Structural and Quantitative Analysis of Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Para-Phenylenediamines (PPDs) by Direct Analysis in Real Time Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry (DART-IM-MS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
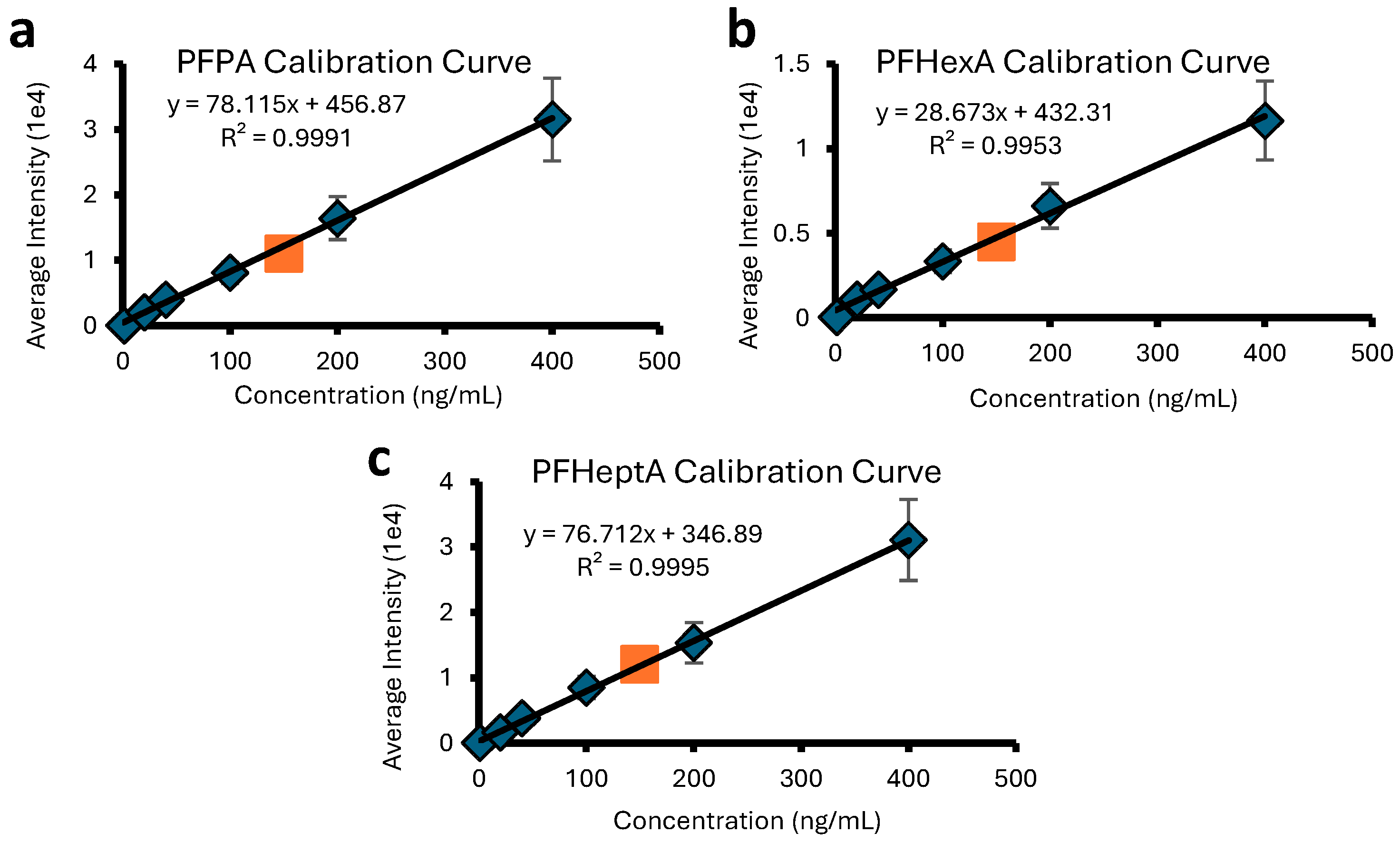
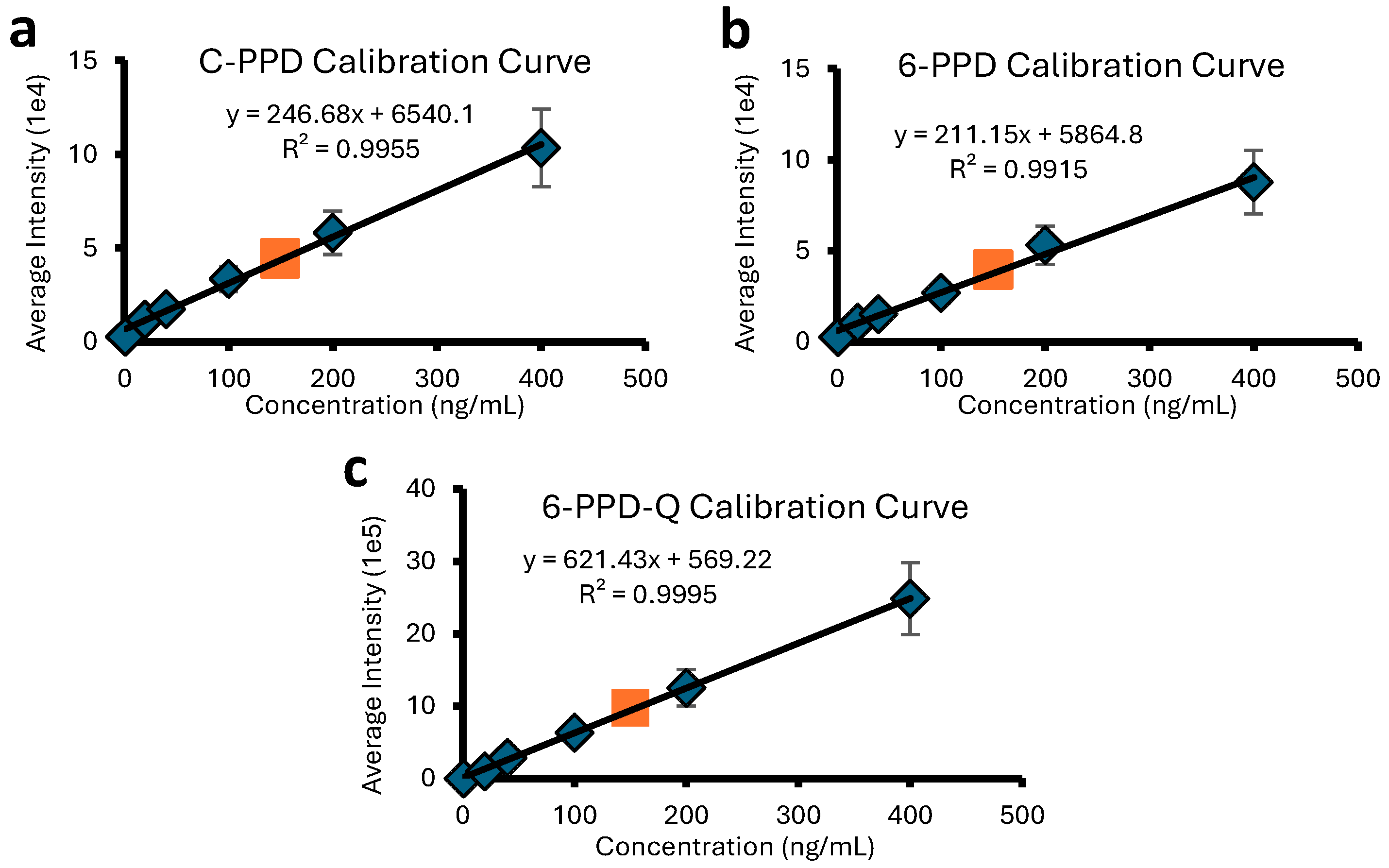
2.1. DART Quantitation of PFASs and PPDs
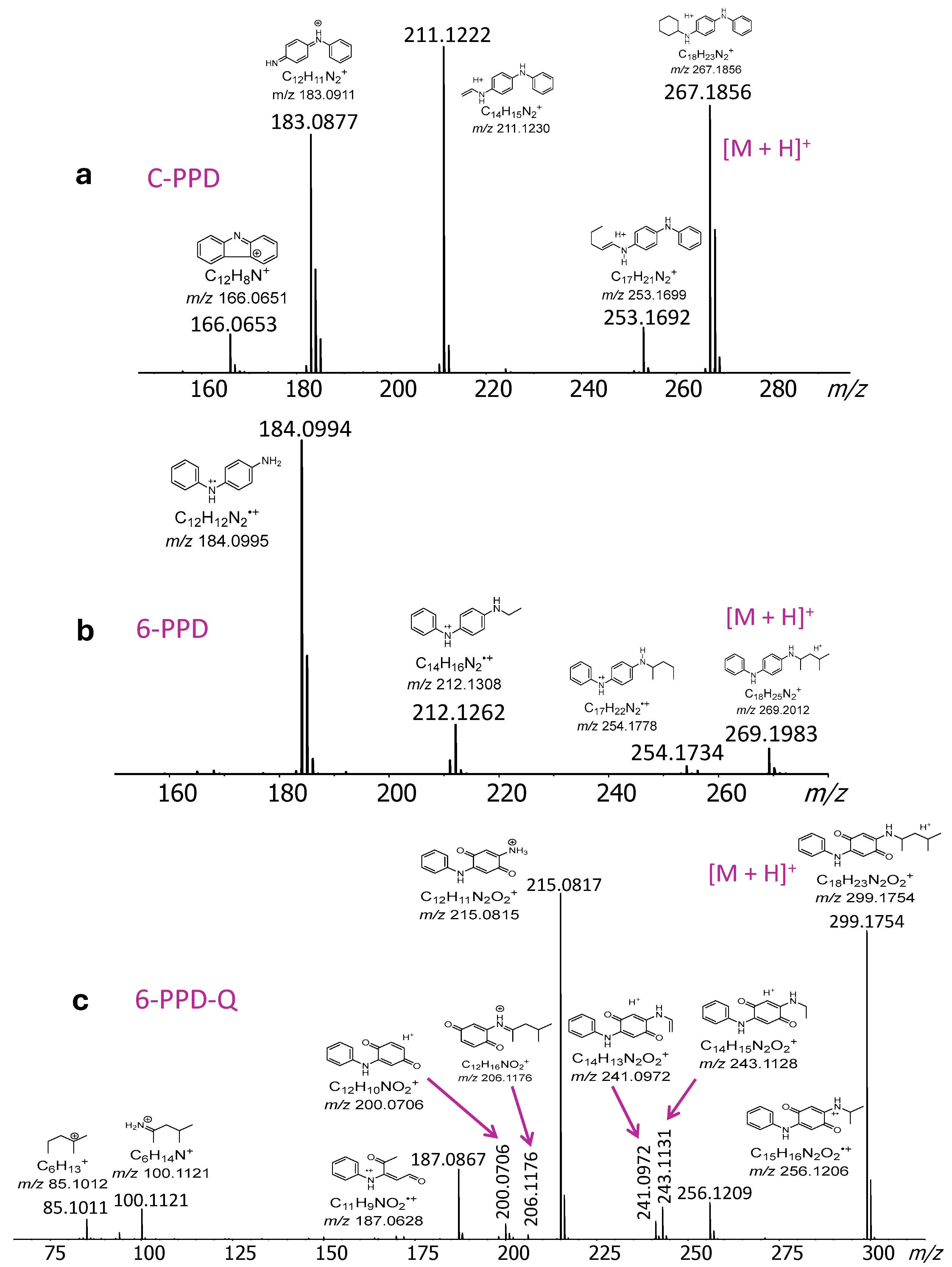
2.2. DART-MS/MS Analysis of PFASs and PPDs
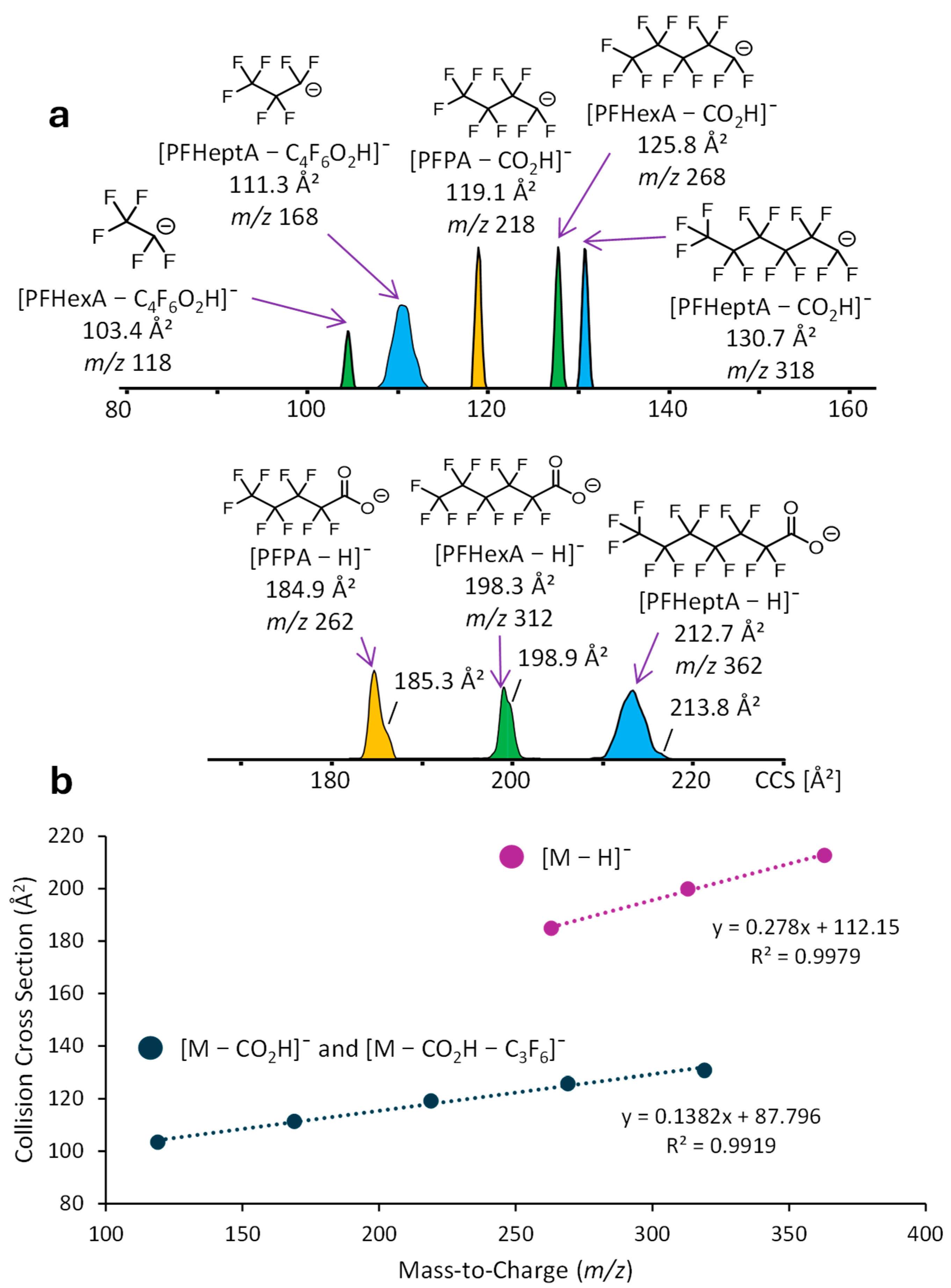
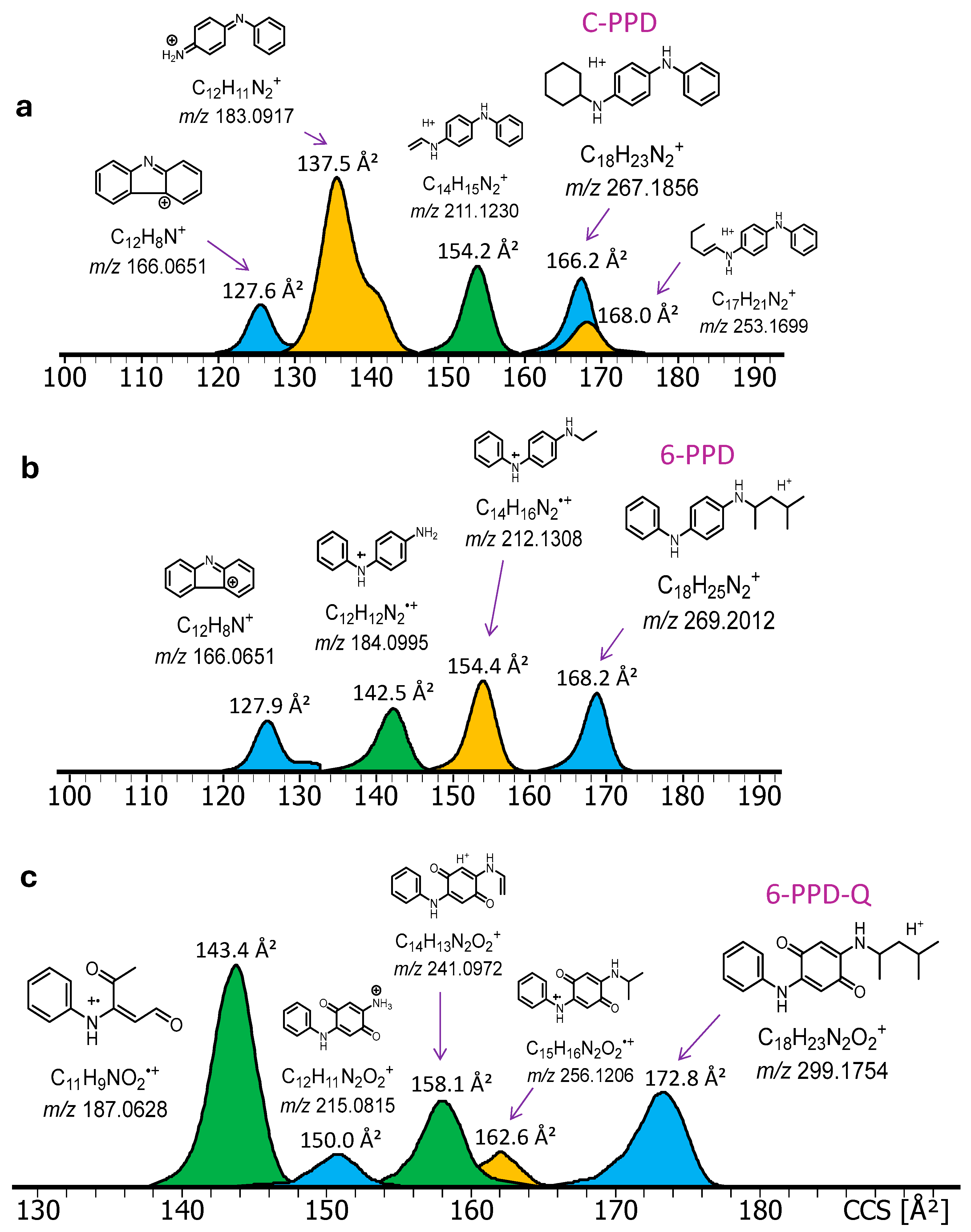
2.3. DART-IM-MS Analysis of PFAS and PPDs
2.4. DART-IM-MS Analysis of 6-PPD in Tire Treads
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of PFAS and PPD Samples and Internal Standards
3.3. Instrumentation and Software
3.3.1. Mass Spectrometer
3.3.2. DART Ionization Source Parameters
3.3.3. Data Processing and Analysis Software
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Buser, A.M.; Cousins, I.T.; Demattio, S.; Drost, W.; Johansson, O.; Ohno, K.; Patlewicz, G.; Richard, A.M.; Walker, G.W.; et al. A New OECD Definition for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15575–15578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, M.E.; Schaefer, C.; Richards, T.; Backe, W.J.; Field, J.A.; Houtz, E.; Sedlak, D.L.; Guelfo, J.L.; Wunsch, A.; Higgins, C.P. Evidence of Remediation-Induced Alteration of Subsurface Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substance Distribution at a Former Firefighter Training Area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6644–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.F.; Peldszus, S.; Anderson, W.B. Behaviour and Fate of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Drinking Water Treatment: A Review. Water Res. 2014, 50, 318–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strynar, M.; McCord, J.; Newton, S.; Washington, J.; Barzen-Hanson, K.; Trier, X.; Liu, Y.; Dimzon, I.K.; Bugsel, B.; Zwiener, C.; et al. Practical Application Guide for the Discovery of Novel PFAS in Environmental Samples Using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 33, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesy, J.P.; Kannan, K. Global Distribution of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate in Wildlife. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boiteux, V.; Dauchy, X.; Rosin, C.; Boiteux, J.F.V. National Screening Study on 10 Perfluorinated Compounds in Raw and Treated Tap Water in France. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 63, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Marques Dos Santos, M.; Li, C.; Snyder, S.A. Recent Advances in Mass Spectrometry Analytical Techniques for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 2795–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, I.T.; Dewitt, J.C.; Glüge, J.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Scheringer, M.; Wang, Z. The High Persistence of PFAS Is Sufficient for Their Management as a Chemical Class. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.H.; Yang, W.J.; Lv, S.H.; Zhu, T.T.; Adeel Sharif, H.M.; Yang, C.; Du, J.; Lin, H. Is HFPO-DA (GenX) a Suitable Substitute for PFOA? A Comprehensive Degradation Comparison of PFOA and GenX via Electrooxidation. Environ. Res. 2022, 204 Pt A, 111995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, D.F.; Belisle, J.; Johnson, J.D.; Venkateswarlu, P. Characterization of Fluorinated Metabolites by a Gas Chromatographic-Helium Microwave Plasma Detector-The Biotransformation of 1H,1H,2H,2H-Perfluorodecanol to Perfluorooctanoate. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 118, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Kuroda, K.; Sato, N.; Fukushi, T.; Takizawa, S.; Takada, H. Groundwater Pollution by Perfluorinated Surfactants in Tokyo. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3480–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L. Polyfluoroalkyl Compounds in the Aquatic Environment: A Review of Their Occurrence and Fate. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, N.L.; Lau, F.K.; Ellis, D.A.; Martin, J.W.; Muir, D.C.G.; Mabury, S.A. Polyfluorinated Telomer Alcohols and Sulfonamides in the North American Troposphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoeib, M.; Harner, T.; Ikonomou, M.; Kannan, K. Indoor and Outdoor Air Concentrations and Phase Partitioning of Perfluoroalkyl Sulfonamides and Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Deon, J.; Mabury, S.A. Biodegradation of Polyfluoroalkyl Phosphates as a Source of Perfluorinated Acids to the Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3305–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.T.; Adami, H.O.; Boffetta, P.; Wedner, H.J.; Mandel, J.S. A Critical Review of Perfluorooctanoate and Perfluorooctanesulfonate Exposure and Immunological Health Conditions in Humans. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2016, 46, 279–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Zhao, L.; Winquist, A.; Parks, C. Ulcerative Colitis and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in a Highly Exposed Population of Community Residents and Workers in the Mid-Ohio Valley. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsley, S.L.; Walker, D.I.; Calafat, A.M.; Chen, A.; Papandonatos, G.D.; Xu, Y.; Jones, D.P.; Lanphear, B.P.; Pennell, K.D.; Braun, J.M. Metabolomics of Childhood Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances: A Cross-Sectional Study. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, V.; Winquist, A.; Steenland, K. Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) Exposures and Incident Cancers among Adults Living near a Chemical Plant. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health-based Guidance Values for PFAS for Use in Site Investigations in Australia. Available online: https://www.health.gov.au/resources/publications/health-based-guidance-values-for-pfas-for-use-in-site-investigations-in-australia?language=en (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Ahmed, E.; Mohibul Kabir, K.M.; Wang, H.; Xiao, D.; Fletcher, J.; Donald, W.A. Rapid Separation of Isomeric Perfluoroalkyl Substances by High-Resolution Differential Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1058, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotad, P.S.; Bochenek, C.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Jana, S.C. Separation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid from Water Using Meso- and Macroporous Syndiotactic Polystyrene Gels. Langmuir 2024, 40, 10208–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Li, J.; Wan, X.; Ge, Y.; Liang, G.; Zhou, Y. P-Phenylenediamine Antioxidants and Their Quinone Derivatives: A Review of Their Environmental Occurrence, Accessibility, Potential Toxicity, and Human Exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, D.; Duan, X.; Zhong, L. Exposure to N-(1,3-Dimethylbutyl)-N′-Phenyl-p-Phenylenediamine (6PPD) Affects the Growth and Development of Zebrafish Embryos/Larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Wang, D. Exposure to 6-PPD Quinone at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations Inhibits Both Lifespan and Healthspan in C. Elegans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 19295–19303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhang, F.; Qu, G.; Cai, Z. Toxicity of Substituted P-Phenylenediamine Antioxidants and Their Derived Novel Quinones on Aquatic Bacterium: Acute Effects and Mechanistic Insights. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, L.J.; Parker-Jurd, F.N.F.; Al-Sid-Cheikh, M.; Thompson, R.C. Tyre Wear Particles: An Abundant yet Widely Unreported Microplastic? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18345–18354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Wu, W.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, X.; Ma, J.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, G. Responses of Soil and Collembolan (Folsomia Candida) Gut Microbiomes to 6PPD-Q Pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; Fischer, K. Oxidative Transformation Processes and Products of Para-Phenylenediamine (PPD) and Para-Toluenediamine (PTD)—A Review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2015, 27, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.; Mama, J.; Hawkes, J. A Review of Aspects of Oxidative Hair Dye Chemistry with Special Reference to N-Nitrosamine Formation. Materials 2013, 6, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Chang, J.; Croué, J.P.; Zhang, T. Transformation of 6PPDQ during Disinfection: Kinetics, Products, and Eco-Toxicity Assessment. Water Res. 2024, 250, 121070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, S.F.; Yoshikane, M.; Onoda, Y.; Nishihama, Y.; Iwai-Shimada, M.; Takagi, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Isobe, T. Worldwide Trends in Tracing Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in the Environment. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2019, 121, 115410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Niu, H.; Pan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Cai, Y. Chitosan-Coated Octadecyl-Functionalized Magnetite Nanoparticles: Preparation and Application in Extraction of Trace Pollutants from Environmental Water Samples. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Amin, M.; Sobhani, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dharmaraja, R.; Chadalavada, S.; Naidu, R.; Chalker, J.M.; Fang, C. Recent Advances in the Analysis of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)—A Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okaru, A.O.; Brunner, T.S.; Ackermann, S.M.; Kuballa, T.; Walch, S.G.; Kohl-Himmelseher, M.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Application of 19F NMR Spectroscopy for Content Determination of Fluorinated Pharmaceuticals. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2017, 2017, 9206297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boča, M.; Barborík, P.; Mičušík, M.; Omastová, M. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy as Detection Tool for Coordinated or Uncoordinated Fluorine Atoms Demonstrated on Fluoride Systems NaF, K2TaF7, K3TaF8, K2ZrF6, NaZr6F31 and K3ZrF7. Solid State Sci. 2012, 14, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cao, G.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, H.; Wang, F.; Cai, Z. Recent Applications of Mass Spectrometry in the Analysis of transformation Products of Emerging Contaminants in PM2.5. Anal. Sci. Adv. 2023, 4, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viehland, L.A.; Mason, E.A. Gaseous Ion Mobility in Electric Fields of Arbitrary Strength. Ann. Phys. 1975, 91, 499–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, J.N.; Baker, E.S. Ion Mobility Spectrometry: Fundamental Concepts, Instrumentation, Applications, and the Road Ahead. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 30, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, J.A.; Ridgeway, M.E.; Park, M.A. High Resolution Trapped Ion Mobility Spectrometry of Peptides. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5624–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cody, R.; Maleknia, S.D. Coated Glass Capillaries as SPME Devices for DART Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 34, e8946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmons, R.V.; Fatigante, W.; Olomukoro, A.A.; Musselman, B.; Gionfriddo, E. Rapid Screening and Quantification of PFAS Enabled by SPME-DART-MS. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 34, 1890–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borotto, N.B.; Graham, K.A. Fragmentation and Mobility Separation of Peptide and Protein Ions in a Trapped-Ion Mobility Device. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 9959–9964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borotto, N.B.; Osho, K.E.; Richards, T.K.; Graham, K.A. Collision-Induced Unfolding of Native-like Protein Ions Within a Trapped Ion Mobility Spectrometry Device. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 33, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunn, C.W.; Howells, E.R. Structures of Molecules and Crystals of Fluorocarbons. Nature 1954, 174, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.S.; Blanco, M.; Goddard, W.A.; Caldwell, G.; Ross, R.B. The Source of Helicity in Perfluorinated N-Alkanes. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 5331–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, W.G.; Brown, E.M.; Solem, S.F.; Zoellner, R.W. Complete Conformational Analyses of Perfluoro-n-Pentane, Perfluoro-n-Hexane, and Perfluoro-n-Heptane. J. Mol. Struct. Theochem 2008, 867, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.; Nova, D.; Teixeira, M.; Cardoso, V.; Morgado, P.; Nunes, B.; Colaço, R.; Faurém, M.-C.; Fontaine, P.; Goldmann, M.; et al. Langmuir Films of Perfluorinated Fatty Alcohols: Evidence of Spontaneous Formation of Solid Aggregates at Zero Surface Pressure and Very Low Surface Density. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravin, C.; Mazzeo, G.; Abbate, S.; Licini, G.; Longhi, G.; Zonta, C. Helicity Control of a Perfluorinated Carbon Chain Within a Chiral Supramolecular Cage Monitored by VCD. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 2152–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palenčár, P.; Bleha, T. Gas-Phase Compaction of Helical Polymers. Polymer 2013, 54, 4955–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Department of Toxic Substances Control. Product—Chemical Profile for Motor Vehicle Tires Containing N-(1,3-Dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine (6PPD). March 2022. Available online: https://dtsc.ca.gov/wp-content/uploads/sites/31/2022/05/6PPD-in-Tires-Priority-Product-Profile_FINAL-VERSION_accessible.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Gabelica, V.; Shvartsburg, A.A.; Afonso, C.; Barran, P.; Benesch, J.L.P.; Bleiholder, C.; Bowers, M.T.; Bilbao, A.; Bush, M.F.; Campbell, J.L.; et al. Recommendations for Reporting Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry Measurements. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2019, 38, 291–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
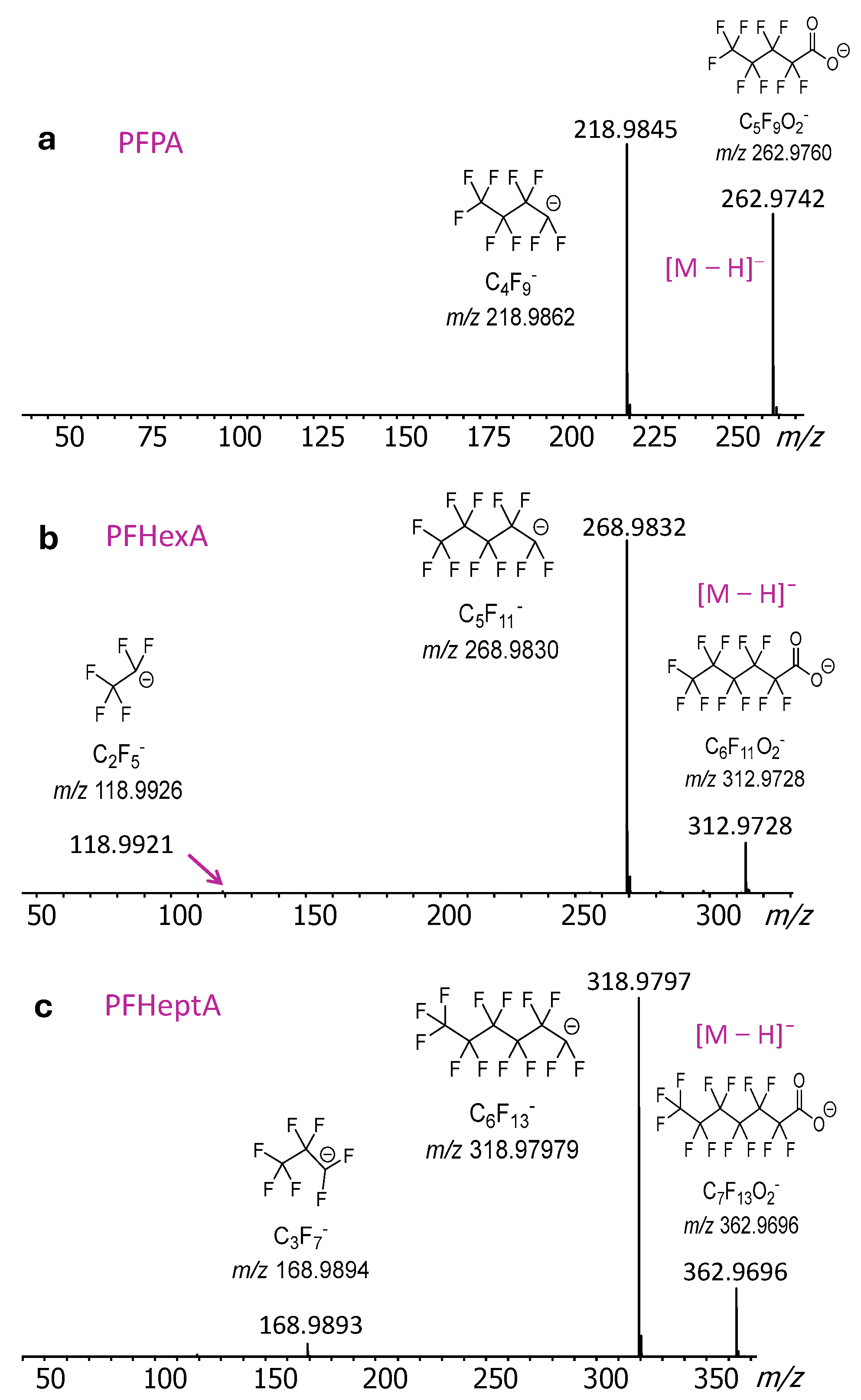
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bochenek, C.; Edwards, J.; Liu, Z.; Wesdemiotis, C. Structural and Quantitative Analysis of Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Para-Phenylenediamines (PPDs) by Direct Analysis in Real Time Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry (DART-IM-MS). Molecules 2025, 30, 2828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132828
Bochenek C, Edwards J, Liu Z, Wesdemiotis C. Structural and Quantitative Analysis of Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Para-Phenylenediamines (PPDs) by Direct Analysis in Real Time Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry (DART-IM-MS). Molecules. 2025; 30(13):2828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132828
Chicago/Turabian StyleBochenek, Calum, Jack Edwards, Zhibo Liu, and Chrys Wesdemiotis. 2025. "Structural and Quantitative Analysis of Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Para-Phenylenediamines (PPDs) by Direct Analysis in Real Time Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry (DART-IM-MS)" Molecules 30, no. 13: 2828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132828
APA StyleBochenek, C., Edwards, J., Liu, Z., & Wesdemiotis, C. (2025). Structural and Quantitative Analysis of Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Para-Phenylenediamines (PPDs) by Direct Analysis in Real Time Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry (DART-IM-MS). Molecules, 30(13), 2828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132828






