Triazine Calixarene as a Dual-Channel Chemosensor for the Reversible Detection of Cu2+ and I− Ions via Water Content Modulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
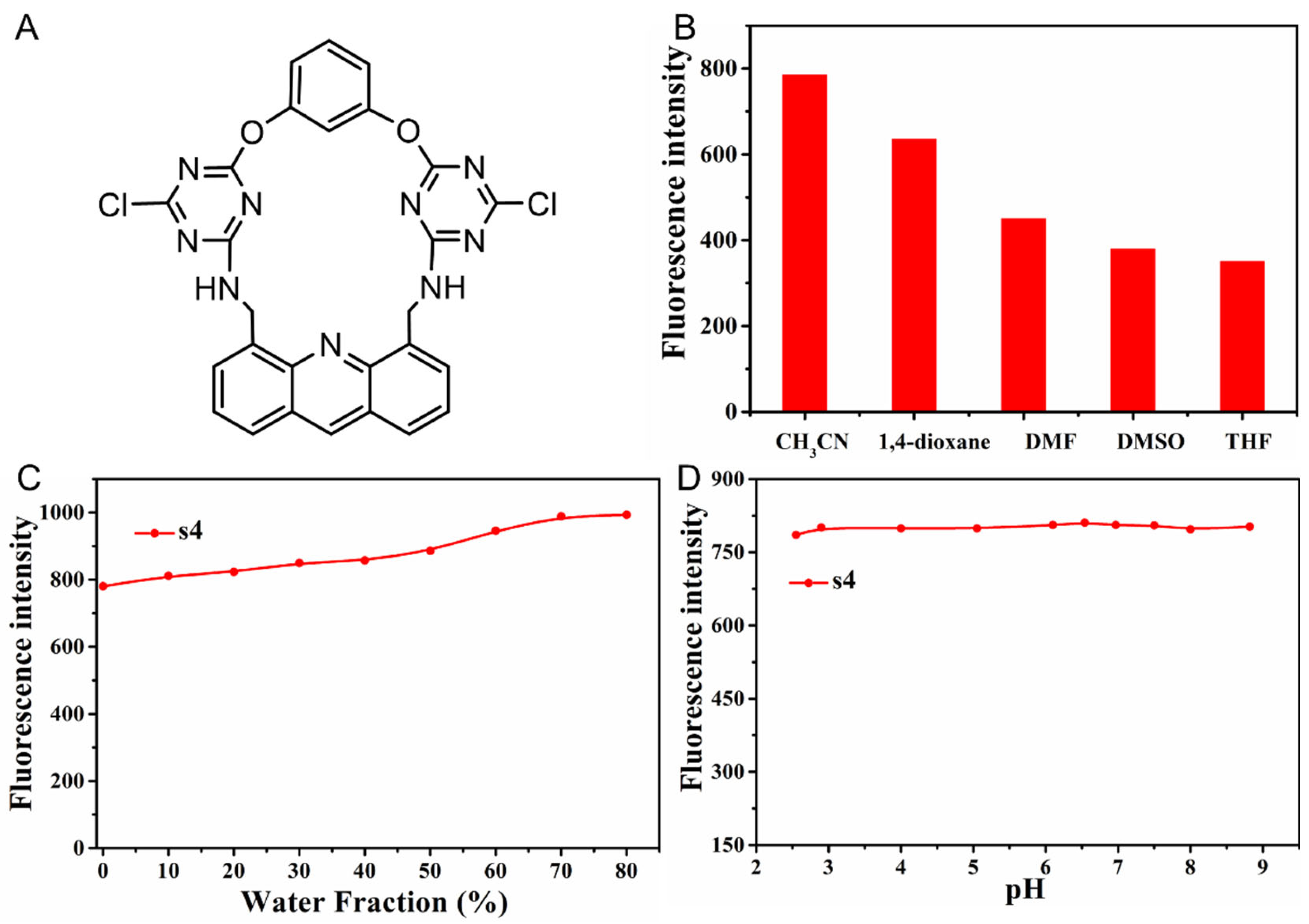
2.1. The Solvent Effects of Fluorescent Probe s4
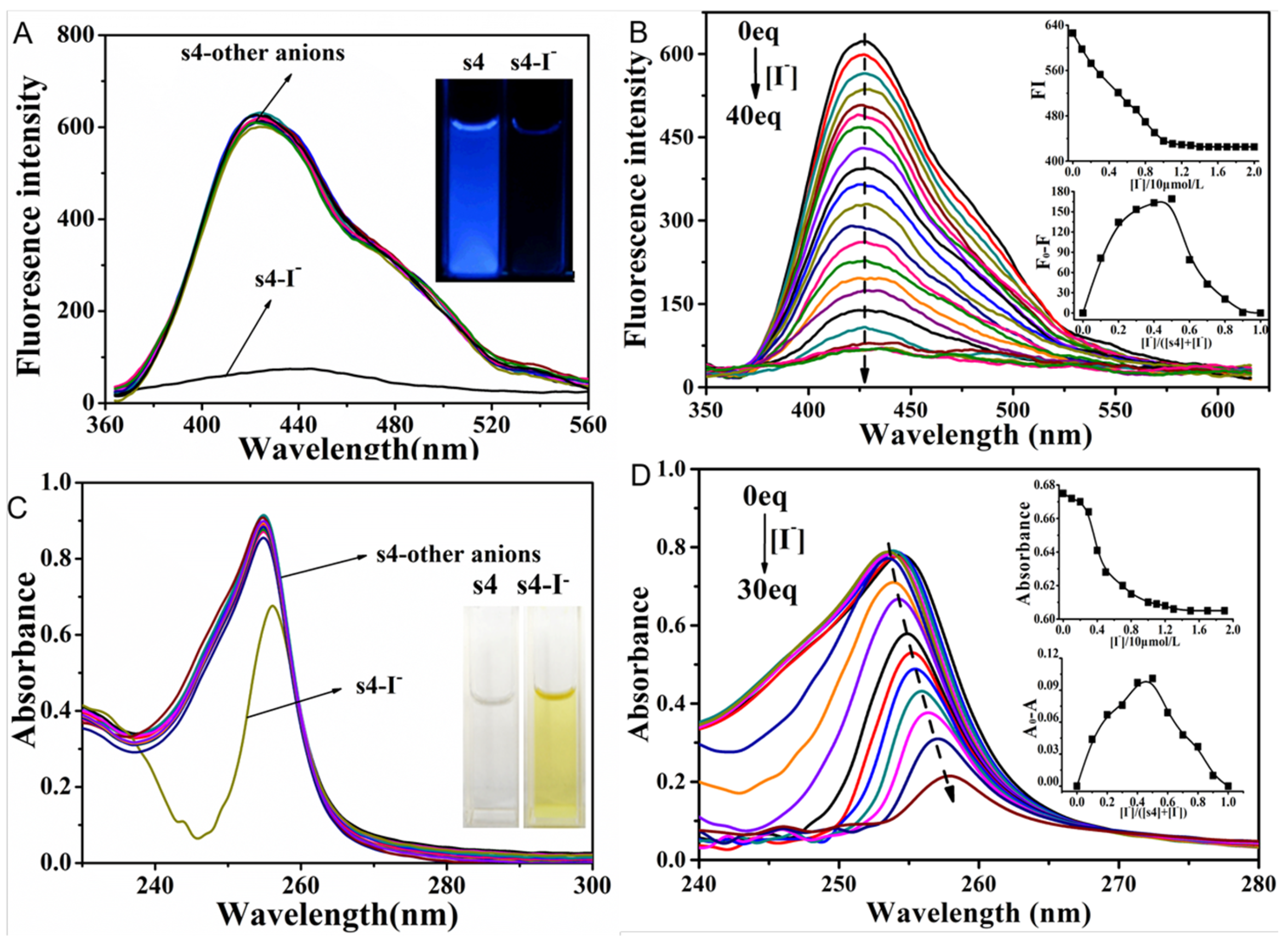
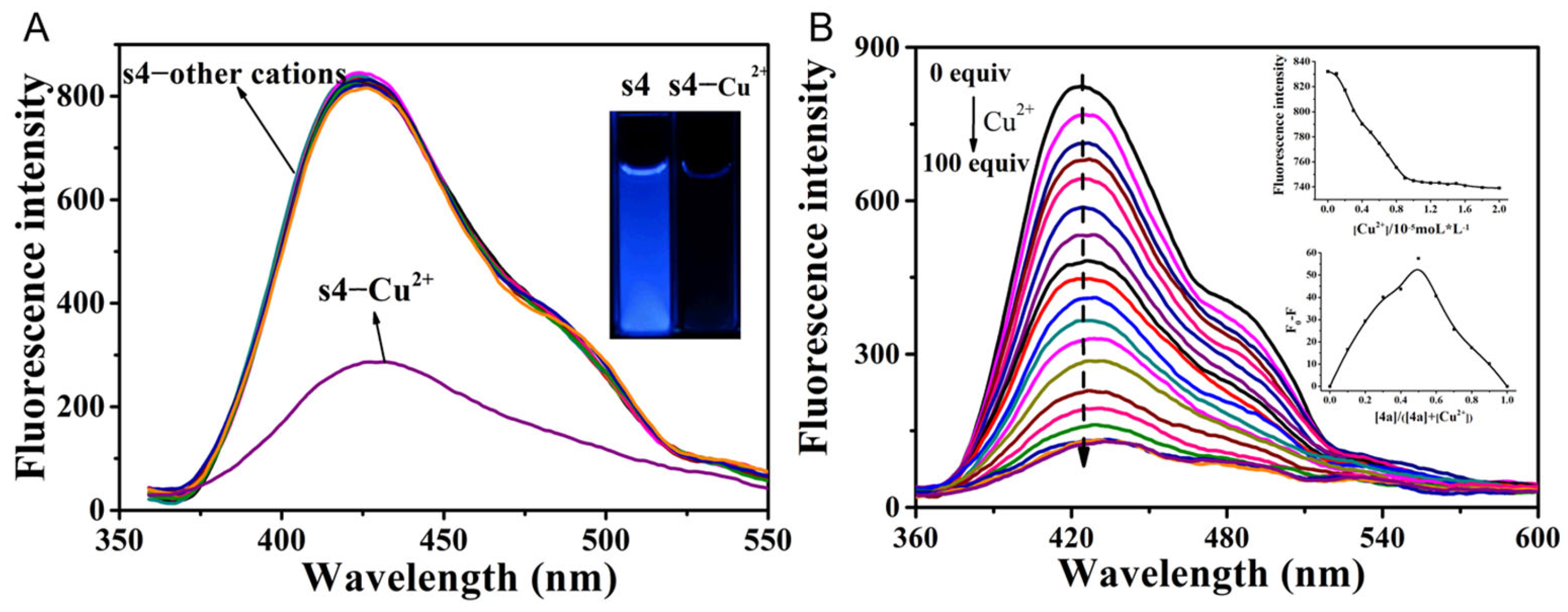
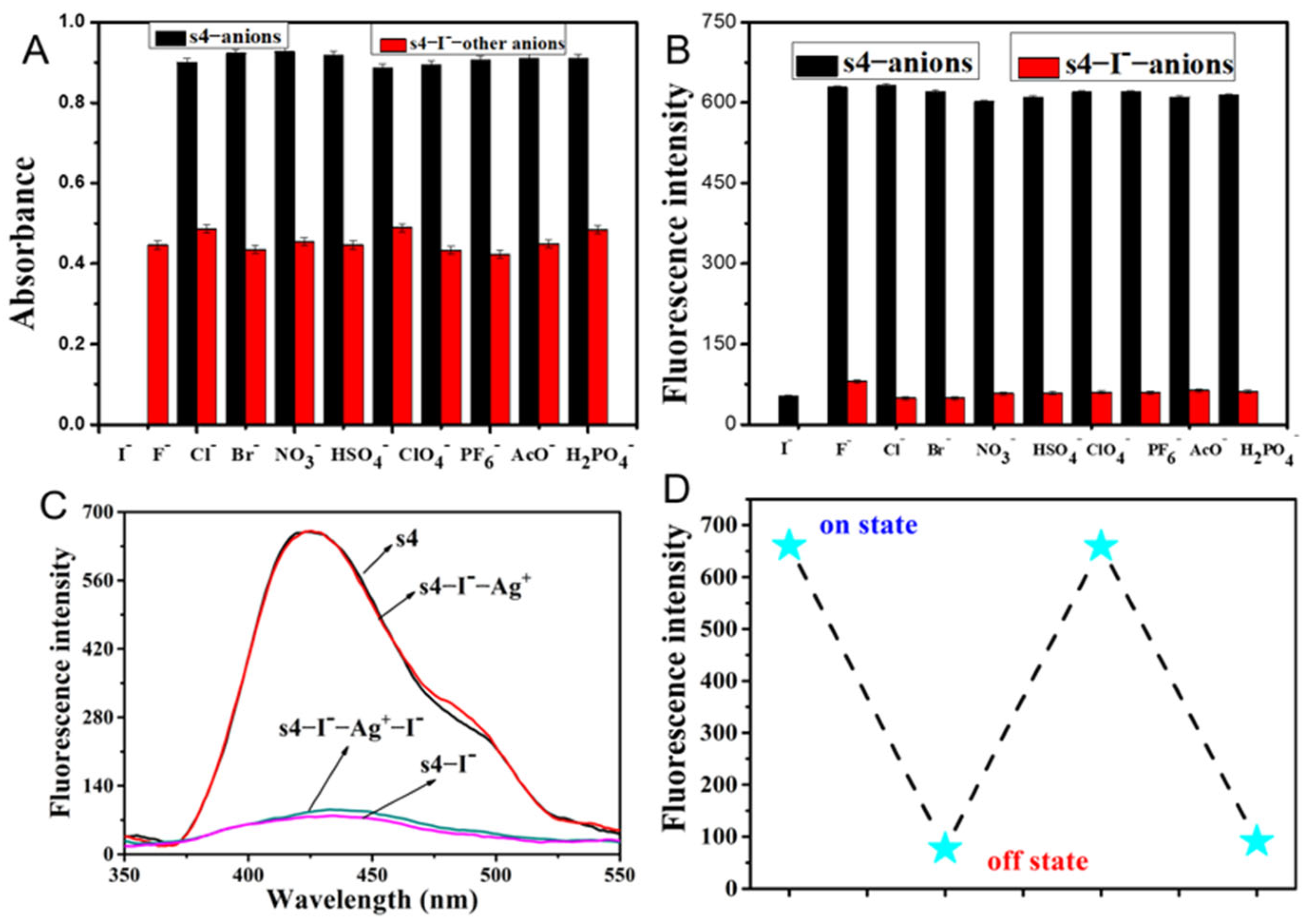
2.2. The Fluorescent Emission Quenching of Probe s4 in Response to Cu2+ and I−
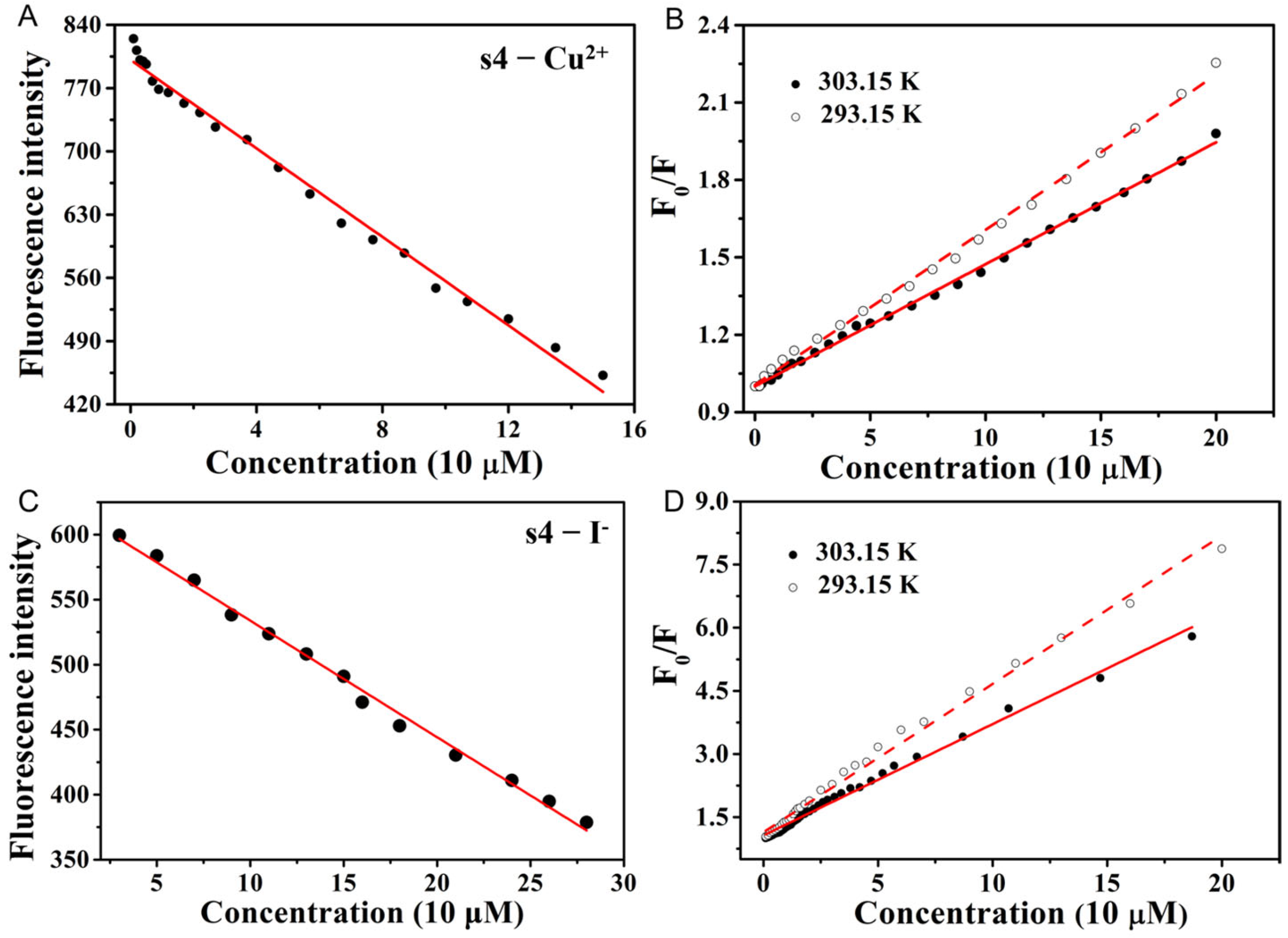
2.3. The Concentration and Temperature Effects of Fluorescent Probe s4
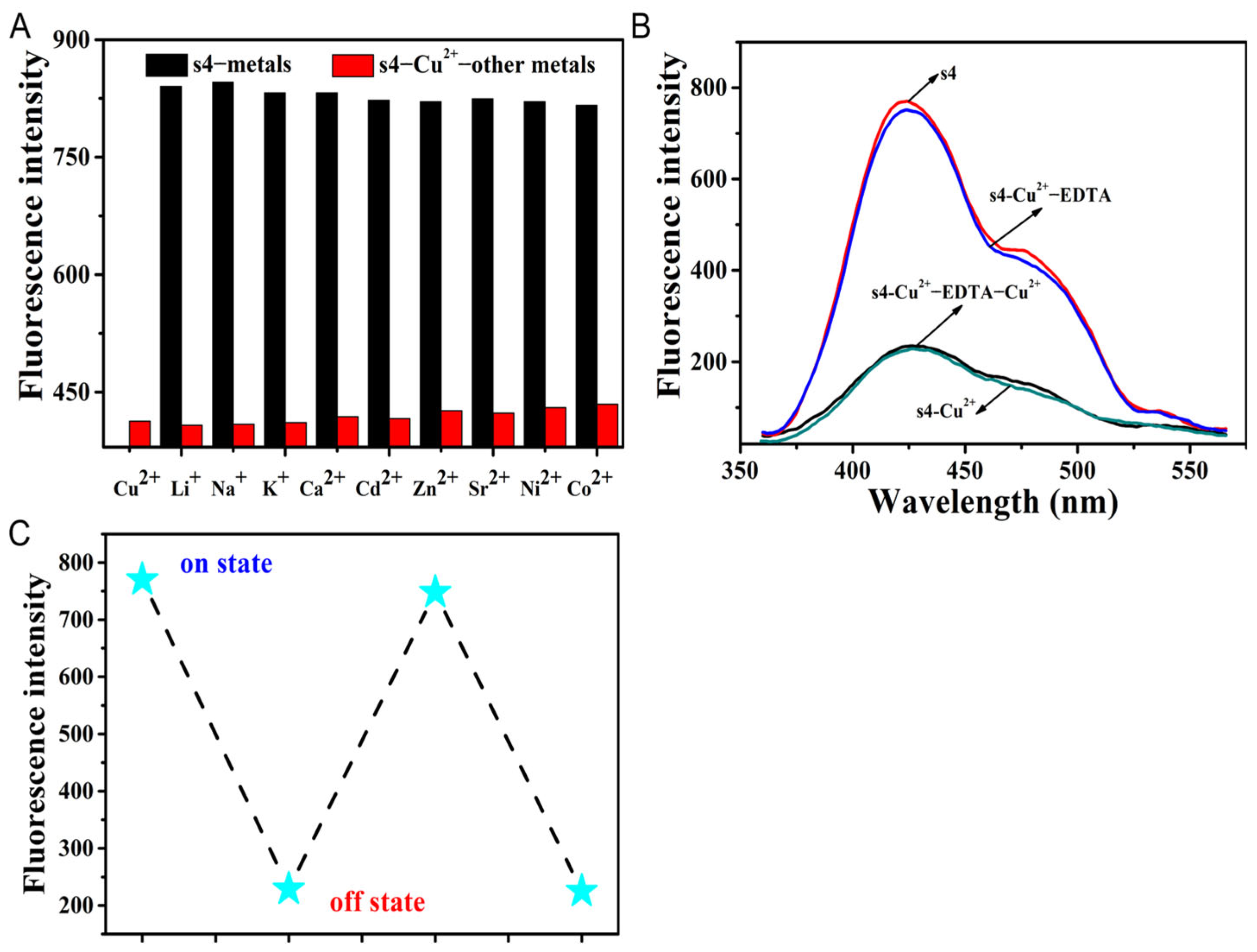
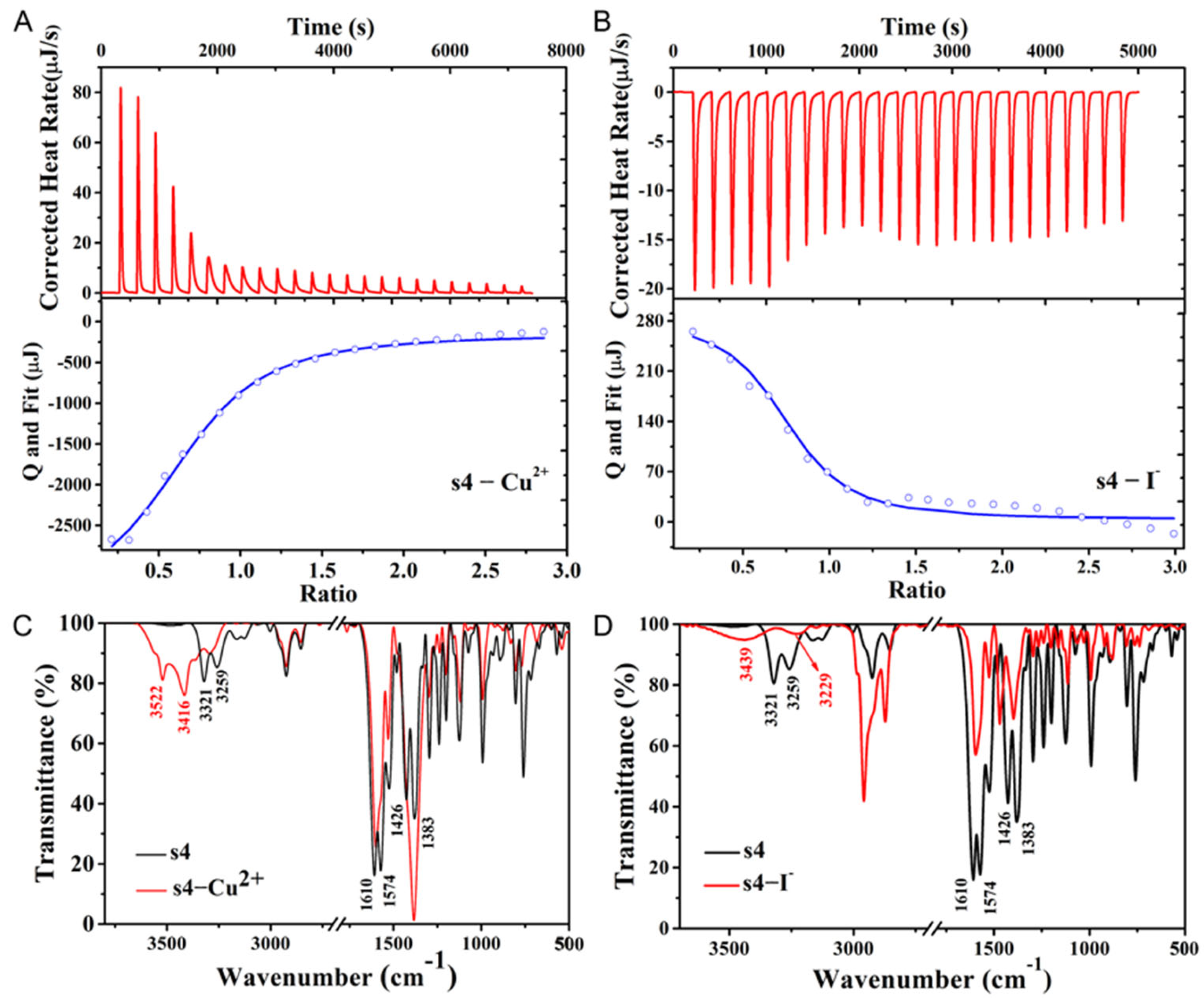
2.4. The Mechanism of Cu2+ Fluorescent Probe s4
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Experimental Methods
4.1. Molecular Design and Synthesis
4.2. Fluorescence and UV-Vis Spectra
4.3. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
4.4. IR Spectra
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quang, D.T.; Kim, J.S. Fluoro- and Chromogenic Chemodosimeters for Heavy Metal Ion Detection in Solution and Biospecimens. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6280–6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orvig, C.; Abrams, M.J. Medicinal Inorganic Chemistry: Introduction. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2201–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, R.; Bagchi, P.; Sumalekshmy, S.; Fahrni, C.J. In Situ Imaging of Metals in Cells and Tissues. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4780–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, G.; Iniya, M.; Anand, T.; Kotla, N.G.; Sunnapu, O.; Singaravadivel, S.; Gulyani, A.; Chellappa, D. Chemically diverse small molecule fluorescent chemosensors for copper ion. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 357, 50–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Levy, O.; Carrasco, N. Cloning and characterization of the thyroid iodide transporter. Nature 1996, 379, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Eastman, C.J. The changing epidemiology of iodine deficiency. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.M.; Braverman, L.E. Consequences of excess iodine. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 10, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trusso Sfrazzetto, G.; Satriano, C.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Rizzarelli, E. Synthetic fluorescent probes to map metallostasis and intracellular fate of zinc and copper. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 311, 125–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes-García, J.; Rosales-Vázquez, L.D.; Bazany-Rodríguez, I.J.; Dorazco-González, A. Recent Advances in Luminescent Recognition and Chemosensing of Iodide in Water. Chem.-Asian J. 2020, 15, 2925–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, K.; Prabhu, J.; Tang, L.; Chidambaram, T.; Noel, M.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Nandhakumar, R. A simple chalcone-based fluorescent chemosensor for the detection and removal of Fe3+ ions using a membrane separation method. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2883–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassos, B.H.; Hirsch, R.F.; Letterman, H. X-ray microdetermination of chromium, cobalt, copper, mercury, nickel, and zinc in water using electrochemical preconcentration. Anal. Chem. 1973, 45, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.S.; Zoriy, M.V.; Pickhardt, C.; Palomero-Gallagher, N.; Zilles, K. Imaging of Copper, Zinc, and Other Elements in Thin Section of Human Brain Samples (Hippocampus) by Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 3208–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, W.; Li, F. Luminescent Chemodosimeters for Bioimaging. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 192–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Guo, S.; Hu, C.; Fan, J.; Peng, X. Recent Development of Chemosensors Based on Cyanine Platforms. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7768–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Shi, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Yi, T.; et al. Highly Sensitive and Fast Responsive Fluorescence Turn-On Chemodosimeter for Cu2+ and Its Application in Live Cell Imaging. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2008, 14, 6892–6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Singh, N.; Kim, M.J.; Jang, D.O. Chromogenic and Fluorescent Recognition of Iodide with a Benzimidazole-Based Tripodal Receptor. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 3024–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lin, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, W.-T.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Wei, T.-B. A highly selective colorimetric chemosensor for detection of iodide ions in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 86627–86631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.X.; Li, P.F.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, N.; Zhao, N. A highly sensitive fluorescent sensor with aggregation-induced emission characteristics for the detection of iodide and mercury ions in aqueous solution. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 10479–10485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.G.; Kim, K.B.; Park, G.J.; Na, Y.J.; Jo, H.Y.; Lee, S.A.; Kim, C. An anthracene-based fluorescent sensor for sequential detection of zinc and copper ions. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2014, 39, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.-C.; Yang, Z.-Y. Design of a novel coumarin-based multifunctional fluorescent probe for Zn2+/Cu2+/S2− in aqueous solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 57, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, S.; Sadhukhan, M. Facile bulk production of highly blue fluorescent graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots and their application as highly selective and sensitive sensors for the detection of mercuric and iodide ions in aqueous media. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 21832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Ou, D.; Li, Q.; Li, Z. An indirect approach for anion detection: The displacement strategy and its application. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.R.; Nandre, J.P.; Jadhav, D.; Bothra, S.; Sahoo, S.K.; Devi, M.; Pradeep, C.P.; Mahulikar, P.P.; Patil, U.D. Imatinib intermediate as a two in one dual channel sensor for the recognition of Cu2+ and I−ions in aqueous media and its practical applications. Dalton Trans 2014, 43, 13299–13306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, S.; Jin, Y.; Pang, X.F.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J. A near-infrared “turn-on” fluorescent probe for selective detection of copper (II) ions in aqueous media and its application in cell imaging. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 336, 126036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavalishin, M.; Gamov, G.; Kiselev, A.; Nikitin, G. A fluorescein conjugate as colorimetric and red-emissive fluorescence chemosensor for selective recognition Cu2+ ions. Opt. Mater. 2024, 153, 115580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Jiang, L.; Mou, L.; Zeng, X.; Wang, R.; Peng, T.; Wu, F.; Shi, T. A “Pincer” Type of Acridine–Triazole Fluorescent Dye for Iodine Detection by Both ‘Naked-Eye’Colorimetric and Fluorometric Modes. Molecules 2024, 29, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Xie, Z.; Mo, X.; Feng, Y.; Peng, T.; Wu, F.; Yu, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J. Synthesis and Application of Salicylhydrazone Probes with High Selectivity for Rapid Detection of Cu2+. Molecules 2024, 29, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; de Oliveira, C.S.; Sonntag, G.; Gibb, C.L.D.; Gibb, B.C.; Bohne, C. Dynamics of a Supramolecular Capsule Assembly with Pyrene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5544–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Meng, X.; Chu, R.; Xu, K.; Tang, B. A turn-on fluorescence probe for imaging iodide in living cells based on an elimination reaction. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6925–6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-X.; Yang, H.-B. A General and High Yielding Fragment Coupling Synthesis of Heteroatom-Bridged Calixarenes and the Unprecedented Examples of Calixarene Cavity Fine-Tuned by Bridging Heteroatoms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15412–15422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laronze-Cochard, M.; Kim, Y.-M.; Brassart, B.; Riou, J.-F.; Laronze, J.-Y.; Sapi, J. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 4,5-bis(dialkylaminoalkyl)-substituted acridines as potent telomeric G-quadruplex ligands. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 3880–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-X.; Mu, L.; Zeng, X.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, J. Synthesis and Crystal Structure of a Novel Homo[2]Heterocalix[2]arene[2]triazines containing Acridine Moiety. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 8566–8568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, F.; Chen, L.; Yu, M.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, L.; Shi, T.; Guo, J.; Zheng, H.; Wang, R.; Liao, M. Triazine Calixarene as a Dual-Channel Chemosensor for the Reversible Detection of Cu2+ and I− Ions via Water Content Modulation. Molecules 2025, 30, 2815. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132815
Wu F, Chen L, Yu M, Zhao L, Jiang L, Shi T, Guo J, Zheng H, Wang R, Liao M. Triazine Calixarene as a Dual-Channel Chemosensor for the Reversible Detection of Cu2+ and I− Ions via Water Content Modulation. Molecules. 2025; 30(13):2815. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132815
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Fuyong, Long Chen, Mei Yu, Liang Zhao, Lu Jiang, Tianzhu Shi, Ju Guo, Huayan Zheng, Ruixiao Wang, and Mingrui Liao. 2025. "Triazine Calixarene as a Dual-Channel Chemosensor for the Reversible Detection of Cu2+ and I− Ions via Water Content Modulation" Molecules 30, no. 13: 2815. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132815
APA StyleWu, F., Chen, L., Yu, M., Zhao, L., Jiang, L., Shi, T., Guo, J., Zheng, H., Wang, R., & Liao, M. (2025). Triazine Calixarene as a Dual-Channel Chemosensor for the Reversible Detection of Cu2+ and I− Ions via Water Content Modulation. Molecules, 30(13), 2815. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132815





