Development of TaqMan Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Method for Identification and Quantification of Sinomenium acutum-Originated Herbal Drugs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments and Reagents
2.2. Sample Collection and Identification
2.3. Preparation of the Freeze-Dried Powder of QFT Aqueous Decoction
2.4. DNA Extraction
2.5. ITS2 Sequence Analysis and Probe/Primer Design
2.6. Optimization of qPCR Amplification System
2.7. Specificity Test
2.8. Amplification Efficiency (E), Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
2.9. Repeatability and Robustness Test
2.10. Applicability Test
2.11. Accuracy Test
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Specificity of Probes and Primers
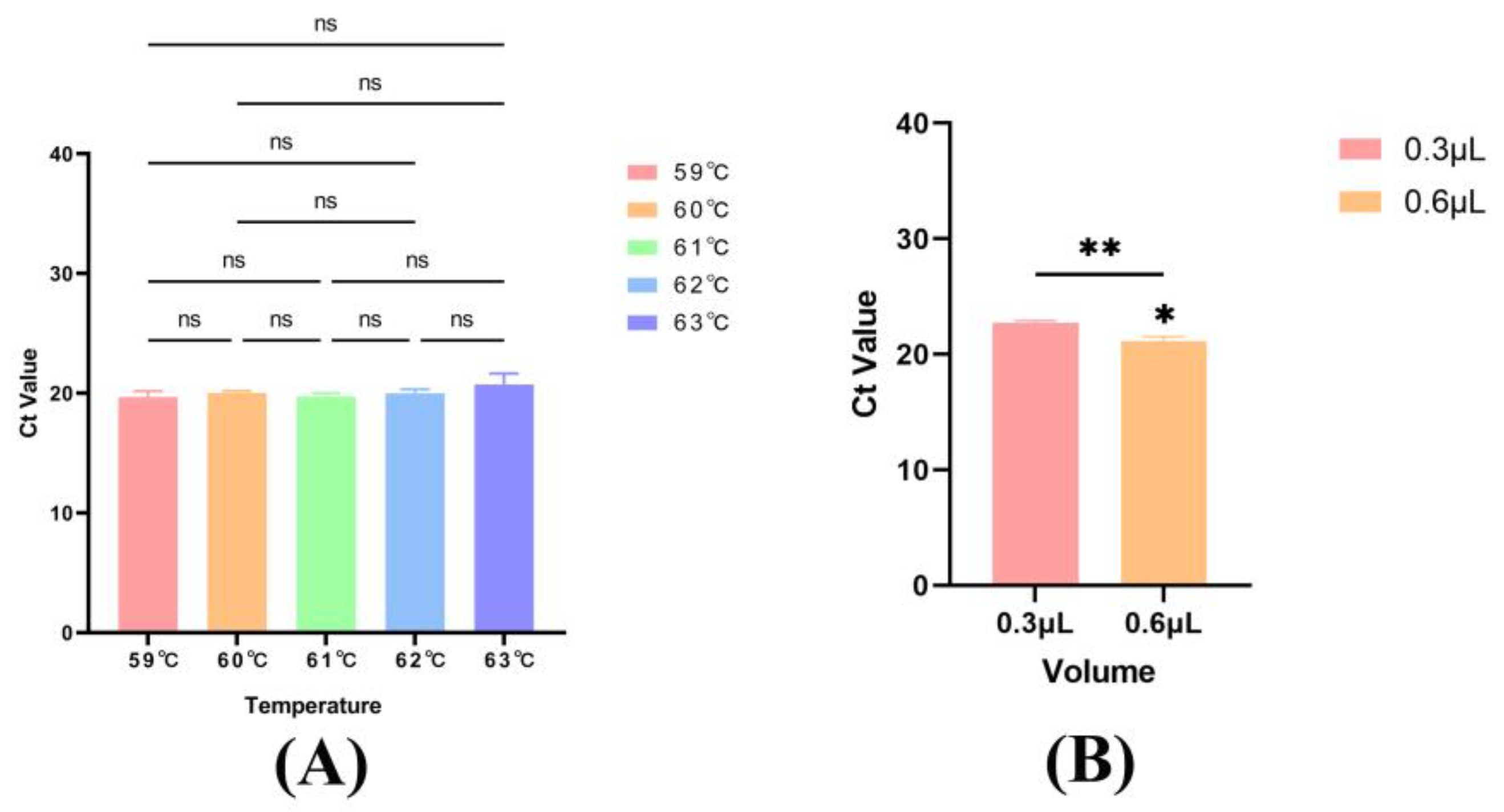
3.2. Optimization of Annealing Temperature, Probe and Primer Concentration
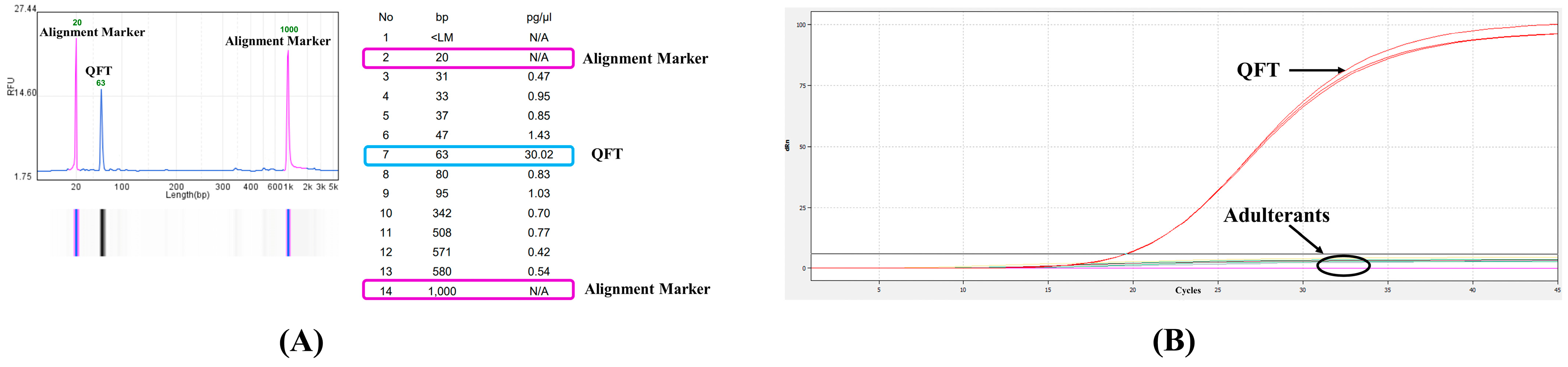
3.3. Specificity Evaluation
3.4. Amplification Efficiency (E), LOD and LOQ
3.5. Repeatability and Robustness Analysis
3.6. Applicability
3.7. Accuracy Analysis
3.8. Analysis of BiKePian and Laboratory-Prepared Aqueous Decoctions Using qPCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Committee, N.P. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, M.-J.; Hu, Y.-F.; Zhu, Y.-B.; Chou, P.; Li, Z.; Li, W.-L. Quality control of Sinomenii caulis based on chromatographic fingerprints and content determination. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2022, 53, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, Y.-Q.; Li, X.-S.; Lu, Y.-Y.; Tu, P.-F. Development of an integrated strategy for comprehensive characterization of Sinomenii caulis extract and metabolites in rats based on UPLC/Q-TOF-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 249, 116391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M.; Yao, Y.-D.; Luo, J.-F.; Liu, J.-X.; Lu, L.-L.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Dong, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, H. Pharmacological mechanisms of sinomenine in anti-inflammatory immunity and osteoprotection in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Phytomedicine 2023, 121, 155114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-F. Pharmacodynamics and Mechanism of BKP on Gouty Arthritis. Master’s Thesis, Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.-Y.; Qiao, K.-W.; Li, Y.-Y.; Zhou, X.-X.; Yang, H.; Xiong, X.-Y. Analysis of sinomenine synthesis pathway based on transcriptome sequencing in Sinomenii caulis. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2019, 50, 5537–5544. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, H.-N.; Zeng, K.-W.; Cao, N.-K.; Zhao, M.-B.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, P.-F. Alkaloids from the stems and rhizomes of Sinomenium acutum from the Qinling Mountains, China. Phytochemistry 2018, 156, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C. Research and Application of Sinomenium acutun DNA Barcoding. Master’s Thesis, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Han, W.-K.; Chayanis, S.; Cui, Y.-J.; Zeng, X.-Y. Pharmacognosy research on Sinomenii caulis and its adulterants. Acad. J. Shanghai Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 36, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, S.; Hossain, M.-M.; Azlan, A.; Johan, M.-R.; Chowdhury, Z.-Z.; Ali, M.-E. TaqMan probe based multiplex quantitative PCR assay for determination of bovine, porcine and fish DNA in gelatin admixture, food products and dietary supplements. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Gómez, S.; Busto, M.-D.; Ortega, N. Detection of Hazelnut and Almond Adulteration in Olive Oil: An Approach by qPCR. Molecules 2023, 28, 4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenuga, B.-M.; Biltes, R.; Villa, C.; Costa, J.; Spychaj, A.; Montowska, M.; Mafra, I. A Novel Normalized Quantitative Real-Time PCR Approach for Ensuring Roe Deer (Capreolus capreolus) Meat Authenticity in Game Meat Foods. Foods 2024, 13, 3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.-Q.; Yang, G.-P.; Hu, Z.; Chen, K.-W.; Guo, W.; Wang, X.-J.; Du, C. Development of a Real-Time Quantitative PCR Based on a TaqMan-MGB Probe for the Rapid Detection of Theileria haneyi. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yossa, N.; Huang, S.; Canida, T.; Binet, R.; Macarisin, D.; Bell, R.; Tallent, S.; Brown, E.; Hammack, T. qPCR detection of viable Bacillus cereus group cells in cosmetic products. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-X.; Shi, J.-H.; Li, X.; Coin, L.; O’Brien, J.-W.; Sivakumar, M.; Hai, F.; Jiang, G.-M. Triplex qPCR assay for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli monitoring in wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Q.; Xin, T.-Y.; Xu, W.-J.; Li, R.-J.; Song, J.-Y. TaqMan Probe-Based Quantitative Real-Time PCR to Detect Panax notoginseng in Traditional Chinese Patent Medicines. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 828948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-J.; Cui, S.-H.; Cheng, X.-L.; Wei, F.; Ma, S.-C. An optimized TaqMan real-time PCR method for authentication of ASINI CORII COLLA (donkey-hide gelatin). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 170, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Ren, Y.; Su, Y.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.-F.; Zhao, H.-X.; Zhang, H.-X.; Han, J.-P. Identification of toxic Gelsemium elegans in processed food and honey based on real-time PCR analysis. Food Res. Int. 2024, 182, 114188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-J.; Zhu, P.-Y.; Xin, T.-Y.; Lou, Q.; Li, R.-J.; Fu, W.; Ma, T.-Y.; Song, J.-Y. Droplet digital PCR for the identification of plant-derived adulterants in highly processed products. Phytomedicine 2022, 105, 154376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.-L.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Wang, Y.-D.; Cheng, X.-L.; Jin, H.-Y.; Wei, F.; Ma, S.-C. MGB probe-based multiplex droplet digital PCR for the interspecific identification of Notopterygii Rhizoma et Radix in herbal materials and preparations. Phytomedicine 2025, 136, 156325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Scientific and Technical Research Reports. Definition of Minimum Performance Requirements for Analytical Methods of GMO Testing European Network of GMO Laboratories (ENGL); Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bustin, S.-A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.-A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.-W.; Shipley, G.-L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwobi, A.; Sebah, D.; Kraemer, I.; Losher, C.; Fishcher, G.; Busch, U.; Huber, I. A multiplex real-time PCR method for the quantification of beef and pork fractions in minced meat. Food Chem. 2015, 169, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Andreo, M.; Aldeguer, M.; Guillén, I.; Gabaldón, J.-A.; Puyet, A. Detection and quantification of meat species by qPCR in heat-processed food containing highly fragmented DNA. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulca, P.; Balta, H.; Çağın, İ.; Senyuva, H.Z. Meat species identification and Halal authentication using PCR analysis of raw and cooked traditional Turkish foods. Meat Sci. 2013, 94, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druml, B.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Hochegger, R.; Cichna-Markl, M. A novel reference real-time PCR assay for the relative quantification of (game) meat species in raw and heat-processed food. Food Control 2016, 70, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-H.; Zheng, T.; Yue, G.-G.-L.; Li, M.-C.; Wu, H.-Y.; Tong, M.-H.; Zhao, X.-L.; Chen, H.-B.; Lau, C.-B.-S.; Shaw, P.-C.; et al. A systematic approach for authentication of medicinal Patrinia species using an integration of morphological, chemical and molecular methods. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.-T.; Shaw, P.-C. Quantification of concentrated Chinese medicine granules by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Dosage Form | Sample NO. | Latin Name | Place of Production/Collection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medicinal materials | QFT01 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | National Institutes for Food and Drug Control; Beijing, China |
| Decoction pieces | QFT02 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Anhui Jiren pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; Bozhou, China |
| QFT03 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange/Hubei; Bozhou, China | |
| QFT04 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange/Hubei; Bozhou, China | |
| QFT05 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange/Hubei; Bozhou, China | |
| QFT06 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange/Yuexi, Anqing, Anhui, China; Bozhou, China | |
| QFT07 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange/Enshi, Hubei, China; Bozhou, China | |
| QFT08 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange/Huaihua, Hunan, China; Bozhou, China | |
| Medicinal materials | QFT09 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Fangxian, Shiyan, Hubei, China; Hubei, China |
| QFT10 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils.var. cinereum Rehd. et Wils. | Fangxian, Shiyan, Hubei, China; Hubei, China | |
| Decoction pieces | QFT11 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Yuzhou Chinese Medicine Exchange/Hubei; Yuzhou, Henan, China |
| QFT12 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange/Hubei; Bozhou, China | |
| QFT13 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange/Hubei; Bozhou, China | |
| QFT14 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange/Hubei; Bozhou, China | |
| QFT15 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange; Bozhou, China | |
| QFT16 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange; Bozhou, China | |
| QFT17 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Yulin Chinese Medicine Exchange/Hubei; Yulin, Guangxi, China | |
| QFT18 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Yulin Chinese Medicine Exchange/Hunan; Yulin, Guangxi, China | |
| QFT19 | Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils. | Yulin Chinese Medicine Exchange/Hubei; Yulin, Guangxi, China | |
| Medicinal materials | BDG01 | Menispermum dauricum DC. | National Institutes for Food and Drug Control; Beijing, China |
| Decoction pieces | BDG02 | Menispermum dauricum DC. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange; Bozhou, China |
| BDG03 | Menispermum dauricum DC. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange; Bozhou, China | |
| BDG04 | Menispermum dauricum DC. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange; Bozhou, China | |
| BDG05 | Menispermum dauricum DC. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange/Heilongjiang; Bozhou, China | |
| BDG06 | Menispermum dauricum DC. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange; Bozhou, China | |
| BDG07 | Menispermum dauricum DC. | Yulin Chinese Medicine Exchange/Hubei; Yulin, Guangxi, China | |
| BDG08 | Menispermum dauricum DC. | Yulin Chinese Medicine Exchange; Yulin, Guangxi, China | |
| KJT01-05 | Tinospora sinensis (Lour.) Merr. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange; Bozhou, China | |
| JST01-05 | Paederia foetida L. | Bozhou Chinese Medicine Exchange; Bozhou, China | |
| HBQFT01-05 | Sabia discolor Dunn | Yulin Chinese Medicine Exchange/Guilin; Yulin, Guangxi, China | |
| QST01-05 | Periploca calophylla (Wight) Falc. | Hehuachi Chinese Medicine Exchange/Zhejiang; Chengdu, Sichuan, China | |
| Preparations | BKP01-06 | / | Hefei Jinyue Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; Hefei, China |
| Laboratory-prepared QFT aqueous decoctions | LAD01-06 | Laboratory-prepared; Beijing, China |
| NO. | Sequence (5′→3′) | Primers and Probe | Length (bp) | Detection Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | FAM-TCCCAACCCAAAGGGAGGGAGTG-BHQ | QFT-1_P | 55 | ITS2 regions of QFT |
| CCTGCATTGCGCCAC | QFT-1_F | |||
| GTCACGGGAGGCCAATT | QFT-1_R | |||
| b | FAM-TTGCCATCGAGGGTAAATTGAACCCTTGT-BHQ | QFT-2_P | 77 | |
| GAAATAGGATGACTTGATCGAGTAG | QFT-2_F | |||
| TGGGGTCGCATGGTATATG | QFT-2_R | |||
| c | FAM-CCATCGAGGGTAAATTGAACCCTTGTAGCT-BHQ | QFT-3_P | 73 | |
| TAGGATGACTTGATCGAGTAGTTG | QFT-3_F | |||
| TGGGGTCGCATGGTATATG | QFT-3_R | |||
| d | FAM-CCAACCCAAAGGGAGGGAGTGAA-BHQ | QFT-4_P | 57 | |
| CTGCATTGCGCCACTC | QFT-4_F | |||
| GAGTCACGGGAGGCC | QFT-4_R |
| DNA Concentration (ng/µL) | Ct (Mean ± SD) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.33 | 21.32 ± 0.28 | 1.31% |
| 0.133 | 25.84 ± 0.28 | 1.08% |
| 0.0133 | 29.54 ± 0.64 | 2.17% |
| 0.00133 | 33.30 ± 0.69 | 2.07% |
| 0.000133 (LOD, LOQ) | 36.24 ± 0.71 | 1.96% |
| 0.0000133 | ND (Not detected) |
| QFT | Adulterants | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | Ct (Mean ± SD) | CV (%) | NO. | Ct (Mean ± SD) | CV (%) | NO. | Ct |
| QFT01 | 18.39 ± 0.10 | 0.54 | QFT11 | 18.45 ± 0.17 | 0.92 | BDG01~08 | - |
| QFT02 | 19.00 ± 0.45 | 2.37 | QFT12 | 19.20 ± 0.23 | 1.20 | JST01~05 | - |
| QFT03 | 19.44 ± 0.33 | 1.70 | QFT13 | 19.37 ± 0.36 | 1.86 | KJT01~05 | - |
| QFT04 | 19.97 ± 0.09 | 0.45 | QFT14 | 19.34 ± 0.19 | 0.98 | QST01~05 | - |
| QFT05 | 19.56 ± 0.02 | 0.10 | QFT15 | 20.71 ± 0.16 | 0.77 | HBQFT01~05 | - |
| QFT06 | 20.02 ± 0.34 | 1.70 | QFT16 | 19.50 ± 0.06 | 0.31 | ||
| QFT07 | 19.64 ± 0.27 | 1.37 | QFT17 | 19.05 ± 0.04 | 0.21 | ||
| QFT08 | 19.29 ± 0.08 | 0.41 | QFT18 | 20.81 ± 0.12 | 0.58 | ||
| QFT09 | 20.88 ± 0.17 | 0.81 | QFT19 | 19.14 ± 0.39 | 2.04 | ||
| QFT10 | 19.32 ± 0.10 | 0.52 | |||||
| Theoretical Value of QFT (%) | Ct (Mean ± SD) | Measured Value (%) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50% | 19.90 ± 0.25 | 40.90% | 81.79% |
| 95% | 18.65 ± 0.15 | 97.27% | 102.38% |
| 99% | 19.03 ± 0.41 | 95.93% | 96.90% |
| 100% | 18.61 ± 0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, Y.; Duan, S.; Yu, K.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, F. Development of TaqMan Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Method for Identification and Quantification of Sinomenium acutum-Originated Herbal Drugs. Molecules 2025, 30, 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183763
Tao Y, Duan S, Yu K, Cheng X, Li X, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Wei F. Development of TaqMan Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Method for Identification and Quantification of Sinomenium acutum-Originated Herbal Drugs. Molecules. 2025; 30(18):3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183763
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Ye, Shuchen Duan, Kunzi Yu, Xianlong Cheng, Xiangri Li, Wenjuan Zhang, Yazhong Zhang, and Feng Wei. 2025. "Development of TaqMan Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Method for Identification and Quantification of Sinomenium acutum-Originated Herbal Drugs" Molecules 30, no. 18: 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183763
APA StyleTao, Y., Duan, S., Yu, K., Cheng, X., Li, X., Zhang, W., Zhang, Y., & Wei, F. (2025). Development of TaqMan Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Method for Identification and Quantification of Sinomenium acutum-Originated Herbal Drugs. Molecules, 30(18), 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183763






