Recent Advances in the Development of Metal-Glycoconjugates for Medicinal Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Why Targeting Tumor Glucose Metabolism?
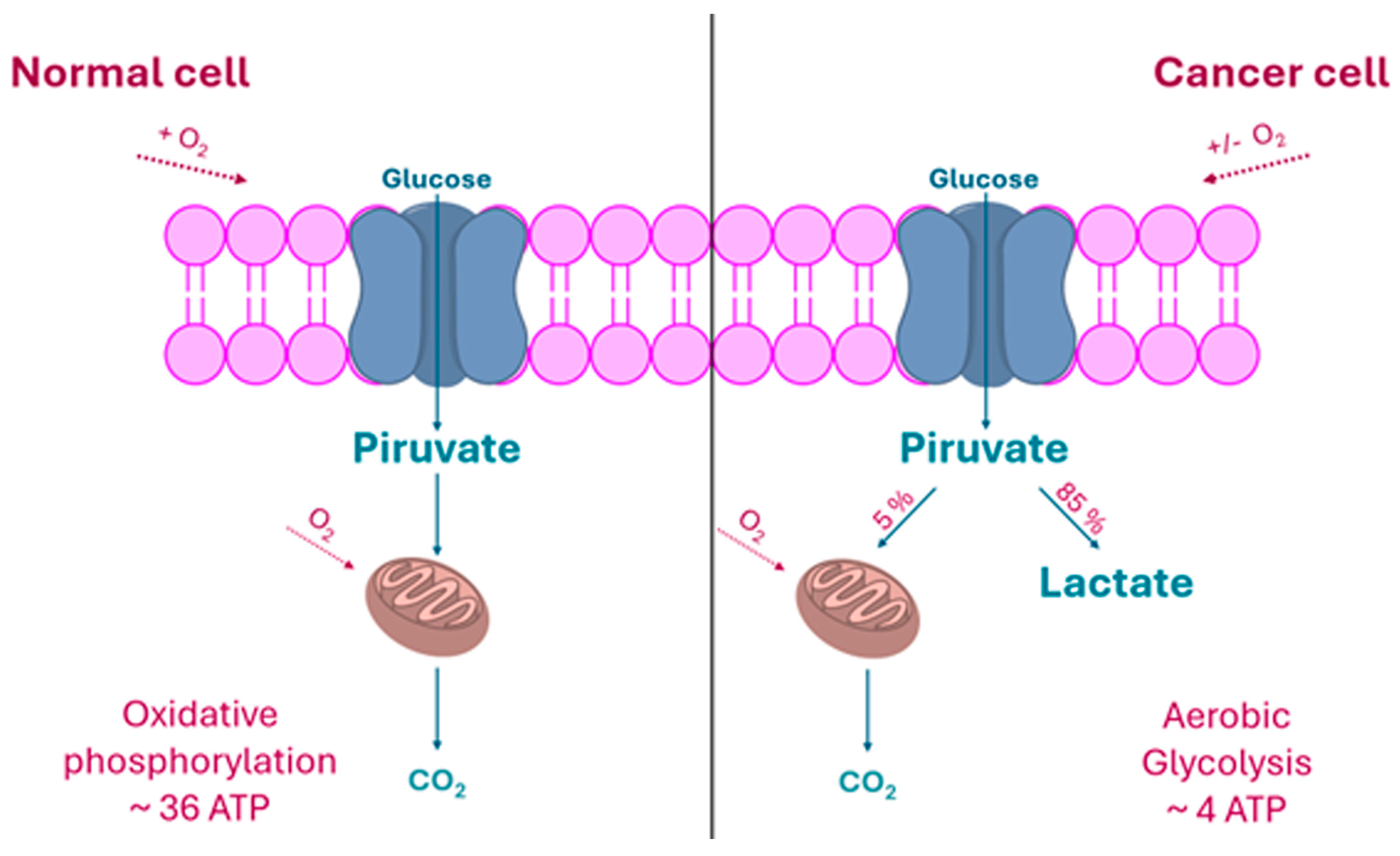
2.1. The “Warburg Effect” and Its Consequences
2.2. The Rationale of Metal-Carbohydrate Conjugation
- Metabolic targeting via GLUTs overexpressed in tumors.
- Improved pharmacokinetic properties (e.g., water solubility, biodistribution).
- Reduced systemic toxicity.
- Possibility of controlled activation within the tumor microenvironment through enzyme-mediated cleavage.
3. Metal-Glycoconjugates for Oncological Applications
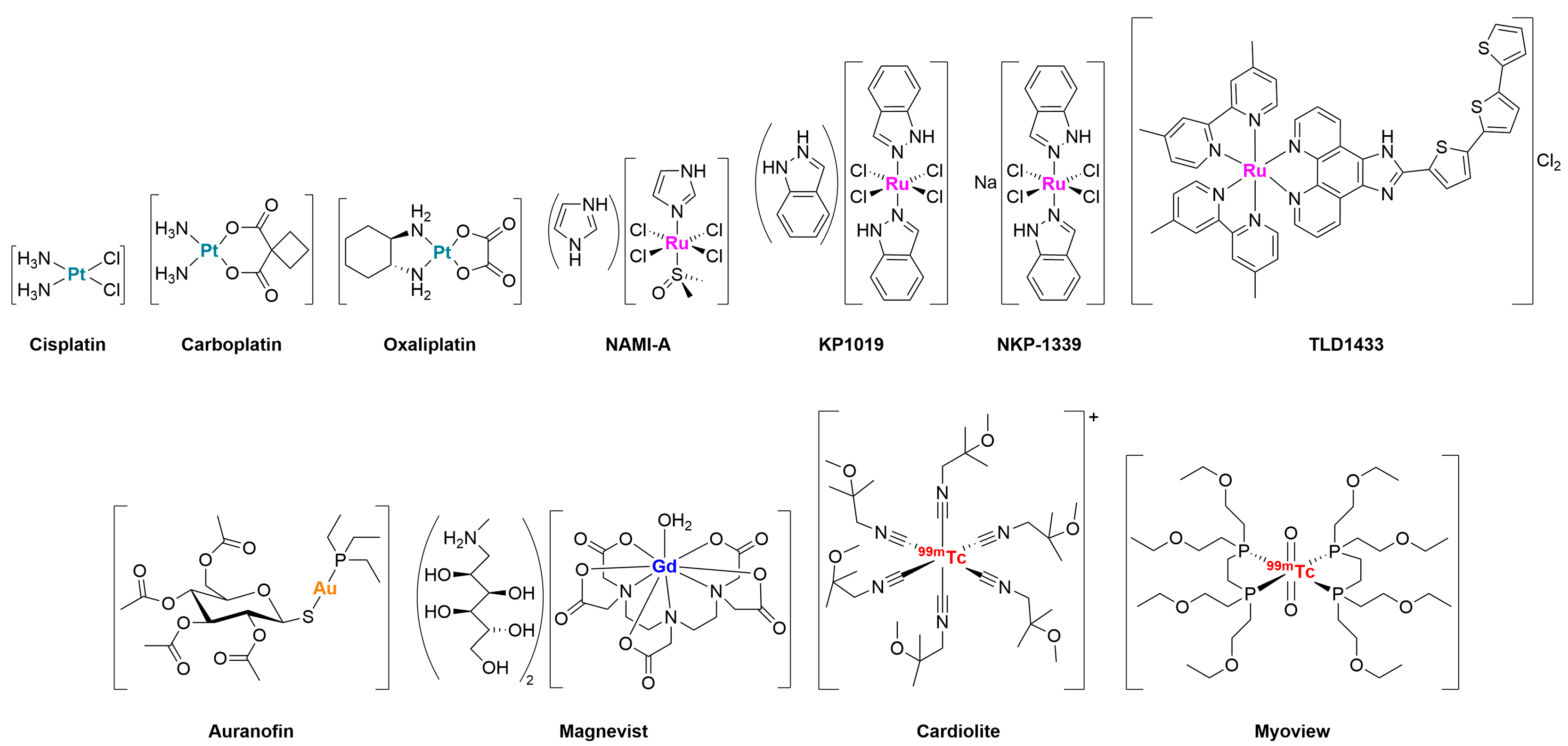
3.1. Platinum Complexes
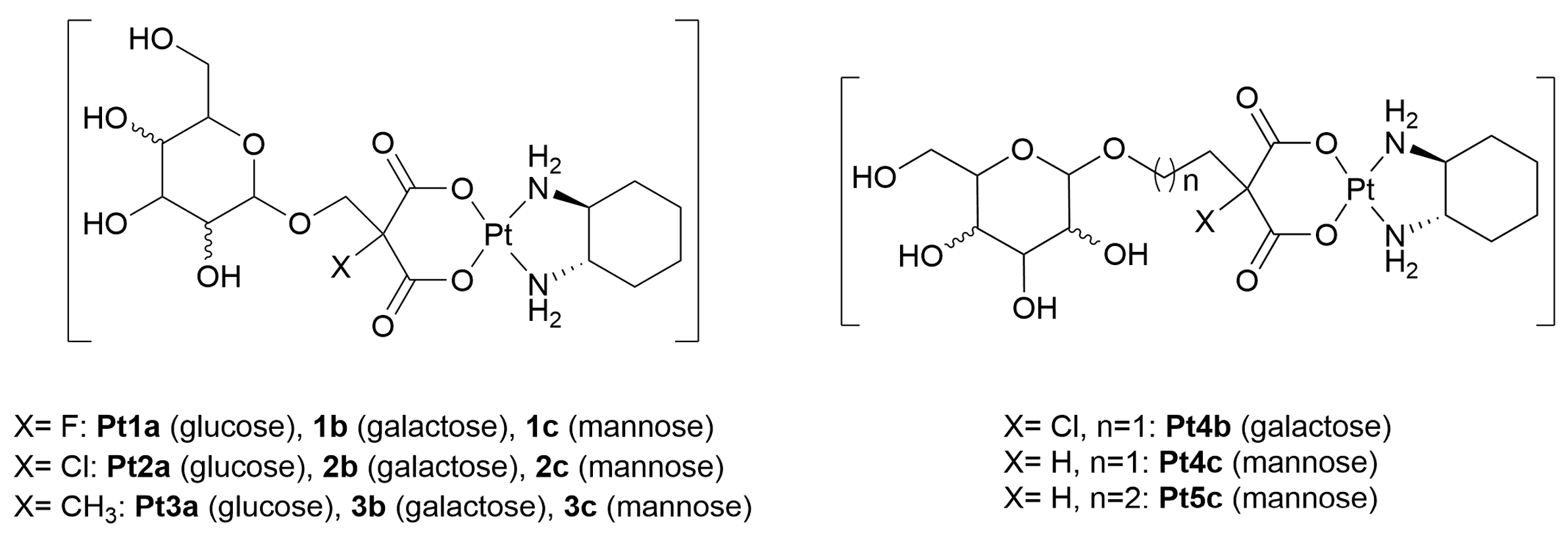
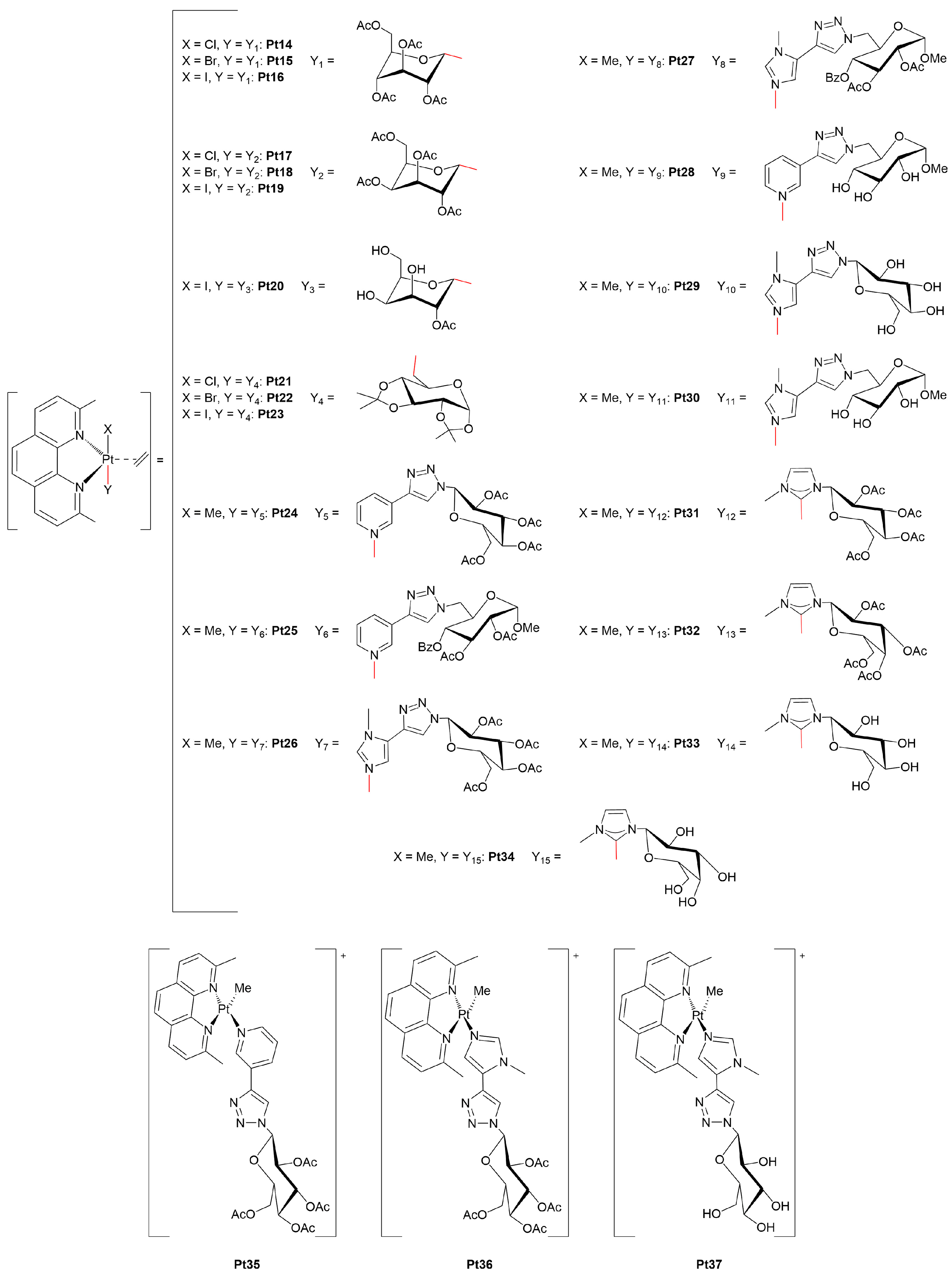
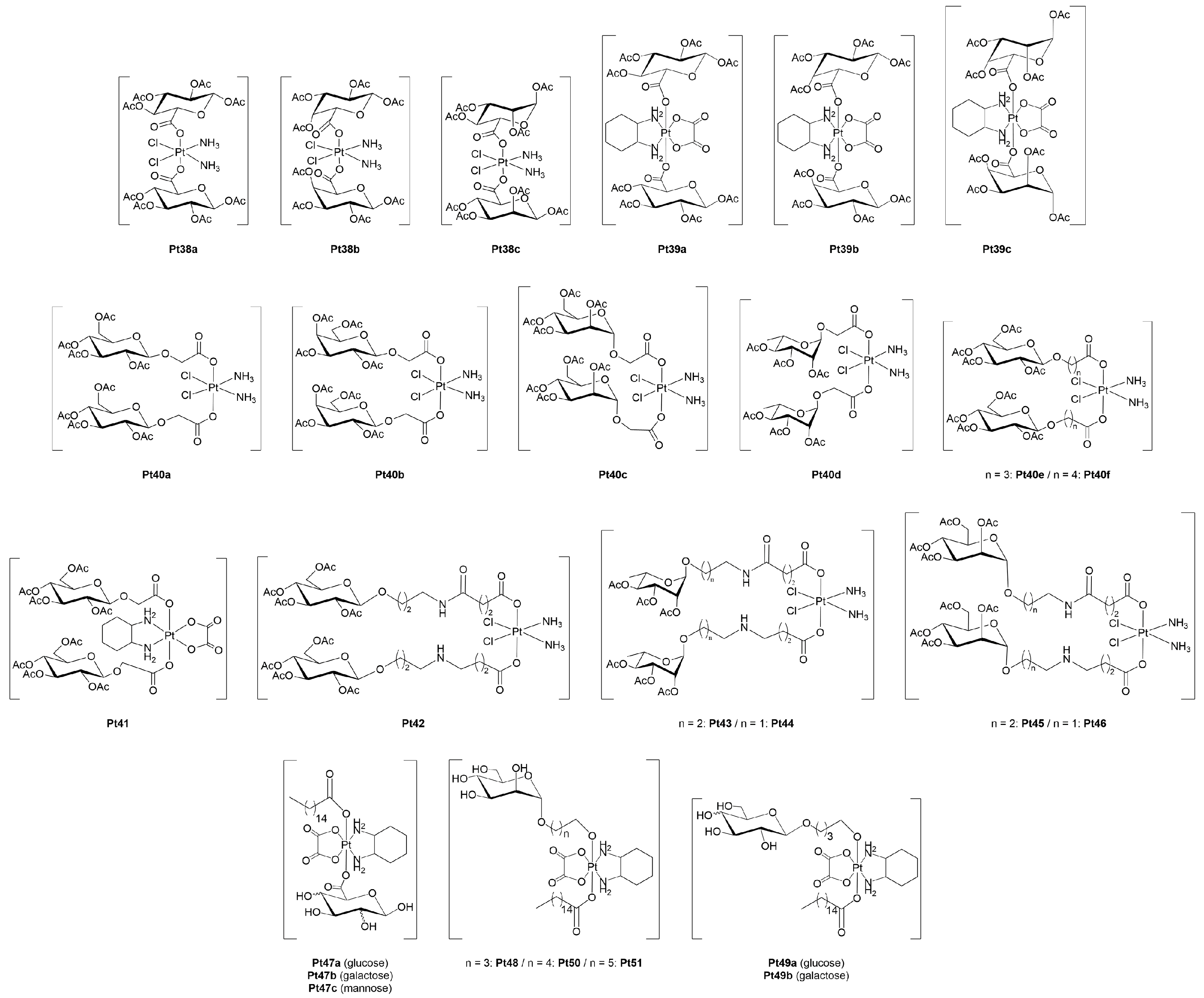
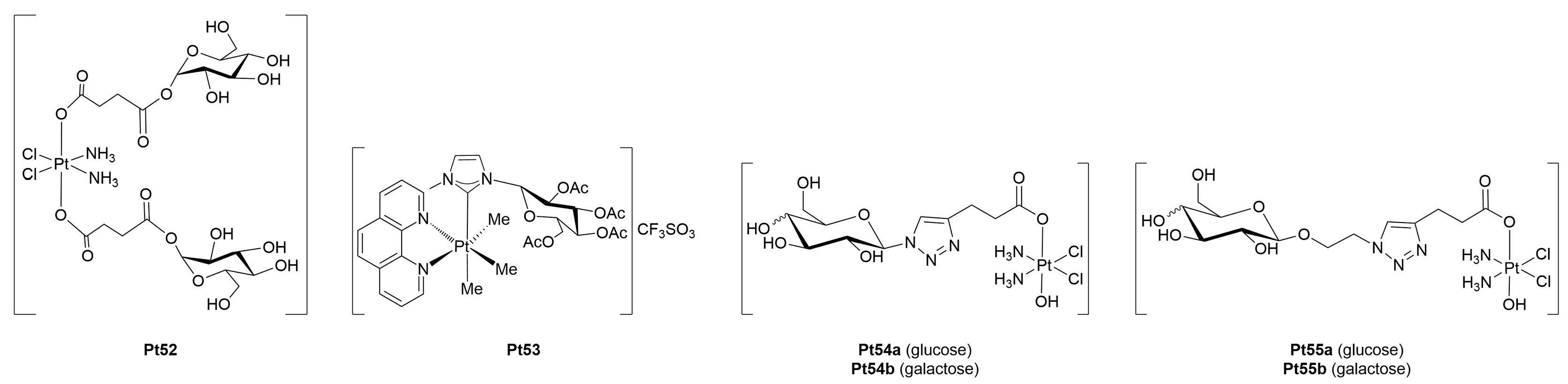
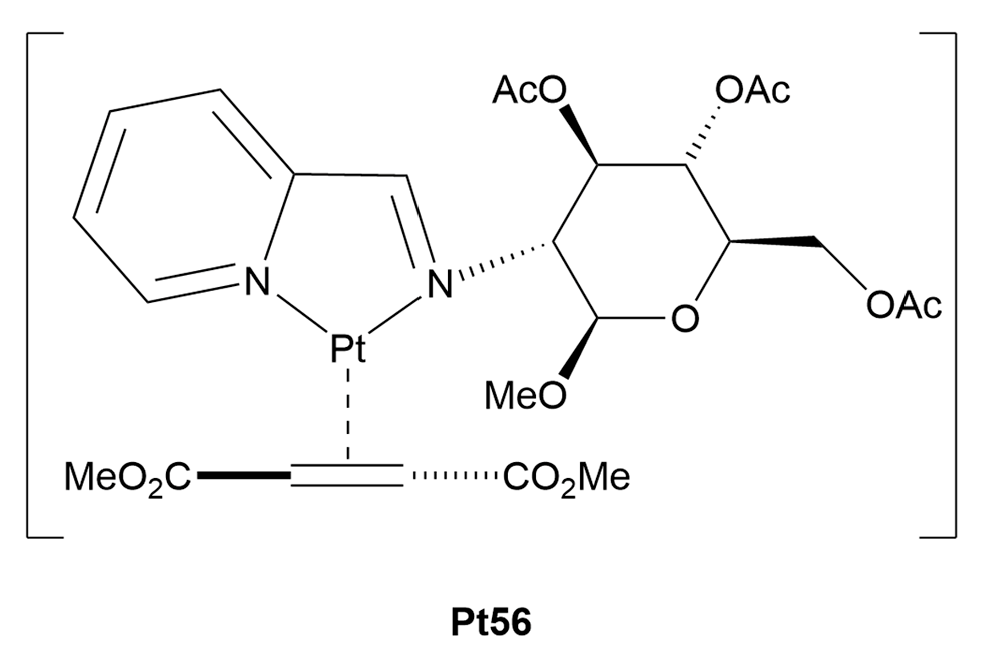
3.1.1. Platinum(II)-Glycoconjugates
3.1.2. Platinum(IV)-Glycoconjugates
3.1.3. Are Platinum(0)-Glycoconjugates a Feasible Alternative?
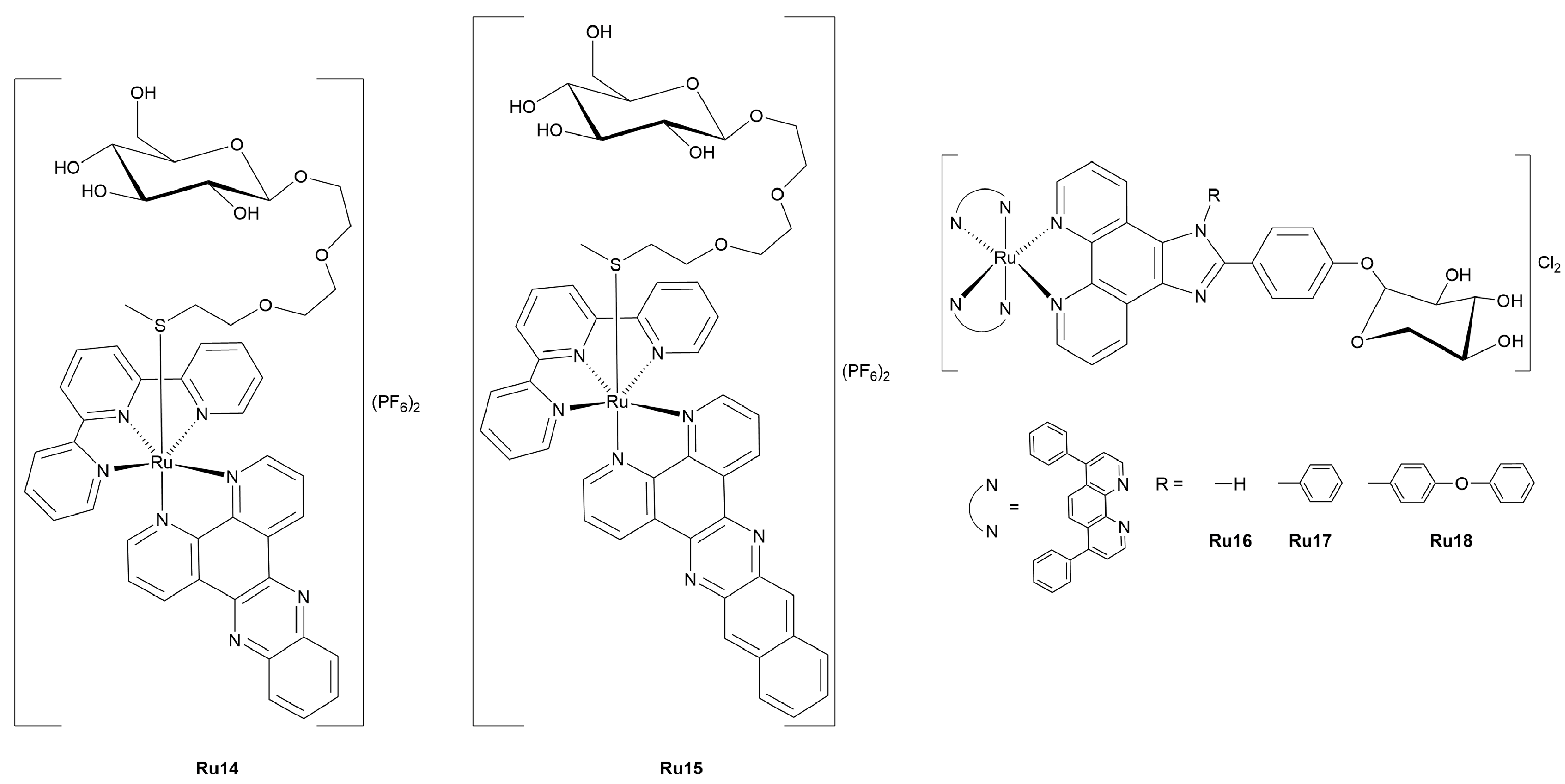
3.2. Ruthenium Complexes
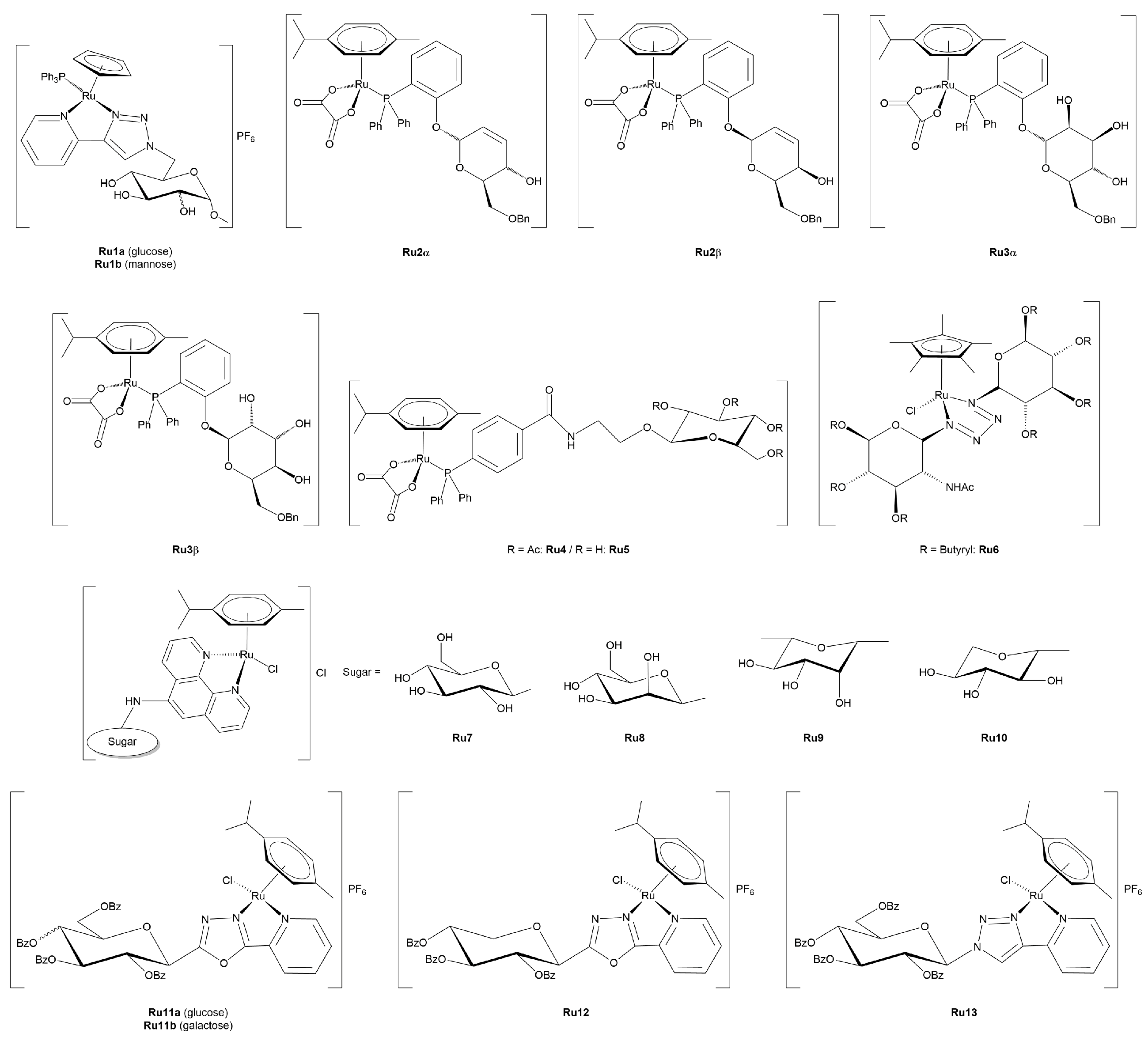
3.2.1. Ruthenium(II)-Glycoconjugates
3.2.2. Photoactivatable Ruthenium(II)-Glycoconjugates
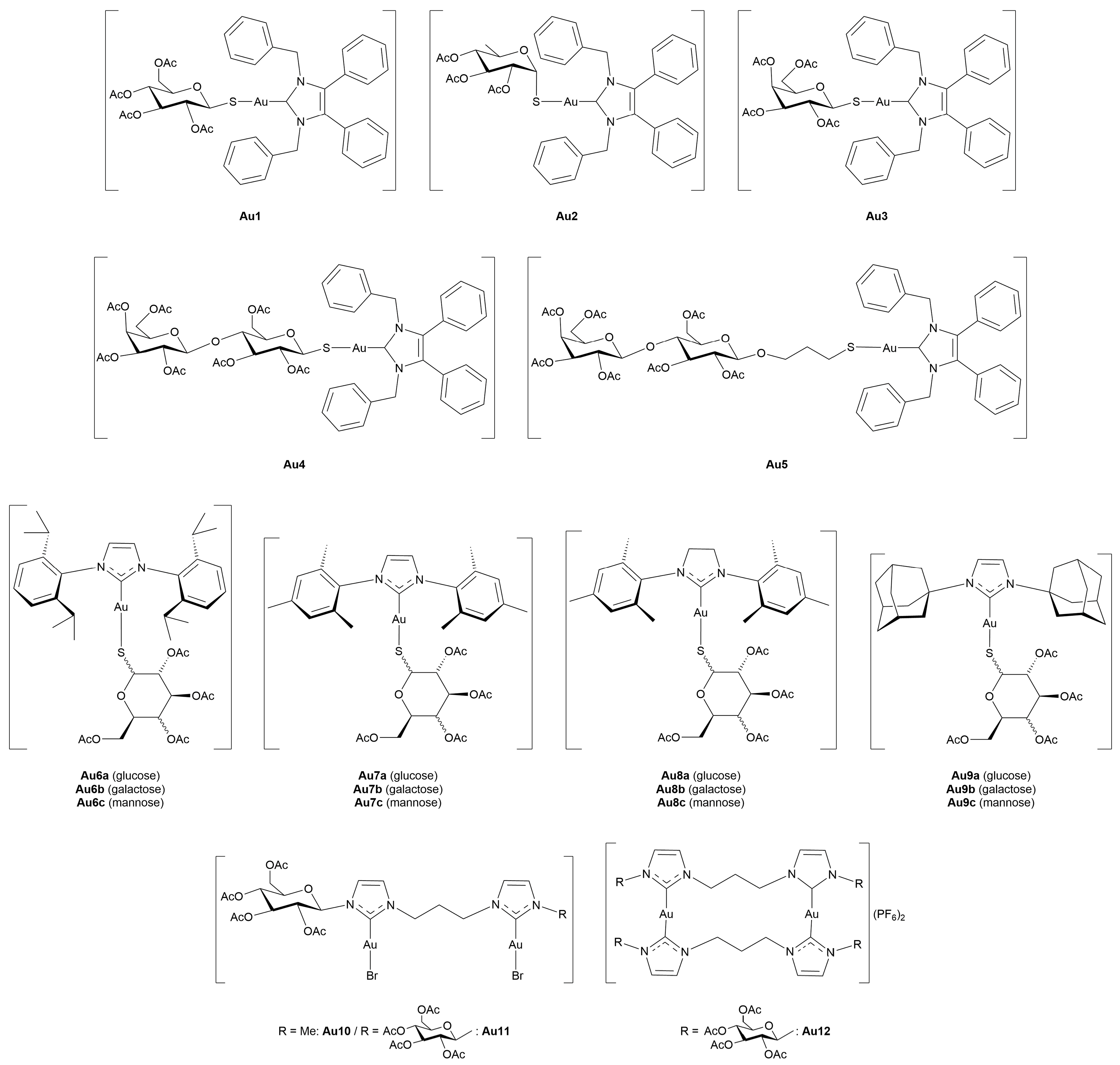
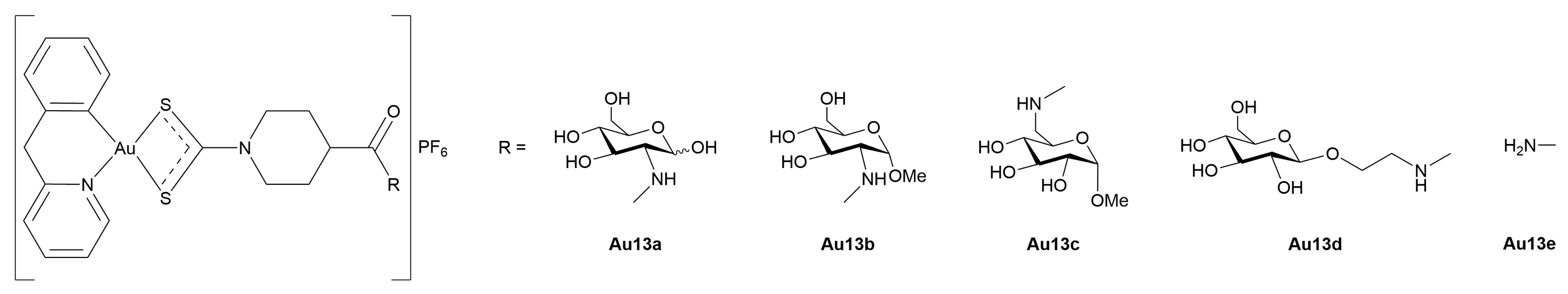
3.3. Gold Complexes
3.3.1. Gold(I)-Glycoconjugates
3.3.2. Gold(III)-Glycoconjugates
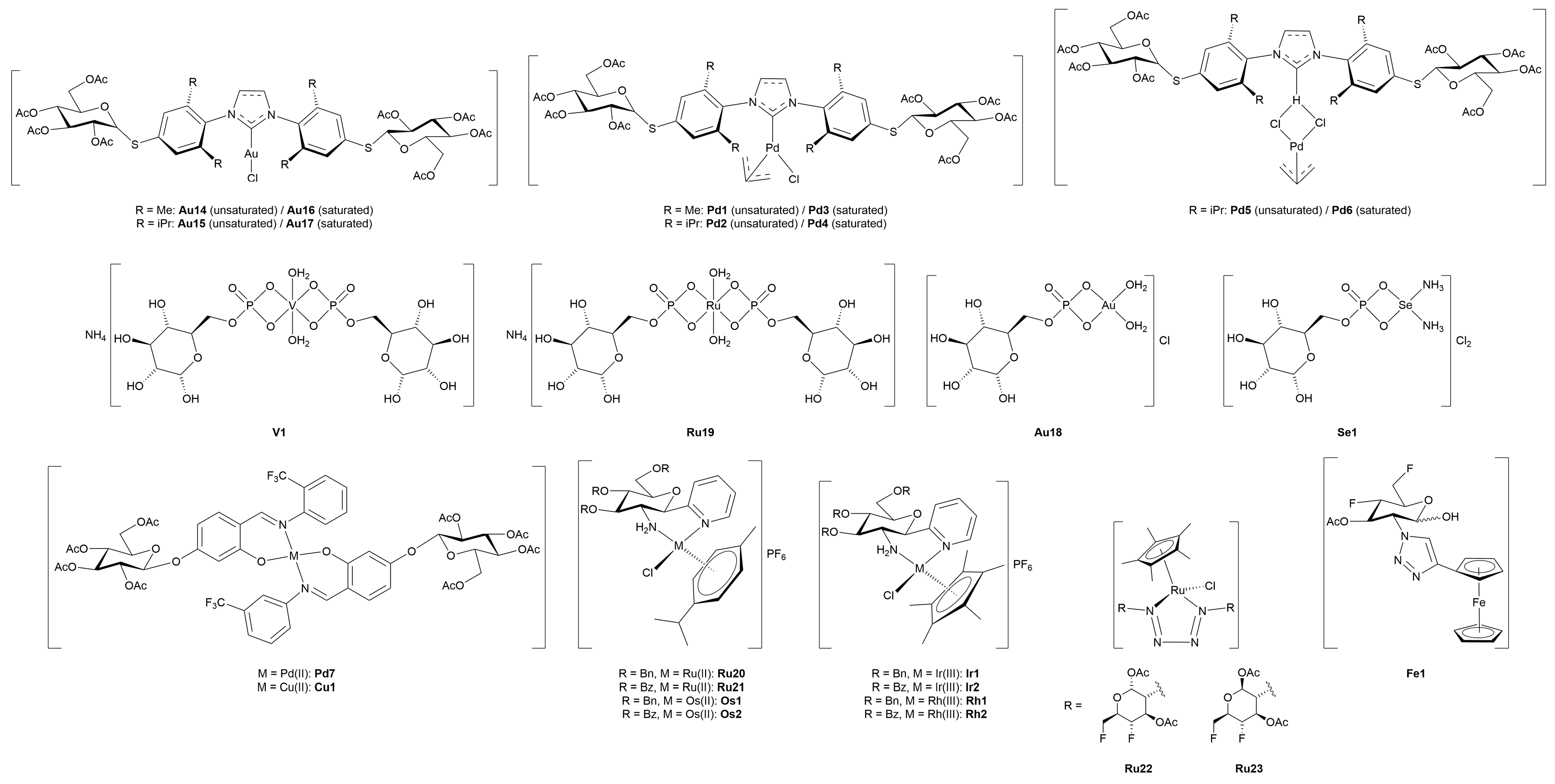
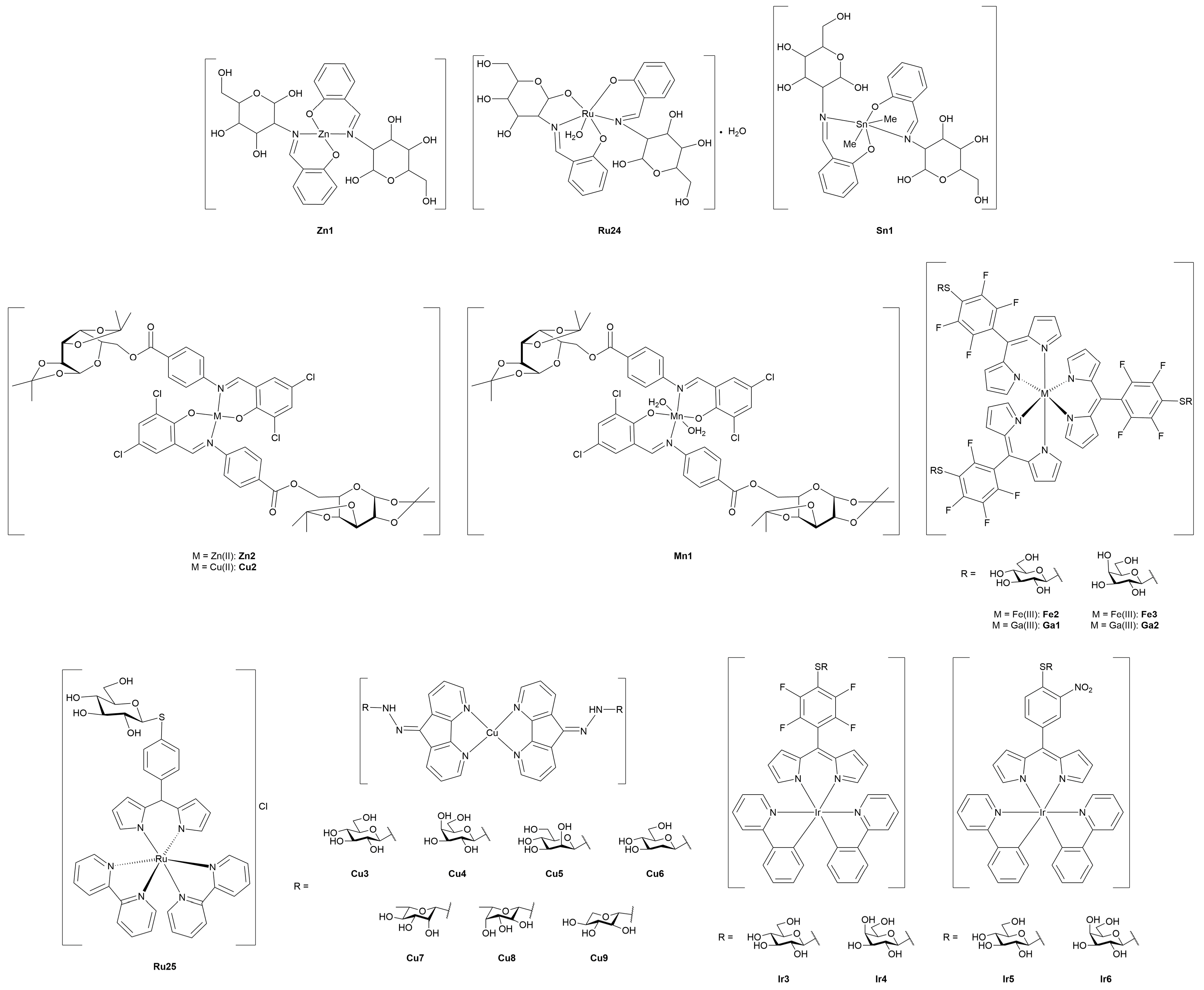
3.4. Miscellaneous Metal Complexes with Anticancer and Antimicrobial Activity
3.4.1. Monometallic-Glycoconjugates
3.4.2. Bimetallic-Glycoconjugates
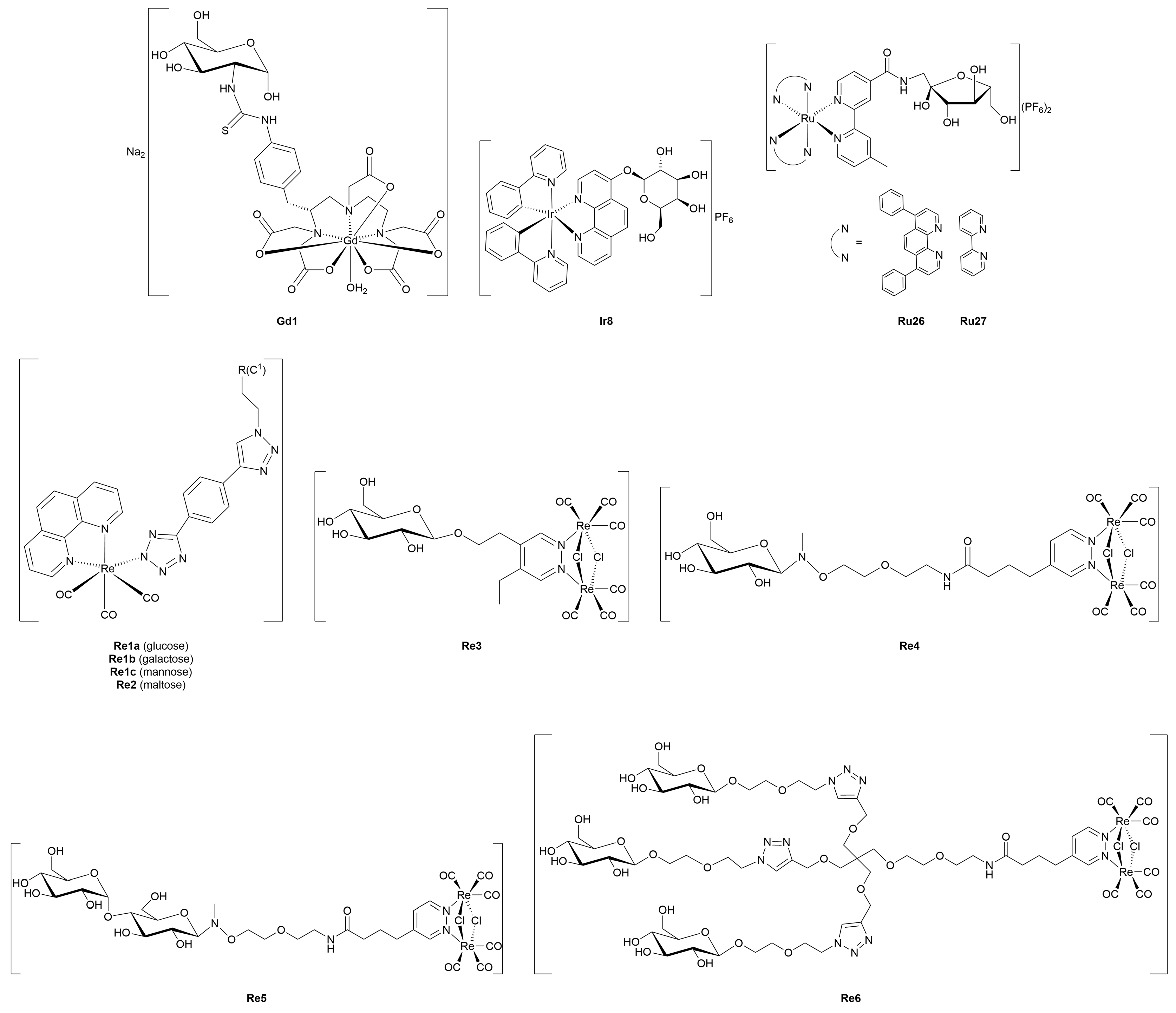
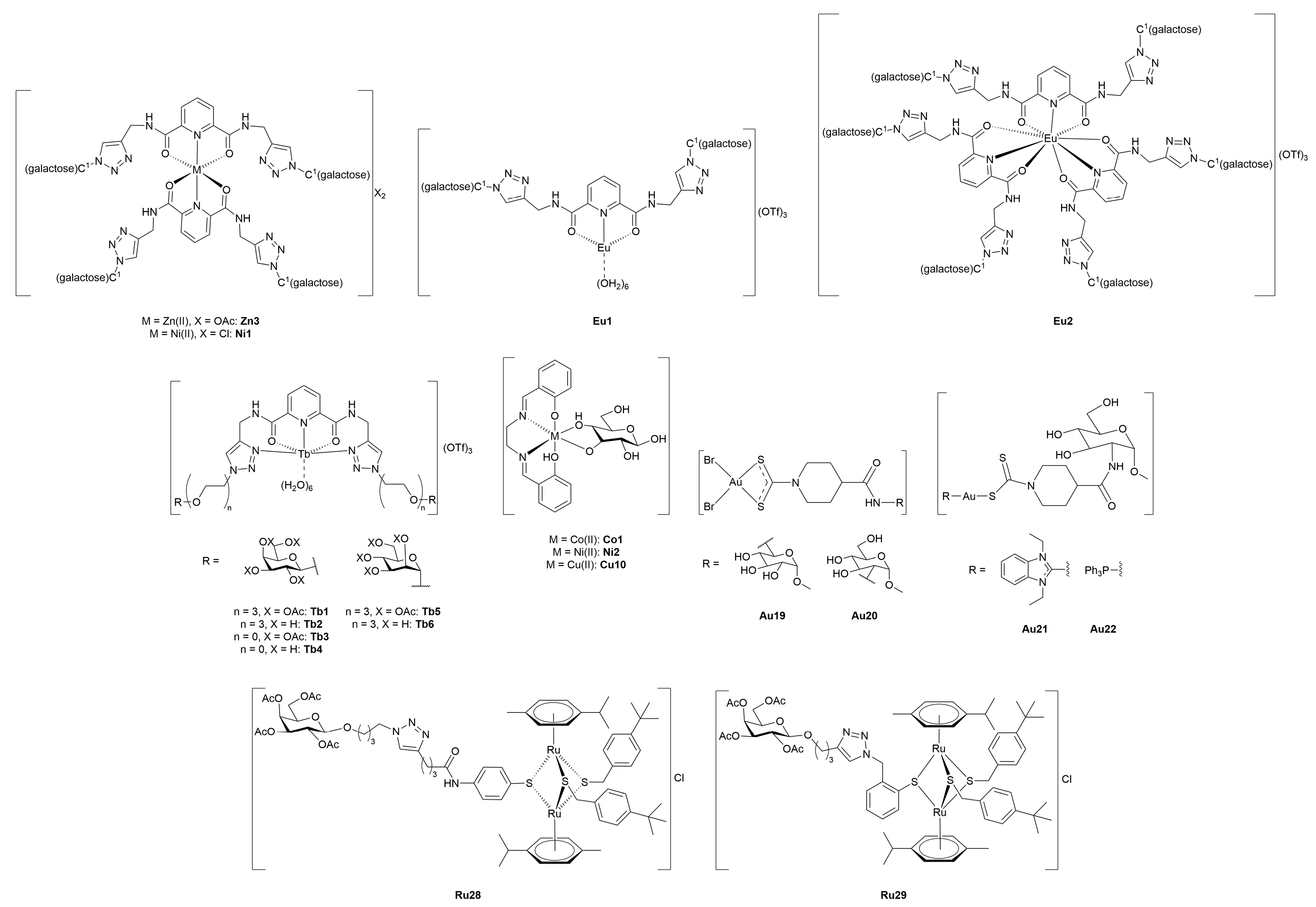
4. Metal-Glycoconjugates for Tumor Imaging Applications
5. Therapeutic Metal-Glycoconjugates Beyond Oncological Applications
5.1. Antimicrobial, Antiviral, and Antiparasitic Metal-Glycoconjugates
5.2. Metal-Glycoconjugates for Neurological Disorders
6. Conclusions
- Although platinum scaffolds (especially Pt(II)-based) still account for the largest class of metal-glycoconjugates, other metal centers are being explored more and more often to exploit alternative transport pathways and mechanisms of action. Interestingly, along with ruthenium complexes, other metal ions such as gold, zinc, iron and lanthanides are now gaining ground in the rush to metal-glycoconjugation.
- Glucose and glucose-like moieties are still the most widely employed scaffolds for metal-glycoconjugation. However, it was proven in many cases that more favorable outcomes may be obtained with other monosaccharides, in particular galactose and mannose.
- The exploitation of GLUTs overexpressed in cancer cells to achieve selective tumor-targeting is still the first choice, driving the overall design of metal complexes functionalized with carbohydrates. However, it has been clearly demonstrated that metal-glycoconjugates may turn out to be biologically active without necessarily being transported and/or taken up by cells through GLUTs (and the other way around).
- As previously pointed out, detailed mechanistic studies have unveiled a number of unexpected targets for different metal-glycoconjugates (for instance, SGLTs or GLUTs other than the expected GLUT1).
- Contrary to the past, when the large majority of metal-glycoconjugates had been developed only as potential anticancer agents, such compounds have been designed also for different bio-applications. In particular, a major push to the generation of lanthanide-based tumor imaging probes has been observed, as well as the development of glyco-functionalized small metal complexes for non-oncological applications (e.g., antivirals and antimicrobials).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2-DG | 2-deoxy-d-glucose |
| 2-FDG | 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose |
| 2-NBDG | (2-[N-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)amino]-2-deoxy-d-glucose) |
| acetyl-CoA | acetyl-coenzyme A |
| ADEPT | antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy |
| ATP | adenosine-5’-triphosphate |
| Cp | cyclopentadienyl |
| DTPA | diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid |
| EDG | 4,6-O-ethylidene-α-d-glucose |
| FADH2 | flavin adenine dinucleotide |
| GLUT | glucose transporter |
| HIF-1a | hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| MTD | maximum tolerated doses |
| NADH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NADPH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| NHC | N-heterocyclic carbene |
| OCT2 | organic cation transporter 2 |
| OXPHOS | mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation |
| PACT | photoactivated chemotherapy |
| PARP-1 | poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 |
| PDK1 | pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 |
| PDT | photodynamic therapy |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| RNase | ribonuclease |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SGLT | sodium-dependent transporters |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| SPECT | single photon emission computed tomography |
| TBP | trigonal bipyramidal |
| TRES | time-resolved emission spectroscopy |
| TrxR | thioredoxin reductase |
| TUNEL | terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling |
References
- Karges, J.; Stokes, R.W.; Cohen, S.M. Metal complexes for therapeutic applications. Trends Chem. 2021, 3, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, A.; Pöthig, A. Metals in cancer research: Beyond platinum metallodrugs. ACS Cent. Sci. 2024, 10, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, A.M.P. Cisplatin in cancer treatment. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 206, 115323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dowd, P.D.; Sutcliffe, D.F.; Griffith, D.M. Oxaliplatin and its derivatives—An overview. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 497, 215439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oun, R.; Moussa, Y.E.; Wheate, N.J. The side effects of platinum-based chemotherapy drugs: A review for chemists. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 6645–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacca, A.; Bruno, M.; Boccarelli, A.; Coluccia, M.; Ribatti, D.; Bergamo, A.; Garbisa, S.; Sartor, L.; Sava, G. Inhibition of endothelial cell functions and of angiogenesis by the metastasis inhibitor NAMI-A. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessio, E.; Messori, L. NAMI-A and KP1019/1339, two iconic ruthenium anticancer drug candidates face-to-face: A case story in medicinal inorganic chemistry. Molecules 2019, 24, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trondl, R.; Heffeter, P.; Kowol, C.R.; Jakupec, M.A.; Berger, W.; Keppler, B.K. NKP-1339, the first ruthenium-based anticancer drug on the edge to clinical application. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 2925–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monro, S.; Colón, K.L.; Yin, H.; Roque, J., III; Konda, P.; Gujar, S.; Thummel, R.P.; Lilge, L.; Cameron, C.G.; McFarland, S.A. Transition metal complexes and photodynamic therapy from a tumor-centered approach: Challenges, opportunities, and highlights from the development of TLD1433. Chem. Rev. 2018, 119, 797–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamberi, T.; Chiappetta, G.; Fiaschi, T.; Modesti, A.; Sorbi, F.; Magherini, F. Upgrade of an old drug: Auranofin in innovative cancer therapies to overcome drug resistance and to increase drug effectiveness. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 1111–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Meade, T.J. Molecular magnetic resonance imaging with Gd(III)-based contrast agents: Challenges and key advances. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17025–17041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-T.; Padmanabhan, P.; Gulyás, B.Z. Gadolinium(III) based nanoparticles for T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging probes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 60945–60966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duatti, A. Review on 99mTc radiopharmaceuticals with emphasis on new advancements. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2021, 92, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilworth, J.R.; Parrott, S.J. The biomedical chemistry of technetium and rhenium. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1998, 27, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, K.; Liu, S.; Mao, Z.; Mo, Z.; Huang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W.; Wei, J.; et al. A cyclometalated iridium(III) complex exerts high anticancer efficacy via fatty acid beta-oxidation inhibition and sphingolipid metabolism reprogramming. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 14912–14926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Wilson, J.J. Therapeutic and diagnostic applications of multimetallic rhenium(I) tricarbonyl complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 14, 1312–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, G.M. The development and causes of cancer. In The Cell: A Molecular Approach, 2nd ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2000; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9963/ (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Tufail, M.; Jiang, C.H.; Li, N. Altered metabolism in cancer: Insights into energy pathways and therapeutic targets. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of cancer: New dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granchi, C.; Minutolo, F. Anticancer agents that counteract tumor glycolysis. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 1318–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettenuzzo, A.; Pigot, R.; Ronconi, L. Metal-based glycoconjugates and their potential in targeted anticancer chemotherapy. Metallodrugs 2015, 1, 36–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bononi, G.; Iacopini, D.; Cicio, G.; Di Pietro, S.; Granchi, C.; Di Bussolo, V.; Minutolo, F. Glycoconjugated metal complexes as cancer diagnostic and therapeutic agents. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 30–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956, 123, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Han, F.; Du, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, W. Hypoxic microenvironment in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Sig. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, R.; Varacallo, M.A. Biochemistry, Glycolysis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482303/ (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Gladden, L.B. Lactate metabolism: A new paradigm for the third millennium. J. Physiol. 2004, 558, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiaradonna, F.; Sacco, E.; Manzoni, R.; Giorgio, M.; Vanoni, M.; Alberghina, L. Ras-dependent carbon metabolism and transformation in mouse fibroblasts. Oncogene 2006, 25, 5391–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Board, M.; Humm, S.; Newsholme, E.A. Maximum activities of key enzymes of glycolysis, glutaminolysis, pentose phosphate pathway and tricarboxylic acid cycle in normal, neoplastic and suppressed cells. Biochem. J. 1990, 265, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.V.; Semenza, G.L. Oncogenic alterations of metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999, 24, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, S.; Eigenbrodt, E. The tumor metabolome. Anticancer Res. 2003, 23, 1149–1154. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12820363/ (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Ramanathan, A.; Wang, C.; Schreiber, S.L. Perturbational profiling of a cell-line model of tumorigenesis by using metabolic measurements. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5992–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qannita, R.A.; Alalami, A.I.; Harb, A.A.; Aleidi, S.M.; Taneera, J.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; El-Huneidi, W.; Saleh, M.A.; Alzoubi, K.H.; Semreen, M.H.; et al. Targeting Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 (HIF-1) in cancer: Emerging therapeutic strategies and pathway regulation. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengo, A.; Gui, D.Y.; Vander Heiden, M.G. Targeting metabolism for cancer therapy. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 1161–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, N.M.; Andreana, P.R. Glycomimetics and glycoconjugates in drug discovery. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, G.D. Structure, function and regulation of mammalian glucose transporters of the SLC2 family. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2020, 472, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvaresi, E.C.; Hergenrother, P.J. Glucose conjugation for the specific targeting and treatment of cancer. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 2319–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Hess, S.; Braad, P.-E.N.; Olsen, B.B.; Inglev, S.; Høilund-Carlsen, P.F. The basic principles of FDG-PET/CT imaging. PET Clin. 2014, 9, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Fu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Gao, X.; Li, H.; Mi, Q.; Liu, P.; Yang, J.; Yao, Z.; Gao, Q. GLUT1-mediated selective tumor targeting with fluorine containing platinum(II) glycoconjugates. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 39476–39496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Akam, E.A.; Tomat, E. Targeting iron in colon cancer via glycoconjugation of thiosemicarbazone prochelators. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Xu, C.; Sun, P.; Wu, J.; Yan, C.; Hu, M.; Yan, N. Crystal structure of the human glucose transporter GLUT1. Nature 2014, 510, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custódio, T.F.; Paulsen, P.A.; Frain, K.M.; Pedersen, B.P. Structural comparison of GLUT1 to GLUT3 reveal transport regulation mechanism in sugar porter family. Life Sci. Alliance 2021, 4, e202000858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zeng, X.; Yan, C.; Sun, X.; Gong, X.; Rao, Y.; Yan, N. Crystal structure of a bacterial homologue of glucose transporters GLUT1–4. Nature 2012, 490, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, M.; Johnstone, T.C.; Suntharalingam, K.; Lippard, S.J. A potent glucose–platinum conjugate exploits glucose transporters and preferentially accumulates in cancer cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 128, 2596–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajak, B.; Siwiak, E.; Sołtyka, M.; Priebe, A.; Zieliński, R.; Fokt, I.; Ziemniak, M.; Jaśkiewicz, A.; Borowski, R.; Domoradzki, T.; et al. 2-Deoxy-d-glucose and its analogs: From diagnostic to therapeutic agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.-Q.; Keating, A.F. Functional properties and genomics of glucose transporters. Curr. Genom. 2007, 8, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, K.; Freeze, H.H. Mannose enters mammalian cells using a specific transporter that is insensitive to glucose. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 9417–9421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tromp, R.A.; van Boom, S.S.; Timmers, C.M.; van Zutphen, S.; van der Marel, G.A.; Overkleeft, H.S.; van Boom, J.H.; Reedijk, J. The β-glucuronyl-based prodrug strategy allows for its application on β-glucuronyl-platinum conjugates. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 4273–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, M.; Awuah, S.G.; Lippard, S.J. Chemical approach to positional isomers of glucose–platinum conjugates reveals specific cancer targeting through glucose-transporter-mediated uptake in vitro and in vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 12541–12551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabik, C.A.; Dolan, M.E. Molecular mechanisms of resistance and toxicity associated with platinating agents. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2007, 33, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Heeg, M.J.; Braunschweiger, P.G.; Xie, W.; Wang, P.G. A carbohydrate-linked cisplatin analogue having antitumor activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 1768–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Gao, X.; Liu, R.; Yang, J.; Zhang, M.; Mi, Y.; Shi, Y.; Gao, Q. Design, synthesis of novel platinum(II) glycoconjugates, and evaluation of their antitumor effects. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2016, 87, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloj, L.; Caracó, C.; Jagoda, E.; Eckelman, W.C.; Neumann, R.D. Glut-1 and hexokinase expression: Relationship with 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose uptake in A431 and T47D cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4709–4714. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10493529/ (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Kwon, O.; Eck, P.; Chen, S.; Corpe, C.P.; Lee, J.-H.; Kruhlak, M.; Levine, M. Inhibition of the intestinal glucose transporter GLUT2 by flavonoids. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, S.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Z.; Mi, Y.; Mi, Q.; Yang, J.; Gao, Q. Mechanistic and biological characteristics of different sugar conjugated 2-methyl malonatoplatinum(II) complexes as new tumor targeting agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, H.; Liu, R.; Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, P.; Fu, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang-Negrerie, D.; Gao, Q. Galactose conjugated platinum(II) complex targeting the Warburg effect for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer and colon cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 110, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, H.; Gao, X.; Mi, Q.; Zhao, H.; Gao, Q. Mannose-conjugated platinum complexes reveals effective tumor targeting mediated by glucose transporter 1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 487, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezzi, C.; Perez, S.; Ryan, K.; Wong, A.; Chen, B.Y.; Damoiseaux, R.; Clark, P.M. Early reduction of glucose consumption is a biomarker of kinase inhibitor efficacy which can be reversed with GLUT1 overexpression in lung cancer cells. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2023, 25, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitras, S.; Sechaud, R.; Drollmann, A.; Pal, P.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Camenisch, G.; Kaiser, G. Effect of cimetidine, a model drug for inhibition of the organic cation transport (OCT2/MATE1) in the kidney, on the pharmacokinetics of glycopyrronium. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 51, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, F. Immunolocalization of GLUT1 and GLUT3 glucose transporters in primary cultured neurons and glia. J. Neurosci. Res. 1995, 42, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucciolito, M.E.; Bossa, F.D.L.; Esposito, R.; Ferraro, G.; Iadonisi, A.; Petruk, G.; D’Elia, L.; Romanetti, C.; Traboni, S.; Tuzi, A.; et al. C-Glycosylation in platinum-based agents: A viable strategy to improve cytotoxicity and selectivity. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 2921–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucciolito, M.E.; D’Amora, A.; De Feo, G.; Ferraro, G.; Giorgio, A.; Petruk, G.; Monti, D.M.; Merlino, A.; Ruffo, F. Five-coordinate platinum(II) compounds containing sugar ligands: Synthesis, characterization, cytotoxic activity, and interaction with biological macromolecules. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 3133–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, A.; Cucciolito, M.E.; Esposito, R.; Ferraro, G.; Monti, D.M.; Merlino, A.; Ruffo, F. Five-coordinate platinum(II) compounds as potential anticancer agents. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 2020, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, A.; Liberti, D.; Bedini, E.; Cucciolito, M.E.; Loreto, D.; Monti, D.M.; Merlino, A.; Ruffo, F. Square-planar vs. trigonal bipyramidal geometry in Pt(II) complexes containing triazole-based glucose ligands as potential anticancer agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, T.C.; Suntharalingam, K.; Lippard, S.J. The next generation of platinum drugs: Targeted Pt(II) agents, nanoparticle delivery, and Pt (IV) prodrugs. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3436–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, R.G.; Chuah, S.W.; Crawford, A.; Marmion, C.J. Platinum(IV) prodrugs—A step closer to Ehrlich’s vision? Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 2017, 1596–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Ma, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.G. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of a novel series of glycosylated platinum(IV) complexes as antitumor agents. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 10366–10374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Hao, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.G. Glycosylated platinum(IV) prodrugs demonstrated significant therapeutic efficacy in cancer cells and minimized side-effects. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 11830–11838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Yang, X.; Nie, Q.; Hao, W.; Wang, P.G.; Wang, X. Glycosylated platinum(IV) complexes as substrates for glucose transporters (GLUTs) and organic cation transporters (OCTs) exhibited cancer targeting and human serum albumin binding properties for drug delivery. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 5736–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wei, Y.; Lei, L.; Li, Y.; Tan, G.; Xiao, M.; Wu, T. Glucose-modification of cisplatin to facilitate cellular uptake, mitigate toxicity to normal cells, and improve anti-cancer effect in cancer cells. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1203, 127361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, A.; Amoresano, A.; Cucciolito, M.E.; Esposito, R.; Ferraro, G.; Iacobucci, I.; Imbimbo, P.; Lucignano, R.; Melchiorre, M.; Monti, M.; et al. Pt(II) versus Pt(IV) in carbene glycoconjugate antitumor agents: Minimal structural variations and great performance changes. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 4002–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynihan, E.; Panseri, S.; Bassi, G.; Rossi, A.; Campodoni, E.; Dempsey, E.; Montesi, M.; Velasco-Torrijos, T.; Montagner, D. Development of novel Pt(IV)-carbohydrate derivatives as targeted anticancer agents against osteosarcoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, T.; Maegdefrau, U.; Hartmann, A.; Agaimy, A.; Marienhagen, J.; Weiss, T.S.; Stoeltzing, O.; Warnecke, C.; Schölmerich, J.; Oefner, P.J.; et al. GLUT1 expression is increased in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumorigenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durfee, R.A.; Mohammed, M.; Luu, H.H. Review of osteosarcoma and current management. Rheumatol. Ther. 2016, 3, 221–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, A.; Cucciolito, M.E.; Imbimbo, P.; Silipo, A.; Ruffo, F. A hydrophilic olefin Pt(0) complex containing a glucoconjugated 2-iminopyridine ligand: Synthesis, characterization, stereochemistry and biological activity. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2021, 516, 120092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darensbourg, D.J.; Decuir, T.J.; Stafford, N.W.; Robertson, J.B.; Draper, J.D.; Reibenspies, J.H.; Kathó, A.; Joó, F. Water-soluble organometallic compounds. 6. Synthesis, spectral properties, and crystal structures of complexes of 1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane with Group 10 metals. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 4218–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genêt, J.-P.; Darses, S.; Michelet, V. Organometallic catalysts in synthetic organic chemistry: From reactions in aqueous media to gold catalysis. Pure Appl. Chem. 2008, 80, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Emadi, A. Ruthenium-based chemotherapeutics: Are they ready for prime time? Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 66, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, M.A.; Graminha, A.E.; Vegas, L.C.; Luna-Dulcey, L.; Honorato, J.; Menezes, A.C.S.; Batista, A.A.; Cominetti, M.R. Transport of the ruthenium complex [Ru(GA)(dppe)2]PF6 into triple-negative breast cancer cells is facilitated by transferrin receptors. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1167–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabec, V.; Nováková, O. DNA binding mode of ruthenium complexes and relationship to tumor cell toxicity. Drug Resist. Updat. 2006, 9, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbaghi, G.; Pitard, I.; Lucas, M.; Haghdoost, M.M.; de Los Santos, Y.L.; Doucet, N.; Patten, S.A.; Sanderson, J.T.; Castonguay, A. Synthesis and biological assessment of a ruthenium(II) cyclopentadienyl complex in breast cancer cells and on the development of zebrafish embryos. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 188, 112030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaz, A.I.; Jakusch, T.; Morais, T.S.; Marques, F.; De Almeida, R.F.; Mendes, F.; Enyedy, É.A.; Santos, I.; Pessoa, J.C.; Kiss, T.; et al. [RuII(η5-C5H5)(bipy)(PPh3)]+, a promising large spectrum antitumor agent: Cytotoxic activity and interaction with human serum albumin. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 117, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, P.R.; Pereira, D.M.; Borralho, P.M.; Costa, P.J.; Piedade, M.F.M.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Fernandes, A.C. New [(η5-C5H5) Ru(N–N)(PPh3)][PF6] compounds: Colon anticancer activity and GLUT-mediated cellular uptake of carbohydrate-appended complexes. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 11926–11930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopini, D.; Vančo, J.; Di Pietro, S.; Bordoni, V.; Zacchini, S.; Marchetti, F.; Dvořák, Z.; Malina, T.; Biancalana, L.; Trávníček, Z.; et al. New glycoconjugation strategies for ruthenium(II) arene complexes via phosphane ligands and assessment of their antiproliferative activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 126, 105901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamala, V.; Martišová, A.; Červenková Šťastná, L.; Karban, J.; Dančo, A.; Šimarek, A.; Lamač, M.; Horáček, M.; Kolářová, T.; Hrstka, R.; et al. Ruthenium tetrazene complexes bearing glucose moieties on their periphery: Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro cytotoxicity. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre-Rubio, E.; Muñoz-Moreno, L.; Bajo, A.M.; Arias-Pérez, M.-S.; Cuenca, T.; Gude, L.; Royo, E. Carbohydrate effect of novel arene Ru(II) phenanthroline-glycoconjugates on metastatic biological processes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2023, 247, 112326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kacsir, I.; Sipos, A.; Ujlaki, G.; Buglyó, P.; Somsák, L.; Bai, P.; Bokor, É. Ruthenium half-sandwich type complexes with bidentate monosaccharide ligands show antineoplastic activity in ovarian cancer cell models through reactive oxygen species production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mari, C.; Pierroz, V.; Ferrari, S.; Gasser, G. Combination of Ru(II) complexes and light: New frontiers in cancer therapy. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 2660–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lameijer, L.N.; Brevé, T.G.; van Rixel, V.H.S.; Askes, S.H.C.; Siegler, M.A.; Bonnet, S. Effects of the bidentate ligand on the photophysical properties, cellular uptake, and (photo)cytotoxicity of glycoconjugates based on the [Ru(tpy)(NN)(L)]2+ scaffold. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lameijer, L.N.; Hopkins, S.L.; Brevé, T.G.; Askes, S.H.C.; Bonnet, S. d-versus l-glucose conjugation: Mitochondrial targeting of a light-activated dual-mode-of-action ruthenium-based anticancer prodrug. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 18484–18491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liao, X.; Xiong, K.; Kuang, S.; Jin, C.; Ji, L.; Chao, H. Boosting two-photon photodynamic therapy with mitochondria-targeting ruthenium–glucose conjugates. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 5839–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Lum, C.T.; Lok, C.-N.; Zhang, J.-J.; Che, C.-M. Chemical biology of anticancer gold(III) and gold(I) complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8786–8801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, O.; Sánchez-Sanz, G.; Tacke, M.; Zhu, X. Synthesis and anticancer activity of novel NHC-gold(I)-sugar complexes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 2904–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safir Filho, M.; Scattolin, T.; Dao, P.; Tzouras, N.V.; Benhida, R.; Saab, M.; Van Hecke, K.; Lippmann, P.; Martin, A.R.; Ott, I.; et al. Straightforward synthetic route to gold(I)-thiolato glycoconjugate complexes bearing NHC ligands (NHC = N-heterocyclic carbene) and their promising anticancer activity. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 9995–10001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresin, F.; Stoppa, V.; Baron, M.; Biffis, A.; Annunziata, A.; D’Elia, L.; Monti, D.M.; Ruffo, F.; Roverso, M.; Sgarbossa, P.; et al. Synthesis and biological studies on dinuclear gold(I) complexes with di-(N-heterocyclic carbene) ligands functionalized with carbohydrates. Molecules 2020, 25, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Cancer Institute’s Developmental Therapeutics Program (DTP)—NCI-60 Human Tumor Cell Lines Screen. Available online: https://dtp.cancer.gov/discovery_development/nci-60/ (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Ott, I.; Gust, R. Non platinum metal complexes as anti-cancer drugs. Arch. Pharm. 2007, 340, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brescia, F.; Ronconi, L. Gold: Not just jewelry…. Future Med. Chem. 2023, 15, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettenuzzo, A.; Vezzù, K.; Di Paolo, M.L.; Fotopoulou, E.; Marchiò, L.; Dalla Via, L.; Ronconi, L. Design, physico-chemical characterization and in vitro biological activity of organogold(III) glycoconjugates. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 8963–8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartinger, C.G.; Nazarov, A.A.; Ashraf, S.M.; Dyson, P.J.; Keppler, B.K. Carbohydrate-metal complexes and their potential as anticancer agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 2574–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geersing, A.; Ségaud, N.; van der Wijst, M.G.P.; Rots, M.G.; Roelfes, G. Importance of metal-ion exchange for the biological activity of coordination complexes of the biomimetic ligand N4Py. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 7748–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bru, F.; Vanwynsberghe, M.; Botter, E.; Tonon, G.; Visentin, F.; Schiavo, A.; Rizzolio, F.; Cazin, C.S.; Scattolin, T. Synthesis of gold(I) and palladium(II) complexes bearing N-heterocyclic carbene thioglucosides with selective cytotoxicity towards ovarian cancer cells. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2025, 28, e202400822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, A.M.A.; Refat, M.S.; Ismail, L.A.; Naglah, A.M.; Al-Omar, M.A.; Al-Wasidi, A.S. Insights into the complexation of glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) with V(III), Ru(III), Au(III), and Se(IV) ions in binary solvent system. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 296, 111999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Narváez, M.E.; Arenaza-Corona, A.; González-Sebastián, L.; Ramírez, T.A.; Ortega, S.H.; Cruz-Navarro, J.A.; Alí-Torres, J.; Orjuela, A.L.; Reyes-Marquez, V.; Lomas-Romero, L.; et al. Glycoconjugate Pd(II) and Cu(II) complexes of fluorinated N,O. Schiff base ligands for targeted cancer therapy: Synthesis, characterization and in vitro cytotoxic activity evaluation. New J. Chem. 2025, 49, 5187–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacsir, I.; Sipos, A.; Major, E.; Bajusz, N.; Bényei, A.; Buglyó, P.; Somsák, L.; Kardos, G.; Bai, P.; Bokor, É. Half-sandwich type platinum-group metal complexes of C-glucosaminyl azines: Synthesis and antineoplastic and antimicrobial activities. Molecules 2023, 28, 3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamala, V.; Ondrášková, K.; Červenková Šťastná, L.; Krčil, A.; Müllerová, M.; Kurfiřt, M.; Hiršová, K.; Holčáková, J.; Gyepes, R.; Císařová, I.; et al. Improving the anticancer activity of fluorinated glucosamine and galactosamine analogs by attachment of a ferrocene or ruthenium tetrazene motif. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2024, 38, e7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Shukla, S.; Rattan, R.; Fatima, M.; Goel, M.; Bhat, M.; Dutta, S.; Ranjan, R.K.; Sharma, M. Antimicrobial agents based on metal complexes: Present situation and future prospects. Int. J. Biomater. 2022, 2022, 6819080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calfee, D.P. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant enterococci, and other Gram-positives in healthcare. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 25, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Otaibi, W.A.; Al Motwaa, S.M.; Abubakr, A.S.; Hassan, S.S.; Rashidi, F.B. Targeted colon cancer and chemotherapeutic through metal glycoconjugates: Design, synthesis, molecular docking, and DFT investigations. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2025, 39, e70000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghonimi, N.A.M.; Elsharkawi, K.A.; Khyal, D.S.M.; Abdelghani, A.A. Serum malondialdehyde as a lipid peroxidation marker in multiple sclerosis patients and its relation to disease characteristics. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 51, 102941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, H.; Madrange, L.; Lemonnier, T.; Deslys, J.-P.; Yates, F.; Vigneron, P.-A. Development and optimization of a lactate dehydrogenase assay adapted to 3D cell cultures. Organoids 2024, 3, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, O.M.; Neurath, M.F.; Waldner, M.J. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and their therapeutic potential in colorectal cancer treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 757120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.S.; Jaiswal, N.; Tripathy, R.K.; Bera, P.S.; Chanda, N.; Behera, J.N.; Ghosal, S.; Saha, T.K. Monosaccharide linked Schiff base metal complexes of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Mn(II): Exploring the antiproliferative activity and cell death mechanism. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202200060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsche, C.S.; Gräfe, S.; Gitter, B.; Flanagan, K.J.; Senge, M.O.; Kulak, N.; Wiehe, A. Pre-/post-functionalization in dipyrrin metal complexes—Antitumor and antibacterial activity of their glycosylated derivatives. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 12373–12384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, S.; Gude, L.; Arias-Perez, M.-S. 4,5-Diazafluorene N-glycopyranosyl hydrazones as scaffolds for potential bioactive metallo-organic compounds: Synthesis, structural study and cytotoxic activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 81, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohlfeld, B.F.; Gitter, B.; Kingsbury, C.J.; Flanagan, K.J.; Steen, D.; Wieland, G.D.; Kulak, N.; Senge, M.O.; Wiehe, A. Dipyrrinato-iridium(III) complexes for application in photodynamic therapy and antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 6440–6459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaravadi, R.K.; Thompson, C.B. The roles of therapy-induced autophagy and necrosis in cancer treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 7271–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, G.; Ott, I.; Metzler-Nolte, N. Organometallic anticancer compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Usman, M.; Tabassum, S. Carbohydrate-based heteronuclear complexes as topoisomerase Iα inhibitor: Approach toward anticancer chemotherapeutics. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 37, 1494–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, S.; Iacopini, D.; Dalla Pozza, M.; Di Pietro, S.; Degano, I.; Gasser, G.; Di Bussolo, V.; Marchetti, F. Tethering carbohydrates to the vinyliminium ligand of antiproliferative organometallic diiron complexes. Organometallics 2022, 41, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, D.A.; Palle, K.; Bot, E.S.; Bjornsti, M.A.; Dekker, N.H. Antitumour drugs impede DNA uncoiling by topoisomerase I. Nature 2007, 448, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, F.; Arrigoni, F.; Mariani, S.; Splendiani, A.; Di Cesare, E.; Masciocchi, C.; Barile, A. Advanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of soft tissue tumors: Techniques and applications. Radiol. Med. 2019, 124, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyad, N.; Ahmad, M.S.; Alkhatib, S.G.; Hjouj, M. Gadolinium contrast agents—Challenges and opportunities of a multidisciplinary approach: Literature review. Eur. J. Radiol. Open. 2023, 11, 100503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, A.; Ahmad, M.W.; Al Saidi, A.K.A.; Choudhury, A.; Chang, Y.; Lee, G.H. Recent advances in gadolinium based contrast agents for bioimaging applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanlou, M.; Hashemi, E.; Oghabian, M.A.; Ardestani, M.S. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a novel glucosylated derivative of gadolinium diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid for tumor Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 49–60. Available online: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6487411/ (accessed on 30 June 2025). [PubMed]
- Lau, C.T.-S.; Chan, C.; Zhang, K.Y.; Roy, V.A.L.; Lo, K.K.-W. Photophysical, cellular-uptake, and bioimaging studies of luminescent ruthenium(II)–polypyridine complexes containing a d-fructose pendant. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 2017, 5288–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Vellaisamy, K.; Li, G.; Wu, C.; Ko, C.-N.; Leung, C.-H.; Ma, D.-L. Development of a long-lived luminescence probe for visualizing β-galactosidase in ovarian carcinoma cells. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11679–11684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillam, T.A.; Caporale, C.; Brooks, R.D.; Bader, C.A.; Sorvina, A.; Werrett, M.V.; Wright, P.J.; Morrison, J.L.; Massi, M.; Brooks, D.A.; et al. Neutral Re(I) Complex Platform for Live Intracellular Imaging. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 10173–10185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmioli, A.; Aliprandi, A.; Septiadi, D.; Mauro, M.; Bernardi, A.; De Cola, L.; Panigati, M. Glyco-functionalized dinuclear rhenium(I) complexes for cell imaging. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 1686–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.C.-C.; Lo, K.K.-W. Strategic design of luminescent rhenium(I), ruthenium(II), and iridium(III) complexes as activity-based probes for bioimaging and biosensing. Chem. Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechota, M.; Sunderland, P.; Wysocka, A.; Nalberczak, M.; Sliwinska, M.A.; Radwanska, K.; Sikora, E. Is senescence-associated β-galactosidase a marker of neuronal senescence? Oncotarget 2016, 7, 81099–81109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valieva, Y.; Ivanova, E.; Fayzullin, A.; Kurkov, A.; Igrunkova, A. Senescence-associated β-galactosidase detection in pathology. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, L.; Ramponi, V.; Gupta, K.; Stevenson, T.; Mathew, A.B.; Barinda, A.J.; Herbstein, F.; Morsli, S. Emerging insights in senescence: Pathways from preclinical models to therapeutic innovations. npj Aging 2024, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.-H.; Tian, H.; Zang, Y.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Li, J.; Sessler, J.L.; He, X.-P.; James, T.D. Small-molecule fluorescence-based probes for interrogating major organ diseases. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 9391–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.; Wu, X.; Niu, D.; Wang, J.; Leung, C.-H.; Wang, W. Recent advances in organometallic NIR iridium(III) complexes for detection and therapy. Molecules 2024, 29, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, N.P.; Thatyana, M.; Mokgalaka-Fleischmann, N.S.; Mansour, A.M.; Tembu, V.J.; Manicum, A.E. Review on the applications of selected metal-based complexes on infectious diseases. Molecules 2024, 29, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, M.M.; Fraziano, M.; Thaller, M.C.; Rossolini, G.M. The urgent need for novel antimicrobial agents and strategies to fight antibiotic resistance. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Hilgenfeld, R.; Whitley, R.; De Clercq, E. Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: Progress and lessons learned. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 449–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessenne, C.; Mariller, C.; Vidal, O.; Huvent, I.; Guerardel, Y.; Elass-Rochard, E.; Rossez, Y. Glycan-mediated adhesion mechanisms in antibiotic-resistant bacteria. BBA Adv. 2025, 7, 100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behren, S.; Westerlind, U. Novel Approaches to design glycan-based antibacterial inhibitors. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 26, e202200795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtczak, K.; Gillon, E.; Bura, D.; Richmond, K.; Joyce, M.; Caraher, E.; Kessie, K.; Velasco-Torrijos, T.; Trujillo, C.; Imberty, A.; et al. Antiadhesive glycoconjugate metal complexes targeting pathogens Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida albicans. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2025; in press (Advance Article). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtczak, K.; Zahorska, E.; Murphy, I.J.; Koppel, F.; Cooke, G.; Titz, A.; Byrne, J.P. Switch-on luminescent sensing of unlabelled bacterial lectin by terbium(III) glycoconjugate systems. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 8384–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bufarwa, S.; El-Seifat, R.; Binhamad, H.; Hesien, R. Synthesis, characterization, thermal, theoretical studies, antimicrobial, antioxidant activity, superoxide dismutase-like activity and catalase mimetics of metal(II) complexes derived from sugar and Schiff base. Rev. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 44, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Moles, M.; Türck, S.; Basu, U.; Pettenuzzo, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Rajan, A.; Ma, X.; Büssing, R.; Wölker, J.; Burmeister, H.; et al. Metallodrug profiling against SARS-CoV-2 target proteins identifies highly potent inhibitors of the S/ACE2 interaction and the papain-like protease PLpro. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 17928–17940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettenuzzo, A.; Montagner, D.; McArdle, P.; Ronconi, L. An innovative and efficient route to the synthesis of metal-based glycoconjugates: Proof-of-concept and potential applications. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 10721–10736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, I.; Desiatkina, O.; Anghel, N.; Johns, S.K.; Boubaker, G.; Hemphill, A.; Furrer, J.; Păunescu, E. Synthesis and antiparasitic activity of new trithiolato-bridged dinuclear ruthenium(II)-arene-carbohydrate conjugates. Molecules 2023, 28, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO)—WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240093461 (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Yuan, S.; Jin, G.; Cui, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z. Transmission and control strategies of antimicrobial resistance from the environment to the clinic: A holistic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, S.A.R.; Kahler, C.M. Bench-to-bedside review: Bacterial virulence and subversion of host defences. Crit. Care 2008, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, N. Bacterial lectins, cell-cell recognition and infectious disease. FEBS Lett. 1987, 217, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, P.W.; Bader, O.; de Boer, A.D.; Weig, M.; Chauhan, N. Adhesins in human fungal pathogens: Glue with plenty of stick. Eukaryot. Cell 2013, 12, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krachler, A.M.; Orth, K. Targeting the bacteria-host interface: Strategies in anti-adhesion therapy. Virulence 2013, 4, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diggle, S.P.; Stacey, R.E.; Dodd, C.; Cámara, M.; Williams, P.; Winzer, K. The galactophilic lectin, LecA, contributes to biofilm development in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katrlík, J.; Škrabana, R.; Mislovičová, D.; Gemeiner, P. Binding of d-mannose-containing glycoproteins to d-mannose-specific lectins studied by surface plasmon resonance. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 382, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Empel, V.P.M.; Bertrand, A.T.; van Oort, R.J.; van der Nagel, R.; Engelen, M.; van Rijen, H.V.; Doevendans, P.A.; Crijns, H.J.; Ackerman, S.L.; Sluiter, W.; et al. EUK-8, a superoxide dismutase and catalase mimetic, reduces cardiac oxidative stress and ameliorates pressure overload-induced heart failure in the harlequin mouse mutant. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.B.; Farzan, M.; Chen, B.; Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Mukherjee, R.; Grewe, D.; Bojkova, D.; Baek, K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Schulz, L.; Widera, M.; Mehdipour, A.R.; Tascher, G.; et al. Papain-like protease regulates SARS-CoV-2 viral spread and innate immunity. Nature 2020, 587, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basto Afonso, P.; Müller, J.; Rubbiani, R.; Stibal, D.; Giannini, F.; Süss-Fink, G.; Balmer, V.; Hemphill, A.; Gasser, G.; Furrer, J. Characterization of the activities of dinuclear thiolato-bridged arene ruthenium complexes against Toxoplasma gondii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01031-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basto, A.P.; Anghel, N.; Rubbiani, R.; Müller, J.; Stibal, D.; Giannini, F.; Süss-Fink, G.; Balmer, V.; Gasser, G.; Furrer, J.; et al. Targeting of the mitochondrion by dinuclear thiolato-bridged arene ruthenium complexes in cancer cells and in the apicomplexan parasite Neospora caninum. Metallomics 2019, 11, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruankham, W.; Songtawee, N.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Worachartcheewan, A.; Suwanjang, W.; Pingaew, R.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Phopin, K. Promising 8-aminoquinoline-based metal complexes in the modulation of SIRT1/3-FOXO3a axis against oxidative damage-induced preclinical neurons. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 46977–46988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjos, K.D.; Orvig, C. Metallodrugs in medicinal inorganic chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4540–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristóvão, J.S.; Santos, R.; Gomes, C.M. Metals and neuronal metal binding proteins implicated in Alzheimer’s disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9812178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.-M.; Kim, G.; Kang, J.; Lim, M.H. Strategies employing transition metal complexes to modulate Amyloid-β aggregation. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, C.J.; Bush, A.I.; Masters, C.L.; Cappai, R.; Li, Q.-X. Metals and amyloid-β in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2005, 86, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Manna, S.; Leone, M.; Iacobucci, I.; Annuziata, A.; Di Natale, C.; Lagreca, E.; Malfitano, A.M.; Ruffo, F.; Merlino, A.; Monti, M.; et al. Glucosyl platinum(II) complexes inhibit aggregation of the C-terminal region of the Aβ peptide. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 3540–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, C.J.; Walencewicz-Wasserman, A.J.; Kosmoski, J.; Cribbs, D.H.; Glabe, C.G.; Cotman, C.W. Structure-activity analyses of beta-amyloid peptides: Contributions of the beta 25-35 region to aggregation and neurotoxicity. J. Neurochem. 1995, 64, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Józsa, É.; Ősz, K.; Kállay, C.; de Bona, P.; Damante, C.A.; Pappalardo, G.; Rizzarelli, E.; Sóvágó, I. Nickel(II) and mixed metal complexes of amyloid-β N-terminus. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 7046–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brescia, F.; Titilas, I.; Cacciapuoti, S.; Ronconi, L. Recent Advances in the Development of Metal-Glycoconjugates for Medicinal Applications. Molecules 2025, 30, 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173537
Brescia F, Titilas I, Cacciapuoti S, Ronconi L. Recent Advances in the Development of Metal-Glycoconjugates for Medicinal Applications. Molecules. 2025; 30(17):3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173537
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrescia, Federica, Ioannis Titilas, Simona Cacciapuoti, and Luca Ronconi. 2025. "Recent Advances in the Development of Metal-Glycoconjugates for Medicinal Applications" Molecules 30, no. 17: 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173537
APA StyleBrescia, F., Titilas, I., Cacciapuoti, S., & Ronconi, L. (2025). Recent Advances in the Development of Metal-Glycoconjugates for Medicinal Applications. Molecules, 30(17), 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173537





