Structure-Based Design of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Human Interleukin-6
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Homology Modeling
2.2. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations
2.3. Ensemble Docking Algorithm to Select Distinct Conformations of HIL-6 for Screening
2.4. Docking Protocol and Selection of Database for Docking
2.5. Selection Criteria for Choosing Compounds for In Vitro Screening
2.6. In Vitro Functional Assays
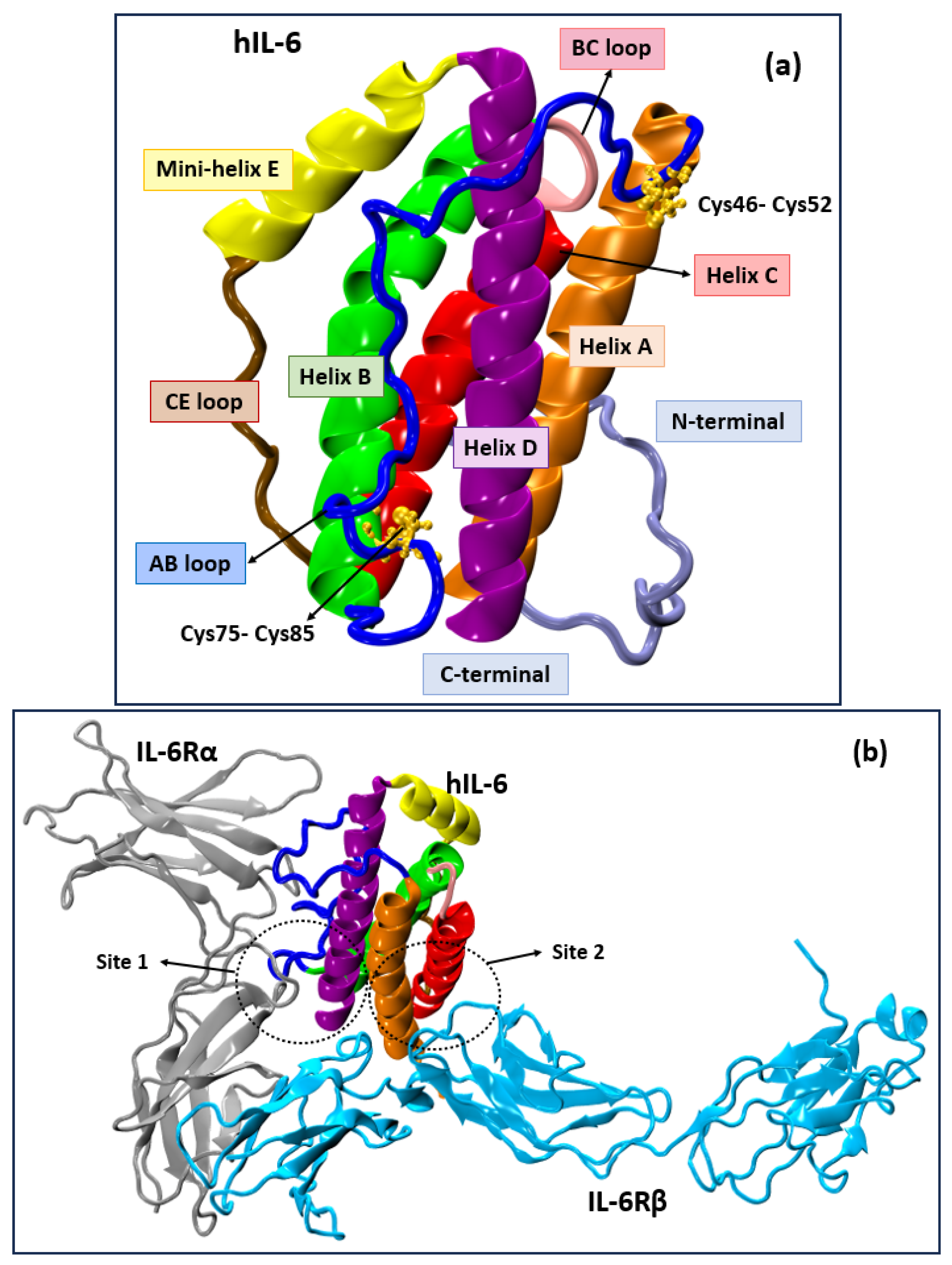
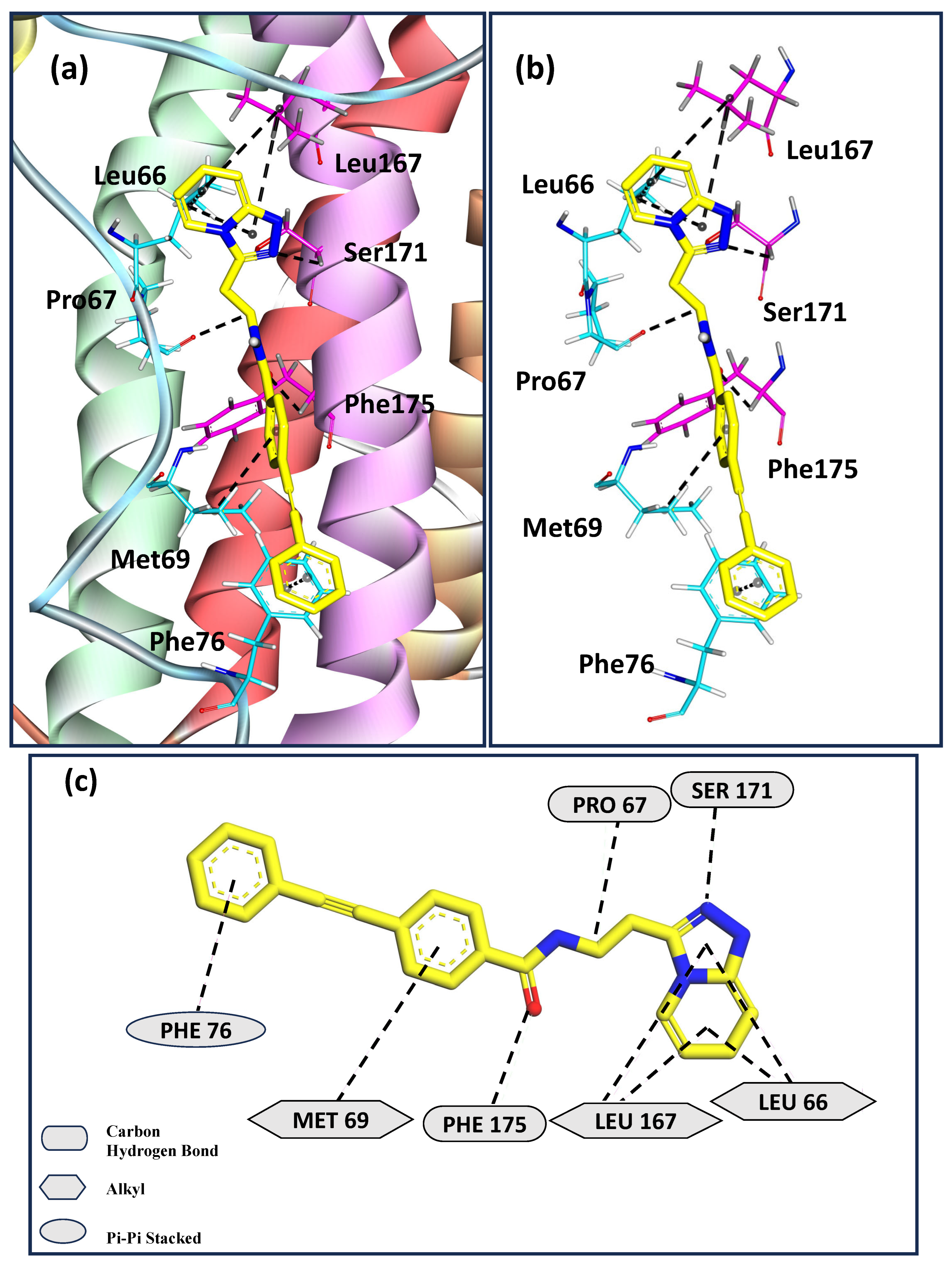
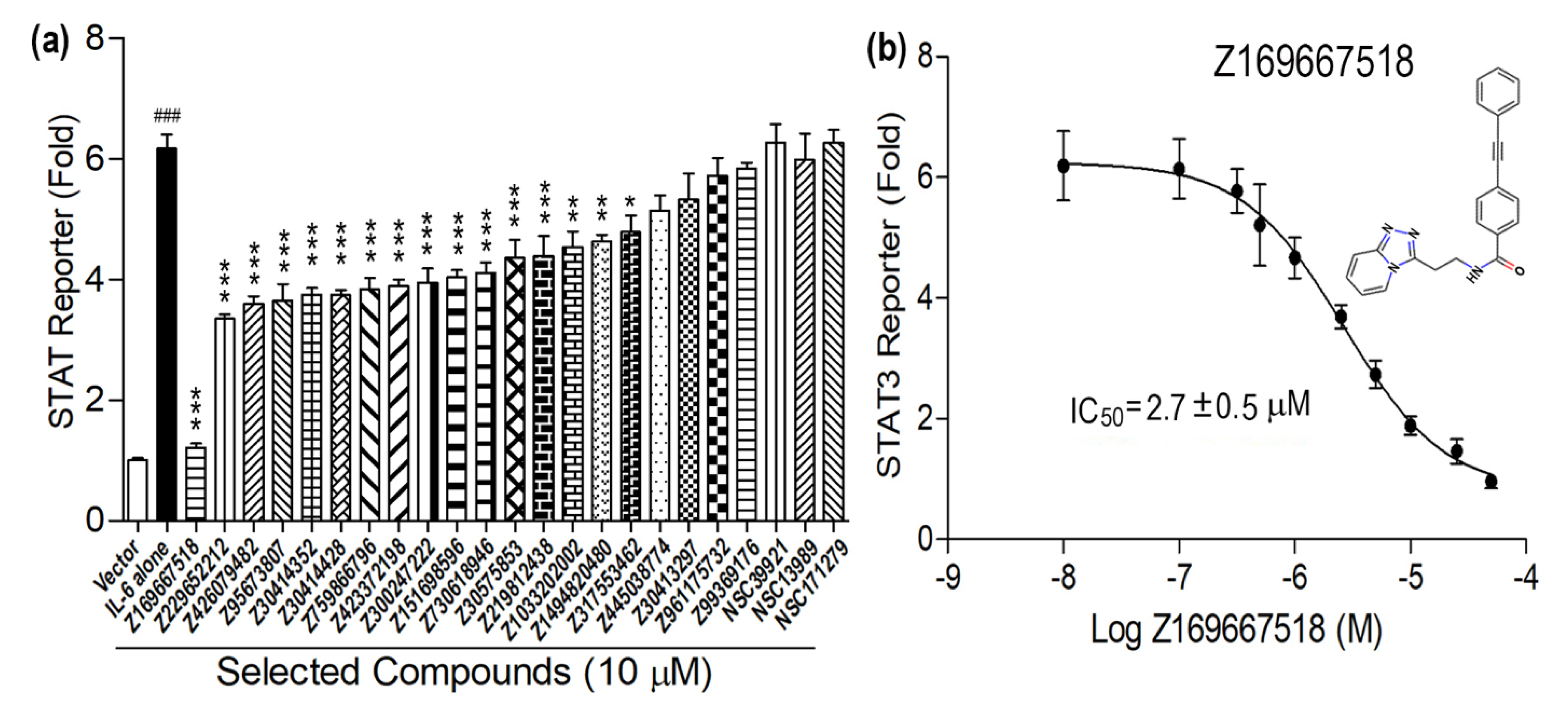
3. Results and Discussion
| Compound ID | Mol. Formula | Mol. Wt. | logP | Net Charge | H-Bond Donors | H-Bond Acceptors | tPSA | Docking Score (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z229652212 | C27H34N4O2 | 446.595 | 4.442 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 77 | −9.150 |
| Z169667518 | C23H18N4O | 366.424 | 3.102 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 59 | −8.881 |
| Z30414428 | C24H30N4O | 390.531 | 4.826 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 59 | −8.840 |
| Z423372198 | C24H24N4O4 | 432.48 | 3.033 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 126 | −8.774 |
| Z30575853 | C22H20F3N3O3S | 463.481 | 4.35 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 78 | −8.711 |
| Z219812438 | C22H15F3N6O2 | 452.396 | 4.19 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 98 | −8.701 |
| Z95673807 | C23H22N4O2 | 386.455 | 4.086 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 69 | −8.627 |
| Z1494820480 | C23H21N5O2 | 399.454 | 3.07 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 81 | −8.618 |
| Z30414352 | C30H29N5O2 | 491.595 | 4.877 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 80 | −8.611 |
| Z730618946 | C26H23F3N4O2 | 480.49 | 4.189 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 75 | −8.582 |
| Z30413297 | C26H27N5O4 | 473.533 | 3.434 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 98 | −8.574 |
| Z99369176 | C21H22N6O3S | 438.513 | 1.502 | - | 1 | 6 | - | −8.287 |
| Z151698596 | C27H26N4O3S | 486.597 | 4.552 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 84 | −8.281 |
| Z759866796 | C24H19FN4O3 | 430.439 | 4.516 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 88 | −8.258 |
| Z317553462 | C22H14F3N5O2 | 437.381 | 4.21 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 92 | −8.238 |
| Z426079482 | C22H20FN3O3S | 425.485 | 3.67 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 82 | −8.208 |
| Z1033202002 | C26H27F2N5O2 | 479.531 | 4.313 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 79 | −7.879 |
| Z961175732 | C17H18N4O | 294.358 | 3.101 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 64 | −7.772 |
| Z300247222 | C18H18BrN3O4S | 452.33 | 2.13 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 95 | −7.331 |
| Z445038774 | C20H14ClFN4O2 | 396.809 | 5.084 | 0 | 2 | 4 | - | −7.280 |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ehlers, M.; Grötzinger, J.; Dehon, F.D.; Müllberg, J.; Brakenhoff, J.P.; Liu, J.; Wollmer, A.; Rose-John, S. Identification of Two Novel Regions of Human IL-6 Responsible for Receptor Binding and Signal Transduction. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taga, T.; Kishimoto, T. Gp130 and the Interleukin-6 Family of Cytokines. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 797–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T.; Akira, S.; Narazaki, M.; Taga, T. Interleukin-6 Family of Cytokines and Gp130. Blood 1995, 86, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Müller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F.; Graeve, L. Interleukin-6-Type Cytokine Signalling through the Gp130/Jak/STAT Pathway. Biochem. J. 1998, 334, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The Pro-and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of the Cytokine Interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.; Fantini, M.C.; Schramm, C.; Lehr, H.A.; Wirtz, S.; Nikolaev, A.; Burg, J.; Strand, S.; Kiesslich, R.; Huber, S.; et al. TGF-Suppresses Tumor Progression in Colon Cancer by Inhibition of IL-6 trans-Signaling. Immunity 2004, 21, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.; Karin, E.; Terzic, J.; Mucida, D.; Yu, G.-Y.; Vallabhapurapu, S.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S.; Cheroutre, H.; Eckmann, L.; et al. IL-6 and Stat3 Are Required for Survival of Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Development of Colitis-Associated Cancer. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Udagawa, N.; Takahashi, N.; Miyaura, C.; Tanaka, S.; Yamada, Y.; Koishihara, Y.; Ohsugi, Y.; Kumaki, K.; Taga, T. Soluble Interleukin-6 Receptor Triggers Osteoclast Formation by Interleukin 6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11924–11928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hénaut, L.; Massy, Z.A. New Insights into the Key Role of Interleukin 6 in Vascular Calcification of Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Matsuda, T.; Turner, M.; Miyasaka, N.; Buchan, G.; Tang, B.; Sato, K.; Shimi, M.; Maid, R.; Feldmann, M.; et al. Excessive Production of Interleukin 6/B Cell Stimulatory Factor-2 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 1988, 18, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonagle, D.; Sharif, K.; O’REgan, A.; Bridgewood, C. The Role of Cytokines Including Interleukin-6 in COVID-19 Induced Pneumonia and Macrophage Activation Syndrome-Like Disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElvaney, O.J.; Curley, G.F.; Rose-John, S.; McElvaney, N.G. Interleukin-6: Obstacles to Targeting a Complex Cytokine in Critical Illness. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorov, A.; Chasnyk, V.; Kostik, M.; Snegireva, L.; Kalashnikova, O.; Dubko, M.; Masalova, V.; Likhacheva, T.; Fedorova, E. Anemia in Children with JIA: Is It Really Driven by Hepcidin Level, or by a Set of Factors of a Chronic Disease. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2014, 12, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, N.; Murakami, M.; Tomiita, M. Tomiita Tocilizumab in the Treatment of Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Open Access Rheumatol. Res. Rev. 2012, 4, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Emery, P.; Keystone, E.; Tony, H.P.; Cantagrel, A.; Van Vollenhoven, R.; Sanchez, A.; Alecock, E.; Lee, J.; Kremer, J. IL-6 Receptor Inhibition with Tocilizumab Improves Treatment Outcomes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Refractory to Anti-Tumour Necrosis Factor Biologicals: Results from a 24-Week Multicentre Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1516–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, S.C.; Choi, J.; Kim, I.; Wu, G.; Toyoda, M.; Shin, B.; Vo, A. Interleukin-6, A Cytokine Critical to Mediation of Inflammation, Autoimmunity and Allograft Rejection. Transplantation 2017, 101, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Bhattacharya, M.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.; Agoramoorthy, G. COVID-19: Consider IL-6 Receptor Antagonist for the Therapy of Cytokine Storm Syndrome in SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patients. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2260–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casper, C.; Chaturvedi, S.; Munshi, N.; Wong, R.; Qi, M.; Schaffer, M.; Bandekar, R.; Hall, B.; Van de Velde, H.; Vermeulen, J.; et al. Analysis of Inflammatory and Anemia-Related Biomarkers in a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of Siltuximab (Anti-IL6 Monoclonal Antibody) in Patients With Multicentric Castleman Disease. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4294–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Babitt, J.L. Hepcidin Regulation in the Anemia of Inflammation. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2016, 23, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancrile, B.; Lim, K.-H.; Counter, C.M. Oncogenic Ras-Induced Secretion of IL6 Is Required for Tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, B.; Wang, B.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Cao, Q.; Zhong, J.; Shieh, M.-J.; Ran, Z.; Tang, T.; et al. Effect of Induction Therapy With Olamkicept vs Placebo on Clinical Response in Patients With Active Ulcerative Colitis. JAMA 2023, 329, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waetzig, G.H.; Chalaris, A.; Rosenstiel, P.; Suthaus, J.; Holland, C.; Karl, N.; Uriarte, L.V.; Till, A.; Scheller, J.; Grötzinger, J.; et al. N-Linked Glycosylation Is Essential for the Stability but Not the Signaling Function of the Interleukin-6 Signal Transducer Glycoprotein 130. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenhumberg, S.; Waetzig, G.H.; Chalaris, A.; Rabe, B.; Seegert, D.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S.; Grötzinger, J. Structure-guided Optimization of the Interleukin-6 Trans-signaling Antagonist sgp130. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 27200–27207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 Biology Is Coordinated by Membrane Bound and Soluble Receptors. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2003, 50, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbers, C.; Thaiss, W.; Jones, G.W.; Waetzig, G.H.; Lorenzen, I.; Guilhot, F.; Lissilaa, R.; Ferlin, W.G.; Grötzinger, J.; Jones, S.A.; et al. Inhibition of Classic Signaling Is a Novel Function of Soluble Glycoprotein 130 (sgp130), Which Is Controlled by the Ratio of Interleukin 6 and Soluble Interleukin 6 Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 42959–42970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jostock, T.; Müllberg, J.; Özbek, S.; Atreya, R.; Blinn, G.; Voltz, N.; Fischer, M.; Neurath, M.F.; Rose-John, S. Soluble Gp130 Is the Natural Inhibitor of Soluble Interleukin-6 Receptor Transsignaling Responses. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Fleischmann, R.; Cohen, S.; Lee, E.B.; Meijide, J.A.G.; Wagner, S.; Forejtova, S.; Zwillich, S.H.; Gruben, D.; Koncz, T.; et al. Tofacitinib or Adalimumab versus Placebo in Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, M.C.; Smolen, J.S.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Burmester, G.R.; Meerwein, S.; Camp, H.S.; Wang, L.; Othman, A.A.; Khan, N.; Pangan, A.L.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of ABT-494, a Selective JAK-1 Inhibitor, in a Phase IIb Study in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and an Inadequate Response to Methotrexate. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2857–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, J.M.; Emery, P.; Camp, H.S.; Friedman, A.; Wang, L.; Othman, A.A.; Khan, N.; Pangan, A.L.; Jungerwirth, S.; Keystone, E.C. A Phase IIb Study of ABT–494, a Selective JAK–1 Inhibitor, in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and an Inadequate Response to Anti–Tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2867–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbert-Roth, A.; Enejosa, J.; Pangan, A.L.; Haraoui, B.; Rischmueller, M.; Khan, N.; Zhang, Y.; Martin, N.; Xavier, R.M. Trial of Upadacitinib or Abatacept in Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-S.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, Y.-H.; Park, K.-Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Gajulapati, V.; Goo, J.-I.; Singh, S.; et al. A Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor Targeting the IL-6 Receptor Subunit, Glycoprotein 130. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaroop, A.K.; Namboori, P.K.K.; Esakkimuthukumar, M.; Praveen, T.K.; Nagarjuna, P.; Patnaik, S.K.; Selvaraj, J. Leveraging Decagonal In-Silico Strategies for Uncovering IL-6 Inhibitors with Precision. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 163, 107231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, D.C.; Pan, L.; Wang, T.; Booker, C.; Hyder, I.; Hanold, L.; Rubin, G.; Ding, Y.; Lin, J.; Li, C. Carbohydrate-Small Molecule Hybrids as Lead Compounds Targeting IL-6 Signaling. Molecules 2023, 28, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinzalla, G.; Haque, M.R.; Basu, B.P.; Anderson, J.; Kaye, S.L.; Haider, S.; Hasan, F.; Antonow, D.; Essex, S.; Rahman, K.M.; et al. A Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of IL-6 Signalling. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 7029–7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Niu, X.; Li, N. Exploring the Natural Chemiome to Target Interleukin-6 Receptor (IL-6R) Cytokines: An Atomic Scale Investigation for Novel Rheumatoid Arthritis Drug Discovery. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizaki, K.; Matsuda, T.; Nishimoto, N.; Kuritani, T.; Taeho, L.; Aozasa, K.; Nakahata, T.; Kawai, H.; Tagoh, H.; Komori, T. Pathogenic Significance of Interleukin-6 (IL-6/BSF-2) in Castleman’s Disease. Blood 1989, 74, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Fincheira, P.; Sanhueza-Olivares, F.; Norambuena-Soto, I.; Cancino-Arenas, N.; Hernandez-Vargas, F.; Troncoso, R.; Gabrielli, L.; Chiong, M. Role of Interleukin-6 in Vascular Health and Disease. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 641734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T. IL-6 in Inflammation, Autoimmunity and Cancer. Int. Immunol. 2020, 33, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shun, T.Y.; Lazo, J.S.; Sharlow, E.R.; Johnston, P.A. Identifying Actives from HTS Data Sets: Practical Approaches for the Selection of an Appropriate HTS Data-Processing Method and Quality Control Review. Slas Discov. Adv. Sci. Drug Discov. 2011, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Ha, K.; Agarwal, R.; Quarles, L.D.; Smith, J.C. Molecular dynamics analysis of the binding of human interleukin-6 with interleukin-6-receptor. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2020, 89, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qiao, C.; Xiao, H.; Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shen, B.; Fu, T.; Feng, J. Structure-Based Virtual Screening and Characterization of a Novel IL-6 Antagonistic Compound from Synthetic Compound Database. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 4091–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, Q.-H.; Nguyen, Q.-T.; Vo, N.-Q.-H.; Mai, T.T.; Tran, T.-T.-N.; Tran, T.-D.; Le, M.-T.; Trinh, D.-T.T.; Thai, K.-M. Structure-Based 3D-Pharmacophore Modeling to Discover Novel Interleukin 6 Inhibitors: An in Silico Screening, Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Binding Free Energy Calculations. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, H.; Sivaraman, A.; Lu, Q.; Min, K.; Kim, S.; Goo, J.-I.; Choi, Y.; Lee, K. Perspective for Discovery of Small Molecule IL–6 Inhibitors through Study of Structure–Activity Relationships and Molecular Docking. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 4417–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcon, W.E.; Ellingson, S.R.; Smith, J.C.; Baudry, J.Y. Ensemble Docking in Drug Discovery: How Many Protein Configurations from Molecular Dynamics Simulations are Needed To Reproduce Known Ligand Binding? J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 5189–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, R.E.; Baudry, J.; Chodera, J.; Demir, Z.; McCammon, J.A.; Miao, Y.; Smith, J.C. Ensemble Docking in Drug Discovery. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 2271–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, A.; Agarwal, R.; Baker, M.B.; Baudry, J.; Bhowmik, D.; Boehm, S.; Byler, K.G.; Chen, S.Y.; Coates, L.; Cooper, C.J.; et al. Supercomputer-Based Ensemble Docking Drug Discovery Pipeline with Application to COVID-19. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 5832–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Bensing, B.A.; Mi, D.; Vinson, P.N.; Baudry, J.; Iverson, T.M.; Smith, J.C. Structure Based Virtual Screening Identifies Small Molecule Effectors for the Sialoglycan Binding Protein Hsa. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 3695–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.C.; Shah, K.S.; Lechowicz, M.J. Clinical Development of Siltuximab. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, W.; Stahl, M.; Seehra, J.S. 9 Acrystal structure of interleukin 6: Implications for a novel mode of receptor dimerization and signaling. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, M.J.; Chow, D.-C.; Brevnova, E.E.; Garcia, K.C. Hexameric Structure and Assembly of the Interleukin-6/IL-6-Receptor/gp130 Complex. Science 2003, 300, 2101–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; DiMaio, F.; Wang, R.Y.-R.; Kim, D.; Miles, C.; Brunette, T.; Thompson, J.; Baker, D. High-Resolution Comparative Modeling with RosettaCM. Structure 2013, 21, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of Simple Potential Functions for Simulating Liquid Water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A Web-Based Graphical User Interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kalé, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable Molecular Dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; MacKerell, A.D. CHARMM36 All-Atom Additive Protein Force Field: Validation Based on Comparison to NMR Data. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, S.E.; Zhang, Y.; Pastor, R.W.; Brooks, B.R. Constant Pressure Molecular Dynamics Simulation: The Langevin Piston Method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 4613–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An Nlog(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckaert, J.-P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H.J.C. Numerical Integration of the Cartesian Equations of Motion of a System with Constraints: Molecular Dynamics of n-Alkanes. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnell, S.J.; Page, D.; Mitchell, J.C. An Automated Decision-Tree Approach to Predicting Protein Interaction Hot Spots. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2007, 68, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Mitchell, J.C. KFC2: A Knowledge-Based Hot Spot Prediction Method Based on Interface Solvation, Atomic Density, and Plasticity Features. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2011, 79, 2671–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leebeek, F.W.; Kariya, K.; Schwabe, M.; Fowlkes, D.M. Identification of a Receptor Binding Site in the Carboxyl Terminus of Human Interleukin-6. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 14832–14838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, V.; Savino, R.; Arcone, R.; De Wit, L.; Brakenhoff, J.P.J.; Content, J.; Ciliberto, G. Involvement of the Arg179 in the Active Site of Human IL-6. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 211, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütticken, C.; Krüttgen, A.; Möller, C.; Heinrich, P.C.; Rose-John, S. Evidence for the importance of a positive charge and an α-helical structure of the C-terminus for biological activity of human IL-6. FEBS Lett. 1991, 282, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüttgen, A.; Rose-John, S.; Möller, C.; Wroblowski, B.; Wollmer, A.; Müllberg, J.; Hirano, T.; Kishimoto, T.; Heinrich, P.C. Structure-Function Analysis of Human Interleukin-6. FEBS Lett. 1990, 262, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High Performance Molecular Simulations through Multi-Level Parallelism from Laptops to Supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingson, S.R.; Smith, J.C.; Baudry, J. VinaMPI: Facilitating Multiple Receptor High-Throughput Virtual Docking on High-Performance Computers. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2212–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, J.H.; Bienfait, B.; Wang, S.; Nicklaus, M.C. Comparison of the NCI Open Database with Seven Large Chemical Structural Databases. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2001, 41, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enamine Discovery Diversity Set. Available online: https://enamine.net/compound-libraries/diversity-libraries/dds-50240 (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Enamine PPI Library. Available online: https://enamine.net/compound-libraries/targeted-libraries/ppi-library (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Novick, P.A.; Ortiz, O.F.; Poelman, J.; Abdulhay, A.Y.; Pande, V.S. SWEETLEAD: An In Silico Database of Approved Drugs, Regulated Chemicals, and Herbal Isolates for Computer-Aided Drug Discovery. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanner, M.F. Python: A Programming Language for Software Integration and Development. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 1999, 17, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- O’BOyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An Open Chemical Toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagorce, D.; Bouslama, L.; Becot, J.; Miteva, M.A.; Villoutreix, B.O. FAF-Drugs4: Free ADME-Tox Filtering Computations for Chemical Biology and Early Stages Drug Discovery. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3658–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, D.M.; Agarwal, R.; Vermaas, J.V.; Smith, M.D.; Rajeshwar, R.T.; Cooper, C.; Sedova, A.; Boehm, S.; Baker, M.; Glaser, J.; et al. SARS-CoV2 Billion-Compound Docking. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like Properties and the Causes of Poor Solubility and Poor Permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Estimate Solubility and Permeability in Drug Discovery and Development Settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeson, P.D.; Bento, A.P.; Gaulton, A.; Hersey, A.; Manners, E.J.; Radoux, C.J.; Leach, A.R. Target-Based Evaluation of Drug-Like Properties and Ligand Efficiencies. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 7210–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A. Lead-and Drug-like Compounds: The Rule-of-Five Revolution. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2004, 1, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doak, B.C.; Kihlberg, J. Drug discovery beyond the rule of 5—Opportunities and challenges. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2016, 12, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, T.I. Property distribution of drug-related chemical databases*. J. Comput. Mol. Des. 2000, 14, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verboogen, D.R.J.; Revelo, N.H.; Beest, M.T.; Van Den Bogaart, G. Interleukin-6 Secretion Is Limited by Self-Signaling in Endosomes. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 11, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barillé, S.; Bataille, R.; Amiot, M. The Role of Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-6/Interleukin-6 Receptor-Alpha Complex in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Myeloma. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2000, 11, 546–551. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Vandenbriele, C.; Kauskot, A.; Verhamme, P.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Wright, G.J. A Human Platelet Receptor Protein Microarray Identifies FcepsilonR1alpha as an Activating PEAR1 Ligand. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2015, 14, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeg, G.-H.; Zhou, R.; Perrimon, N. Genome-Wide RNAi Analysis of JAK/STAT Signaling Components in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.-H.; Petridis, L.; Cai, C.; Cao, L.; Wang, G.; Chin, A.L.; Cleveland, J.W.; Ikedionwu, M.O.; et al. Novel Small Molecule Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Inhibitors Increase Serum Phosphate and Improve Skeletal Abnormalities in Hyp Mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 2022, 101, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, S.; Trievel, R.C. Carbon-Oxygen Hydrogen Bonding in Biological Structure and Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 41576–41582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, J.J.; Tang, K.G.; Young, J.; Dandarchuluun, C.; Wong, B.R.; Khurelbaatar, M.; Moroz, Y.S.; Mayfield, J.; Sayle, R.A. ZINC20A Free Ultralarge-Scale Chemical Database for Ligand Discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 6065–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, K.; Nur-E-Alam, M.; Ahmad, A.; Ul-Haq, Z. Taming the cytokine storm: Small molecule inhibitors targeting IL-6/IL-6 receptor. Mol. Divers. 2024, 28, 4151–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, Q.-H.; Nguyen, Q.-T.; Tran, T.-T.N.; Tran, T.-D.; Le, M.-T.; Trinh, D.-T.T.; Tran, V.-T.; Tran, V.-H.; Thai, K.-M. Identification of Small Molecules as Potential Inhibitors of Interleukin 6: A Multi-Computational Investigation. Mol. Divers. 2022, 27, 2315–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapriniotis, K.; Lampridis, S.; Mitsos, S.; Patrini, D.; Lawrence, D.R.; Panagiotopoulos, N. Biologic Agents in the Treatment of Multicentric Castleman Disease. Turk. Thorac. J. 2018, 19, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imazio, M.; Lazaros, G.; Gattorno, M.; LeWinter, M.; Abbate, A.; Brucato, A.; Klein, A. Anti-Interleukin-1 Agents for Pericarditis: A Primer for Cardiologists. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 43, 2946–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compound ID | Mol. Formula | Mol. Wt. | logP | Net Charge | H-Bond Donors | H-Bond Acceptors | tPSA | Docking Score (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSC39921 | C43H43N3O6S2 | 762.0 | 6.3 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 192.9 | −11.1 |
| NSC13989 | C34H18O2 | 458.5 | 8.8 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 34.1 | −10.6 |
| NSC171279 | C30H30 | 390.6 | 7.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −10.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joshi, A.; Xiao, Z.; Suman, S.; Cooper, C.; Ha, K.; Carson, J.A.; Quarles, L.D.; Smith, J.C.; Gupta, M. Structure-Based Design of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Human Interleukin-6. Molecules 2025, 30, 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142919
Joshi A, Xiao Z, Suman S, Cooper C, Ha K, Carson JA, Quarles LD, Smith JC, Gupta M. Structure-Based Design of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Human Interleukin-6. Molecules. 2025; 30(14):2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142919
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoshi, Ankit, Zhousheng Xiao, Shreya Suman, Connor Cooper, Khanh Ha, James A. Carson, Leigh Darryl Quarles, Jeremy C. Smith, and Madhulika Gupta. 2025. "Structure-Based Design of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Human Interleukin-6" Molecules 30, no. 14: 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142919
APA StyleJoshi, A., Xiao, Z., Suman, S., Cooper, C., Ha, K., Carson, J. A., Quarles, L. D., Smith, J. C., & Gupta, M. (2025). Structure-Based Design of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Human Interleukin-6. Molecules, 30(14), 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142919








