Methylation Enables Sensitive LC-MS/MS Quantification of Ciclopirox in a Mouse Pharmacokinetics Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Method Development
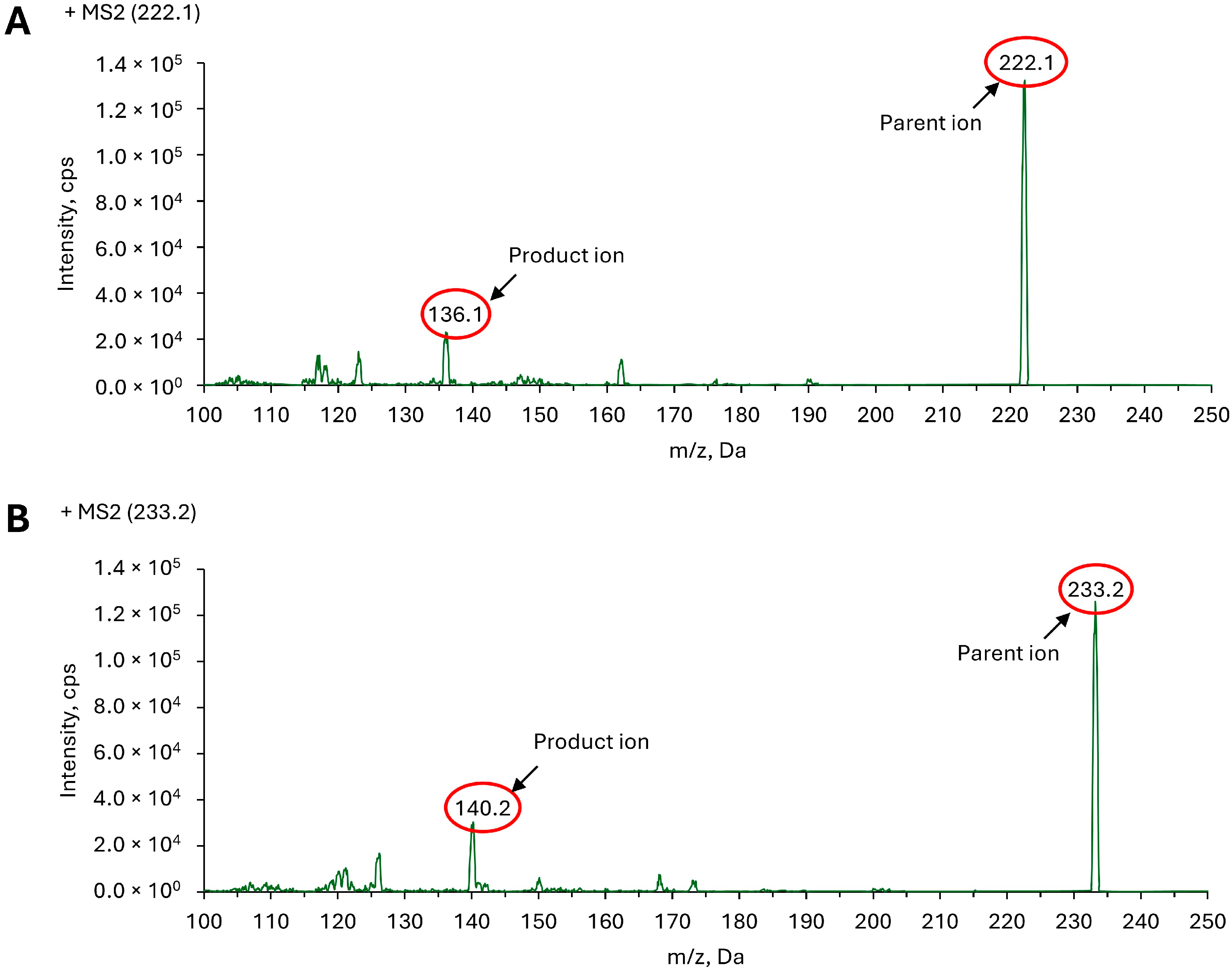
2.1.1. Analytical Condition Optimization and Instrumentation
2.1.2. Procedure for Sample Preparation
2.2. Bioanalytical Method Validation
2.2.1. Recovery
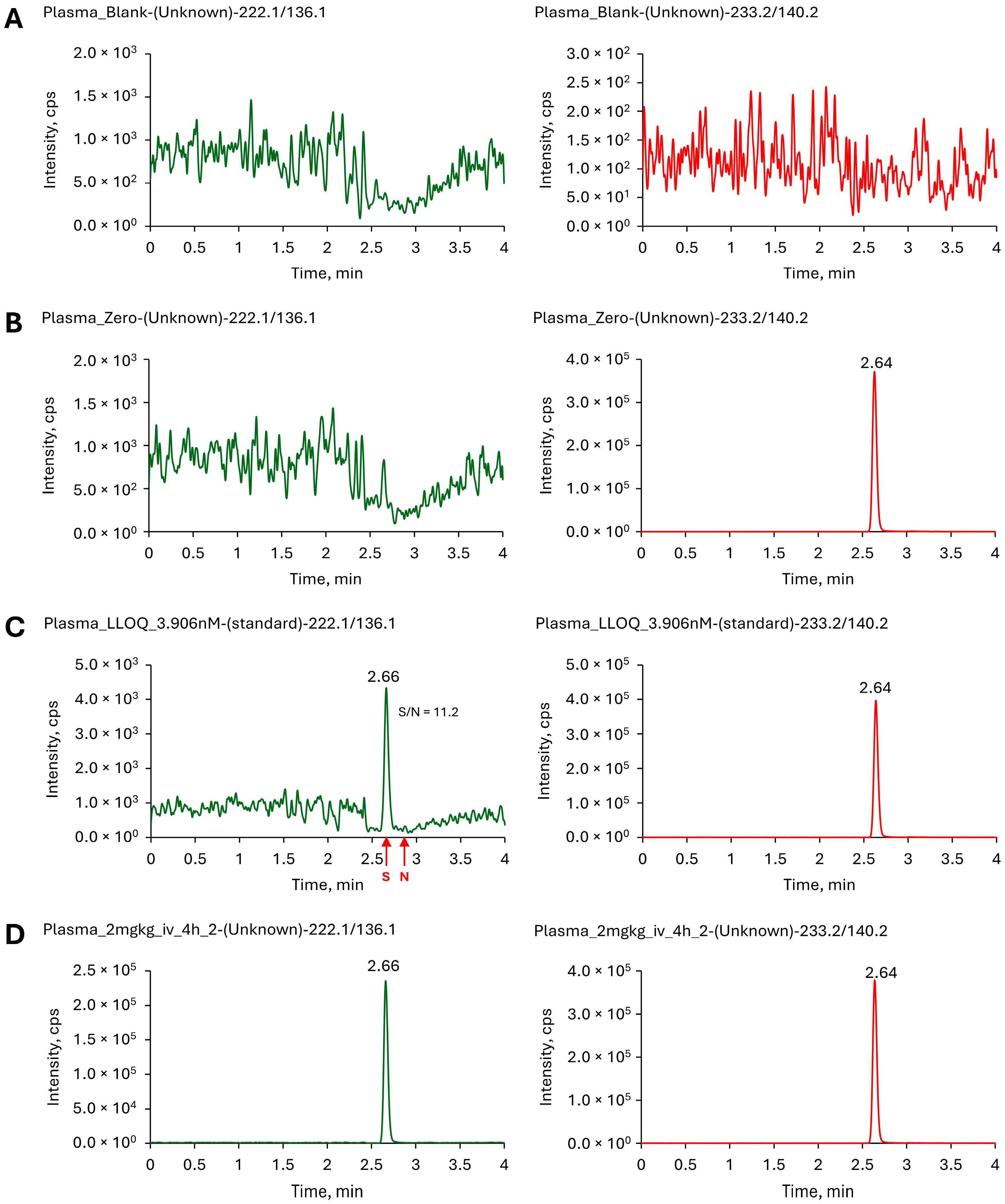
2.2.2. Selectivity and Sensitivity
2.2.3. Calibration Curve and Range
2.2.4. Accuracy and Precision
2.2.5. Matrix Effect
2.2.6. Carryover Effect
2.2.7. Dilution Integrity
2.2.8. Stability Studies
2.2.9. Reinjection Reproducibility
2.3. Application of Bioanalytical Method
2.3.1. In Vitro Plasma Protein Binding
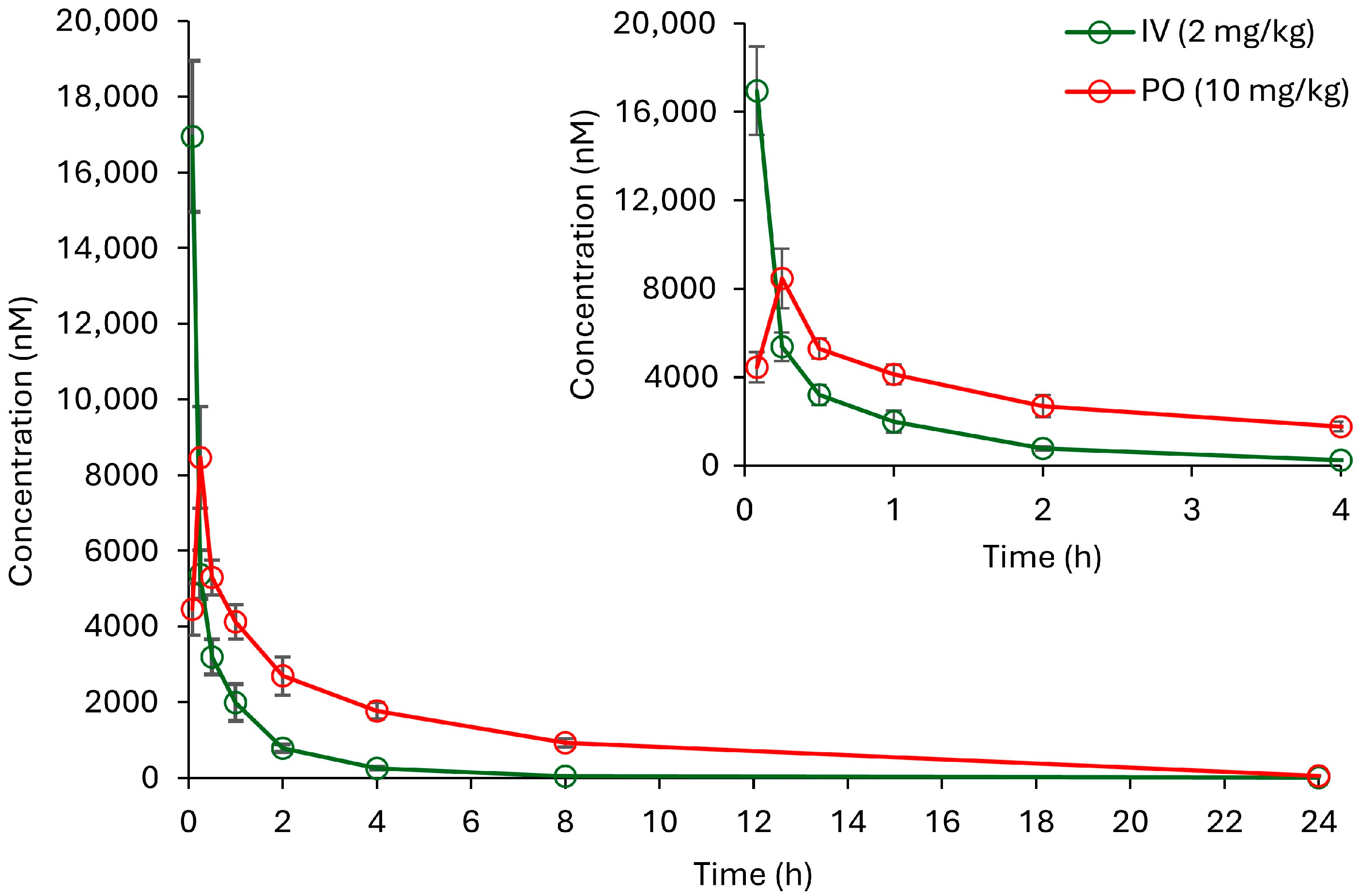
2.3.2. In Vivo Pharmacokinetics Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Method Development
3.2.1. Analytical Condition Optimization and Instrumentation
3.2.2. Procedure for Sample Preparation
3.3. Bioanalytical Method Validation
3.3.1. Recovery
3.3.2. Selectivity and Sensitivity
3.3.3. Calibration Curve and Range
3.3.4. Accuracy and Precision
3.3.5. Matrix Effect
3.3.6. Carryover Effect
3.3.7. Dilution Integrity
3.3.8. Stability Studies
3.3.9. Reinjection Reproducibility
3.4. Application of Bioanalytical Method
3.4.1. In Vitro Plasma Protein Binding
3.4.2. In Vivo Pharmacokinetics Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CPX | Ciclopirox |
| Me-CPX | Methylated Ciclopirox |
| LLOQ | Lower Limit of Quantification |
| ICH | International Council for Harmonisation |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| PK | Pharmacokinetics |
| ADME | Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion |
| UV-HPLC | Ultraviolet-High Pressure Liquid Chromatography |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| MEKC | Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| MRM | Multiple Reaction Monitoring |
| QC | Quality Control |
| LQC | Low Quality Control |
| MQC | Medium Quality Control |
| HQC | High Quality Control |
| CV | Coefficient of Variation |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| PPB | Plasma Protein Binding |
| IV | Intravenous |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| IACUC | Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee |
References
- Gupta, A.K.; Fleckman, P.; Baran, R. Ciclopirox nail lacquer topical solution 8% in the treatment of toenail onychomycosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2000, 43, S70–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonthalia, S.; Agrawal, M.; Sehgal, V.N. Topical Ciclopirox Olamine 1%: Revisiting a Unique Antifungal. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2019, 10, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zangi, M.; Kumar, T.; Shakar Reddy, M.; Reddy, L.V.R.; Sadhukhan, S.K.; Bradley, D.P.; Moreira-Walsh, B.; Edwards, T.C.; O’Dea, A.T.; et al. Synthetic Derivatives of Ciclopirox are Effective Inhibitors of Cryptococcus neoformans. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 8477–8487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, R.; Fisher, G.; Katz, I.; Levine, N.; Lookingbill, D.P.; Lowe, N.; Menter, A.; Morman, M.; Pariser, D.M.; Roth, H.L.; et al. Ciclopirox gel in the treatment of patients with interdigital tinea pedis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2003, 42, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Li, Y.; Gong, S.; Wang, J.; Lu, X.; Jin, Q.; Lu, B.; Chen, Q. Ciclopirox targets cellular bioenergetics and activates ER stress to induce apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Che, G.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, L.; Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Yan, S. Ciclopirox Olamine Exerts Tumor-Suppressor Effects via Topoisomerase II Alpha in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 791916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhou, N.; Li, L.; Mo, S.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, Y.; Chen, T.; Shan, C.; Chen, Q.; Lu, B. Ciclopirox activates PERK-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress to drive cell death in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minden, M.D.; Hogge, D.E.; Weir, S.J.; Kasper, J.; Webster, D.A.; Patton, L.; Jitkova, Y.; Hurren, R.; Gronda, M.; Goard, C.A.; et al. Oral ciclopirox olamine displays biological activity in a phase I study in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, B.; Huang, S. Inhibition of Chk1 with Prexasertib Enhances the Anticancer Activity of Ciclopirox in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Cells 2024, 13, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquiza, P.; Lain, A.; Sanz-Parra, A.; Moreno, J.; Bernardo-Seisdedos, G.; Dubus, P.; Gonzalez, E.; Gutierrez-de-Juan, V.; Garcia, S.; Erana, H.; et al. Repurposing ciclopirox as a pharmacological chaperone in a model of congenital erythropoietic porphyria. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Kim, K.S. Repurposing of Ciclopirox to Overcome the Limitations of Zidovudine (Azidothymidine) against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Hu, L.; Zhu, H.; Tao, L.; Wu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Gao, Y.; Gong, Q.; Mao, F.; Li, X.; et al. Repurposing antimycotic ciclopirox olamine as a promising anti-ischemic stroke agent. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. B. 2020, 10, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, X.; Fan, L.; Liu, D.; Gao, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, W.; et al. Ciclopirox inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication by promoting the degradation of the nucleocapsid protein. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. B. 2024, 14, 2505–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.A.; Kim, S.; Park, M.; Park, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.; Hwang, J.R.; Kim, Y.C.; Jun Kim, Y.; Cho, Y.; et al. Ciclopirox inhibits Hepatitis B Virus secretion by blocking capsid assembly. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, A.; Belhaouari, D.B.; Dsouza, L.; Udayanga, D.M.N.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z. Ciclopirox suppresses poxvirus replication by targeting iron metabolism. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehr, K.H.; Damm, P. Quantification of ciclopirox by high-performance liquid chromatography after pre-column derivatization. An example of efficient clean-up using silica-bonded cyano phases. J. Chromatogr. 1985, 339, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, W.; Fan, X.; Sexton, H.; Heyman, I. A direct LC/MS/MS method for the determination of ciclopirox penetration across human nail plate in in vitro penetration studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, T.; Ren, S. Fast and simple method for assay of ciclopirox olamine by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghel, M.; Rajput, S. Degradation and Impurity Profile Study of Ciclopirox Olamine after Pre-column Derivatization: A Risk Based Approach. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2017, 55, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escarrone, A.L.V.; Bittencourt, C.F.; Laporta, L.V.; dos Santos, M.R.; Primel, E.G.; Caldas, S.S. LC–UV method with pre-column derivatization for the determination of ciclopirox olamine in raw material and topical solution. Chromatographia 2008, 67, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju-Hyun, K.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, H.-K. A method to measure the amount of drug penetrated across the nail plate. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo-Seisdedos, G.; Charco, J.M.; SanJuan, I.; Garcia-Martinez, S.; Urquiza, P.; Erana, H.; Castilla, J.; Millet, O. Improving the Pharmacological Properties of Ciclopirox for Its Use in Congenital Erythropoietic Porphyria. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, S.J.; Dandawate, P.; Standing, D.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Ramamoorthy, P.; Rangarajan, P.; Wood, R.; Brinker, A.E.; Woolbright, B.L.; Tanol, M.; et al. Fosciclopirox suppresses growth of high-grade urothelial cancer by targeting the gamma-secretase complex. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Sun, M.; Bai, L.; Chen, T.; Liu, D.Q.; Kord, A. A practical derivatization LC/MS approach for determination of trace level alkyl sulfonates and dialkyl sulfates genotoxic impurities in drug substances. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 48, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dongen, M.J.; Kadam, R.U.; Juraszek, J.; Lawson, E.; Brandenburg, B.; Schmitz, F.; Schepens, W.B.; Stoops, B.; van Diepen, H.A.; Jongeneelen, M. A small-molecule fusion inhibitor of influenza virus is orally active in mice. Science 2019, 363, eaar6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, S.; Scott, R.C. 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD): A toxicology review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Darzi, N.; Mast, N.; Petrov, A.M.; Pikuleva, I.A. 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin reduces retinal cholesterol in wild-type and Cyp27a1−/− Cyp46a1−/− mice with deficiency in the oxysterol production. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 3220–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). ICH Harmonised Guideline: Bioanalytical Method Validation and Study Sample Analysis: M10; ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/M10_Guideline_Step4_2022_0524.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2025).

| Level | CPX | CPX-d11 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovery (%) | Precision (%CV) | Recovery (%) | Precision (%CV) | |
| LQC, 10.417 nM | 101.621 ± 3.006 | 2.958 | 100.742 ± 1.385 | 1.375 |
| HQC, 750 nM | 99.772 ± 1.278 | 1.281 | 101.378 ± 1.487 | 1.467 |
| Actual Concentration (nM) | Calculated Concentration (nM) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%CV) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | #2 | #3 | |||
| 3.906 | 3.932 | 3.875 | 4.005 | 100.802 ± 1.668 | 1.655 |
| 7.813 | 7.247 | 7.747 | 7.610 | 96.438 ± 3.307 | 3.429 |
| 15.625 | 16.640 | 15.610 | 15.680 | 102.251 ± 3.683 | 3.602 |
| 31.25 | 31.110 | 31.420 | 31.160 | 99.936 ± 0.533 | 0.533 |
| 62.5 | 61.160 | 61.240 | 60.850 | 97.733 ± 0.330 | 0.337 |
| 125 | 128.100 | 127.500 | 128.200 | 102.347 ± 0.303 | 0.296 |
| 250 | 253.100 | 251.900 | 251.500 | 100.867 ± 0.333 | 0.330 |
| 500 | 494.700 | 507.600 | 498.000 | 100.020 ± 1.340 | 1.340 |
| 1000 | 1000.000 | 989.200 | 999.100 | 99.610 ± 0.599 | 0.602 |
| Batch | Slope (m) | S.E. (m) a | Y-intercept (b) | S.E. (b) b | r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00253 | 1.24 × 10−5 | 0.000613 | 0.000774 | 0.99992 |
| 2 | 0.00253 | 1.27 × 10−5 | 0.000254 | 0.000793 | 0.99991 |
| 3 | 0.00249 | 8.58 × 10−6 | 0.000877 | 0.000536 | 0.99996 |
| Batch | Actual Concentration (nM) | Calculated Concentration (nM) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%CV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.906 | 3.828 ± 0.146 | 98.007 ± 3.739 | 3.815 |
| 10.417 | 10.710 ± 0.227 | 102.813 ± 2.175 | 2.115 | |
| 83.333 | 85.740 ± 0.922 | 102.888 ± 1.107 | 1.076 | |
| 750 | 769.417 ± 10.929 | 102.589 ± 1.457 | 1.420 | |
| 2 | 3.906 | 3.586 ± 0.167 | 91.812 ± 4.285 | 4.667 |
| 10.417 | 10.235 ± 0.263 | 98.250 ± 2.524 | 2.569 | |
| 83.333 | 85.368 ± 0.725 | 102.442 ± 0.870 | 0.849 | |
| 750 | 774.433 ± 7.231 | 103.258 ± 0.964 | 0.934 | |
| 3 | 3.906 | 3.780 ± 0.146 | 96.761 ± 3.735 | 3.860 |
| 10.417 | 10.307 ± 0.213 | 98.941 ± 2.045 | 2.067 | |
| 83.333 | 84.640 ± 0.815 | 101.568 ± 0.978 | 0.963 | |
| 750 | 760.617 ± 12.913 | 101.416 ± 1.722 | 1.698 |
| Batch | Actual Concentration (nM) | Calculated Concentration (nM) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%CV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1, 2, 3 | 3.906 | 3.731 ± 0.132 | 95.527 ± 3.389 | 3.547 |
| 10.417 | 10.417 ± 0.125 | 100.001 ± 1.197 | 1.197 | |
| 83.333 | 85.249 ± 0.490 | 102.300 ± 0.588 | 0.575 | |
| 750 | 768.156 ± 7.356 | 102.421 ± 0.981 | 0.958 |
| Source | Actual Concentration (nM) | Calculated Concentration (nM) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%CV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 10.417 | 10.587 ± 0.124 | 101.629 ± 1.193 | 1.173 |
| S2 | 10.377 ± 0.170 | 99.613 ± 1.636 | 1.642 | |
| S3 | 9.634 ± 0.508 | 92.487 ± 4.872 | 5.268 | |
| S4 | 9.963 ± 0.022 | 95.642 ± 0.209 | 0.219 | |
| S5 | 10.420 ± 0.282 | 100.029 ± 2.703 | 2.703 | |
| S6 | 10.760 ± 0.177 | 103.293 ± 1.698 | 1.644 | |
| S1 | 750 | 742.900 ± 12.101 | 99.053 ± 1.613 | 1.629 |
| S2 | 748.367 ± 3.412 | 99.782 ± 0.455 | 0.456 | |
| S3 | 700.900 ± 7.749 | 93.453 ± 1.033 | 1.106 | |
| S4 | 691.867 ± 13.724 | 92.249 ± 1.830 | 1.984 | |
| S5 | 742.333 ± 4.680 | 98.978 ± 0.624 | 0.630 | |
| S6 | 746.033 ± 3.308 | 99.471 ± 0.441 | 0.443 |
| Batch | Me-CPX Area in LLOQ | 20% of Me-CPX Area of LLOQ | Me-CPX Area in Blank | Me-CPX-d11 Area in LLOQ | 5% of Me-CPX-d11 Area of LLOQ | Me-CPX-d11 Area in Blank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.15 × 104 | 4.29 × 103 | 1.30 × 103 | 2.03 × 106 | 1.02 × 105 | 6.11 × 102 |
| 2 | 2.25 × 104 | 4.50 × 103 | 5.75 × 102 | 2.24 × 106 | 1.12 × 105 | 3.00 × 102 |
| 3 | 2.86 × 104 | 5.72 × 103 | 5.49 × 102 | 2.64 × 106 | 1.32 × 105 | 4.67 × 102 |
| Actual Concentration (nM) | Df | Calculated Concentration (nM) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%CV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 2 | 212.916 ± 1.805 | 106.458 ± 0.902 | 0.848 |
| 1500 | 2 | 1423.338 ± 44.739 | 94.889 ± 2.983 | 3.143 |
| 10,000 | 100 | 10,186.060 ± 95.356 | 101.861 ± 0.954 | 0.936 |
| 75,000 | 100 | 70,824.886 ± 3302.731 | 94.433 ± 4.404 | 4.663 |
| Actual Concentration (nM) | Calculated Concentration (nM) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%CV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autosampler stability (6 °C, 24 h) | 10.417 | 10.890 ± 0.036 | 104.541 ± 0.346 | 0.331 |
| 750 | 766.600 ± 6.139 | 102.213 ± 0.819 | 0.801 | |
| Bench-top stability (2 h, 22 ± 2 °C) | 10.417 | 10.873 ± 0.240 | 104.381 ± 2.305 | 2.208 |
| 750 | 756.167 ± 9.808 | 100.822 ± 1.308 | 1.297 | |
| Bench-top stability (4 h, 22 ± 2 °C) | 10.417 | 9.735 ± 0.169 | 93.453 ± 1.621 | 1.735 |
| 750 | 745.133 ± 2.702 | 99.351 ± 0.360 | 0.363 | |
| Freeze–thaw stability (−80 ± 5 °C, 3 cycles) | 10.417 | 10.001 ± 0.365 | 96.010 ± 3.507 | 3.653 |
| 750 | 746.167 ± 5.713 | 99.489 ± 0.762 | 0.766 | |
| Long-term stability (−80 ± 5 °C, 28 days) | 10.417 | 9.656 ± 0.180 | 92.695 ± 1.729 | 1.866 |
| 750 | 700.500 ± 7.134 | 93.400 ± 0.951 | 1.018 |
| Actual Concentration (nM) | Calculated Concentration (nM) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%CV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection 1 | 10.417 | 10.387 ± 0.247 | 99.709 ± 2.371 | 2.378 |
| 83.333 | 83.132 ± 0.981 | 99.758 ± 1.177 | 1.180 | |
| 750 | 748.733 ± 6.833 | 99.831 ± 0.911 | 0.913 | |
| Injection 2, After 24 h | 10.417 | 10.257 ± 0.182 | 98.466 ± 1.743 | 1.770 |
| 83.333 | 83.013 ± 1.425 | 99.616 ± 1.710 | 1.717 | |
| 750 | 737.650 ± 4.504 | 98.353 ± 0.601 | 0.611 |
| Pharmacokinetic Parameters | IV, 2 mg/kg | PO, 10 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|
| t1/2 (h) | 1.464 ± 0.138 | 4.140 ± 0.287 |
| Tmax (h) | 0.083 ± 0.000 | 0.250 ± 0.000 |
| Cmax (nM) | 16,950.769 ± 1997.664 | 8464.616 ± 1347.941 |
| AUC0-t (h.nM) | 9257.315 ± 1174.154 | 24,310.486 ± 4778.712 |
| AUC0-∞ (h.nM) | 9338.659 ± 1188.429 | 26,183.827 ± 2276.947 |
| MRT0-t (h) | 1.024 ± 0.199 | 3.986 ± 0.808 |
| V (L/kg) | 2.213 ± 0.391 | 11.090 ± 1.489 |
| Cl (L/h/kg) | 1.046 ± 0.131 | 1.852 ± 0.151 |
| Bioavailability (%F) | - | 52.522 ± 10.324 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katekar, R.; Wang, Z.; Xie, J. Methylation Enables Sensitive LC-MS/MS Quantification of Ciclopirox in a Mouse Pharmacokinetics Study. Molecules 2025, 30, 3599. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173599
Katekar R, Wang Z, Xie J. Methylation Enables Sensitive LC-MS/MS Quantification of Ciclopirox in a Mouse Pharmacokinetics Study. Molecules. 2025; 30(17):3599. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173599
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatekar, Roshan, Zhengqiang Wang, and Jiashu Xie. 2025. "Methylation Enables Sensitive LC-MS/MS Quantification of Ciclopirox in a Mouse Pharmacokinetics Study" Molecules 30, no. 17: 3599. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173599
APA StyleKatekar, R., Wang, Z., & Xie, J. (2025). Methylation Enables Sensitive LC-MS/MS Quantification of Ciclopirox in a Mouse Pharmacokinetics Study. Molecules, 30(17), 3599. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173599








