Exosomal MicroRNA: Diagnostic Potential and Role in Breast Cancer Dissemination
Abstract
1. Introduction
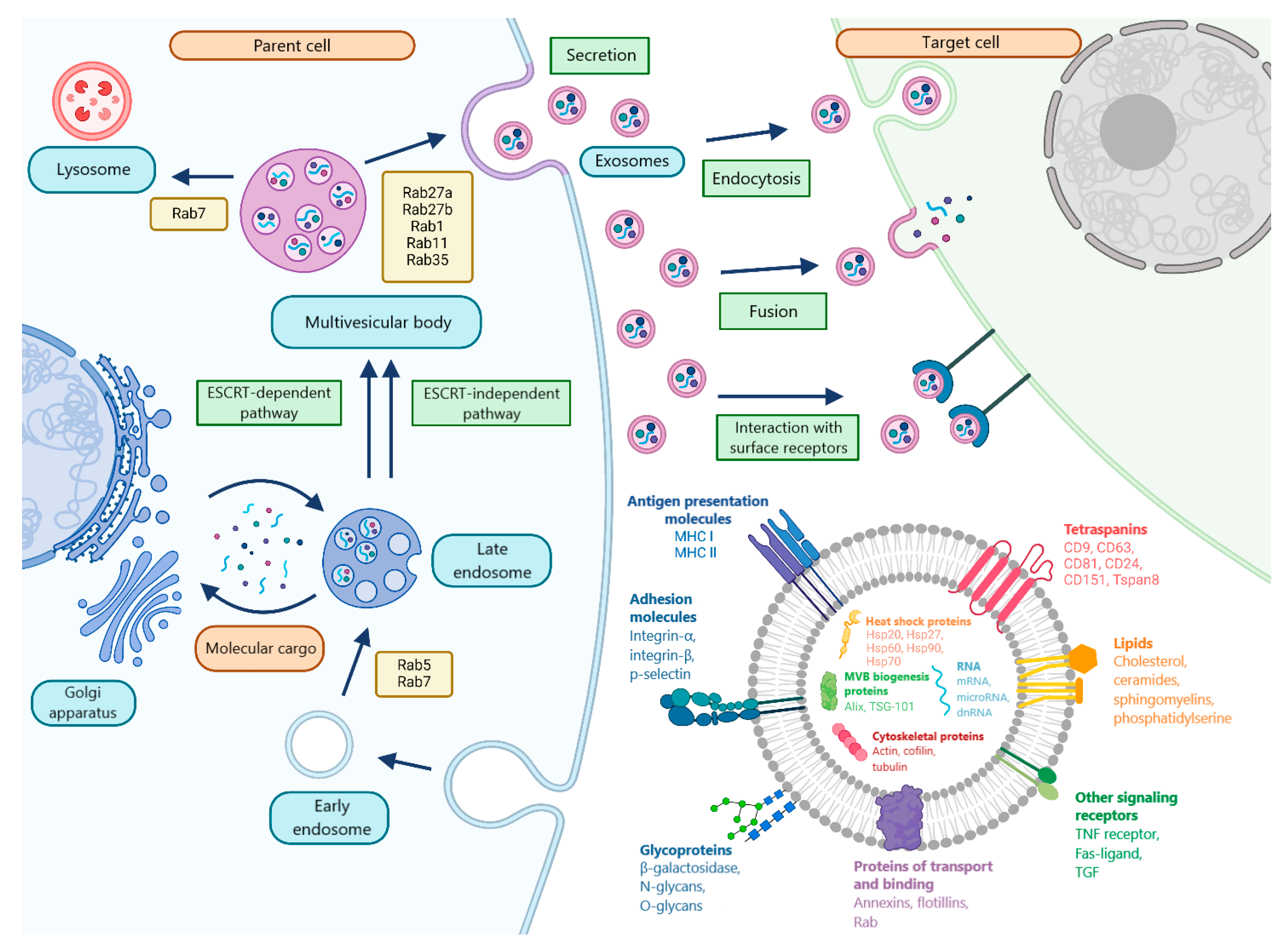
2. MicroRNA Biogenesis and Packaging into Exosomes
3. Molecular Cargo and Features of Exosome Circulation in the Blood
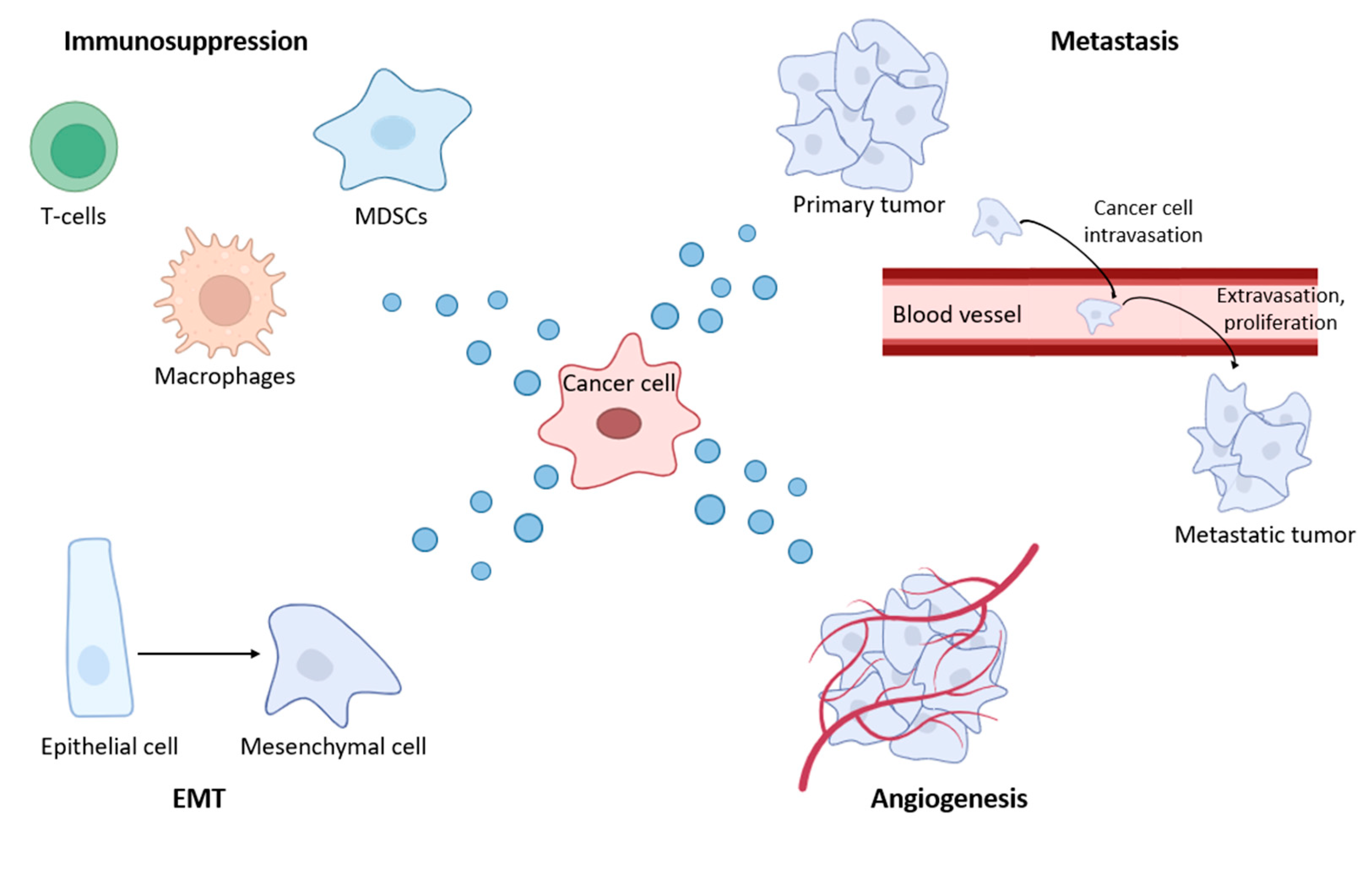
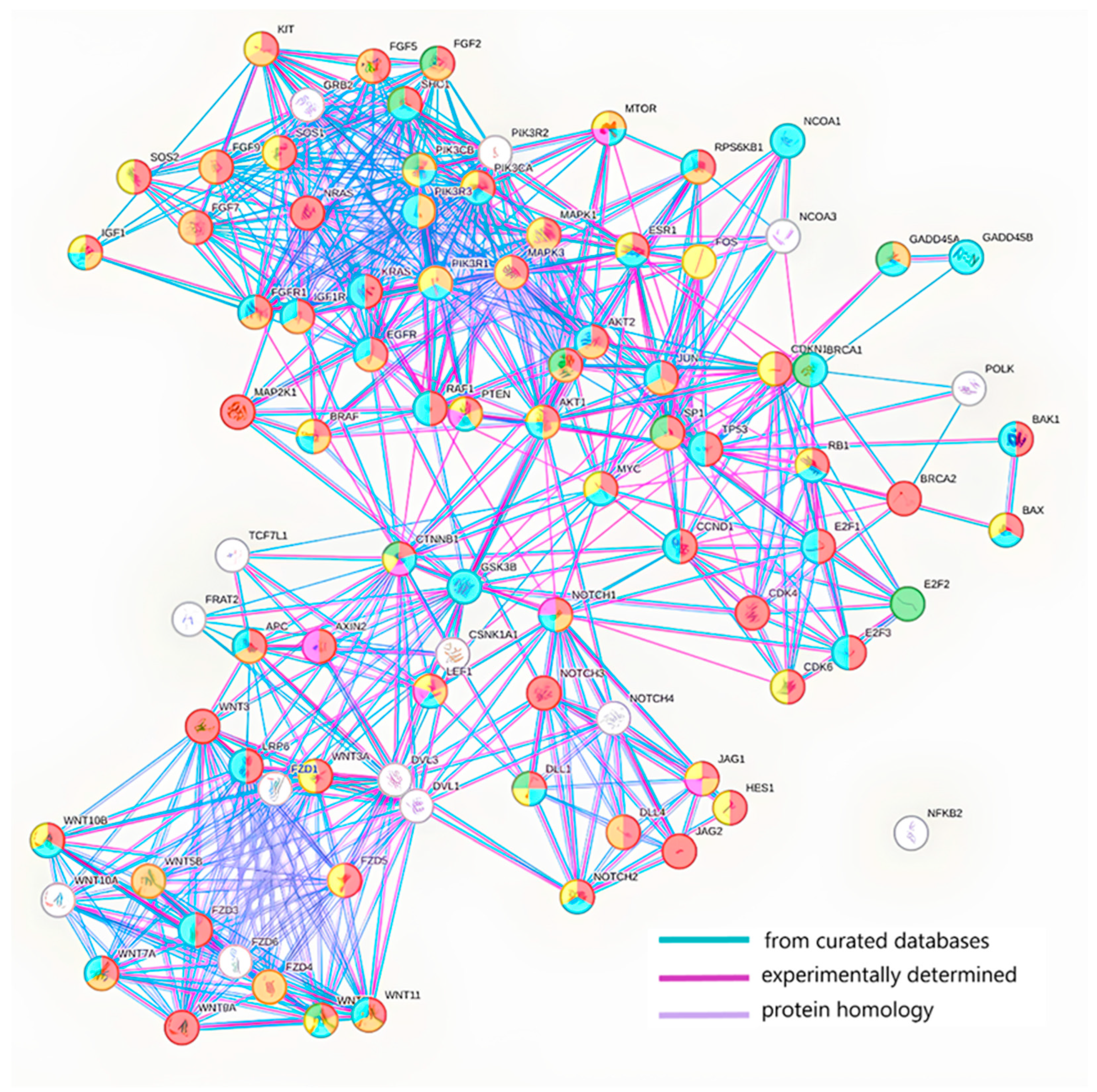
4. The Role of Exosomal MicroRNA in BC Dissemination
4.1. The Influence of BC Exosomes on the Functional Activity of the Immune System
4.2. BC-Derived Exosomes Stimulate EMT, Proliferation, Invasion and Migration
4.3. BC-Derived Exosomes Stimulate Angiogenesis and Metastasis
5. Exosomal MicroRNAs as Markers for BC Detection
6. Exosomal MicroRNAs Associated with BC Relapse
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BC | Breast cancer |
| CAF | Cancer-associated fibroblasts |
| CTC | Circulating tumor cells |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| ILV | Intraluminal vesicles |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MVB | Multivesicular body |
| NGS | Next Generation sequencing |
| NPC | Nucleoprotein complex |
| pCR | Pathological complete response |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| sEVs | Small extracellular vesicles |
| TAM | Tumor-associated macrophages |
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer |
| US | Ultrasound examination |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starinskij, V.V.; Shahzadova, A.O.; Kaprin, A.D. Malignant Neoplasms in Russia in 2023 (Incidence and Mortality); MNIOI im. P.A. Gercena−filial FGBU «NMIC radiologii» Minzdrava Rossii: Moscow, Russia, 2023; p. 252. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Winters, S.; Martin, C.; Murphy, D.; Shokar, N.K. Breast Cancer Epidemiology, Prevention, and Screening. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 151, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connal, S.; Cameron, J.M.; Sala, A.; Brennan, P.M.; Palmer, D.S.; Palmer, J.D.; Perlow, H.; Baker, M.J. Liquid biopsies: The future of cancer early detection. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhzadova, A.O.; Starinsky, V.V.; Lisichnikova, I.V. Cancer care to the population of Russia in 2022. Sib. J. Oncol. 2023, 22, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiglazov, V.F.; Semiglazov, V.V.; Krivorotko, P.V.; Paltuev, R.M.; Dashyan, G.A.; Semiglazova, T.Y.; Bessonov, A.A.; Nikolaev, K.S. Guidelines for the Treatment of Early Breast Cancer; PJSC “T8 Publishing Technologies”: Sankt-Peretburg, Russia, 2016; p. 154. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Radenkovic, S.; Konjevic, G.; Isakovic, A.; Stevanovic, P.; Gopcevic, K.; Jurisic, V. HER2-positive breast cancer patients: Correlation between mammographic and pathological findings. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2014, 162, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.H.F.; Coopey, S.B.; Freer, P.E.; Hughes, K.S. False-negative rate of combined mammography and ultrasound for women with palpable breast masses. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 153, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, E.S.; Clark, A.S.; Tchou, J.; Zhang, P.; Freedman, G.M. Clinical Diagnosis and Management of Breast Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 9S–16S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, C.D. Clinical indications: What is the evidence? Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, S82–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisel, J.; Raghu, M.; Hooley, R. The Role of Ultrasound in Breast Cancer Screening: The Case for and Against Ultrasound. Semin. Ultrasound. CT MRI 2018, 39, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamkovich, S.N.; Voytsitskiy, V.E.; Laktionov, P.P. Modern Methods in Breast Cancer Diagnostics. Biochem. Suppl. Ser. B Biomed. Chem. 2014, 8, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.H.; Saadatpour, Z.; Salmaninejad, A.; Momeni, F.; Mokhtari, M.; Nahand, J.S.; Rahmati, M.; Mirzaei, H.; Kianmehr, M. Breast cancer diagnosis: Imaging techniques and biochemical markers. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 5200–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, N.S.; Novikov, S.N.; Krzhivitsky, P.I.; Zhukova, L.A.; Krivorotko, P.V.; Artemyeva, A.S.; Valitova, A.A.; Khoroshavina, A.A.; Chernaya, A.V.; Bryanceva, Z.V.; et al. Diagnostic capabilities of scintimammography in detecting multicentric and minimal breast cancer of various molecular subtypes. Vopr. Onkologii. 2023, 69, 708–714. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basova, T.S.; Fedorov, N.M.; Fadeeva, A.I.; Shmalts, E.A.; Kovalik, A.V.; Sepiashvili, G.G. Mammoscintigraphy and OFECT with 99MTS-MIBI in diagnostics of breast neoplasms. Acad. J. West Sib. 2019, 15, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Pesapane, F.; Suter, M.B.; Rotili, A.; Penco, S.; Nigro, O.; Cremonesi, M.; Bellomi, M.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A.; Pinotti, G.; Cassano, E. Will traditional biopsy be substituted by radiomics and liquid biopsy for breast cancer diagnosis and characterisation? Med. Oncol. 2020, 37, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesoła, M.; Jeleń, M. The diagnostic efficiency of fine needle aspiration biopsy in breast cancers—Review. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 22, 887–892. [Google Scholar]
- Kunihiko, H.; Kornelia, P. Intratumoral Heterogeneity: More Than Just Mutations. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, A.; Shiino, S.; Kawauchi, J.; Takizawa, S.; Sakamoto, H.; Matsuzaki, J.; Ono, M.; Takeshita, F.; Niida, S.; Shimizu, C.; et al. Novel combination of serum microRNA for detecting breast cancer in the early stage. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satomi-Tsushita, N.; Shimomura, A.; Matsuzaki, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kawauchi, J.; Takizawa, S.; Aoki, Y.; Sakamoto, H.; Kato, K.; Shimizu, C.; et al. Serum microRNA-based prediction of responsiveness to eribulin in metastatic breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiino, S.; Matsuzaki, J.; Shimomura, A.; Kawauchi, J.; Takizawa, S.; Sakamoto, H.; Aoki, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Tamura, K.; Kato, K.; et al. Serum miRNA-based Prediction of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, J.; Shimomura, A.; Kawauchi, J.; Matsuzaki, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takizawa, S.; Sakamoto, H.; Ohno, M.; Narita, Y.; Ochiya, T.; et al. Brain metastasis-related microRNAs in patients with advanced breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Ling, S.; Zheng, S.; Xu, X. Liquid biopsy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, T.K.Y.; Tan, P.H. Liquid Biopsy in Breast Cancer: A Focused Review. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 145, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamkovich, S.; Tupikin, A.; Kozyakov, A.; Laktionov, P. Size and Methylation Index of Cell-Free and Cell-Surface-Bound DNA in Blood of Breast Cancer Patients in the Contest of Liquid Biopsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shefer, A.; Tutanov, O.; Belenikin, M.; Tsentalovich, Y.P.; Tamkovich, S. Blood Plasma Circulating DNA-Protein Complexes: Involvement in Carcinogenesis and Prospects for Liquid Biopsy of Breast Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutanov, O.; Shefer, A.; Shefer, E.; Ruzankin, P.; Tsentalovich, Y.; Tamkovich, S. DNA-Binding Proteins and Passenger Proteins in Plasma DNA-Protein Complexes: Imprint of Parental Cells or Key Mediators of Carcinogenesis Processes? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Dong, T.; Yu, W.; Jia, Z.; Hou, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y. Global biomarker trends in triple-negative breast cancer research: A bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 7962–7983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, S.; Konjevic, G.; Gopcevic, K.; Jovic, V.; Inic, M.; Jurisic, V. Activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in sera of breast cancer patients. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2010, 206, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radenkovic, S.; Konjevic, G.; Jurisic, V.; Karadzic, K.; Nikitovic, M.; Gopcevic, K. Values of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in tumor tissue of basal-like breast cancer patients. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 68, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurisic, V.; Radenkovic, S.; Konjevic, G. The Actual Role of LDH as Tumor Marker, Biochemical and Clinical Aspects. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 867, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konjević, G.; Jurisić, V.; Spuzić, I. Association of NK cell dysfunction with changes in LDH characteristics of peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2001, 66, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurisić, V.; Konjević, G.; Jancić-Nedeljkov, R.; Sretenović, M.; Banicević, B.; Colović, M.; Spuzić, I. The comparison of spontaneous LDH release activity from cultured PBMC with sera LDH activity in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients. Med. Oncol. 2004, 21, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchegolev, Y.Y.; Sorokin, D.V.; Scherbakov, A.M.; Andreeva, O.E.; Salnikova, D.I.; Mikhaevich, E.I.; Gudkova, M.V.; Krasil’nikov, M.A. Exosomes are involved in the intercellular transfer of rapamycin resistance in the breast cancer cells. Bioimpacts 2023, 13, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, V.C.; Yu, C.-C. Cancer-Derived Exosomes: Their Role in Cancer Biology and Biomarker Development. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8019–8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Janku, F.; Zhan, Q.; Fan, J.-B. Accessing Genetic Information with Liquid Biopsies. Trends Genet. 2015, 31, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Whiteside, T.L.; Reichert, T.E. Challenges in Exosome Isolation and Analysis in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutanov, O.; Orlova, E.; Proskura, K.; Grigor’eva, A.; Yunusova, N.; Tsentalovich, Y.; Alexandrova, A.; Tamkovich, S. Proteomic Analysis of Blood Exosomes from Healthy Females and Breast Cancer Patients Reveals an Association between Different Exosomal Bioactivity on Non-tumorigenic Epithelial Cell and Breast Cancer Cell Migration in Vitro. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.-L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Tesic Mark, M.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Bai, Y.; Xie, X.; Lu, Z. miRNA in plasma exosome is stable under different storage conditions. Molecules 2014, 19, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Hurley, J.; Roberts, D.; Chakrabortty, S.K.; Enderle, D.; Noerholm, M.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J.K. Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: Opportunities and challenges. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Sharples, R.A.; Scicluna, B.J.; Hill, A.F. Exosomes provide a protective and enriched source of miRNA for biomarker profiling compared to intracellular and cell-free blood. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoshenko, M.; Sagaradze, G.; Orlova, E.; Shtam, T.; Proskura, K.; Kamyshinsky, R.; Yunusova, N.; Alexandrova, A.; Efimenko, A.; Tamkovich, S. Total Blood Exosomes in Breast Cancer: Potential Role in Crucial Steps of Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Bai, X.; Ni, J.; Zhang, H.; Duan, W.; Graham, P.; Li, Y. Exosomes and breast cancer drug resistance. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Zhu, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Wei, R.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, G.; Li, P.; et al. Evaluation of circulating small extracellular vesicles derived miRNAs as biomarkers of early colon cancer: A comparison with plasma total miRNAs. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1643670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, N.; Johnson, C.; Kao, D.; Gurnani, P.; Alexander, C.; Polytarchou, C.; Monaghan, T.M. MicroRNA-based therapeutics for inflammatory disorders of the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 194, 106870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhu, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Jin, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Zou, P.; Xie, C.; Cui, R. Dissecting miRNA signature in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2021, 501, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Madawi, N.A.; Darwish, Z.E.; Omar, E.M. Targeted gene therapy for cancer: The impact of microRNA multipotentiality. Med. Oncol. 2024, 41, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; Yao, J.; Mi, S. Exosome and exosomal microRNA: Trafficking, sorting, and function. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.T.B.; Clark, I.M.; Le, L.T.T. MicroRNA-Based Diagnosis and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Cao, Y.; Sun, M.; Feng, H. Expression, regulation, and function of exosome-derived miRNAs in cancer progression and therapy. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, M.; Lee, H. Sorting Mechanisms for MicroRNAs into Extracellular Vesicles and Their Associated Diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenjaroenpun, P.; Kremenska, Y.; Nair, V.M.; Kremenskoy, M.; Joseph, B.; Kurochkin, I.V. Characterization of RNA in exosomes secreted by human breast cancer cell lines using next-generation sequencing. PeerJ 2013, 1, e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, S.; Perocheau, D.; Touramanidou, L.; Baruteau, J. The exosome journey: From biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun. Signal 2021, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossinova, O.A.; Gopanenko, A.V.; Tamkovich, S.N.; Krasheninina, O.A.; Tupikin, A.E.; Kiseleva, E.; Yanshina, D.D.; Malygin, A.A.; Ven’yaminova, A.G.; Kabilov, M.R.; et al. Cytosolic YB-1 and NSUN2 are the only proteins recognizing specific motifs present in mRNAs enriched in exosomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2017, 1865, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajkovic, K.; Hsu, C.; Chiantia, S.; Rajendran, L.; Wenzel, D.; Wieland, F.; Schwille, P.; Brügger, B.; Simons, M. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 2008, 319, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Matsuki, Y.; Ochiya, T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17442–17452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Hagiwara, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. Neutral Sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2)-dependent Exosomal Transfer of Angiogenic MicroRNAs Regulate Cancer Cell Metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 10849–10859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Sánchez-Cabo, F.; Pérez-Hernández, D.; Vázquez, J.; Martin-Cofreces, N.; Martinez-Herrera, D.J.; Pascual-Montano, A.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Zou, W.; Chen, X.; Roizman, B.; Zhou, G.G. hnRNPA2B1 Associated with Recruitment of RNA into Exosomes Plays a Key Role in Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Release from Infected Cells. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00367-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, L.; Giurato, G.; Cicchini, C.; Montaldo, C.; Mancone, C.; Tarallo, R.; Battistelli, C.; Alonzi, T.; Weisz, A.; Tripodi, M. The RNA-Binding Protein SYNCRIP Is a Component of the Hepatocyte Exosomal Machinery Controlling MicroRNA Sorting. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, A.J.; Hoshino, D.; Hong, N.H.; Cha, D.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Coffey, R.J.; Patton, J.G.; Weaver, A.M. KRAS-MEK Signaling Controls Ago2 Sorting into Exosomes. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J.; Arras, G.; Colombo, M.; Jouve, M.; Morath, J.P.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temoche-Diaz, M.M.; Shurtleff, M.J.; Nottingham, R.M.; Yao, J.; Fadadu, R.P.; Lambowitz, A.M.; Schekman, R. Distinct mechanisms of microRNA sorting into cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicle subtypes. eLife 2019, 8, e47544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppers-Lalic, D.; Hackenberg, M.; Bijnsdorp, I.V.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.J.; Sadek, P.; Sie, D.; Zini, N.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Ylstra, B.; de Menezes, R.X.; et al. Nontemplated Nucleotide Additions Distinguish the Small RNA Composition in Cells from Exosomes. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Ru, W.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; Lei, C.; Chen, H. Exosome biogenesis, secretion and function of exosomal miRNAs in skeletal muscle myogenesis. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chen, Q.; Lin, L.; Sha, C.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Yin, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, W.; et al. Regulation of exosome production and cargo sorting. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekström, K.; Crescitelli, R.; Pétursson, H.I.; Johansson, J.; Lässer, C.; Olofsson Bagge, R. Characterization of surface markers on extracellular vesicles isolated from lymphatic exudate from patients with breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunusova, N.V.; Tugutova, E.A.; Tamkovich, S.N.; Kondakova, I.V. Role of tetraspanins and exosomal proteases in tumor progression. Biomed. Chem. 2018, 64, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, A.L.; Noy, P.J.; Reyat, J.S.; Tomlinson, M.G. Regulation of A disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) family sheddases ADAM10 and ADAM17: The emerging role of tetraspanins and rhomboids. Platelets 2017, 28, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, M.; Khokha, R. Metalloproteinases in extracellular vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1864, 1989–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunusova, N.V.; Patysheva, M.R.; Molchanov, S.V.; Zambalova, E.A.; Grigor’eva, A.E.; Kolomiets, L.A.; Ochirov, M.O.; Tamkovich, S.N.; Kondakova, I.V. Metalloproteinases at the surface of small extrcellular vesicles in advanced ovarian cancer: Relationships with ascites volume and peritoneal canceromatosis index. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 494, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, G.; Jain, A.; Kumar, A.; Agarwal, C.; Kim, S.; Leevy, W.M.; Agarwal, R. Exosomes secreted by prostate cancer cells under hypoxia promote matrix metalloproteinases activity at pre-metastatic niches. Mol. Cancerogen. 2020, 59, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamkovich, S.N.; Yunusova, N.V.; Tugutova, E.; Somov, A.K.; Proskura, K.V.; Kolomiets, L.A.; Stakheeva, M.N.; Grigor’eva, A.E.; Laktionov, P.P.; Kondakova, I.V. Protease Cargo in Circulating Exosomes of Breast Cancer and Ovarian Cancer Patients. Asian. Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somov, A.K.; Yunusova, N.V.; Shtam, T.A.; Proskura, K.V.; Zambalova, E.A.; Laktionov, P.P.; Tamkovich, S.N. ADAM-10 on the surface of exosomes from breast cancer patients blood: Newly mechanisms tumor dissemination. Vopr. Onkol. 2019, 65, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, L.S.; Overgaard, M.T.; Søe, R.; Boldt, H.B.; Sottrup-Jensen, L.; Giudice, L.C.; Conover, C.A.; Oxvig, C. Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) cleaves insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-5 independent of IGF: Implications for the mechanism of IGFBP-4 proteolysis by PAPP-A. FEBS Lett. 2001, 504, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisselev, A.F.; Callard, A.; Goldberg, A.L. Importance of the different proteolytic sites of the proteasome and the efficacy of inhibitors varies with the protein substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8582–8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunusova, N.; Kolegova, E.; Sereda, E.; Kolomiets, L.; Villert, A.; Patysheva, M.; Rekeda, I.; Grigor’eva, A.; Tarabanovskaya, N.; Kondakova, I.; et al. Plasma Exosomes of Patients with Breast and Ovarian Tumors Contain an Inactive 20S Proteasome. Molecules 2021, 26, 6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Ochiya, T.; Shimomura, A. Liquid biopsy using non-coding RNAs and extracellular vesicles for breast cancer management. Breast Cancer 2025, 32, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, Y.; Yu, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, L.; Shu, Y. Role of exosomal non-coding RNAs from tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 3133–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Liu, L.C.; Hung, Y.; Chen, C.J.; Lin, Y.Z.; Wu, W.R.; Wang, S.C. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in circulatory exosomes is correlated with ErbB2/HER2 positivity in breast cancer. Breast 2019, 46, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, D.; Sharma, R.; Goel, N.; Buttar, H.S.; Garg, V.K.; Pal, D.; Rajab, K.; Shaikh, A. Coding roles of long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer: Emerging molecular diagnostic biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets with special reference to chemotherapy resistance. Front. Genet. 2023, 13, 993687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X. Roles of lncRNA in the diagnosis and prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2023, 24, 1123–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ke, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Ao, L.; Zou, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Nie, J.; Wu, C.; et al. LncRNA MIR100HG promotes cell proliferation in triple-negative breast cancer through triplex formation with p27 loci. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Dai, W.; Guo, X.; Wang, K. LncRNA-SNHG1 promotes macrophage M2-like polarization and contributes to breast cancer growth and metastasis. Aging 2021, 13, 23169–23181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, V.M.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Conn, S.J. Circular RNA in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2024, 24, 597–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.Y.; Cai, Z.R.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.S.; Ju, H.Q.; Xu, R.H. Circular RNA: Metabolism, functions and interactions with proteins. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, F.; Wu, L.; Zhang, X.; Tian, J.; Li, J.; Cao, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L. Identification of Hsa_circ_0104824 as a Potential Biomarkers for Breast Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820960745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, D.; Feng, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhong, S. Circular RNA expression in exosomes derived from breast cancer cells and patients. Epigenomics 2019, 11, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuno, Y.; Kanke, T.; Maruyama, N.; Fujii, W.; Naito, K.; Sugiura, K. Characterization of mRNA profiles of the exosome-like vesicles in porcine follicular fluid. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutkin, A.; Uziel, O.; Beery, E.; Nordenberg, J.; Pinchasi, M.; Goldvaser, H.; Henick, S.; Goldberg, M.; Lahav, M. Tumor cells derived exosomes contain hTERT mRNA and transform nonmalignant fibroblasts into telomerase positive cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59173–59188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menck, K.; Klemm, F.; Gross, J.C.; Pukrop, T.; Wenzel, D.; Binder, C. Induction and transport of Wnt 5a during macrophage-induced malignant invasion is mediated by two types of extracellular vesicles. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, K.S.; Kaufman, J.; Munavalli, G.S.; Robertson, K.; Behfar, A.; Wyles, S.P. Exosomes: The latest in regenerative aesthetics. Regen. Med. 2023, 18, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.T.; Kay, M.K.; Kang, M.H.; Rahman, M.M.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Choudhury, M.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Hussain, F.; Rahman, S.M. Tumor-Associated Macrophages as Multifaceted Regulators of Breast Tumor Growth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Gao, X.; et al. Prognostic significance of tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer: A meta-analysis of the literature. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30576–30586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, Y.J.; Kim, H.S.; Hwang, E.H.; Woo, J.; Zhang, M.; Moon, W.K. Breast cancer cell-derived exosomes and macrophage polarization are associated with lymph node metastasis. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 7398–7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, D.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Feng, Z.; Qin, X. Exosomal miR-222 from adriamycin-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells promote macrophages M2 polarization via PTEN/Akt to induce tumor progression. Aging 2021, 13, 10415–10430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Tu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yao, F.; Zhang, X. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced exosomal mir-27a-3p promotes immune escape in breast cancer via regulating pd-L1 expression in macrophages. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 9560–9573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, R.; Liu, P.; Ye, Y.; Yu, W.; Guo, X.; Yu, J. Cancer exosome-derived miR-9 and miR-181a promote the development of early-stage MDSCs via interfering with SOCS3 and PIAS3 respectively in breast cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4681–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khani, A.T.; Sharifzad, F.; Mardpour, S.; Hassan, Z.M.; Ebrahimi, M. Tumor extracellular vesicles loaded with exogenous Let-7i and miR-142 can modulate both immune response and tumor microenvironment to initiate a powerful anti-tumor response. Cancer Lett. 2021, 501, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Xia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lu, L.; Dai, C.; Song, Y.; Xu, K.; Ji, W.; et al. Lin28B-high breast cancer cells promote immune suppression in the lung pre-metastatic niche via exosomes and support cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otmani, K.; Rouas, R.; Lagneaux, L.; Krayem, M.; Duvillier, H.; Berehab, M.; Lewalle, P. Acute myeloid leukemia-derived exosomes deliver miR-24-3p to hinder the T-cell immune response through DENN/MADD targeting in the NF-κB signaling pathways. Cell Commun. Signal 2023, 21, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, J.; Atay, S.; Banskota, S.; Artale, B.; Schmitt, S.; Godwin, A.K. Exosomes as mediators of platinum resistance in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 11917–11936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, H.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Chen, A.; Li, Z. MicroRNA-181d-5p-Containing Exosomes Derived from CAFs Promote EMT by Regulating CDX2/HOXA5 in Breast Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic. Acids 2020, 19, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Liu, W.; Zhao, H.; Chen, B.; Yue, X. MiR-191-5p inhibits KLF6 to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Technol. Health Care 2023, 31, 2251–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.C.; Lima, N.D.S.; Sarian, L.O.; Matheu, A.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Derchain, S.F.M. Exosome-mediated breast cancer chemoresistance via miR-155 transfer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhu, M.; Gu, Y. Breast Cancer Stem Cells-derived Extracellular Vesicles Affect PPARG Expression by Delivering MicroRNA-197 in Breast Cancer Cells. Clin. Breast Cancer 2022, 22, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnarumma, E.; Fiore, D.; Nappa, M.; Roscigno, G.; Adamo, A.; Iaboni, M.; Russo, V.; Affinitom, A.; Puoti, I.; Quintavalle, C.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts release exosomal microRNAs that dictate an aggressive phenotype in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 19592–19608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Lv, M.; Yu, Q.; Bao, J.; Lou, K.; Li, X. MicroRNA-370-3p shuttled by breast cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles induces fibroblast activation through the CYLD/Nf-kappaB axis to promote breast cancer progression. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, S.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; Hawke, D.H.; Wörner, P.M.; Jansen, D.A.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Alt, E.U.; Izadpanah, R. Molecular characterization of exosome-like vesicles from breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirina, L.V.; Kondakova, I.V.; Klisho, E.V.; Kakurina, G.V.; Shishkin, D.A. Metaloproteinases as neoangiogenesis regulators in cancer. Sib. J. Oncol. 2007, 1, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Pochampally, R.; Watabe, K.; Lu, Z.; Mo, Y.-Y. Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-10b promotes cell invasion in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Fong, M.Y.; Min, Y.; Somlo, G.; Liu, L.; Palomares, M.R.; Yu, Y.; Chow, A.; O’Connor, S.T.F.; Chin, A.R.; et al. Cancer-secreted miR-105 destroys vascular endothelial barriers to promote metastasis. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, Z.; Xin, B.; Shi, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, X. LSD1 inhibits the invasion and migration of breast cancer through exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Ye, X.; Zhou, T.; Gan, D.; Qian, H.; Fang, W.; Yao, M.; Zhang, D.; Shi, H.; Chen, T. PGRN-/- TAMs-derived exosomes inhibit breast cancer cell invasion and migration and its mechanism exploration. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-X.; Cheng, L.; Pan, M.; Qian, Q.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Xu, L.-Y.; Ding, Q. D Rhamnose β-Hederin against human breast cancer by reducing tumor-derived exosomes. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 5172–5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, P.M.M.; Alkhilaiwi, F.; Cavalli, I.J.; Malheiros, D.; de Souza Fonseca Ribeiro, E.M.; Cavalli, L.R. Extracellular vesicles from triple-negative breast cancer cells promote proliferation and drug resistance in non-tumorigenic breast cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 172, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, C.; Hu, W.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Tang, J. Exosome-mediated miR-222 transferring: An insight into NF-κB-mediated breast cancer metastasis. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 369, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengo-Gil, G.; Gonzalez-Billalabeitia, E.; Perez-Henarejos, S.A.; Navarro Manzano, E.; Chaves-Benito, A.; Garcia-Martinez, E.; Garcia-Garre, E.; Vicente, V.; Ayala de la Peña, F. Angiogenic role of miR-20a in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Zhao, X.; Shao, C.; Fu, B.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Dou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, R.; et al. STIM1 promotes angiogenesis by reducing exosomal miR-145 in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, Q.; Hou, Z. Exosomal miR-92a-3p modulates M2 macrophage polarization in colorectal cancer: Implications for tumor migration and angiogenesis. Med. Oncol. 2025, 42, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Luo, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Cui, Z.; He, A.; He, S.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, N.; et al. Retinoblastoma cell-derived exosomes promote angiogenesis of human vesicle endothelial cells through microRNA-92a-3p. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, M.Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, L.; Alontaga, A.Y.; Chandra, M.; Ashby, J.; Chow, A.; O’Connor, S.T.F.; Li, S.; Chin, A.R.; et al. Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.T.N.; Hamar, P.; Guo, C.; Basar, E.; Perdigão-Henriques, R.; Balaj, L.; Lieberman, J. miR-200-containing extracellular vesicles promote breast cancer cell metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 5109–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.; Silva, J.; Herrera, A.; Herrera, M.; Peña, C.; Martín, P.; Gil-Calderón, B.; Larriba, M.J.; Coronado, M.J.; Soldevilla, B.; et al. Exosomes enriched in stemness/metastatic-related mRNAS promote oncogenic potential in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 40575–40587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, V.; Paryan, M.; Mortazavi, Y.; Biglari, A.; Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S. Evaluation of exosomal miR-9 and miR-155 targeting PTEN and DUSP14 in highly metastatic breast cancer and their effect on low metastatic cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 5666–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, S.; Yin, G.; Yu, G.; Cui, H. Breast cancer cell-derived exosomal miR-20a-5p promotes the proliferation and differentiation of osteoclasts by targeting SRCIN1. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 5687–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, T.; Chen, J.; Li, R.; Chen, H.; Luo, S.; Chen, D.; Cai, C.; Li, W. The role of Exosomal miRNAs in cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, N.; Kosaka, N.; Ono, M.; Katsuda, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Tamura, K.; Lötvall, J.; Nakagama, H.; Ochiya, T. Brain metastatic cancer cells release microRNA-181c-containing extracellular vesicles capable of destructing blood-brain barrier. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Yang, J.; Han, Y.; Lu, Q.; Cao, J.; Syed, L. High expression of miR-210 predicts poor survival in patients with breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Gene 2012, 507, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, P.; Torres-Ruiz, S.; Adam-Artigues, A.; Forés-Martos, J.; Martínez, M.T.; Hernando, C.; Zazo, S.; Madoz-Gúrpide, J.; Rovira, A.; Burgués, O.; et al. miR-146a-5p Promotes Angiogenesis and Confers Trastuzumab Resistance in HER2+ Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, S.; Moradi-Chaleshtori, M.; Paryan, M.; Koochaki, A.; Sharifi, K.; Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes enriched with miR-218 reduce the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Hu, B. Breast cancer derived exosomes promoted angiogenesis of endothelial cells in microenvironment via circHIPK3/miR-124-3p/MTDH axis. Cell Signal 2022, 95, 110338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunusova, N.; Dzhugashvili, E.; Yalovaya, A.; Kolomiets, L.; Shefer, A.; Grigor’eva, A.; Tupikin, A.; Kondakova, I.; Tamkovich, S. Comparative Analysis of Tumor-Associated microRNAs and Tetraspanines from Exosomes of Plasma and Ascitic Fluids of Ovarian Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKiernan, J.; Donovan, M.J.; O’Neill, V.; Bentink, S.; Noerholm, M.; Belzer, S.; Skog, J.; Kattan, M.W.; Partin, A.; Andriole, G.; et al. A Novel Urine Exosome Gene Expression Assay to Predict High-grade Prostate Cancer at Initial Biopsy. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, A.; de Miguel-Pérez, D.; Ortega, F.G.; García-Puche, J.L.; Robles-Fernández, I.; Exposito, J.; Martorell-Marugan, J.; Carmona-Sáez, P.; Garrido-Navas, M.D.C.; Rolfo, C.; et al. Exosomal miRNA profile as complementary tool in the diagnostic and prediction of treatment response in localized breast cancer under neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.-J.; Yang, H.-B.; Jing, J.-F.; Jia, M.-M.; Zhang, X.-J.; Guo, F.; Gao, J.-N. Identification of serum exosomal miR-148a as a novel prognostic biomarker for breast cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 7303–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Iinuma, H.; Umemoto, Y.; Yanagisawa, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Jinno, H. Exosome-encapsulated microRNA-223-3p as a minimally invasive biomarker for the early detection of invasive breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9584–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamkovich, S.; Tutanov, O.; Efimenko, A.; Grigor’eva, A.; Ryabchikova, E.; Kirushina, N.; Vlassov, V.; Tkachuk, V.; Laktionov, P. Blood circulating exosomes contain distinguishable fractions of free and cell-surface-associated vesicles. Curr. Mol. Med. 2019, 19, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschfeld, M.; Rücker, G.; Weiß, D.; Berner, K.; Ritter, A.; Jäger, M.; Erbes, T. Urinary Exosomal MicroRNAs as Potential Non-invasive Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Detection. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 24, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, P.M.M.; Vieira, E.; Lemos, D.S.; Souza, I.L.M.; Zanata, S.M.; Pankievicz, V.C.; Tuleski, T.R.; Souza, E.M.; Wowk, P.F.; Urban, C.; et al. Identification of miRNAs Enriched in Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Serum Samples of Breast Cancer Patients. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, F.S.; Slaibi-Filho, J.; Calasans dos Santos, G.; Carmo, N.T.; Kaneto, C.M.; Borin, T.F.; Luiz, W.B.; Gastalho Campos, L.C. MicroRNA as a promising molecular biomarker in the diagnosis of breast cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1337706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L. Roles and Applications of Red Blood Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Health and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, M.; Sachan, M. An overview of challenges associated with exosomal miRNA isolation toward liquid biopsy-based ovarian cancer detection. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Loke, S.Y.; Tang, Y.C.; Too, H.-P.; Zhou, L.; Lee, A.S.G.; Hartman, M. Development and validation of a circulating microRNA panel for the early detection of breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekka, L.M.S.; Langaee, T.; Johnson, J.A. Comparison of Data Normalization Strategies for Array-Based MicroRNA Profiling Experiments and Identification and Validation of Circulating MicroRNAs as Endogenous Controls in Hypertension. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 836636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; da Silva, A.M.; Calin, G.; Pantel, K. Data Normalization Strategies for MicroRNA Quantification. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skryabin, G.O.; Vinokurova, S.V.; Elkina, N.V.; Denisova, D.A.; Beliaeva, A.A.; Zhordania, K.I.; Bagrov, D.V.; Enikeev, A.D.; Galetsky, S.A.; Komelkov, A.V.; et al. Comparison of methods for microRNA isolation from extracellular vesicles obtained from ascitic fluids. Biochemistry 2022, 87, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueta, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tomiguchi, M.; Takeshita, T.; Yamamoto-Ibusuki, M.; Iwase, H. Differential expression of exosomal miRNAs between breast cancer patients with and without recurrence. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 69934–69944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueta, A.; Fujiki, Y.; Goto-Yamaguchi, L.; Tomiguchi, M.; Yamamoto-Ibusuki, M.; Iwase, H.; Yamamoto, Y. Exosomal miRNA profiles of triple-negative breast cancer in neoadjuvant treatment. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevic, I.; Müller, V.; Weber, K.; Fasching, P.A.; Karn, T.; Marmé, F.; Schem, C.; Stickeler, E.; Denkert, C.; van Mackelenbergh, M.; et al. Specific microRNA signatures in exosomes of triple-negative and HER2-positive breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy within the GeparSixto trial. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Stevic, I.; Pan, C.; Müller, V.; Oliveira-Ferrer, L.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Different signatures of miR-16, miR-30b and miR-93 in exosomes from breast cancer and DCIS patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| # | MicroRNAs | Level Change |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | miR-338-3p | ↑ in serum exosomes of patients with relapse compared to patients without relapse [150] |
| 2 | miR-340-5p | |
| 3 | miR-124-3p | |
| 4 | miR-29b-3p | ↓ in serum exosomes of patients with relapse compared to patients without relapse [150] |
| 5 | miR-20b-5p | |
| 6 | miR-17-5p | |
| 7 | miR-130a-3p | |
| 8 | miR-18a-5p | |
| 9 | miR-195-5p | ↓ in serum exosomes of patients with relapse compared to patients without relapse [150] ↑ in serum exosomes of non-pCR patients with relapse compared to those without it [151] |
| 10 | miR-486-5p | ↓ in serum exosomes of patients with relapse compared to patients without relapse [150] |
| 11 | miR-93-5p | |
| 12 | miR-548ab | ↓ in serum exosomes of non-pCR patients with relapse compared to those without it [151] |
| 13 | miR-155 | ↓ plasma exosomes after therapy, associated with pCR [152] |
| 14 | miR-301 | |
| 15 | miR-30b | ↓ in plasma exosomes of patients with relapse compared with primary BC patients [153] |
| 16 | miR-16 | ↑ in plasma exosomes of patients with relapse compared with healthy donors [153] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamkovich, S.; Borisova, A.; Shevela, A.; Chernyavskiy, A.; Chernyshovа, A. Exosomal MicroRNA: Diagnostic Potential and Role in Breast Cancer Dissemination. Molecules 2025, 30, 3858. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193858
Tamkovich S, Borisova A, Shevela A, Chernyavskiy A, Chernyshovа A. Exosomal MicroRNA: Diagnostic Potential and Role in Breast Cancer Dissemination. Molecules. 2025; 30(19):3858. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193858
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamkovich, Svetlana, Alexandra Borisova, Andrey Shevela, Alexander Chernyavskiy, and Alyona Chernyshovа. 2025. "Exosomal MicroRNA: Diagnostic Potential and Role in Breast Cancer Dissemination" Molecules 30, no. 19: 3858. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193858
APA StyleTamkovich, S., Borisova, A., Shevela, A., Chernyavskiy, A., & Chernyshovа, A. (2025). Exosomal MicroRNA: Diagnostic Potential and Role in Breast Cancer Dissemination. Molecules, 30(19), 3858. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193858







