Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is considered to be one of the most common types of dementia, threatening the health of elderly individuals. Enhancing the brain’s cholinergic activity is currently the primary therapeutic strategy for treating AD patients. Acetylcholine and butyrylcholine are key targets in this approach, as they function as neuromodulators within the cerebrum—particularly in its various cholinergic regions responsible for essential functions like memory, thought, inspiration, and excitement. Oxidative stress and free radicals are considered to play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of AD and may be key factors in its etiology. Additionally, oxidants and oxidative stress-induced products can upregulate amyloid precursor protein (APP) expression, promoting Aβ aggregation. Another major factor in the pathogenesis of AD is the imbalance of metal homeostasis in the brain. Notably, the mammalian brain contains significantly higher concentrations of Cu, Zn, and Fe ions compared to other tissues. The present review focuses on novel bifunctional metal chelators with potential antioxidant activity for the treatment of AD.
1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a heterogeneous disease with a complex pathobiology, accounting for 60–70% of dementia cases, occurring after the age of 65 [1,2]. AD is the leading cause of dementia, often beginning with mild and easily overlooked memory impairment that progressively worsens over time and is one of the most expensive, deadly, and burdensome diseases of our century [3,4]. AD is neuropathologically marked by the presence of senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) [5]. AD is broadly categorized into two principal types: early-onset AD (EOAD) and sporadic or late-onset AD (LOAD), with LOAD accounting for over 95% of all cases. An abnormal accumulation of the toxic form of amyloid-β (Aβ) is observed in both types, resulting from an imbalance between its production and clearance [2,6,7]. Pathologically, there is severe neuronal loss, formation of intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles composed of hyperphosphorylated tau protein, and aggregation of Aβ in extracellular senile plaques [8,9]. These characteristics are recognied as the primary neuropathological criteria for the diagnosis of AD [10]. The blood–brain barrier (BBB) protects the central nervous system (CNS) from toxins and pathogens in the blood. The BBB prevents most chemical drugs and biopharmaceuticals from entering the brain, making it hard to treat CNS disorders. The barrier regulates the entrance and expulsion of molecules from the vascular compartment to the brain in conjunction with a group of receptors, transporters, efflux pumps, and other cellular components [11]. Selective BBB and neurovascular coupling are two unique central nervous system vasculature features. In AD, vascular dysfunction and BBB disruption are observed, mediated by various molecular and genetic alterations [12].
1.1. Amyloid Plaques
In the brain, there is high expression of a single-pass transmembrane protein called APP. APP is rapidly metabolized through a complex process [13,14]. Alpha- and gamma-secretases are responsible for the cleavage of APP that leads to the production of insoluble Aβ peptides [15,16,17]. Aβ, initially discovered in senile plaques, was originally believed to be an abnormal protein [18]. In a healthy brain, APP is initially cleaved by β-secretase, generating soluble APP fragments. Subsequently, γ-secretase cleaves the remaining membrane-bound portion, producing peptides that are released extracellularly and are rapidly degraded or cleared [15,19]. Current studies suggest that Aβ—whether in the form of plaques or as non-fibrillar, soluble, oligomeric forms—initiates a pathophysiological cascade that results in tau misfolding and aggregation, which subsequently propagates throughout the cortex [20,21]. The toxic effects of Aβ may involve synaptic impairment, excitotoxic damage, changes in membrane permeability, disruption of calcium balance, inflammation, and oxidative stress [22,23].
1.2. Neurofibrillary Tangles (NFTs)
NFTs represent a core neuropathological feature of AD [24]. NFTs are composed of abnormally phosphorylated forms of the microtubule-associated protein tau [25]. The tau filaments observed in AD have been termed “paired helical filaments” (PHFs). In AD, tau proteins undergo hyperphosphorylation and abnormal folding, which reduce their ability to bind to and stabilize microtubules in the axon. The loss of normal tau function, combined with the enhanced accumulation of abnormal tau, facilitates the aggregation of PHFs with normal tau proteins [26]. When NFTs occur in the absence of Aβ plaques, the condition is termed primary age-related tauopathy (PART). When Aβ plaques are also present, NFT pathology is currently recognized as AD neuropathological change (ADNC) [27]. Synapse loss and the formation of NFTs have been shown to be strongly correlated throughout the progression of AD. Both factors play a crucial role in cognitive decline, suggesting that these AD lesions occur in a related, rather than independent, manner [24].
1.3. Synaptic Loss
Synaptic loss is regarded as a key pathological feature contributing to the progression of AD. Several studies have reported that cognitive dysfunction is associated with a loss of dendritic spines. The shape of spines is primarily determined by the cytoskeletal protein F-actin (fibrillar actin), and exposure to Aβ can trigger F-actin depolymerization into G-actin (globular actin), leading to spine collapse [28]. Synaptic proteins, such as neurogranin, a postsynaptic neuronal protein, visinin-like protein-1 (VILIP-1), and synaptotagmin-1 serve as biomarkers for the detection and quantification of synaptic loss and its severity [29].
1.4. Oxidative Stress and Alzheimer’s Disease
A significant imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) is known as oxidative stress [30,31,32]. Evidence suggests that oxidative stress and free radicals are involved in pathogenesis and may play a role in the etiology of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). This results in the damage of essential cellular components, including nucleic acids, lipids and proteins [33,34,35,36]. Indeed, it has been shown that mitochondrial dysfunction, plays a significant role in the pathophysiology of AD, through the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [37]. Oxidative stress has been shown to play a pivotal role in the modification of APP and the regulation of secretase enzyme activities. Oxidants and oxidative products produced through oxidative stress can affect the expression of APP by increasing it, which in turn promotes the aggregation of Aβ [38]. Concurrently, peptide Aβ and the presence of trace metal ions, such as iron and copper, have been identified as potential sources of oxidative stress. The insertion of Aβ oligomers into the lipid bilayer can lead to the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [37].
1.5. Metal Dyshomeostasis in Alzheimer’s Disease
An imbalance of metal homeostasis in the brain is one of the most crucial factors in the pathogenesis of AD. Significantly high concentrations of Cu, Zn, and Fe ions are detected in the mammalian brain in comparison to other tissues [39,40,41,42]. The concentrations of Cu, Zn, and Fe in the brain are tightly regulated at the level of the BBB [40]. Furthermore, oxidative stress is closely linked to the imbalance of metal homeostasis in the brain [41]. It has been reported that restoring proper metal ion balance in the brain can halt Aβ aggregation, disassemble amyloid plaques, and slow AD-related cognitive decline in both patients with AD and AD transgenic mouse models [41,43]. Copper and zinc play crucial roles in brain function. Copper is a vital trace element involved in energy production, neurotransmission, and free radical scavenging. Zinc is also an essential trace element that participates in neurotransmission and redox regulation. Aβ plaques exhibit a high binding affinity for the trace metals copper and zinc and have been found to contain elevated concentrations of these metals [44]. Iron, an essential trace element, serves as a cofactor for numerous physiological processes in the brain, including oxygen transport, mitochondrial respiration, DNA synthesis, and phospholipid synthesis [45].
1.6. Metal Chelators as Potential Drugs Against AD
Aβ deposition and oxidative stress are two of the main pathognomonic features of AD (Figure 1), both of which are driven by Aβ’s interactions with metal ions [46]. Copper is considered a crucial metal in the development of chelators for treating AD. It not only shows the most pronounced dyshomeostasis in amyloid plaques, but also significantly affects Aβ homeostasis by increasing Aβ deposition and contributing to neuroinflammation. Another possible risk is zinc dyshomeostasis, due to extracellular overload within the amyloid plaques or intracellular overload/deficit [47].
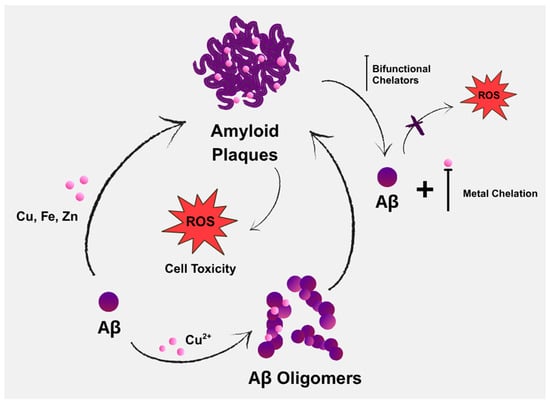
Figure 1.
Contribution of endogenous metals in the aggregation of amyloid-beta (Aβ), along with the potential role of bifunctional chelators in AD therapy through chelation.
2. Novel Bifuctional Metal Chelators
2.1. Zinc Metal Carboxylates
Zafar, R. et al. [48] synthesized and biologically evaluated novel zinc metal carboxylates. All synthesized compounds were evaluated for their inhibitory activity against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) using Ellman’s assay. Compounds 1 and 2 exhibited promising AChE inhibitory activity, with IC50 values of 59.52 and 33.07 μM, respectively, compared to the reference compound galantamine (IC50 = 1.67 μM). In the BChE assay, compound 3 demonstrated remarkable inhibitory activity, with an IC50 value of 0.056 μM. Galantamine was used as the reference compound, exhibiting an IC50 of 2.13 μM. Despite its extraordinary results in the BChE assay, compound 3 exhibited weak AChE inhibition. In the BChE assay, compound 3 exhibited activity comparable to its performance in the AChE assay, with an IC50 value of 55.56 μM. To evaluate their antioxidant potential, the DPPH radical scavenging activity of all six synthesized compounds was assessed. Ascorbic acid was used as a standard with IC50 = 3.62 µM. Compounds 1, 2 and 3 (Figure 2) were proved to be strong antioxidants with IC50 values of 0.927, 0.245 and 0.401 µM. In addition, the ABTS assay revealed that the compounds possessed significantly elevated antioxidant activity. In particular, compound 2 exhibited the strongest antioxidant activity, with an IC50 value of 0.070 µM. Compounds 1 and 3 also showed notable activity, with IC50 values of 1.15 and 0.721 µM, respectively. Ascorbic acid was used as the reference compound (IC50 = 2.03 µM). Molecular docking analysis of compound 5 was performed at the active site of the crystal structure of acetyl cholinesterase AChE enzyme. The results showed that compounds 1, 2 and 3 binds to the enzyme with docking energy of −8.3, −8.8 and −7.9 kcal/mol, respectively. Compound 2 exhibited the best results in all assays except for BChE inhibition. In terms of AChE inhibition, the 2-nitro and 4-methoxy substitutions on the aromatic ring, as present in compound 2 (IC50 = 33.07 µM), were more favorable compared to compound 1 (IC50 = 141.02 µM). This was also observed in the DPPH and ABTS assays. The presence of 2-(piperidin-2-yl)pyridine in compound 2 appeared to enhance its potency relative to the 1,10-phenanthroline moiety in compound 3 in all assays, with the exception of BChE inhibition, where compound 3 exhibited superior activity (Table 1).
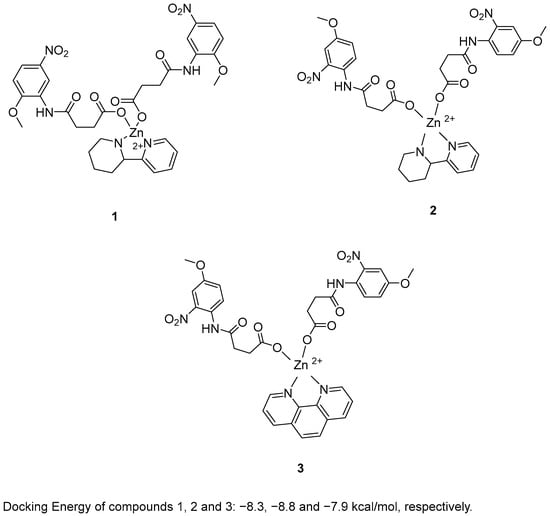
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of zinc metal carboxylates (1–3) [48].

Table 1.
Bioassay results for compounds 1–3 and reference compounds [48].
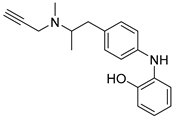
2.2. 4-N-Phenylaminoquinoline Derivatives
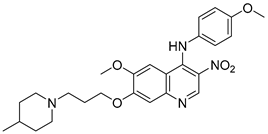
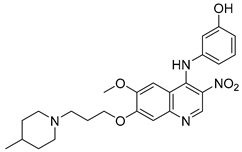
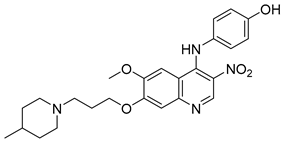
Cai, R. et al. [49] developed and analyzed a series of new 4-N-phenylaminoquinoline derivatives. Their AChE inhibitory activities were assessed against electric eel acetylcholinesterase (eeAChE) and equine serum butyrylcholinesterase (eqBChE) using Ellman’s method, with galantamine as the reference compound. Compound 4, featuring a para-methoxy group, exhibited the most potent inhibitory effect, with an IC50 value of 1.20 ± 0.18 μM, compared to galantamine (IC50 = 1.28 ± 0.01 μM). Moreover, compounds 5 and 6 showed remarkable results with IC50 values of 1.23 ± 0.03 and 1.40 ± 0.23 μM, respectively. In terms of inhibitory activity against eqBChE, compounds 4, 5 and 6 (Figure 3) exhibited significant biological activities. Notably, compound 4 once again demonstrated the highest activity, with an IC50 value of 18.52 ± 1.21 μM. Compounds 5 and 6 also demonstrated considerable activity, with IC50 values of 22.11 ± 1.43 and 28.43 ± 4.70 μM, respectively. Galantamine was used as the reference compound (IC50 = 24.41 ± 2.01 μM). The selectivity index (SI) for AChE, calculated as IC50(eqBChE)/IC50(eeAChE), was calculated for compounds 4, 5, and 6 (15.43, 17.98, and 20.31, respectively), compared to galantamine (SI = 19.07). These values indicate that the inhibitory activity of these compounds is stronger toward AChE than BChE. Propidium iodide displacement (a selective PAS-AChE inhibitor) assay was conducted. From the results derived, compound 5 has been proved to be more efficient at displace propidium (25.80%) than donepezil (18.50%). DPPH radical scavenging activity was tested to assess their antioxidant effects. Compound 6 exhibited excellent DPPH radical scavenging activity (84% at 1 mg/mL) compared to the standard, ascorbic acid 97% (at 1 mg/mL). The results indicated that the radical scavenging activity of compound 6 increased with increasing concentration. Compound 6 exhibited a remarkable EC50 value of 0.328 μM, highlighting its strong antioxidant effect in the submicromolar range, comparable to that of ascorbic acid (EC50 = 0.095 μM). Compounds 4, 5, and 6 were selected for their chelating abilities toward Cu2+, Fe2+, Al3+, and Zn2+, using an UV spectrophotometer across a wavelength range of 200 nm to 600 nm. All synthesized compounds exhibited significant biometal chelation activities towards Al3+, Fe2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+ ions. Compound 6 was selected for molecular docking and shown to interact with the catalytic anionic site (CAS) and the peripheral anionic site (PAS) of both AChE and BChE. The presence of a 4-methoxy substitution appears to enhance activity against AChE more than BChE, as observed in compound 4 (IC50 = 1.20 ± 0.18 and 18.52 ± 1.21, respectively). Additionally, the presence of para-hydroxy substitution (compound 6), appears to slightly reduce both AChE and BChE inhibitory activity. Although para-hydroxy substitution is considered crucial for DPPH scavenging activity, the other two compounds showed low interaction. Therefore, compound 6 stands out as the most effective, due to its ability to interact with the DPPH radical and inhibit both AChE and BChE (Table 2).
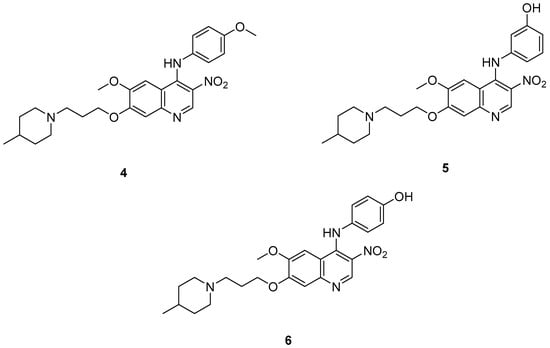
Figure 3.
Chemical structures of 4-N-phenylaminoquinoline derivatives (4–6) [49].

Table 2.
Bioassay results for compounds 4–6 and reference compounds [49].
2.3. 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroacridine Derivatives
In their recent research, Wang, Y. et al. [50] synthesized novel 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridine derivatives and evaluated their potential for acetylcholinesterase from bovine serum (bAChE) inhibition, metal ion chelation, and antioxidant activity. All of the compounds exhibited excellent inhibitory effect against bAChE, with compounds 7 and 11 (Figure 4) showing lower IC50 values (13.5 ± 0.82 and 13.7 ± 0.21 μM, respectively) compared to the reference compound, tacrine (IC50 = 14.1 ± 0.33 μM). The results were determined by the ELISA method. To test their antioxidant activity, a DPPH assay was conducted. Compound 7 exhibited the highest antioxidant activity among the synthesized compounds, with 32.0 ± 0.23%. Compounds 8 and 9 also showed moderate activity, with 34.0 ± 0.56% and 39.0 ± 0.42%, respectively. However, none of the synthesized compounds demonstrated stronger antioxidant activity than the reference compound, deferasirox (23.0 ± 0.52%). To evaluate the cytotoxicity of the compounds, cell viability was assessed using the rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cell line through the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Tacrine and deferasirox were included as reference compounds. Moreover, compound 11 showed low cytotoxicity and demonstrated effective protective activity against H2O2. An in vitro blood–brain barrier permeation assay was conducted by calculating cLogP values using the ChemDraw 17.0. The cLogP values of all compounds were greater than 5, suggesting their potential to cross the blood–brain barrier. They also tested the metal-chelating properties of compound 11 by using the UV–vis spectrometric method across a wavelength range of 200 to 500 nm. The results showed that compound 11 was able to bind Fe3+ and Cu2+ to form chelate metal complexes. Molecular modeling studies showed that compound 11 could simultaneously occupy the CAS and the PAS of the Torpedo californica variant of AChE (TcAChE). The chain length does not appear to significantly affect acetylcholinesterase (bAChE) inhibition, as both compound 7 (n = 4) and compound 11 (n = 11) exhibited the strongest activities. In addition, in the DPPH assay, an increase in chain length appears to enhance interaction with the radical, as observed in the results for compound 11. As a result, compound 11 is considered the most potent, due to its strong acetylcholinesterase (bAChE) inhibitory activity and its ability to effectively scavenge DPPH radical (Table 3).
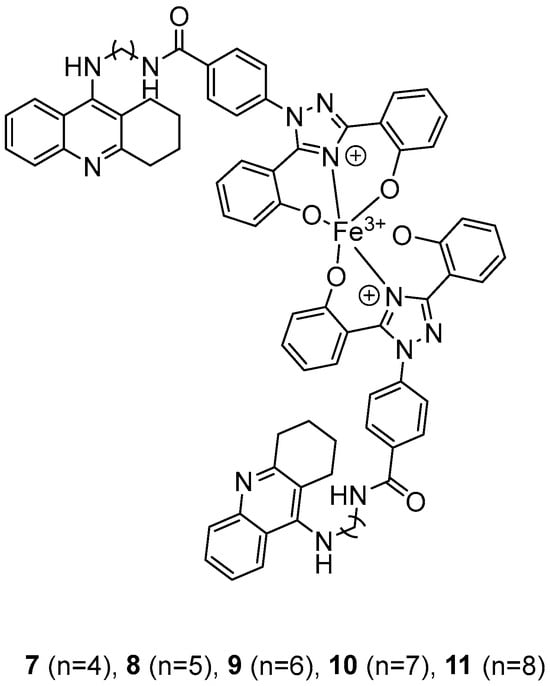
Figure 4.
Chemical structures of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridine derivatives (7–11) [50].

Table 3.
Bioassay results for compounds 7–11 and reference compounds [50].
2.4. Deferiprone–Resveratrol Hybrids
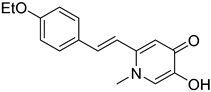
Xu, P. et al. [51], constructed a series of deferiprone–-resveratrol hybrids as multitarget-directed ligands (MTDLs). To assess the ligand affinity for the metal under biological conditions they used the pFe(III) value, which is defined as the negative logarithm of free iron concentration in solution. The pFe(III) values of all synthesized compounds were measured using a fluorescence-based method, with deferiprone being the reference compound (pFe(III) = 20.60). Most of the synthesized compounds exhibited excellent pFe(III) values, with compound 18 (Figure 5) showing the highest, at 20.58 ± 0.18. A Thioflavin-T (ThT) based fluorometric assay was used to test the ability of compounds to inhibit Aβ1–42 self-induced aggregation. Resveratrol and curcumin were used as reference compounds with IC50 values of 11.89 ± 2.52, and 18.73 ± 0.32 μM, respectively. Compounds 12, 16, 19, and 20 demonstrated potent inhibitory activities with IC50 values of 18.97 ± 2.22, 8.94 ± 0.84, 10.72 ± 0.5, and 15.38 ± 0.30 μM, respectively. The antioxidant capacity of the compounds was assessed using the ABTS [2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)] radical scavenging assay, with Trolox (IC50 = 3.89 ± 0.09 μM) used as a reference compound. Compounds showed moderate to good radical scavenging activities, with compound 13 being the most potent with IC50 value of 1.31 ± 0.07 μM. Molecular docking studies were conducted and confirmed that compounds 16 and 19 efficiently interact with the C-terminus of Aβ1–42 by hydrogen bonds. It can be concluded that adding a methyl group at position-1 of the pyridine ring may improve the ability of some compounds, such as compound 16 compared to 15, and compound 18 compared to 17, to inhibit Aβ1–42 self-induced aggregation. However, this effect is not observed in compound 13 compared to 12, or in compound 20 compared to 19. The para-hydroxy substitution in compound 20 increases the inhibition of Aβ1–42 self-induced aggregation compared to the sterically hindered ortho-substitution in compound 21. Additionally, the ortho-methoxy substitution (compound 17) appears to enhance the inhibition of Aβ1–42 self-induced aggregation compared to the ortho-hydroxy substitution (compound 21). The para-hydroxy substitution in compound 19, a stronger electron-donating group compared to the para-ethoxy group in compound 15, is associated with a lower IC50 value in the inhibition of Aβ1–42 self-induced aggregation. In the antioxidant assay, the presence of a methyl group at the 1-position of the pyridine ring was correlated with excellent radical scavenging activity. As expected, the compounds bearing two hydroxyl groups on the benzene ring (compounds 19, 20, and 21) demonstrated greater antioxidant activities than Trolox. Among them, compound 20 showed the highest activity, which may be attributed to the non-sterically hindered para-substitution (Table 4).
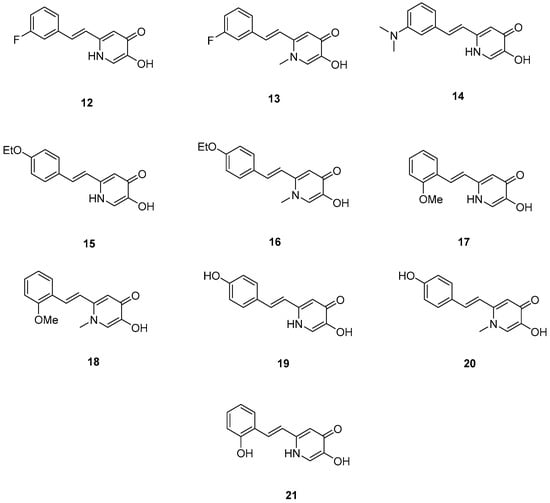
Figure 5.
Chemical structures of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridine derivatives (12–21) [51].

Table 4.
Bioassay results for compounds 12–21 and reference compounds [51].
2.5. Tacrine–(Hydroxybenzoyl-Pyridone) Hybrids
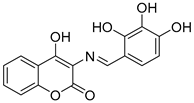
Three novel potentially site-activated multitarget tacrine–-(hydroxybenzoyl-pyridone) (TAC-HBP) hybrids were synthesized and assessed by Chand, K. et al. [52], as AChE inhibitors, antioxidants, and biometal chelators. The AChE inhibitory activity was evaluated by adaptation of the spectroscopic method described by Ellman. All the synthesized compounds exhibited excellent inhibitory effects, with compound 24 (Figure 6) being the most potent, with IC50 = 0.57 ± 0.05 μM. Tacrine was used as the reference compound, with an IC50 value of 0.31 ± 0.02 μM. In DPPH free radical scavenging (EC50), all the derivatives showed similar results, which significantly improved compared to the parent drug tacrine (EC50 > 1000 μM). Notably, compound 24 exhibited the strongest DPPH radical scavenging activity, which may be attributed to the 2′,4′-dihydroxy substitution on the aromatic ring (Table 5). In the AChE inhibitory assay, the results suggested that the length of the linker between the two coupled moieties may play a role in enhancing inhibitory potency against AChE. Compound 24, which contains a four-methylene-unit linker, was the most potent and appears to fit well between the CAS and the PAS of the enzyme. As for the chelating capability against redox-active and/or Aβ-binding metal ions (Fe(III), Cu(II)), and Zn(II)) it has been proved that the HBP moiety is a moderate/good chelator of these biometals and is capable of forming complexes with β-phenol-keto coordination mode.
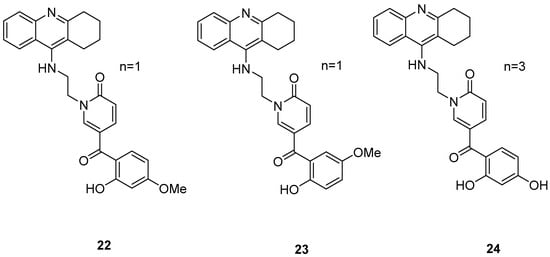
Figure 6.
Chemical structures of tacrine-(hydroxybenzoyl-pyridone) hybrids (22–24) [52].

Table 5.
Bioassay results for compounds 22–24 and reference compound [52].
2.6. Diallyl Disulfide (DADS) Derivatives
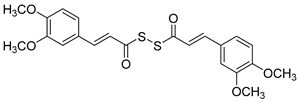
Manral, A. et al. [53], designed, synthesized, and evaluated a series of novel diallyl disulfide (DADS) derivatives. They tested the inhibition of self-mediated Aβ1–42 aggregation using in vitro assays with ThT to monitor and quantify the aggregation of Aβ1–42 synthetic peptide into fibrils. Curcumin was used as the reference compound (51.5 ± 2.68%). All the synthesized compounds showed high % inhibition, with compounds 26 and 27 (74.16 ± 2.10 and 71.41 ± 3.04, respectively) exhibiting the best effects. To investigate the inhibitory effect of the synthesized AChE and BuChE, they used modified Ellman’s method. Donepezil was the reference compound with an IC50 value of 8.71 ± 1.36 µM for BuChE assay and 0.049 ± 0.05 µM for AChE assay. In the AChE assay, the compounds exhibited moderate inhibitory activities, with compounds 26 and 27 (Figure 7) showing the most potent effects, having IC50 values of 13.64 ± 0.27 µM and 12.87 ± 0.81 µM, respectively. In the BuChE assay, compounds 26 and 27 once again demonstrated the most potent activities, with IC50 values of 0.056 ± 0.05 µM and 0.121 ± 0.06 µM, respectively (Table 6). The results suggest that substitutions on the aromatic ring significantly influence the inhibitory effects of the compounds on both AChE and BuChE. Compounds 26 and 27 were the most potent towards cholinesterase enzymes. Particularly, the activity ranging of the substituted groups on the ring is as follows: 3,4-dimethoxy > 4-hydroxy, 3-methoxy > 4-methoxy > 4-hydroxy. Consequently, the electron density of the aromatic ring appears to play a crucial role in the inhibitory activity of the compounds against cholinesterase enzymes. Moreover, the antioxidant activities of the synthesized compounds were evaluated through the oxygen radical absorbance capacity assay using fluorescein (ORAC-FL). The vitamin E analogue Trolox was used as a standard. All the synthesized compounds demonstrated excellent antioxidant activities, with compounds 26 and 27 showing the most potent results, exhibiting ORAC-FL values of 5.24 ± 0.37 µM and 5.86 ± 0.98 µM, respectively. Compounds 26 and 27 have a free -OH and -OCH3 group on the phenyl ring, which might be crucial to the radical scavenging ability. Compounds 26 and 27 were able to disaggregate Aβ fibrils formed by Cu2+-induced aggregation, achieving disaggregation rates of 80.9% and 78.5%, respectively, as further confirmed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis. Furthermore, the ability of compound 26 to chelate biometals like Cu2+ and Fe2+ by UV- visible spectrometry was studied. The results showed that compound 26 possesses a chelating ability and it is attributed to the presence of the dimethoxy group on the phenyl ring and keto-moieties in the core structure of the compound. Compound 26 can simultaneously bind to both bivalent cations. The stoichiometry of the compound 26–Cu2+ complex was determined by the molar ratio method. The results indicated 1:1 stoichiometry for the complex. Molecular modeling studies showed that compounds 26 and 27 could simultaneously occupy the CAS and the PAS of AChE. Moreover, cytotoxicity assays performed in compounds 26 and 27 did not indicate toxicity and revealed that they have druglike properties.
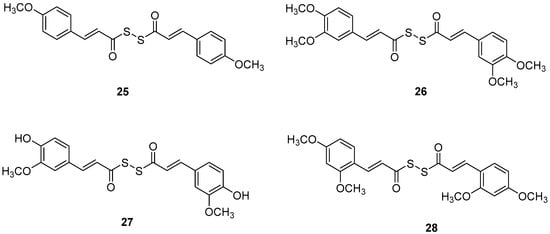
Figure 7.
Chemical structures of tacrine-(hydroxybenzoyl-pyridone) hybrids (25–28) [53].

Table 6.
Bioassay results for compounds 25–28 and reference compounds [53].
2.7. 3-Schiff Base-4-Hydroxycoumarin Derivatives
Wang, Z.-M. et al. [54] designed and synthesized a series of 3-Schiff base-4-hydroxycoumarin derivatives which were further evaluated for their monoamine oxidase inhibitory activities. All the synthesized compounds exhibited good inhibitory activities against hMAO-A and hMAO-B. Compound 30 showed the best hMAO-A inhibition, with IC50 value of 0.673 ± 0.011 µM. Iproniazid was used as the reference compound, with IC50 = 7.14 ± 0.38 µM. In the hMAO-B inhibitory assay, compound 4 exhibited the most potent inhibitory activity, with an IC50 value of 0.711 ± 0.013 µM, while the other compounds showed moderate to good activity. Pargyline and Iproniazid were the reference compounds, with IC50 values of 0.214 ± 0.036 µM and 8.54 ± 0.64 µM, respectively. The ability to inhibit self-induced Aβ1–42 aggregation was tested by using a ThT based fluorometric assay. All the compounds exhibited moderate to good results with compound 31 (Figure 8) exhibiting the highest efficacy (82.3 ± 6.6%). Curcumin and resveratrol were used as reference compounds, with 50.2 ± 5.9 and 67.3 ± 3.4%. Compounds 29, 30, 31, and 35 were selected to investigate their ability to inhibit Cu2+-induced Aβ1–42 aggregation by the ThT-binding assay. The results indicate that these compounds could inhibit Cu2+-induced Aβ1–42 aggregation effectively. Additionally, they have been tested for their antioxidant activity through the ABTS and DPPH radical scavenging protocols. Trolox was the reference compound, and curcumin was determined for comparison. The best activity was observed for 35 with 1.57 trolox equivalents. For the DPPH radical scavenging assay resveratrol and curcumin were used as reference compounds with IC50 values of 137 ± 4 and 39.6 ± 2.1 µM, respectively. Among the tested derivatives, compounds 30 and 35 were the most potent with IC50 values of 45.8 ± 1.2 and 38.6 ± 2.0 µM, respectively (Table 7). Molecular docking and kinetic studies revealed that compound 30 was a reversible and noncompetitive MAO-B inhibitor. Moreover, these compounds showed low PC12 cells toxicity. To determine the ability of the compounds to cross the BBB, a parallel artificial membrane permeation assay for the BBB (PAMPA-BBB) was used. It can be concluded that compound 35 has shown higher Pe values than 4.5 being capable of crossing the blood–brain barrier, but compound 30 was uncertain for BBB permeation (CNS±). To assess BBB permeability, the compounds were categorized as follows: those with Pe (10−6 cm/s) > 4.5 were classified as having high BBB permeability (CNS+); those with Pe < 2.1 as having low permeability (CNS−); and compounds with Pe values between 2.1 and 4.5 as having uncertain BBB permeability (CNS±). Compound 30 exhibited the most potent hMAO-A and hMAO-B inhibitory activity, likely due to the presence of three hydroxyl groups in the ortho, meta, and para positions. Methoxy and methyl substitutions, which are weaker electron-donating groups than hydroxy, at the meta position appear to reduce hMAO-A inhibitory activity. For their antioxidant activity compound 35 had the best results with an additional nitro group in 5-position of the benzaldehyde ring. Ortho or para substitution of hydroxyl groups on the benzene ring favors the ABTS radical scavenging activity.
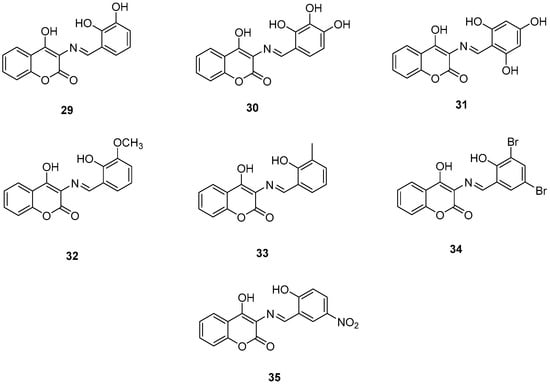
Figure 8.
Chemical structures of 3-Schiff base-4-hydroxycoumarin derivatives (29–35) [54].

Table 7.
Bioassay results for compounds 29–35 and reference compounds.
2.8. Selegiline Derivatives
Xie, S. et al. [55] designed and synthesized a new series of selegiline derivatives. In vitro inhibition studies of hMAO-A and hMAO-B were conducted, using clorgyline and pargyline as reference compounds. All the synthesized compounds showed excellent hMAO-B inhibitory activity, with compound 38 (Figure 9) being the most potent (IC50 = 0.21 ± 0.04 μM), comparable to the reference compound pargyline (IC50 = 0.1880 μM). Compound 38 has no substituents other than the hydroxy group on the phenyl ring. It appears that substitution at the ortho and meta positions relative to the hydroxyl group on the benzene ring is not essential for the inhibitory activity. The presence of a strong electron-donating group in the ortho position, as in compound 36, enhances hMAO-A and hMAO-B inhibitory activity compared to compound 37, bearing a methyl group in the same position. The results indicate that the compounds also exhibit effective MAO-A inhibition, with compound 40 showing the most potent activity (IC50 = 0.70 ± 0.01 μM). The antioxidant activities using the oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC-FL) assay was studied, with fluorescein as the probe and the vitamin E analogue Trolox as the standard. The results revealed that all the synthesized compounds possessed excellent antioxidant capacity with ORAC-FL values of 1.49–5.65 Trolox equivalents. In general, compound 41, bearing two hydroxy groups on the phenyl ring, exhibited the best result (5.67 Trolox equivalents). The metal-chelating ability of compound 38 was investigated using UV–vis spectrometry. Based on the shifts in the absorption spectra, it was suggested that compound 38 can interact with iron(II) and zinc(II). High-resolution mass spectrometry was performed to determine the stoichiometry of the compound 38–Cu(II) complex. The results showed that the stoichiometry of the complex is 2:1. Additionally, the biometal chelating ability of compound 38, was evaluated and the results demonstrated that it can effectively inhibit Cu(II)-induced Aβ1–42 aggregation. To determine whether the compounds could cross the BBB, a PAMPA-BBB was used. In fact, compounds with a permeability above 4.7 × 10−6 cm/s are likely to cross the BBB via passive diffusion (CNS+), while those with Pe values between 1.8 × 10−6 cm/s and 4.7 × 10−6 cm/s were classified as having uncertain BBB permeability (CNS+/−). Compounds 36, 37, 38 and 39 can cross the BBB (Table 8).
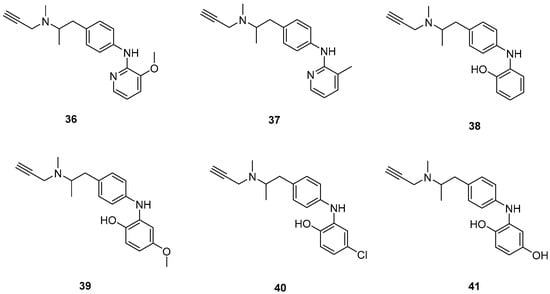
Figure 9.
Chemical structures of selegiline derivatives (36–41) [55].

Table 8.
Bioassay results for compounds 36–42 and reference compounds.
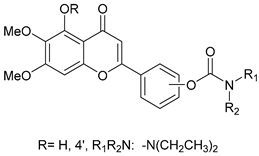
2.9. Scutellarein Carbamate Derivatives
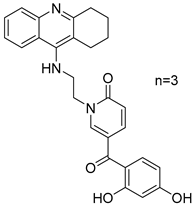
Sang, Z. et al. [56] produced a series of scutellarein carbamate derivatives as multifunctional agents for the treatment of AD. To determine the AChEand BuChE inhibitory activities of the synthesized compounds the modified Ell man method was applied using AChE from rat cortex homogenate (RatAChE) and BuChE from rat serum (RatBuChE). Rivastigmine was used as a reference compound with IC50 = 5.6 ± 0.02 μM for AChE and 1.4 ± 0.01 μM for BuChE. All the synthesized compounds exhibited good inhibitory activity against AChE with compounds 44 and 47 (Figure 10) showing the best results with IC50 values of 0.34 ± 0.03 μM and 0.57 ± 0.02 μM, respectively. Both compounds contain the N,N-diethylcarbamate moiety in their structure. Almost all the compounds exhibited weak activity against BuChE and showed higher selectivity towards AChE over BuChE. Compound 43 had the best results against BuChE with IC50 = 6.2 ± 0.21 μM. Substitutions at the 5-position of the flavonoid core significantly influenced AChE inhibitory activity; derivatives with a 5-methoxy group (compounds 42–45 and 50–51) exhibited greater activity than those with a 5-hydroxyl group (46–49). The results also showed that placing the carbamate group at the 4′-position (compounds 42–45 and 46–49) led to stronger inhibitory activity compared to placement at the 3′-position (compounds 50–51). This suggests that the carbamate group at the 4′-position is more favorably oriented to interact with the CAS of AChE. The ability of compounds 44 and 47 to chelate biometals such as Cu2+, Zn2+, Al3+ and Fe2+ was evaluated by UV–vis spectrometry. The chelating ability can be attributed to the 5-hydroxyl and 4-carbonyl groups at the flavonoid nucleus. The stoichiometry of the compound 47–Cu2+ complex was calculated and the results showed 1:1 stoichiometry for the complex. In conclusion, compounds 44 and 47 were the most potent and were selected for further studies on their metal-chelating abilities. The kinetic characterization on compound 47 suggests a mixed-type inhibition, binding to both CAS and PAS of AChE, which was consistent with the result of the molecular modeling study. The compounds have been further evaluated for their antioxidant activity, by using the well-established ORAC-FL method (Oxygen Radicals Absorbance Capacity by Fluorescence). The vitamin E analogue Trolox was used as a standard, and the results were expressed as Trolox equivalents. Compounds 46, 47, 48 and 49 exhibited the highest antioxidant activities with ORAC-FL values of 1.1 ± 0.05, 1.3 ± 0.02, 1.0 ± 0.03 and 0.9 ± 0.01, respectively (Table 9). These compounds contain a hydroxyl group at position 5 of the flavonoid core and exhibited superior antioxidant activity compared to compounds 42–45, which contain a 5-methoxyl group. The neuroprotective potential of the selected carbamate derivatives under oxidative stress was evaluated by assessing their ability to protect PC12 cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced injury. Cell viability was determined using the MTT assay. Compound 47 exhibited remarkable neuroprotective effects, and the cell viability was 78.5%. The possible in vivo BBB permeability of compound 47 was evaluated with the PAMPA–BBB. Compound 47 exhibited a permeability (Pe × 10−6 cm/s) of 8.42 ± 0.37, suggesting its potential to cross the BBB and reach targets within the CNS. The protective effects of compound 47 on scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment in mice, were evaluated using the Y-maze test. The results revealed that compound 47 can decrease the vitality of AChE and increase the vitality of ChAT in the hippocampus of mice.
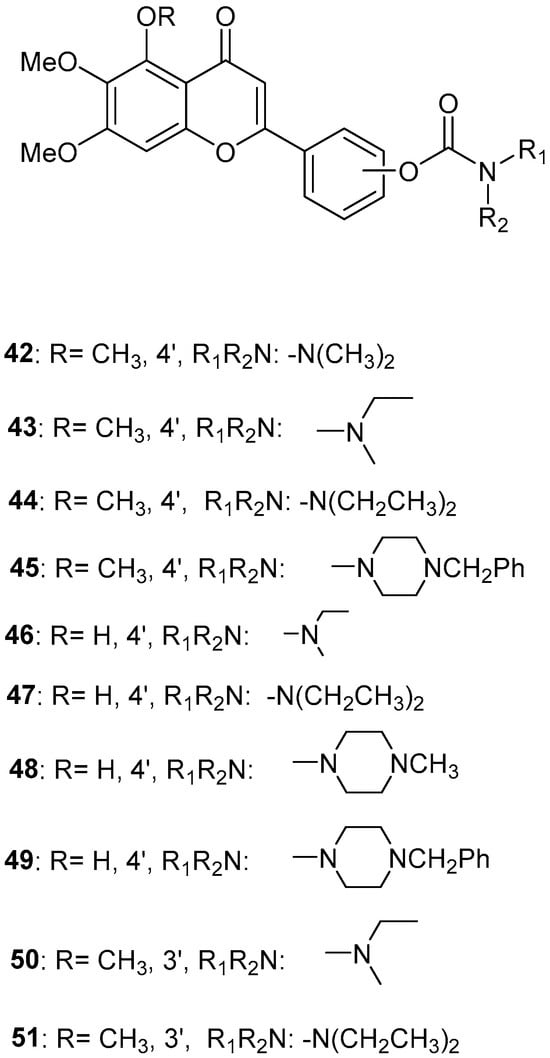
Figure 10.
Chemical structures of scutellarein carbamate derivatives (42–51) [56].

Table 9.
Bioassay results for compounds 42–51 and reference compounds.
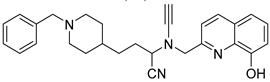
2.10. Donepezil-Related Derivatives
Wu, M.-Y. et al. [57] constructed a series of donepezil-related derivatives possessing metal chelating properties, and being capable of targeting different enzymatic systems related to AD (cholinesterases, ChEs, and monoamine oxidase A, MAO-A). Compound 52 (Figure 11) showed the best activity, inhibiting AChE activity with an IC50 value of 0.029 μM. Additionally, compound 52 demonstrated excellent inhibitory activity (IC50 = 0.039 μM) against the BuChE being more potent than the reference compound, donepezil (IC50 = 7.5 μM). Compound 52 was found to be a selective MAO-A (vs MAO-B) inhibitor with IC50 = 10.1 μM. An in vitro assay to establish its metal-chelating properties of compound 52 was applied using UV–vis spectrometry. The results showed that compound 52 was able to interact with Cu2+, Fe2+ and Zn2+. The results indicated a 1:2 stoichiometric complexation between compound 52 and both Cu2+ and Zn2+, revealing a metal-to-compound 52 ratio of 1:2. The antioxidant activity was evaluated in vitro using the linoleic acid assay and 2,2′-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride (AAPH). The tested compounds exhibited 50–60% activity compared to the reference compound Trolox, which showed 100–120% activity. Finally, compound 52 exhibited weak radical scavenging activity (RSA) in the DPPH assay, compared to Trolox (Table 10).
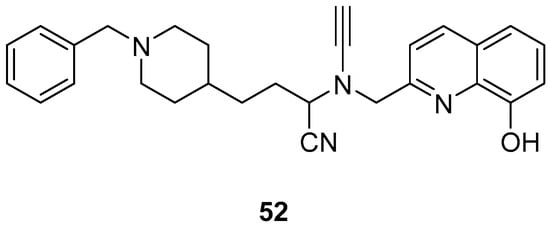
Figure 11.
Chemical structures of donepezil-related derivative (52) [57].

Table 10.
Bioassay results for compound 52 and reference compounds.
3. Conclusions
Metal-chelating agents have gained significant importance in medicine in recent years, and many researchers are synthesizing them for the treatment of AD. Oxidative stress has emerged as an important factor involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease and consequently, antioxidants can be a key factor in AD treatment. In this review, the role of bifunctional metal chelators with antioxidant properties for the treatment of Alzheimer’s was described. It was found that several potent inhibitors exhibited good to excellent activity against AChE, BuChE, hMAO-A, and hMAO-B, as well as in antioxidant assays and self-induced Aβ1–42 aggregation. Several of the synthesized compounds exhibited excellent AChE inhibitory activity, with compounds 4, 5, 7, 11, 16, 19, and 43–48 showing the highest potency, as indicated by IC50 values (1.20 ± 0.18, 1.23 ± 0.03, 13.5 ± 0.82, 13.7 ± 0.21, 8.94 ± 0.84, 10.72 ± 0.5, 1.54 ± 0.04, 0.34 ± 0.03, 1.04 ± 0.05, 2.10 ± 0.05, 0.57 ± 0.02 and 5.0 ± 0.05 μM, respectively) lower than those of the reference compounds. Most of these compounds possess substituted hydroxyl and methoxy aromatic rings. Several compounds also demonstrated good BuChE inhibitory activity; however, the results indicated greater selectivity toward AChE. Compounds 29, 30, 34, 35, and 39–41 exhibited excellent dual inhibitory activity against hMAO-A and hMAO-B. Compounds 29, 30, 34, and 35 possess at least one hydroxyl group on the aromatic ring, with compound 30 exhibiting the most potent activity, likely due to the presence of three hydroxyl groups located at the ortho, meta, and para positions. This may be attributed to the stronger electron-donating ability of the hydroxyl group compared to other substituents. Compound 35, having a nitro moiety on the aromatic ring, presented the best antioxidant activity. In the self-induced Aβ1–42 aggregation assay, compounds 16, 19, 20, 25–28, 31, and 35 showed the most effective inhibition compared to the reference compounds. Substitution with methoxy or hydroxyl groups on the phenyl ring of compounds 25–28 seems to contribute to the activity. In general, hydroxyl groups on aromatic rings enhance the activity of the synthesized compounds. Additionally, compounds with good antioxidant activities possess free hydroxyl, methoxy or ethoxy moieties. Compounds 1–3, 6, 10, 11, 13, 14, 19–25, 29, 30, and 35–52 exhibit potent dual metal- chelating, and antioxidant properties for the treatment of AD. Regarding metal-chelating properties, most of the compounds can interact with Fe2+ and Cu2+ ions, while a few also show affinity for Zn2+ and Al3+. A considerable number of the synthesized compounds exhibited good antioxidant activity, and their biometal chelating abilities also yielded promising results. All the above discussed results have been included in Table 11, summarizing the metal-binding or metal-related properties of the discussed compounds (Table 11).

Table 11.
Summary of metal-binding and metal-related properties of the discussed compounds.
Author Contributions
E.C. contributed to the writing and preparation of the manuscript. E.P. contributed to the supervision, writing, reviewing, and editing of this manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to E. Maniati, Queen Mary University of London and M. Konstantinidou, University of California San Francisco for the final English editing of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Aβ | Amyloid-β |
| AAPH | 2,2′-Azobis(2-Amidinopropane) Dihydrochloride |
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| AD | Alzheimer Dease |
| ADNC | Alzheimer Dease Neuropathological Change |
| APP | Amyloid Precursor Protein |
| BBB | Blood Brain Barrier |
| BChE | Butyrylcholinesterase |
| CAS | Catalytic Anionic Site |
| ChAT | Choline Acetyltransferase |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| DADS | Diallyl Disulfide Derivatives |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl |
| eeAChE | Electric Eel Acetylcholinesterase |
| EOAD | Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease |
| eqBChE | Equine Serum Butyrylcholinesterase |
| F-actin | Fibrillar Actin |
| G-actin | Globular Actin |
| HBP | Hydroxybenzoyl-Pyridone |
| hMAO-A | Human Monoamine Oxidase A |
| hMAO-B | Human Monoamine Oxidase B |
| LOAD | Late-Onset Alzheimer Dease |
| MTDLs | Multitarget-Directed Ligands |
| NFT | Neurofibrillary Tangle |
| ORAC-FL | Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity by Fluorescein |
| PAMPA | Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeation Assay |
| PART | Primary Age-related Tauopathy |
| PAS | Peripheral Anionic Site |
| PHFs | Paired Helical Filaments |
| RSA | Radical Scavenging Activity |
| RNS | Reactive Nitrogen Species |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SI | Selectivity Index |
| TAC-HBP | Tacrine-(Hydroxybenzoyl-Pyridone) |
| TcAChE | Torpedo Californica Variant of AChE |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| ThT | Thioflavin-T |
| VILIP-1 | Visinin-Like Protein-1 |
References
- Huang, L.-K.; Chao, S.-P.; Hu, C.-J. Clinical trials of new drugs for Alzheimer disease. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Alzheimer Disease: An Update on Pathobiology and Treatment Strategies. Cell 2019, 179, 312–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M.M. Sex and Gender Differences in Alzheimer’s Disease Dementia. Psychiatr. Times 2018, 35, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo, G.; Holtzman, D.M. Amyloid-β and Tau at the Crossroads of Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1184, 187–203. [Google Scholar]
- Tarasoff-Conway, J.M.; Carare, R.O.; Osorio, R.S.; Glodzik, L.; Butler, T.; Fieremans, E.; Axel, L.; Rusinek, H.; Nicholson, C.; Zlokovic, B.V.; et al. Clearance systems in the brain—Implications for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Guerrero, J.; Santiago-Balmaseda, A.; Jeronimo-Aguilar, P.; Vargas-Rodríguez, I.; Cadena-Suárez, A.R.; Sánchez-Garibay, C.; Pozo-Molina, G.; Méndez-Catalá, C.F.; Cardenas-Aguayo, M.-D.; Diaz-Cintra, S.; et al. Alzheimer’s Disease: An Updated Overview of Its Genetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, C.; Van Broeckhoven, C.; Sleegers, K. The genetic landscape of Alzheimer disease: Clinical implications and perspectives. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Liu, R.; Qin, Y.; Wang, T. Brain metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease: Biological mechanisms of exercise. Transl. Neurodegener. 2023, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiannopoulou, K.G.; Papageorgiou, S.G. Current and Future Treatments in Alzheimer Disease: An Update. J. Central Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2020, 12, 1179573520907397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. The blood–brain barrier: Structure, regulation and drug delivery. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, J.A.; Bernardes, C.; Bernardo-Castro, S.; Lino, M.; Albino, I.; Ferreira, L.; Brás, J.; Guerreiro, R.; Tábuas-Pereira, M.; Baldeiras, I.; et al. Reconsidering the role of blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer’s disease: From delivery to target. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1102809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Sabermarouf, B.; Majdi, A.; Talebi, M.; Farhoudi, M.; Mahmoudi, J. Amyloid-Beta: A Crucial Factor in Alzheimer’s Disease. Med Princ. Practice 2015, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.-S.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.; Deng, J.; Zeng, L.-H.; Tan, J. Amyloid Precursor Protein: A Regulatory Hub in Alzheimer’s Disease. Aging Dis. 2023, 15, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehar, U.; Rawat, P.; Reddy, A.P.; Kopel, J.; Reddy, P.H. Amyloid Beta in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czuczwar, S.J.; Kocki, J.; Miziak, B.; Bogucki, J.; Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Pluta, R. Alpha-, Beta-, and Gamma-Secretase, Amyloid Precursor Protein, and Tau Protein Genes in the Hippocampal CA3 Subfield in an Ischemic Model of Alzheimer’s Disease with Survival up to 2 Years. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 98, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Anand, P.; Singh, S. Proposed Therapeutic Strategy to Combat Alzheimer’s Disease by Targeting Beta and Gamma Secretases. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2025, 22, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K.; de Leon, M.J.; Zetterberg, H. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2006, 368, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Hardy, J.; Blennow, K.; Chen, C.; Perry, G.; Kim, S.H.; Villemagne, V.L.; Aisen, P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; et al. The Amyloid-β Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5481–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busche, M.A.; Hyman, B.T. Synergy between amyloid-β and tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Sun, H.; Cai, Q.; Tai, H.-C. The Enigma of Tau Protein Aggregation: Mechanistic Insights and Future Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Mora, P.; Luna, R.; Colín-Barenque, L. Amyloid Beta: Multiple Mechanisms of Toxicity and Only Some Protective Effects? Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 795375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Yu, S.; Battaglia, G.; Tian, X. Amyloid—β in Alzheimer’s disease: Structure, toxicity, distribution, treatment, and prospects. Ibrain 2024, 10, 266–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metaxas, A.; Kempf, S. Neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer′s disease: Elucidation of the molecular mechanism by immunohistochemistry and tau protein phospho-proteomics. Neural Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 1579–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brion, J.-P. Neurofibrillary Tangles and Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. Neurol. 1998, 40, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ture, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thal, D.R.; Tomé, S.O. The central role of tau in Alzheimer’s disease: From neurofibrillary tangle maturation to the induction of cell death. Brain Res. Bull. 2022, 190, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, G.; Bapat, D.; Das, D.; Gowaikar, R.; Amritkar, R.E.; Rangarajan, G.; Ravindranath, V.; Ambika, G. Synapse loss and progress of Alzheimer’s disease -A network model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Halliwell, B. Oxidative stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufarelli, V.; Colonna, M.A.; Losacco, C.; Puvača, N. Biological Health Markers Associated with Oxidative Stress in Dairy Cows during Lactation Period. Metabolites 2023, 13, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militello, R.; Luti, S.; Gamberi, T.; Pellegrino, A.; Modesti, A.; Modesti, P.A. Physical Activity and Oxidative Stress in Aging. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, G.; Cash, A.D.; Smith, M.A. Alzheimer Disease and Oxidative Stress. BioMed Res. Int. 2002, 2, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, R.; Butterfield, D.A. Role of Oxidative Stress in the Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 19, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, T.; Deore, S.L.; Kide, A.A.; Shende, B.A.; Sharma, R.; Chakole, R.D.; Nemade, L.S.; Kale, N.K.; Borah, S.; Deokar, S.S.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis -An updated review. Mitochondrion 2023, 71, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhapola, R.; Beura, S.K.; Sharma, P.; Singh, S.K.; HariKrishnaReddy, D. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease: Current knowledge of signaling pathways and therapeutics. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramutola, A.; Lanzillotta, C.; Perluigi, M.; Butterfield, D.A. Oxidative stress, protein modification and Alzheimer disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2017, 133, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Guo, J.; Ye, X.-Y.; Xie, Y.; Xie, T. Oxidative stress: The core pathogenesis and mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 77, 101619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, O.; Utkilen, H.; Duale, N.; Brunborg, G.; Hofer, T. Metal Dyshomeostasis and Inflammation in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases: Possible Impact of Environmental Exposures. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 726954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenough, M.A.; Camakaris, J.; Bush, A.I. Metal dyshomeostasis and oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Y.-L.; Liu, X.-Z.; Shen, P.; Zheng, Y.-G.; Lan, X.-R.; Lu, C.-B.; Wang, J.-Z. Current understanding of metal ions in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leko, M.B.; Horvat, L.L.; Popovački, E.Š.; Zubčić, K.; Hof, P.R.; Šimić, G. Metals in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Liu, H.; Ma, D.-L.; Leung, C.-H. Rebalancing metal dyshomeostasis for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 24, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metaxas, A. Imbalances in Copper or Zinc Concentrations Trigger Further Trace Metal Dyshomeostasis in Amyloid-Beta Producing Caenorhabditis elegans. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 755475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Ma, X.; Song, N.; Xie, J. Homeostasis and metabolism of iron and other metal ions in neurodegenerative diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenche, V.B.; Barnham, K.J. Alzheimer’s disease & metals: Therapeutic opportunities. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.A.; Chand, K.; Chaves, S. Recent progress in multifunctional metal chelators as potential drugs for Alzheimer’s disease. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 327–328, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, R.; Zubair, M.; Ali, S.; Shahid, K.; Waseem, W.; Naureen, H.; Haider, A.; Jan, M.S.; Ullah, F.; Sirajuddin, M.; et al. Zinc metal carboxylates as potential anti-Alzheimer’s candidate: In vitro anticholinesterase, antioxidant and molecular docking studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Wang, L.-N.; Fan, J.-J.; Geng, S.-Q.; Liu, Y.-M. New 4-N-phenylaminoquinoline derivatives as antioxidant, metal chelating and cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 93, 103328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hong, K.H.; Ning, Y.; Yu, P.; Ren, J.; Ji, M.; Cai, J. Design, synthesis and evaluation of a novel metal chelator as multifunctional agents for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, M.; Sheng, R.; Ma, Y. Synthesis and biological evaluation of deferiprone-resveratrol hybrids as antioxidants, Aβ 1–42 aggregation inhibitors and metal-chelating agents for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chand, K.; Alsoghier, H.M.; Chaves, S.; Santos, M.A. Tacrine-(hydroxybenzoyl-pyridone) hybrids as potential multifunctional anti-Alzheimer’s agents: AChE inhibition, antioxidant activity and metal chelating capacity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 163, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manral, A.; Saini, V.; Meena, P.; Tiwari, M. Multifunctional novel Diallyl disulfide (DADS) derivatives with β-amyloid-reducing, cholinergic, antioxidant and metal chelating properties for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 6389–6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-M.; Xie, S.-S.; Li, X.-M.; Wu, J.-J.; Wang, X.-B.; Kong, L.-Y. Multifunctional 3-Schiff base-4-hydroxycoumarin derivatives with monoamine oxidase inhibition, anti-β-amyloid aggregation, metal chelation, antioxidant and neuroprotection properties against Alzheimer’s disease. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 70395–70409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Su, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; Li, X. Synthesis and evaluation of selegiline derivatives as monoamine oxidase inhibitor, antioxidant and metal chelator against Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3722–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Z.; Li, Y.; Qiang, X.; Xiao, G.; Liu, Q.; Tan, Z.; Deng, Y. Multifunctional scutellarin–rivastigmine hybrids with cholinergic, antioxidant, biometal chelating and neuroprotective properties for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-Y.; Esteban, G.; Brogi, S.; Shionoya, M.; Wang, L.; Campiani, G.; Unzeta, M.; Inokuchi, T.; Butini, S.; Marco-Contelles, J. Donepezil-like multifunctional agents: Design, synthesis, molecular modeling and biological evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 121, 864–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).