Therapeutic Potential of Ellagic Acid in Liver Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
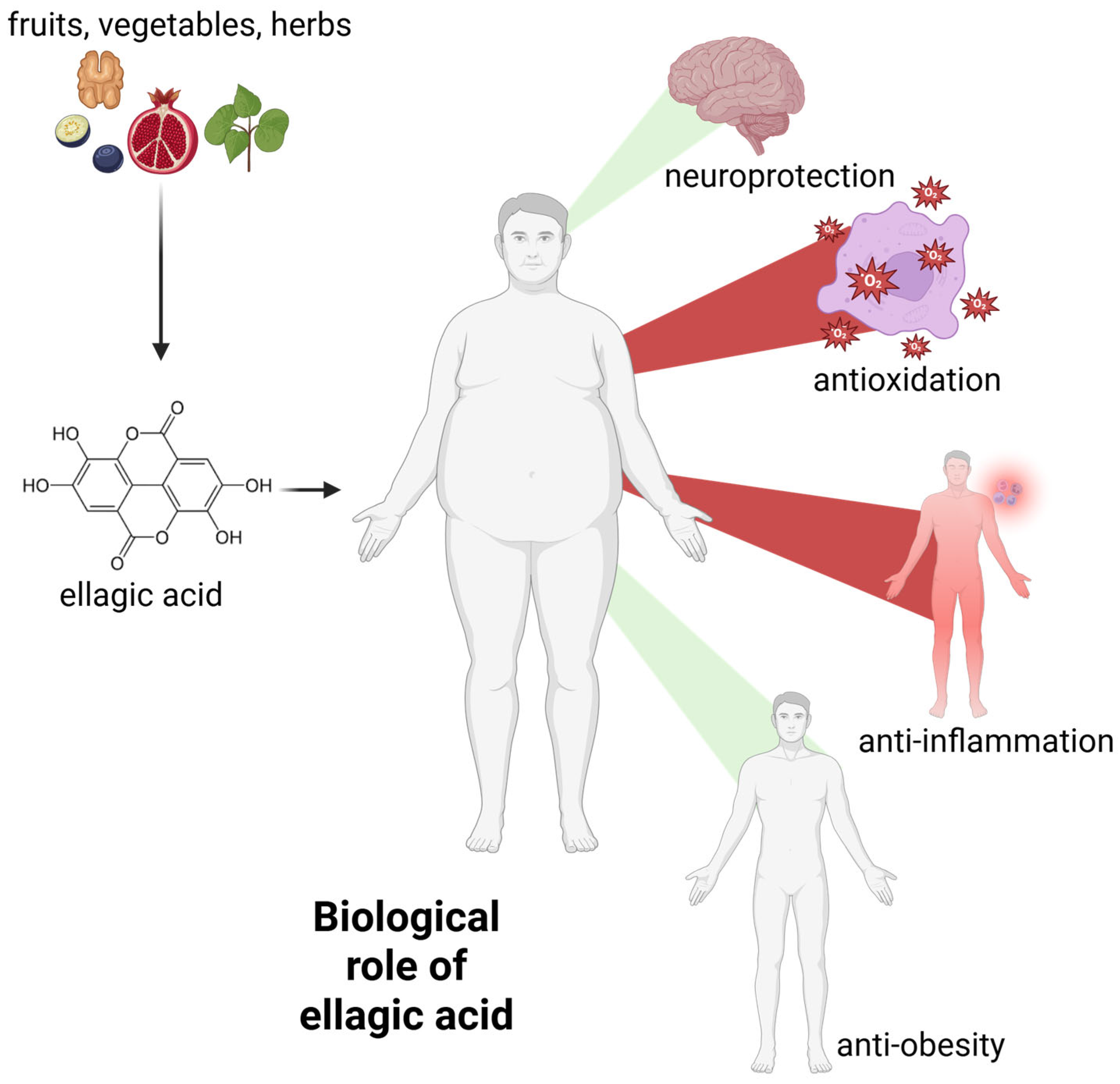
2. Sources and Biological Functions of Ellagic Acid
2.1. Sources of Ellagic Acid
2.2. Biological Functions of Ellagic Acid
2.2.1. Antioxidant and Free Radical Scavenging Activity
2.2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
2.2.3. Neuroprotective Activity
2.2.4. Anti-Obesity Activity
3. Bioavailability and Safety of Ellagic Acid
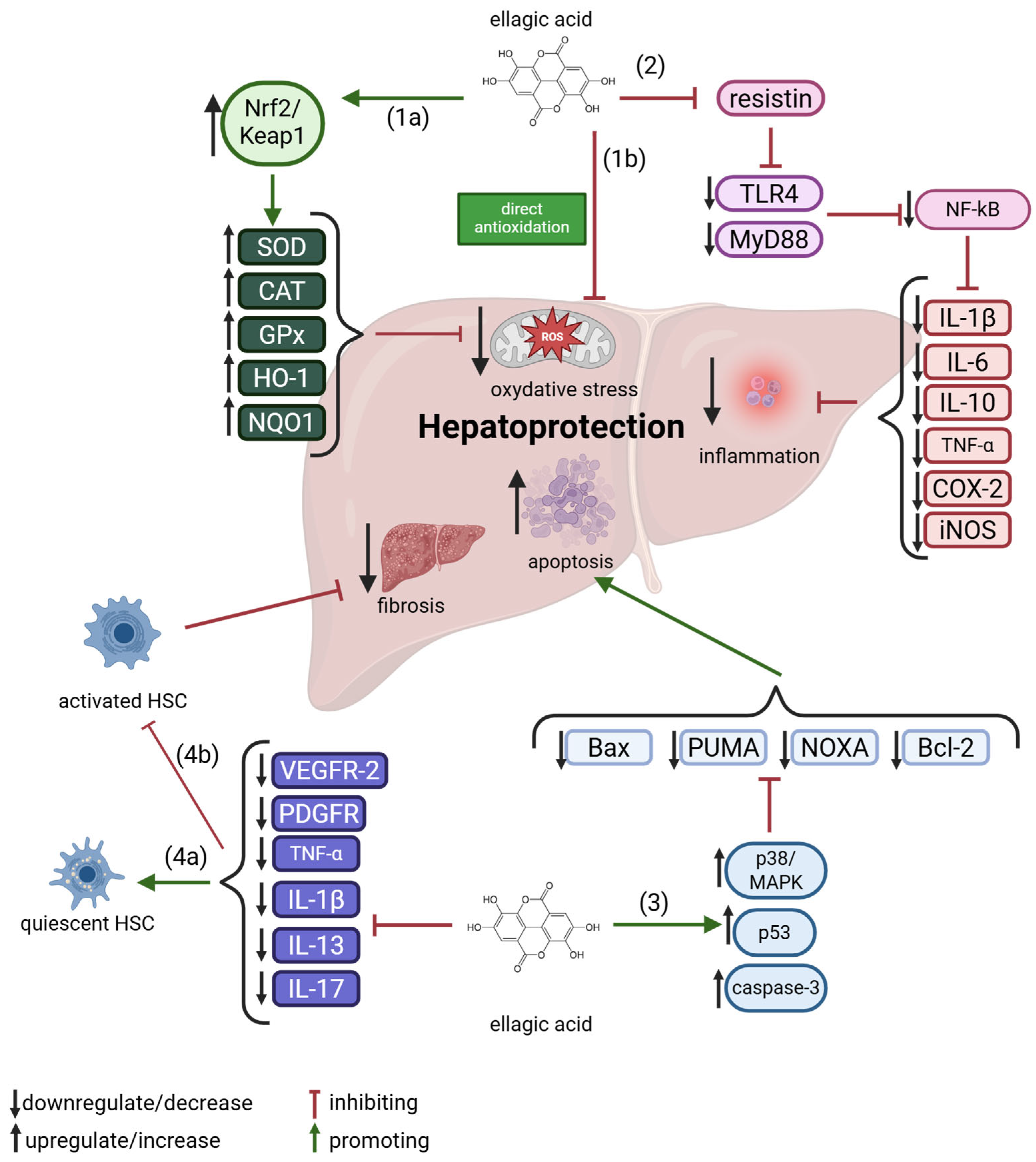
4. Effect of Ellagic Acid on Liver Condition
4.1. Inhibition of Hepatic Inflammation
4.2. Apoptosis Mediating Effect of EA
4.3. Anti-Fibrotic Effect of EA
4.4. Modulation of Gut Microbiota
5. Role of Ellagic Acid in MASLD
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| ALD | Alcohol-Related Liver Disease |
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| AMPK | AMP-Activated Protein Kinase |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| Bax | Bcl-2 Associated X Protein |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell Lymphoma 2 |
| BS | Blood Sugar |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CCl4 | Carbon Tetrachloride |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| CPT1 | Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1 |
| CYP2D6 | Cytochrome P450 2D6 |
| EA | Ellagic Acid |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases 1/2 |
| FASN | Fatty Acid Synthase |
| GPx | Glutathione Peroxidase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| HO-1 | Heme Oxygenase-1 |
| HSC | Hepatic Stellate Cell |
| IC50 | Half-Maximal Inhibitory Concentration |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1 Beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IκB-α | Inhibitor of NF-κB Alpha |
| iNOS | Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| IR | Insulin Resistance |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal Kinase |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MASLD | Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease |
| MCV | Mean Corpuscular Volume |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| MIF | Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor |
| NAFLD | Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| NOXA | Phorbol-12-Myristate-13-Acetate-Induced Protein 1 |
| NSAIDs | Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs |
| NQO1 | NAD(P)H Quinone Dehydrogenase 1 |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2–Related Factor 2 |
| PCC | Protein Carbonyl Content |
| PD | Parkinson’s Disease |
| PDGFR | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase |
| PUMA | p53 Upregulated Modulator of Apoptosis |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SCFAs | Short-Chain Fatty Acids |
| Smad2/3 | Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Homolog 2/3 |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| SREBP-1 | Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein 1 |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
| TAC | Total Antioxidant Capacity |
| TBARS | Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances |
| TC | Total Cholesterol |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| TLR2 | Toll-Like Receptor 2 |
| TLR4 | Toll-Like Receptor 4 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| URO/URO-A/URO-B/URO-C | Urolithins A, B, C—gut microbial metabolites of EA |
| UM-A/UM-B/URO-0 | Urolithin Metabotypes A, B, and Non-producer |
| VEGFR-2 | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 |
References
- Shakeri, A.; Zirak, M.R.; Sahebkar, A. Ellagic Acid: A Logical Lead for Drug Development? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos, J.-L.; Giner, R.M.; Marín, M.; Recio, M.C. A Pharmacological Update of Ellagic Acid. Planta Medica 2018, 84, 1068–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedel, H.A.; Usta, C. Effect of Ellagic Acid on BDNF/PI3K/AKT-Mediated Signaling Pathways in Mouse Models of Depression. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2025, 28, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galano, A.; Francisco Marquez, M.; Pérez-González, A. Ellagic Acid: An Unusually Versatile Protector against Oxidative Stress. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 904–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran Rahimi, V.; Ghadiri, M.; Ramezani, M.; Askari, V.R. Antiinflammatory and Anti-Cancer Activities of Pomegranate and Its Constituent, Ellagic Acid: Evidence from Cellular, Animal, and Clinical Studies. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 685–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Jamieson, S.; Pandey, A.K.; Bishayee, A. Neuroprotective Potential of Ellagic Acid: A Critical Review. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1211–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, M.K.; Mishra, P.C. Modeling the Scavenging Activity of Ellagic Acid and Its Methyl Derivatives towards Hydroxyl, Methoxy, and Nitrogen Dioxide Radicals. J. Mol. Model. 2013, 19, 5445–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, A.M.; Mohammaden, T.F.; Ali, M.A.M.; Mohamed, E.A.; Hasan, H.F. Ellagic and Ferulic Acids Alleviate Gamma Radiation and Aluminium Chloride-Induced Oxidative Damage. Life Sci. 2016, 160, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, I.; Yeşiloğlu, Y.; Bayrak, Y. Spectroscopic Studies on the Antioxidant Activity of Ellagic Acid. Spectrochim. Acta Part. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 130, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.R. The Effects of Ellagic Acid upon Brain Cells: A Mechanistic View and Future Directions. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shitany, N.A.; El-Bastawissy, E.A.; El-desoky, K. Ellagic Acid Protects against Carrageenan-Induced Acute Inflammation through Inhibition of Nuclear Factor Kappa B, Inducible Cyclooxygenase and Proinflammatory Cytokines and Enhancement of Interleukin-10 via an Antioxidant Mechanism. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 19, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Niño, W.R.; Zazueta, C. Ellagic Acid: Pharmacological Activities and Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Liver Protection. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 97, 84–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, I.; Buckner, T.; Shay, N.F.; Gu, L.; Chung, S. Improvements in Metabolic Health with Consumption of Ellagic Acid and Subsequent Conversion into Urolithins: Evidence and Mechanisms. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naraki, K.; Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M.; Ajiboye, B.O.; Hosseinzadeh, H. The Effect of Ellagic Acid on the Metabolic Syndrome: A Review Article. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Mehmood, A.; Soliman, M.M.; Iftikhar, A.; Iftikhar, M.; Aboelenin, S.M.; Wang, C. Protective Effects of Ellagic Acid Against Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 744520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, O.D.; Kulkarni, Y.A. Mini-Review of Analytical Methods Used in Quantification of Ellagic Acid. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 39, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez de Molina, A.; Vargas, T.; Molina, S.; Sánchez, J.; Martínez-Romero, J.; González-Vallinas, M.; Martín-Hernández, R.; Sánchez-Martínez, R.; Gómez de Cedrón, M.; Dávalos, A.; et al. The Ellagic Acid Derivative 4,4’-Di-O-Methylellagic Acid Efficiently Inhibits Colon Cancer Cell Growth through a Mechanism Involving WNT16. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 353, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siraj, M.A.; Shilpi, J.A.; Hossain, M.G.; Uddin, S.J.; Islam, M.K.; Jahan, I.A.; Hossain, H. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activity of Acalypha Hispida Leaf and Analysis of Its Major Bioactive Polyphenols by HPLC. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 6, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuyen, P.T.; Xuan, T.D.; Tu Anh, T.T.; Mai Van, T.; Ahmad, A.; Elzaawely, A.A.; Khanh, T.D. Weed Suppressing Potential and Isolation of Potent Plant Growth Inhibitors from Castanea Crenata Sieb. et Zucc. Molecules 2018, 23, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Bayertai; Tang, S.; Zhou, X. Analysis of Gallic Acid and Ellagic Acid in Leaves of Elaeagnus Angustifolia L. from Different Habitats and Times in Xinjiang by HPLC with Cluster Analysis. Acta Chromatogr. 2020, 33, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, T.R.; de Araújo, A.A.; Soares, L.A.L.; de Moraes Ramos, R.T.; Bezerra, I.C.F.; Ferreira, M.R.A.; de Souza Neto, M.A.; Melo, M.C.N.; de Araújo, R.F.; de Aguiar Guerra, A.C.V.; et al. Crude Extract and Fractions from Eugenia Uniflora Linn Leaves Showed Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Antibacterial Activities. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-de-Cerio, E.; Arráez-Román, D.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Ferranti, P.; Nicoletti, R.; Perrotta, G.M.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M. Establishment of Pressurized-Liquid Extraction by Response Surface Methodology Approach Coupled to HPLC-DAD-TOF-MS for the Determination of Phenolic Compounds of Myrtle Leaves. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3547–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ifeanacho, M.O.; Ikewuchi, C.C.; Ikewuchi, J.C. Investigation of the Profile of Phenolic Compounds in the Leaves and Stems of Pandiaka Heudelotii Using Gas Chromatography Coupled with Flame Ionization Detector. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 5, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhooghe, L.; Meert, H.; Cimanga, R.K.; Vlietinck, A.J.; Pieters, L.; Apers, S. The Quantification of Ellagic Acid in the Crude Extract of Phyllanthus Amarus Schum. & Thonn. (Euphorbiaceae). Phytochem. Anal. 2011, 22, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadage, D.M.; Kshirsagar, P.R.; Pai, S.R.; Chavan, J.J. Extraction Efficiency, Phytochemical Profiles and Antioxidative Properties of Different Parts of Saptarangi (Salacia chinensis L.)—An Important Underutilized Plant. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 12, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyanarayanan, S.; Chandran, R.; Thankarajan, S.; Abrahamse, H.; Thangaraj, P. Phytochemical Composition, Antioxidant and Anti-Bacterial Activity of Syzygium Calophyllifolium Walp. Fruit. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, K.-S.; Cha, H.-H.; Shin, J.-W.; Na, H.-K.; Park, K.-K.; Chung, W.-Y.; Surh, Y.-J. Nitric Oxide Induces Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Mouse Skin through Activation of NF-κB. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sarrías, A.; Larrosa, M.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Dolara, P.; Espín, J.C. NF-κB-Dependent Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Urolithins, Gut Microbiota Ellagic Acid-Derived Metabolites, in Human Colonic Fibroblasts. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, E.A.; Walter, A.C.; Alsharif, N.Z.; Stohs, S.J. Modulation of TCDD-Induced Fetotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Embryonic and Placental Tissues of C57BL/6J Mice by Vitamin E Succinate and Ellagic Acid. Toxicology 1997, 124, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amić, D.; Stepanić, V.; Lučić, B.; Marković, Z.; Dimitrić Marković, J.M. PM6 Study of Free Radical Scavenging Mechanisms of Flavonoids: Why Does O-H Bond Dissociation Enthalpy Effectively Represent Free Radical Scavenging Activity? J. Mol. Model. 2013, 19, 2593–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, G.; Toscano, M.; Russo, N. Density Functional Predictions of Antioxidant Activity and UV Spectral Features of Nasutin A, Isonasutin, Ellagic Acid, and One of Its Possible Derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9650–9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Kaushik, P.; Incerpi, S.; Pedersen, J.Z.; Goel, S.; Prasad, A.K.; Rohil, V.; Parmar, V.S.; Saso, L.; Len, C. Evaluation of the Free Radical Scavenging Activities of Ellagic Acid and Ellagic Acid Peracetate by EPR Spectrometry. Molecules 2021, 26, 4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przewloka, S.R.; Shearer, B.J. The Further Chemistry of Ellagic Acid II. Ellagic Acid and Water-Soluble Ellagates as Metal Precipitants. Holzforschung 2002, 56, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvi, L.T.; Moreira, D.C.; Andrade, R.; Ginani, J.; Alonso, A.; Hermes-Lima, M. Ellagic Acid Inhibits Iron-Mediated Free Radical Formation. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 173, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.M.; Cho, J.S.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, Y.I. Ellagic Acid Protects Hepatocytes from Damage by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Production of Reactive Oxygen Species. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2010, 64, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Y.-C.; Chou, C.-W.; Senthil Kumar, K.J.; Fu, K.-T.; Wang, H.-M.; Hsu, L.-S.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-R.; Chen, S.-C.; Yang, H.-L. Ellagic Acid Protects Human Keratinocyte (HaCaT) Cells against UVA-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis through the Upregulation of the HO-1 and Nrf-2 Antioxidant Genes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Xiang, Z.; Xu, H. Progress in Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Ellagic Acid. Med. Res. 2024, 8, 240002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nworu, C.S.; Akah, P.A. ANTI-INFLAMMATORY HERBS AND THEIR MOLECULAR MECHANISMS OF ACTION. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 12, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornélio Favarin, D.; Martins Teixeira, M.; Lemos de Andrade, E.; de Freitas Alves, C.; Lazo Chica, J.E.; Artério Sorgi, C.; Faccioli, L.H.; Paula Rogerio, A. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ellagic Acid on Acute Lung Injury Induced by Acid in Mice. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 164202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, M.T.; Hemmati, A.A.; Naghizadeh, B.; Mard, S.A.; Rezaie, A.; Ghorbanzadeh, B. A Study of the Mechanisms Underlying the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Ellagic Acid in Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema in Rats. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2015, 47, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, M.; María Giner, R.; Ríos, J.-L.; Recio, M.C. Intestinal Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Ellagic Acid in the Acute and Chronic Dextrane Sulfate Sodium Models of Mice Colitis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allahverdi, T.D.; Allahverdi, E.; Yayla, S.; Deprem, T.; Merhan, O.; Vural, S. The Comparison of the Effects of Ellagic Acid and Diclofenac Sodium on Intra-Abdominal Adhesion: An In Vivo Study in the Rat Model. Int. Surg. 2014, 99, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Mazumder, S.; De, R.; Saha, S.J.; Banerjee, C.; Iqbal, M.S.; Adhikari, S.; Alam, A.; Roy, S.; et al. Ellagic Acid, a Dietary Polyphenol, Inhibits Tautomerase Activity of Human Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor and Its Pro-Inflammatory Responses in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4988–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Lin, C.; Fu, C.; Lu, H.; Jin, H.; Chen, Q.; Pan, J. The Protective Effect of Ellagic Acid (EA) in Osteoarthritis: An in Vitro and in Vivo Study. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Lombó, C.; Posadas, Y.; Quintanar, L.; Gonsebatt, M.E.; Franco, R. Neurotoxicity Linked to Dysfunctional Metal Ion Homeostasis and Xenobiotic Metal Exposure: Redox Signaling and Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2018, 28, 1669–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamu, A.; Li, S.; Gao, F.; Xue, G. The Role of Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Current Understanding and Future Therapeutic Targets. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1347987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, N.; Shah, M.A.; Rasul, A.; Chauhdary, Z.; Saleem, U.; Khan, H.; Ahmed, N.; Uddin, M.S.; Mathew, B.; Behl, T.; et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Ellagic Acid in Alzheimer’s Disease: Focus on Underlying Molecular Mechanisms of Therapeutic Potential. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, X. Ellagic Acid and Its Anti-Aging Effects on Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, M.; Amiri, S.; Nesari, A.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Mansouri, E.; Mehrzadi, S. The Possible Neuroprotective Effect of Ellagic Acid on Sodium Arsenate-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats. Life Sci. 2018, 198, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozben, T.; Ozben, S. Neuro-Inflammation and Anti-Inflammatory Treatment Options for Alzheimer’s Disease. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 72, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanadgol, N.; Golab, F.; Mostafaie, A.; Mehdizadeh, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Ravan, H. Ellagic Acid Ameliorates Cuprizone-Induced Acute CNS Inflammation via Restriction of Microgliosis and down-Regulation of CCL2 and CCL3 pro-Inflammatory Chemokines. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Mehan, S.; Khanna, D.; Kalra, S.; Parveen, S. Precautionary Ellagic Acid Treatment Ameliorates Chronically Administered Scopolamine Induced Alzheimer’s Type Memory and Cognitive Dysfunctions in Rats. Pharmacologia 2015, 6, 192–212. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.; Kumar, S. Inhibition of BACE1, MAO-B, Cholinesterase Enzymes, and Anti-Amyloidogenic Potential of Selected Natural Phytoconstituents: Multi-Target-Directed Ligand Approach. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardah, M.T.; Bharathan, G.; Kitada, T.; Haque, M.E. Ellagic Acid Prevents Dopamine Neuron Degeneration from Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in MPTP Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, L.C.; Adrian, C.W.; Khamki, K.A.; Ying, K.Y.; Shahfri, M.F.M.; Hee, N.B.; Nelly, N.M.N.; Santhirasaygaran, P.; Han, S.Y.; Yi, T.C.; et al. Physical Health Impacts of Obesity: Comprehensive Review. Prog. Drug Discov. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Nagaoka, S. Ellagic Acid Affects mRNA Expression Levels of Genes That Regulate Cholesterol Metabolism in HepG2 Cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia-Meza, E.I.; Yáñez, J.A.; Remsberg, C.M.; Takemoto, J.K.; Davies, N.M.; Rasco, B.; Clary, C. Effect of Dehydration on Raspberries: Polyphenol and Anthocyanin Retention, Antioxidant Capacity, and Antiadipogenic Activity. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, H5–H12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, L.; Ran, X.; Long, M.; Zhang, M.; Tao, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Halmurati, U.; et al. Ellagic Acid Reduces Adipogenesis through Inhibition of Differentiation-Prevention of the Induction of Rb Phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 287534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino-Wakagi, Y.; Yoshimura, Y.; Uzawa, Y.; Zaima, N.; Moriyama, T.; Kawamura, Y. Ellagic Acid in Pomegranate Suppresses Resistin Secretion by a Novel Regulatory Mechanism Involving the Degradation of Intracellular Resistin Protein in Adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; Ning, C.; Zhang, M.; Fan, P.; Lei, D.; Du, J.; Gale, M.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y. Ellagic Acid Promotes Browning of White Adipose Tissues in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats through Suppressing White Adipocyte Maintaining Genes. Endocr. J. 2019, 66, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Jeong, E.-S.; Lee, K.H.; Na, J.-R.; Park, S.; Kim, J.S.; Na, C.-S.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, S. Unripe Rubus Coreanus Miquel Extract Containing Ellagic Acid Promotes Lipolysis and Thermogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo. Molecules 2020, 25, 5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceci, C.; Graziani, G.; Faraoni, I.; Cacciotti, I. Strategies to Improve Ellagic Acid Bioavailability: From Natural or Semisynthetic Derivatives to Nanotechnological Approaches Based on Innovative Carriers. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 382001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeram, N.P.; Lee, R.; Heber, D. Bioavailability of Ellagic Acid in Human Plasma after Consumption of Ellagitannins from Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Juice. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 348, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccari, G.; Baldassari, S.; Ailuno, G.; Turrini, F.; Alfei, S.; Caviglioli, G. Formulation Strategies to Improve Oral Bioavailability of Ellagic Acid. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, F.M.; Ibrahim, S.R.-M. Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponge for Improvement of Solubility and Oral Bioavailability of Ellagic Acid. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 31, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Loo, W.T.; Jin, L.J.; Cheung, M.N.; Chow, L.W. Evaluation of Ellagic Acid on the Activities of Oral Bacteria with the Use of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Bioluminescence Assay. AJB 2010, 9, 3938–3943. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose, S.S.; Solairaj, P.; Subramoniam, A. Effectiveness of Ellagic Acid on Isoniazid-Rifampicin Induced Liver Damage in Rats. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2013, 4, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trefts, E.; Gannon, M.; Wasserman, D.H. The Liver. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R1147–R1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, D.J.; McCullough, A.J. The Impact of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome on Alcoholic Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2014, 18, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimpin, L.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Negro, F.; Corbould, E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Webber, L.; Sheron, N. Burden of Liver Disease in Europe: Epidemiology and Analysis of Risk Factors to Identify Prevention Policies. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 718–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Qiu, S.; Li, J.; Shen, J.; Zu, Y.; Shi, J.; Sui, G. Ellagic Acid Synergistically Potentiates Inhibitory Activities of Chemotherapeutic Agents to Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Phytomedicine 2019, 59, 152921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshtzar, E.; Khodayar, M.J.; Javadipour, M.; Ghaffari, M.A.; Bolduc, D.L.; Rezaei, M. Ellagic Acid Protects against Arsenic Toxicity in Isolated Rat Mitochondria Possibly through the Maintaining of Complex II. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athukuri, B.L.; Neerati, P. Enhanced Oral Bioavailability of Metoprolol with Gallic Acid and Ellagic Acid in Male Wistar Rats: Involvement of CYP2D6 Inhibition. Drug Metab. Pers. Ther. 2016, 31, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Jian, T.; Wu, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, H.; Ma, L.; Ren, B.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; et al. Ellagic Acid Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Insulin Resistance in High Glucose-Treated HepG2 Cells via miR-223/Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, M.; Amigo-Benavent, M.; Mesias, M.; Baeza, G.; Gökmen, V.; Bravo, L.; Morales, F.J. An Aqueous Pomegranate Seed Extract Ameliorates Oxidative Stress of Human Hepatoma HepG2 Cells. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1622–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarsini, K.I.; Khopde, S.M.; Kumar, S.S.; Mohan, H. Free Radical Studies of Ellagic Acid, a Natural Phenolic Antioxidant. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2200–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, N.F.; Elyamany, M.; Gad, A.M.; Assaf, N.; Fawzy, H.M.; Elesawy, W.H. Ellagic Acid Attenuates Liver Toxicity Induced by Valproic Acid in Rats. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 143, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, G.; Semiz, A.; Karakurt, S.; Arslan, S.; Adali, O.; Sen, A. A Comparative Study for the Evaluation of Two Doses of Ellagic Acid on Hepatic Drug Metabolizing and Antioxidant Enzymes in the Rat. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 358945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, K.I.; Koch, A.C.; Mead, M.N.; Tothy, P.K.; Newman, R.A.; Gyllenhaal, C. Impact of Antioxidant Supplementation on Chemotherapeutic Toxicity: A Systematic Review of the Evidence from Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K. Does the Interdependence between Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Explain the Antioxidant Paradox? Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5698931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhad, A.; Chopra, K. Attenuation of Diabetic Nephropathy by Tocotrienol: Involvement of NFkB Signaling Pathway. Life Sci. 2009, 84, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahad, A.; Ganai, A.A.; Mujeeb, M.; Siddiqui, W.A. Ellagic Acid, an NF-κB Inhibitor, Ameliorates Renal Function in Experimental Diabetic Nephropathy. Chem. -Biol. Interact. 2014, 219, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winand, J.; Schneider, Y.-J. The Anti-Inflammatory Effect of a Pomegranate Husk Extract on Inflamed Adipocytes and Macrophages Cultivated Independently, but Not on the Inflammatory Vicious Cycle between Adipocytes and Macrophages. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, C.-S.; Jeong, S.-J.; Yoo, S.-R.; Lee, N.-R.; Shin, H.-K. Quantitative Analysis and In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Gallic Acid, Ellagic Acid, and Quercetin from Radix Sanguisorbae. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, R.R.; Rangwala, S.M.; Shapiro, J.S.; Rich, A.S.; Rhoades, B.; Qi, Y.; Wang, J.; Rajala, M.W.; Pocai, A.; Scherer, P.E.; et al. Regulation of Fasted Blood Glucose by Resistin. Science 2004, 303, 1195–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Nishii, S.; Zaima, N.; Moriyama, T.; Kawamura, Y. Ellagic Acid Improves Hepatic Steatosis and Serum Lipid Composition through Reduction of Serum Resistin Levels and Transcriptional Activation of Hepatic Ppara in Obese, Diabetic KK-Ay Mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 434, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Seki, E. Inflammation and Liver Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Semin. Liver Dis. 2019, 39, 026–042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, B.P.; Fong, L.; Kelley, R.K. Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Complex Interface between Inflammation, Fibrosis, and the Immune Response. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønning, S.B.; Voldvik, V.; Bergum, S.K.; Aaby, K.; Borge, G.I.A. Ellagic Acid and Urolithin A Modulate the Immune Response in LPS-Stimulated U937 Monocytic Cells and THP-1 Differentiated Macrophages. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7946–7959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, M.; Hou, C. Pomegranate Peel Polyphenols Inhibits Inflammation in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Macrophages via the Suppression of TLR4/NF-κB Pathway Activation. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 43, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.Y.; Fatemi, I.; Kalantari, H.; Mombeini, M.A.; Mehrzadi, S.; Goudarzi, M. Ellagic Acid Prevents Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Histopathological Alterations in Acrylamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Wistar Rats. J. Diet. Suppl. 2020, 17, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Deng, W.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Sun, L.; Sun, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, H. Ellagic Acid Protects Lipopolysaccharide/d-Galactosamine-Induced Acute Hepatic Injury in Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori, M.; Jafari, B.; Hekmatdoost, A. Pomegranate Juice Prevents Development of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Rats by Attenuating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2327–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrecque, L.; Lamy, S.; Chapus, A.; Mihoubi, S.; Durocher, Y.; Cass, B.; Bojanowski, M.W.; Gingras, D.; Béliveau, R. Combined Inhibition of PDGF and VEGF Receptors by Ellagic Acid, a Dietary-Derived Phenolic Compound. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Zhou, B.; Liu, C.; Ruan, J.; Yan, Q.; Liao, J.; Zhu, F. In Vitro Antiproliferative and Antioxidant Effects of Urolithin A, the Colonic Metabolite of Ellagic Acid, on Hepatocellular Carcinomas HepG2 Cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, R.; Sepand, M.R.; Seyednejad, S.A.; Omidi, A.; Akbariani, M.; Gholami, M.; Sabzevari, O. Ellagic Acid Reduces Methotrexate-Induced Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Dysfunction via up-Regulating Nrf2 Expression and Inhibiting the IĸBα/NFĸB in Rats. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 27, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, A.; Gok, O.; Erman, O.; Kuloglu, T. Ellagic Acid Impedes Carbontetrachloride-Induced Liver Damage in Rats through Suppression of NF-kB, Bcl-2 and Regulating Nrf-2 and Caspase Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shendge, A.K.; Basu, T.; Panja, S.; Chaudhuri, D.; Mandal, N. An Ellagic Acid Isolated from Clerodendrum Viscosum Leaves Ameliorates Iron-Overload Induced Hepatotoxicity in Swiss Albino Mice through Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and the Apoptotic Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Vinayak, M. Role of Ellagic Acid in Regulation of Apoptosis by Modulating Novel and Atypical PKC in Lymphoma Bearing Mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehal, W.Z.; Schuppan, D. Antifibrotic Therapies in the Liver. Semin. Liver Dis. 2015, 35, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buniatian, G.H.; Weiskirchen, R.; Weiss, T.S.; Schwinghammer, U.; Fritz, M.; Seferyan, T.; Proksch, B.; Glaser, M.; Lourhmati, A.; Buadze, M.; et al. Antifibrotic Effects of Amyloid-Beta and Its Loss in Cirrhotic Liver. Cells 2020, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, T.; Friedman, S.L.; Hoshida, Y. Hepatic Stellate Cells as Key Target in Liver Fibrosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 121, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Murata, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Matsuzaki, K.; Okazaki, K. Reversible Human TGF-β Signal Shifting between Tumor Suppression and Fibro-Carcinogenesis: Implications of Smad Phospho-Isoforms for Hepatic Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Won, J.H.; Choi, J.M.; Cha, H.H.; Jang, Y.J.; Park, S.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, D.K. Protective Effect of Ellagic Acid on Concanavalin A-Induced Hepatitis via Toll-Like Receptor and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase/Nuclear Factor κB Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10110–10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchal, S.K.; Ward, L.; Brown, L. Ellagic Acid Attenuates High-Carbohydrate, High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nankar, R.P.; Doble, M. Hybrid Drug Combination: Anti-Diabetic Treatment of Type 2 Diabetic Wistar Rats with Combination of Ellagic Acid and Pioglitazone. Phytomedicine 2017, 37, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, P.-C.; Hsu, C.-C.; Yin, M.-C. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Coagulatory Activities of Caffeic Acid and Ellagic Acid in Cardiac Tissue of Diabetic Mice. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, J.; Sheng, L.; Yuan, M.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, G.; Qiu, Z. Ellagic Acid Ameliorates AKT-Driven Hepatic Steatosis in Mice by Suppressing de Novo Lipogenesis via the AKT/SREBP-1/FASN Pathway. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3410–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, Y.; Koul, A.; Ranawat, P. Ellagic Acid Ameliorates Cisplatin Induced Hepatotoxicity in Colon Carcinogenesis. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ren, X.; He, K.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Roller, M.; Zheng, B.; Zheng, Q.; Ho, C.-T.; Bai, N. The Anti-Diabetic Effect of Eight Lagerstroemia Speciosa Leaf Extracts Based on the Contents of Ellagitannins and Ellagic Acid Derivatives. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polce, S.A.; Burke, C.; França, L.M.; Kramer, B.; Paes, A.M.d.A.; Carrillo-Sepulveda, M.A. Ellagic Acid Alleviates Hepatic Oxidative Stress and Insulin Resistance in Diabetic Female Rats. Nutrients 2018, 10, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, N.; Hafizur, R.M.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S.; Nisar, M.; Kabir, N. Ellagic Acid in Emblica Officinalis Exerts Anti-Diabetic Activity through the Action on β-Cells of Pancreas. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadimi, M.; Foroughi, F.; Hashemipour, S.; Rashidi Nooshabadi, M.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Ahadi Nezhad, B.; Khadem Haghighian, H. Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Examining the Ellagic Acid Effects on Glycemic Status, Insulin Resistance, Antioxidant, and Inflammatory Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sarrías, A.; García-Villalba, R.; Núñez-Sánchez, M.Á.; Tomé-Carneiro, J.; Zafrilla, P.; Mulero, J.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Espín, J.C. Identifying the Limits for Ellagic Acid Bioavailability: A Crossover Pharmacokinetic Study in Healthy Volunteers after Consumption of Pomegranate Extracts. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cui, S.; Mao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Tang, X.; Chen, W. Ellagic Acid and Intestinal Microflora Metabolite Urolithin A: A Review on Its Sources, Metabolic Distribution, Health Benefits, and Biotransformation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 6900–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lv, D.; Guan, Y. Appeal of Urolithins from Synthesis to Biological Activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 11477–11494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; García-Villalba, R.; González-Sarrías, A.; Selma, M.V.; Espín, J.C. Ellagic Acid Metabolism by Human Gut Microbiota: Consistent Observation of Three Urolithin Phenotypes in Intervention Trials, Independent of Food Source, Age, and Health Status. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6535–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Han, L.; Xiao, Y.; Bian, J.; Liu, C.; Gong, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M. MUP1 Mediates Urolithin A Alleviation of Chronic Alcohol-Related Liver Disease via Gut-Microbiota-Liver Axis. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2367342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Tan, Z.; Chen, C.; Li, W.; Yang, R. Ellagic Acid Alleviates High-Fructose Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating Liver Metabolic Profiles and Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 76, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, M.; Yi, X.; Lu, X.; Zhu, M.; Xue, M.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: New Prospects for Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Therapeutic Targets. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jian, Y.-P.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Li, Y.; Gu, L.-T.; Sun, H.-H.; Liu, M.-D.; Zhou, H.-L.; Wang, Y.-S.; Xu, Z.-X. Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Diseases. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, P.; Wang, Y.; Xie, M. Ellagic Acid and Gut Microbiota: Interactions, and Implications for Health. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liang, J.; Han, M.; Gao, Z. Polyphenols Synergistic Drugs to Ameliorate Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Signal Pathway and Gut Microbiota: A Review. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 68, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yin, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Pathogenesis and Natural Products for Prevention and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.P. Natural History of NAFLD: Remarkably Benign in the Absence of Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinn, D.H.; Kang, D.; Guallar, E.; Choi, S.C.; Hong, Y.S.; Park, Y.; Cho, J.; Gwak, G.-Y. Regression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Associated with Reduced Risk of Incident Diabetes: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyas, F.; Ali, H.; Patel, P.; Sarfraz, S.; Basuli, D.; Giammarino, A.; Satapathy, S.K. Increasing Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease–Related Mortality Rates in the United States from 1999 to 2022. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e00207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.L.; Ng, C.H.; Huang, D.Q.; Chan, K.E.; Tan, D.J.; Lim, W.H.; Yang, J.D.; Tan, E.; Muthiah, M.D. Global Incidence and Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S32–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.M.; Henry, L.; Younossi, Y.; Ong, J.; Alqahtani, S.; Younossi, Z.M. The Burden of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Is Rapidly Growing in Every Region of the World from 1990 to 2019. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A Multisociety Delphi Consensus Statement on New Fatty Liver Disease Nomenclature. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E.; Moschen, A.R. Multiple Parallel Hits Hypothesis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Revisited After a Decade. Hepatology 2021, 73, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The Multiple-Hit Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, P.; Byrne, C.D. Bidirectional Relationships and Disconnects between NAFLD and Features of the Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-S.; Song, B.-J.; Cho, Y.-E. Pomegranate-Derived Exosome-Like Nanovesicles Containing Ellagic Acid Alleviate Gut Leakage and Liver Injury in MASLD. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.-M.; Zhang, Q.-Z.; Chen, M.-L.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.-J.; Wang, D.-M.; Pan, Y.-N.; Liu, X.-Q. Anti-NAFLD Effect of Defatted Walnut Powder Extract in High Fat Diet-Induced C57BL/6 Mice by Modulating the Gut Microbiota. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 270, 113814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Tian, H.; Ji, Y.; Dong, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Shi, H.; Li, H.; Yang, L. Urolithin C Reveals Anti-NAFLD Potential via AMPK-Ferroptosis Axis and Modulating Gut Microbiota. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 2687–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.; Rivera, L.; Furness, J.B.; Angus, P.W. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in NAFLD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elseweidy, M.M.; Elesawy, A.E.; Sobh, M.S.; Elnagar, G.M. Ellagic Acid Ameliorates High Fructose-Induced Hyperuricemia and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver in Wistar Rats: Focusing on the Role of C1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Protein-3 and ATP Citrate Lyase. Life Sci. 2022, 305, 120751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mighani, S.; Samimi, R.; Nooshabadi, M.R.; Farzam, S.A.; Haghighian, H.K.; Javadi, M. A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Investigating the Effects of Ellagic Acid on Glycemic Status, Liver Enzymes, and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2025, 25, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
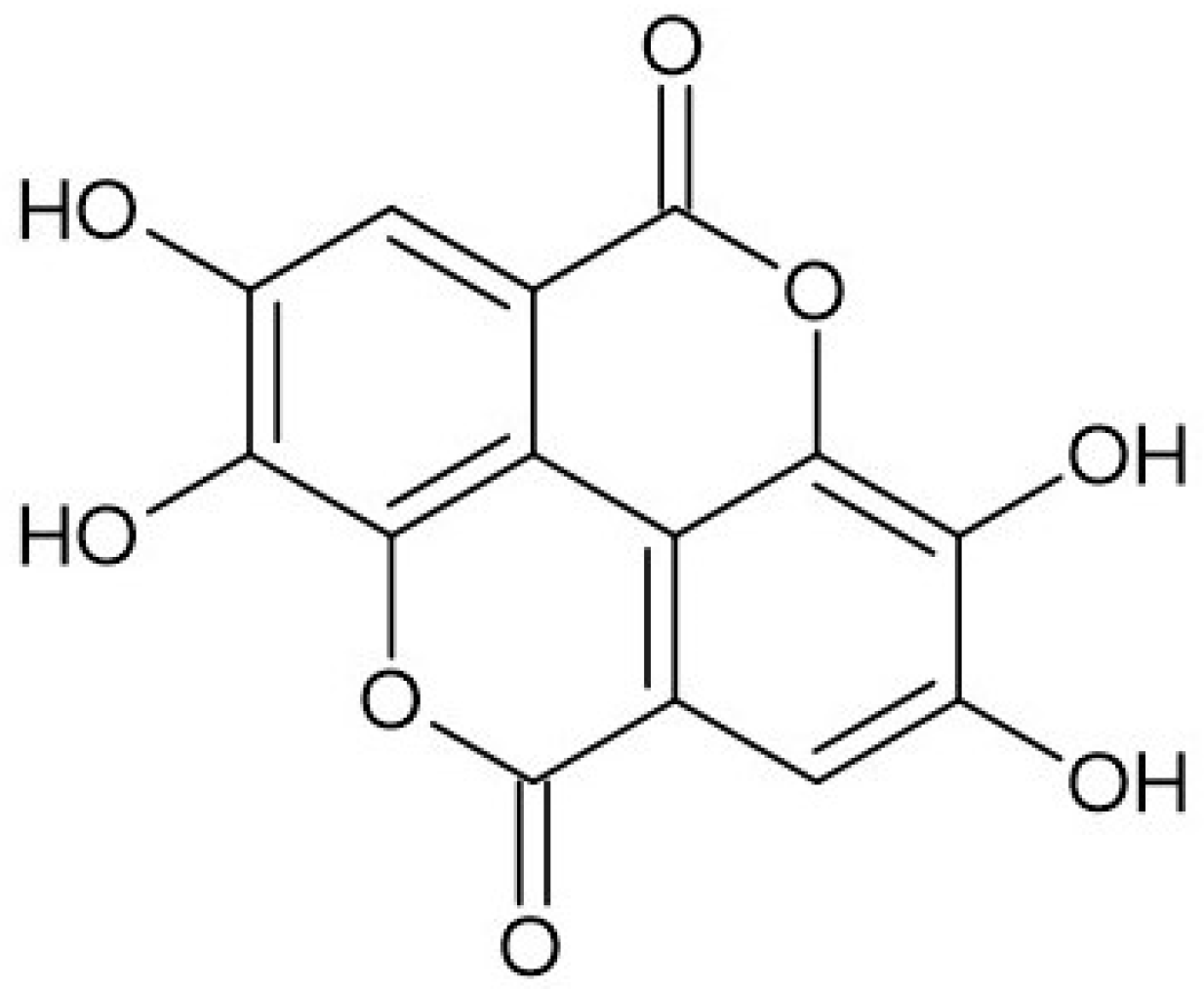
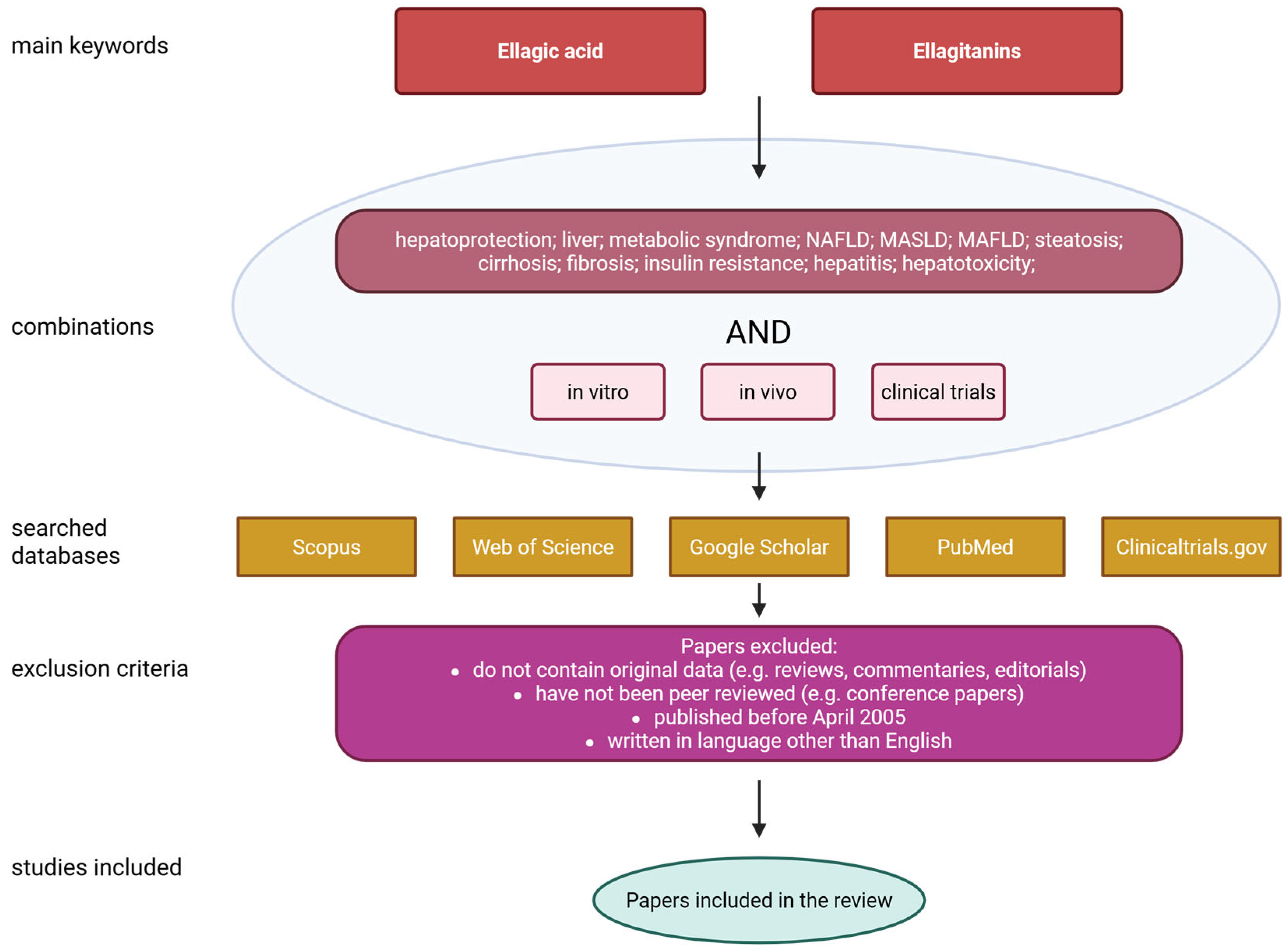
| Source of EA | Amount/Comments | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Acalypha hispida Burm.f. | 119.4 mg/100 g and 540.9 mg/100 g of dry ethanol and aqueous extracts, respectively | [18] |
| Castanea crenata Sieb. & Zucc. | 1.74 mg/g extract and 2.26 mg/g leaves | [19] |
| E. angustifolia L. | 8.52 mg/g in leaf water extract | [20] |
| Eugenia uniflora L. | 0.2% (2.72 w/w)—crude extract; 0.035% (3.90 w/w)—aqua fractions; 0.323% (4.05 w/w)—ethyl acetate fraction | [21] |
| Myrtus communis L. | 3.88 mg/g leaf dry weight | [22] |
| Pandiaka angustifolia (Vahl) Hepper | 65.44% in leaves | [23] |
| Phyllanthus amarus Schum. & Thonn. (Euphorbiaceae) | 2.06% determined in extract using HPLC method | [24] |
| Salacia chinensis L. | 51.60 mg/g of dry weight | [25] |
| Syzygium calophyllifolium (Wight) Walp. | 88% of TPC analyzed in fruits | [26] |
| Type of Study | Cell Line/Model | Dose | Results | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In vivo | BALB/c mice | 50–200 mg/kg of body weight | ↓ plasma aminotransferase ↓ liver necrosis ↓ levels of TLR2 and TLR4 mRNA in liver ↓ NF-κB in liver ↓ IκB-α degradation levels in liver ↓ TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β | [104] |
| In vivo | Wistar rats | 0.8 g/kg food | ↓ NF-κB in liver ↑ Nrf2 i CPT1 in liver | [105] |
| In vivo | Nicotinamide induced diabetic rats | 20 mg/kg BW | improvement in liver function markers ↓ hyperglycemia ↓ dyslipidemia | [106] |
| In vivo | BALB/c mice | 2 g/100 g diet | ↑ plasma insulin and ↓ plasma glucose levels ↓ triglyceride in plasma | [107] |
| In vivo | FVB/N mice HepG2 | 150 or 300 mg/kg BW 0–40 μM | ↓ SREBP-1/FASN axis ↓ AKT-triggered hepatic de novo lipogenesis, | [108] |
| In vivo and in vitro | Sprague-Dawley rats | 60 mg/kg BW | ↓valproic acid induced hepatic injury | [77] |
| Mice | 10 mg/kg BW | ↓ cisplatin induced hepatotoxicity ↓ peroxidative damage to liver tissue | [109] | |
| In vivo | Wistar rats | 10 mg/kg BW | ↓ CCl4 induced liver damage ↑ Nrf2 in liver ↓ NF-κB in liver | [97] |
| In vivo | Wistar rats | 60 mg/kg BW | ↓ AlCl3 induced hepatic function impairment, ↓ dyslipidemia and hepatic histological alterations ↓ MDA and PCC ↑ CAT, GPx and SOD activity in liver ↑ GSH | [8] |
| In vivo | Diabetic male mice | Lagerstroemia speciosa extracts (4 g of ellagic acid) | ↓ blood glucose, body weight, body fat ↑ insulin | [110] |
| In vivo | Goto-Kakizaki female rats | 50 mg/kg BW | ↓ IR lipid accumulation and oxidative stress ↑ insulin signaling pathway in the liver | [111] |
| In vivo | Non-obese type 2 diabetic rats | 50 mg/kg BW | ↑ serum insulin, β-cell size, β-cells number ↓ liver TBARS and glucose intolerance in rats | [112] |
| Clinical trial | 180 mg, for 8 weeks, p.o. | 44 patients | ↓ BS, IR, HbA1c, TC, TG, MDA and TNF-α ↑ TAC level and activity of GPx, SOD | [113] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wojtunik-Kulesza, K.; Niziński, P.; Krajewska, A.; Oniszczuk, T.; Combrzyński, M.; Oniszczuk, A. Therapeutic Potential of Ellagic Acid in Liver Diseases. Molecules 2025, 30, 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122596
Wojtunik-Kulesza K, Niziński P, Krajewska A, Oniszczuk T, Combrzyński M, Oniszczuk A. Therapeutic Potential of Ellagic Acid in Liver Diseases. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122596
Chicago/Turabian StyleWojtunik-Kulesza, Karolina, Przemysław Niziński, Anna Krajewska, Tomasz Oniszczuk, Maciej Combrzyński, and Anna Oniszczuk. 2025. "Therapeutic Potential of Ellagic Acid in Liver Diseases" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122596
APA StyleWojtunik-Kulesza, K., Niziński, P., Krajewska, A., Oniszczuk, T., Combrzyński, M., & Oniszczuk, A. (2025). Therapeutic Potential of Ellagic Acid in Liver Diseases. Molecules, 30(12), 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122596









