Efficient Tetracycline Hydrochloride Degradation by Urchin-Like Structured MoS2@CoFe2O4 Derived from Steel Pickling Sludge via Peroxymonosulfate Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
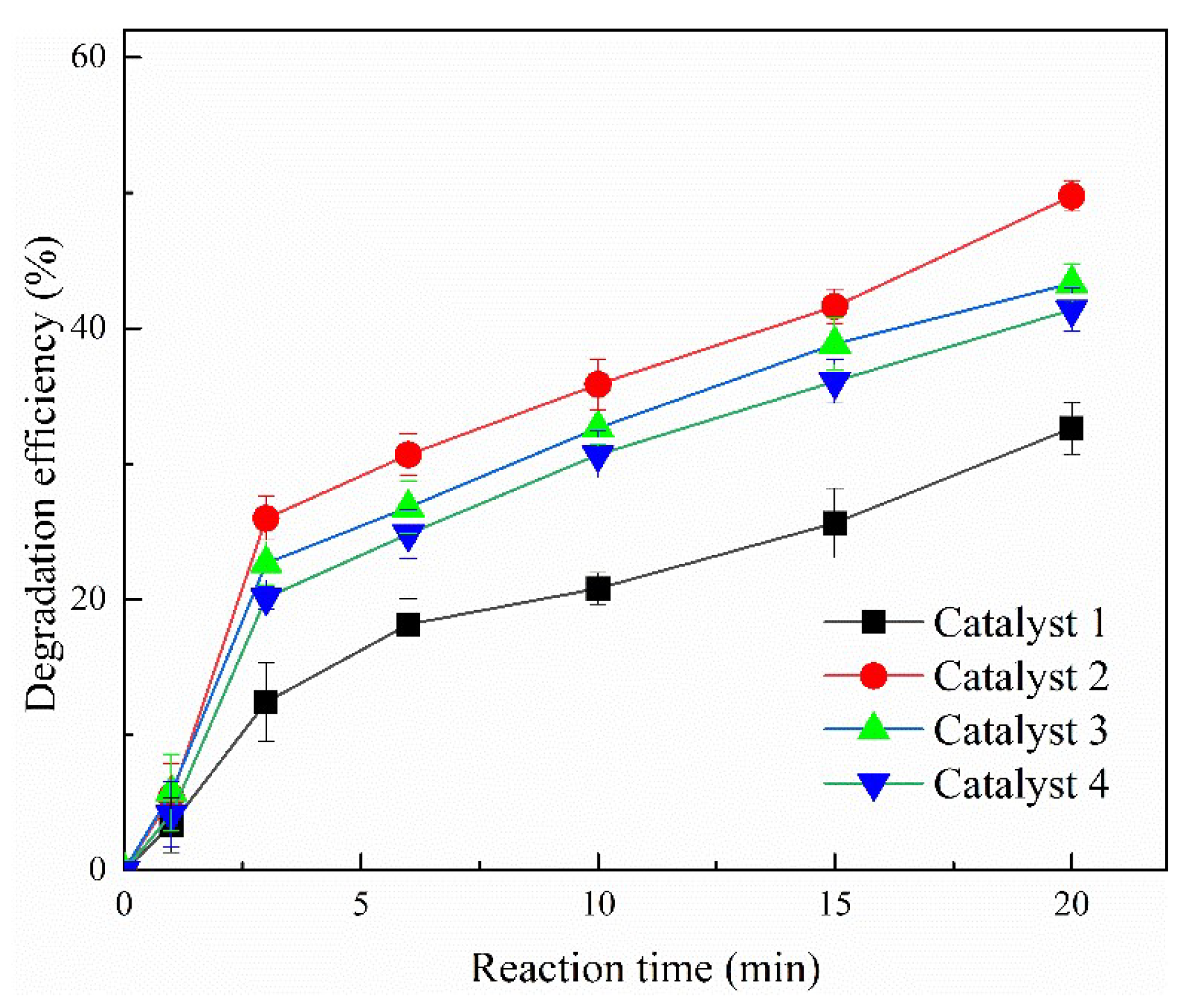
2.1. Comparison of Degradation Efficiencies by Different Catalysts
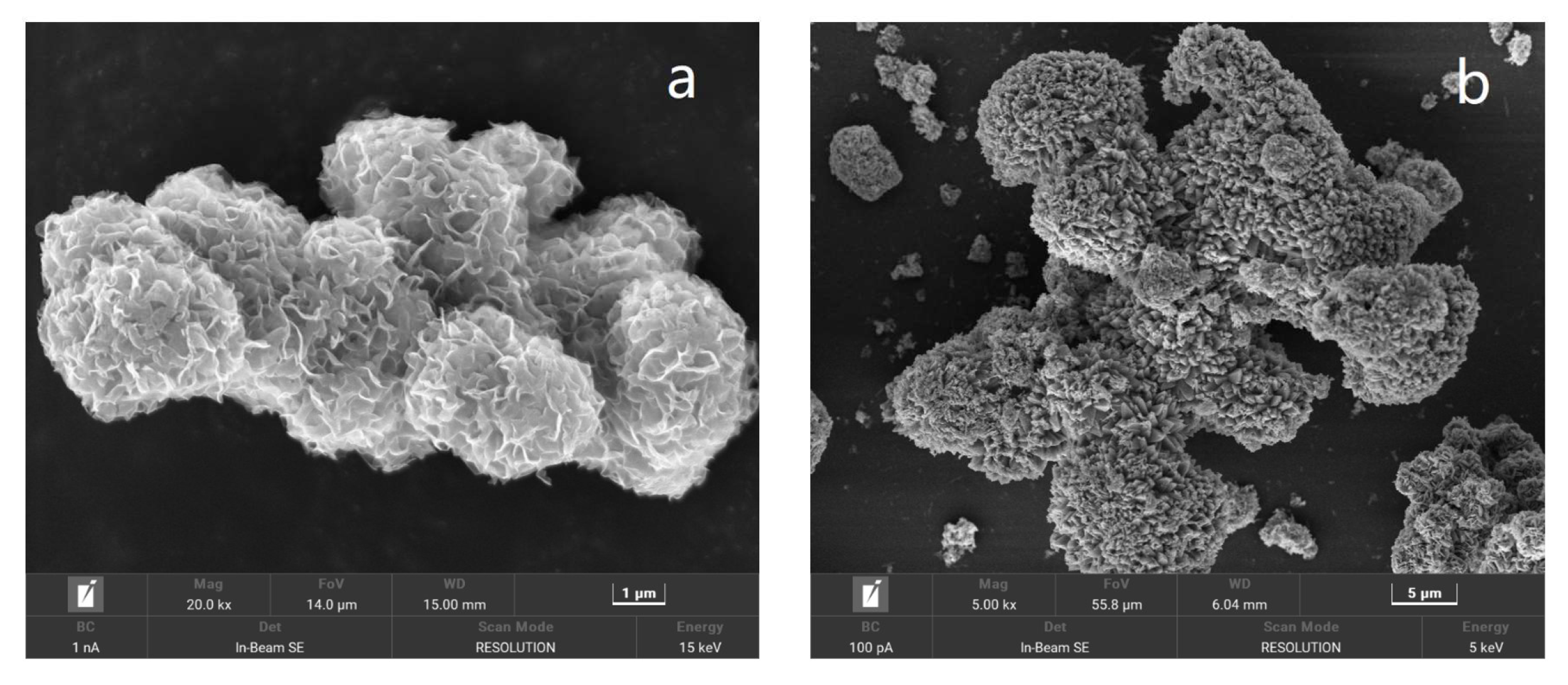
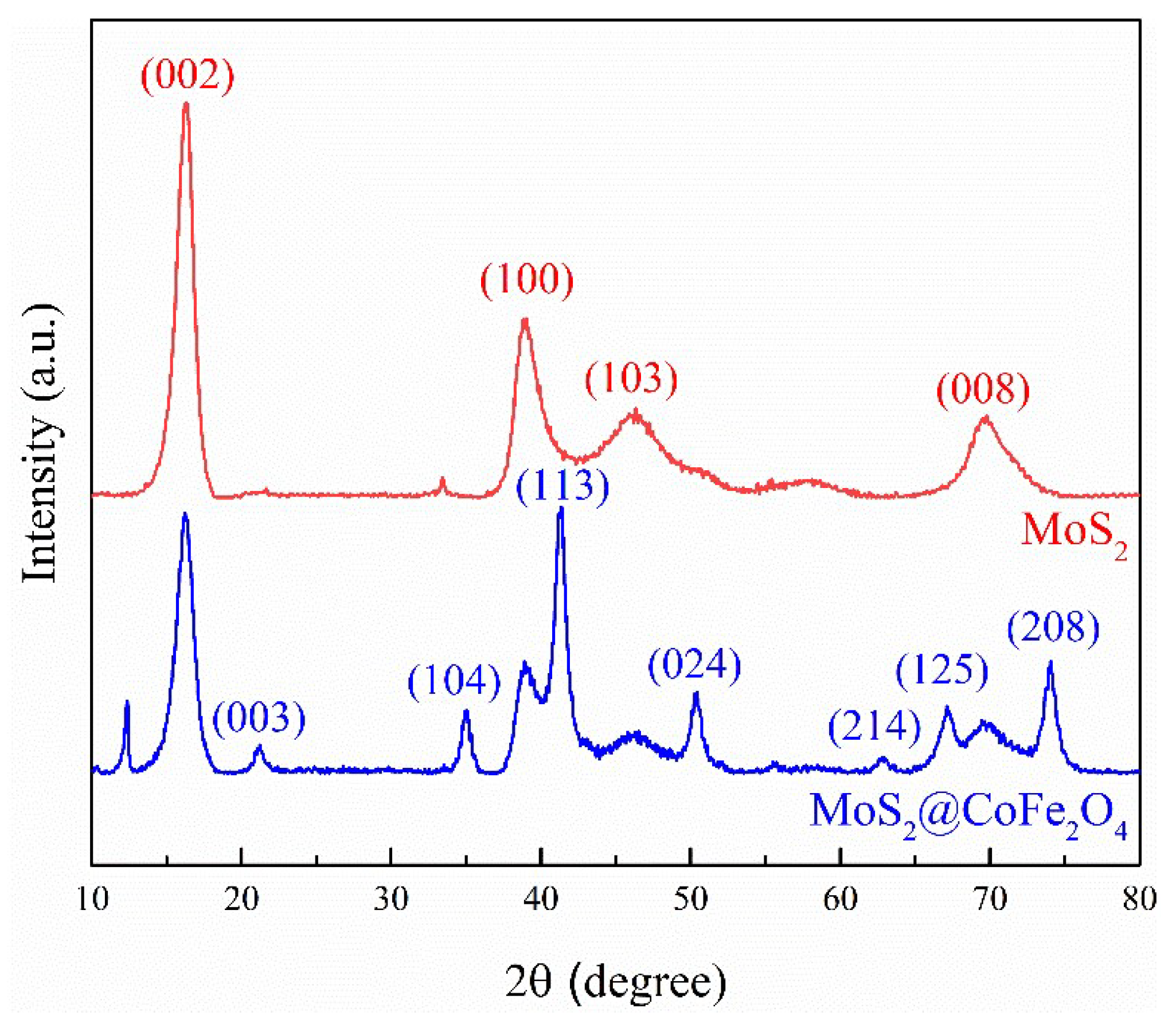
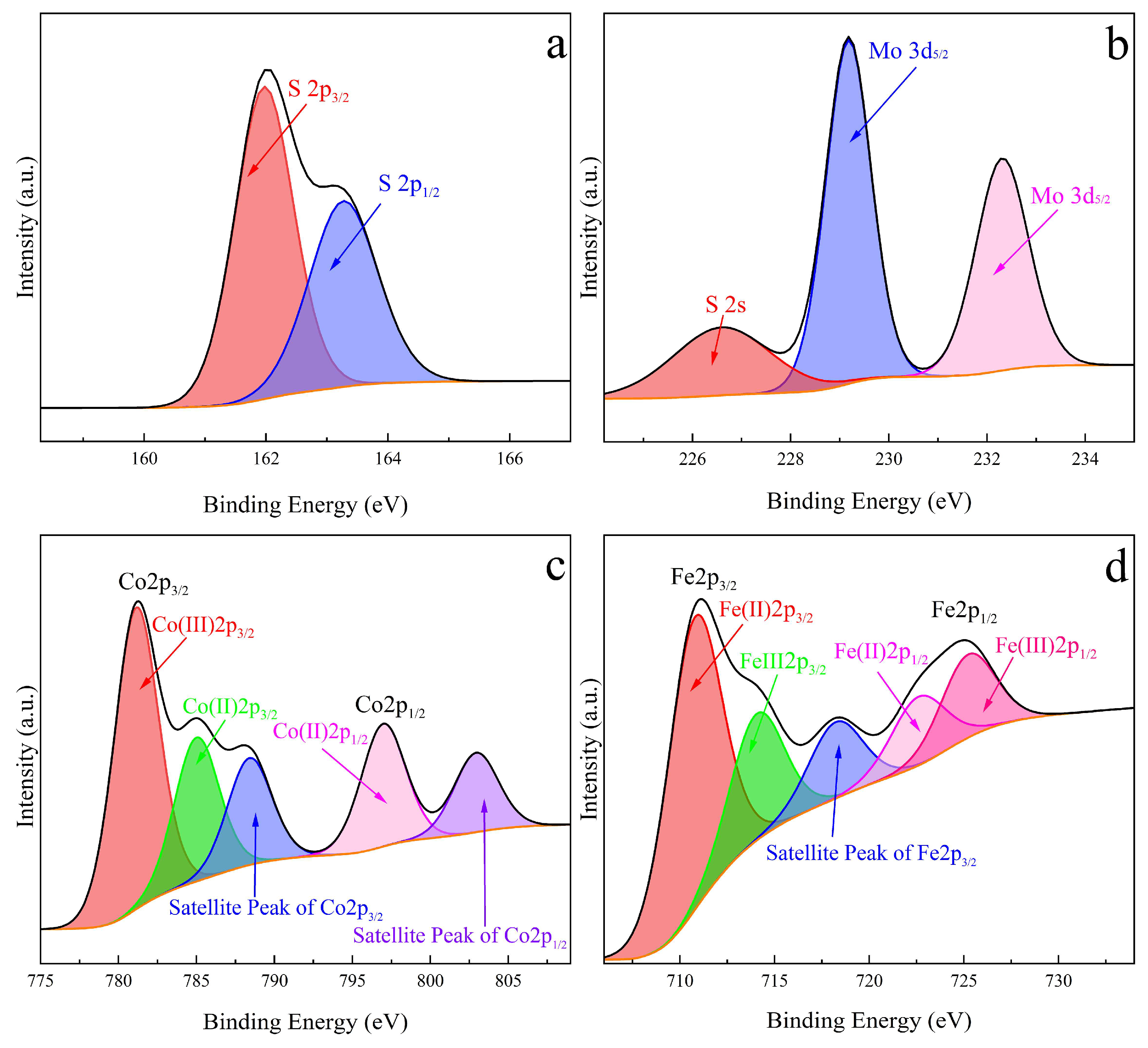
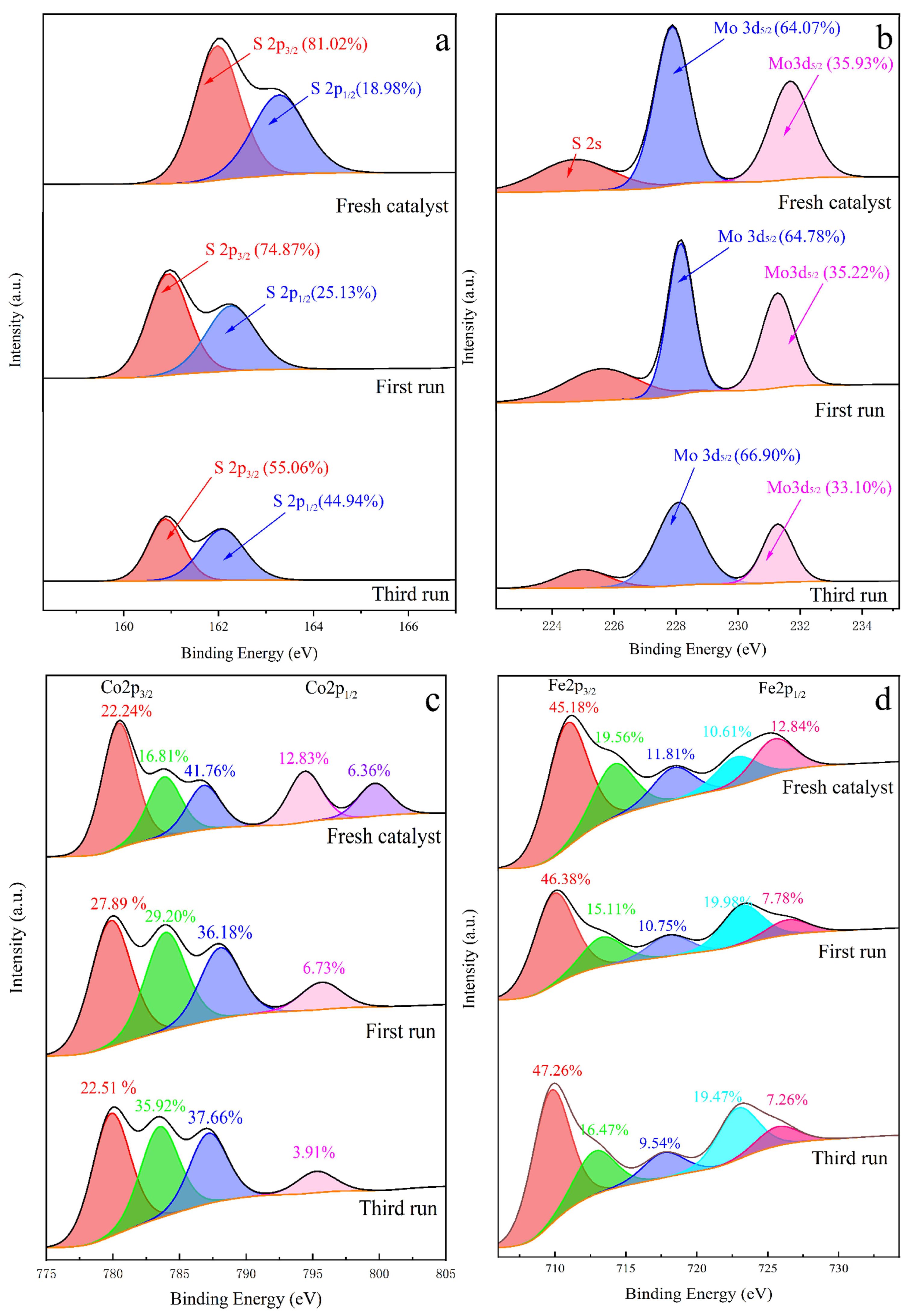
2.2. Characterization of the Prepared Catalyst
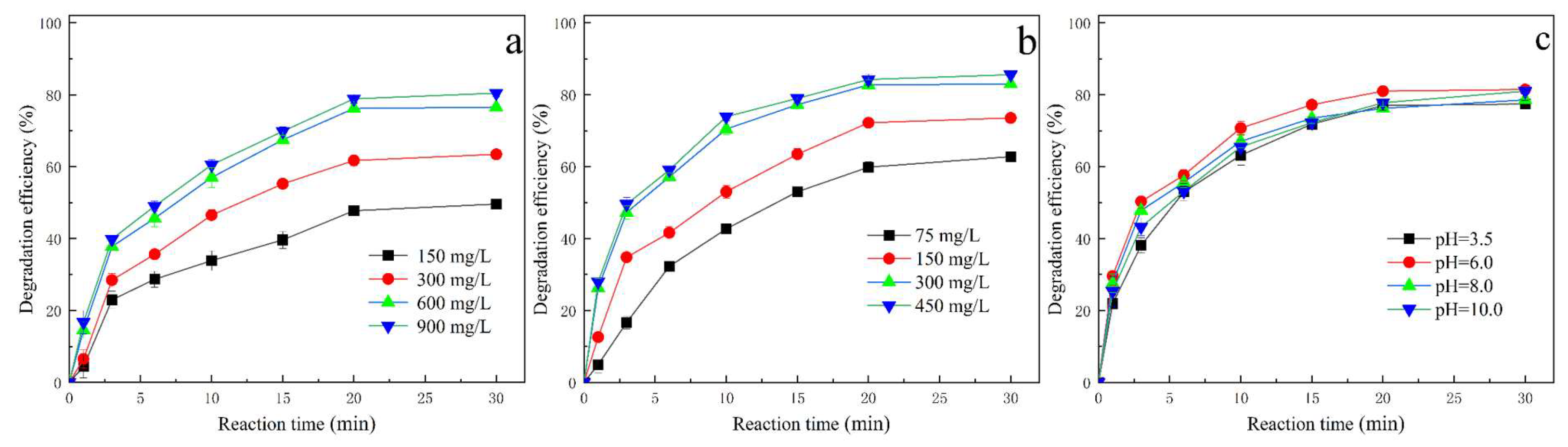
2.3. Effects of Operational Parameters on Degradation Efficiency
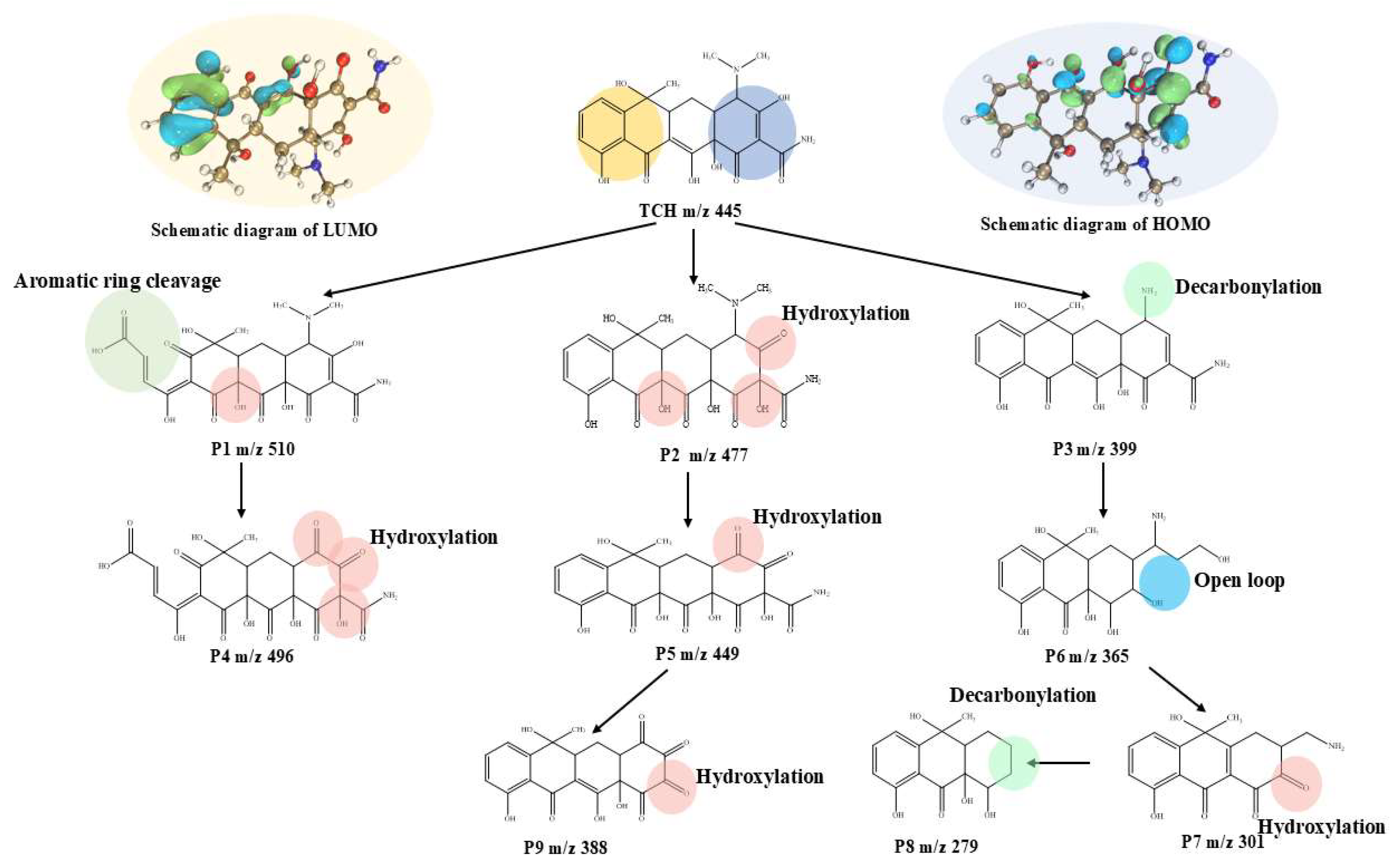
2.4. Identification of Reactive Species and Plausible Mechanism
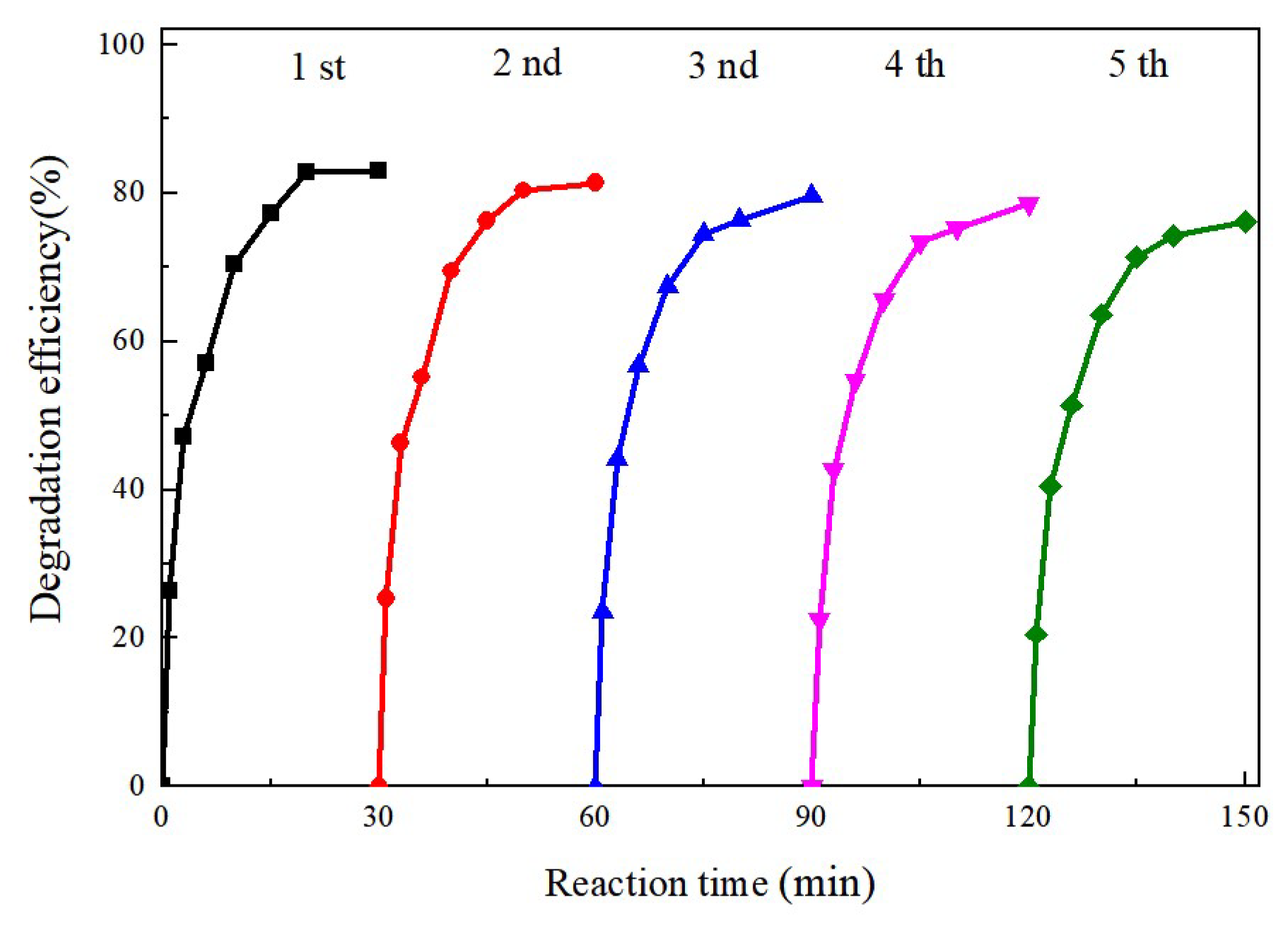
2.5. Stability of the MoS2@CoFe2O4 Catalyst
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of the Catalysts
3.3. Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride
3.4. Analytic Methods and Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dias, I.M.; Mourão, L.C.; Andrade, L.A.; Souza, G.B.M.; Viana, J.C.V.; Oliveira, S.B.; Alonso, C.G. Degradation of antibiotic amoxicillin from pharmaceutical industry wastewater into a continuous flow reactor using supercritical water gasification. Water Res. 2023, 234, 119826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, H.; Dong, X.; Leong, Y.K.; Chang, J.S. Advances and challenges in the removal of organic pollutants via sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes by Fe-based metal-organic frameworks: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.; Song, Y. Recent advance of Fe-based bimetallic persulfate activation catalysts for antibiotics removal: Performance, mechanism, contribution of the key ROSs and degradation pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.; Do, Q.C.; Kang, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kang, S. Boosted micropollutant removal over urchin-like structured hydroxyapatite-incorporated nickel magnetite catalyst via peroxydisulfate activation. Water Res. 2024, 249, 120951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Han, Y.; Yue, D.; Cao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Qian, X. Highly Efficient Utilization of Nano-Fe(0) Embedded in Mesoporous Carbon for Activation of Peroxydisulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9081–9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, A.; Scaria, J.; Ghanbari, F.; Nidheesh, P.V. Sulfate radicals-based advanced oxidation processes for the degradation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products: A review on relevant activation mechanisms, performance, and perspectives. Environ. Res. 2023, 217, 114789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Gong, S.; Liu, J.; Shi, J.; Deng, H. Progress and problems of water treatment based on UV/persulfate oxidation process for degradation of emerging contaminants: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neacșu, V.A.; Tudorache, A.; Bilea, F.; Oancea, P.; Răducan, A. Cobalt-catalysed bicarbonate-activated peroxide as a promising system for the advanced oxidation of epirubicin in wastewaters. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 458, 142462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Guo, M.; Cao, Y.; Zhong, W.; Ding, C.; Ye, H.; Chen, L.; Xu, H.; Fang, Z.; He, W. Switch PMS activation pathway from free radical to non-radical by introducing hexagonal boron nitride in supported CoFe2O4: The role of lattice oxygen and PMS adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qin, X.; Wang, K.; Ma, T.; Shang, Y. Insight into metal-based catalysts for heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate activation: A critical review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 333, 125900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yi, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, L. Construction of core–shell magnetic metal–organic framework composites Fe3O4@MIL-101(Fe, Co) for degradation of RhB by efficiently activating PMS. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 16727–16735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, H.M.A.; Asif, M.B.; Wang, Y.; Khan, K.; Cai, Y.; Xiao, X.; Li, C. Construction and elucidation of zerovalent iron@terephthalic acid/iron oxide catalyst to activate peroxymonosulfate for accelerating and long-lasting NOx removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Pan, J.; Wang, X.; Fan, Z.; Shi, T.; Wang, L.; Gao, B. Insights into the fundamental role of Mo doping in facilitating the activation of peroxydisulfate by iron-based catalysts: Accelerating the generation of sulfate radicals. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickavasagam, G.; He, C.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Saaid, M.; Oh, W.-D. Recent advances in catalyst design, performance, and challenges of metal-heteroatom-co-doped biochar as peroxymonosulfate activator for environmental remediation. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zhu, L.; Nan, Z. Ni-doped Fe3O4 nanoparticles coupled with SnS2 nanosheets as 0D/2D heterogeneous catalyst for photo-Fenton reaction. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 224, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zheng, J.; Fan, X.; Xu, K.; Liu, Y.; He, J. Fe-Cu co-doped carbon-based catalyst activating peroxydisulfate for the degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A: The dominant role of superoxide radicals. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Shen, Q.; Nan, T.; Zhou, M.; Xia, Y.; Hu, G.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Y.; Bian, T.; Wei, T.; et al. Cobalt-based catalysts for heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activation in degradation of organic contaminants: Recent advances and perspectives. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 958, 170370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Xiong, B.; Bai, F.; Wang, S.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xie, P.; Wiesner, M.R. Application of Cobalt/Peracetic Acid to Degrade Sulfamethoxazole at Neutral Condition: Efficiency and Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.-H.; He, C.-S.; He, Y.-L.; Yang, S.-R.; Yu, S.-Y.; Xiong, Z.; Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Z.-C.; Yao, G.; et al. Peracetic acid activation via the synergic effect of Co and Fe in CoFe-LDH for efficient degradation of pharmaceuticals in hospital wastewater. Water Res. 2023, 232, 119666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-T.; Li, Y.-L.; Guo, Q.; Shao, D.-W.; He, M.-M.; Qi, T. Harmless treatment and resource utilization of stainless steel pickling sludge via direct reduction and magnetic separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 118187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Yu, C.; Dongxu, L.; Suiyi, Z.; Yidi, G.; Yuxin, Z.; Yang, H. Recovery of Fe from steel pickling wastewater as polymeric Fe/S rods for effective adsorption of phosphate from electrophoresis effluent. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, T. Progress of CCUS technology in the iron and steel industry and the suggestion of the integrated application schemes for China. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, H.; Wang, J.; She, X.; Wang, G.; Zuo, H.; Xue, Q. Current status of the technology for utilizing difficult-to-treat dust and sludge produced from the steel industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 367, 132909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, K.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by CoFe2O4 layered catalyst derived from steel pickling sludge for the decolorization of tartrazine solution. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Chang, Y.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zou, W.; Zhou, M. Enhanced removal of atrazine by a MoS2–Fe–BC/peroxydisulfate system: Key role of MoS2 and Fe(IV). Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Upadhyay, S.; Pandey, A.; Pandey, O.P.; Srivastava, M.; Khatri, O.P. Fruit waste-derived cellulose-templated hierarchical spheres of ultrathin MoS2 nanosheets for oxygen evolution reactions. FlatChem 2023, 41, 100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Banerjee, S.; Bairagi, S.; Singh, P.; Kumar, B.; Singh, P.; Kale, R.D.; Mulvihill, D.M.; Ali, S.W. Recent progress in molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) based flexible nanogenerators: An inclusive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 147963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, M.; Shang, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Sun, F.; Li, M.; Li, X. Singlet oxygen dominated core-shell Co nanoparticle to synergistically degrade methylene blue through efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 308, 122849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xiong, W.; Xing, S.; Shao, Y.; Guo, R.; Zhang, H. Oxidation of organic contaminant in a self-driven electro/natural maghemite/peroxydisulfate system: Efficiency and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Feng, S.; Ma, X.; Tan, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, T.; Li, J. Heterogeneous degradation of Orange II with peroxymonosulfate activated by ordered mesoporous MnFe2O4. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 167, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Y.; Gao, H.; Cao, Y.; Cao, R.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J. Cobalt ferrite supported on carbon nitride matrix prepared using waste battery materials as a peroxymonosulfate activator for the degradation of levofloxacin hydrochloride. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Divyapriya, G.; Ezzahra Titchou, F.; Hamdani, M. Treatment of textile wastewater by sulfate radical based advanced oxidation processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 293, 121115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirsaheb, M.; Moradi, N. A systematic review of the sonophotocatalytic process for the decolorization of dyes in aqueous solution: Synergistic mechanisms, degradation pathways, and process optimization. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 44, 102314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.-H.; Liu, W.-Z.; Tang, Z.-E.; Cui, D. Recent advancements in azo dye decolorization in bio-electrochemical systems (BESs): Insights into decolorization mechanism and practical application. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.H.; Ma, J.; Li, X.C.; Fang, J.Y.; Chen, L.W. Influence of pH on the formation of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in the UV/peroxymonosulfate system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9308–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Leiknes, T. Oxidation of Refractory Benzothiazoles with PMS/CuFe2O4: Kinetics and Transformation Intermediates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5864–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaafarzadeh, N.; Ghanbari, F.; Ahmadi, M. Efficient degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by peroxymonosulfate/magnetic copper ferrite nanoparticles/ozone: A novel combination of advanced oxidation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 320, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qiu, W.; Pang, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, J. Relative contribution of ferryl ion species (Fe(IV)) and sulfate radical formed in nanoscale zero valent iron activated peroxydisulfate and peroxymonosulfate processes. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Mi, X.; Chen, Z.; Xu, W.; Liu, W.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Ni, B.-J. Efficient emerging contaminants (EM) decomposition via peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activation by Co3O4/carbonized polyaniline (CPANI) composite: Characterization of tetracycline (TC) degradation property and application for the remediation of EM-polluted water body. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 405, 137023. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, Y. Catalytic degradation of bisphenol A by heterogeneous bimetal composite carbon in the PMS and H2O2 systems: Performance and mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, C.; Ao, Z.; Zhou, Y. Dramatic enhancement effects of l-cysteine on the degradation of sulfadiazine in Fe3+/CaO2 system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Lu, Q.; Di, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y. Iron-based biochar as efficient persulfate activation catalyst for emerging pollutants removal: A review. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan, S.D.; Daeschel, M.A. 5,5-Dimethyl-2-pyrrolidone-N-oxyl formation in electron spin resonance studies of electrolyzed NaCl solution using 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide as a spin trapping agent. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4906–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranguelova, K.; Rice, A.B.; Khajo, A.; Triquigneaux, M.; Garantziotis, S.; Magliozzo, R.S.; Mason, R.P. Formation of reactive sulfite-derived free radicals by the activation of human neutrophils: An ESR study. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-Q.; Gao, N.-Y.; Wang, W.; Kang, S.-F.; Xu, J.-H.; Xiang, H.-M.; Yin, D.-Q. Ultrasound-assisted heterogeneous activation of persulfate by nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) for the propranolol degradation in water. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2018, 49, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.Q.; Gao, N.Y.; Yin, D.Q.; Tian, F.X.; Zheng, Q.F. Oxidation of the β-blocker propranolol by UV/persulfate: Effect, mechanism and toxicity investigation. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, W.; Lu, J.; Hou, D.; Ke, Y.; Li, G.; Tang, Z.; Kang, X.; Chen, S. Hierarchical spheres constructed by defect-rich MoS2/carbon nanosheets for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nano Energy 2016, 22, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lin, L.; Li, P.; Li, X.; Zhong, Y.; Yu, Y.; Qiu, Y. Core-shell MoS2 nanosheet-bonded carbon nanotubes through dispersant molecules for enhanced photoelectrical and photocatalytic performances. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 284, 121211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Liu, F.; Dong, Q.; Ma, Z.; Liu, W. Magnetic Fe3O4-deposited flower-like MoS2 nanocomposites for the Fenton-like Escherichia coli disinfection and diclofenac degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by magnetic Co-Fe/SiO2 layered catalyst derived from iron sludge for ciprofloxacin degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, J.; Zhu, K.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Duan, P.; Huang, L. Efficient Tetracycline Hydrochloride Degradation by Urchin-Like Structured MoS2@CoFe2O4 Derived from Steel Pickling Sludge via Peroxymonosulfate Activation. Molecules 2025, 30, 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153194
Qi J, Zhu K, Li M, Liu Y, Duan P, Huang L. Efficient Tetracycline Hydrochloride Degradation by Urchin-Like Structured MoS2@CoFe2O4 Derived from Steel Pickling Sludge via Peroxymonosulfate Activation. Molecules. 2025; 30(15):3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153194
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Jin, Kai Zhu, Ming Li, Yucan Liu, Pingzhou Duan, and Lihua Huang. 2025. "Efficient Tetracycline Hydrochloride Degradation by Urchin-Like Structured MoS2@CoFe2O4 Derived from Steel Pickling Sludge via Peroxymonosulfate Activation" Molecules 30, no. 15: 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153194
APA StyleQi, J., Zhu, K., Li, M., Liu, Y., Duan, P., & Huang, L. (2025). Efficient Tetracycline Hydrochloride Degradation by Urchin-Like Structured MoS2@CoFe2O4 Derived from Steel Pickling Sludge via Peroxymonosulfate Activation. Molecules, 30(15), 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153194





