A Novel Pattern Recognition Method for Non-Destructive and Accurate Origin Identification of Food and Medicine Homologous Substances with Portable Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Spectra of FMHSs
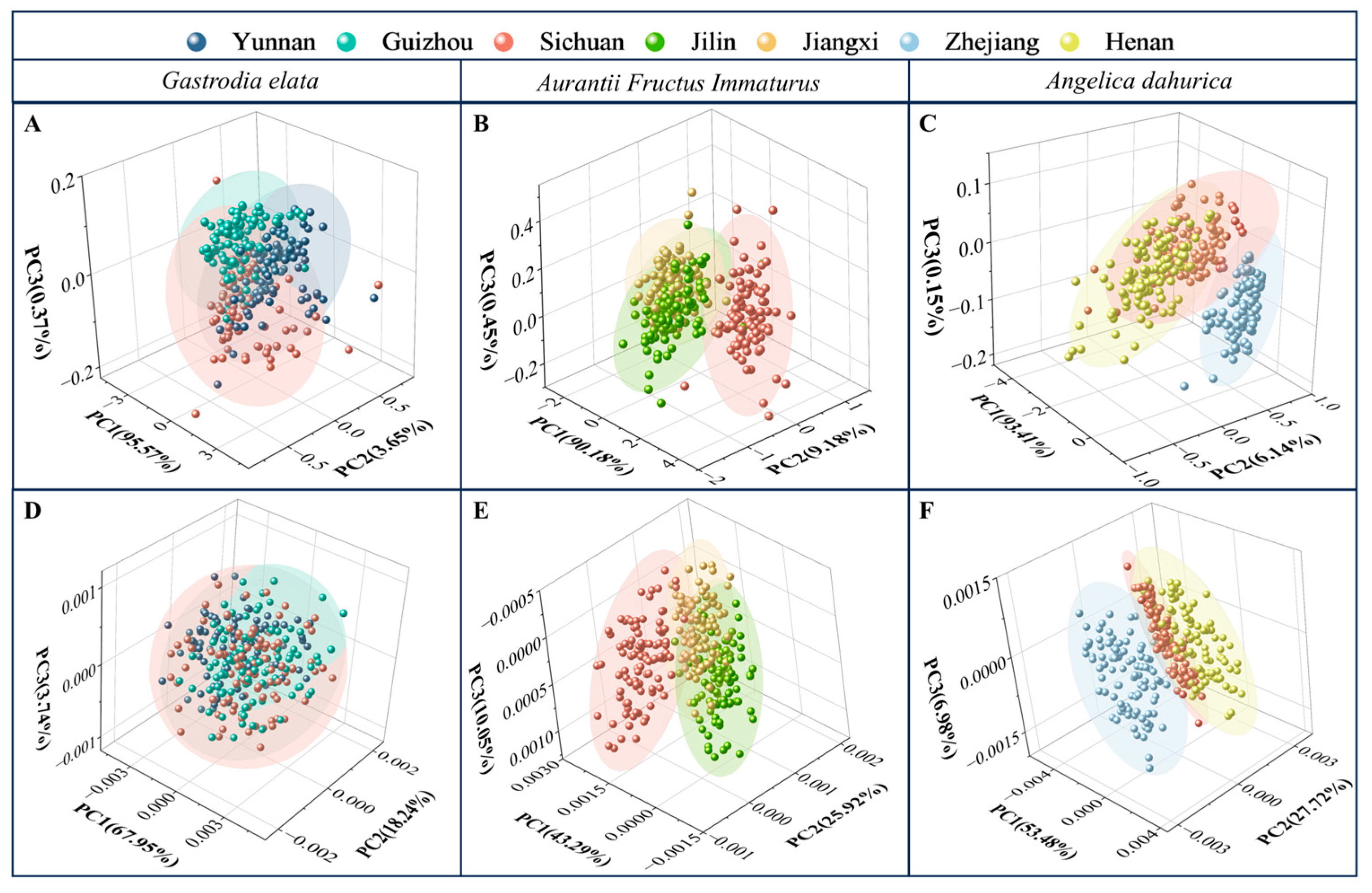
2.2. Identification Results of PCA
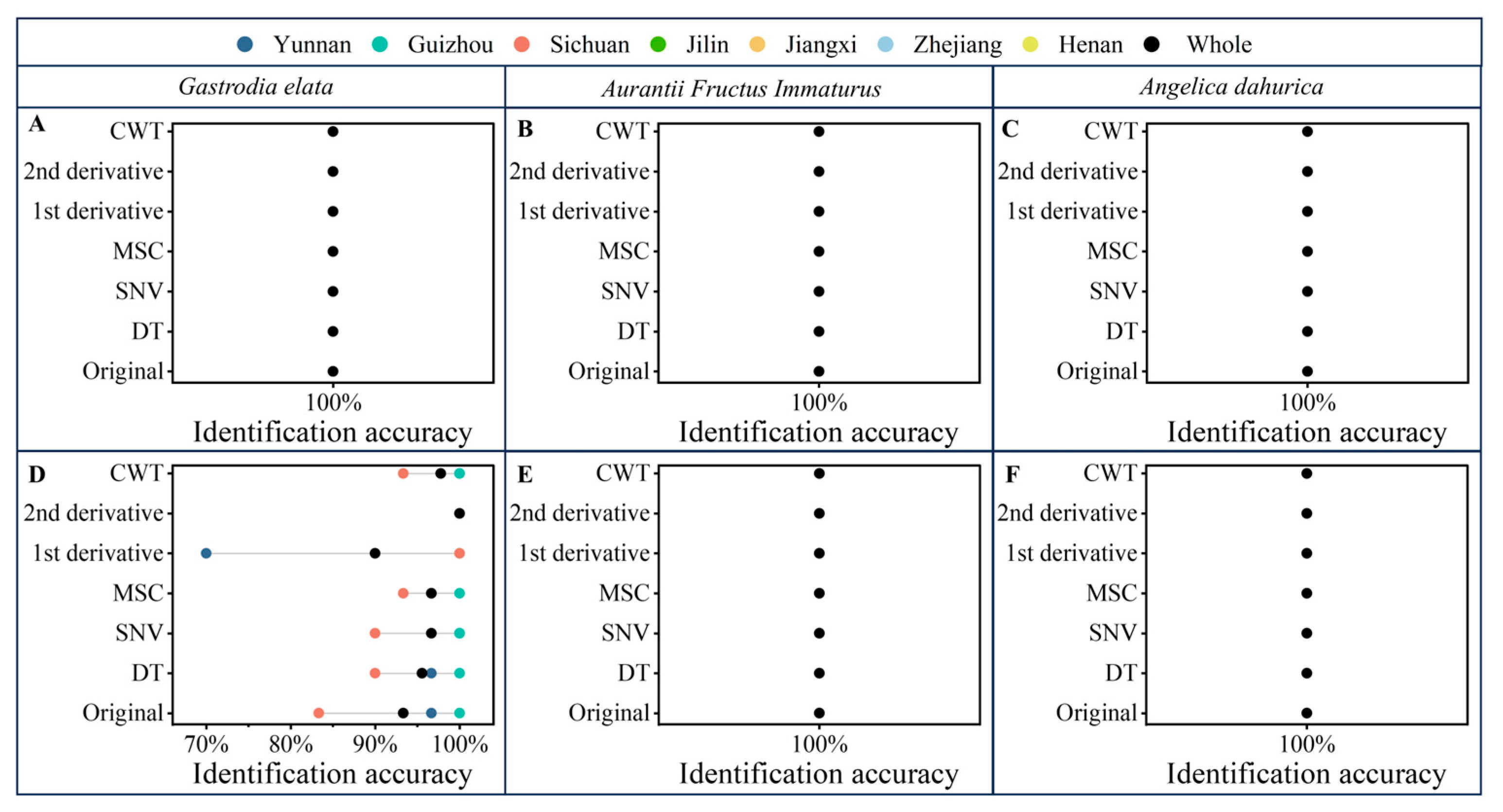
2.3. Identification Results of PLS-DA and Boosting-PLS-DA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples
4.2. Instrumentation and Spectra Measurement
4.3. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.Q.; Zhang, J.L.; Sang, Y.M.; Wei, Y.N.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Xue, H.K. Polysaccharides from medicine and food homology materials: A review on their extraction, purification, structure, and biological activities. Molecules 2022, 27, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.X.; Fang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Yang, J.; Fu, H.Y.; Yang, X.L.; Li, X.F.; Chen, Z.P.; Yu, R.Q. Data fusion of synchronous fluorescence and surface enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopies for geographical origin traceability of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. Spectrosc. Lett. 2022, 55, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.M.; Zhao, Y.F.; Shang, D.R.; Zhai, Y.X.; Ning, J.S.; Ding, H.Y.; Sheng, X.F. Identification of the geographical origins of sea cucumbers in China: The application of stable isotope ratios and compositions of C, N, O and H. Food Control 2019, 111, 107036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.H.; Gong, S.; Liu, Y.S.; Li, X.H.; Li, M.F.; Zeng, D.F.; Li, J.G.; Guo, Y.P.; Guo, L. Rapid discrimination of the authenticity and geographical origin of bear bile powder using stable isotope ratio and elemental analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Bai, X.Y.; Wen, F.M.; Liu, K.H.; Yang, J.; Chen, H.Y.; Yang, X.L. Accurate origin identification of Chinese white Chrysanthemi Flos by analysis of C, N, O, H stable isotope ratios and mineral elements combined with chemometrics. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 124, 105703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Fan, J.F.; An, Y.B.; Meng, G.L.; Ji, B.Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, C.H. Quality evaluation, health risk assessment, and geographic origin tracing of Ophiocordyceps sinensis through mineral element analysis. Microchem. J. 2024, 201, 110512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ye, L.H.; Li, J.H.; Huang, W.K.; Huo, Y.J.; Gao, J.X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.T. Identification of Ophiopogonis Radix from different producing areas by headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry analysis. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e13850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.F.; Wang, M.J.; Zeng, Z.M.; Dai, C.Y.; Ren, F.L.; Yin, H.B.; Chen, L. Data fusion of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and high-performance liquid chromatography for the origin identification of different medicinal rhizomes of genus Atractylodes. Microchem. J. 2025, 211, 113110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubert, J.; Lacina, O.; Zachariasova, M.; Hajslova, J. Saffron authentication based on liquid chromatography high resolution tandem mass spectrometry and multivariate data analysis. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, S.; Yan, H.; Wang, J.M.; Zhou, J.Q.; Yang, J.; Duan, J.A. Headspace GC/MS and fast GC e-nose combined with chemometric analysis to identify the varieties and geographical origins of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Yu, M.; Li, M.Q.; Zheng, Y.; Li, P. Nondestructive identification of different chrysanthemum varieties based on near-infrared spectroscopy and pattern recognition methods. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2022, 42, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.P.; Altaner, C.; Feng, L.; Liu, P.P.; Song, Z.Y.; Li, L.Q.; Gui, A.H.; Wang, X.P.; Ning, J.M.; Zheng, P.C. A review: Integration of NIRS and chemometric methods for tea quality control-principles, spectral preprocessing methods, machine learning algorithms, research progress, and future directions. Food Res. Int. 2025, 205, 115870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Y.; Yu, M.; Li, S.K.; Jiang, L.W.; Zheng, Y.; Li, P. A novel strategy of “pick the best of the best” for the nondestructive identification of Poria cocos based on near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4176–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Ping, J.C.; Wang, X.; Sha, X.; Wang, Y.S.; Miao, P.Q.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, W.L. Data fusion of near-infrared and mid-infrared spectroscopy for rapid origin identification and quality evaluation of Lonicerae japonicae flos. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 320, 124590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.L.; Lei, W.; Li, J.; Wang, X.T.; Su, J.Y.; Sahati, T.; Aierkenjiang, X.; Tian, R.Y.; Zhou, W.H.; Zhang, J.X.; et al. A dual-technology approach: Handheld NIR spectrometer and CNN for Fritillaria spp. quality control. Foods 2025, 14, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.X.; Li, S.K.; Du, G.R.; Jiang, L.W.; Liu, X.; Ding, S.H.; Shan, Y. A rapid and nondestructive approach for the classification of different-age Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium using portable near infrared spectroscopy. Sensors 2020, 20, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.W.; Dong, Y.Q.; Jiang, L.W.; Fan, W.; Du, G.R.; Li, P. Portable near-infrared spectroscopy with variable selection-linear discriminant analysis technology for accurate and nondestructive detection of sulfur-fumigated Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium. LWT 2024, 205, 116518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitorus, A.; Pambudi, S.; Boodnon, W.; Lapcharoensuk, R. Near-infrared spectroscopy with machine learning for classifying and quantifying nutmeg adulteration. Anal. Lett. 2024, 57, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.T.; Yang, Q.W.; Li, C.Y.; Liu, X.L.; Niu, B.X. Rapid and simultaneous quality analysis of the three active components in Lonicerae Japonicae Flos by near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, X.T.; Huang, J.; Cao, X.Q.; Wu, M.J.; Yang, Y. Rapid measurement of total saponins, mannitol, and naringenin in Dendrobium officinale by near-Infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Foods 2024, 13, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.Q.; Zhong, H.S.; Wu, J.H.; Li, K.X.; Huang, Y.; Fang, H.M.; Hassan, M.; Yao, L.J.; Zhao, C. Application of portable near-infrared spectroscopy for quantitative prediction of protein content in Torreya grandis kernels under different states. Foods 2025, 14, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.Z.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Fan, W.; Jiang, L.W.; Li, P. Accurate discrimination of mold-damaged Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium using partial least-squares discriminant analysis and selected wavelengths. Foods 2024, 13, 3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.Q.; Shan, Y.; Li, P.; Jiang, L.W.; Liu, X. Nondestructive characterization of citrus fruit by near-Infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (NIRDRS) with principal component analysis (PCA) and Fisher linear discriminant analysis (FLDA). Anal. Lett. 2022, 55, 2554–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.C.; Liong, C.Y.; Jemain, A.A. Partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) for classification of high-dimensional (HD) data: A review of contemporary practice strategies and knowledge gaps. Analyst 2018, 143, 3526–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.Y.; Wu, Z.S.; Qiao, Y.J. Comparison of ensemble strategies in online NIR for monitoring the extraction process of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae based on different variable selections. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinzawa, H.; Jiang, J.H.; Ritthiruangdej, P.; Ozaki, Y. Investigations of bagged kernel partial least squares (KPLS) and boosting KPLS with applications to near-infrared (NIR) spectra. J. Chemom. 2006, 20, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Wang, J.Y.; Wu, T.; Qin, X.; Li, M.L. Determination of nicotine in tobacco samples by near-infrared spectroscopy and boosting partial least squares. Vib. Spectrosc. 2010, 54, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Dong, Y.Q.; Jiang, L.W.; Du, G.R.; Shan, Y. Nondestructive prediction of lime acidity with a single scan using two types of near infrared spectrometers and ensemble learning strategy. J. Food Eng. 2024, 368, 111917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, T.; Wang, Y.T.; Wang, Z.J.; Hu, X.Y.; Yuan, T.J.; Yu, Q.; Xie, J.H.; Chen, Y. Rapid classification of Camellia seed varieties and non-destructive high-throughput quantitative analysis of fatty acids based on non-targeted fingerprint spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. Food Chem. 2025, 474, 143181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Perez, D.; Guan, H.B.; Madhivanan, P.; Mathee, K.; Narasimhan, G. So you think you can PLS-DA? BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.P.; Zeng, Z.D.; Hou, Y.; Chen, A.M.; Xu, J.; Zhao, L.Q.; Liu, X.Y. Rapid authentication of variants of Gastrodia elata Blume using near-infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometric methods. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 235, 115592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.M.; Luo, R.M.; Zhou, Y.P.; Xu, H.; Song, D.D.; Ze, T.; Yang, T.M.; Nie, Y. Boosting partial least-squares discriminant analysis with application to near infrared spectroscopic tea variety discrimination. J. Chemometr. 2012, 26, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.C.; Qu, F.F.; Lin, L.; Dong, T.; He, Y.; Shao, Y.N.; Zhang, Y. Detection of water content in rapeseed leaves using terahertz spectroscopy. Sensors 2017, 17, 2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.Y.; Liu, H.G.; Li, T.; Li, J.Q.; Wang, Y.Z. Two dimensional correlation spectroscopy combined with ResNet: Efficient method to identify bolete species compared to traditional machine learning. LWT 2022, 162, 113490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.H.; Wen, S.Z.; Li, S.F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, X.G.; Niu, L.Y. Based on near-infrared spectroscopy combined with data enhancement CNN algorithm origin traceability method of Angelica dahurica. Chin. Pharm. J. 2024, 59, 2022–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Fan, M.Y.; Lei, J.W.; Xie, C.X.; Zhang, Q. Rapid quantitative determination of ethanol-extract in Aurantii Fructus Immaturus by near-infrared spectroscopy. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae. 2015, 21, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zhou, X.Y.; He, M.Y.; Li, C.; Cai, Z.Y.; Zhou, L.; Qi, H.N.; Zhang, C. A novel method combining deep learning with the Kennard-Stone algorithm for training dataset selection for image-based rice seed variety identification. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 8332–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.H.; Yang, W.B.; Zhang, K.X.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, W.L.; Kollenburg, G.V. A review on sample subset selection methods for multivariate modelling. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2025, 265, 105493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinnan, Å.; Berg, F.V.D.; Engelsen, S.B. Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra. Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Romero-Lorres, S.; Moshgbar, M. Practical considerations in data pre-treatment for NIR and Raman spectroscopy. Am. Pharm. Rev. 2010, 13, 116–127. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, P.; Fan, W. A Novel Pattern Recognition Method for Non-Destructive and Accurate Origin Identification of Food and Medicine Homologous Substances with Portable Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Molecules 2025, 30, 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173565
Liu W, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Jiang L, Li P, Fan W. A Novel Pattern Recognition Method for Non-Destructive and Accurate Origin Identification of Food and Medicine Homologous Substances with Portable Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Molecules. 2025; 30(17):3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173565
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wei, Ziqin Zhang, Yang Liu, Liwen Jiang, Pao Li, and Wei Fan. 2025. "A Novel Pattern Recognition Method for Non-Destructive and Accurate Origin Identification of Food and Medicine Homologous Substances with Portable Near-Infrared Spectroscopy" Molecules 30, no. 17: 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173565
APA StyleLiu, W., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Jiang, L., Li, P., & Fan, W. (2025). A Novel Pattern Recognition Method for Non-Destructive and Accurate Origin Identification of Food and Medicine Homologous Substances with Portable Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Molecules, 30(17), 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173565





