.; Walte, H.G.; Krause, T.; Steinberg, P.; Schwake-Anduschus, C. Transfer of Tropane Alkaloids (Atropine and Scopolamine) into the Milk of Subclinically Exposed Dairy Cows. Food Control 2021, 126, 108056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, K.H.; Kang, M.J.; Sharma, N.; An, S.S.A. Beauty of the Beast: Anticholinergic Tropane Alkaloids in Therapeutics. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2022, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pintor, B.; Paniagua, G.; Gañán, J.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Garcinuño, R.M.; Fernández, P.; Sierra, I. Determination of Atropine and Scopolamine in Honey Using a Miniaturized Polymer-Based Solid-Phase Extraction Protocol Prior to the Analysis by HPLC-MS/MS. Polymer 2024, 298, 126904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romera-Torres, A.; Romero-González, R.; Martínez Vidal, J.L.; Garrido Frenich, A. Comprehensive Tropane Alkaloids Analysis and Retrospective Screening of Contaminants in Honey Samples Using Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (Orbitrap). Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, E.; Kwiatek, K. Simultaneous Determination of Pyrrolizidine and Tropane Alkaloids in Honey by Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 66, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, N.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Sierra, I. Miniaturized Analytical Strategy Based on μ-SPEed for Monitoring the Occurrence of Pyrrolizidine and Tropane Alkaloids in Honey. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeuchi, K.; Haraguchi, S.; Yamada, H.; Tanino, K. Model Synthetic Study of Tutin, a Picrotoxane-Type Sesquiterpene: Stereoselective Construction of a Cis-Fused 5,6-Ring Skeleton. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 70, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, S.F.; Morton, T.R. Tutu Toxicity: Three Case Reports of Coriaria Arborea Ingestion, Review of Literature and Recommendations for Management. N. Zeal. Med. J. 2013, 126, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Q.T.; Yang, W.Q.; Zang, C.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, C.J.; Bao, X.; Cai, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Q.; Wang, X.L.; et al. The Toxic Natural Product Tutin Causes Epileptic Seizures in Mice by Activating Calcineurin. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentealba, J.; Muñoz, B.; Yévenes, G.; Moraga-Cid, G.; Pérez, C.; Guzmán, L.; Rigo, J.M.; Aguayo, L.G. Potentiation and Inhibition of Glycine Receptors by Tutin. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, L.; Joyce, N.I.; Sansom, C.E.; Cooney, J.M.; Jensen, D.J.; Perry, N.B. Sweet Poisons: Honeys Contaminated with Glycosides of the Neurotoxin Tutin. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, O.C.; Joyce, N.I.; Gould, N.; Perry, N.B. Glycosides of the Neurotoxin Tutin in Toxic Honeys Are from Coriaria Arborea Phloem Sap, Not Insect Metabolism. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Szwaczko, K. Coumarins Synthesis and Transformation via C–H Bond Activation—A Review. Inorganics 2022, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanachi, A.; Leonetti, F.; Pisani, L.; Catto, M.; Carotti, A. Coumarin: A Natural, Privileged and Versatile Scaffold for Bioactive Compounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringlis, I.A.; De Jonge, R.; Pieterse, C.M.J. The Age of Coumarins in Plant–Microbe Interactions. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 1405–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasicka-Misiak, I.; Makowicz, E.; Stanek, N. Polish Yellow Sweet Clover (Melilotus officinalis L.) Honey, Chromatographic Fingerprints, and Chemical Markers. Molecules 2017, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyot-Declerck, C.; Renson, S.; Bouseta, A.; Collin, S. Floral Quality and Discrimination of Lavandula Stoechas, Lavandula Angustifolia, and Lavandula Angustifolia×latifolia Honeys. Food Chem. 2002, 79, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerkovic, I.; Marijanovic, Z.; Staver, M.M. Screening of Natural Organic Volatiles from Prunus Mahaleb L. Honey: Coumarin and Vomifoliol as Nonspecific Biomarkers. Molecules 2011, 16, 2507–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heghes, S.C.; Vostinaru, O.; Mogosan, C.; Miere, D.; Iuga, C.A.; Filip, L. Safety Profile of Nutraceuticals Rich in Coumarins: An Update. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 803338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, B.G. Coumarin Metabolism, Toxicity and Carcinogenicity: Relevance for Human Risk Assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 423–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Majid, I.; Aggarwal, P.; Suri, S. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) Formation, Occurrence and Potential Health Concerns: Recent Developments. Toxin Rev. 2021, 40, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, E.; Fogliano, V. Acrylamide and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF): A Review on Metabolism, Toxicity, Occurrence in Food and Mitigation Strategies. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, T.; Gao, C.; Zeng, W.; Zhao, W.; Yu, H.; Chen, S.; Shen, J.; Ji, M. Analysis of Key Targets for 5-Hydroxymethyl-2-Furfural-Induced Lung Cancer Based on Network Toxicology, Network Informatics, and in Vitro Experiments. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2025, 48, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švecová, B.; Mach, M. Content of 5-Hydroxymethyl-2-Furfural in Biscuits for Kids. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2018, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Lin, N.; Hao, R.; Fan, X.; Lin, L.; Hu, G.; Lin, S.; He, J.; Zhu, Q.; Jin, H. 5-HMF Induces Anaphylactoid Reactions in Vivo and in Vitro. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkök, D.; Silici, S. Effects of Honey HMF on Enzyme Activities and Serum Biochemical Parameters of Wistar Rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 20186–20193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Huang, Z.Y.; Miao, X. Pathway of 5-Hydroxymethyl-2-Furaldehyde Formation in Honey. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2417–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasias, I.N.; Kiriakou, I.K.; Proestos, C. HMF and Diastase Activity in Honeys: A Fully Validated Approach and a Chemometric Analysis for Identification of Honey Freshness and Adulteration. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Singh, S. Honey Moisture Reduction and Its Quality. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 3861–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, C.A.; Valderrama, P.; Boroski, M. HMF Monitoring: Storage Condition and Honey Quality. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 3162–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of the European Union. Council Directive 2001/110/EC of 20 December 2001 Relating to Honey. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2002, L10, 47–52. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02001L0110-20140623 (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Khalil, M.I.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Gan, S.H. High 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Concentrations Are Found in Malaysian Honey Samples Stored for More than One Year. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2388–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zembrzuska, J.; Pakulski, Ł.; Karbowska, B.; Bartoszewicz, J.; Janeba-Bartoszewicz, E.; Selech, J.; Kurczewski, P. Comparison of Different Methods for Determining 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural in Assessing the Quality of Honey from Greater Poland. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.B.; Gardiner, M.M. Trace Metals in Nectar of Important Urban Pollinator Forage Plants: A Direct Exposure Risk to Pollinators and Nectar-Feeding Animals in Cities. Ecol. Evol. 2025, 15, e71238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good Beekeeping Practices for Sustainable Apiculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Burden, C.M.; Morgan, M.O.; Hladun, K.R.; Amdam, G.V.; Trumble, J.J.; Smith, B.H. Acute Sublethal Exposure to Toxic Heavy Metals Alters Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Feeding Behavior. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monchanin, C.; Burden, C.; Barron, A.B.; Smith, B.H. Heavy Metal Pollutants: The Hidden Pervasive Threat to Honey Bees and Other Pollinators. Adv. Insect Phys. 2023, 64, 255–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godebo, T.R.; Stoner, H.; Taylor, P.; Jeuland, M. Metals in Honey from Bees as a Proxy for Environmental Contamination in the United States. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 364, 125221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, E.L.; Mustatea, G. Toxicity of Heavy Metals. In Environmental Impact and Remediation of Heavy Metals; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glevitzky, M.; Corcheş, M.T.; Popa, M.; Vică, M.L. Honey as a Bioindicator: Pollution’s Effects on Its Quality in Mining vs. Protected Sites. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šerevičienė, V.; Zigmontienė, A.; Paliulis, D. Heavy Metals in Honey Collected from Contaminated Locations: A Case of Lithuania. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, J.P.; Wise, R.M.; Hoffert, A.; Wise, J.T.F.; Specht, A.J. Elevated Metal Levels in U.S. Honeys: Is There a Concern for Human Health? Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2025, 203, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibebe, D.; Hussen, M.; Mulugeta, M.; Yenealem, D.; Moges, Z.; Gedefaw, M.; Kassa, Y. Assessment of Selected Heavy Metals in Honey Samples Using Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (FAAS), Ethiopia. BMC Chem. 2022, 16, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adugna, E.; Hymete, A.; Birhanu, G.; Ashenef, A. Determination of Some Heavy Metals in Honey from Different Regions of Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1764182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.L.G.; Brito, J.C.M.; Almeida, M.O.; Gomes, M.P.; Calaça, P. Unbounded Bees: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Investigating Pesticide Contamination in Brazilian Bees and Hive Products. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 17, 100632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiatly-Blaszkiewicz, A.; Klupczynska-Gabryszak, A.; Matuszewska-Mach, E.; Matysiak, J.; Attard, E.; Kowalczyk, D.; Adamkiewicz, A.; Kupcewicz, B.; Matysiak, J. Pesticides in Honeybee Products—Determination of Pesticides in Bee Pollen, Propolis, and Royal Jelly from Polish Apiary. Molecules 2025, 30, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Singh, S.; Nagarajaiah, R.P.K.; Kumar, G.; Singh, S.; Nagarajaiah, R.P.K. Detailed Review on Pesticidal Toxicity to Honey Bees and Its Management. In Modern Beekeeping—Bases for Sustainable Production; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisamoto, S.; Ikegami, M.; Goka, K.; Sakamoto, Y. The Impact of Landscape Structure on Pesticide Exposure to Honey Bees. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlikova, K.; Vaclavikova, M.; Halesova, T.; Kamler, M.; Markovic, M.; Erban, T. The Investigation of Honey Bee Pesticide Poisoning Incidents in Czechia. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.A.; Mahmood, D.; Elkhalifa, A.E.O.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Khan, M.I.; Ashfaq, F.; Patel, M.; Snoussi, M.; Kieliszek, M.; Adnan, M. Exposure to Pesticide Residues in Honey and Its Potential Cancer Risk Assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 180, 114014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balayiannis, G.; Balayiannis, P. Bee Honey as an Environmental Bioindicator of Pesticides’ Occurrence in Six Agricultural Areas of Greece. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 55, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REGULATION (EC) NO 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 February 2005 on Maximum Residue Levels of Pesticides in or on Food and Feed of Plant and Animal Origin and Amending Council Directive 91/414/EEC. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2005, L70, 1–16.
- Kędzierska-Matysek, M.; Teter, A.; Skałecki, P.; Topyła, B.; Domaradzki, P.; Poleszak, E.; Florek, M. Residues of Pesticides and Heavy Metals in Polish Varietal Honey. Foods 2022, 11, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, J.; Shen, L.; Ji, X.; Li, R. Occurrence of Pesticide Residues in Honey from Apiaries with Incidents of Honeybee Poisoning in East China and a Corresponding Risk Assessment for Honeybees and Chinese Consumers. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 3607–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butovskaya, E.; Gasparini, M.; Angelone, B.; Cancemi, G.; Tranquillo, V.; Prestini, G.; Bosi, F.; Menotta, S. Occurrence of Glyphosate and Other Polar Pesticides in Honey from Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna Regions in Italy: Three-Year Monitoring Results. Foods 2023, 12, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsalini, M.; Inchingolo, F.; Dipalma, G.; Wegierska, A.E.; Charitos, I.A.; Potenza, M.A.; Scarano, A.; Lorusso, F.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Montagnani, M.; et al. Botulinum Neurotoxins (BoNTs) and Their Biological, Pharmacological, and Toxicological Issues: A Scoping Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilena, R.; Pozzato, M.; Baselli, L.; Chidini, G.; Barbieri, S.; Scalfaro, C.; Finazzi, G.; Lonati, D.; Locatelli, C.A.; Cappellari, A.; et al. Infant Botulism: Checklist for Timely Clinical Diagnosis and New Possible Risk Factors Originated from a Case Report and Literature Review. Toxins 2021, 13, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, M.W.; Smith, T.J.; Anniballi, F.; Austin, J.W.; Bano, L.; Bradshaw, M.; Cuervo, P.; Cheng, L.W.; Derman, Y.; Dorner, B.G.; et al. Historical Perspectives and Guidelines for Botulinum Neurotoxin Subtype Nomenclature. Toxins 2017, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.A.; Dabritz, H.A. Infant Botulism: In Search of Clostridium botulinum Spores. Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikanov, B.; Mustafina, R.; Auteleyeva, L.; Wiśniewski, J.; Anusz, K.; Grenda, T.; Kwiatek, K.; Goldsztejn, M.; Grabczak, M. Clostridium botulinum and Clostridium Perfringens Occurrence in Kazakh Honey Samples. Toxins 2019, 11, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenda, T.; Grabczak, M.; Sieradzki, Z.; Kwiatek, K.; Pohorecka, K.; Skubida, M.; Bober, A. Clostridium botulinum Spores in Polish Honey Samples. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 19, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtacka, J.; Wysok, B.; Lipiński, Z.; Gomółka-Pawlicka, M.; Rybak-Chmielewska, H.; Wiszniewska-Łaszczych, A. Clostridium botulinum Spores Found in Honey from Small Apiaries in Poland. J. Apic. Sci. 2016, 60, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steininger, J.; Heyne, S.; Abraham, S.; Beissert, S.; Bauer, A. Honey as a Rare Cause of Severe Anaphylaxis: Case Report and Review of Literature. JEADV Clin. Pract. 2025, 4, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, L.; Kohlich, A.; Hirschwehr, R.; Siemann, U.; Ebner, H.; Scheiner, O.; Kraft, D.; Ebner, C. Food Allergy to Honey: Pollen or Bee Products? Characterization of Allergenic Proteins in Honey by Means of Immunoblotting. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 97, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Costanzo, M.; De Paulis, N.; Peveri, S.; Montagni, M.; Berni Canani, R.; Biasucci, G. Anaphylaxis Caused by Artisanal Honey in a Child: A Case Report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 15, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, R.; Duarte, F.C.; Mendes, A.; Bartolomé, B.; Barbosa, M.P. Anaphylaxis Caused by Honey: A Case Report. Asia Pac. Allergy 2017, 7, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncel, T.; Uysal, P.; Hocaoglu, A.B.; Erge, D.O.; Firinci, F.; Karaman, O.; Uzuner, N. Anaphylaxis Caused by Honey Ingestion in an Infant. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2011, 39, 112–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhawar, N.; Gonzalez-Estrada, A. Honey-Induced Anaphylaxis in an Adult. QJM Int. J. Med. 2022, 115, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermingham, M.D.; Klekotko, K.; Oliver, M.A.; Blaxland, J.A. Low Levels of Gluten and Major Milk Allergens Bos d 5 and Bos d 11 Identified in Commercially Available Honey. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2022, 52, 904–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarella, S.; Guerriero, E.; Quici, L.; Ianiri, G.; Cerasa, M.; Notardonato, I.; Protano, C.; Vitali, M.; Russo, M.V.; De Cristofaro, A.; et al. PAHs Presence and Source Apportionment in Honey Samples: Fingerprint Identification of Rural and Urban Contamination by Means of Chemometric Approach. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcolin, L.C.; de Oliveira Arias, J.L.; Kupski, L.; Barbosa, S.C.; Primel, E.G. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Honey from Stingless Bees (Meliponinae) in Southern Brazil. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari, M.F.; Gurkan Ayyildiz, E.; Esen, F. Determination of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Honeybee, Pollen, and Honey Samples from Urban and Semi-Urban Areas in Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 4414–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari, M.F.; Esen, F.; Tasdemir, Y. Levels of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Honeybees and Bee Products and Their Evaluation with Ambient Air Concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunn, H.; Arnold, G.; Körner, W.; Rippen, G.; Steinhäuser, K.G.; Valentin, I. PFAS: Forever Chemicals—Persistent, Bioaccumulative and Mobile. Reviewing the Status and the Need for Their Phase out and Remediation of Contaminated Sites. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surma, M.; Zieliński, H.; Piskuła, M. Levels of Contamination by Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Honey from Selected European Countries. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 97, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, E.; Eyupoglu, O.E. Determination of Mycotoxins by HPLC, LC-MS/MS and Health Risk Assessment of the Mycotoxins in Bee Products of Turkey. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadok, I.; Krzyszczak-Turczyn, A.; Szmagara, A.; Łopucki, R. Honey Analysis in Terms of Nicotine, Patulin and Other Mycotoxins Contamination by UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS—Method Development and Validation. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, H.; Leite, M.; Oliveira, B.; Freitas, A. Antibiotics in Honey: A Comprehensive Review on Occurrence and Analytical Methodologies. Open Res. Eur. 2024, 4, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, F.; Taha, E.K.A. Contaminants in Honey: An Analysis of EU RASFF Notifications from 2002 to 2022. J. Fur Verbraucherschutz Und Leb. 2023, 18, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuente-Ballesteros, A.; Brugnerotto, P.; Costa, A.C.O.; Nozal, M.J.; Ares, A.M.; Bernal, J. Determination of Acaricides in Honeys from Different Botanical Origins by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2023, 408, 135245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
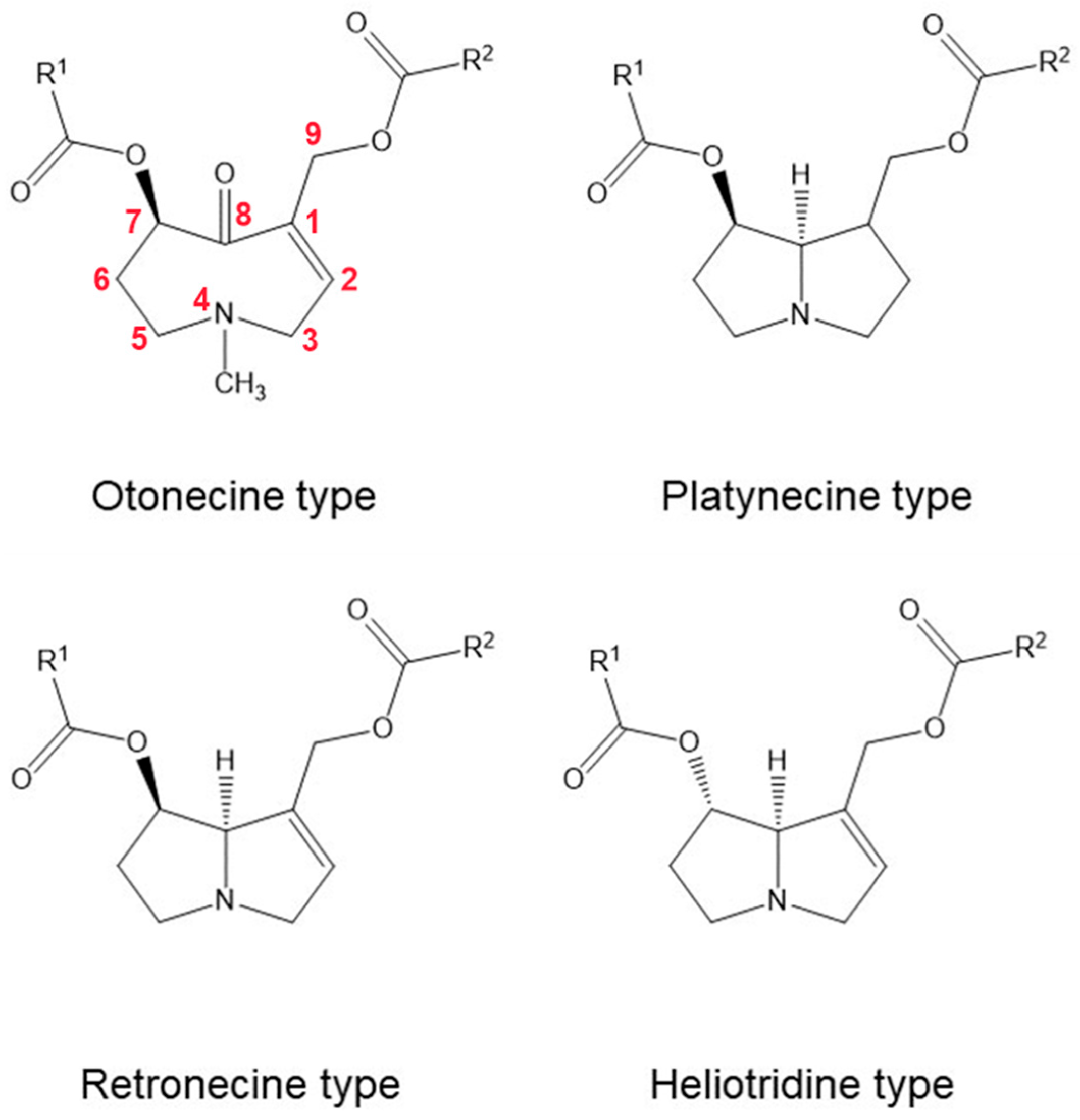







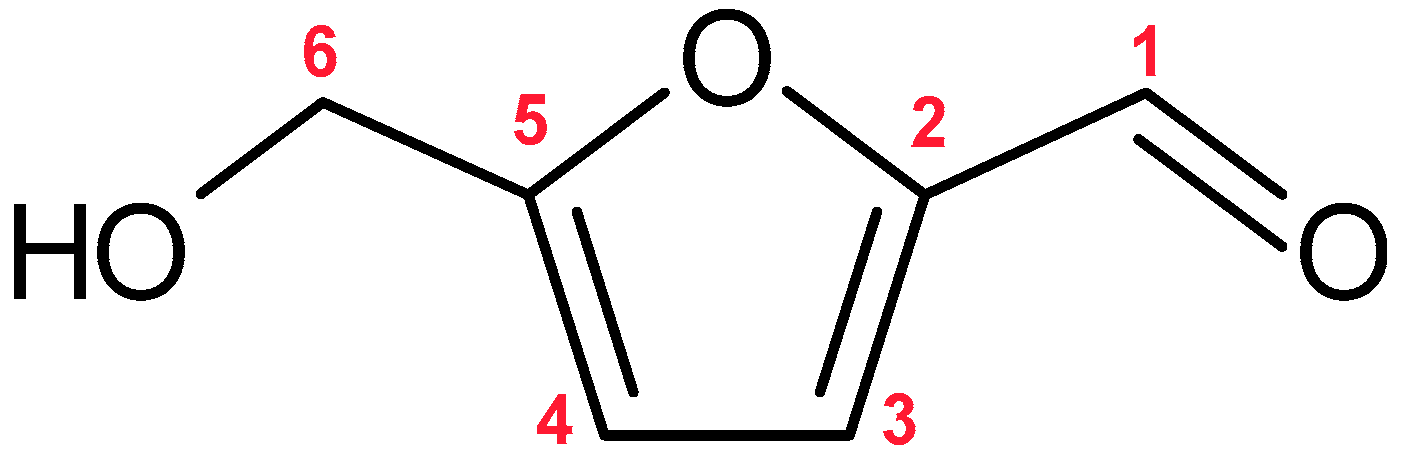
| Compound | Probability of Ingestion | Details | Harmful Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| pyrrolizidine alkaloids | medium-high | - | cancerogenic, hepatotoxicity |
| grayanotoxins | low | regionally high | cardiotoxicity, genotoxicity |
| triptolide | low | regionally high | organ toxicity, death |
| celastrol | low | regionally high | hepatotoxicity, neurotoxicity |
| gelsedine-type alkaloids | low | regionally high | neurotoxicity |
| tutin | low | regionally high | neurotoxicity |
| tropane alkaloids | medium | - | N/A 1 |
| coumarins | high | - | probably hepatotoxicity |
| Compound | Probability of Ingestion | Details | Harmful Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) | high | increases with storage time | cancerogenic |
| trace metals | medium | - | chronic toxicity |
| pesticides | high | - | chronic toxicity |
| C. botulinum spores | medium | - | infant botulism |
| allergens | high | extremely rare cases | allergies (extremely rare) |
| PAHs, PCBs, PFAS, mycotoxins, veterinary drug residues | high | probably cumulative | N/A 1 (probably chronic toxicity) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kulawik, M.; Kulawik, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J.; Zalewski, P. Liquid Gold with a Dark Side—A Toxicological Overview of Bioactive Components in Honey. Molecules 2025, 30, 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193925
Kulawik M, Kulawik A, Cielecka-Piontek J, Zalewski P. Liquid Gold with a Dark Side—A Toxicological Overview of Bioactive Components in Honey. Molecules. 2025; 30(19):3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193925
Chicago/Turabian StyleKulawik, Maciej, Anna Kulawik, Judyta Cielecka-Piontek, and Przemysław Zalewski. 2025. "Liquid Gold with a Dark Side—A Toxicological Overview of Bioactive Components in Honey" Molecules 30, no. 19: 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193925
APA StyleKulawik, M., Kulawik, A., Cielecka-Piontek, J., & Zalewski, P. (2025). Liquid Gold with a Dark Side—A Toxicological Overview of Bioactive Components in Honey. Molecules, 30(19), 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193925










