Semi-Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Sinomenine Derivatives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
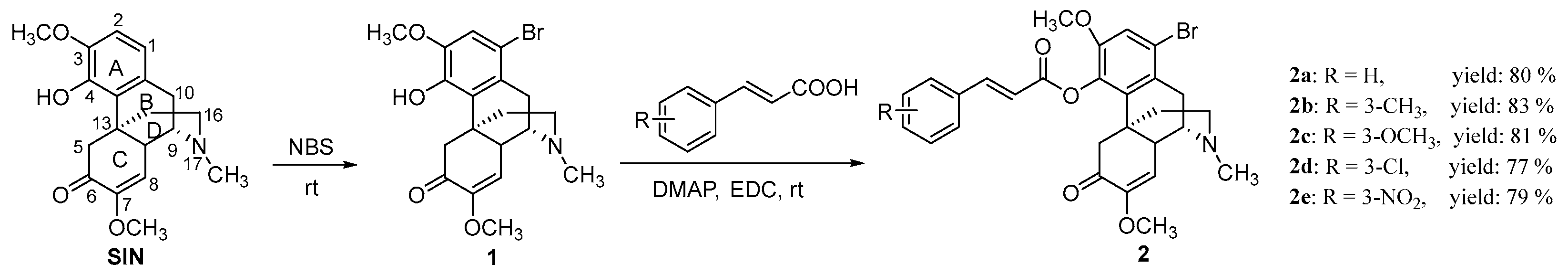
2.1. Chemical Synthesis
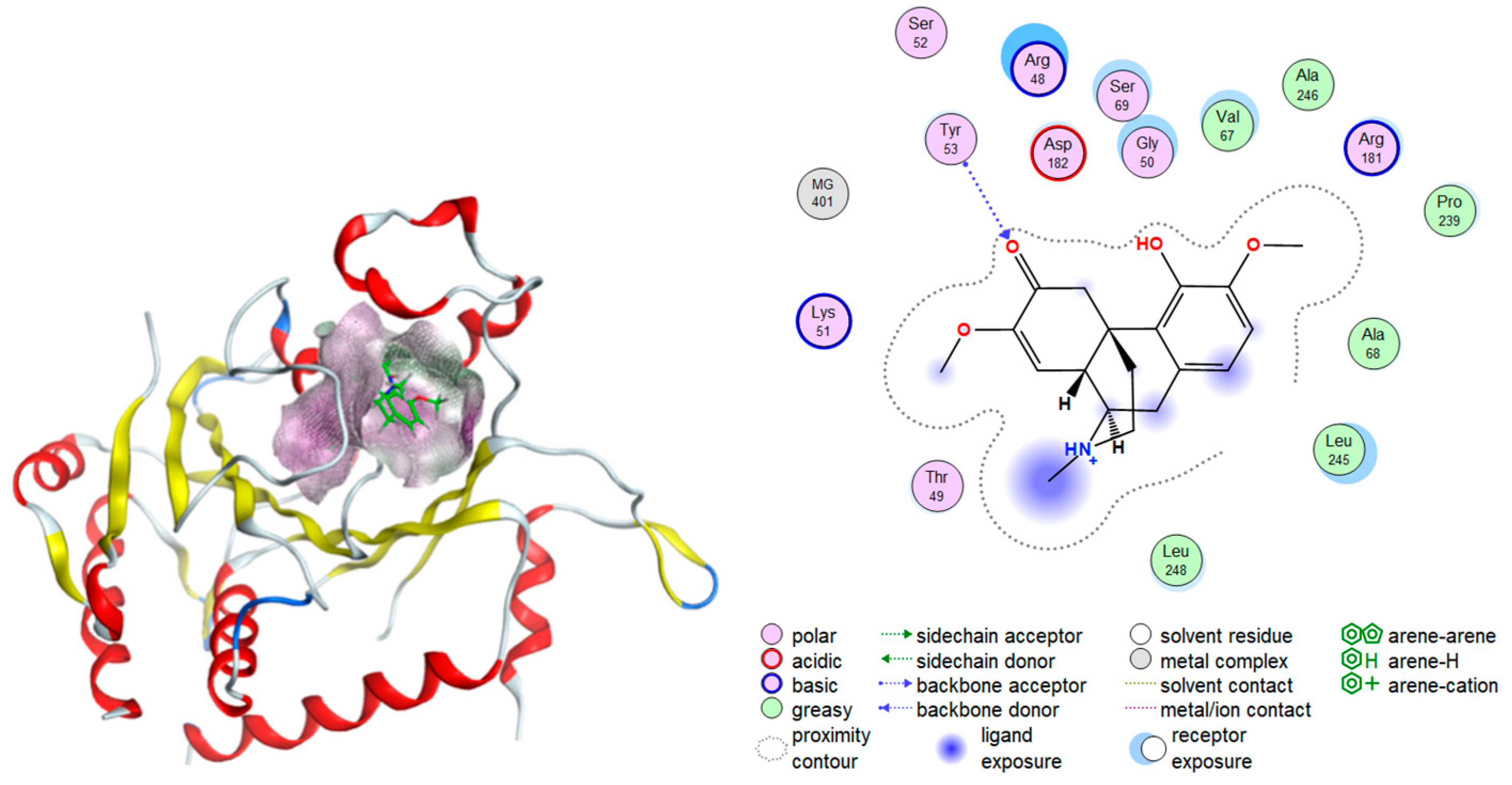
2.2. Molecular Docking Test
2.3. Druggability Analysis
2.4. Hot Plate Method
2.5. Acetic Acid-Induced Writhing Test
2.6. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Capacity in Mouse Ear Edema Model
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Synthesis and Chemical Characterization
3.3. Molecular Docking Test
3.4. Druggability Analysis
3.5. Bioassay for In Vivo Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3.5.1. Hot Plate Method
3.5.2. Acetic Acid-Induced Writhing Test
3.5.3. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Capacity in Mouse Ear Edema Model
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.-X.; Yin, M.-J.; Sun, R.-Z.; Xue, L.; Huang, X.-S.; Wang, C.-H.; Yan, X.-H. Full-Length Transcriptome and Metabolite Analysis Reveal Reticuline Epimerase-Independent Pathways for Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloids Biosynthesis in Sinomenium Acutum. Front. Plant. Sci. 2022, 13, 1086335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lai, F.; Xiang, T.; Xu, Y. Integrated Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Experimental Validation to Explore Potential Mechanisms of Sinomenine in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2024, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ji, J.-Y.; Feng, Z.-T.; Hou, X.-Q.; Luo, Y.-N.; Mei, Z.-G. A network pharmacology approach to explore the potential targets underlying the effect of sinomenine on rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, N.; Wang, L.; An, L.-L.; Xu, Y.-K. Exploring the active ingredients and potential mechanisms of action of sinomenium acutum in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis based on systems biology and network pharmacology. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1065171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Mao, J.-Y.; Zhou, X.-H.; Xu, Z.-D. Network pharmacological investigation of sinomenine action against synovitis. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 18, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Dong, L.; Pan, H.-M.; Wu, X.-D.; Chen, X.; Gu, W.-G.; Tao, N.-L.; Wang, A.; Zhang, K.-H.; Jin, J. Design and synthesis of C-ring quinoxaline-substituted sinomenine 1,2,3-triazole derivatives via click reactions. J. Chem. Res. 2020, 44, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Riese, J.; Resch, K.; Kaever, V. Impairment of macrophage eicosanoid and nitric oxide production by an alkaloid from Sinomenium acutum. Arzneimittel-Forschung. 1994, 44, 1223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsov, A.V.; Schneeberger, S.; Seiler, R.; Brandacher, G.; Mark, W.; Steurer, W.; Saks, V.; Usson, Y.; Maimund, M.; Gnaiger, E. Mitochondrial defects and heterogeneous cytochrome c release after cardiac cold ischemia and reperfusion. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart C 2004, 286, H1633–H1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.F.; Han, Z.Y.; Zhou, X.L.; Gong, L.Z. ChemInform Abstract: Asymmetric Organocatalysis Combined with Metal Catalysis: Concept, Proof of Concept, and Beyond. J. Chem. Res. 2014, 38, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, P.; Liu, H.-L.; Zhang, L.; Feng, L.-L.; Huai, Y.; Deng, Z.-S.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Q.; Li, J.-X. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel sinomenine derivatives as anti-inflammatory agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 50, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.-Y.; Guan, Z.-J.; Yu, S.-C.; Zhao, Q.-J.; Hu, H.-G.; Zou, Y.; Tao, X.; Wu, Q.-Y. Design, synthesis and molecular docking studies of sinomenine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 5849. [Google Scholar]
- Selfridge, B.R.; Wang, X.-H.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Yin, H.; Grace, P.M.; Watkins, L.R.; Jacobson, A.E.; Rice, K.C. Structure–Activity Relationships of (+)-Naltrexone-Inspired Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.P.; Hoye, T.R. Reactions of hexadehydro-Diels–Alder benzynes with structurally complex multifunctional natural products. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-J.; Luo, D.; Gao, H.-S.; Jiang, N.-F.; Ding, A.-S. Highly regioselective synthesis of C-4 (ring A) sinomenine ether derivatives. J. Chem. Res. 2012, 36, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-J.; Gao, M.-J.; Nian, X.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Li, J.-J.; Cui, D.-M.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, C.-Q. Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Silico Prediction of Novel Sinomenine Derivatives. Molecules 2021, 26, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Zhang, S.-J.; Liao, J.-J.; Gong, Z.-P.; Chai, X.; Lyu, H.-N. Towards Better Sinomenine-Type Drugs to Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis: Molecular Mechanisms and Structural Modification. Molecules 2022, 27, 8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Fan, L.-P.; Yu, Q.; Li, Y.-Q.; Tong, L.; Gao, C.-F. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of acerola based on LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages and xylene-induced ear edema in mouse. J. Funct. Foods 2025, 124, 106639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoareau, L.; Buyse, M.; Festy, F.; Ravanan, P.; Gonthier, M.-P.; Matias, I.; Petrosino, S.; Tallet, F.; D’Hellencourt, C.L.; Cesari, M.; et al. Anti-inflammatory Effect of Palmitoylethanolamide on Human Adipocytes. Obesity 2012, 17, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, C.-B.; Raza, A.; Tang, J.; Ouyang, Z.; Su, Z.-L.; Xu, H.-X. Synthesis and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Sinomenine 4-Hydroxy Esters. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2018, 54, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Deng, H.-S.; Yao, Y.-D.; Wang, W.-T.; Hu, J.-Q.; Dong, Y.; Wang, P.-X.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Xie, Y.; et al. Sinomenine ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by targeting GBP5 and regulating the P2X7 receptor to suppress NLRP3-related signaling pathways. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 2504–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, P.C.; Afiukwa, C.A.; Orji, O.U.; Ezeh, E.; Ofoke, I.H.; Ogbu, C.O.; Ugwuja, E.I.; Aja, P.M. Molecular docking as a tool for the discovery of molecular targets of nutraceuticals in diseases management. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Dai, Z.-Q.; Zhang, T.; Gu, Y.-H.; Cai, D.-S.; Lu, M.-J.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Zeng, Q.; Shang, B.-X.; Xu, B.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel sinomenine derivatives as anti-inflammatory and analgaesic agent. RSC Advances 2022, 12, 30001–30007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Q.; Wang, H.-J.; Yuan, J.-Q.; Li, X.-Y.; Fang, N.; Lin, M.-B.; Hou, Q.; Ji, T.-F. Design, synthesis, and pharmacological evaluation of sinomenine derivatives on rings A and C: Novel compounds screening for aplastic anemia targeting on cytotoxic T lymphocyte. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 225, 113791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, R.H.S.; Pessoa, R.B.; Alshehri, S.A.; Wahab, S.; Ahmad, M.F.; Suliman, M.; Da Silva, L.Y.S.; Alcantara, I.S.; Guedes, A.; Ramos, B.; et al. Mechanisms of Actions Involved in The Antinociceptive Effect of Estragole and its β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex in Animal Models. Plants 2022, 11, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, T.; Hasan, T.; Ahmed, K.S.; Hossain, H.; Debnath, T.; Jahan, E.; Rahman, N.; Shuvo, M.S.R.; Daula, A.S.U. Phenolic compounds and extracts from Crotalaria calycina Schrank potentially alleviate pain and inflammation through inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2: An in vivo and molecular dynamics studies. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.C.; Jeong, Y.; Cho, W.K.; Ha, J.H.; Gu, M.; Ma, J. Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effects of Pyeongwisan on LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages and Mouse Models of Acetic Acid-Induced Writhing Response and Xylene-Induced Ear Edema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1232–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Model | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|
| SIN | −6.65 |
| 2a | −7.61 |
| 2b | −7.17 |
| 2c | −9.31 |
| 2d | −7.54 |
| 2e | −8.57 |
| Drug | logP | F50% | PPB | BBB | HLM Stability | T1/2 | HH | DIN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIN | 0.67 | 0.7–0.9 | 39.2% | 0.1–0.3 | 0.5–0.7 | 3.60 | 0.583 | 0.255 |
| 2a | 3.75 | 0.3–0.5 | 96.0% | 0.7–0.9 | 0–0.1 | 1.88 | 0.675 | 0.425 |
| 2b | 4.01 | 0.3–0.5 | 96.5% | 0.7–0.9 | 0.1–0.3 | 1.52 | 0.685 | 0.448 |
| 2c | 3.78 | 0.5–0.7 | 95.7% | 0.1–0.3 | 0–0.1 | 1.70 | 0.621 | 0.524 |
| 2d | 4.06 | 0.3–0.5 | 97.3% | 0.9–1.0 | 0–0.1 | 1.31 | 0.685 | 0.621 |
| 2e | 3.57 | 0.1–0.3 | 97.6% | 0.1–0.3 | 0–0.1 | 1.57 | 0.676 | 0.343 |
| Compounds | Dose (mg/kg) | Pain Threshold Before Administration ± s (s) | Pain Threshold at Different Times After Administration (s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 min | 30 min | 60 min | |||
| SIN | 15 | 9.91 ± 2.62 | 10.39 ± 3.26 ▲ | 11.63 ± 2.36 *▲ | 10.72 ± 3.07 |
| 2aC1 | 30 | 7.59 ± 1.67 | 9.92 ± 2.66 *▲ | 9.26 ± 3.19 Δ | 8.85 ± 2.08 * |
| 2aC2 | 15 | 8.34 ± 3.14 | 8.33 ± 1.87 | 6.88 ± 3.17 *Δ | 8.15 ± 2.49 Δ |
| 2aC3 | 7.5 | 7.62 ± 2.35 | 8.74 ± 3.46 | 9.96 ± 2.79 ▲ | 8.42 ± 3.26 |
| 2bC1 | 30 | 7.25 ± 2.19 | 10.30 ± 2.51 *▲ | 9.67 ± 3.19 *▲ | 7.66 ± 2.95 Δ |
| 2bC2 | 15 | 6.36 ± 1.24 | 7.63 ± 1.43 *Δ | 6.57 ± 1.61 Δ | 7.18 ± 2.25 Δ |
| 2bC3 | 7.5 | 6.10 ± 1.04 | 7.52 ± 2.51 *Δ | 7.92 ± 2.19 *Δ | 6.97 ± 2.20 Δ |
| 2cC1 | 30 | 8.72 ± 1.86 | 8.05 ± 2.27 | 9.85 ± 1.20 *▲Δ | 10.29 ± 1.57 *▲ |
| 2cC2 | 15 | 8.40 ± 2.44 | 7.85 ± 1.85 Δ | 7.63 ± 1.22 Δ | 7.39 ± 0.68 Δ |
| 2cC3 | 7.5 | 7.72 ± 1.30 | 7.77 ± 1.52 Δ | 8.76 ± 1.62 Δ | 6.71 ± 2.24 Δ |
| 2dC1 | 30 | 8.30 ± 2.71 | 10.88 ± 3.10 *▲ | 8.17 ± 3.60 Δ | 10.07 ± 3.57 * |
| 2dC2 | 15 | 6.40 ± 2.76 | 7.67 ± 3.02 * | 7.57 ± 2.00 Δ | 9.21 ± 2.75 * |
| 2dC3 | 7.5 | 8.20 ± 2.05 | 9.31 ± 2.58 | 8.36 ± 2.56 Δ | 8.72 ± 1.79 |
| 2eC1 | 30 | 8.36 ± 1.30 | 11.17 ± 2.53 *▲ | 8.26 ± 2.12 Δ | 10.96 ± 3.48 ▲ |
| 2eC2 | 15 | 7.50 ± 2.80 | 9.30 ± 2.52 | 9.19 ± 4.32 | 10.26 ± 3.63 * |
| 2eC3 | 7.5 | 6.56 ± 0.99 | 7.43 ± 2.09 Δ | 7.65 ± 2.56 Δ | 8.17 ± 2.48 Δ |
| saline | 7.70 ± 1.56 | 7.53 ± 1.59 | 7.07 ± 1.65 | 8.26 ± 1.79 | |
| Compounds | Dose (mg/kg) | The Prolonged Rate of Latency (%) | Writhing Times Inhibition Rate (%) | Percentage of Analgesia (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIN | 15 | 39.10 | 29.47 | 0 |
| 2aC1 | 30 | 31.33 | 43.72 | 0 |
| 2aC2 | 15 | 32.25 | 36.59 | 0 |
| 2aC3 | 7.5 | 24.99 | 46.85 | 0 |
| 2bC1 | 30 | 35.50 | 33.07 | 0 |
| 2bC2 | 15 | 33.05 | 25.12 | 0 |
| 2bC3 | 7.5 | 17.64 | 18.36 | 0 |
| 2cC1 | 30 | 11.44 | 57.13 | 0 |
| 2cC2 | 15 | 27.77 | 29.95 | 0 |
| 2cC3 | 7.5 | 38.31 | 28.14 | 0 |
| 2dC1 | 30 | 11.56 | 35.27 | 0 |
| 2dC2 | 15 | 23.08 | 39.61 | 0 |
| 2dC3 | 7.5 | 28.51 | 37.20 | 0 |
| 2eC1 | 30 | 55.56 | 57.00 | 0 |
| 2eC2 | 15 | 20.85 | 45.65 | 0 |
| 2eC3 | 7.5 | 19.79 | 24.64 | 0 |
| saline | 18.10 | 0 |
| Compounds | Dose (mg/kg) | Auricular Swelling Degree (X ± s) | Swelling Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIN | 30 | 0.0043 ± 0.0016 ▲ | 32.26 |
| 2a | 30 | 0.0049 ± 0.0018 | 20.98 |
| 2b | 30 | 0.0040 ± 0.0016 ▲ | 35.48 |
| 2c | 30 | 0.0047 ± 0.0026 | 24.19 |
| 2d | 30 | 0.0061 ± 0.0028 | 1.61 |
| 2e | 30 | 0.0044 ± 0.0017 ▲ | 29.03 |
| saline | 0.0062 ± 0.0024 Δ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Z. Semi-Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Sinomenine Derivatives. Molecules 2025, 30, 3802. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183802
Wu M, Zhang Z, Li Z, Zhao Z. Semi-Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Sinomenine Derivatives. Molecules. 2025; 30(18):3802. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183802
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Meichun, Zhewei Zhang, Ze Li, and Zijian Zhao. 2025. "Semi-Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Sinomenine Derivatives" Molecules 30, no. 18: 3802. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183802
APA StyleWu, M., Zhang, Z., Li, Z., & Zhao, Z. (2025). Semi-Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Sinomenine Derivatives. Molecules, 30(18), 3802. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183802





