Recent Advances in the Mechanisms and Applications of Astragalus Polysaccharides in Liver Cancer Treatment: An Overview
Abstract
1. Introduction
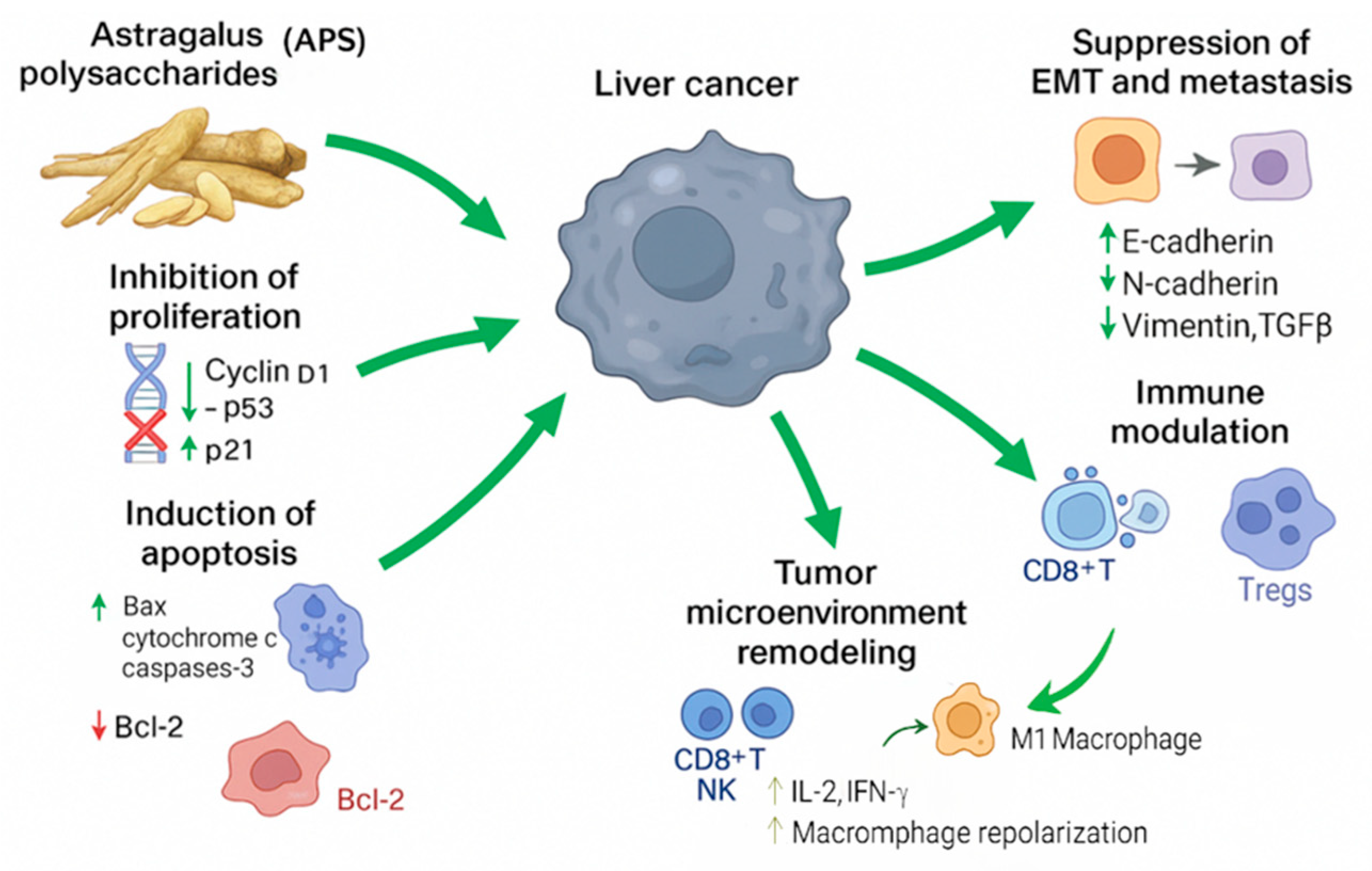
2. Anti-Liver Cancer Effects of Astragalus Polysaccharides (APS)
3. Mechanisms of Action: APS Exert Their Effects Through Multiple Pathways
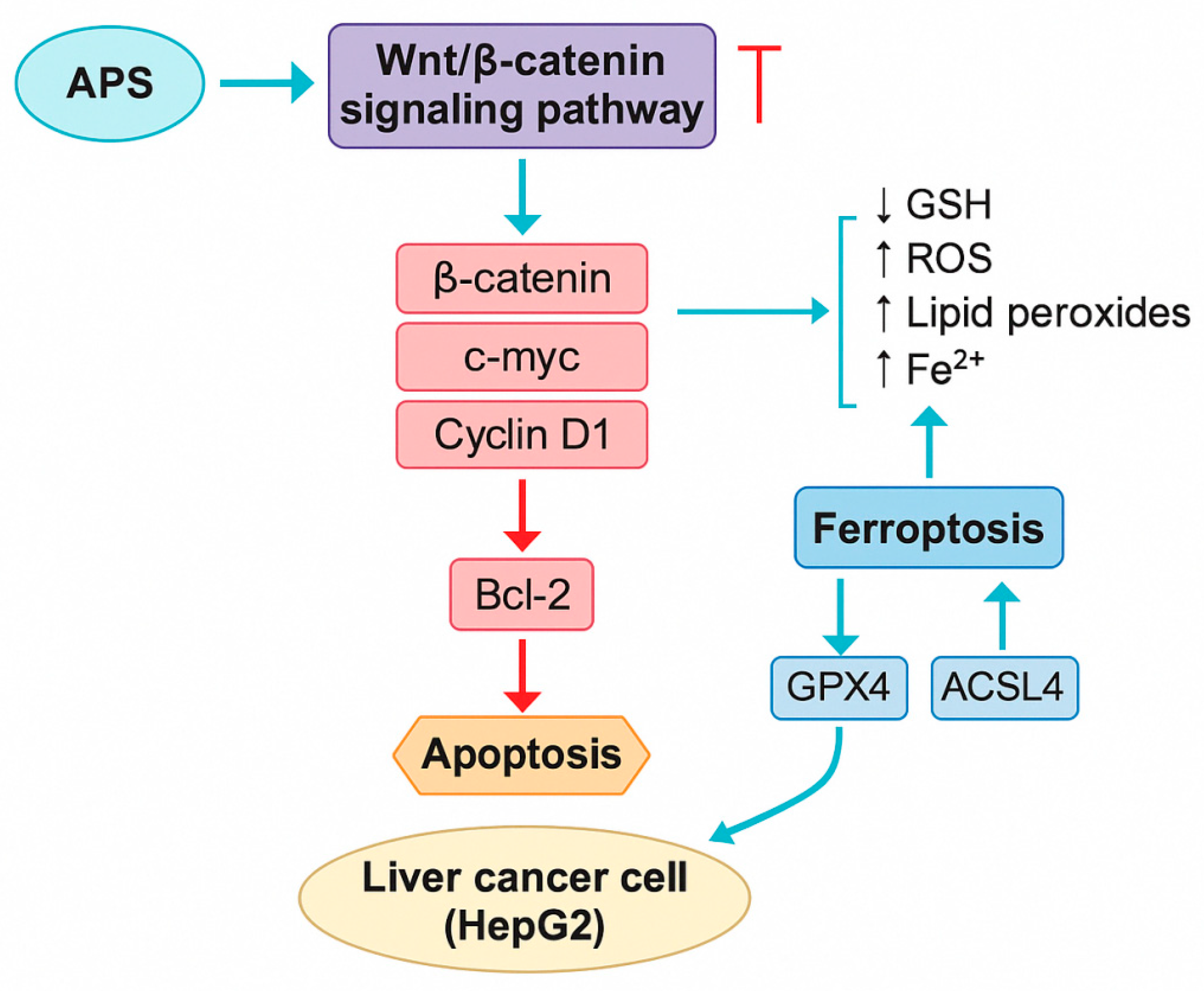
3.1. Induction of Apoptosis
3.2. Inhibition of Proliferation
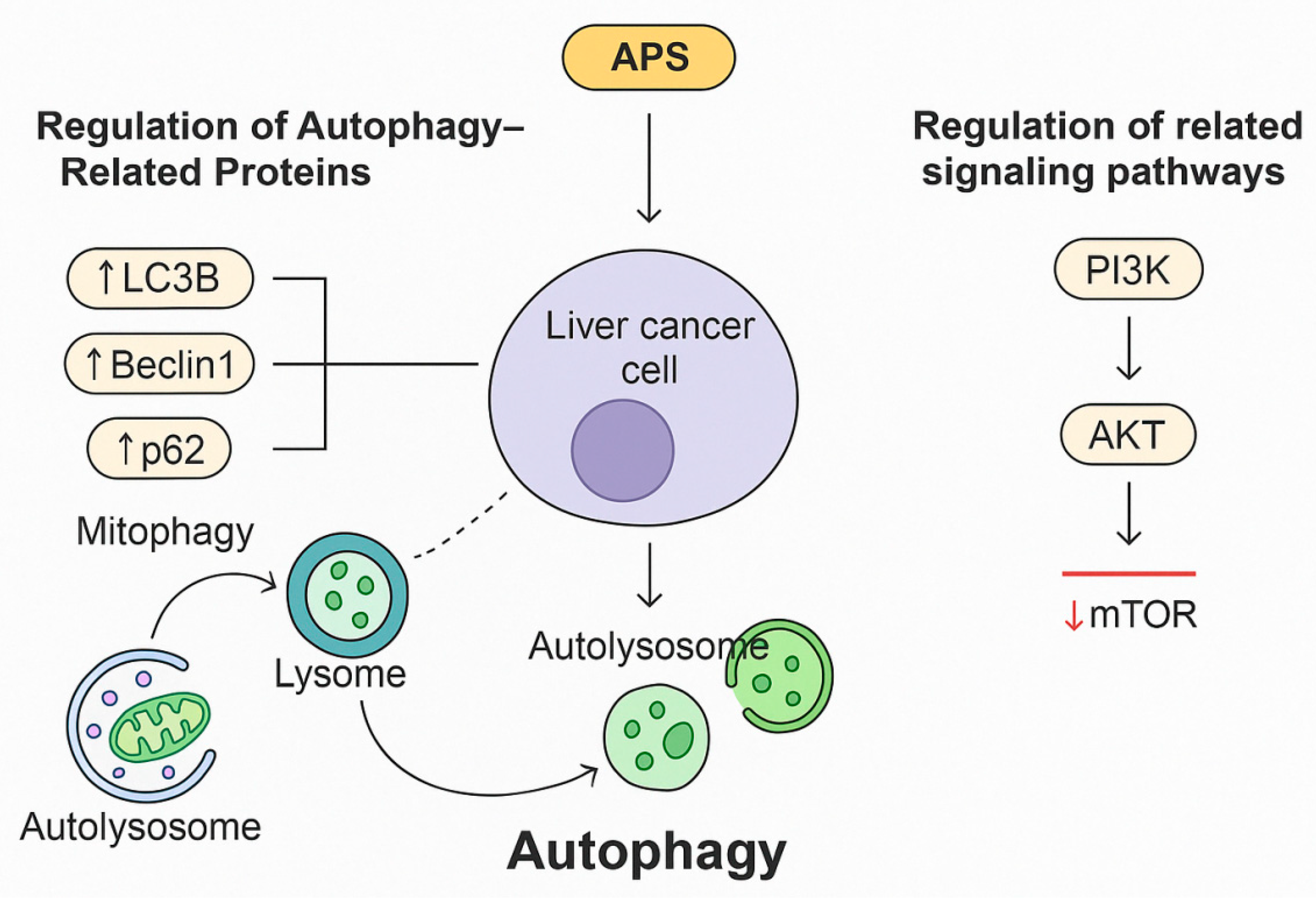
3.3. Autophagy Regulation
3.3.1. Regulation of Autophagy-Related Proteins
3.3.2. Regulation of Related Signalling Pathways
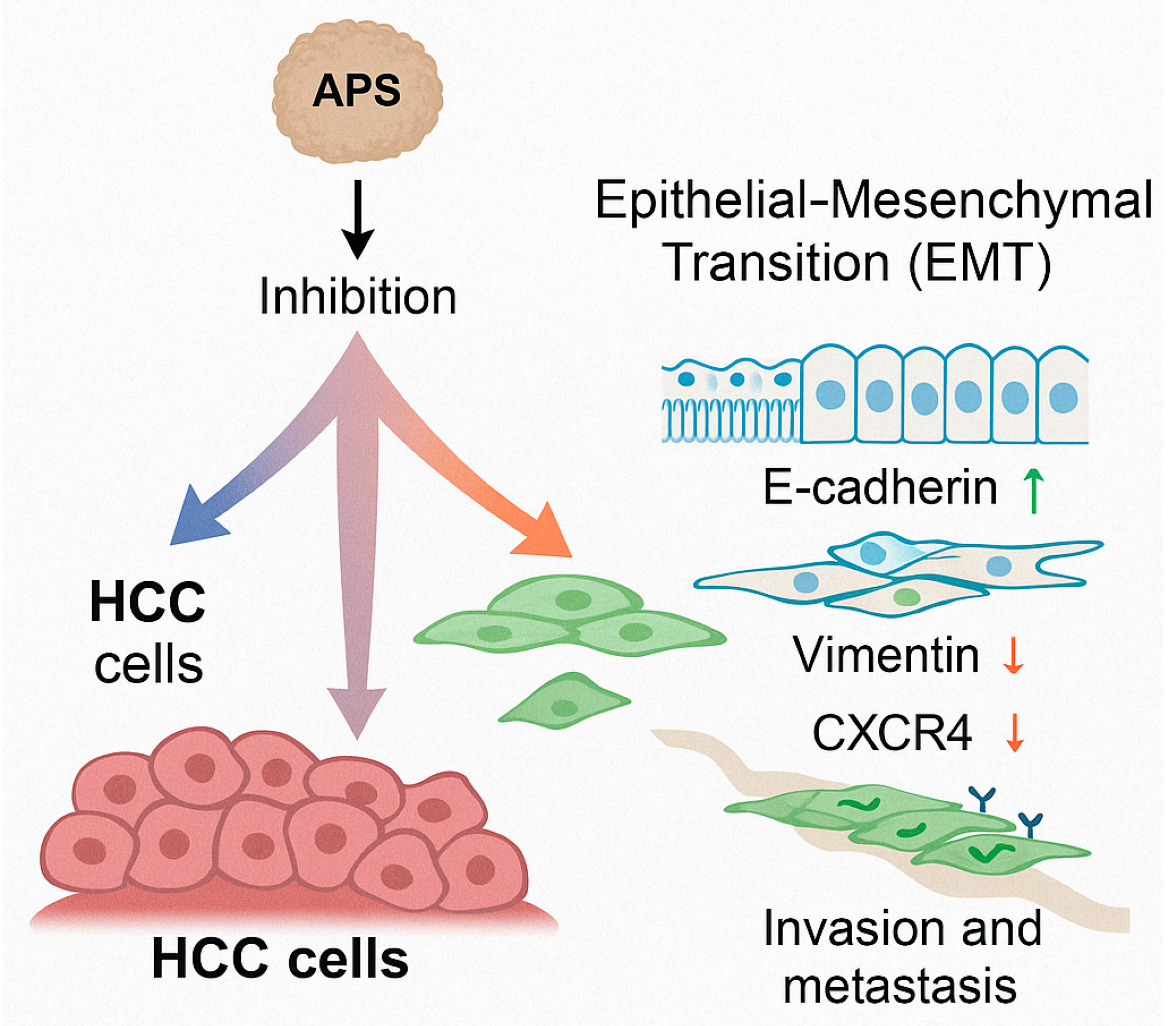
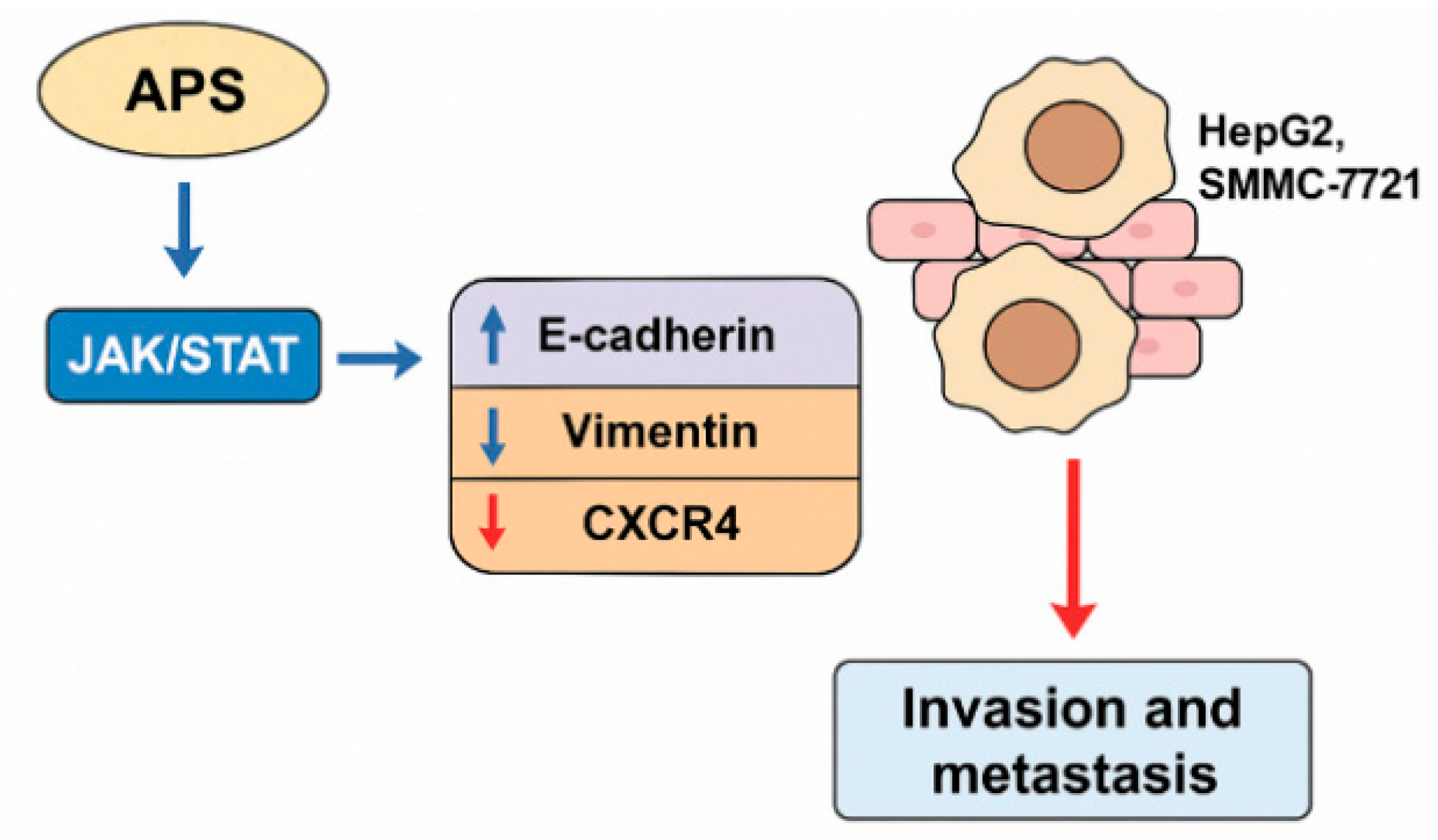
3.4. Inhibition of the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Metastasis
3.5. Modulation of the Immune Response
3.5.1. Enhancement of Immune Organ Indices
3.5.2. Inhibition of Immune Checkpoints
3.5.3. Optimisation of CAR-T Cell Therapy for Liver Cancer
3.5.4. Regulation of Macrophage Polarisation
3.5.5. Regulation of Regulatory T Cells (Tregs)
3.6. Regulation of the Tumour Microenvironment
4. Mechanisms of Synergistic Therapies: APS Enhance Standard Chemotherapeutics and Reverse Resistance
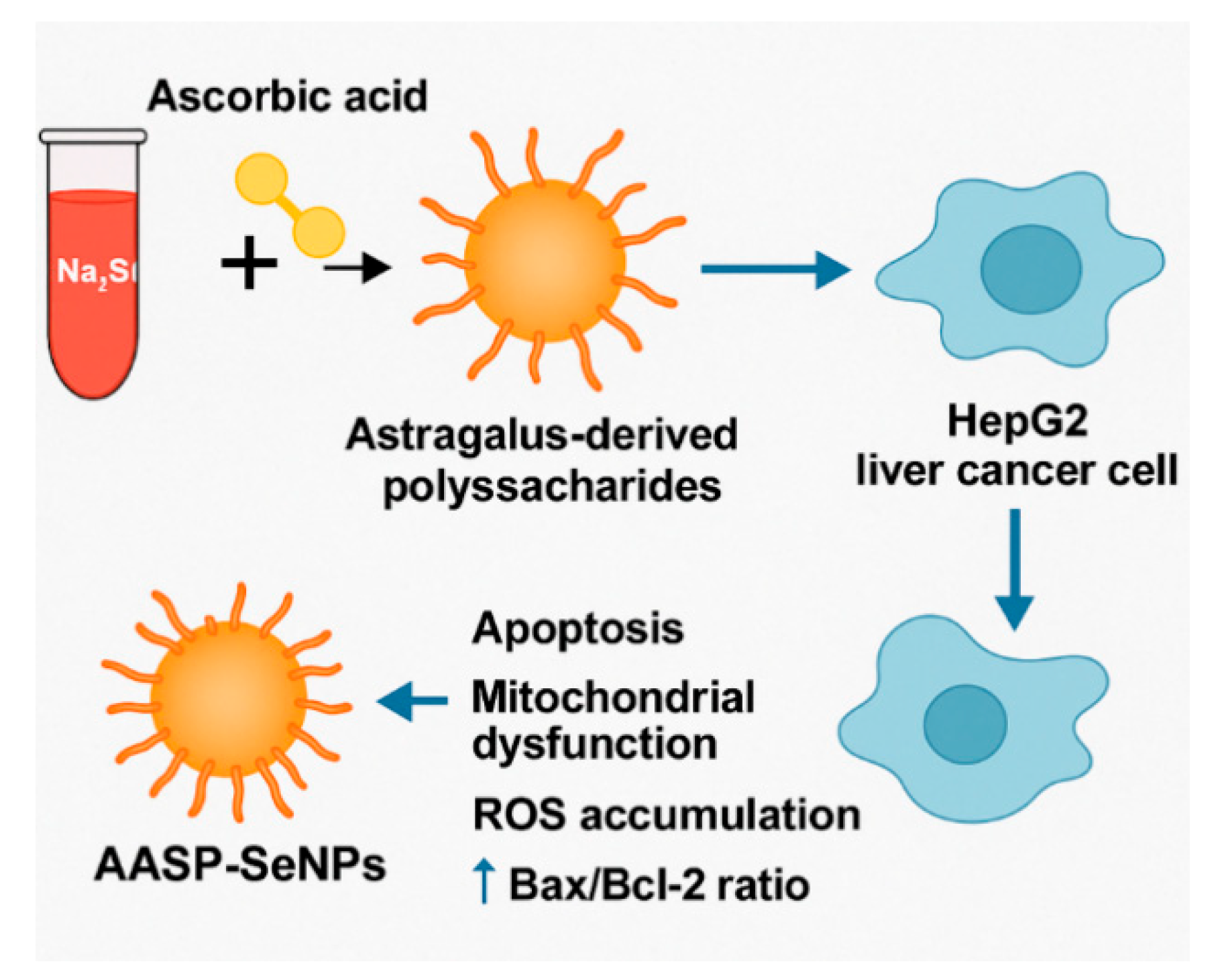
4.1. Antitumour Applications of APS-Modified Selenium Nanoparticle Composites
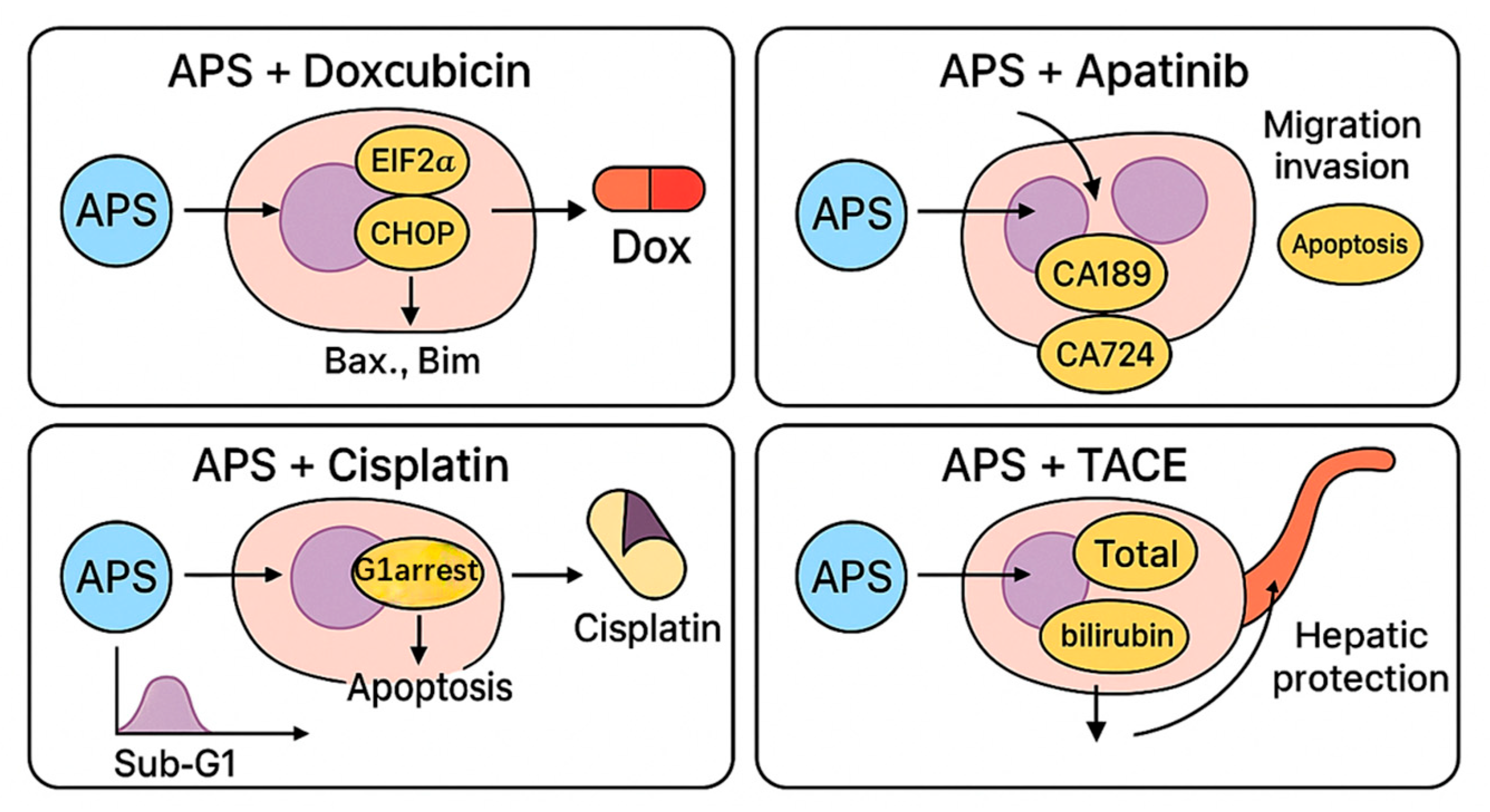
4.2. Combination with Doxorubicin
4.3. Combination with Apatinib
4.4. Combination with Cisplatin
4.5. Combination with Transarterial Chemoembolisation (TACE)
4.6. Combination with 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU)
4.7. Combination with Cantharidin (CTD)
4.8. Combination with Docetaxel (DTX), Cyclophosphamide (CTX), and Epirubicin (EPI)
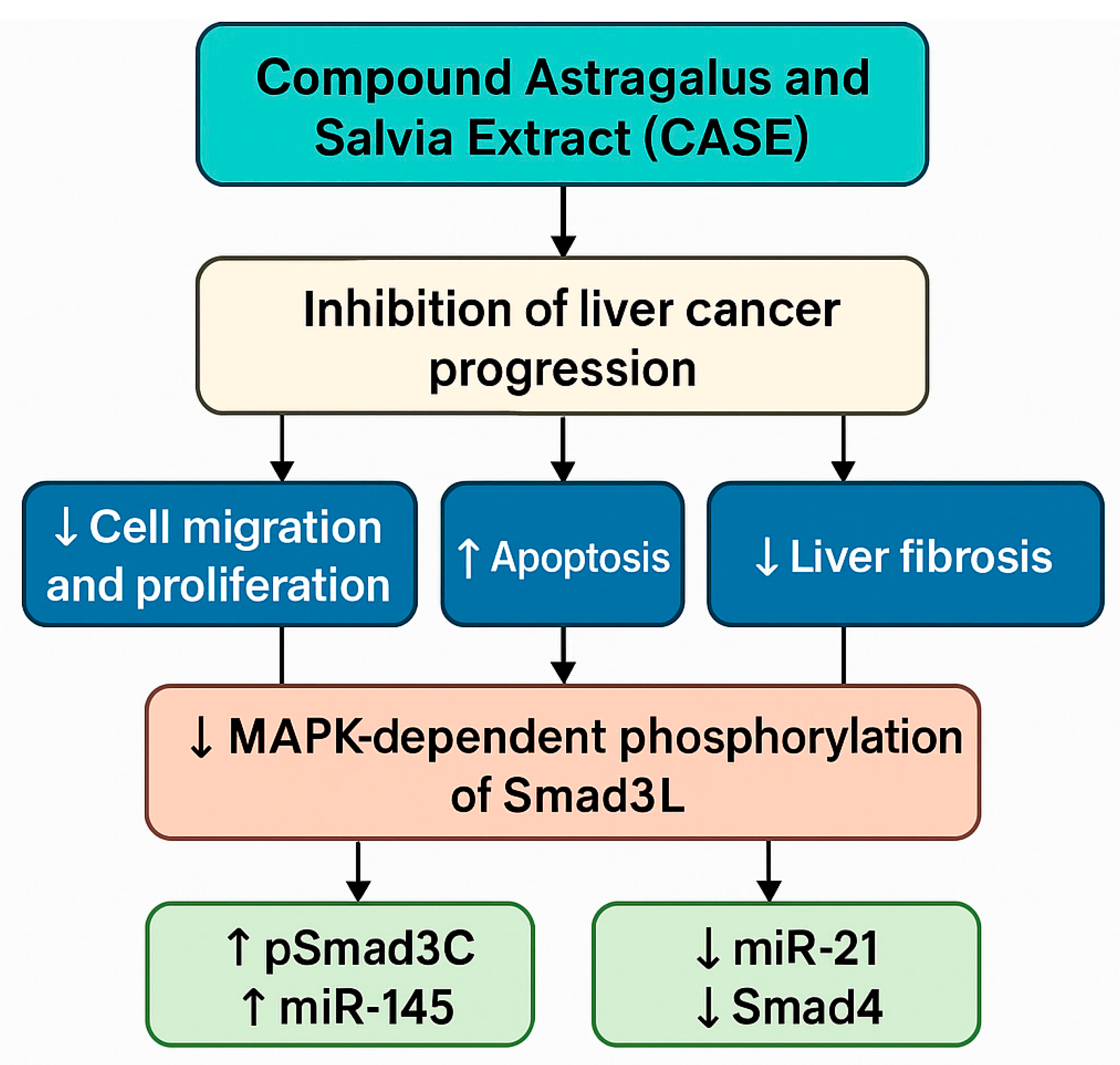
4.9. Antitumour Effects of the Compound Astragalus and Salvia Extract (CASE)
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Qiu, K.; Zhou, S.; Gan, Y.; Jiang, K.; Wang, D.; Wang, H. Risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma: An umbrella review of systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 2455539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhu, X.; Beeraka, N.M.; Zhao, R.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Mahesh, P.A.; Nikolenko, V.N.; Fan, R.; Liu, J. Projected epidemiological trends and burden of liver cancer by 2040 based on GBD, CI5plus, and WHO data. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.G.; Zhang, Y.H.; Lu, J.H.; Kensler, T.W. Liver Cancer Etiology: Old Issues and New Perspectives. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2024, 26, 1452–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Gu, Y.; Qi, W.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Zao, X.; Li, S.; Liu, S.; Xue, T.; Ye, Y. Traditional chinese medicine for liver cancer treatment: Network pharmacology research. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2025, advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Gao, Q.; Huang, C.; Wang, K.; Qiu, F. Herb-drug interaction potential of Astragali Radix: A metabolic perspective. Drug Metab. Rev. 2025, 57, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Li, M.; Wei, J. Biosynthesis and pharmacological activities of flavonoids, triterpene saponins and polysaccharides derived from Astragalus membranaceus. Molecules 2023, 28, 5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, H.; Xie, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, R.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Li, Y. From traditional efficacy to drug design: A review of astragali radix. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Gu, M.; Kong, W.; Lin, Z.; Mao, J.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y. High-throughput phytochemical unscrambling of flowers originating from Astragalus membranaceus (fisch.) bge. var. mongholicus (bge.) P. K. Hsiao and Astragalus membranaceus (fisch.) bug. by applying the intagretive plant metabolomics method using UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. Molecules 2023, 28, 6115. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; An, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; Gao, W.; Li, X. Review of Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharides: Extraction process, structural features, bioactivities and applications. Chin. Herb. Med. 2025, 17, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Niu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Jiang, W.; Jiao, T.; Dou, H.; Nan, Y. Research progress in the medicine-food dual use of Astragalus for gastrointestinal tumors. J. Med. Food 2024, 27, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ren, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y. A Review of the Pharmacological Action of Astragalus Polysaccharide. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H. Effect of Astragalus polysaccharide in treatment of diabetes mellitus: A narrative review. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 39, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Peng, T.; Shao, C.; Liu, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, Y. The Antioxidant Action of Astragali radix: Its Active Components and Molecular Basis. Molecules 2024, 29, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xia, H.; He, W.; Lv, C.; Zhang, J.; Lin, X.; Qin, S. The inhibitory effect of Astragalus flavone extract on hyperuricemia and its underlying molecular mechanism by targeting JNK/AP-1/NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2025, 140, 156622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.Y.; Zhao, J.X.; Zang, Y.; Li, P.; Yang, S.Q.; Li, X.M.; Wang, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.G. New flavonoid glycosides from the stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus. Fitoterapia 2025, 180, 106321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Huang, G. Extraction, structure, and activity of polysaccharide from radix astragali. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 113015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Dong, Q.; Yang, D.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Y. Astragali radix (Huangqi): A time-honored nourishing herbal medicine. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klichkhanov, N.K.; Suleimanova, M.N. Chemical composition and therapeutic effects of several Astragalus species (Fabaceae). Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2024, 518, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Li, K.; Qin, X.; Li, Z.; Du, Y. Structural Characterization and Screening for Anti-inflammatory Activity of Polysaccharides with Different Molecular Weights from Astragali Radix. Chem. Biodivers. 2024, 21, e202400262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auyeung, K.K.; Han, Q.-B.; Ko, J.K. Astragalus membranaceus: A Review of its Protection Against Inflammation and Gastrointestinal Cancers. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, B.; Liang, D.; Quan, X.; Gu, R.; Meng, Z.; Gan, H.; Wu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S. Pharmacological Effects of Astragaloside IV: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.-F.; Tang, P.C.-T.; Sham, T.-T.; Lam, W.-S.; Mok, D.K.-W.; Chan, S.-W. Semen Astragali Complanati: An ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and pharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y. Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicine Penthorum chinense Pursh: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.-X.; Guo, S.; Shen, K.-X.; Li, H.-W.; Zhang, H.-K.; Xie, Y.-J.; Shang, E.-X.; Duan, J.-A. Chemical composition analysis and value evaluation of stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2023, 48, 6600–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Si, L.; Cao, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Cloning, Identification, and Functional Analysis of the Chalcone Isomerase Gene from Astragalus sinicus. Genes 2023, 14, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, K.; Ranga, F.; Elemer, S.; Varvara, R.A.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Dulf, F.V.; Vodnar, D.C. Evaluation of the Astragalus exscapus L. subsp. transsilvanicus Roots’ Chemical Profile, Phenolic Composition and Biological Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-H.; Yang, X.; Wei, J.-R.; Chen, N.-M.; Xu, J.-P.; Bi, Y.-Q.; Yang, M.; Gong, X.; Li, Z.-Y.; Ren, K. Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Toxicology and Clinical Applications of Radix Astragali. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 27, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Xu, F.; Wei, D.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z. Pharmacokinetics of two triterpenoid saponins and three flavonoids in Astragalus membranaceus leaves by UHPLC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 251, 116419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, F.; Yang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, G. A Seasonal Change of Active Ingredients and Mineral Elements in Root of Astragalus membranaceus in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biol. Trace Element. Res. 2020, 199, 3950–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkader, H.-T.A.E.A.; Essawy, A.E.; Al-Shami, A.S. Astragalus species: Phytochemistry, biological actions and molecular mechanisms underlying their potential neuroprotective effects on neurological diseases. Phytochemistry 2022, 202, 113293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.; Xia, W.; Wei, J.; Ding, X. Therapeutic effect of Astragalus polysaccharides on hepatocellular carcinoma H22-bearing mice. Dose-Response 2017, 15, 1559325816685182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xiao, B.; Sun, T. Antitumor and immunomodulatory activity of Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharides in H22 tumor-bearing mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yuan, C.; Guo, J.; Yu, T.; Lv, X.; Liu, J.; Lai, X. Inhibitory effect and possible mechanism of Astragalus polysaccharides on HepG2 cell proliferation. Pract. Prev. Med. 2018, 25, 385–387. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, L.J.; Yang, S.W.; Yan, Y.D. Study on the inhibitory effect and mechanism of Astragalus polysaccharides on Hep G2.215 cells. Infect. Dis. Inf. 2022, 35, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, L.I.; Bao, J.M.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, T.; Shen, X.H. Inhibiting effect of Astragalus polysaccharides on the functions of CD4+CD25high Treg cells in the tumor microenvironment of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin. Med. J. 2012, 125, 786–793. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Duan, F.; Pan, Z.; Liu, X.; Lu, W.; Liang, C.; Fang, Z.; Peng, P.; Jia, D. Astragalus polysaccharide promotes doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by reducing O-GlcNAcylation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cells 2023, 12, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.E.; De Li, H.; Yan, M.; Cai, H.L.; Tan, Q.Y.; Zhang, W.Y. Effects of Astragalus polysaccharides on P-glycoprotein efflux pump function and protein expression in H22 hepatoma cells in vitro. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C. Study on the Efficacy and Mechanism of Astragalus Polysaccharides Combined with TACE in the Treatment of Intermediate and Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, R.; Hu, L.; Liu, E.; Qu, P. Epigenetics in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. Cell Signal. 2025, 130, 111684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zheng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Cheng, K.; Yuan, J.; Liu, H.; Zhu, P. Astragalus polysaccharide alleviates alcoholic-induced hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting polymerase I and transcript release factor and the TLR4/JNK/NF-κB/MyD88 pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 314, 116662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Fu, C.; Jin, X.; Lei, C.; Zhu, X. Neonatal lupus erythematosus: An acquired autoimmune disease to be taken seriously. Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 2476049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.Y.; Liu, X.B.; Lu, J.X.; Zhang, Z.P.; Yan, X.Y.; Ma, W. Research Progress on the antitumor mechanisms of active components from Astragalus membranaceus. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2022, 53, 7613–7623. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, C.F.A.; Wong-Brown, M.W.; Bowden, N.A. BCL-2 family isoforms in apoptosis and cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitz, A.Z.; Gavathiotis, E. Physiological and pharmacological modulation of BAX. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, H.; Yu, P.Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhu, Y.; Li, F.C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Xiao, M. Recent advances in caspase-3, breast cancer, and traditional Chinese medicine: A review. J. Chemother. 2024, 36, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.H.; Liao, W.R.; Sun, R.X. Astragalus polysaccharide induces the apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of Notch1. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, Q.; An, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Guan, Y.; Peng, C.; Du, Z. Targeting NEDD8 in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: An integrated bioinformatics and experimental approach. Hematology 2025, 30, 2478650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Ji, Q.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Gut microbiota in hepatocellular carcinoma immunotherapy: Immune microenvironment remodeling and gut microbiota modification. Cancer Med. 2025, 17, 2486519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Tang, Y.; Liang, H.; Cao, M.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhong, Z.; Xiong, Z.; He, Z. CircPIK3C3 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression and lenvatinib resistance by suppressing the wnt/β-catenin pathway via the miR-452-5p/SOX15 axis. Genomics 2025, 117, 110999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhu, P.F.; Liu, Y.M.; Zeng, Q.L.; Yu, Z.J. Astragalus polysaccharide promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2018, 49, 5155–5160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.Q.; Wang, Z.X.; Cao, H.; Tong, N.; Zhang, Y.L. Astragalus polysaccharide promotes ferroptosis and inhibits cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. Surg. 2025, 31, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Feng, X.; He, H.; Li, L.; Wen, Y.; Liu, X.; He, B.; Hua, S.; Sun, S. Crosstalk between autophagy and other forms of programmed cell death. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 995, 177414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariosa, A.R.; Lahiri, V.; Lei, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Klionsky, D.J. A perspective on the role of autophagy in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.R.; Qian, M.; Li, M. Astragalus polysaccharide inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cells via mitophagy. Northwest Pharm. J. 2021, 36, 426–429. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Ai, D.; Zhang, J.Q.; Chen, T.G.; Wang, L. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in the treatment of human diseases: Current status, trends, and solutions. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 16033–16061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Dong, L.J. Study on the Mechanism of Astragalus Polysaccharides in Inhibiting the Proliferation of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. West China J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 35, 402–406. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Li, Y.Z.; Qi, Y.J.; Long, Q.F. Effect of Astragalus polysaccharides combined with 5-FU on the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Chin. J. Comp. Med. 2021, 31, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; An, T.Z.; Piao, S.H.; Sun, Y. Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharides on the Invasion and Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma SMMC-7721 Cells via the Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (JAK/STAT) Signaling Pathway. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 36, 1499–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Stuelten, C.H.; Parent, C.A.; Montell, D.J. Cell motility in cancer invasion and metastasis: Insights from simple model organisms. Nature Reviews. Cancer 2018, 18, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, R.; Yu, Y.; Xue, H.; Shen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, J. Effects of cell shape and nucleus shape on epithelial-mesenchymal transition revealed using chimeric micropatterns. Biomaterials 2025, 317, 123013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Xu, K.; Niu, L.; Lin, L. Astragalus polysaccharide (APS) attenuated PD-L1-mediated immunosuppression via the miR-133a-3p/MSN axis in HCC. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 1710–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Su, C.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, F.; Liang, C.L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Qiu, F.; Liu, Y.; Feng, W. Astragalus polysaccharide enhances antitumoral effects of chimeric antigen receptor- engineered (CAR) T cells by increasing CD122+CXCR3+PD-1− memory T cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 179, 117401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hu, X.; Wang, S.; Jiao, Z.; Sun, T.; Liu, T.; Song, K. Characterization and anti-tumor bioactivity of Astragalus polysaccharides by immunomodulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Gu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; Chen, W.; Weng, L.; Liu, X. Application of PD-1 blockade in cancer immunotherapy. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Pan, J.; Huang, S.; Peng, X.; Zou, X.; Luo, Y.; Ren, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, R.; He, P.; et al. Downregulation of miR-133a-3p promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis via activating PI3K/AKT signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2018, 37, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, W.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, L.; Yang, X.; Li, H.; He, X.; Wang, H.L.; Zhou, Y.B.; Huang, S.; et al. Interfering MSN-NONO complex-activated CREB signaling serves as a therapeutic strategy for triple-negative breast cancer. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaw9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, E. CAR-T cell therapies: Patient access and affordability solutions. Future Sci. OA 2025, 11, 2483613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, P.; Gagliardi, F.; Roncelli, F.; Snider, S.; Mortini, P. Tumor-infiltrating and circulating B cells mediate local and systemic immunomodulatory mechanisms in glioblastoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2025, 172, 527–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Askari Rizvi, S.F.; Yang, Y.; Liu, G. Emerging nanomedicines for macrophage-mediated cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2025, 316, 123028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Jhong, J.H.; Chen, Q.; Huang, K.Y.; Strittmatter, K.; Kreuzer, J.; DeRan, M.; Wu, X.; Lee, T.Y.; Slavov, N.; et al. Global characterization of macrophage polarization mechanisms and identification of M2-type polarization inhibitors. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Pan, X.Y.; Ma, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, F.; Lv, Y.P. Astragalus polysacharin inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma-like phenotypes in a murine HCC model through repression of M2 polarization of tumour-associated macrophages. Pharm. Biol. 2021, 59, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Elzallat, M.; Mohammed, D.M.; Balata, M.; El-Maadawy, W.H. Exploiting regulatory T cells (tregs): Cutting-edge therapy for autoimmune diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 155, 114624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, D.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhuo, Z.; Guo, H.; Liu, J.; Zhuo, Y.; Tang, J.; He, J.; et al. Leptin decreases Th17/treg ratio to facilitate neuroblastoma via inhibiting long-chain fatty acid catabolism in tumor cells. Oncoimmunology 2025, 14, 2460281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akabane, M.; Imaoka, Y.; Kawashima, J.; Pawlik, T. Advancing precision medicine in hepatocellular carcinoma: Current challenges and future directions in liquid biopsy, immune microenvironment, single nucleotide polymorphisms, and conversion therapy. Hepatic Oncol. 2025, 12, 2493457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, C.J.; Tian, J. Advancing the understanding of the role of apoptosis in lung cancer immunotherapy: Global research trends, key themes, and emerging frontiers. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2025, 21, 2488074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Li, W.; Sun, J.; Jia, L.; Guan, Q.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y. A review on plant polysaccharide based on drug delivery system for construction and application, with emphasis on traditional chinese medicine polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 211, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, D.; Kaur, L.; Sohal, H.S.; Malhi, D.S.; Garg, S.; Thakur, D. Application of selenium nanoparticles in localized drug targeting for Cancer Therapy. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem.-Anti-Cancer Agents 2022, 22, 2715–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Hu, W.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Tian, H.; Lu, A.; Wang, J. Construction and structure-activity mechanism of polysaccharide nano-selenium carrier. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Lou, X.; Jiao, J.; Li, Y.; Dai, K.; Jia, X. Preliminary Structural Characterization of Selenium Nanoparticle Composites Modified by Astragalus Polysaccharide and the Cytotoxicity Mechanism on Liver Cancer Cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Li, Y.; Shi, F.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Y.; Tang, F.; Li, H. Nano co-delivery of doxorubicin and plumbagin achieves synergistic chemotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 661, 124424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abboud, H.A.; Zelkó, R.; Kazsoki, A. A systematic review of liposomal nanofibrous scaffolds as a drug delivery system: A decade of progress in controlled release and therapeutic efficacy. Drug Deliv. 2025, 32, 2445259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.W.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, Y.F.; Tang, Z.Q.; Liang, Y.X.; Liu, L.B.; Tian, G.X.; Wu, J.L. Preparation of Astragalus polysaccharide combined with doxorubicin hepatic-targeted liposomes and its anti-hepatocellular carcinoma effects. World Latest Med. Inf. Dig. 2018, 18, 215–216. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Huang, Z.; Liu, P.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Qiu, M.; Xiong, Z.; Yang, S. Apatinib inhibits the invasion and metastasis of liver cancer cells by downregulating MMP-related proteins via regulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 3126182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Z. Enhancement effect of Astragalus polysaccharide on Apatinib against hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its impact on tumor markers CA199 and CA724. Chin. J. Med. Guide 2024, 22, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Che, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, D.; Xie, D.; Jiang, B.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wu, G. The role of cisplatin in modulating the tumor immune microenvironment and its combination therapy strategies: A new approach to enhance anti-tumor efficacy. Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 2447403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.H.; Li, Q.; Lin, P.; Li, K.; Chen, Y.M.; Gao, L.; Zhang, N.N.; Li, M. Synergistic killing effect of Astragalus polysaccharide combined with cisplatin on human hepatocellular carcinoma BEL-7404 cells. J. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 1, 34–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, L.Z.; Yang, W.H.; Yu, C.; Qin, J.; Feng, L.Z.; Liu, Z.; Teng, G.J. Pickering emulsion with tumor vascular destruction and microenvironment modulation for transarterial embolization therapy. Biomaterials 2025, 316, 123018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, H.; Li, Q.; Cai, J.; Miao, Z.; Xie, P.; Tang, S.; He, D. Carrier-free nanoparticles based on self-assembly of 5-FU and copper-genistein complexes for the combined treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2025, 15, 1299–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Wang, X.M.; Xie, L.; Jin, X.W.; Li, Y.L. Astragalus polysaccharide inhibits proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma Bel-7402/5-FU-resistant cells and modulates drug-resistant genes. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Hepatol. 2020, 30, 326–329. [Google Scholar]
- Luu, S.; Fu, N.; Savage, P.; Pacholczyk, K.; Zaslavsky, T.; Conner, J.; Swallow, C.J. The emerging role of FAM46C as a biomarker and therapeutic target in gastric adenocarcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2024, 15, 1870–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ren, W.; Guo, M.; Wu, X.; Guo, Q. A comprehensive review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry of mylabris, and pharmacology of cantharidin. Chem. Biodivers. 2025, 22, e202500266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Huang, N.N.; Wei, J.X. Hepatotoxic mechanism of cantharidin: Insights and strategies for therapeutic intervention. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1201404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tang, W.; Lin, C.; Sa, Z.; Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C. Protective mechanism of Astragalus polysaccharides against cantharidin-induced liver injury determined in vivo by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry metabolomics. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 129, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murialdo, R.; Gallo, M.; Boy, D.; Zoppoli, G.; Tixi, L.; Gonella, R.; Ballestrero, A.; Patrone, F. Sequential dose-dense 5-fluorouracil, epirubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel in patients with early breast cancer with four or more positive lymph nodes. Tumori 2014, 100, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, C.; Macpherson, I.R. A review of the evidence base for utilizing child-pugh criteria for guiding dosing of anticancer drugs in patients with cancer and liver impairment. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gao, F.F.; Li, Q.; Lv, J.W.; Wang, Y.; Hu, P.C.; Xiang, Q.M.; Wei, L. Protective effect of Astragalus polysaccharides on liver injury induced by several different chemotherapeutics in mice. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2014, 15, 10413–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Rui, W.; Wu, C.; He, S.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y. Compound Astragalus and salvia miltiorrhiza extracts suppress hepatocarcinogenesis by modulating transforming growth factor-β/smad signaling. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z. New insights into Smad3 in cardiac fibrosis. Gene 2025, 952, 149418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungefroren, H.; Randeva, H.; Lehnert, H.; Schrader, J.; Marquardt, J.U.; Konukiewitz, B.; Hass, R. Crosstalk of TGF-β and somatostatin signaling in adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas: A brief review. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1511348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, W.; Fang, M.; Boye, A.; Tao, X.; Xu, Y.; Hou, S.; Yang, Y. Compound Astragalus and salvia miltiorrhiza extract inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression via miR-145/miR-21 mediated Smad3 phosphorylation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 231, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, A.; Wu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y. Compound Astragalus and salvia miltiorrhiza extracts modulate MAPK-regulated TGF-β/smad signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma by multi-target mechanism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 169, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
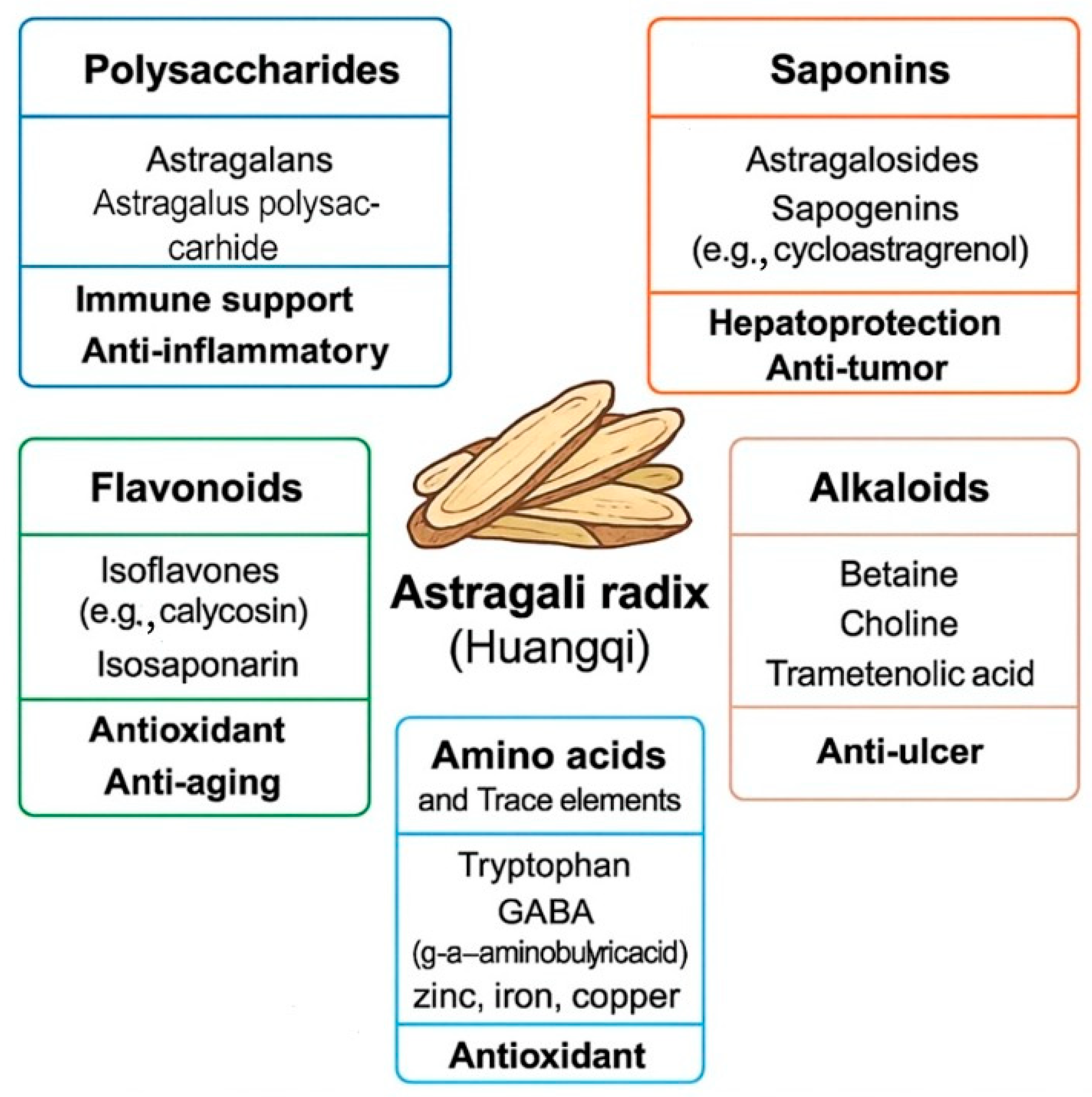


| Category | Representative Compounds | Biological Activities | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polysaccharides | APS-I, APS-II, APS-A1, APS-B1, APS2-I, APS3-I | Immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, hepatoprotective | [18,19,20] |
| Triterpenoid saponins | Astragalosides I–VIII, cycloartane, oleanane, malabaricane saponins | Cardioprotective, immunomodulatory, hepatoprotective, antitumour | [19,21,22] |
| Flavonoids | formononetin, calycosin, isorhamnetin, quercetin, kaempferol | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antitumour, hepatoprotective | [23,24] |
| Amino acids | Lysine, arginine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, proline, alanine | Nutritional supplementation, immunomodulatory | [25,26] |
| Phenolic compounds | Caffeic acid, ferulic acid, syringic acid, vanillic acid | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective | [19,27] |
| Coumarins | umbelliferone, scopoletin, psoralen | Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antioxidant | [19,20] |
| Alkaloids | Pyrimidine and pyrrole-type alkaloids (26 types); betaine | Neuroprotective, immunomodulatory, antioxidant | [20,28] |
| Steroids and terpenoids | Phytosterols, monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, tetracyclic and pentacyclic triterpenes | Anti-inflammatory, antitumour, adaptogenic | [20,29] |
| Minerals and trace elements | Se, Fe, Zn, Cu, Mn, Cr, Mo, Co, Cs | Essential for enzymatic functions, antioxidant, immunomodulatory | [29,30] |
| Fatty acids | Linoleic acid, linolenic acid, palmitic acid, oleic acid | Anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular protection | [19,31] |
| Other components | folic acid, ascorbic acid, quinones, inositols | General health support, metabolic balance | [20,27] |
| Mechanism | Biological Effects | Molecular Targets/Pathways | Supporting Evidence | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition of proliferation | Induces cell cycle arrest | ↓ Cyclin D1, ↓ CDK4, ↑ p21, ↑ p53 | In vitro studies on HepG2, H22 cells | [34,35] |
| Induction of apoptosis | Activates mitochondrial and death receptor pathways | ↑ Bax, ↓ Bcl-2, ↑ caspase-3, ↑ cytochrome c | Animal models and cultured liver cancer cells | [32,47] |
| Regulation of autophagy | Promotes autophagic flux leading to tumour cell death | ↑ LC3-II, ↑ Beclin-1, ↓ mTOR, ↓ PI3K/AKT | Autophagy markers increased in treated cells | [55,57] |
| Inhibition of the EMT and metastasis | Suppresses migration and invasion; reverses the EMT phenotype | ↑ E-cadherin, ↓ N-cadherin, ↓ vimentin, ↓ TGF-β | EMT markers altered in APS-treated models | [58,59] |
| Immune modulation | Enhances innate and adaptive immune responses; reduces immunosuppression | ↑ IL-2, ↑ IFN-γ, ↓ Treg, ↑ CD8+ T, ↑ NK cells | Tumour-bearing mouse models | [32,33,67] |
| Tumour microenvironment regulation | Reduces angiogenesis and hypoxia; repolarises macrophages from the M2 phenotype to the M1 phenotype | ↓ VEGF, ↓ HIF-1α, ↑ iNOS, ↓ Arg-1 | Improved tumour vascular structure and immune shift | [72] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Sen, A.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, L.; Zhou, S. Recent Advances in the Mechanisms and Applications of Astragalus Polysaccharides in Liver Cancer Treatment: An Overview. Molecules 2025, 30, 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132792
Wang W, Zhou H, Sen A, Zhang P, Yuan L, Zhou S. Recent Advances in the Mechanisms and Applications of Astragalus Polysaccharides in Liver Cancer Treatment: An Overview. Molecules. 2025; 30(13):2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132792
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wang, Hanting Zhou, Akanksha Sen, Pengxia Zhang, Linhong Yuan, and Shaobo Zhou. 2025. "Recent Advances in the Mechanisms and Applications of Astragalus Polysaccharides in Liver Cancer Treatment: An Overview" Molecules 30, no. 13: 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132792
APA StyleWang, W., Zhou, H., Sen, A., Zhang, P., Yuan, L., & Zhou, S. (2025). Recent Advances in the Mechanisms and Applications of Astragalus Polysaccharides in Liver Cancer Treatment: An Overview. Molecules, 30(13), 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132792








