Green Approaches in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography for Sustainable Food Analysis: Advances, Challenges, and Regulatory Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principles of Green Analytical Chemistry
2.1. Greenness Assessment Tools in Analytical Chemistry
2.2. Application of GAC in Food Analysis
2.3. Integration with Quality by Design (QbD)
3. Green Innovations in HPLC
3.1. Eco-Friendly Solvent Systems
3.1.1. General Classes of Green Solvents
3.1.2. Emerging Green Solvent Systems
3.1.3. Practical Considerations and Applications in Food Analysis
3.2. Miniaturization and Micro-HPLC
3.2.1. Reduction in Solvent and Sample Volumes
3.2.2. Use of Micro-Columns and Low-Flow Techniques
3.2.3. Operational Challenges and Perspectives
3.3. Sustainable Sample Preparation Prior to Chromatographic Analysis
3.3.1. Microextraction Techniques
3.3.2. Use of Green Solvents
3.3.3. Energy-Assisted Techniques
3.3.4. Miniaturization and Integration Techniques
3.3.5. Sustainability Assessment Tools
4. Applications in Food Analysis
4.1. Analysis of Bioactive Compounds
4.2. Detection of Contaminants and Residues
4.2.1. Mycotoxins
4.2.2. Acrylamide
4.2.3. Pesticides
4.2.4. Drug Residues
4.3. Green Analytics for Clean-Label and Sustainability Claims
5. Regulatory Compliance and Certification Schemes
5.1. ISO 14001 and Green Laboratory Practices
5.2. Integration of ISO 22000 and HACCP
5.3. ESG and GFSI Alignment
6. Challenges and Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| GAC | green analytical chemistry |
| GAPI | Green Analytical Procedure Index |
| AGREE | analytical GREEnness |
| BAGI | Blue Applicability Grade Index |
| WAC | white analytical chemistry |
| RGB | red–green–blue |
| QuEChERS | quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe |
| SPME | solid phase microextraction |
| SBSE | stir-bar sorptive extraction |
| SFE | supercritical fluid extraction |
| ATP | analytical target profile |
| QbD | quality by design |
| DoE | design of experiments |
| NADES | natural deep eutectic solvents |
| ILs | ionic liquids |
| UAE | ultrasound assisted extraction |
| MAE | microwave-assisted extraction |
| ESI | electrospray ionization |
| PDMS | polydimethylsiloxane |
| MI-FPSE | magnet integrated FPSE |
| PLE | pressurized liquid extraction |
| SWE | subcritical water extraction |
| SFC | supercritical fluid chromatography |
| MRLs | maximum residue limits |
| EFSA | European Food Safety Authority |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| CAC | Codex Alimentarius Commission |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| DMIPs | dummy molecularly imprinted polymers |
| HRMS | high-resolution mass spectrometry |
| SANTE | EU Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety guidelines |
| NEMI | National Environmental Method Index |
| EMS | Environmental Management Systems |
| PDCA | plan-do-check-act |
| PRPs | prerequisite programs |
| CCPs | critical control points |
| ESG | environmental, social, and governance |
| GFSI | Global Food Safety Initiative |
References
- Ahmed, M.; Abdullah, E.; Eiman, E.; Al-Ahmary, K.M.; Aftab, F.; Sohail, A.; Raza, H.; Ali, I. Advances in green liquid chromatography for pharmaceutical analysis: A comprehensive review on analytical greenness to sustainable chemistry approaches. Microchem. J. 2024, 205, 111400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhafeez, M.; Arafa, M.; Amro, F.; Youssef, F. Green analytical chemistry to eco-friendly HPLC techniques in pharmaceutical analysis: A review. Egypt. J. Vet. Sci. 2024, 55, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Yu, L.; Guo, Y.; Wang, C.; Ge, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, N.; You, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, M. Green analytical chemistry metrics for evaluating the greenness of analytical procedures. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 14, 101013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros-Vivas, D.; Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Mendiola, J.A.; Ibáñez, E.; Cifuentes, A. Green food analysis: Current trends and perspectives. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 31, 100522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, A.K.; Zarouri, A. Green analytical chemistry—Recent innovations. Analytica 2025, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Deeb, S. Enhancing sustainable analytical chemistry in liquid chromatography: Guideline for transferring classical high-performance liquid chromatography and ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography methods into greener, bluer, and whiter methods. Molecules 2024, 29, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barot, S.; Modi, D.; Patel, A.; Pathak, M.; Patel, K.; Patel, C.N. A comprehensive review on green analytical chemistry. World J. Pharm. Res. 2024, 13, 232–246. [Google Scholar]
- Thakar, I.; Patel, K.; Goswami, J.; Bhavsar, A.; Patel, C.N. Green analytical chemistry: A critical review of eco-friendly techniques. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Res. 2025, 31, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. AGREE—Analytical GREEnness metric approach and software. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10076–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautre, H.K.; Sahu, T.R. Green analytical chemistry: Principles and applications—A review. NeuroQuantology 2021, 19, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psillakis, E. HPLC 2025 preview: The road to sustainable analytical chemistry. In HPLC 2025 Companion: Hot Topics in (U)HPLC; LCGC Europe: Cheshire, UK, 2025; pp. 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Green Chemistry. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/greenchemistry (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.; Namieśnik, J. The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 50, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branković, M. Green chemical analysis: Main principles and current efforts towards greener analytical methodologies. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 5274–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, P.M.; Wietecha-Posłuszny, R.; Woźniakiewicz, M.; Woźniakiewicz, A.; Król, M.; Kozak, J.; Wieczorek, M.; Knihnicki, P.; Paluch, J.; Telk, A.; et al. A perspective of the comprehensive and objective assessment of analytical methods including the greenness and functionality criteria: Application to the determination of zinc in aqueous samples. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 753399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.M.; Konieczka, P.; Namieśnik, J. Analytical Eco-Scale for assessing the greenness of analytical procedures. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallart-Mateu, D. Sustainability assessment in food analysis: The application of green analytical chemistry tools to phthalate residue analysis in edible oils. Explor. Foods Foodomics 2024, 2, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J. A new tool for the evaluation of the analytical procedure: Green Analytical Procedure Index. Talanta 2018, 181, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, R.; Desai, S. Sustainability in pharmaceutical analysis: Greenness assessment of HPLC methods for paclitaxel. Discov. Chem. 2025, 2, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Wojnowski, W. Complementary green analytical procedure index (ComplexGAPI) and software. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 8657–8665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, H.M.; Obaydo, R.H.; Mohamed, E.H. Environmentally sustainable computationally spectrophotometric resolution strategy for analysis single-tablet regimens of antihypertension with overlapped spectra. Talanta Open 2023, 7, 100226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, F.R.; Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Locatelli, M. Modified GAPI (MoGAPI) tool and software for the assessment of method greenness: Case studies and applications. Analytica 2024, 5, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinkaya, A.; Kaya, S.I.; Ozkan, S.A. An overview of the current progress in green analytical chemistry by evaluating recent studies using greenness assessment tools. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 168, 117330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Tobiszewski, M.; Wojnowski, W.; Psillakis, E. Corrigendum to: A tutorial on AGREEprep: An analytical greenness metric for sample preparation. Adv. Sample Prep. 2022, 4, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanidou, V.; Manousi, N.; Wojnowski, W.; Płotka-Wasylka, J. Blue applicability grade index (BAGI) and software: A new tool for the evaluation of method practicality. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 7598–7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Mehta, D.; Mashru, R. Recent application of green analytical chemistry: Eco-friendly approaches for pharmaceutical analysis. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valvi, A.M.; Shelke, R.U.; Ghodke, S.S.; Rishipathak, D.D. Quality by design and green analytical chemistry: A review of novel approaches to chromatographic method development. Biosci. Biotech. Res. Asia 2025, 22, 497–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaljurand, M.; Koel, M. Recent advancements on greening analytical separation. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2011, 41, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, O.; Catani, M.; Bocian, S. Greener and whiter analytical procedure for theobromine and caffeine determination in tea using dimethyl carbonate as an extraction solvent and mobile phase constituent in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 12432–12440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capello, C.; Fischer, U.; Hungerbühler, K. What is a green solvent? A comprehensive framework for the environmental assessment of solvents. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanayutsiri, T.; Mantadilok, S.; Sapsin, J.; Tungwattanaviboon, T.; Wongwatanasin, J.; Opanasopit, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Rojanarata, T. Development of a green and rapid ethanol-based HPLC assay for aspirin tablets and feasibility evaluation of domestically produced bioethanol in Thailand as a sustainable mobile phase. Green Process Synth. 2025, 14, 20240200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterton, N. The green solvent: A critical perspective. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2021, 23, 2499–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalisz, O.; Hulicka, G.; Tobiszewski, M.; Bocian, S. Performance evaluation of green and conventional solvents in reversed-phase liquid chromatography based on the separation of nonpolar and polar substances. Green Chem. 2025, 27, 3020–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudin, K. Potential of green solvents as mobile phases in liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1750, 465810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalisz, O.; Jaworska, A.; Studzińska, S.; Bocian, S. Elimination of toxic solvents from analytical methods in food analysis: Caffeine determination in tea as an example. Foods 2024, 13, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannavacciuolo, C.; Pagliari, S.; Frigerio, J.; Giustra, C.M.; Labra, M.; Campone, L. Natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) combined with sustainable extraction techniques: A review of the green chemistry approach in food analysis. Foods 2023, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankech, T.; Gerhardtova, I.; Stefanik, O.; Chalova, P.; Jampilek, J.; Majerova, P.; Kovac, A.; Piestansky, J. Current green capillary electrophoresis and liquid chromatography methods for analysis of pharmaceutical and biomedical samples (2019–2023)—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1323, 342889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Gorantla, S. Green analytical approaches and eco-friendly solvents: Advancing industrial applications and environmental sustainability—A comprehensive review. Orient J. Chem. 2025, 41, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.; Inamuddin; Siddiq, A.; Naushad, M.; El-Desoky, G.E. Green solvents in thin-layer chromatography. In Green Solvents I: Properties and Applications in Chemistry; Mohammad, A., Inamuddin, Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 305–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Solvents and sustainable chemistry. Proc. R. Soc. A 2015, 471, 20150502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claux, O.; Santerre, C.; Abert-Vian, M.; Touboul, D.; Vallet, N.; Chemat, F. Alternative and sustainable solvents for green analytical chemistry. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 31, 100510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cesaris, M.G.; Antonelli, L.; Lucci, E.; Felli, N.; Dal Bosco, C.; Gentili, A. Current trends to green food sample preparation: A review. J. Chromatogr. Open 2024, 6, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, S.; Shah, U.; Patel, J.; Dua, M. Development of a quality by design-based eco-friendly RP-HPLC method for ticagrelor and aspirin. Green Anal. Chem. 2025, 13, 100271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena Pereira, F.; Kloskowski, A.; Namieśnik, J. Perspectives on the replacement of harmful organic solvents in analytical methodologies: A framework toward the implementation of a generation of eco-friendly alternatives. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3687–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesús, F.; Cutillas, V.; Aguilera del Real, A.M.; Rodríguez Fernández-Alba, A. Advancements in multiresidue pesticide analysis in fruits and vegetables using micro-flow liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1358, 344100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blokland, M.H.; Mol, H.G.J. Advances in micro-ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry in residue and contaminant analysis. LCGC Sup. 2014, 32, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Nazario, C.E.D.; Silva, M.R.; Franco, M.S.; Lanças, F.M. Evolution in miniaturized column liquid chromatography instrumentation and applications: An overview. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1421, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, C.J.; Wu, N.; Biba, M.; Hartman, R.; Brkovic, T.; Gong, X.; Helmy, R.; Schafer, W.; Cuff, J.; Pirzada, Z.; et al. Greening analytical chromatography. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventouri, I.K.; Veelders, S.; Passamonti, M.; Endres, P.; Roemling, R.; Schoenmakers, P.J.; Somsen, G.W.; Haselberg, R.; Gargano, A.F.G. Micro-flow size-exclusion chromatography for enhanced native mass spectrometry of proteins and protein complexes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1266, 341324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozing, G. Micropillar array columns for advancing nanoflow HPLC. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, A. Miniaturized LC Optimized Using HPLC-Based System; LCGC International: Iselin, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mejía-Carmona, K.; Maciel, E.V.S.; Lanças, F.M. Miniaturized liquid chromatography applied to the analysis of residues and contaminants in food: A review. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 1680–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Bautista, S.; Molins-Legua, C.; Campíns-Falcó, P. Miniaturized liquid chromatography in environmental analysis: A review. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1730, 465101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.B.; Chen, A.; Liu, S. Miniaturized high-performance liquid chromatography instrumentation. Talanta 2018, 177, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleston-Rangel, R. Why use miniaturized columns in liquid chromatography? Benefits and challenges. LCGC N. Am. 2021, 17, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas Medina, D.A.; Lanças, F.M. What still hinders the routine application of miniaturized liquid chromatography beyond the omics sciences? J. Chromatogr. Open 2024, 6, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azooz, E.A.; Azooz, E.A.; Tuzen, M.; Ullah, N. Green analytical chemistry: Current status and future perspectives in sample preparation. In Green Analytical Chemistry: Current Status and Future Perspectives in Sample Preparation, 1st ed.; Locatelli, M., Kaya, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2024; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alampanos, V.; Samanidou, V. Current trends in green sample preparation before liquid chromatographic bioanalysis. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 31, 100499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmad, W.; Kaya, S.I.; Cetinkaya, A.; Varanusupakul, P.; Ozkan, S.A. Green chemistry methods for food analysis: Overview of sample preparation and determination. Adv. Sample Prep. 2023, 5, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A.; Locatelli, M.; Ulusoy, H.I. Recent trends in microextraction techniques employed in analytical and bioanalytical sample preparation. Separations 2017, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fabric phase sorptive extraction: A new generation, green sample preparation approach. In Solid-Phase Extraction; Fanali, S., Haddad, P.R., Poole, C.F., Schoenmakers, P.J., Lloyd, D., Eds.; Handbooks in Separation Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 355–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F. (Ed.) . Miniaturization in Sample Preparation; De Gruyter Open: Berlin, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-3-11-041017-4. eISBN 978-3-11-041018-1. [Google Scholar]
- Samanidou, V.; Kabir, A. Magnet integrated fabric phase sorptive extraction (MI-FPSE): A powerful green(er) alternative for sample preparation. Analytica 2022, 3, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, P. Sustainable Green Solvents in Microextraction: Review of Recent Advancements. LCGC N. Am. 2024, 20, 7. Available online: https://www.chromatographyonline.com/view/sustainable-green-solvents-microextraction-recent-advancements (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Rutkowska, M.; Owczarek, K.; Tobiszewski, M.; Namieśnik, J. Extraction with environmentally friendly solvents. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didion, Y.P.; Tjalsma, T.G.; Su, Z.; Malankowska, M.; Pinelo, M. What is next? The greener future of solid–liquid extraction of biobased compounds: Novel techniques and solvents overpower traditional ones. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 320, 124147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramvash, A.; Gholami-Banadkuki, N.; Moazzeni-Zavareh, F.; Hajizadeh-Turchi, S. An environmentally friendly and efficient method for extraction of PHB biopolymer with non-halogenated solvents. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 1936–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Câmara, J.S.; Perestrelo, R.; Berenguer, C.V.; Andrade, C.F.P.; Gomes, T.M.; Olayanju, B.; Kabir, A.; Rocha, C.M.R.; Teixeira, J.A.; Pereira, J.A.M. Green extraction techniques as advanced sample preparation approaches in biological, food, and environmental matrices: A review. Molecules 2022, 27, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patanè, P.; Laganà, P.; Devi, P.; Vig, A.; Haddad, M.A.; Natalello, S.; Cava, M.A.; Ameen, S.M.; Hashim, H.A. Polyphenols and functional foods from the regulatory viewpoint. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadange, Y.A.; Carpenter, J.; Saharan, V.K. A comprehensive review on advanced extraction techniques for retrieving bioactive components from natural sources. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 31274–31297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Singh, V.; Chopra, H.K.; Panesar, P.S. Extraction and characterization of phenolic compounds from mandarin peels using conventional and green techniques: A comparative study. Discov. Food 2024, 4, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Champi, D.; Romero-Orejon, F.L.; Moran-Reyes, A.; Muñoz, A.M.; Ramos-Escudero, F. Bioactive compounds in potato peels, extraction methods, and their applications in the food industry: A review. CyTA J. Food 2023, 21, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, V.; Poul, P.; Oeung, S.; Srey, P.; Mao, K.; Ung, H.; Eng, P.; Heim, M.; Srun, M.; Chheng, C.; et al. Bioactive compounds, antioxidant activities, and HPLC analysis of nine edible sprouts in Cambodia. Molecules 2023, 28, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggia, R.; Turrini, F.; Villa, C.; Lacapra, C.; Zunin, P.; Parodi, B. Green extraction from pomegranate marcs for the production of functional foods and cosmetics. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente Ballesteros, A.; Priovolos, I.; Ares, A.M.; Escobar, D.; Bernal, J. Green sample preparation methods for the analysis of bioactive compounds in bee products: A review. Adv. Sample Prep. 2023, 6, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir-Cerdà, A.; Nuñez, O.; Granados, M.; Sentellas, S.; Saurina, J. An overview of the extraction and characterization of bioactive phenolic compounds from agri-food waste within the framework of circular bioeconomy. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 161, 116994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Zurdo, D.; Gómez-Mejía, E.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Rosales-Conrado, N.; Sierra, I. Analytical strategies for green extraction, characterization, and bioactive evaluation of polyphenols, tocopherols, carotenoids, and fatty acids in agri-food bio-residues. Molecules 2025, 30, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repajić, M.; Cegledi, E.; Kruk, V.; Pedisić, S.; Çınar, F.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Žutić, I.; Dragović-Uzelac, V. Accelerated solvent extraction as a green tool for the recovery of polyphenols and pigments from wild nettle leaves. Processes 2020, 8, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondo, T.F. Advancing Selectivity in Extraction and Analysis of Bioactive Compounds in Seaweed and Plant-Based Foods; Lund University: Lund, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Montero-Calderon, A.; Cortes, C.; Zulueta, A.; Frigola, A.; Esteve, M.J. Green solvents and ultrasound-assisted extraction of bioactive orange (Citrus sinensis) peel compounds. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shalabi, R.; Abdul Samad, N. Moringa oleifera extraction, isolation, quantification and its application in functional foods: A review. Aust. Herbal Insight 2024, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, M.A.; Aktaş, H.; Pokorski, P.; Pogorzelska-Nowicka, E.; Custodio-Mendoza, J.A. A comprehensive review of analytical approaches for carotenoids assessment in plant-based foods: Advances, applications, and future directions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedelmaksoud, T.G.; Younis, M.I.; Altemimi, A.B.; Tlay, R.H.; Hassan, N.A. Bioactive compounds of plant-based food: Extraction, isolation, identification, characteristics, and emerging applications. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Câmara, J.S.; Albuquerque, B.R.; Aguiar, J.; Corrêa, R.C.G.; Gonçalves, J.L.; Granato, D.; Pereira, J.A.M.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Food bioactive compounds and emerging techniques for their extraction: Polyphenols as a case study. Foods 2021, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, L.C.; Grisales-Mejía, J.F.; Strieder, M.M.; Mendiola, J.A.; Ibáñez, E. Innovative Sample Preparation Techniques in Food Analysis: The Rise of Compressed Fluids and Novel Solvents. Adv. Sample Prep. 2025, 15, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, N.; Berenguer, C.V.; Câmara, J.S.; Pereira, J.A.M. What are we eating? Surveying the presence of toxic molecules in the food supply chain using chromatographic approaches. Molecules 2024, 29, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, D.; Morsi, R.; Usman, M.; Meetani, M.A. Recent advances in the chromatographic analysis of emerging pollutants in dairy milk: A review (2018–2023). Molecules 2024, 29, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenta, S.; de la Guardia, M. Green chromatography for the analysis of foods of animal origin. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutillas, V.; Ferrer, C.; Martínez-Bueno, M.J.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Green analytical approaches for contaminants: Sustainable alternatives to conventional chromatographic methods. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1750, 465921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshannaq, A.; Yu, J.H. Occurrence, toxicity, and analysis of major mycotoxins in food. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, J.W. Chromatographic analysis of mycotoxins. In Chromatographic Analysis of Environmental and Food Toxicants, 1st ed.; Nollet, L.M.L., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Jartín, J.M.; Alfonso, A.; Botana, A.M.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Analysis of natural toxins by liquid chromatography. In Liquid Chromatography, 3rd ed.; Fanali, S., Haddad, P.R., Poole, C.F., Schoenmakers, P.J., Lloyd, D., Eds.; Handbooks in Separation Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 2, pp. 257–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, A.; Lippolis, V.; Pascale, M. Overview of recent liquid chromatography mass spectrometry-based methods for natural toxins detection in food products. Toxins 2022, 14, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gab-Allah, M.A.; Tahoun, I.F.; Yamani, R.N.; Rend, E.A.; Shehata, A.B. Eco-friendly and sensitive analytical method for determination of T-2 toxin and HT-2 toxin in cereal products using UPLC-MS/MS. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 107, 104395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizy, A.; Olia, A.; Feizy, J. A graphene reinforced fabric phase sorptive extraction method for determination of ochratoxin A in food samples. Iran. J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 9, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi Moghaddam, N.; Feizy, J.; Es’haghi, Z.; Malvandi, A.M. Fabric phase sorptive extraction increases the accuracy of liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection of zearalenone in food samples. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, N.; Gañán, J.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Sierra, I. New advanced materials and sorbent-based microextraction techniques as strategies in sample preparation to improve the determination of natural toxins in food samples. Molecules 2020, 25, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, H.; Feizi, J.; Eshaghi, Z. Development of a nanoparticle-assisted fabric phase sorptive extraction technique coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for sensitive determination of aflatoxins in food samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res. 2023, 10, 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Esmati, A.; Olia, A.; Mohadesi, A.; Feizy, J. A fabric phase sorptive extraction protocol combined with liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection for the determination of ochratoxin in food samples. Food Anal. Methods 2023, 16, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastià, A.; Pallarés, N.; Bridgeman, L.; Juan-García, A.; Castagnini, J.M.; Ferrer, E.; Barba, F.J.; Berrada, H. A critical review of acrylamide green extraction and determination in food matrices: Current insights and future perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Dionisopoulou, N. Acrylamide: Formation, occurrence in food products, detection methods, and legislation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 708–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahebi, H.; Hashempour-Baltork, F.; Mirza Alizadeh, A.; Hassanzadazar, H.; Hosseini, M.J.; Rastegar, H. Application of green analytical chemistry for acrylamide determination in Iranian traditional breads: A human risk assessment study. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 19, 100799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastià, A.; Ramon-Mascarell, F.; Fernández-Matarredona, C.; Barba, F.J.; Berrada, H.; Pardo, O.; Esteve-Turrillas, F.A.; Ferrer, E. Development of a greener and sustainable method to determine acrylamide in corn products by LC-MS/MS: Evaluation of levels in corn-based products. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.R.; Arabi, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers based on a green synthesis strategy for magnetic solid-phase extraction of acrylamide in food samples. Talanta 2019, 195, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaloo Kermani, P.; Moeenfard, M.; Farhoosh, R.; Alves, A. Modified QuEChERS purification method for analysis of acrylamide in roasted Phoenix dactylifera L. seeds via HPLC–PDA. Food Meas. 2023, 17, 5034–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabee, M.; Said, R.A.M.; Alqarni, M.; Naguib, I.A. Green, white and simple polymeric-coated graphite sensor for rapid in situ determination of acrylamide in food products. BMC Chem. 2025, 19, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albishri, H.M.; Abd El-Hady, D. Eco-friendly ionic liquid-based ultrasonic assisted selective extraction coupled with a simple liquid chromatography for the reliable determination of acrylamide in food samples. Talanta 2014, 118, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oracz, J.; Nebesny, E.; Żyżelewicz, D. New trends in quantification of acrylamide in food products. Talanta 2011, 86, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Liu, K.; Yang, J.; Hong, L.; Xie, X.; Wang, S. Review of research into the determination of acrylamide in foods. Foods 2020, 9, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabajal, M.D.; Arancibia, J.A.; Escandar, G.M. A green-analytical chemistry method for agrochemical-residue analysis in vegetables. Microchem. J. 2016, 128, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrarca, M.H.; Ccanccapa-Cartagena, A.; Masiá, A.; Godoy, H.T.; Picó, Y. Comparison of green sample preparation techniques in the analysis of pyrethrins and pyrethroids in baby food by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1497, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejczak, T.; Tuzimski, T. Recent trends in sample preparation and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry for pesticide residue analysis in food and related matrixes. J. AOAC Int. 2015, 98, 1143–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Khunger, A.; Wallen, S.L.; Kaushik, A.; Chaudhary, G.R.; Varma, R.S. Advanced green analytical chemistry for environmental pesticide detection. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 30, 100488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musarurwa, H.; Chimuka, L.; Tavengwa, N.T. Green pre-concentration techniques during pesticide analysis in food samples. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2019, 54, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagirani, M.S.; Ozalp, O.; Soylak, M. New trend in the extraction of pesticides from environmental and food samples applying microextraction based green chemistry scenario: A review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 1343–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, H.İ.; Köseoğlu, K.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fabric phase sorptive extraction followed by HPLC-PDA detection for the monitoring of pirimicarb and fenitrothion pesticide residues. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gómez, L.; Pereira, J.A.M.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Câmara, J.S.; Sierra, I. Green extraction approach based on μSPEed® followed by HPLC-MS/MS for the determination of atropine and scopolamine in tea and herbal tea infusions. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musarurwa, H.; Tavengwa, N.T. Sustainable extraction of pesticides in food and environmental samples using emerging green adsorbents. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 24, 100545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walorczyk, S.; Drożdżyński, D.; Kierzek, R. Determination of pesticide residues in samples of green minor crops by gas chromatography and ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry. Talanta 2015, 132, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutillas, V.; Martínez Galera, M.; Rajski, Ł.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Evaluation of supercritical fluid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry for pesticide residues in food. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1545, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xie, K.; Lee, K. Veterinary drug residues in animal-derived foods: Sample preparation and analytical methods. Foods 2021, 10, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Tang, S.; Dai, C. Recent advances in pretreatment methods and detection techniques for veterinary drug residues in animal-derived foods. Metabolites 2025, 15, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mookantsa, S.O.S.; Chimuka, L.; Tavengwa, N.T. A cost-effective ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (IL–DLLME) combined with LC–MS/MS for simultaneous determination of multiple veterinary drug residues in beef muscle. Foods 2025, 14, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgou, E.; Manousi, N.; Samanidou, V.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fabric phase sorptive extraction for the fast isolation of sulfonamides residues from raw milk followed by high performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanidou, V.; Michaelidou, K.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fabric phase sorptive extraction of selected penicillin antibiotic residues from intact milk followed by high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanidou, V.; Galanopoulos, L.D.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fast extraction of amphenicols residues from raw milk using novel fabric phase sorptive extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 855, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khataei, M.M.; Huda, E.S.B.; Lood, R.; Spégel, P.; Yamini, Y.; Turner, C. A review of green solvent extraction techniques and their use in antibiotic residue analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 209, 114487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Al-Shaalan, N.H.; Alghamdi, A.H. A green HPLC method for determination of nine sulfonamides in milk and beef, and its greenness assessment with analytical Eco-Scale and Greenness Profile. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazlawy, H.N.; Zaazaa, H.E.; Merey, H.A.; Atty, S.A. Green validated chromatographic methods for simultaneous determination of co-formulated oxytetracycline HCl and flunixin meglumine in the presence of their impurities in different matrices. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2023, 20, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, D.; Fouad, M.M. Application of NEMI, analytical Eco-Scale and GAPI tools for greenness assessment of three developed chromatographic methods for quantification of sulfadiazine and trimethoprim in bovine meat and chicken muscles: Comparison to greenness profile of reported HPLC methods. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkawi, M.M.Z.; Safwat, M.T.; Abdelaleem, E.A.; Abdelwahab, N.S. Chromatographic analysis of bromhexine and oxytetracycline residues in milk as a drug analysis medium with greenness profile appraisal. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 4064–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-C.; Chen, H.; Wei, S.-L.; Ma, J.-K. A Novel Enrichment and Sensitive Method for Rapid Determination of Sulfonamide Antibiotics Residues in Fish. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 199, 116148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14024:2018; Environmental Labels and Declarations—Type I Environmental Labelling—Principles and Procedures. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- European Commission. About the EU Ecolabel; EU Ecolabel Scheme: Brussels, Belgium, 2024; Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/circular-economy/eu-ecolabel_en (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Klintman, M. A review of public policies relating to the use of environmental labelling and information schemes (ELIS). In OECD Environment Working Papers; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiboni-Oschilewski, O.; Abarca, M.; Santa Rosa Pierre, F.; Rosi, A.; Biasini, B.; Menozzi, D.; Scazzina, F. Strengths and weaknesses of food eco-labeling: A review. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1381135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabaja, B.; Wojnarowska, M.; Ćwiklicki, M.; Buffagni, S.C.; Varese, E. Does environmental labelling still matter? Generation Z’s purchasing decisions. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creydt, M.; Fischer, M. Food Profiling Goes Green: Sustainable Analysis Strategies for Food Authentication. Electrophoresis 2025, 46, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, T.; Asif, Z.; Khan, M.K.I. Clean label extraction of bioactive compounds from food waste through microwave-assisted extraction technique: A review. Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnegan, Y.; Krzyzaniak, S.A. Clean labels in the food industry: Regulatory considerations and challenges in balancing consumer demand, safety and sustainability. Food Sci. Nutr. Cases 2024, 20240017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.C.; Morais, C.; Franchini, B.; Pereira, B.; Pinho, O.; Cunha, L.M. Clean-label products: Factors affecting liking and acceptability by Portuguese older adults. Appetite 2024, 197, 107307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). ISO 14000 Family—Environmental Management. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standards/popular/iso-14000-family (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Gustia, R.; Martono, D.N.; Hamzah, U.S. Environmental performance evaluation of applying ISO 14001 in laboratory. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Singapore, 7–11 March 2021; IEOM Society: Singapore, 2021; pp. 4365–4371. [Google Scholar]
- Gammie, A.J.; Lopez, J.B.; Scott, S. Imperative: Reducing the environmental impact of clinical laboratories. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2023, 61, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 22000:2018; Food Safety Management Systems—Requirements for Any Organization in the Food Chain. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) System and Guidelines for Its Application; FAO/WHO: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zimon, D.; Madzik, P.; Domingues, P. Development of key processes along the supply chain by implementing the ISO 22000 standard. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihawi, B. The impact of ISO 22000:2018 on food facilities performance with multiple production lines. CyTA J. Food 2024, 22, 2431281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, A.; Frost, T.; Cao, H. Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosure: A literature review. Br. Account. Rev. 2023, 55, 101149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerardi, A. Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI): Underpinning the safety of the global food chain, facilitating regulatory compliance, trade, and consumer trust. In Present Knowledge in Food Safety: A Risk-Based Approach Through the Food Chain, 1st ed.; Newell, D.G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI). GFSI Case Study Booklet 2020. Available online: https://mygfsi.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/GFSI-Case-Study-Booklet-2020-WEB-.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Crandall, P.G.; Mauromoustakos, A.; O'Bryan, C.A.; Thompson, K.C.; Yiannas, F.; Bridges, K.; Francois, C. Impact of the Global Food Safety Initiative on food safety worldwide: Statistical analysis of a survey of international food processors. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI). Food Safety Culture: A Call to Action; GFSI Publication: Levallois-Perret, France, 2020; Available online: https://mygfsi.com (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Khamisu, M.S.; Paluri, R.A. Emerging trends of environmental social and governance (ESG) disclosure research. Cleaner Prod. Lett. 2024, 7, 100079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiny, A.; Taglialatela, J.; Testa, F.; Iraldo, F. Determinants of environmental social and governance (ESG) performance: A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 456, 142213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-AlGhafar, W.N.; Abo Shabana, R.; El-Shaheny, R.; Tolba, M.M. A Versatile HPLC Method Collaborated with NaDES-Ultrasound-Assisted LLE and Machine Learning for Purity Testing and Trace Analysis of 1,4-Benzodiazepines in Crime Scene Evidence, Hospital Effluents, and Pharmaceuticals. Talanta Open 2025, 11, 100475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, H.M.; Erk, N.; Genc, A.A.; Obaydo, R.H.; Tiris, G. Artificial Intelligence in Chromatography: Greenness and Performance Evaluation of AI-Predicted and In-Lab Optimized HPLC Methods for Simultaneous Separation of Amlodipine, Hydrochlorothiazide, and Candesartan. Talanta Open 2025, 11, 100473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, C.M.; Hussain, G.; Keçili, R. Smart Analytical Chemistry: Integrating Green, Sustainable, White and AI-Driven Approaches in Modern Analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2025, 191, 118295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Principle | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Direct techniques | Use direct analytical techniques to minimize extensive sample preparation. |
| 2 | Reduced sample size | Reduce sample size and number of samples to limit material consumption and waste. |
| 3 | In situ measurements | Favor in situ measurements to avoid transport and contamination risks. |
| 4 | Waste minimization | Minimize waste generation at every stage of the analytical process. |
| 5 | Safer solvents/reagents | Select safer solvents and reagents to reduce toxicity. |
| 6 | Avoid derivatization | Avoid derivatization to limit chemical use and waste. |
| 7 | Energy efficiency | Minimize energy consumption through energy-efficient instrumentation and conditions. |
| 8 | Miniaturization/reagent-free | Develop reagent-free or miniaturized methods. |
| 9 | Automation/integration | Use automation and integration to enhance efficiency and reduce errors. |
| 10 | Multi-analyte approach | Adopt multi-analyte or multi-parameter methods. |
| 11 | Real-time analysis | Pursue real-time analysis for timely decision-making and waste avoidance. |
| 12 | Greenness assessment | Apply greenness metrics to quantify and improve environmental performance. |
| Tool | Graphical Representation | Main Focus | Output Type | Notable Features | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAPI | 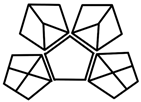 | Entire analytical workflow | Color-coded pictogram | Easy visualization, no total score | [17] |
| BAGI |  | Workflow + total score | Pictogram + % score | Integrates Eco-Scale scoring | [18] |
| Complex-GAPI | 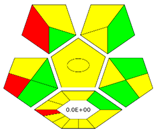 | Includes pre-analytical steps | Extended pictogram | More comprehensive greenness coverage | [19] |
| AGREE | 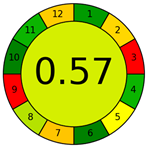 | 12 principles of GAC | Radial chart (0–1) | Holistic single-score metric | [20] |
| AGREEprep | 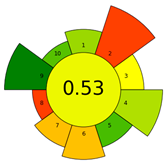 | Sample preparation | Pictogram + score | First dedicated sample prep metric | [21] |
| Application Area | Green Approaches Applied | Example Food Matrices |
|---|---|---|
| Bioactives (polyphenols, carotenoids, alkaloids) | Green solvents (EtOH, NADES), UAE/MAE, SFC, micro-HPLC | Tea, citrus peels, pomegranate, seaweed, bee products, agri-food by-products |
| Contaminants and residues (pesticides, mycotoxins, acrylamide, veterinary drugs) | Miniaturized QuEChERS, FPSE, IL-DLLME, green HPLC phases | Cereal products, honey, potato chips, milk, fish, fruits, and vegetables |
| Clean-label and sustainability claims | Eco-friendly extraction, green profiling, chemometrics | Honey, plant-based foods, eco-labelled products |
| Green HPLC Approach | Application in Food Analysis | Regulation, Certification, and Sustainability |
|---|---|---|
| Eco-friendly solvents | Determination of bioactive compounds (polyphenols, vitamins, natural pigments) | ISO 14001 (environmental management) |
| Miniaturization (µ-HPLC) | Detection of contaminants and residues (pesticides, veterinary drugs) | ISO 22000/HACCP (food safety) |
| Energy-efficient methodologies | Clean-label and sustainability claims (additives, processing markers) | ESG criteria, GFSI alignment |
| Green sample preparation | Broad applicability across food matrices | Contribution to sustainable consumption and production |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karageorgou, E.G.; Kalogiouri, N.P.; Samanidou, V.F. Green Approaches in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography for Sustainable Food Analysis: Advances, Challenges, and Regulatory Perspectives. Molecules 2025, 30, 3573. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173573
Karageorgou EG, Kalogiouri NP, Samanidou VF. Green Approaches in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography for Sustainable Food Analysis: Advances, Challenges, and Regulatory Perspectives. Molecules. 2025; 30(17):3573. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173573
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarageorgou, Eftychia G., Natasa P. Kalogiouri, and Victoria F. Samanidou. 2025. "Green Approaches in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography for Sustainable Food Analysis: Advances, Challenges, and Regulatory Perspectives" Molecules 30, no. 17: 3573. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173573
APA StyleKarageorgou, E. G., Kalogiouri, N. P., & Samanidou, V. F. (2025). Green Approaches in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography for Sustainable Food Analysis: Advances, Challenges, and Regulatory Perspectives. Molecules, 30(17), 3573. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173573







