Preparation of Comb-Shaped Polyether with PDMS and PEG Side Chains and Its Application in Polymer Electrolytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
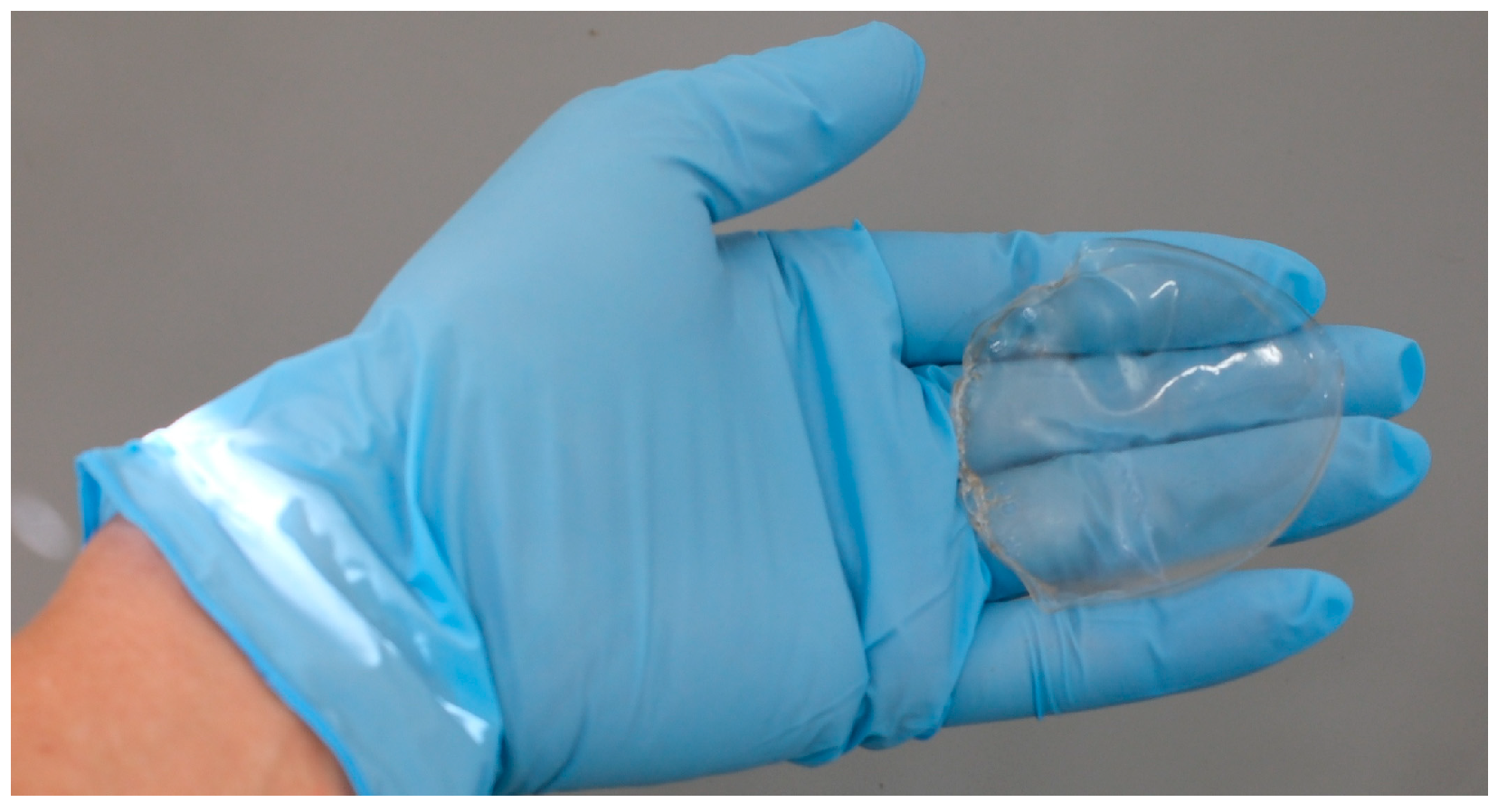
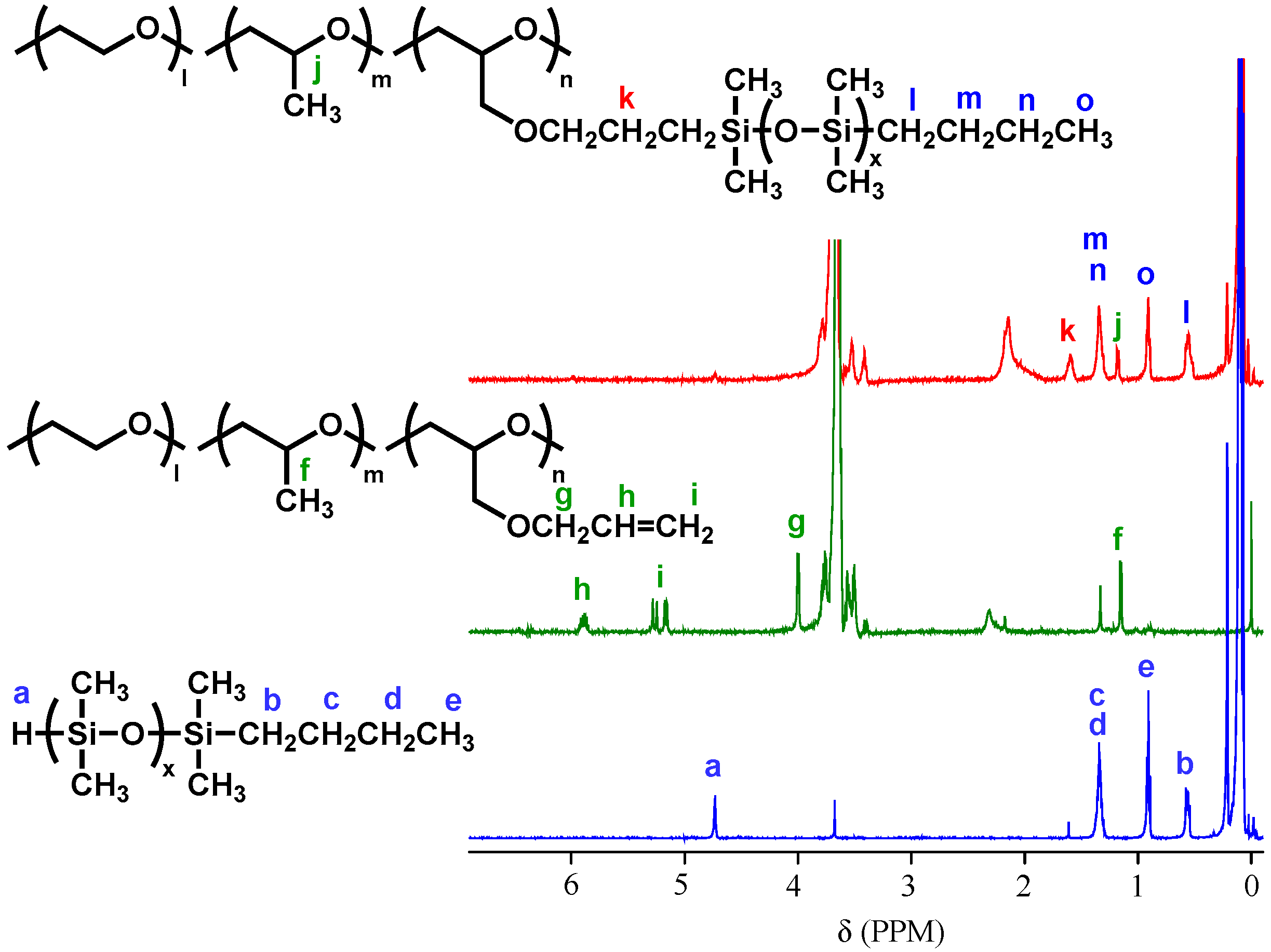
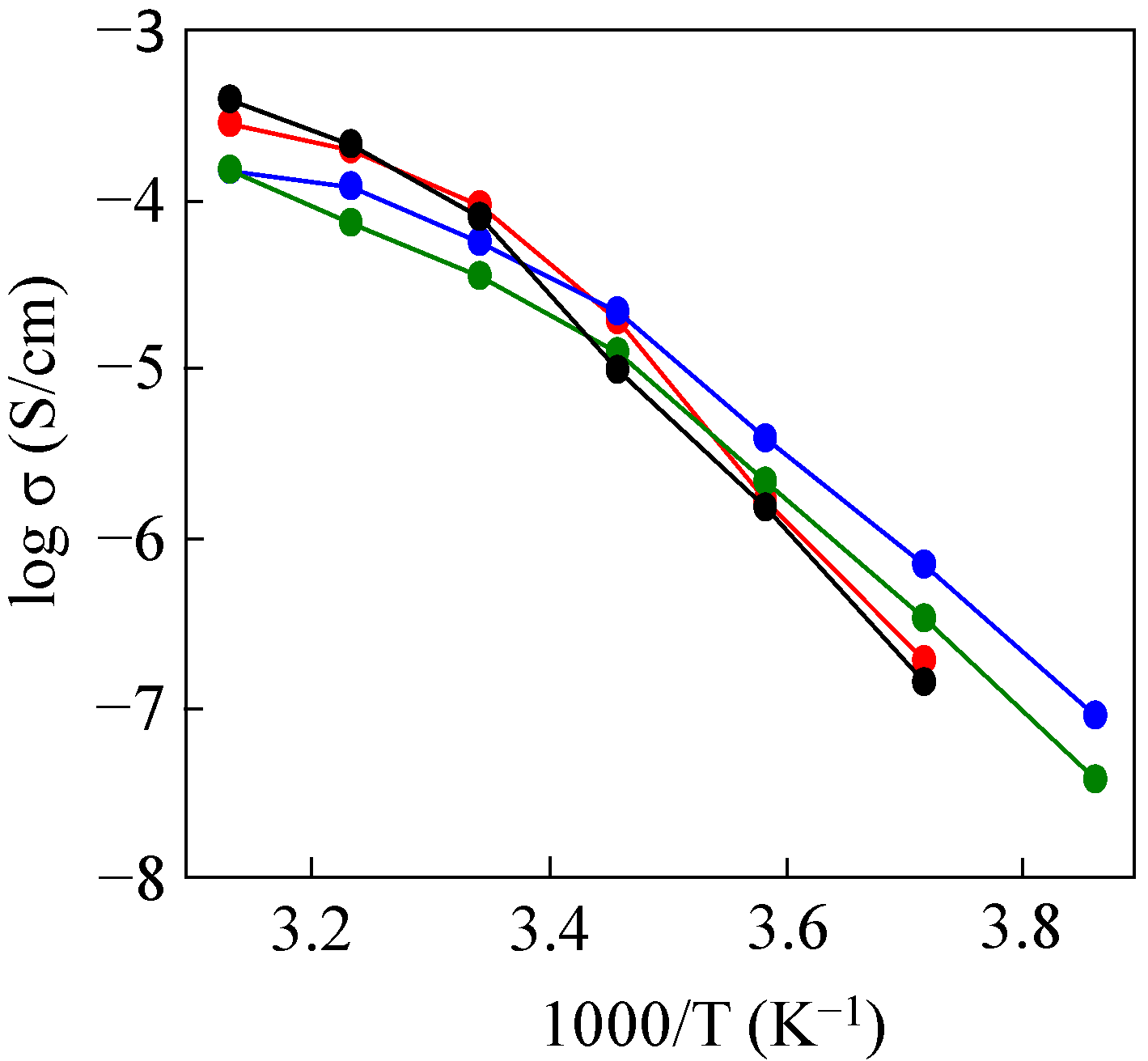
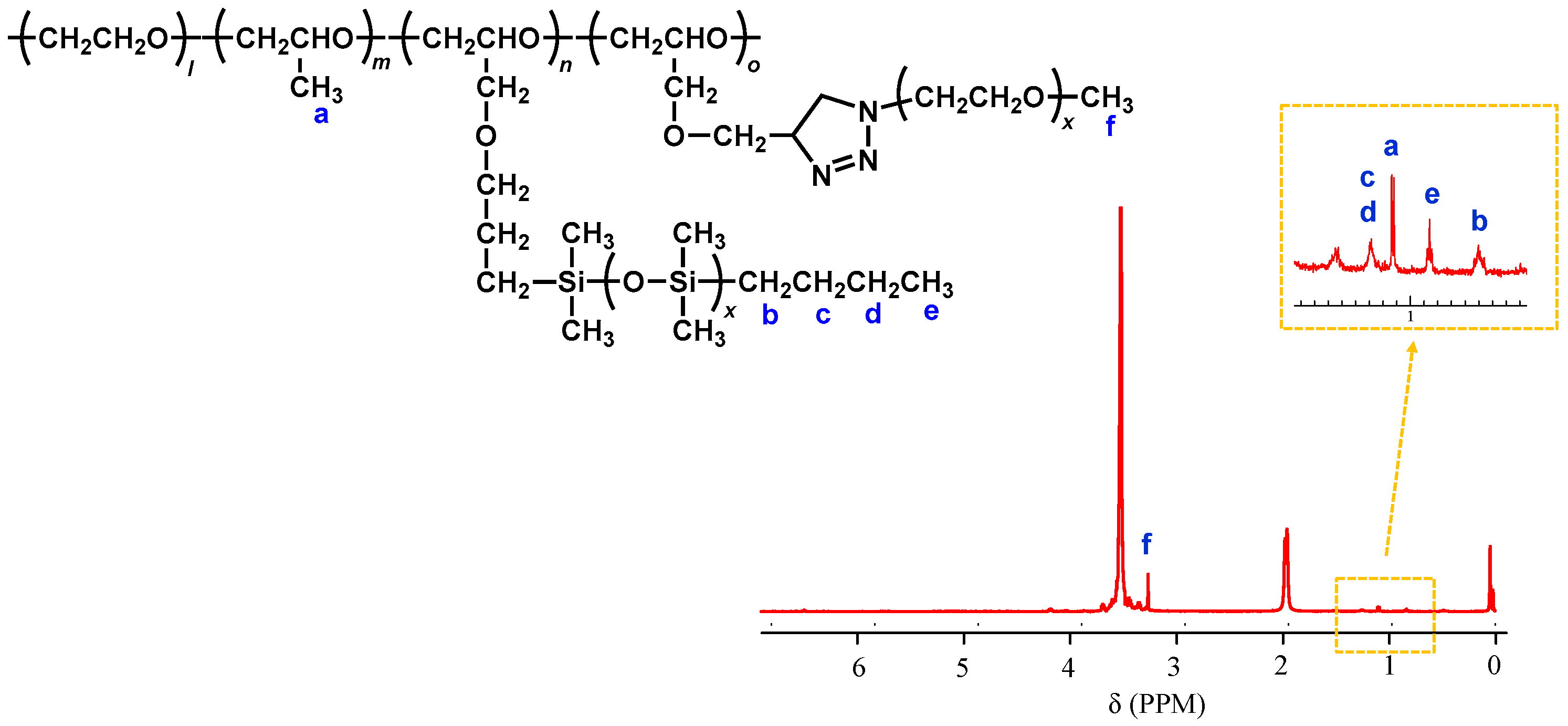
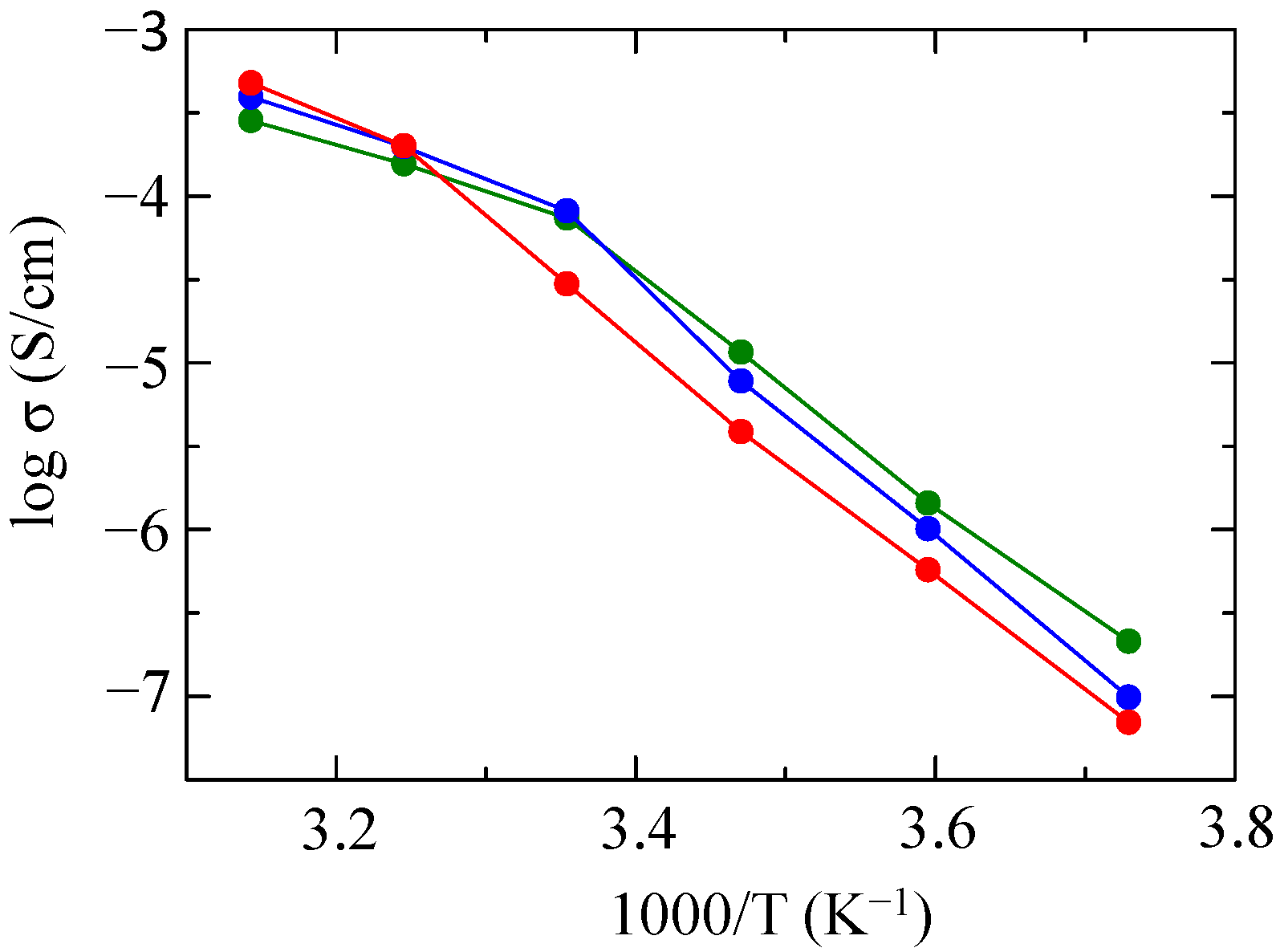
2.1. Preparation and Properties of PDMS-g-P(EO/PO/AGE)
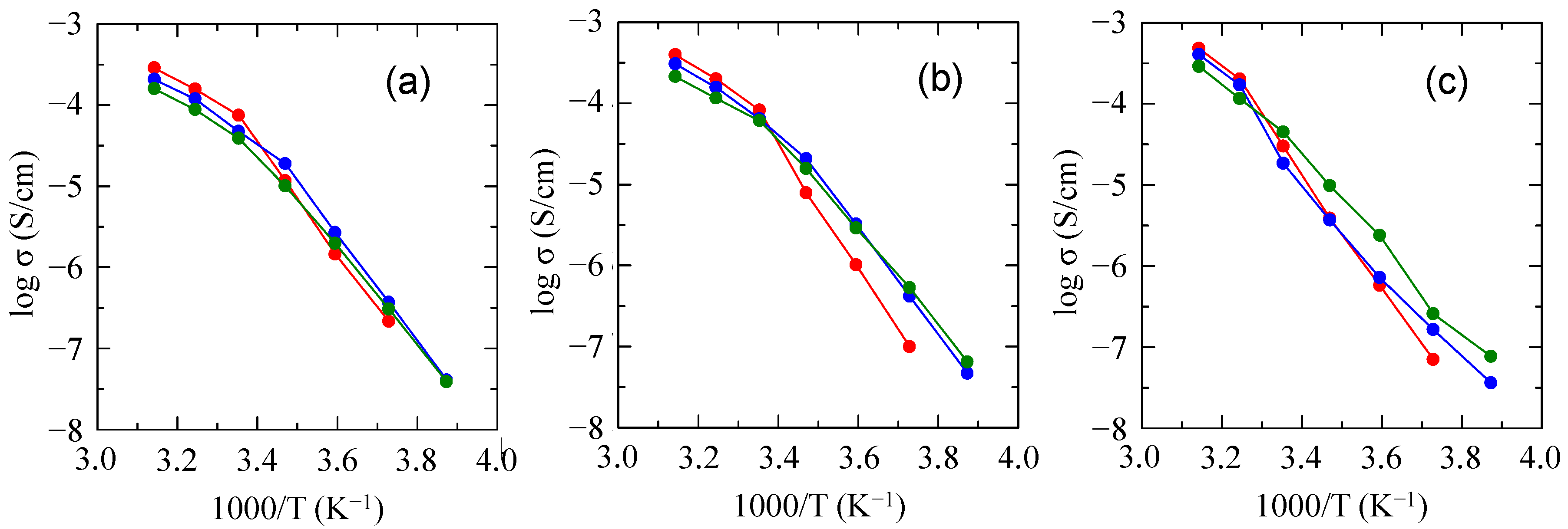
2.2. Preparation of PDMS & mPEG-g-P(EO/PO/AGE)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Preparation of α-p-Toluenesulfonyloxy, ω-Methoxy Heterodifunctional PEG
3.3. Preparation of α-Azide, ω-Methoxy Heterodifunctional PEG (mPEG-N3)
3.4. Preparation of PDMS-g-P(EO/PO/AGE)
3.5. Preparation of PDMS & PEG-g-(EO/PO/AGE)
3.6. Preparation of Solid Polymer Electrolyte
3.7. Ionic Conductivity Measurement
3.8. Instrumentation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PEO | Polyethylene oxide |
| SPE | Solid polymer electrolyte |
| EO | Ethylene oxide |
| PO | Propylene oxide |
| AGE | Allyl glycidyl ether |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| mPEG | Polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether |
| LiTFSI | Lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide |
References
- Zhou, J.; Ma, B.; Wang, Q.; Su, L.; Yang, K.; Song, X.; Dou, X.; Wang, M.; Shangguan, X.; Li, F. Anion-regulated weakly solvation sulfolane-based electrolyte towards high-voltage lithium metal batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 504, 158857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Wang, Q.; Su, L.; Liu, G.; Song, Y.; Shangguan, X.; Li, F. Inorganic/organic composite fluorinated interphase layers for stabilizing ether-based electrolye in high-voltage lithium metal batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.N. Electrical conductivity in ionic complexes of poly(ethylene oxide). Br. Polym. J. 1975, 7, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, M.B.; Chabagno, J.M.; Duclot, M. Polyethers as Solid Electrolytes Fast Ion Transport in Solids. In Electrodes and Electrolytes; Vashitshta, P., Mundy, J.N., Shenoy, G.K., Eds.; Holland Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979; pp. 131–148. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto, A.; Watanabe, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Kojiya, S. High ionic conductivity of new polymer electrolytes based on high molecular weight polyether comb polymers. Electrochim. Acta 1998, 43, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, A.; Sharma, A.L. Insights into the use of polyethylene oxide in energy storage/conversion devices: A critical review. Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 443002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yan, X.; Ma, Z.; Mei, P.; Xiao, W.; You, G.; Zhang, Y. Development of the PEO Based Solid Polymer Electrolytes for All-Solid State Lithium Ion Batteries. Polymers 2018, 10, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindemark, J.; Lacey, M.J.; Bowden, T.; Brandell, D. Beyond PEO—Alternative host materials for Li+-conducting solid polymer electrolytes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 81, 114–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Shanmukaraj, D.; Tkacheva, A.; Armand, M.; Wang, G. Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium-Based Batteries: Advances and Prospects. Chem 2019, 5, 2326–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.Q.; Lv, F.; Xu, N.; Wu, M.T.; Liu, J.; Gao, X.P. Polyethylene Oxide-Based Solid-State Composite Polymer Electrolytes for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 4581–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.V. Polymer electrolytes—The early days. Electrochim. Acta 1998, 43, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Park, J.K.; Kim, W.J. Preparation and ion conductivities of the plasticized polymer electrolytes based on the poly(acrylonitrile- co-lithium methacrylate). J. Polym. Sci. Part B 1999, 37, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupuano, F.; Croce, F.; Scrosati, B. Composite Polymer Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1991, 138, 1918–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, F.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Persi, L.; Scrosati, B. Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Nature 1998, 394, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florjannczyk, Z.; Wieczorek, W. Highly Conducting Solid Electrolytes Based on Polymer Blends. Solid State Phenom. 1994, 39–40, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Hirata, N.; Wen, Z.; Kubo, M.; Yamamoto, O. Polymer electrolytes based on hyperbranched polymers. J. Power Sources 2001, 97–98, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Noba, M.; Uno, T.; Itoh, T.; Kubo, M. Preparation of polypseudorotaxane composed of linear and cyclic polyethylene oxides and its application to solid polymer electrolyte. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 1982–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shen, Z. Ionic Conductivity of Ethylene Oxide and Propylene Oxide Copolymer Complexes with Sodium Thiocyanate. Polym. J. 1990, 22, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Trapa, P.E.; Acar, M.H.; Sadway, D.R.; Mayes, A.M. Synthesis and characterization of single-ion graft copolymer electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, Y.W.; Min, B.R.; Kim, J.H. Nanostructure, Interactions, and Conductivities of Polymer Electrolytes Comprising Silver Salt and Microphase-Separated Graft Copolymer. J. Polym. Sci. 2007, 45, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Thakur, A.K.; Kumar, K. Exploring low temperature Li+ ion conducting plastic battery electrolyte. Ionics 2013, 19, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.N.; Versek, C.; Touminen, M.; Tew, G.N. Tunable Networks from Thiolene Chemistry for Lithium Ion Conduction. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, D.; Torneiro, M.; Lazzari, M. Some Guidelines for the Synthesis and Melting Characterization of Azide Poly(ethylene glycol) Derivatives. Polymers 2020, 12, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santra, S.; Bean, R.; Heckert, B.; Shaw, Z.; Jain, V.; Shrestha, L.; Narayanam, R.; Austin, Q. Alkene-azide chemistry: A facile, one-step, solvent- and catalyst-free approach for developing new functional monomers and polymers. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 3723–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, J.E.; Sullivan, B.; Vojkovsky, T.; Sill, K.N. Synthesis and facile end-group quantification of functionalized PEG azides. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 54, 2888–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

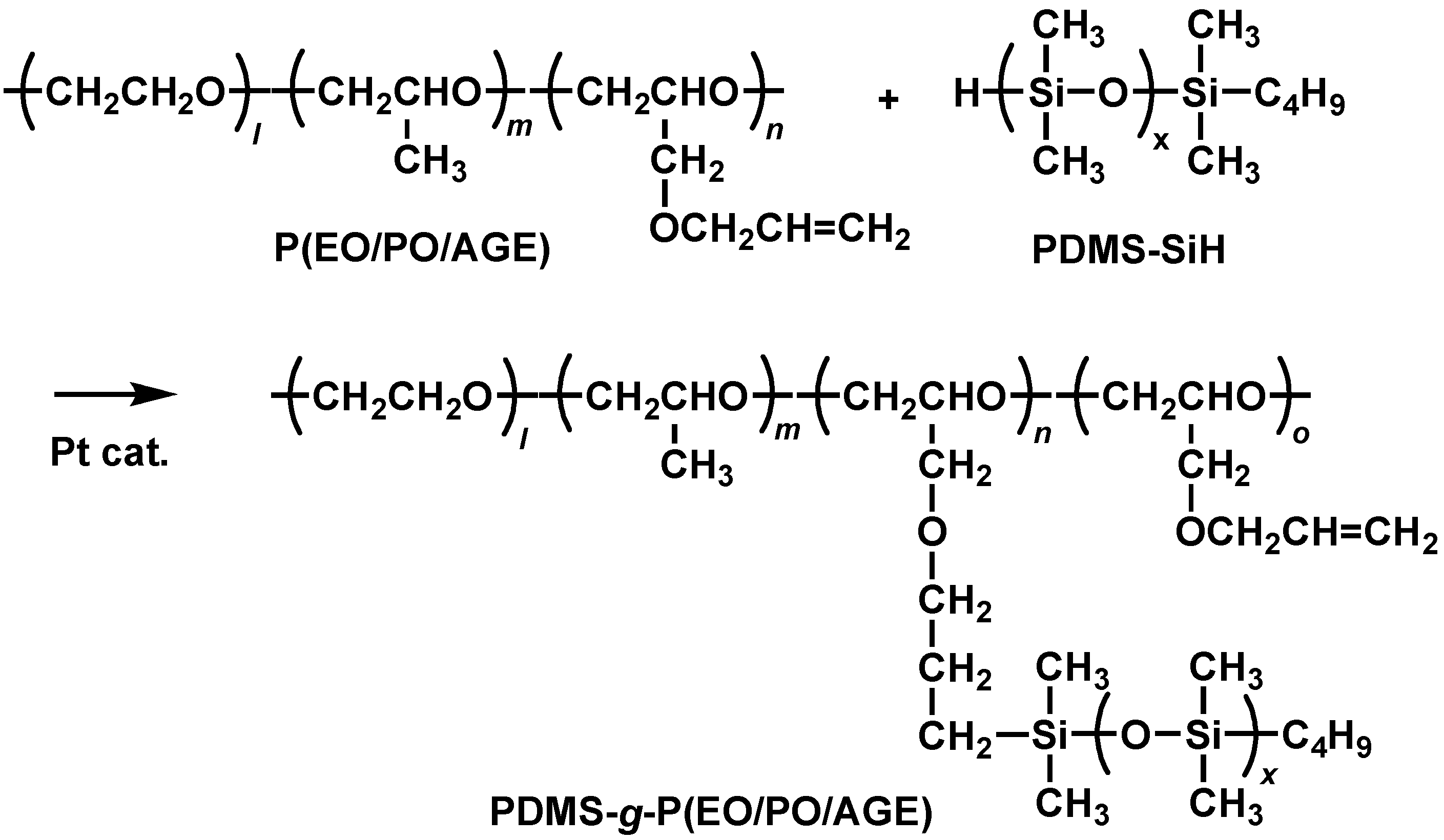

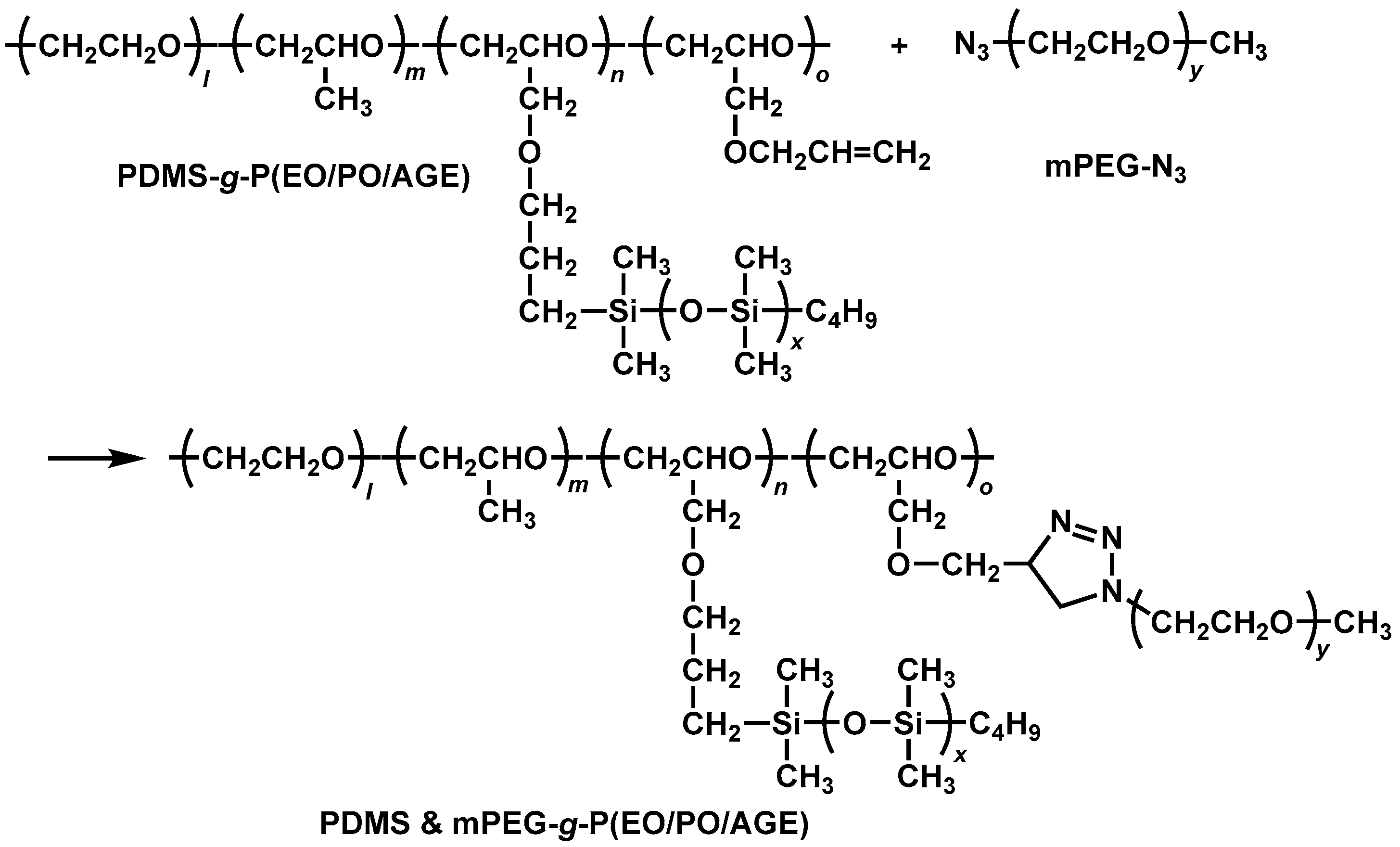



| Polymer | PDMS Content (wt%) | Tc (°C) | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25%PDMS & 75%mPEG1K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 9 | 33 | 50 |
| 25%PDMS & 75%mPEG2K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 7 | 34 | 59 |
| 25%PDMS & 75%mPEG4K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 5 | 40 | 59 |
| 50%PDMS & 50%mPEG1K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 18 | 32 | 51 |
| 50%PDMS & 50%mPEG2K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 15 | 33 | 53 |
| 50%PDMS & 50%mPEG4K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 11 | 36 | 58 |
| 75%PDMS & 25%mPEG1K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 27 | 31 | 49 |
| 75%PDMS & 25%mPEG2K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 25 | 32 | 51 |
| 75%PDMS & 25%mPEG4K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 21 | 34 | 53 |
| Polymer | P(EO/PO/AGE) (g) | PDMS-SiH (g) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25%PDMS-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 6.0 | 0.7 | 93 |
| 50%PDMS-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 6.0 | 1.4 | 95 |
| 75%PDMS-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 6.0 | 2.1 | 96 |
| Polymer | PDMS-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) (g) | mPEG-N3 (g) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25% PDMS & 75% mPEG1K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 25% PDMS-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) (1.0) | mPEG1K-N3 (0.40) | 85 |
| 25% PDMS & 75% mPEG2K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | mPEG2K-N3 (0.80) | 83 | |
| 25% PDMS & 75% mPEG4K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | mPEG4K-N3 (1.6) | 82 | |
| 50% PDMS & 50% mPEG1K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 50% PDMS-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) (1.0) | mPEG1K-N3 (0.24) | 51 |
| 50% PDMS & 50% mPEG2K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | mPEG2K-N3 (0.48) | 53 | |
| 50% PDMS & 50% mPEG4K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | mPEG4K-N3 (0.96) | 58 | |
| 75% PDMS & 25% mPEG1K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | 75% PDMS-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) (1.0) | mPEG1K-N3 (0.11) | 80 |
| 75% PDMS & 25% mPEG2K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | mPEG2K-N3 (0.22) | 82 | |
| 75% PDMS & 25% mPEG4K-g-P(EO/PO/AGE) | mPEG4K-N3 (0.44) | 94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Enoki, T.; Kosono, R.; Zainuddin, N.A.S.; Uno, T.; Kubo, M. Preparation of Comb-Shaped Polyether with PDMS and PEG Side Chains and Its Application in Polymer Electrolytes. Molecules 2025, 30, 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153201
Enoki T, Kosono R, Zainuddin NAS, Uno T, Kubo M. Preparation of Comb-Shaped Polyether with PDMS and PEG Side Chains and Its Application in Polymer Electrolytes. Molecules. 2025; 30(15):3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153201
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnoki, Tomoya, Ryuta Kosono, Nurul Amira Shazwani Zainuddin, Takahiro Uno, and Masataka Kubo. 2025. "Preparation of Comb-Shaped Polyether with PDMS and PEG Side Chains and Its Application in Polymer Electrolytes" Molecules 30, no. 15: 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153201
APA StyleEnoki, T., Kosono, R., Zainuddin, N. A. S., Uno, T., & Kubo, M. (2025). Preparation of Comb-Shaped Polyether with PDMS and PEG Side Chains and Its Application in Polymer Electrolytes. Molecules, 30(15), 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153201





