Formation of Racemic Phases of Amino Acids by Liquid-Assisted Resonant Acoustic Mixing Monitored by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
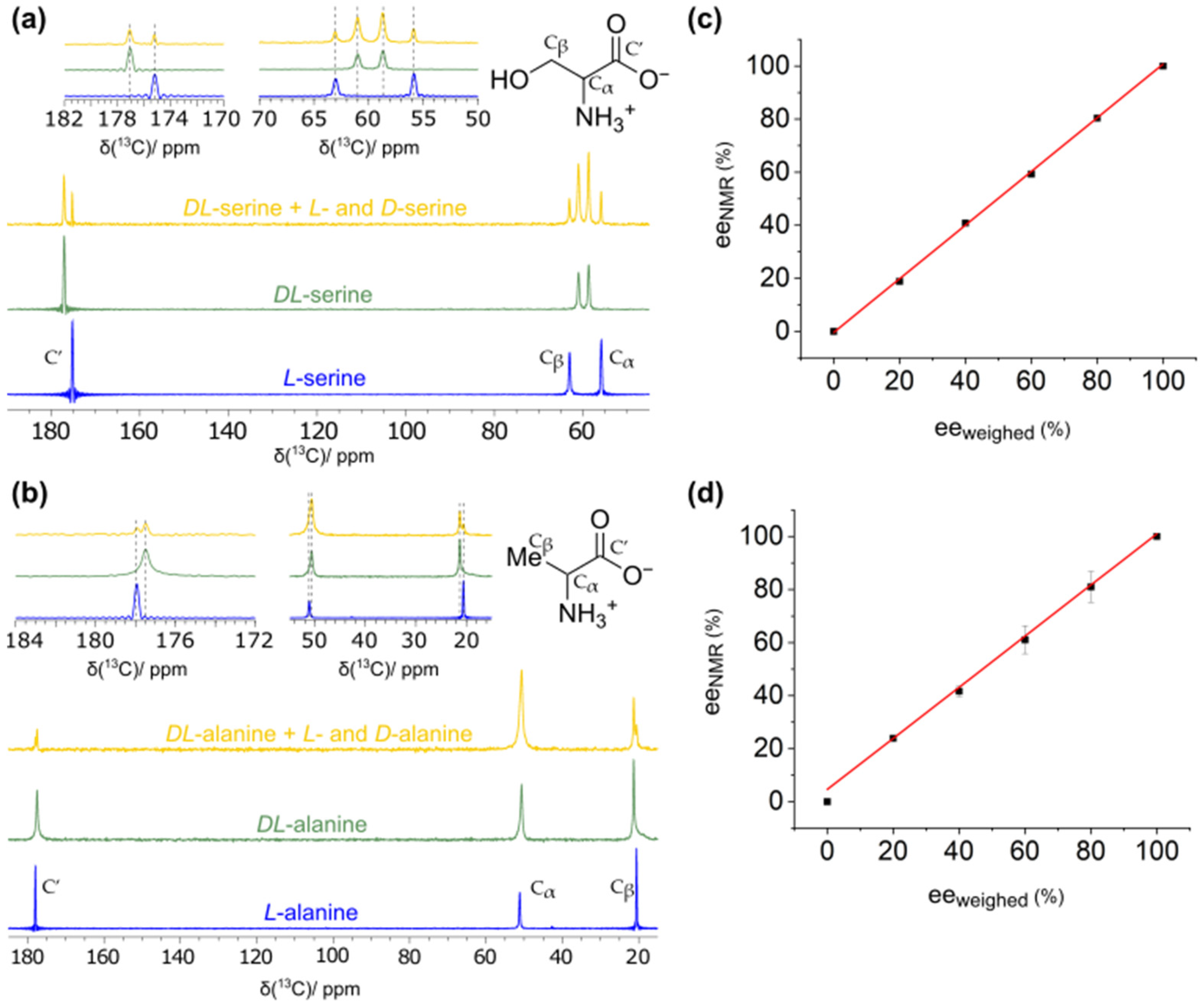
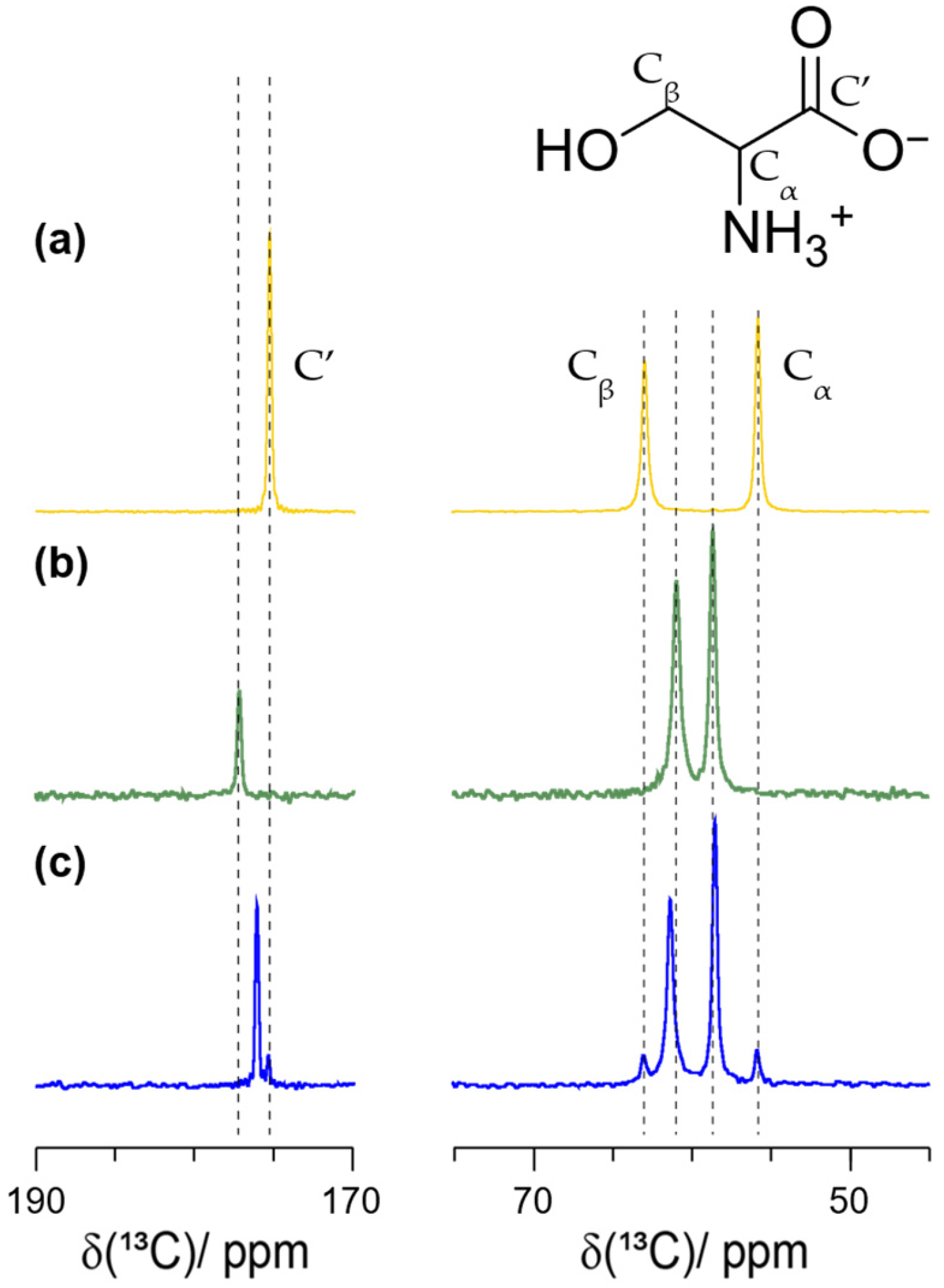
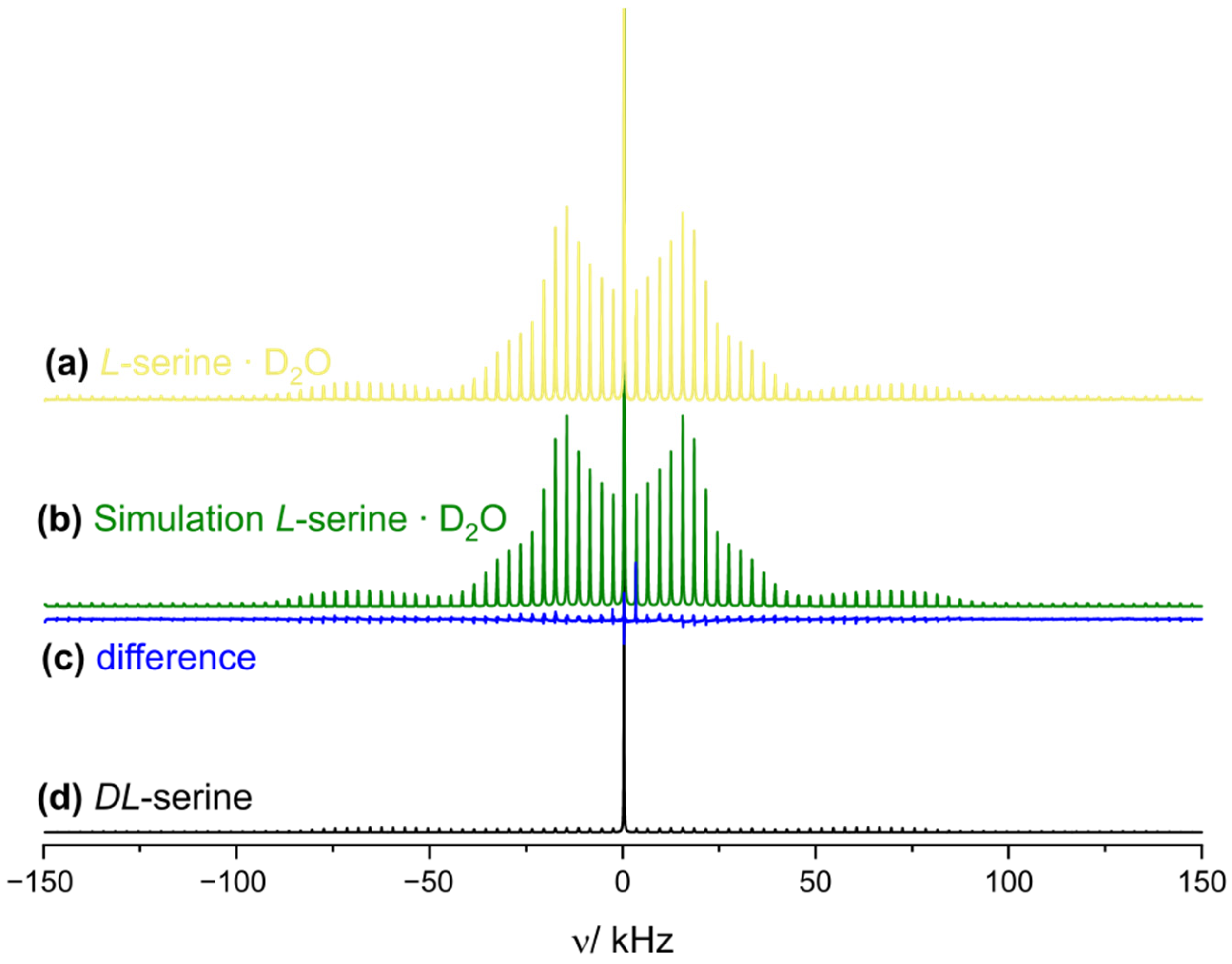
2.1. Determination of Enantiomeric Excesses from Carbon-13-Detected MAS Spectra
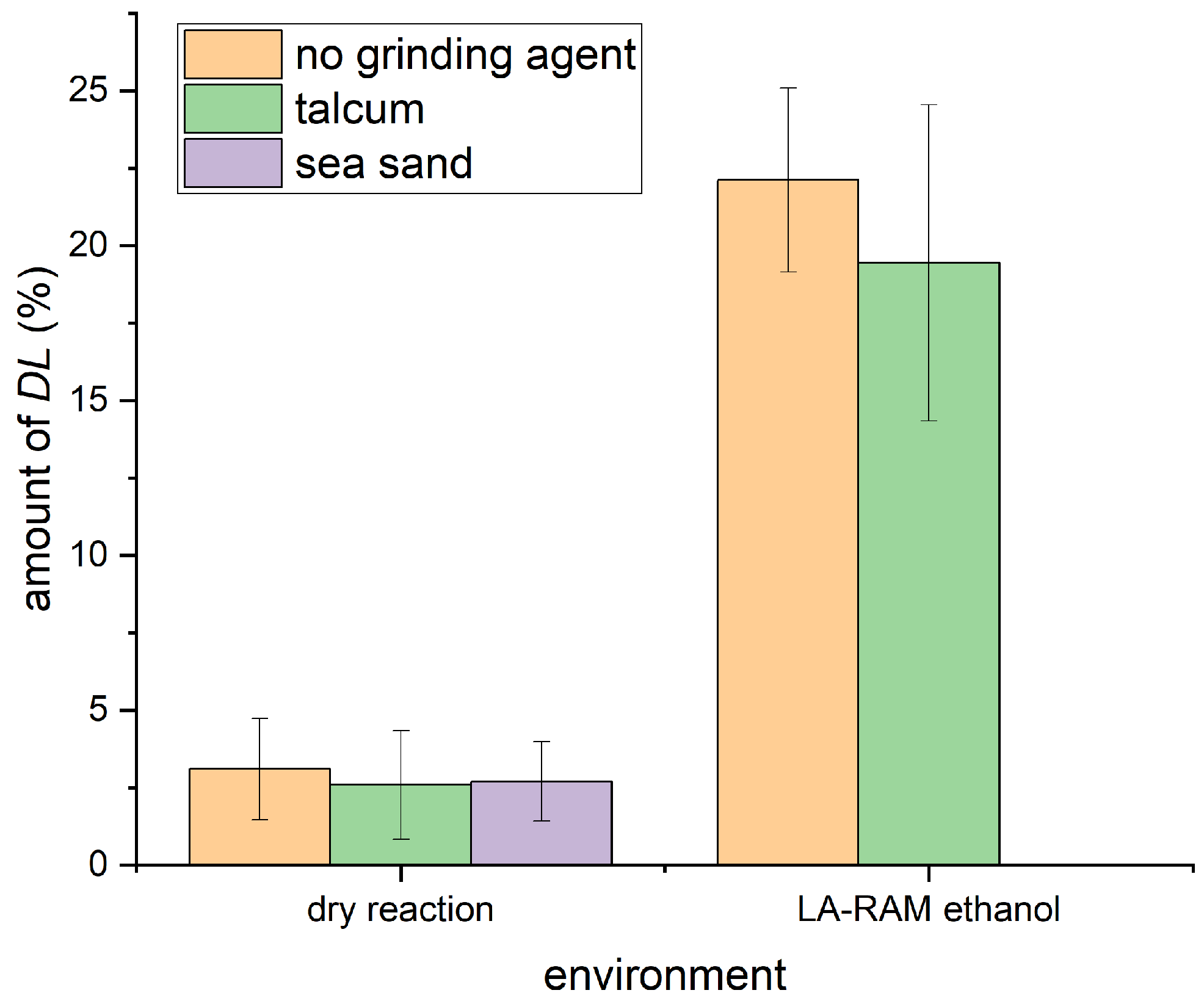
2.2. Efforts Towards Formation of the Racemic Phase by Resonant Acoustic Mixing
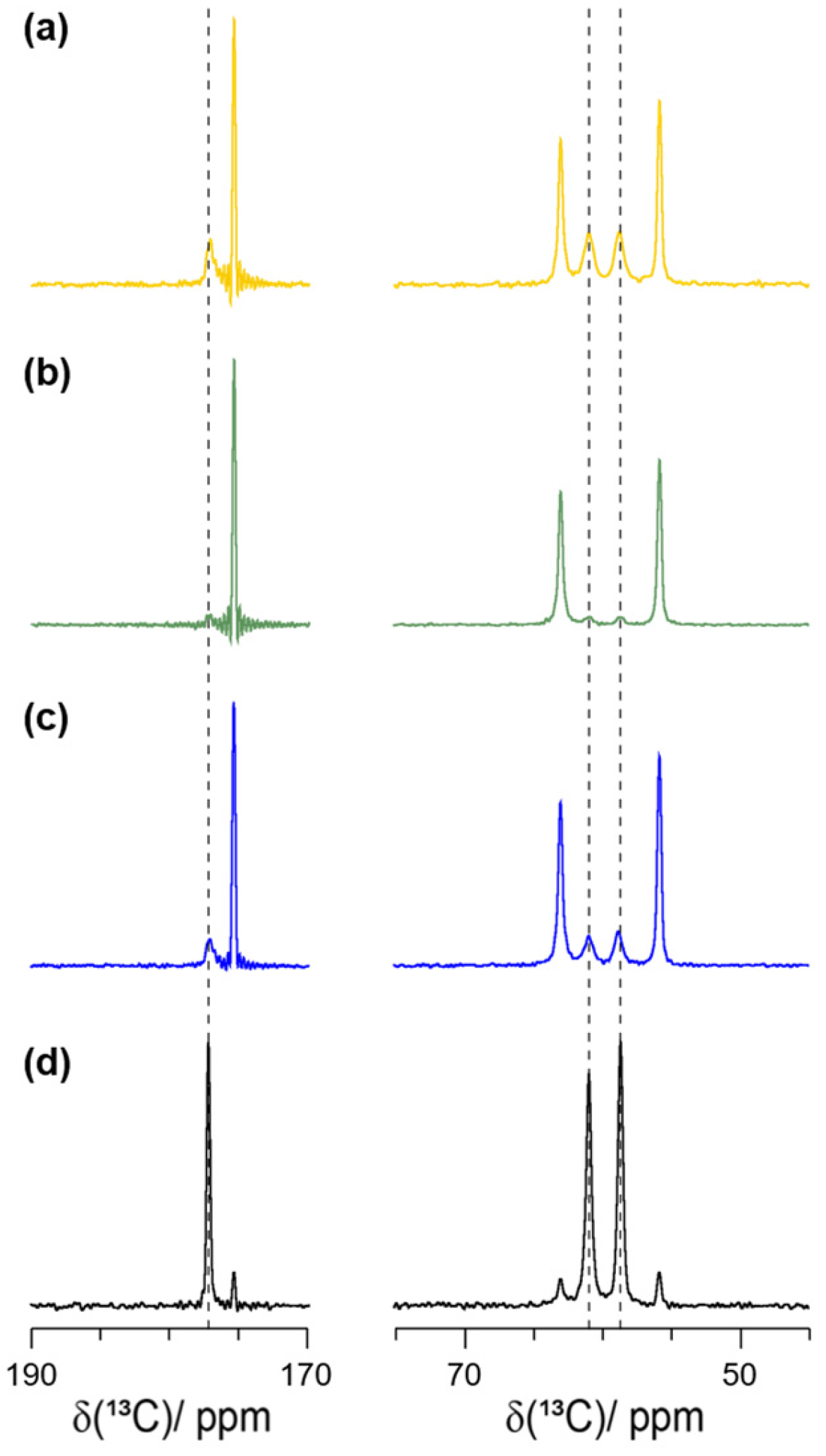
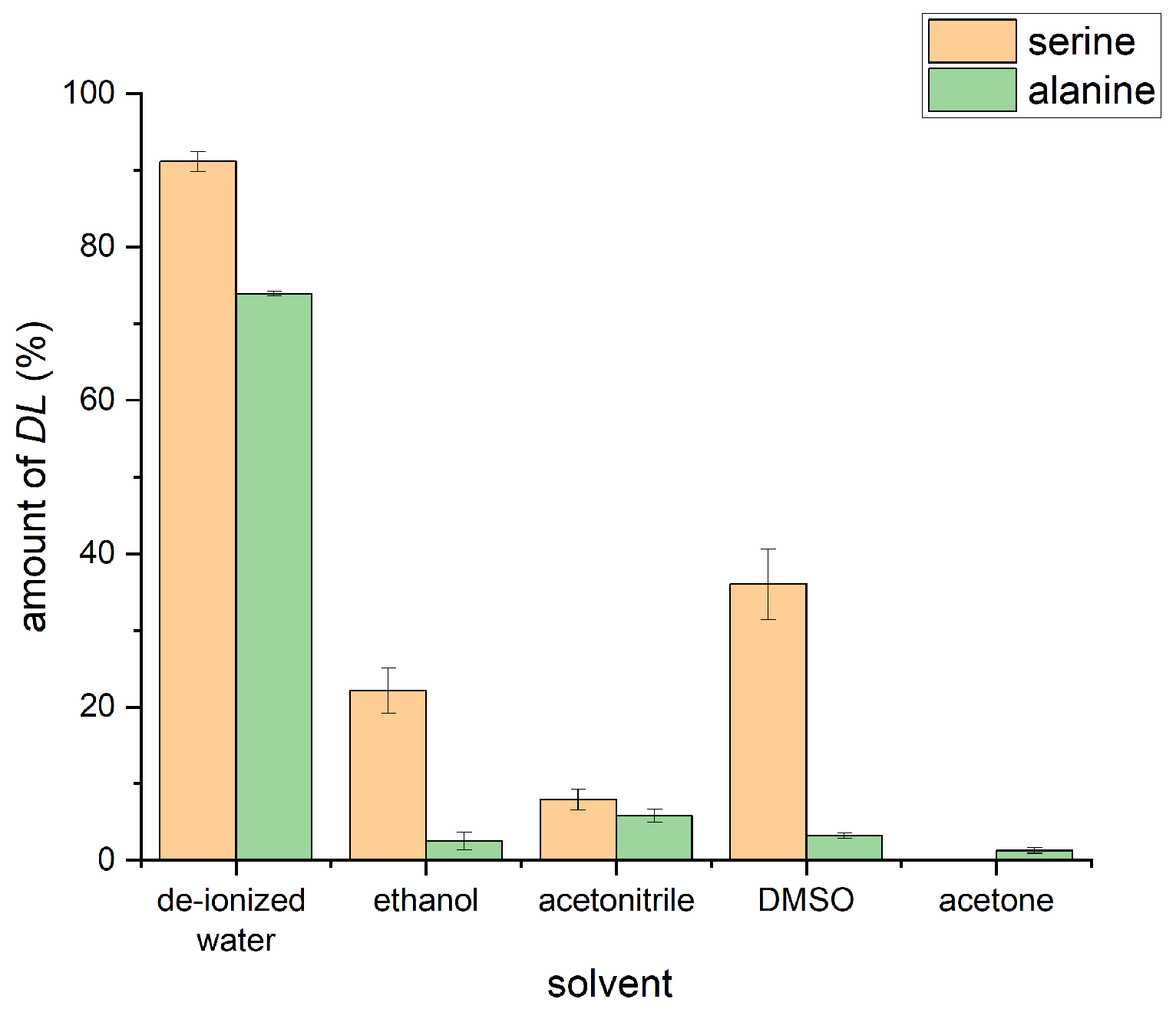
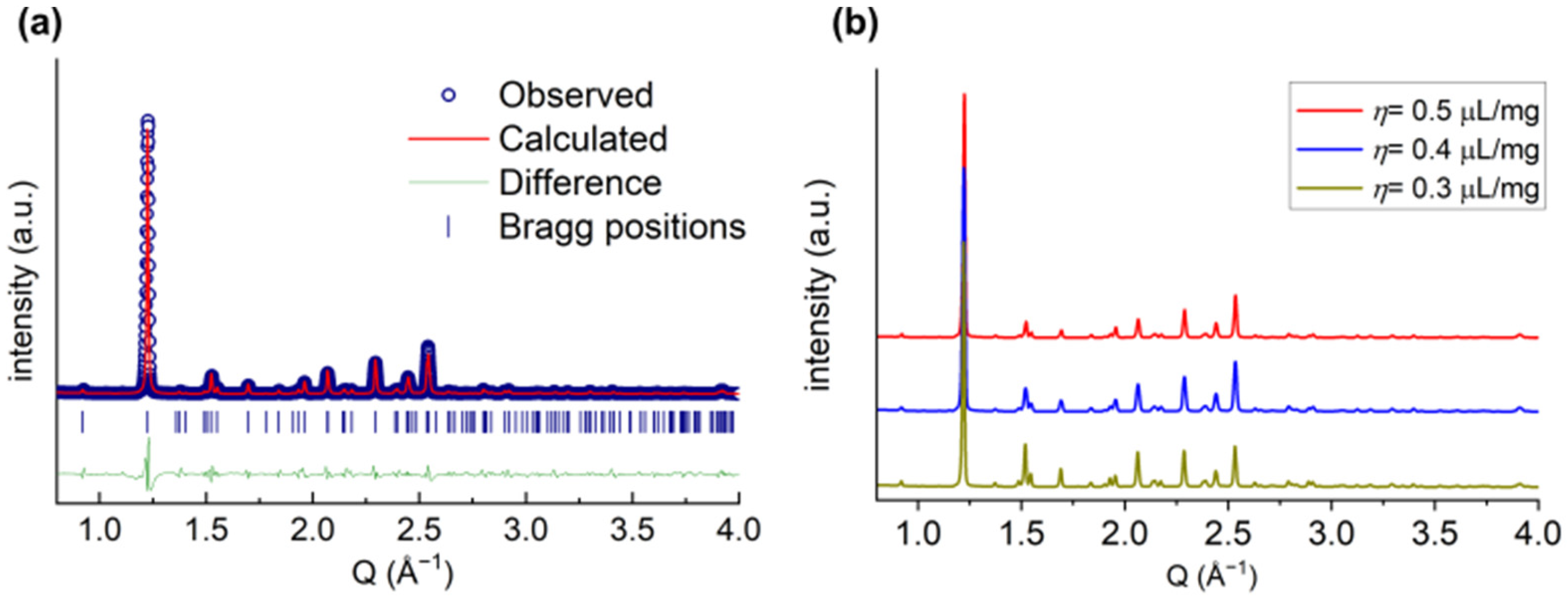
2.3. Formation of the Racemic Phases by LA-RAM
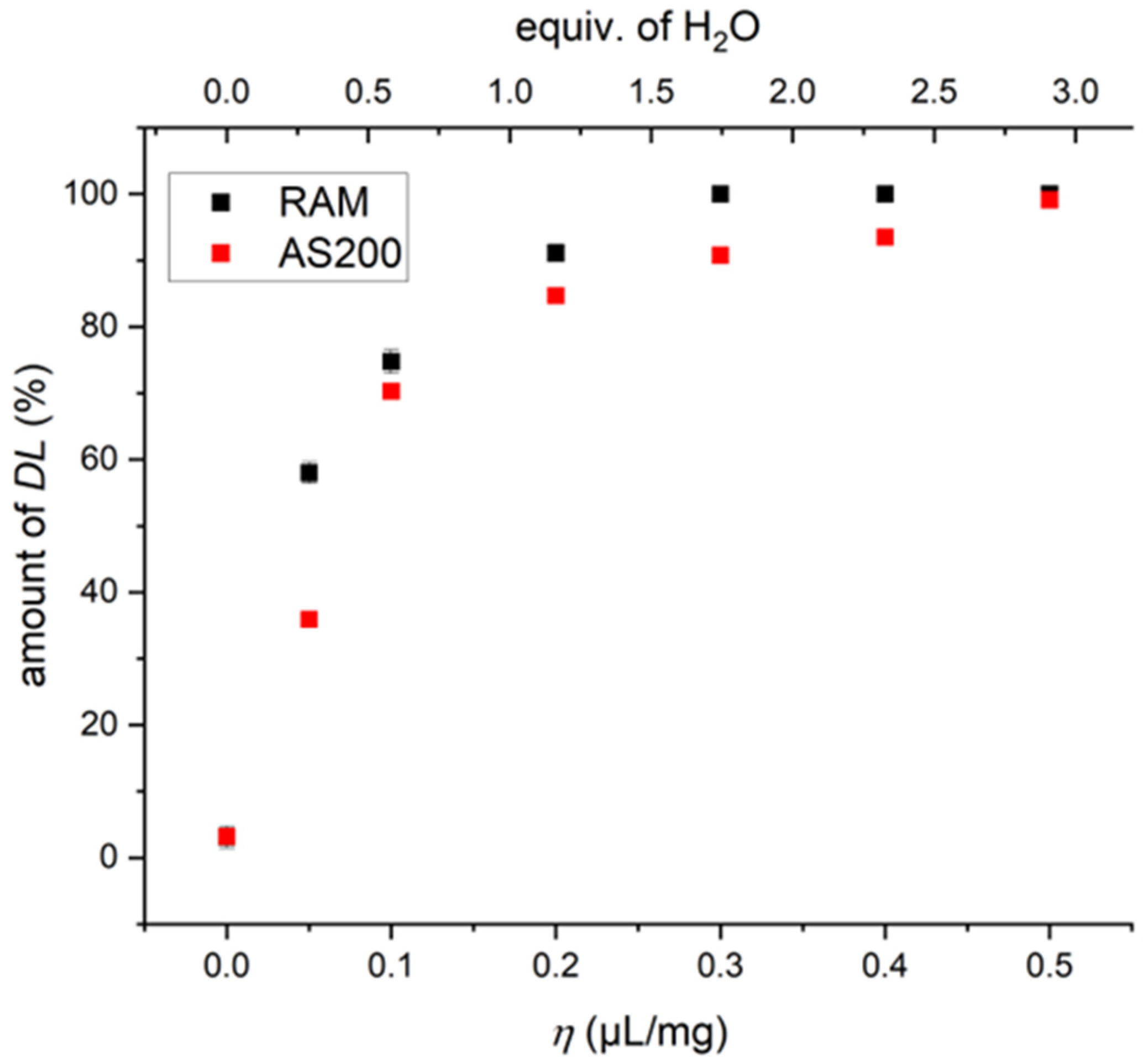
2.4. η-Optimization
2.5. The Influence of Water on Different Serine Phases
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Equipment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CP | Cross-Polarization |
| LA-RAM | Liquid-Assisted Resonant Acoustic Mixing |
| MAS | Magic-Angle Spinning |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| RAM | Resonant Acoustic Mixing |
References and Notes
- Reif, B.; Ashbrook, S.E.; Emsley, L.; Hong, M. Solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlawat, S.; Mote, K.R.; Lakomek, N.-A.; Agarwal, V. Solid-State NMR: Methods for Biological Solids. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 9643–9737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haro Mares, N.; Logrado, M.; Kergassner, J.; Zhang, B.; Gutmann, T.; Buntkowsky, G. Solid-State NMR of Heterogeneous Catalysts. ChemCatChem 2024, 16, e202401159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümich, B.; Hagemeyer, A.; Schaefer, D.; Schmidt-Rohr, K.; Spiess, H.W. Solid State NMR spectroscopy in polymer science. Adv. Mater. 2004, 2, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecher, O.; Carretero-González, J.; Griffith, K.J.; Grey, C.P. Materials’ Methods: NMR in Battery Research. Chem. Mater. 2016, 29, 213–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.d.A.A.; Bartalucci, E.; Bolm, C.; Wiegand, T. Opportunities and Challenges in Applying Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy in Organic Mechanochemistry. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2304092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffmann, J.G.; Emmerling, F.; Martins, I.C.B.; Van Wüllen, L. In-situ reaction monitoring of a mechanochemical ball mill reaction with solid state NMR. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 2020, 109, 101687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccetti, F.; Rinesch, T.; Suljić, S.; Rahimi, K.; Herrmann, A.; Bolm, C. NMR in operando monitoring of mechanochemically accelerated sublimations. Chem 2023, 9, 1318–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, G.; Pardi, A.; Wuethrich, K. Hydrogen bond length and proton NMR chemical shifts in proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 105, 5948–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, C.; Silva, I.D.A.A.; Moos, S.; Bartalucci, E.; Hendrickx, L.; Fahl, B.M.D.; Pasqualini, C.; Puccetti, F.; Zobel, M.; Bolm, C.; et al. Molecular Recognition in Mechanochemistry: Insights from Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202410801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, S. Racemic drug resolution: A comprehensive guide. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 7567–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.G.; Bolm, C. Altering Product Selectivity by Mechanochemistry. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 4007–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virieux, D.; Delogu, F.; Porcheddu, A.; García, F.; Colacino, E. Mechanochemical Rearrangements. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 13885–13894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolm, C.; Hernández, J.G. Mechanochemistry of Gaseous Reactants. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3285–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcheddu, A.; Colacino, E.; De Luca, L.; Delogu, F. Metal-Mediated and Metal-Catalyzed Reactions Under Mechanochemical Conditions. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 8344–8394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlgemuth, M.; Schmidt, S.; Mayer, M.; Pickhardt, W.; Grätz, S.; Borchardt, L. Milling Medium-Free Suzuki Coupling by Direct Mechanocatalysis: From Mixer Mills to Resonant Acoustic Mixers. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202301714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.L.; Adams, C.J.; Bolm, C.; Braga, D.; Collier, P.; Friščić, T.; Grepioni, F.; Harris, K.D.M.; Hyett, G.; Jones, W.; et al. Mechanochemistry: Opportunities for new and cleaner synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 413–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartalucci, E.; Schumacher, C.; Hendrickx, L.; Puccetti, F.; D’Anciães Almeida Silva, I.; Dervişoğlu, R.; Puttreddy, R.; Bolm, C.; Wiegand, T. Disentangling the Effect of Pressure and Mixing on a Mechanochemical Bromination Reaction by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202203466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resodyn Acoustic Mixers, Inc. ResonantAcoustic® Mixing Technical White Paper. 2010. Available online: https://resodynmixers.com/download/resonantacoustic-mixing-technical-white-paper/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Osorio, J.G.; Muzzio, F.J. Evaluation of resonant acoustic mixing performance. Powder Technol. 2015, 278, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effaty, F.; Gonnet, L.; Koenig, S.G.; Nagapudi, K.; Ottenwaelder, X.; Friščić, T. Resonant acoustic mixing (RAM) for efficient mechanoredox catalysis without grinding or impact media. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titi, H.M.; Do, J.-L.; Howarth, A.J.; Nagapudi, K.; Friščić, T. Simple, scalable mechanosynthesis of metal–organic frameworks using liquid-assisted resonant acoustic mixing (LA-RAM). Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 7578–7584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox, C.B.; Borchers, T.H.; Gonnet, L.; Barrett, C.J.; Koenig, S.G.; Nagapudi, K.; Friščić, T. Direct mechanocatalysis by resonant acoustic mixing (RAM). Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 7475–7481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanni, A.; Kong, D.; Zhu, C.; Rueping, M. Nickel-catalyzed cross-coupling aminations via high-throughput mechanochemistry enabled by resonant acoustic mixing. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 8341–8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Yi, L.; Nanni, A.; Rueping, M. A scalable photo-mechanochemical platform for sustainable photoredox catalysis by resonant acoustic mixing. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arhangelskis, M.; Bučar, D.-K.; Bordignon, S.; Chierotti, M.R.; Stratford, S.A.; Voinovich, D.; Jones, W.; Hasa, D. Mechanochemical reactivity inhibited, prohibited and reversed by liquid additives: Examples from crystal-form screens. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 3264–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grätz, S.; Zink, S.; Kraffczyk, H.; Rose, M.; Borchardt, L. Mechanochemical synthesis of hyper-crosslinked polymers: Influences on their pore structure and adsorption behaviour for organic vapors. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyarom, S.; Yonemochi, E.; Oguchi, T.; Yamamoto, K. Effects of Grinding and Humidification on the Transformation of Conglomerate to Racemic Compound in Optically Active Drugs. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1997, 49, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellec, A.; Guillemin, J.-C. A simple explanation of the enhancement or depletion of the enantiomeric excess in the partial sublimation of enantiomerically enriched amino acids. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 1482–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- As reported, the experimental setup in our previous work was far from from being optimal (e.g., the filling heights were too low).
- Ni, T.Q.; Ke, C.J.; Wang, H.; Wu, W.Z. Grinding Aid Effect of Different Siliceous Material for Quick Lime. Adv. Mat. Res. 2011, 399–401, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkareem, S.; Orkuma, G.I.; Apasi, A.A.; Chinesta, F.; Chastel, Y.; El Mansori, M. Talc as a Substitute for Dry Lubricant (an Overview). AIP Conf. Proc. 2011, 1315, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudenko, P.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Talc as friction reducing additive to lubricating oil. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 276, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Mulks, F.F.; Wu, P.; Rissanen, K.; Bolm, C. Mechanochemical Iron-Catalyzed Nitrene Transfer Reactions: Direct Synthesis of N-Acyl Sulfonimidamides from Sulfinamides and Dioxazolones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 63, e202316702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Wu, P.; Bampi, D.; Ward, J.S.; Rissanen, K.; Bolm, C. Mechanochemical Conditions for Intramolecular N−O Couplings via Rhodium Nitrenoids Generated from N-Acyl Sulfonimidamides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202413181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Wu, P.; Hu, Y.; Bolm, C. Mechanochemical syntheses of N-acyl sulfinamidines via iron-nitrenoids and their conversions to sulfur(VI) derivatives. Green Synth. Catal. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonnet, L.; Borchers, T.H.; Lennox, C.B.; Vainauskas, J.; Teoh, Y.; Titi, H.M.; Barrett, C.J.; Koenig, S.G.; Nagapudi, K.; Friščić, T. The “η-sweet-spot” (ηmax) in liquid-assisted mechanochemistry: Polymorph control and the role of a liquid additive as either a catalyst or an inhibitor in resonant acoustic mixing (RAM). Faraday Discuss. 2023, 241, 128–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, P.; Yu, J.; Su, W. Liquid-Assisted Grinding Mechanochemistry in the Synthesis of Pharmaceuticals. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2021, 363, 1246–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spula, C.; Preuß, P.M.; Borchardt, L.; Grätz, S. Solid-State Photochemistry in Resonant Acoustic Mixers. Chem. Eur. J. 2025, 31, e202501137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantozzi, N.; Volle, J.-N.; Porcheddu, A.; Virieux, D.; García, F.; Colacino, E. Green metrics in mechanochemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 6680–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- When tested in combination with talcum, it again resulted in a reduction of racemic phase formed compaired to no grinding agent being used.
- Fan, Y.; Zhu, W.; Hu, Y.; Yang, W.; Xu, Q.; Liu, X.; Heng, B. The Research and Measurement about the Solubility of l-Serine in Eight Common Pure Solvents and Four Binary Mixed Solvents for T = (278.15–333.15) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 4398–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Qiu, J.; Yi, D.; Liu, H.; Hu, S.; Han, J.; Huang, H.; He, H.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Measurement and Correlation for Solubility of l-Alanine in Pure and Binary Solvents at Temperatures from 283.15 to 323.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selleckchem. Datasheet L-Serine Batch:S935301. Available online: https://www.selleckchem.com/datasheet/l-serine-S935301-DataSheet.html (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Selleckchem. Datasheet L-Alanine Batch:S563101. Available online: https://www.selleckchem.com/datasheet/l-alanine-S563101-DataSheet.html (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Newman, A.; Zografi, G. An Examination of Water Vapor Sorption by Multicomponent Crystalline and Amorphous Solids and Its Effects on Their Solid-State Properties. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1061–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, D.P.; Barieau, R.E.; Donohue, J.; Lu, C.S. The crystal structure ofDL-serine. Acta Crystallogr. 1953, 6, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, T.; Teramoto, H. Phase transition of L-Ser monohydrate crystal studied by 13C solid-state NMR. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2006, 44, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apperley, D.C.; Harris, R.K.; Hodgkinson, P. Solid-State NMR: Basic Principles and Practice; Momentum Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Eley, D.D.; Hey, M.J.; Chew, K.F.; Derbyshire, W. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of a clathrate hydrate. Chem. Commun. 1968, 23, 1474b–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, L.W. Chapter 3 The study of water in hydrate crystals by nuclear magnetic resonance. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 1969, 4, 193–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byard, S.; Abraham, A.; Boulton, P.J.T.; Harris, R.K.; Hodgkinson, P. A Multi-Technique Approach to the Study of Structural Stability and Desolvation of Two Unusual Channel Hydrate Solvates of Finasteride. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.J.; MaCkay, A.L. Deuterium and nitrogen pure quadrupole resonance in deuterated amino acids. J. Magn. Reson. 1974, 15, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Harbison, G.S. Deuterium Quadrupolar Tensors of l-Histidine Hydrochloride Monohydrate-d7. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2006, 110, 25059–25065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranka, S.; Deamer, D. Racemic serine is less soluble than pure enantiomers due to stronger intermolecular hydrogen bonds. JEI 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resodyn Acoustic Mixers, Inc. Green Aspects of ResonantAcoustic® Mixing 2018. Available online: https://resodynmixers.com/download/green-aspects-of-ram-mixing/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Toby, B.H.; Von Dreele, R.B. GSAS-II: The genesis of a modern open-source all purpose crystallography software package. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2013, 46, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massiot, D.; Fayon, F.; Capron, M.; King, I.; Le Calvé, S.; Alonso, B.; Durand, J.O.; Bujoli, B.; Gan, Z.; Hoatson, G. Modelling one- and two-dimensional solid-state NMR spectra. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2001, 40, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Chemical | CAS Number | Purity | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| L-serine | 56-45-1 | 99% | abcr GmbH (Karlsruhe, Germany) |
| D-serine | 312-84-5 | 98% | abcr GmbH (Karlsruhe, Germany) |
| DL-serine | 302-84-1 | 99% | abcr GmbH (Karlsruhe, Germany) |
| L-alanine | 56-41-7 | - | Degussa (Wesseling, Germany) |
| D-alanine | 338-69-2 | - | Degussa (Wesseling, Germany) |
| DL-alanine | 302-72-7 | - | - |
| Solvent | CAS Number | Purity | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | - | De-ionized | - |
| Ethanol | 64-17-5 | Technical grade | Julius Hoesch GmbH & Co. KG (Düren, Germany) |
| Acetonitrile | 75-05-8 | >99.9% | Riedel-de Haën (Seelze, Germany) |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) | 67-68-5 | 99.7% | Thermo scientific (Waltham, MA, USA) |
| Deuterium oxide | 7789-20-0 | Analytical grade | Eckert & Ziegler Chemotrade GmbH (Berlin, Germany) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hendrickx, L.; Quaranta, C.; Fuchs, E.; Plekhanov, M.; Zobel, M.; Bolm, C.; Wiegand, T. Formation of Racemic Phases of Amino Acids by Liquid-Assisted Resonant Acoustic Mixing Monitored by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Molecules 2025, 30, 3745. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183745
Hendrickx L, Quaranta C, Fuchs E, Plekhanov M, Zobel M, Bolm C, Wiegand T. Formation of Racemic Phases of Amino Acids by Liquid-Assisted Resonant Acoustic Mixing Monitored by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Molecules. 2025; 30(18):3745. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183745
Chicago/Turabian StyleHendrickx, Leeroy, Calogero Quaranta, Emilian Fuchs, Maksim Plekhanov, Mirijam Zobel, Carsten Bolm, and Thomas Wiegand. 2025. "Formation of Racemic Phases of Amino Acids by Liquid-Assisted Resonant Acoustic Mixing Monitored by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy" Molecules 30, no. 18: 3745. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183745
APA StyleHendrickx, L., Quaranta, C., Fuchs, E., Plekhanov, M., Zobel, M., Bolm, C., & Wiegand, T. (2025). Formation of Racemic Phases of Amino Acids by Liquid-Assisted Resonant Acoustic Mixing Monitored by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Molecules, 30(18), 3745. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183745







