Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of 1-Benzylpiperidine and 1-Benzoylpiperidine Derivatives as Dual-Target Inhibitors of Acetylcholinesterase and Serotonin Transporter for Alzheimer′s Disease †
Abstract
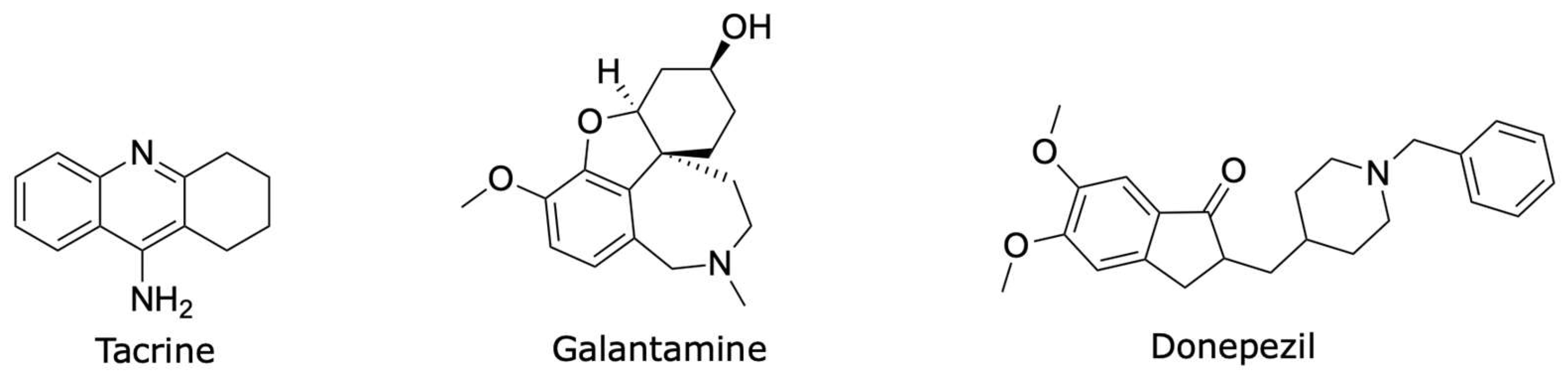
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
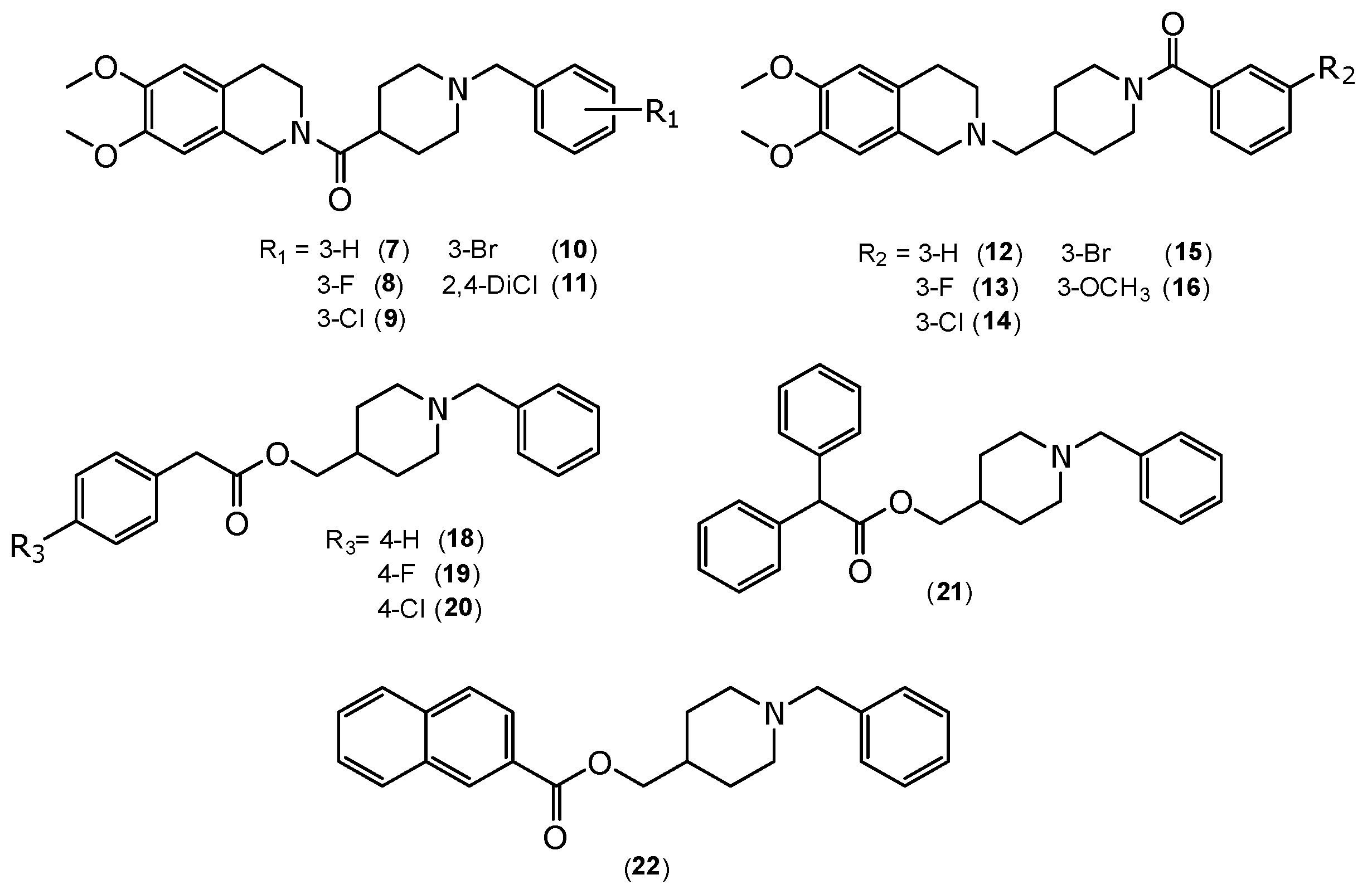
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Evaluation
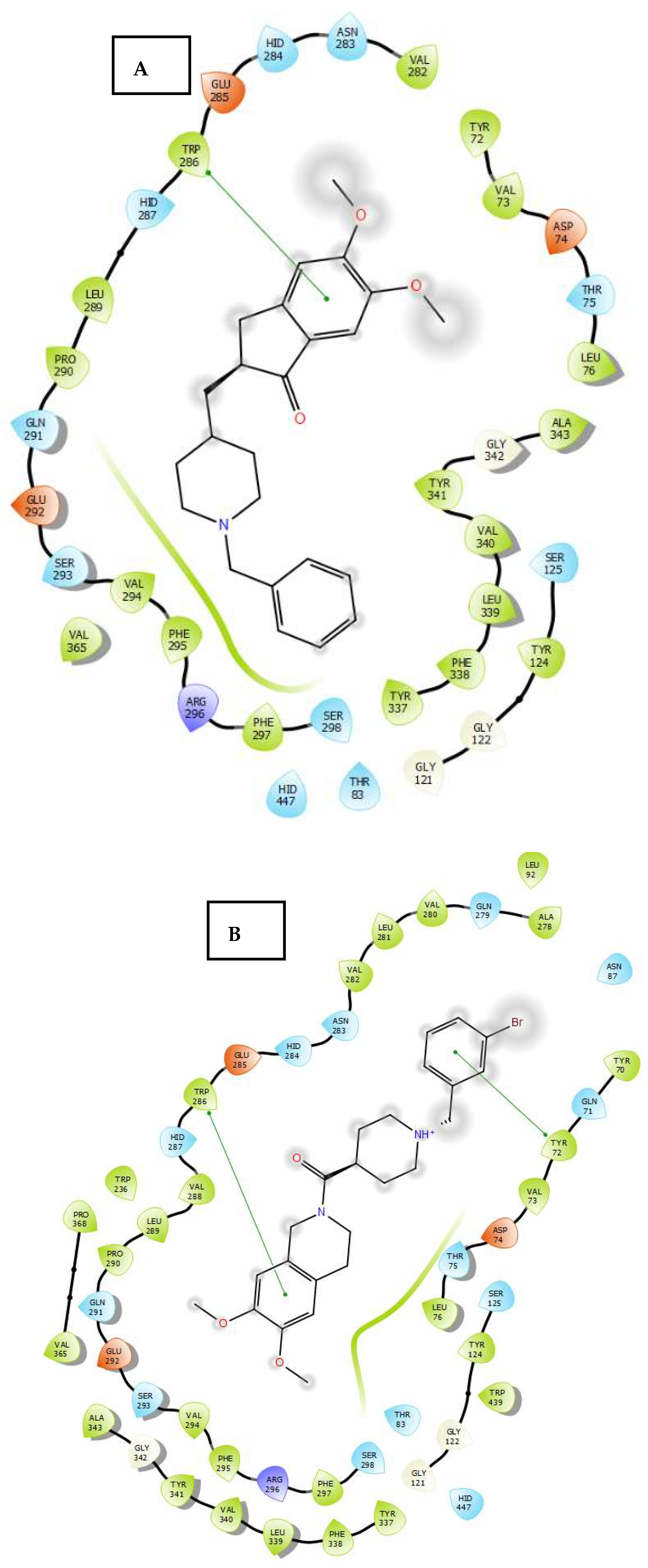
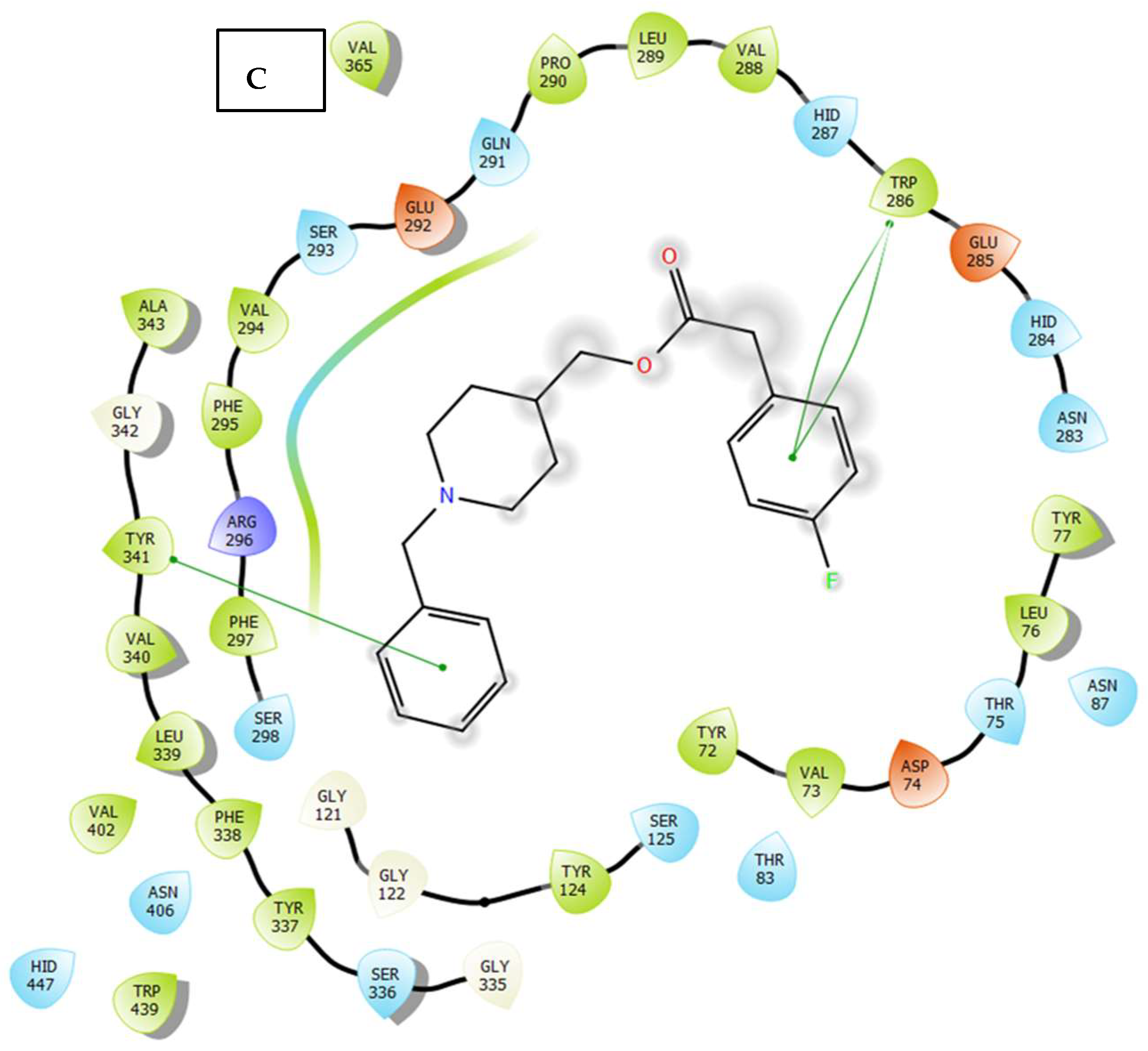
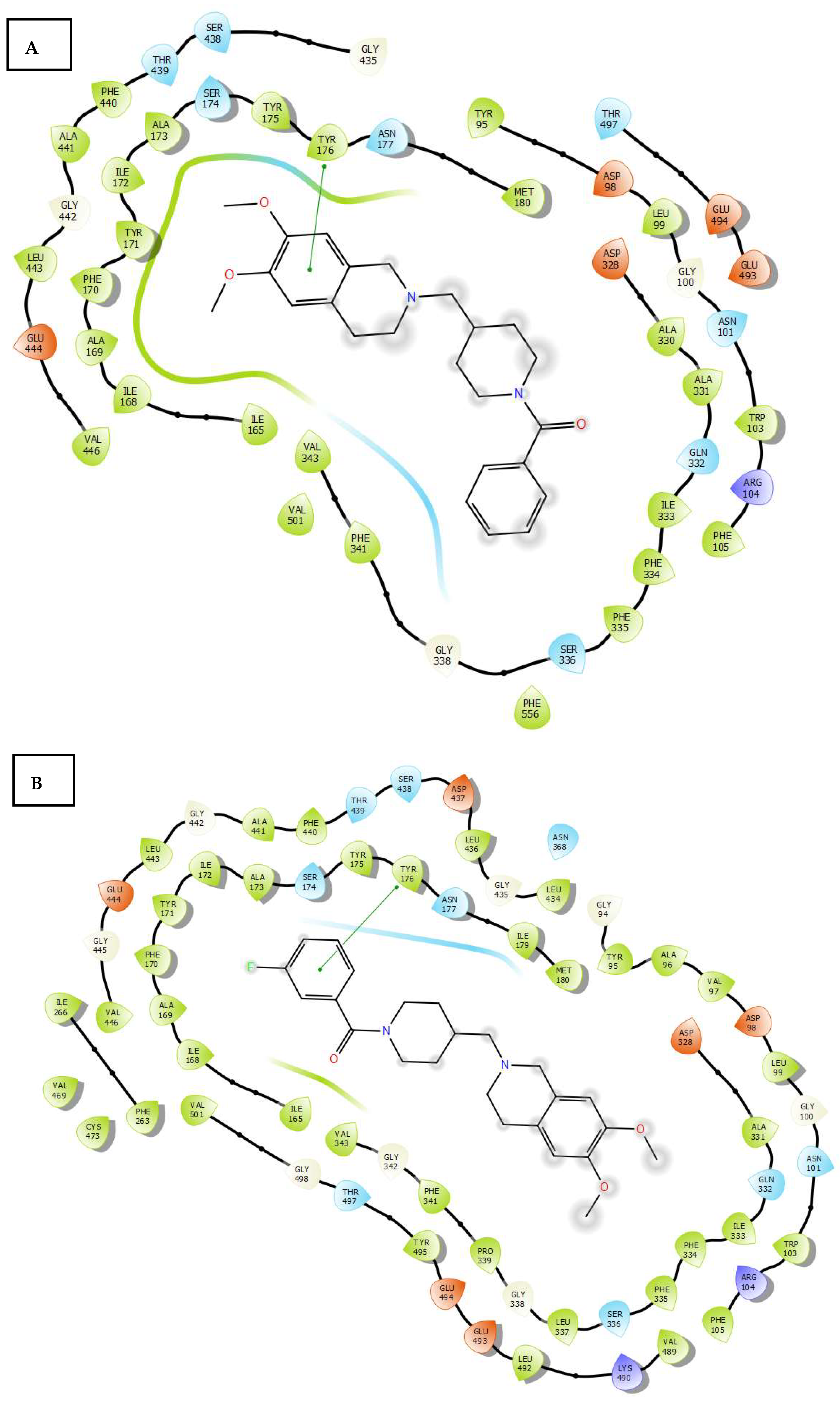
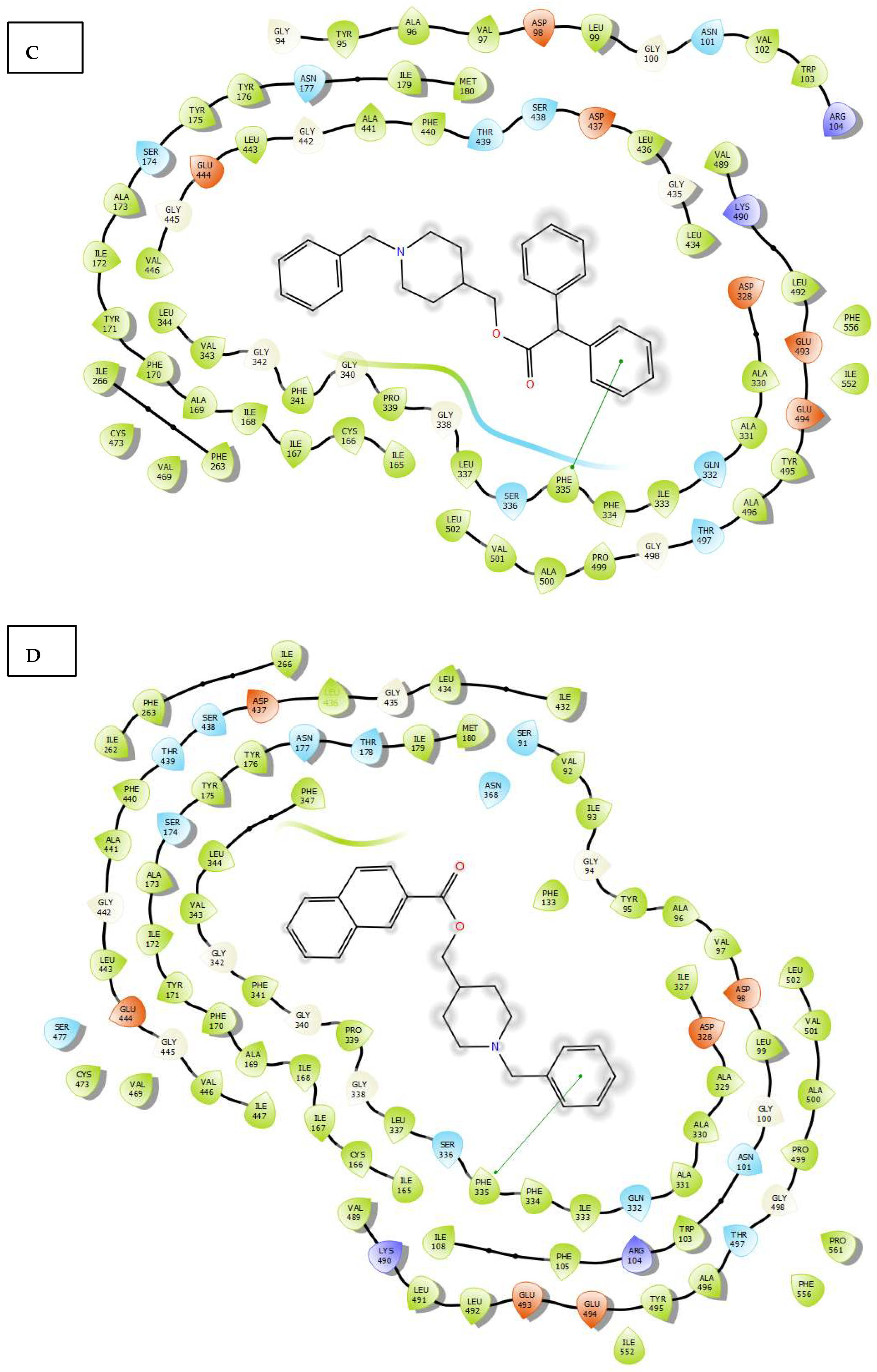
2.3. Molecular Docking
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis and Chemical Characterization
3.1.1. Procedures for the Synthesis of tert-Butyl-4-(chlorocarbonyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate (2)
3.1.2. Procedures for the Synthesis of tert-Butyl-4-(6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-2-carbonyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate (4)
3.1.3. Procedures for the Synthesis of (6,7-Dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)(piperidin-4-yl)methanone (5)
3.1.4. Procedures for the Synthesis of 6,7-Dimethoxy-2-(piperidin-4-ylmethyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline (6)
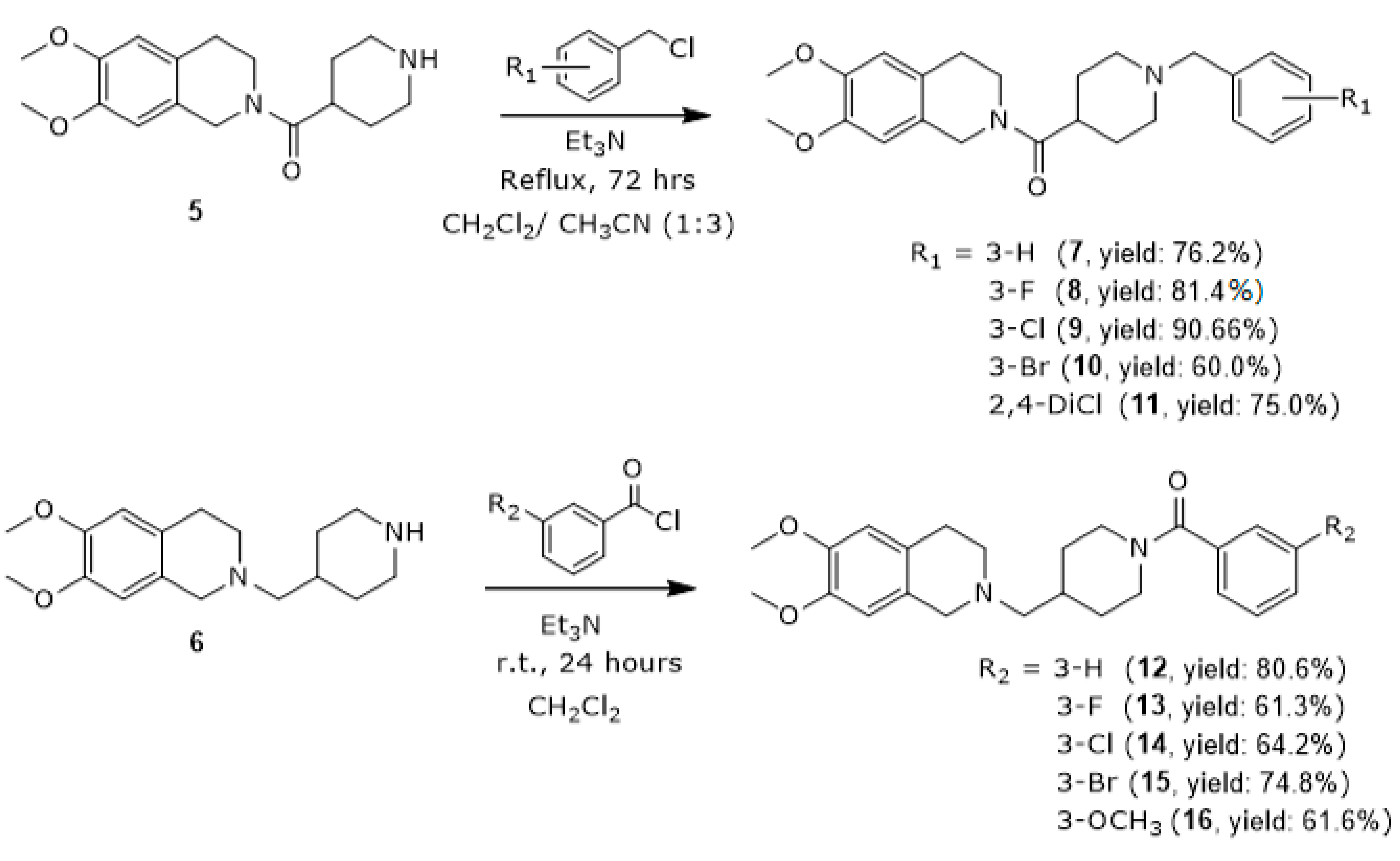
3.1.5. General Procedures for the Synthesis of (1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)(6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)methanone Derivatives (7–11)
(1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)(6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)methanone (7)
(6,7-Dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)(1-(3-fluorobenzyl)piperidin-4-yl)methanone (8)
(1-(3-Chlorobenzyl)piperidin-4-yl)(6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)methanone (9)
(1-(3-Bromobenzyl)piperidin-4-yl)(6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)methanone (10)
(1-(2,4-Dichlorobenzyl)piperidin-4-yl)(6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)methanone (11)
3.1.6. General Procedures for the Synthesis of (4-((6,7-Dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-yl)(phenyl)methanone (12–16)
(4-((6,7-Dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-yl)(phenyl)methanone (12)
(4-((6,7-Dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-yl)(3-fluorophenyl)methanone (13)
(3-Chlorophenyl)(4-((6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-yl)methanone (14)
(3-Bromophenyl)(4-((6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-yl)methanone (15)
(4-((6,7-Dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-yl)(3-methoxyphenyl)methanone (16)
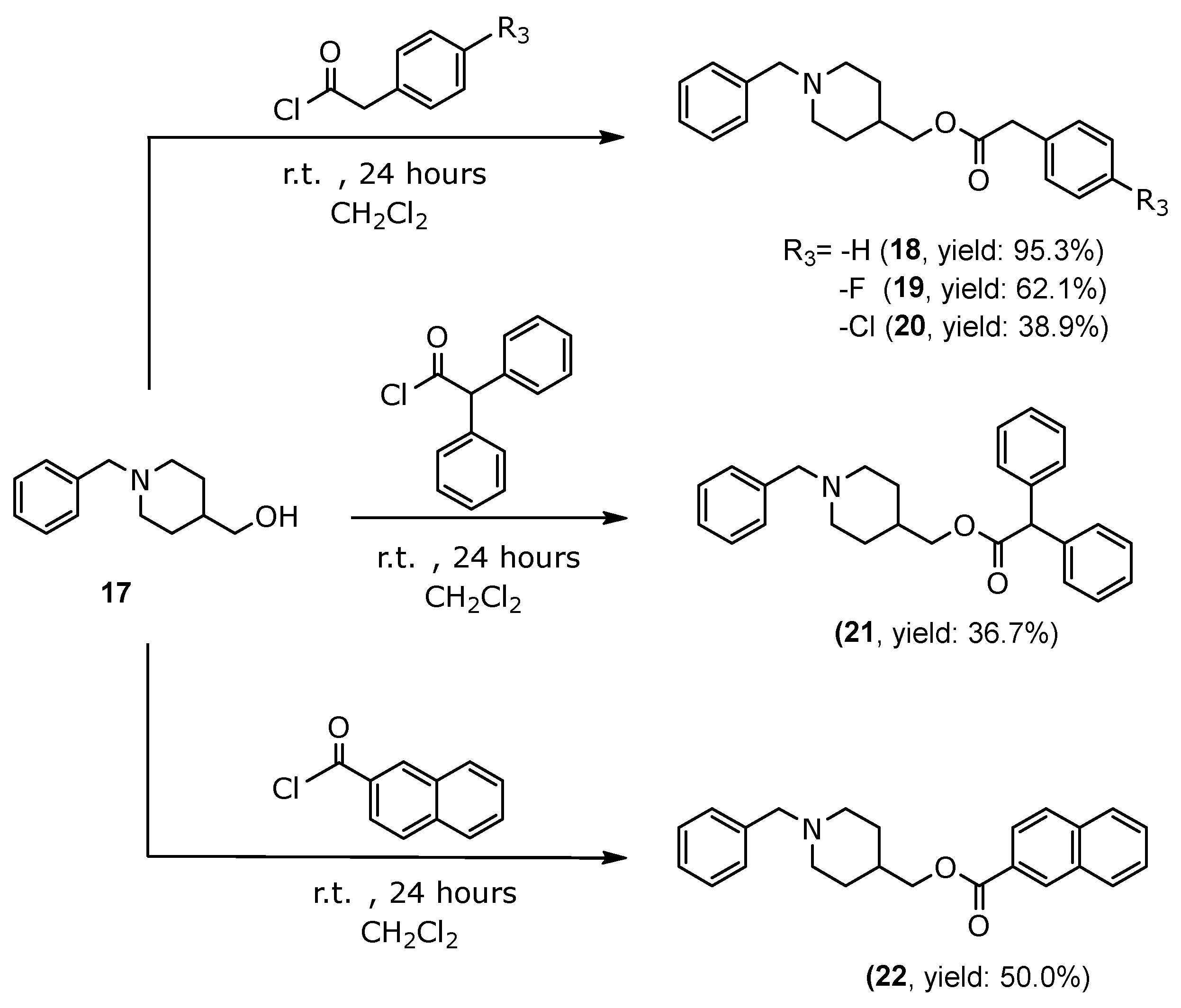
3.1.7. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 2-Phenylacetate of (1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl Derivatives (18–20), 2,2-Diphenylacetate of (1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl (21) and 2-Naphthoate of (1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl (22)
(1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl-2-phenylacetate (18)
(1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl-2-(4-fluorophenyl)acetate (19)
(1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl-2-(4-chlorophenyl)acetate (20)
(1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl-2,2-diphenylacetate (21)
(1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl-2-naphthoate (22)
3.2. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and Butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) Inhibitory Activity
3.3. Protocol Binding of [3H]-Paroxetine on h-SERT Cells
3.4. Molecular Docking Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mount, C.; Downton, C. Alzheimer disease: Progress or profit? Nat Med. 2006, 12, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.L.; Doody, R.; Clark, C. Disease-modifying therapies for Alzheimer disease: Challenges to early intervention. Neurology 2007, 69, 1622–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiannopoulou, K.G.; Papageorgiou, S.G. Current and future treatments for Alzheimer’s disease. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2013, 6, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Xu, T.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Melcher, K.; Xu, H.E. Amyloid beta: Structure, biology and structure-based therapeutic development. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1205–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimberti, D.; Scarpini, E. Disease-modifying treatments for Alzheimer’s disease. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2011, 4, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klafki, H.-W.; Staufenbiel, M.; Kornhuber, J.; Wiltfang, J. Therapeutic approaches to Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2006, 129, 2840–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, P.T.; Palmer, A.M.; Snape, M.; Wilcock, G.K. The cholinergic hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: A review of progress. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 66, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, D.; Choi, D.; Conn, P.J.; Rook, J. Activation of M1 and M4 muscarinic receptors as potential treatments for Alzheimer’s disease and schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2014, 10, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onajole, O.K.; Vallerini, G.P.; Eaton, J.B.; Lukas, R.J.; Brunner, D.; Caldarone, B.J.; Kozikowski, A.P. Synthesis and Behavioral Studies of Chiral Cyclopropanes as Selective α4β2-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Partial Agonists Exhibiting an Antidepressant Profile. Part III. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strachan, J.-P.; Kombo, D.C.; Mazurov, A.; Heemstra, R.; Bhatti, B.S.; Akireddy, R.; Murthy, S.; Miao, L.; Jett, J.E.; Speake, J.; et al. Identification and pharmacological characterization of 3,6-diazabicyclo[3.1.1]heptane-3-carboxamides as novel ligands for the α4β2 and α6/α3β2β3 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 86, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barret, K.E.; Barman, S.M.; Boitano, S.; Brooks, H.L. Ganong’ s Review of Medical Physiology, 24th ed.; Barrett, K.E., Boitano, S., Barman, S.M., Brooks, H.L., Michael Weitz, B.P.K., Eds.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-07-178004-9. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K. Cholinesterase inhibitors as Alzheimer’s therapeutics (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. Acetylcholinesterase: “classical” and “non-classical” functions and pharmacology. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachón-Angona, I.; Refouvelet, B.; Andrýs, R.; Martin, H.; Luzet, V.; Iriepa, I.; Moraleda, I.; Diez-Iriepa, D.; Oset-Gasque, M.-J.; Marco-Contelles, J.; et al. Donepezil + chromone + melatonin hybrids as promising agents for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marucci, G.; Buccioni, M.; Ben, D.D.; Lambertucci, C.; Volpini, R.; Amenta, F. Efficacy of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology. 2021, 190, 108352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilienfeld, S. Galantamine — a Novel Cholinergic Drug with a Unique Dual Mode of Action for the Treatment of Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. CNS Drug Rev. 2002, 8, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, M.; Gobartt, A.L.; Balañá, M. Behavioural symptoms in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and their association with cognitive impairment. BMC Neurol. 2010, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orgeta, V.; Tabet, N.; Nilforooshan, R.; Howard, R. Efficacy of Antidepressants for Depression in Alzheimer’s Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Leoutsakos J-M, editor. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 58, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Day, C.M.; Abdella, S.; Garg, S. Alzheimer’s disease current therapies, novel drug delivery systems and future directions for better disease management. J. Control. Release 2024, 367, 402–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Rojas, C.; Quiroz, G.; Faúndez, M.; Gallardo-Garrido, C.; Pessoa-Mahana, C.D.; Chung, H.; Gallardo-Toledo, E.; Saitz-Barría, C.; Araya-Maturana, R.; Kogan, M.J.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitors based on a benzoxazine core. Arch. Pharm. 2018, 351, 1800024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giancola, J.B.; Bonifazi, A.; Cao, J.; Ku, T.; Haraczy, A.J.; Lam, J.; Rais, R.; Coggiano, M.A.; Tanda, G.; Newman, A.H. Structure-activity relationships for a series of (Bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl)sulfinylethyl-aminopiperidines and -piperidine amines at the dopamine transporter: Bioisosteric replacement of the piperazine improves metabolic stability. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 208, 112674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Añazco, T.; Werner, T.; Torres, M.J.; Hornos-Carneiro, M.F.; Fernández, J.; Zivkovic, A.; Salas, C.O.; Castro-Álvarez, A.; Gutiérrez, M.; Stark, H.; et al. First in class pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives fused to fluorobenzylpiperidines as dual ligands of acetylcholinesterase and histamine H3 receptor. Arch. Pharm. 2025, 358, e2400387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Huang, G. The biological activities of butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, J.A.; Navratna, V.; Antermite, D.; Yang, D.; Bull, J.A.; Gouaux, E. Chemical and structural investigation of the paroxetine-human serotonin transporter complex. eLife. 2020, 9, e56427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mella, M.; Moraga-Nicolás, F.; Machuca, J.; Quiroz, A.; Mutis, A.; Becerra, J.; Astudillo, Á.; Hormazábal, E. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity from Amaryllis belladonna growing in Chile: Enzymatic and molecular docking studies. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.K.; Krohn, R.I.; Hermanson, G.T.; Mallia, A.K.; Gartner, F.H.; Provenzano, M.D.; Fujimoto, E.K.; Goeke, N.M.; Olson, B.J.; Klenk, D.C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugnon, M.; Röhrig, U.F.; Goullieux, M.; Perez, M.A.S.; Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissDock 2024: Major enhancements for small-molecule docking with Attracting Cavities and AutoDock Vina. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W324–W332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compound | AChE IC50 (µM) | BuChE IC50 (µM) | h-SERT KI (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 34.37 ± 0.51 | - | - |
| 8 | 41.16 ± 3.17 | - | - |
| 9 | 34.47 ± 1.97 | 268.20 ± 13.83 | - |
| 10 | 28.28 ± 0.87 | 426.30 ± 28.61 | - |
| 11 | - | - | - |
| 12 | 289.60 ± 10.94 | - | 2.62 ± 0.82 |
| 13 | - | - | 1.91 ± 0.77 |
| 14 | - | - | 2.43 ± 0.24 |
| 15 | 242.40 ± 24.37 | - | 1.47 ± 0.73 |
| 16 | 439.10 ± 28.02 | - | 1.59 ± 0.58 |
| 18 | 199.90 ± 8.61 | 256.20 ± 5.03 | 27.1 ± 3.40 |
| 19 | 5.10 ± 0.24 | 26.78 ± 0.81 | 196.6 ± 11.34 |
| 20 | 259.10 ± 14.57 | - | - |
| 21 | - | 6.16 ± 0.29 | 25.5 ± 1.01 |
| 22 | 61.70 ± 2.56 | 59.30 ± 1.42 | 26.9 ± 2.57 |
| GAL | 1.19 ± 0.046 | 29.05 ± 0.972 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Gutiérrez, J.P.; Castillo-Ríos, D.; Ríos-Campos, V.; González-Gutiérrez, I.A.; Flores Melivilu, D.; Hormazábal Uribe, E.; Moraga-Nicolás, F.; Segura, K.; Hernández, V.; Farías-Cea, A.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of 1-Benzylpiperidine and 1-Benzoylpiperidine Derivatives as Dual-Target Inhibitors of Acetylcholinesterase and Serotonin Transporter for Alzheimer′s Disease. Molecules 2025, 30, 3047. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30143047
González-Gutiérrez JP, Castillo-Ríos D, Ríos-Campos V, González-Gutiérrez IA, Flores Melivilu D, Hormazábal Uribe E, Moraga-Nicolás F, Segura K, Hernández V, Farías-Cea A, et al. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of 1-Benzylpiperidine and 1-Benzoylpiperidine Derivatives as Dual-Target Inhibitors of Acetylcholinesterase and Serotonin Transporter for Alzheimer′s Disease. Molecules. 2025; 30(14):3047. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30143047
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Gutiérrez, Juan Pablo, Damián Castillo-Ríos, Víctor Ríos-Campos, Ignacio Alejandro González-Gutiérrez, Dánae Flores Melivilu, Emilio Hormazábal Uribe, Felipe Moraga-Nicolás, Kerim Segura, Valentina Hernández, Amaury Farías-Cea, and et al. 2025. "Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of 1-Benzylpiperidine and 1-Benzoylpiperidine Derivatives as Dual-Target Inhibitors of Acetylcholinesterase and Serotonin Transporter for Alzheimer′s Disease" Molecules 30, no. 14: 3047. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30143047
APA StyleGonzález-Gutiérrez, J. P., Castillo-Ríos, D., Ríos-Campos, V., González-Gutiérrez, I. A., Flores Melivilu, D., Hormazábal Uribe, E., Moraga-Nicolás, F., Segura, K., Hernández, V., Farías-Cea, A., Pessoa-Mahana, H. A., Reyes-Parada, M. I., & Iturriaga-Vásquez, P. (2025). Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of 1-Benzylpiperidine and 1-Benzoylpiperidine Derivatives as Dual-Target Inhibitors of Acetylcholinesterase and Serotonin Transporter for Alzheimer′s Disease. Molecules, 30(14), 3047. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30143047








