BioGoldNCDB: A Database of Gold Nanoclusters and Related Nanoparticles with Biomedical Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
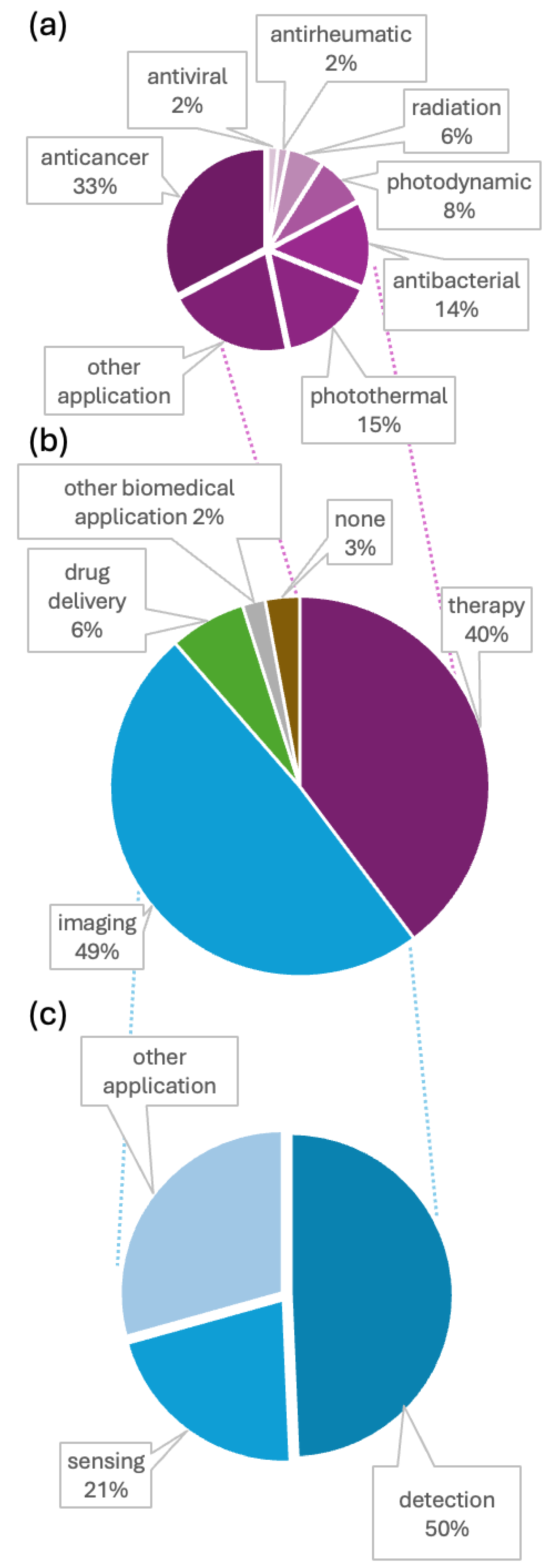
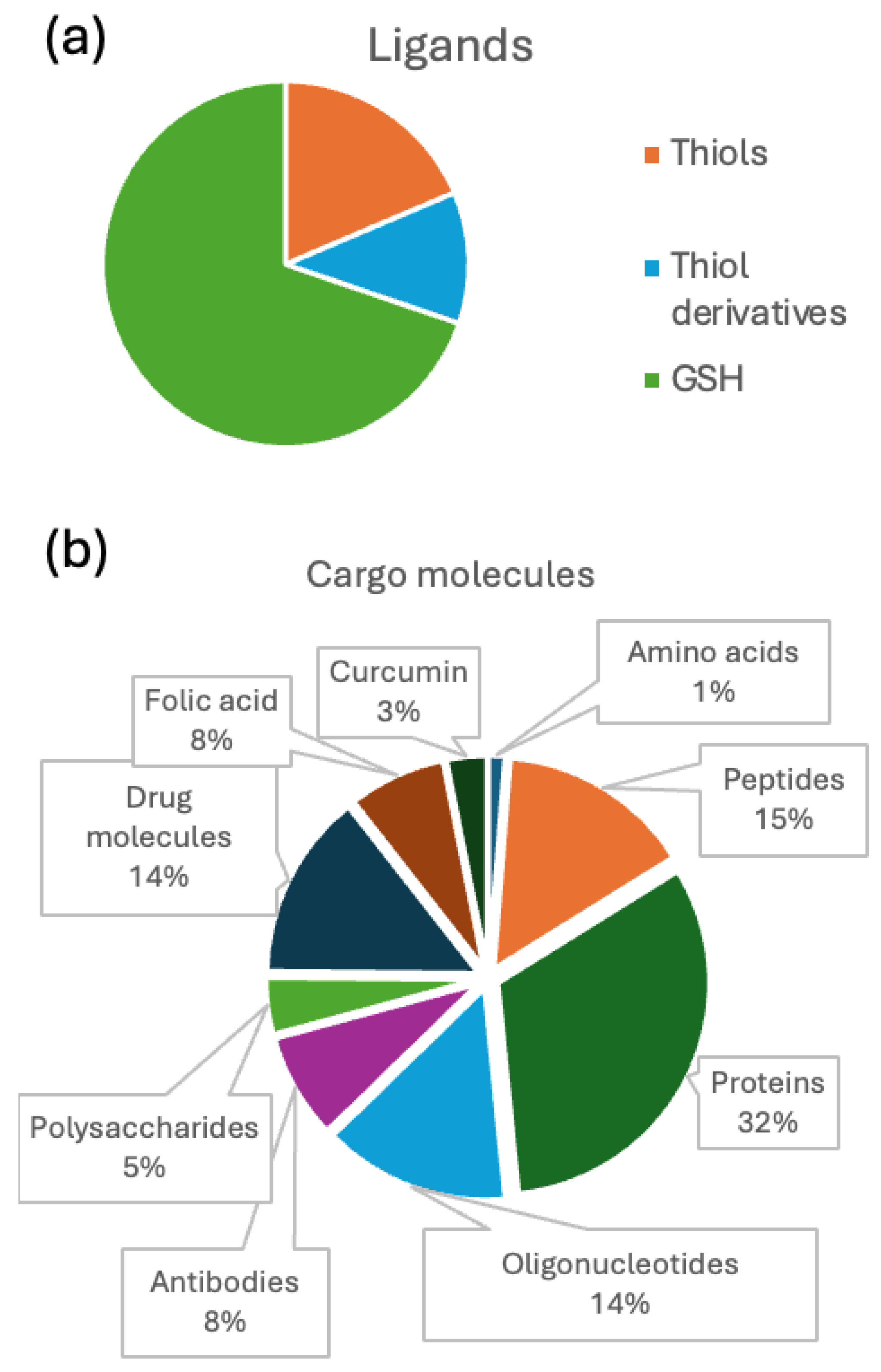
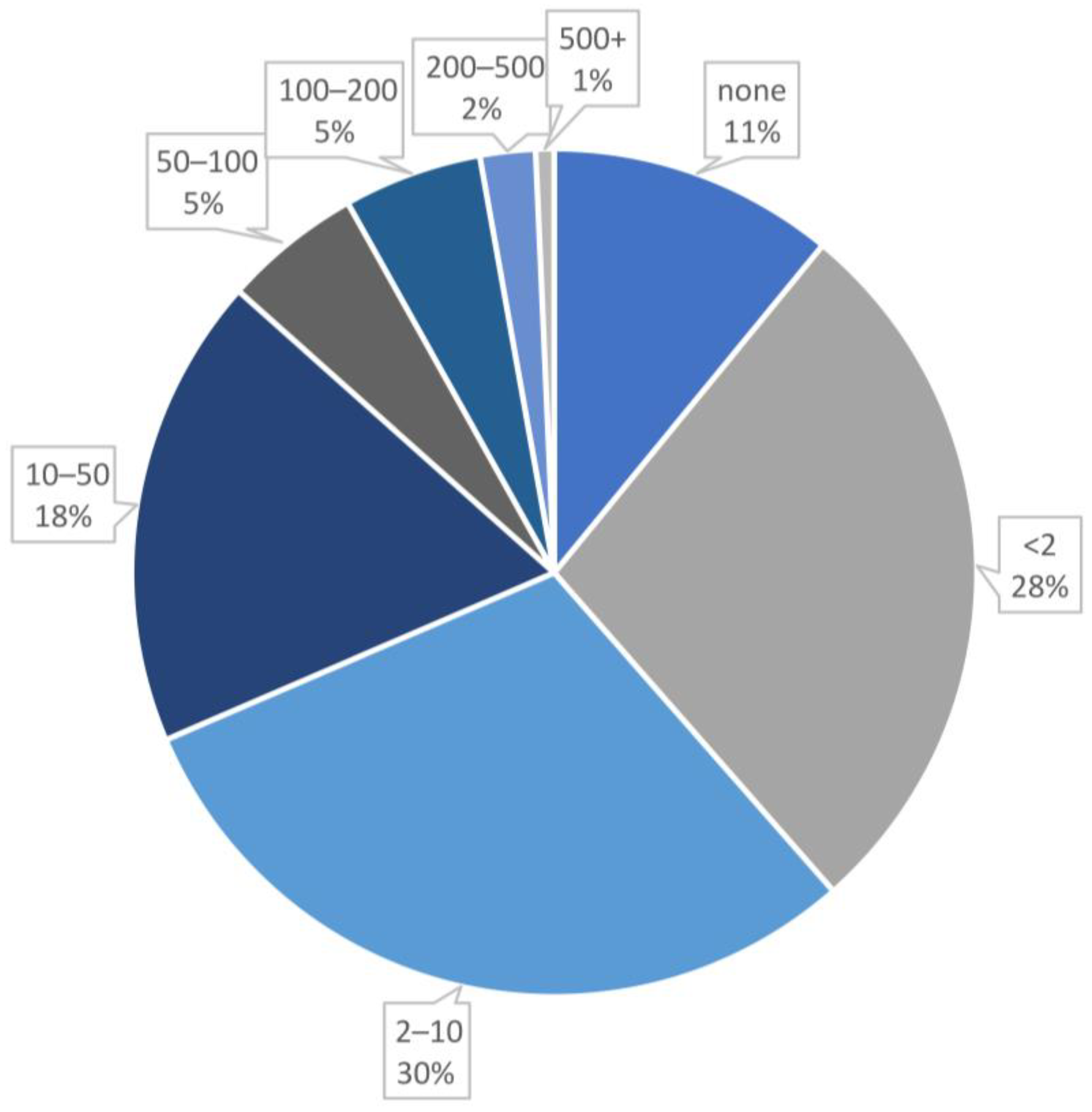
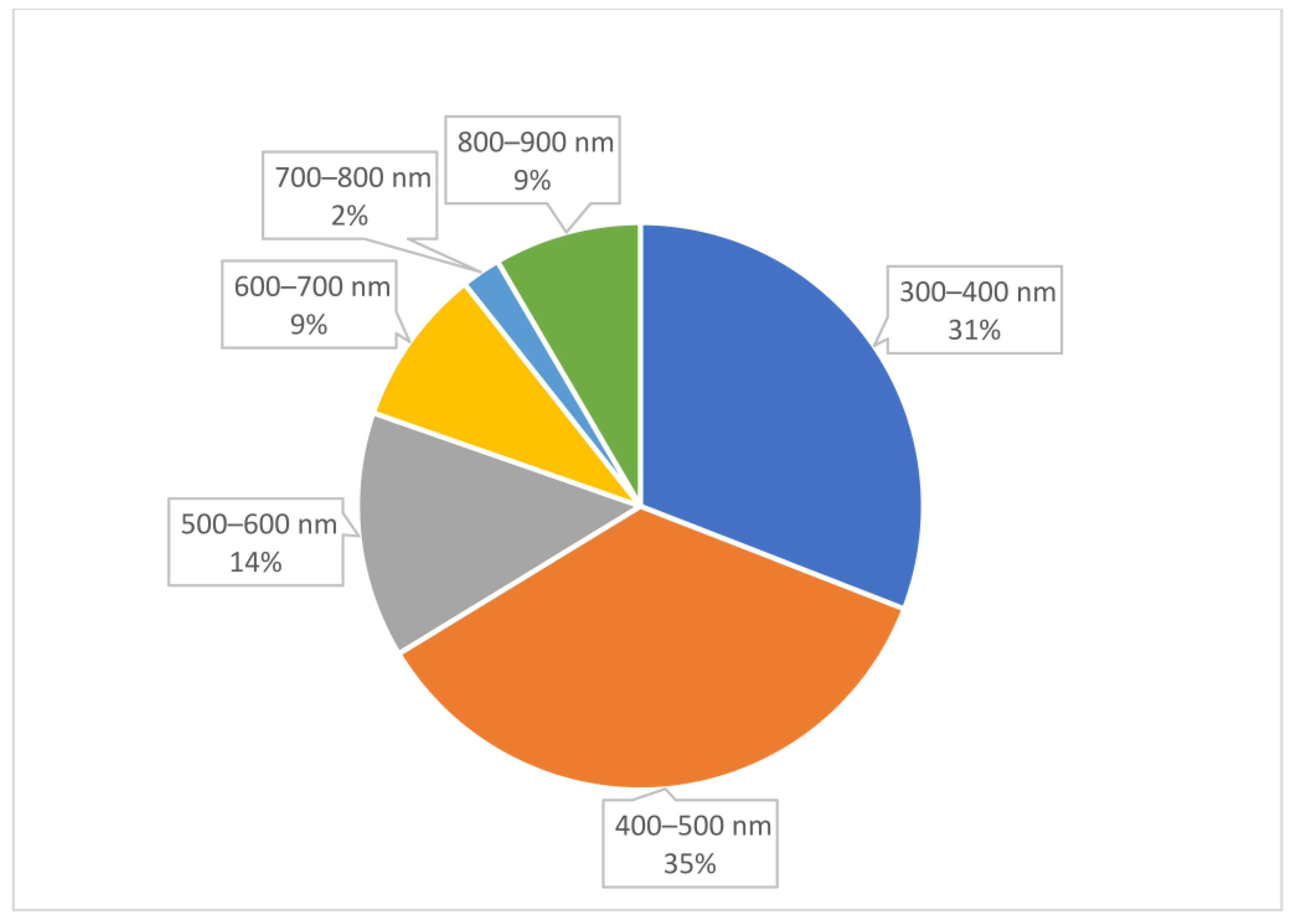
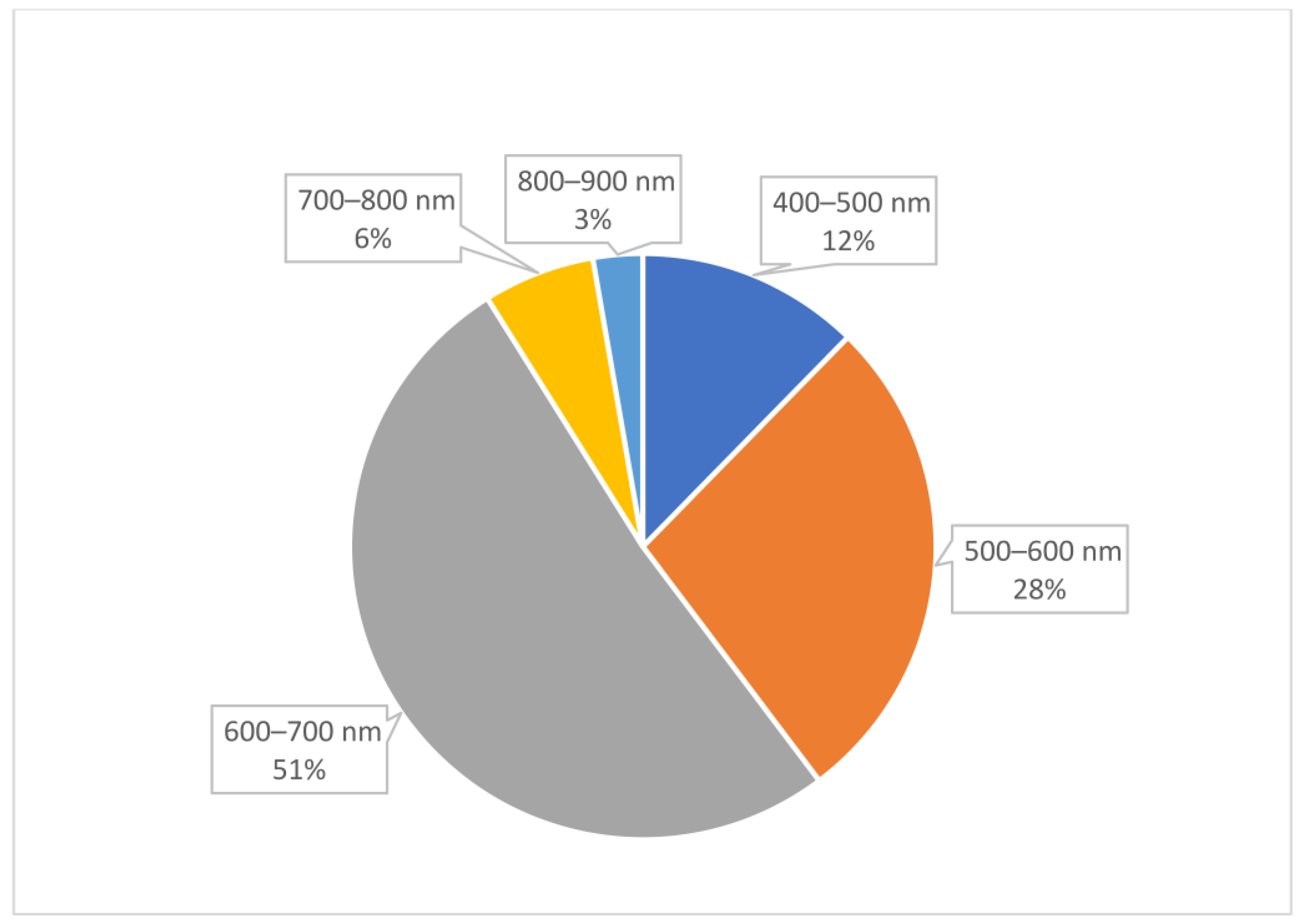
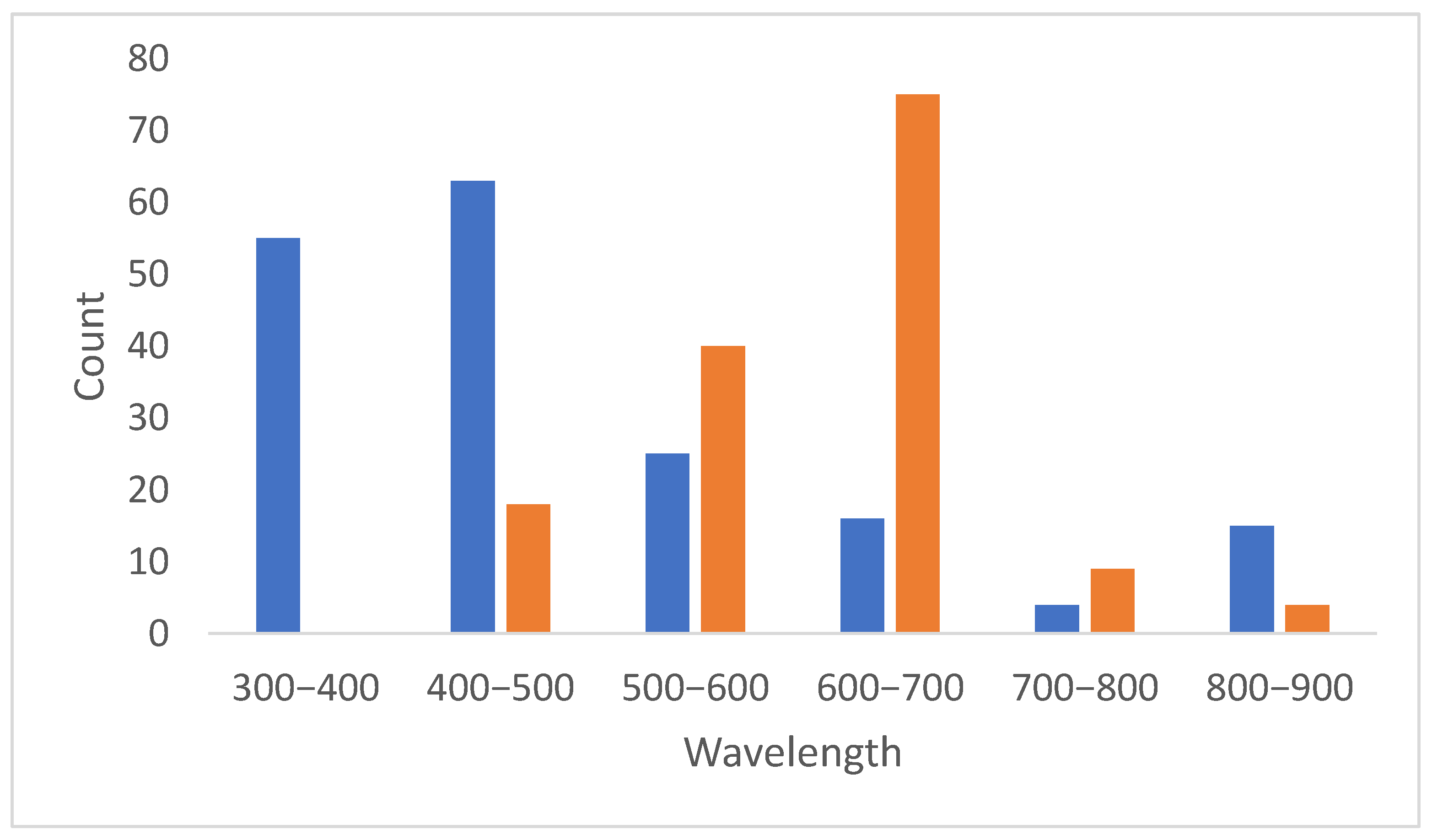
2. Results
Analysis of Conjugate Applications
3. Discussion
3.1. Database Overview
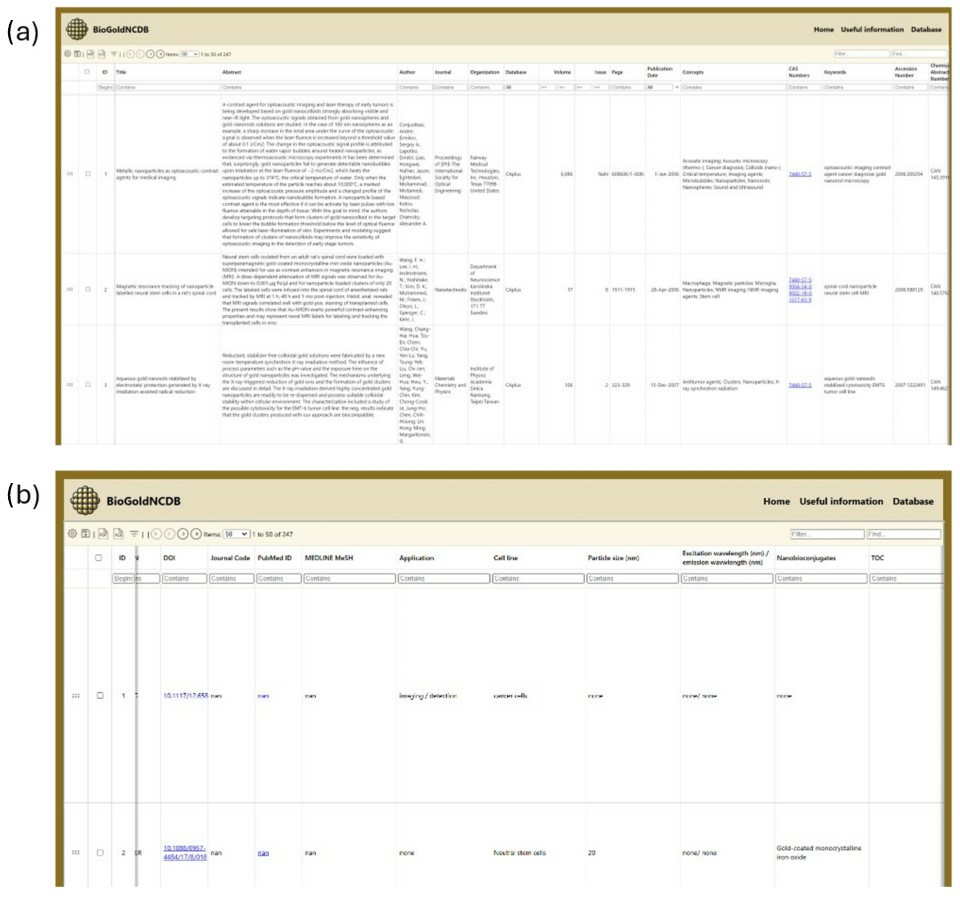
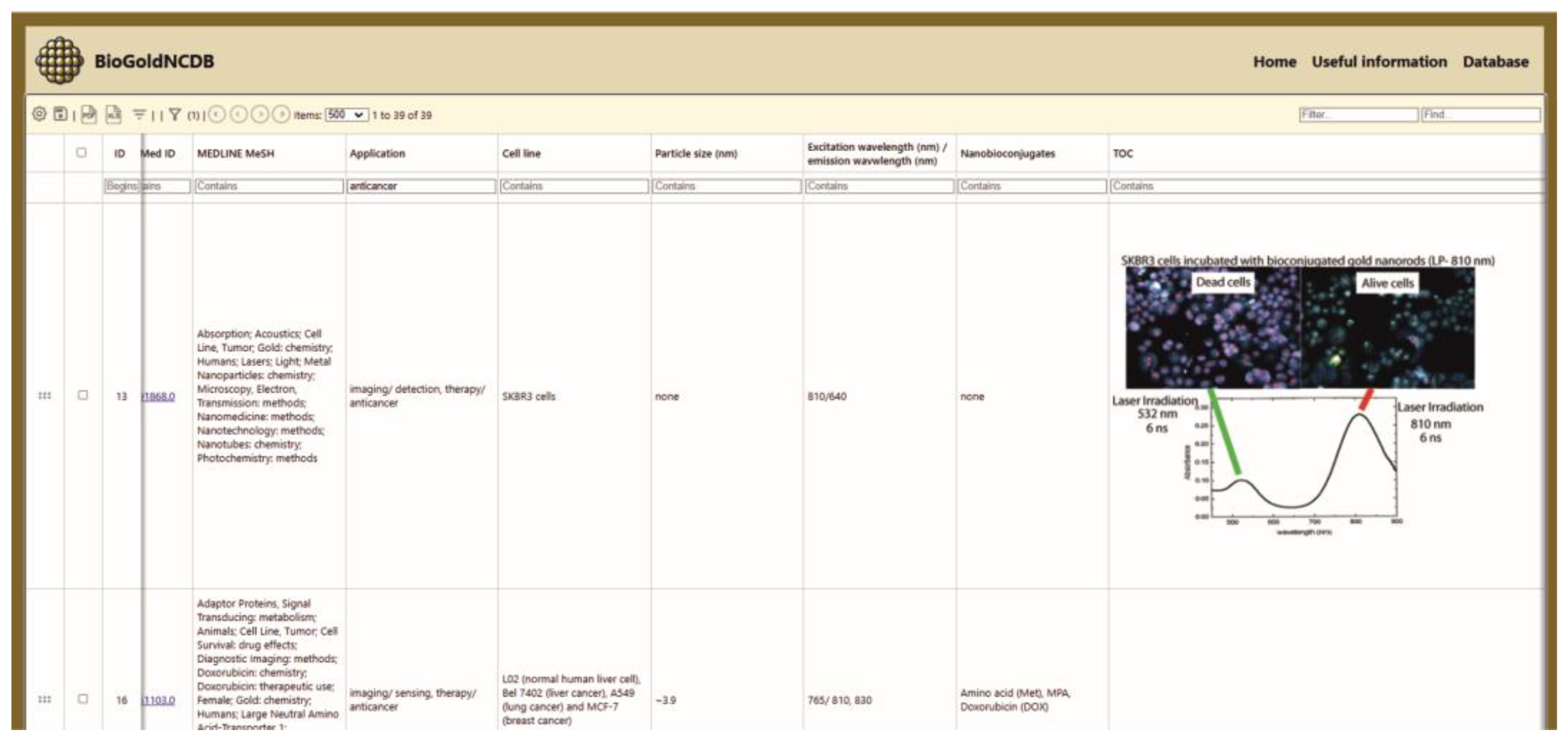
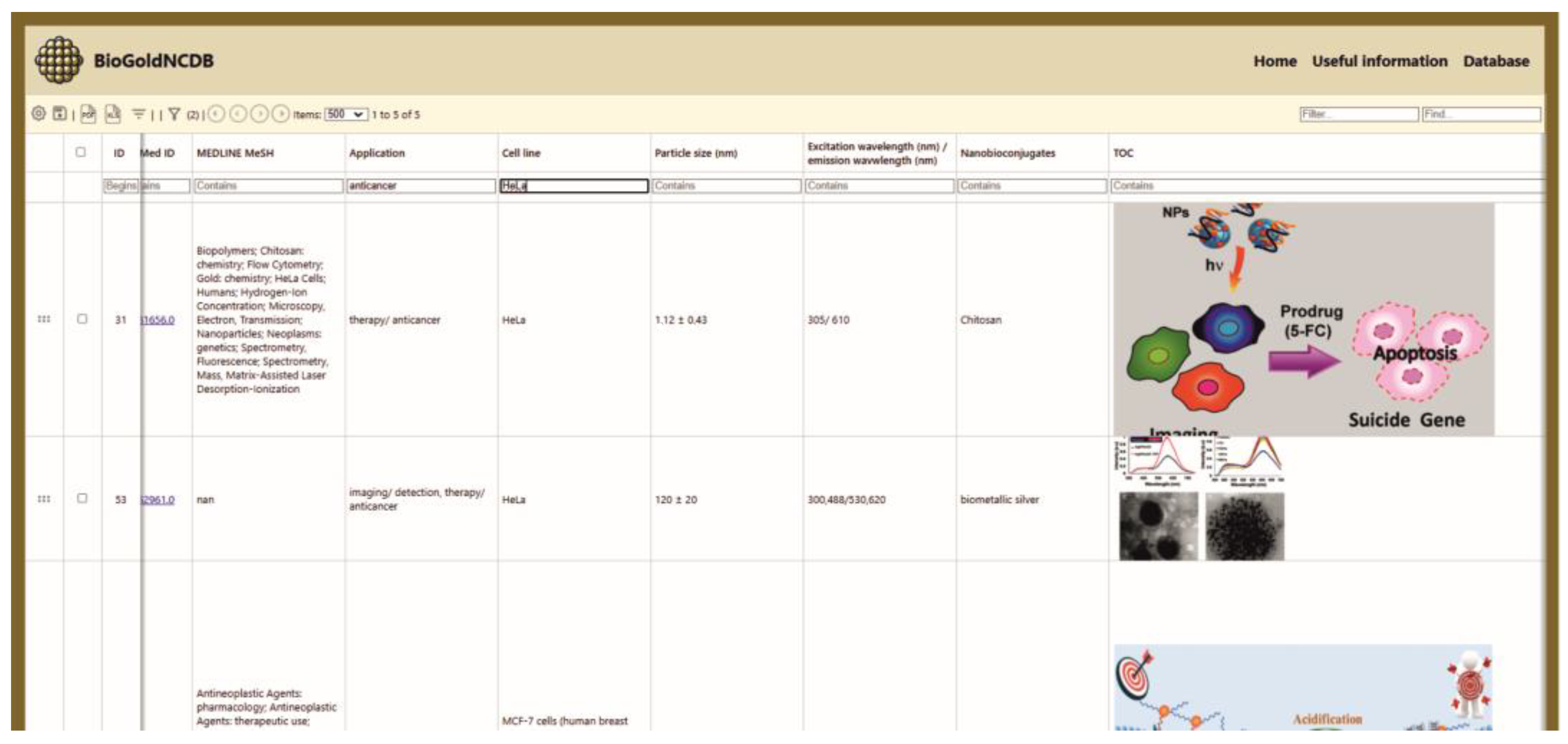
3.1.1. Database Content and User Interface Layout
3.1.2. Manually Curated Data
- Application: The biomedical field in which the AuNCs can be utilized.
- Cell line: The specific cell culture used for testing or biomedical investigation.
- Particle size: Includes both the core size (analyzed by TEM technique) and the total size of the nanobioconjugate, measured in nanometers (nm).
- Excitation/emission wavelength: The excitation wavelength refers to the specific wavelength of light that is absorbed by gold AuNCs to promote their electrons to an excited energy state. The emission wavelength is the wavelength of light emitted as the excited electrons return to their ground state.
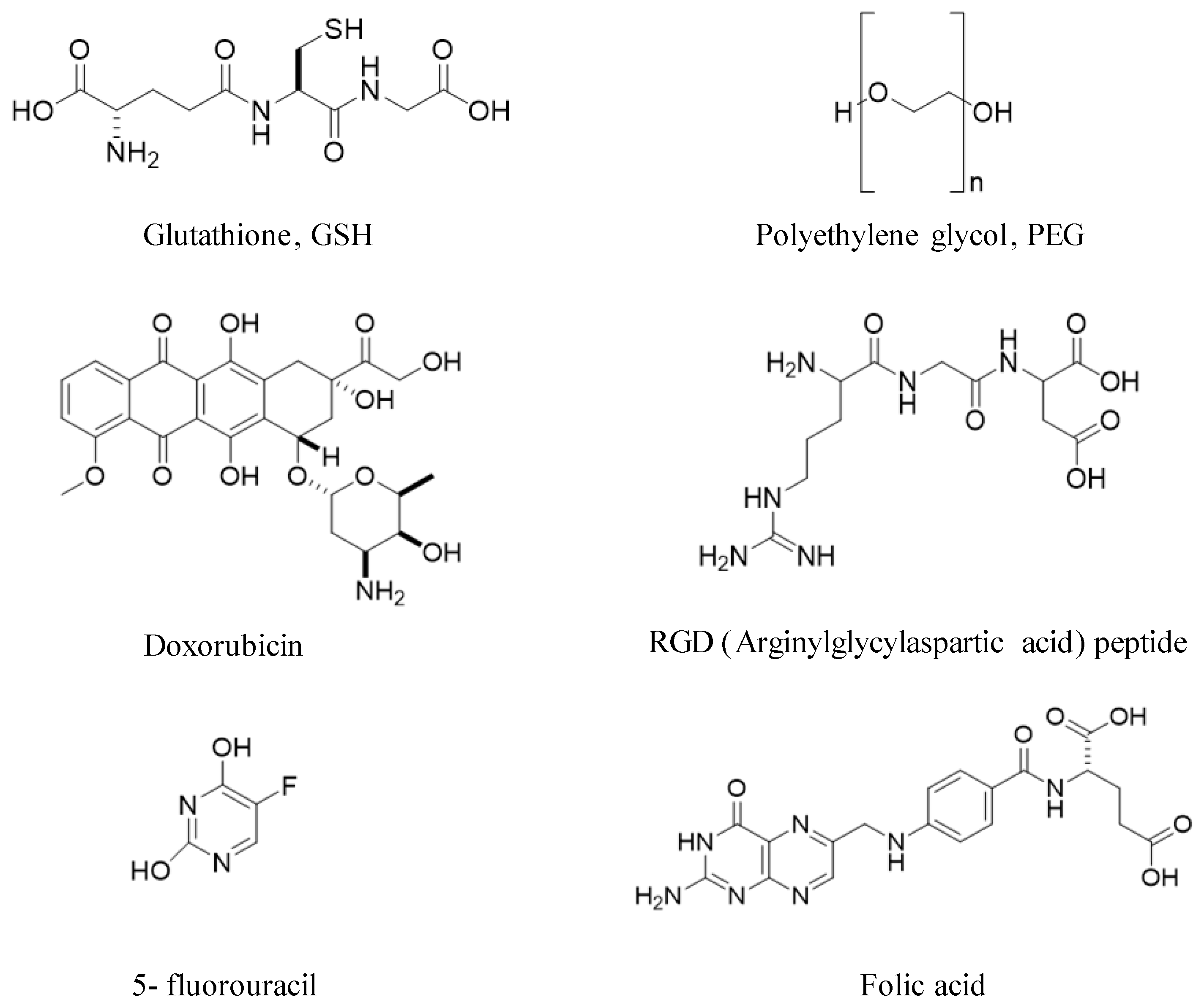
- Nanobioconjugates: Any molecule or material added to gold NCs as part of the functionalization process.
- TOC: Table of Contents figures.
3.1.3. Bibliographic Information
- ID: A unique identifier assigned to the article by the database or journal where it is published. (Usually not shown in the article itself).
- Title: The main heading of the article that concisely captures its content.
- Abstract: A brief summary of the article’s purpose, methodology, key findings, and conclusions.
- Author (s): The person (people) who conducted the research and wrote the article.
- Journal: The scientific publication where the article appears.
- Organization: The affiliation of the author (s), typically their university or research institution.
- Database: The online platform where the article can be accessed (e.g., PubMed Central, ScienceDirect).
- Volume: The volume number of the journal issue where the article is published.
- Issue: The specific issue number within the volume.
- Paper: (uncommon) Sometimes used interchangeably with article.
- Page numbers: The page range where the article appears within the journal issue.
- Publication date: The date the article was published in the journal.
3.1.4. Identification
- Concepts: The main topics or ideas explored in the article.
- CAS Numbers: Unique identifiers assigned by the Chemical Abstracts Service to chemical substances mentioned in the article.
- Keywords: A list of terms relevant to the article’s subject matter used for indexing and searchability.
- Accession Number: An identification number assigned to the article by a specific database.
- Chemical Abstracts Number (CAN): Unique identifier for the abstract text of the publication assigned by Chemical Abstracts Service.
- Section: The specific section of the journal where the article is published (e.g., research articles, reviews).
- Section Cross-Reference: A reference to a related section within the journal where additional relevant information might be found.
3.1.5. Identifiers
- CODEN: A unique six-character code assigned to a specific journal title.
- DOI (Digital Object Identifier): A unique identifier for an article that remains constant even if the location of the article changes online.
- Journal Code: An abbreviation used to identify a specific journal.
- PubMed ID: A unique identifier assigned to an article by the PubMed database.
- MEDLINE MeSH (Medical Subject Headings): A controlled vocabulary used by MEDLINE/PubMed to index articles in the life sciences.
3.2. Examples
- Free Text Search: A keyword-based free text search enables users to explore various database fields, including BioGoldNCDB ID, CAS number, PubMed ID, author name, article title, organization, journal name, and year of publication. More details are available at https://biogoldncdb.ladon.life/.
- Simple Search: Users can also search for specific entries in BioGoldNCDB based on application, cell line type, particle size, nanoconjugates, and excitation/emission wavelengths, etc.
- Multi-criteria search: Users can also search using multiple criteria in BioGoldNCDB.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection and Processing
4.2. Database Design and Implementation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AuNCsI | Gold nanoclusters |
| AuNPsJ | Gold nanoparticles |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
References
- Kumar, D.; Saini, N.; Jain, N.; Sareen, R.; Pandit, V. Gold nanoparticles: An era in bionanotechnology. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.C.W. Bionanotechnology Progress and Advances. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006, 12, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Moon, J.-Y. Introduction to Bionanotechnology; Springer: Singapore, 2020; ISBN 9789811512926. [Google Scholar]
- Jamkhande, P.G.; Ghule, N.W.; Bamer, A.H.; Kalaskar, M.G. Metal nanoparticles synthesis: An overview on methods of preparation, advantages and disadvantages, and applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materón, E.M.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Carr, O.; Joshi, N.; Picciani, P.H.S.; Dalmaschio, C.J.; Davis, F.; Shimizu, F.M. Magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications: A review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 6, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, S.M.; Hunter, A.C.; Murray, J.C. Nanomedicine: Current status and future prospects. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mody, V.; Siwale, R.; Singh, A.; Mody, H. Introduction to metallic nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnoudeh, A.J.; Hamad, I.; Abdo, R.W.; Qadumii, L.; Jaber, A.Y.; Surchi, H.S.; Alkelany, S.Z. Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of Metal Nanoparticles. In Biomaterials and Bionanotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 527–612. ISBN 978-0-12-814427-5. [Google Scholar]
- Chertok, B.; Moffat, B.A.; David, A.E.; Yu, F.; Bergemann, C.; Ross, B.D.; Yang, V.C. Iron oxide nanoparticles as a drug delivery vehicle for MRI monitored magnetic targeting of brain tumors. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.-H.; Qian, X.; Mao, H.; Wang, A.Y.; Chen, Z.G.; Nie, S.; Shin, D.M. Targeted magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for tumor imaging and therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Zafar, H.; Zia, M.; Ul Haq, I.; Phull, A.R.; Ali, J.S.; Hussain, A. Synthesis, characterization, applications, and challenges of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2016, 9, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiyeh, B.S.; Costagliola, M.; Hayek, S.N.; Dibo, S.A. Effect of silver on burn wound infection control and healing: Review of the literature. Burns 2007, 33, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansdown, A.B.G. Silver in Health Care: Antimicrobial Effects and Safety in Use. In Current Problems in Dermatology; Hipler, U.-C., Elsner, P., Eds.; KARGER: Basel, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 33, pp. 17–34. ISBN 978-3-8055-8121-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindran, A.; Chandran, P.; Khan, S.S. Biofunctionalized silver nanoparticles: Advances and prospects. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 105, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salata, O. Applications of nanoparticles in biology and medicine. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2004, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrone, E.; Sancey, L.; Dalonneau, F.; Ricciardi, L.; La Deda, M. Conjugated Human Serum Albumin/Gold-Silica Nanoparticles as Multifunctional Carrier of a Chemotherapeutic Drug. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Creran, B.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles: Preparation, properties, and applications in bionanotechnology. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mout, R.; Moyano, D.F.; Rana, S.; Rotello, V.M. Surface functionalization of nanoparticles for nanomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2539–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Mazouzi, Y.; Salmain, M.; Liedberg, B.; Boujday, S. Antibody-Gold Nanoparticle Bioconjugates for Biosensors: Synthesis, Characterization and Selected Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, Q. Protein-gold nanoparticle interactions and their possible impact on biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2017, 55, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, A.; Liu, Q.; Wen, G.; Jiang, Z. The surface-plasmon-resonance effect of nanogold/silver and its analytical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halawa, M.I.; Lai, J.; Xu, G. Gold nanoclusters: Synthetic strategies and recent advances in fluorescent sensing. Mater. Today Nano 2018, 3, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.A.; Hastman, D.A.; Medintz, I.L.; Oh, E. Understanding energy transfer with luminescent gold nanoclusters: A promising new transduction modality for biorelated applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 7907–7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A.P.; Birla, S.; Yadav, A.; Santos, C.A. Strategic role of selected noble metal nanoparticles in medicine. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 19, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R. The use of gold nanoparticles in diagnostics and detection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 2028–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztandera, K.; Gorzkiewicz, M.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B. Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Alkilany, A.M.; Huang, X.; Murphy, C.J.; El-Sayed, M.A. The golden age: Gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2740–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonia; Komal; Kukreti, S.; Kaushik, M. Gold nanoclusters: An ultrasmall platform for multifaceted applications. Talanta 2021, 234, 122623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yañez-Aulestia, A.; Gupta, N.K.; Hernández, M.; Osorio-Toribio, G.; Sánchez-González, E.; Guzmán-Vargas, A.; Rivera, J.L.; Ibarra, I.A.; Lima, E. Gold nanoparticles: Current and upcoming biomedical applications in sensing, drug, and gene delivery. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 10886–10895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, R.; Funston, A.M.; Mulvaney, P.; Murray, R.W. Gold Nanoparticles: Past, Present, and Future. Langmuir 2009, 25, 13840–13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancey, L.; Motto-Ros, V.; Busser, B. Preclinical Evaluation of Nanoparticle Behavior in Biological Tissues by LIBS. In Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy in Biological, Forensic and Materials Sciences; Galbács, G., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 191–198. ISBN 978-3-031-85974-8. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, H.; Zhu, M.; Wu, Z.; Jin, R. Quantum Sized Gold Nanoclusters with Atomic Precision. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengani, M.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Rajeswari, V.D. Recent trends and methodologies in gold nanoparticle synthesis—A prospective review on drug delivery aspect. OpenNano 2017, 2, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wei, Q.-Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.-C.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, Z. Role of thiol-containing polyethylene glycol (thiol-PEG) in the modification process of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs): Stabilizer or coagulant? J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 404, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sham, T.K.; Kim, P.-S.G.; Zhang, P. Electronic structure of molecular-capped gold nanoparticles from X-ray spectroscopy studies: Implications for coulomb blockade, luminescence and non-Fermi behavior. Solid State Commun. 2006, 138, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, Z.; Mousavi, M.-M.; Mahmoudpour, M. Surface functionalized gold nanoclusters based on optical biosensors for detecting pesticide residues in agricultural foods: A critical review. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 111988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez-Mosqueda, R.; Malola, S.; Häkkinen, H. Ab initio molecular dynamics studies of Au38(SR)24 isomers under heating. Eur. Phys. J. D 2019, 73, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Kong, J.; Li, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, M. Coherent vibrational dynamics of Au144(SR)60 nanoclusters. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 8124–8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez-Mosqueda, R.; Mpourmpakis, G. Elucidating the optical spectra of [Au25(SR)18]q nanoclusters. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 22272–22282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maysinger, D.; Maršić, Ž.S.; Gran, E.R.; Shobo, A.; Macairan, J.-R.; Zhang, I.; Bakulić, M.P.; Antoine, R.; Multhaup, G.; Bonačić-Kouteckỳ, V. Insights into the Impact of Gold Nanoclusters Au10 SG10 on Human Microglia. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Shu, T.; Su, L.; Zhang, X. Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters for Biosensor and Bioimaging Application. Crystals 2020, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maysinger, D.; Gran, E.R.; Bertorelle, F.; Fakhouri, H.; Antoine, R.; Kaul, E.S.; Samhadaneh, D.M.; Stochaj, U. Gold nanoclusters elicit homeostatic perturbations in glioblastoma cells and adaptive changes of lysosomes. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1633–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-Y.; Wang, C.-W.; Yuan, Z.; Chang, H.-T. Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters: Recent Advances in Sensing and Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Nano-Gold as Artificial Enzymes: Hidden Talents. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4200–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, D.; Su, J.; Weber, J.K.; Gao, X.; Zhou, R.; Li, J. A Peptide-Coated Gold Nanocluster Exhibits Unique Behavior in Protein Activity Inhibition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8412–8418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, I.; Maysinger, D.; Beus, M.; Mravak, A.; Yu, Z.; Bakulić, M.P.; Dion, P.A.; Rouleau, G.A.; Bonačić-Koutecký, V.; Antoine, R.; et al. Gold nanoclusters Au25 AcCys18 normalize intracellular ROS without increasing cytoplasmic alarmin acHMGB1 abundance in human microglia and neurons. Nanoscale 2025, 17, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Setyawati, M.I.; Leong, D.T.; Xie, J. Antimicrobial Gold Nanoclusters. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 6904–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, G.R.; Lin, Z.-C.; Chiu, T.-S.; Alalaiwe, A.; Liao, C.-C.; Fang, J.-Y. Chemo-photothermal therapy of chitosan/gold nanorod clusters for antibacterial treatment against the infection of planktonic and biofilm MRSA. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268, 131673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G. Sunlight-Mediated Antibacterial Activity Enhancement of Gold Nanoclusters and Graphene Co-decorated Titanium Dioxide Nanocomposites. J. Clust. Sci. 2019, 30, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yang, D.; Zhao, C.; Song, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shen, J. Protein–Gold Hybrid Nanocubes for Cell Imaging and Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4713–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhouri, H.; Bakulić, M.P.; Zhang, I.; Yuan, H.; Bain, D.; Rondepierre, F.; Brevet, P.-F.; Maršić, Ž.S.; Antoine, R.; Bonačić-Koutecký, V.; et al. Ligand impact on reactive oxygen species generation of Au10 and Au25 nanoclusters upon one- and two-photon excitation. Commun. Chem. 2023, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Li, B.; Cai, S.; Wang, P.; Peng, S.; Sheng, Y.; He, Y.; Gu, Y.; Chen, H. Dual targeting luminescent gold nanoclusters for tumor imaging and deep tissue therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 100, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Li, M.; Auguste, D.T. Pattern-based sensing of triple negative breast cancer cells with dual-ligand cofunctionalized gold nanoclusters. Biomaterials 2017, 116, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, R.K.; Tavakoli, M.B.; Maghsoudinia, F.; Motaghi, H.; Hejazi, S.H.; Mehrgardi, M.A. Trastuzumab and folic acid functionalized gold nanoclusters as a dual-targeted radiosensitizer for megavoltage radiation therapy of human breast cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 153, 105487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Yuan, H.; Verma, R.; Mehla, N.; Hemant, H.; Sagar, P.; Comby-Zerbino, C.; Russier-Antoine, I.; Moulin, C.; Brevet, P.; et al. Intrinsically Pro-Apoptotic Gold Nanoclusters for Optical Tracing and Inhibition of Solid Tumors. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2405005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Wang, X.; Zeng, S.; Ramamurthy, G.; Burda, C.; Basilion, J.P. Targeted Gold Nanocluster-Enhanced Radiotherapy of Prostate Cancer. Small 2019, 15, 1900968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, N.M.C.; Clainche, T.L.; Bulin, A.; Leo, S.; Kadri, M.; Abdelhamid, A.G.A.; Pujol-Solé, N.; Obaid, G.; Hograindleur, M.; Gardette, V.; et al. Engineering Radiocatalytic Nanoliposomes with Hydrophobic Gold Nanoclusters for Radiotherapy Enhancement. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2404605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shi, D.; Guo, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X. Radiofrequency-Activated Pyroptosis of Bi-Valent Gold Nanocluster for Cancer Immunotherapy. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Q. TiC2: A new two-dimensional sheet beyond MXenes. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Feng, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X. Precise therapeutic effect of self-assembling gold nanocluster–PTEN complexes on an orthotropic model of liver cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasulu, Y.G.; Mozhi, A.; Goswami, N.; Yao, Q.; Xie, J. Traceable Nanocluster–Prodrug Conjugate for Chemo-photodynamic Combinatorial Therapy of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 3232–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerón, M.R.; Izquierdo, M.; Alegret, N.; Valdez, J.A.; Rodríguez-Fortea, A.; Olmstead, M.M.; Balch, A.L.; Poblet, J.M.; Echegoyen, L. Reactivity differences of Sc3N@C2n (2n = 68 and 80). Synthesis of the first methanofullerene derivatives of Sc3N@D5h-C80. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; He, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Xu, H.; Nau, W.M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, F. Active tumor-targeting luminescent gold clusters with efficient urinary excretion. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 9232–9235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shome, R.; Ghosh, S.S. Transferrin Coated d-penicillamine–Au-Cu Nanocluster PLGA Nanocomposite Reverses Hypoxia-Induced EMT and MDR of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 5033–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.-C.; Wen, X.; Johnson, C.A.; Shae, D.; Ayala, O.D.; Webb, J.A.; Lin, E.C.; DeLapp, R.C.; Boyd, K.L.; Richmond, A.; et al. Multimodal Multiplexed Immunoimaging with Nanostars to Detect Multiple Immunomarkers and Monitor Response to Immunotherapies. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Next.js/React. Official Documentation. Available online: https://react.dev/ (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Node.js. Official Documentation. Available online: https://nodejs.org/en/docs (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- MySQL. Official Documentation. Available online: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/ (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- EZGrid React DataGrid Component. Available online: https://reactdatagrid.com/ (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- DigitalOcean Cloud Hosting. Official Website. Available online: https://www.digitalocean.com/ (accessed on 5 August 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erdei, E.; Mándoki, A.; Deák, A.; Balogh, B.; Molnár, L.; Mándity, I.M. BioGoldNCDB: A Database of Gold Nanoclusters and Related Nanoparticles with Biomedical Activity. Molecules 2025, 30, 3310. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153310
Erdei E, Mándoki A, Deák A, Balogh B, Molnár L, Mándity IM. BioGoldNCDB: A Database of Gold Nanoclusters and Related Nanoparticles with Biomedical Activity. Molecules. 2025; 30(15):3310. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153310
Chicago/Turabian StyleErdei, Eszter, András Mándoki, Andrea Deák, Balázs Balogh, László Molnár, and István M. Mándity. 2025. "BioGoldNCDB: A Database of Gold Nanoclusters and Related Nanoparticles with Biomedical Activity" Molecules 30, no. 15: 3310. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153310
APA StyleErdei, E., Mándoki, A., Deák, A., Balogh, B., Molnár, L., & Mándity, I. M. (2025). BioGoldNCDB: A Database of Gold Nanoclusters and Related Nanoparticles with Biomedical Activity. Molecules, 30(15), 3310. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153310





