Proteolytic Activity of Silkworm Thorn (Cudrania tricuspidata) Fruit for Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Food Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Proteolytic Characteristics of ESF
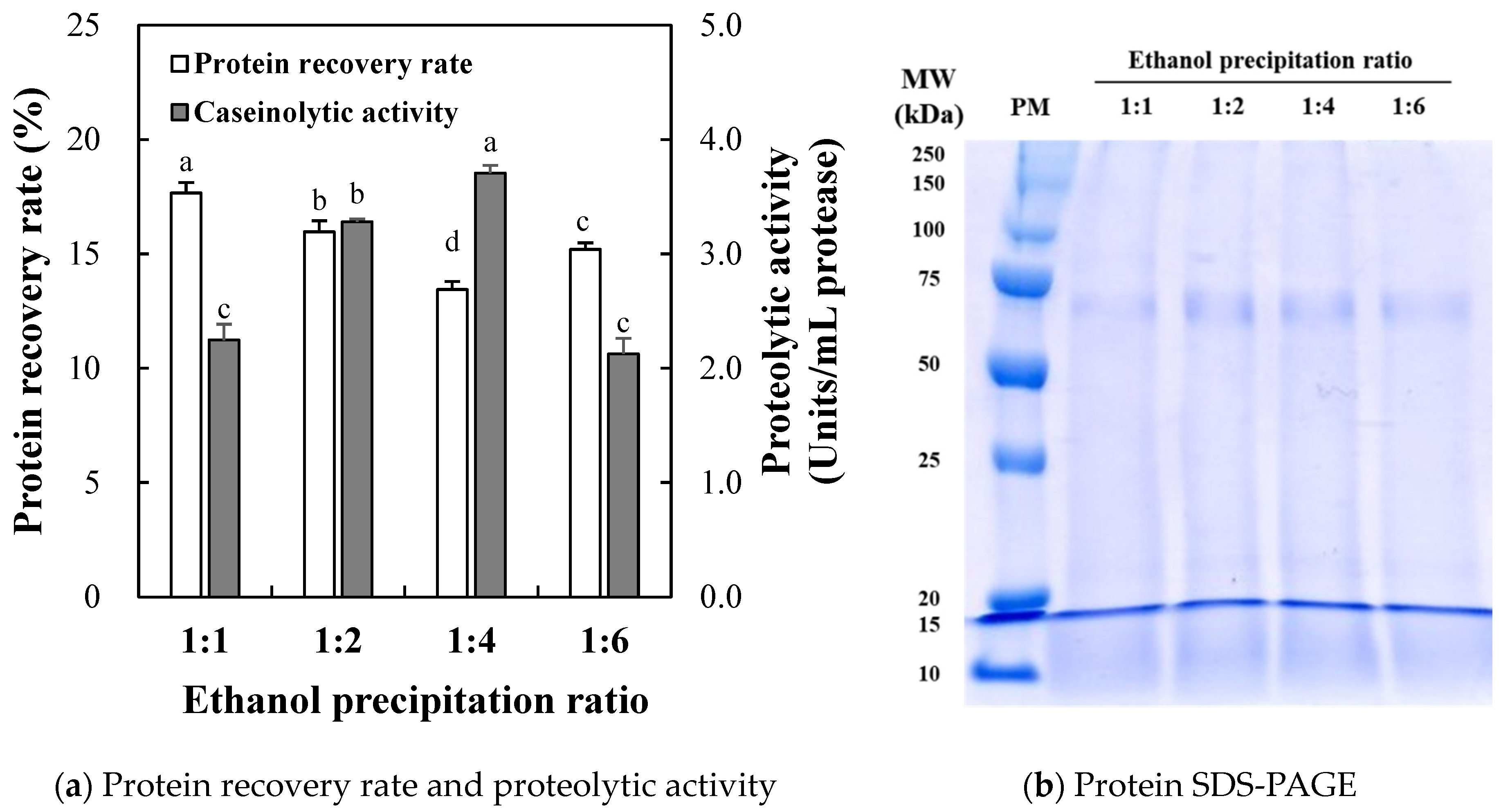
2.1.1. Protein Recovery Rate and Proteolytic Activity
2.1.2. Proteolytic Activity
2.1.3. SDS-PAGE
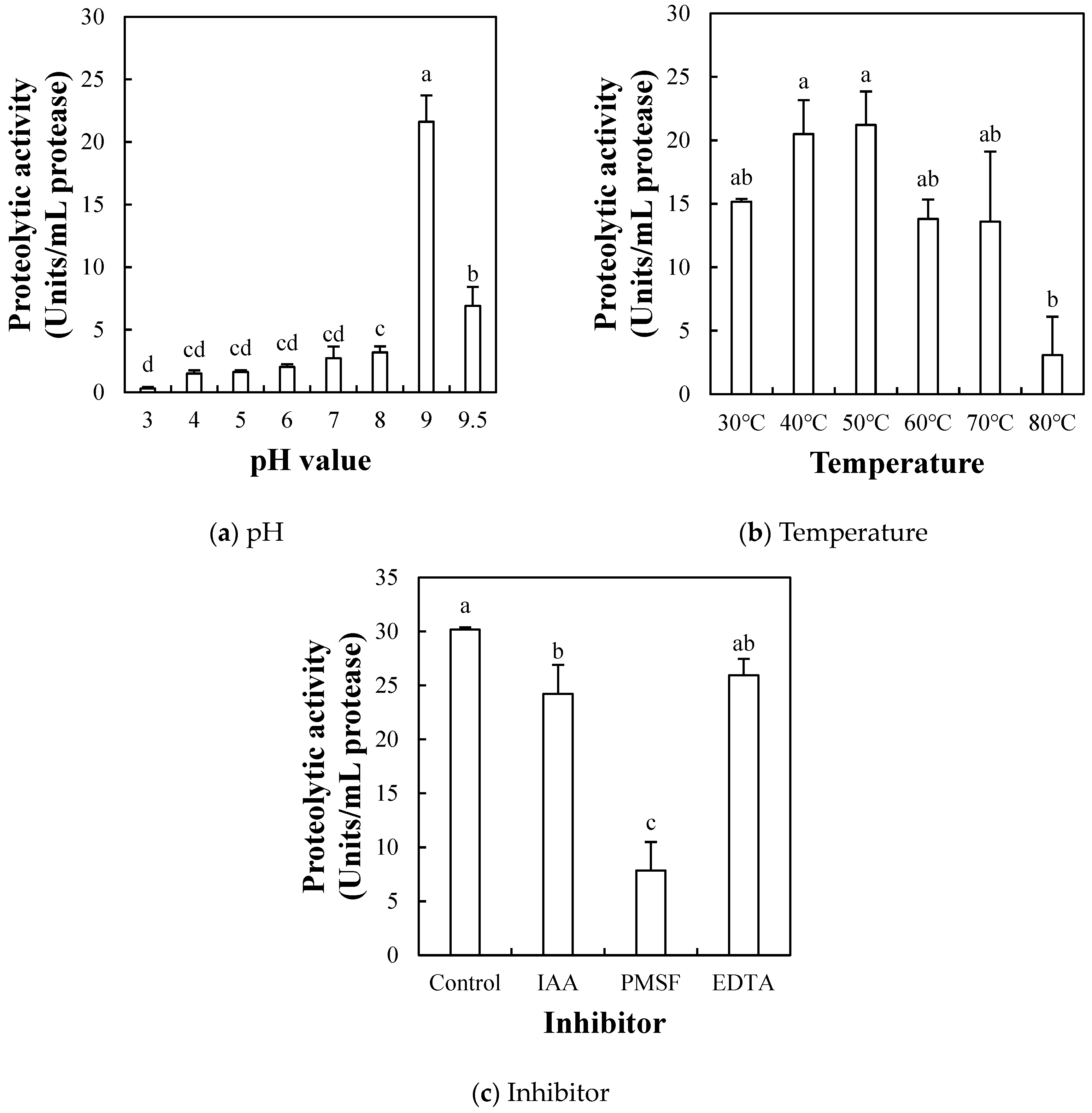
2.1.4. Effect of pH, Temperature, and Inhibitor on Proteolytic Activity
2.2. Hydrolysis and Antioxidant Characteristics of Protein Hydrolyzate Using SF Powder
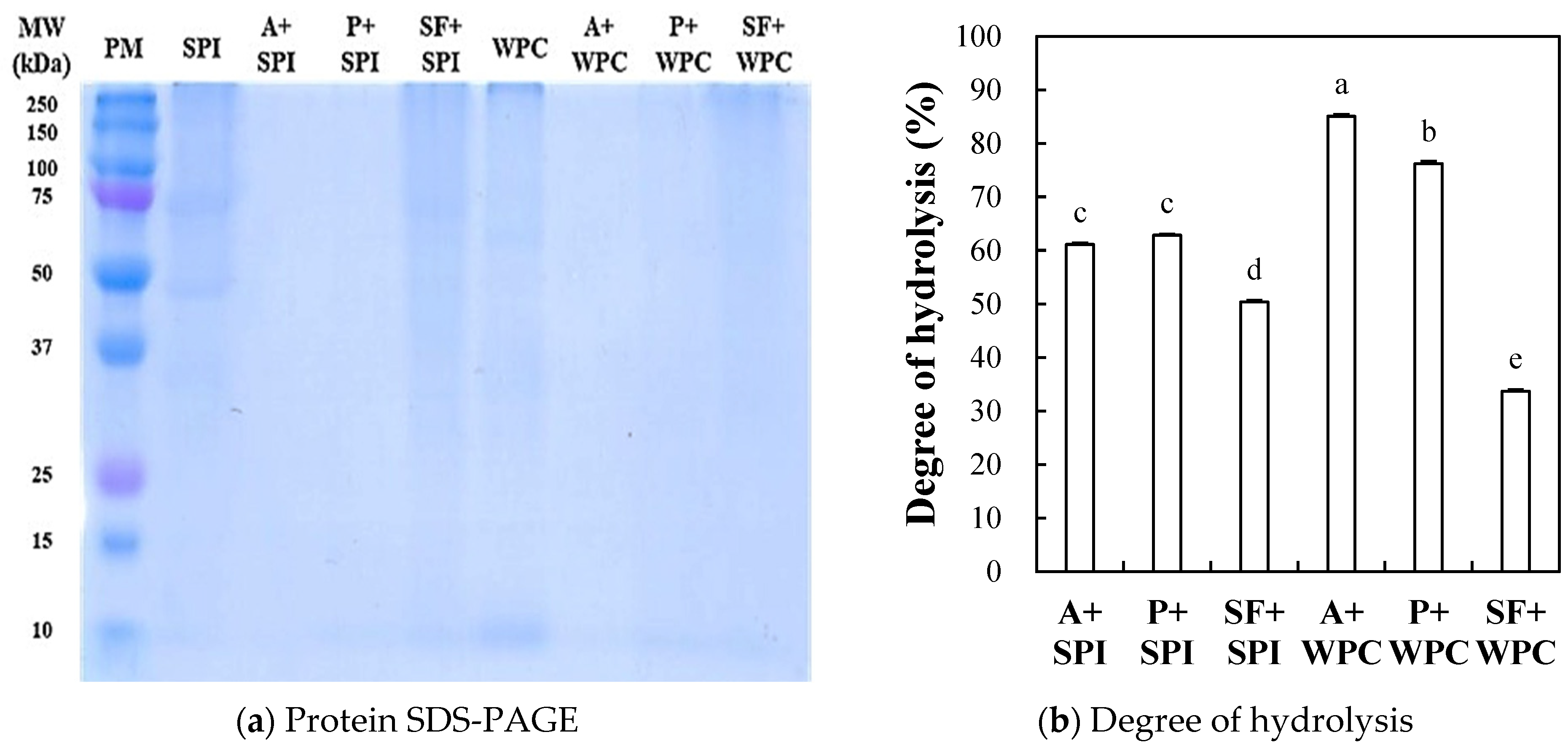
2.2.1. Protein SDS-PAGE
2.2.2. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH)
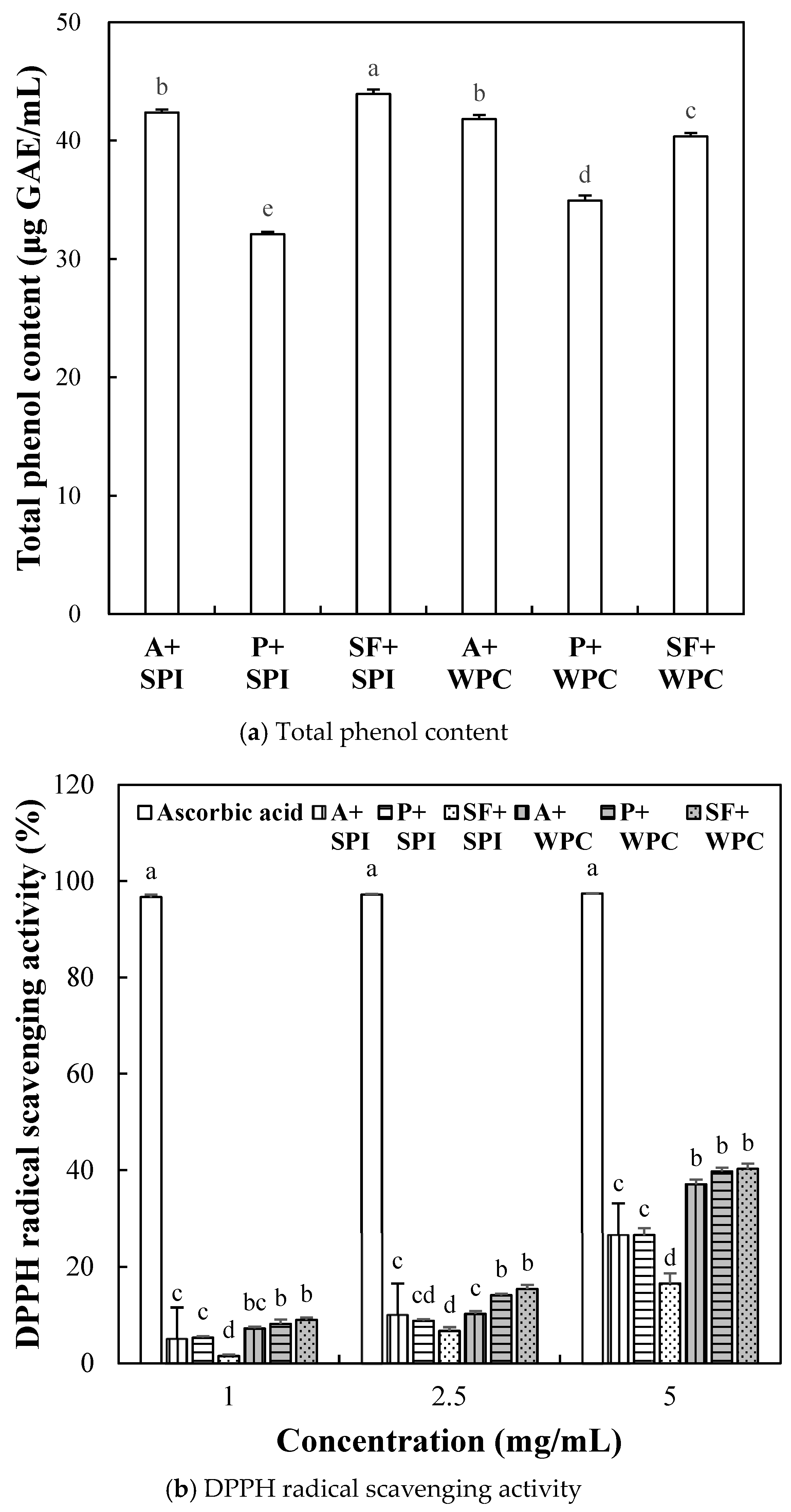
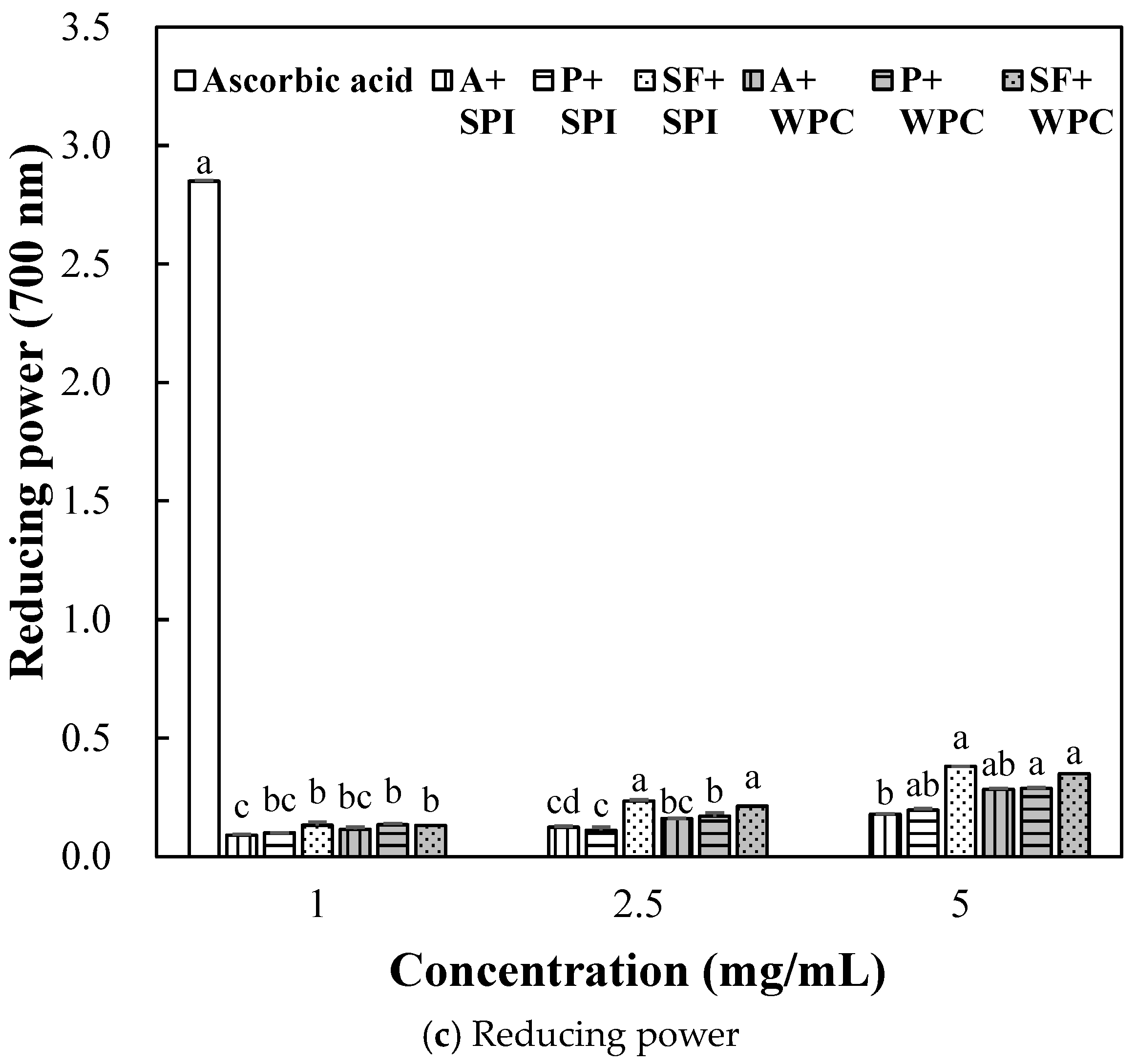
2.2.3. Antioxidant Activity of SPI and WPC Hydrolyzate
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Raw Material
3.2. Isolation and Partial Purification of Proteolytic Fraction
3.3. Proteolytic Characteristics of ESF
3.3.1. Protein Recovery Rate
3.3.2. Proteolytic Activity
- VT = total volume (mL) of assay.
- VE = volume of protease (mL).
- T = time of assay (min) as per the unit definition.
- VA = volume (mL) used in colorimetric determination.
3.3.3. Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
3.3.4. Effects of pH, Temperature, and Inhibitor on Proteolytic Activity
3.4. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Soy and Whey Proteins
3.5. Hydrolysis and Antioxidant Characteristics of SPI and WPC Hydrolyzates
3.5.1. SDS-PAGE
3.5.2. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH)
3.5.3. Total Phenol Content
3.5.4. 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Radical Scavenging Activity
3.5.5. Reducing Power
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asaithambi, N.; Singha, P.; Singh, S.K. Recent application of protein hydrolysates in food texture modification. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 10412–10443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinlschmidt, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Eisner, P. Soy protein hydrolysates fermentation: Effect of debittering and degradation of major soy allergens. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; van der Veer, F.; Sforza, S.; Gruppen, H.; Wierenga, P.A. Towards predicting protein hydrolysis by bovine trypsin. Process Biochem. 2018, 65, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Casas, D.E.; Aguilar, C.N.; Ascacio-Valdés, J.A.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Chávez-González, M.L.; Flores-Gallegos, A.C. Enzymatic hydrolysis and microbial fermentation: The most favorable biotechnological methods for the release of bioactive peptides. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2021, 3, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijoo-Siota, L.; Villa, T.G. Native and biotechnologically engineered plant proteases with industrial applications. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2011, 4, 1066–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Mittal, A.; Kumar, M.; Mehta, P.K. Microbial proteases in commercial applications. J. Pharm. Chem. Biol. Sci. 2016, 4, 365–374. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, K.S.; Kim, J.W. Antioxidant Activity and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme I Inhibitory Activity of Schisandra chinensis Fruit Extracts according to Drying Methods. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 41, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.Y.; Cho, Y.S. Antioxidant Activity of Schisandra chinensis Fruits. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2001, 30, 547–551. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, O.K.; Ho, J.N.; Nam, D.E.; Jeon, W.J.; Hwang, K.T.; Kang, J.E.; Lee, J.M. Hepatoprotective Effects of Schisandra chinensis Leaf, Fruit, and Stem Extracts against Oxidative Damage. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 41, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.E.; Jo, E.J.; Byun, E.H. Antioxidant Activity and Neuroprotective Effects of Schisandra chinensis Fruit Polysaccharide Fractions. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 50, 543–548. [Google Scholar]
- Rudenskaya, G.N.; Bogdanova, E.A.; Revina, L.P.; Golovkin, B.N.; Stepanov, V.M. Macluralisin—A serine proteinase from fruits of Maclura pomifera (Raf.) Schneid. Planta 1995, 196, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumari, M.; Jagannadham, M.V. Benghalensin, a highly stable serine protease from the latex of medicinal plant Ficus benghalensis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 11120–11126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Chin, K.B. Effects of different drying methods on antioxidant activities of Cudrania Tricuspidata fruit powder and its effects on the product quality of marinated chicken breast. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lencastre Novaes, L.C.; Jozala, A.F.; Lopes, A.M.; de Carvalho Santos-Ebinuma, V.; Mazzola, P.G.; Pessoa Junior, A. Stability, purification, and applications of bromelain: A review. Biotechnol. Prog. 2016, 32, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, A.M.R.; Liggieri, C.S.; Bruno, M.A. Preparation of soy protein hydrolysates with antioxidant activity by using peptidases from latex of Maclura pomifera fruits. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, L.; McClements, D.J. Current insights into protein solubility: A review of its importance for alternative proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Qi, T.; Wei, X.; Qu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Luo, F.; Qian, Z. Thermosensitive polymeric hydrogels as drug delivery systems. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagerman, A.E.; Rice, M.E.; Ritchard, N.T. Mechanisms of protein precipitation for two tannins, pentagalloyl glucose and epicatechin16 (4→8) catechin (procyanidin). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2590–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Sarteshnizi, R.A.; Udenigwe, C.C. Recent advances in protein–polyphenol interactions focusing on structural properties related to antioxidant activities. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 45, 100840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, G.T.; Ju, I.O.; Choi, S.R.; You, D.H.; Noh, J.J. Food nutritional characteristics of fruit of Cudrania tricuspidata in its various maturation stages. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2013, 20, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuso, A.; Viscusi, P.; Larocca, S.; Sangari, F.S.; Lolli, V.; Caligiani, A. Protease-assisted mild extraction of soluble fibre and protein from fruit by-products: A biorefinery perspective. Foods 2022, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrons, M.A.; Bertucci, J.I.; Liggieri, C.S.; López, L.M.I.; Bruno, M.A. Milk clotting activity and production of bioactive peptides from whey using Maclura pomifera proteases. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antão, C.M.; Malcata, F.X. Plant serine proteases: Biochemical, physiological and molecular features. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 43, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaei, A.A.; Sajedi, R.H.; Sariri, R.; Seyfzadeh, S.; Stevanato, R. Cysteine enhances activity and stability of immobilized papain. Amino Acids 2010, 38, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.N.; Zhang, C.R.; Qi, B.K.; Sui, X.N.; Jiang, L.Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.Z. Immobilized alcalase alkaline protease on the magnetic chitosan nanoparticles used for soy protein isolate hydrolysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 239, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Long, C.; Xia, J.; Tong, P.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. Enzymatic characterisation of the immobilised Alcalase to hydrolyse egg white protein for potential allergenicity reduction. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncoso, D.; Sánchez, D.A.; Ferreira, M.L. Production of plant proteases and new biotechnological applications: An updated review. ChemistryOpen 2022, 11, e202200017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, L.M.; Brullo, A.; Natalucci, C.L.; Caffini, N.O.; Sorgentini, D.A.; Wagner, J.R. Thermal behavior, solubility and structural properties of soy concentrate hydrolyzed by new plant proteases. J. Food Biochem. 1998, 22, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, M.E.; Roblet, C.; Moresoli, C.; Ramassamy, C.; Bazinet, L. Comparative application of pressure-and electrically-driven membrane processes for isolation of bioactive peptides from soy protein hydrolysate. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 403, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mejia, E.; Ben, O. Soybean bioactive peptides: A new horizon in preventing chronic diseases. Sex. Reprod. Menopause 2006, 4, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullius, A.; Goettert, M.I.; de Souza, C.F.V. Whey protein hydrolysates as a source of bioactive peptides for functional foods–Biotechnological facilitation of industrial scale-up. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 42, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Wang, C.S. Formation and characterization of amyloid-like fibrils from soy β-conglycinin and glycinin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11058–11066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livney, Y.D. Milk proteins as vehicles for bioactives. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, N.P.; Santivarangkna, C.; Rajput, M.S.; Benjakul, S.; Maqsood, S. Valorization of fish byproducts: Sources to end-product applications of bioactive protein hydrolysate. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1803–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embiriekah, S.; Bulatović, M.; Borić, M.; Zarić, D.; Arsić, S.; Rakin, M. Selection of Lactobacillus strains for improvement of antioxidant activity of different soy, whey and milk protein substrates. J. Hyg. Eng. Des. 2016, 16, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Stout, M.A.; Park, C.W.; Drake, M.A. The effect of bleaching agents on the degradation of vitamins and carotenoids in spray-dried whey protein concentrate. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7922–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Yoon, Y.; Oh, E.; Sung, B.; Kim, Y. Effects of soy protein hydrolysates on antioxidant activity and inhibition of muscle loss. Int. Food Res. J. 2022, 29, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyug, T.S.; Prasad, K.N.; Ismail, A. Antioxidant capacity, phenolics and isoflavones in soybean by-products. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dande, S.; Manchala, R. Antioxidant and phenolic content of nuts, oil seeds, milk and milk products commonly consumed in India. Food Nutr. Sci. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.H.; Choi, G.N.; Kim, J.H.; Kwak, J.H.; Heo, H.J.; Shim, K.H.; Choi, J.S. In vitro antioxidative activities and phenolic composition of hot water extract from different parts of Cudrania tricuspidata. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2009, 14, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budryn, G.; Zaczyńska, D.; Rachwał-Rosiak, D.; Oracz, J. Changes in properties of food proteins after interaction with free and β-cyclodextrin encapsulated hydroxycinnamic acids. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abu-Salem, F.M.; Mahmoud, M.H.; El-Kalyoub, M.H.; Gibriel, A.Y.; Abou-Arab, A. Characterization of antioxidant peptides of soybean protein hydrolysate. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2013, 79, 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, T.H.; Benjakul, S.; Sae-leaw, T.; Balange, A.K.; Maqsood, S. Protein–polyphenol conjugates: Antioxidant property, functionalities and their applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.H.; Zhang, S.S.; Sun, B.Z.; Xie, P.; Wen, K.X.; Xu, C.C. Changes in physical meat traits, protein solubility, and the microstructure of different beef muscles during post-mortem aging. Foods 2020, 9, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupp-Enyard, C. Sigma’s non-specific protease activity assay-casein as a substrate. J. Vis. Exp. 2008, 19, e899. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmmed, M.K.; Carne, A.; Tian, H.S.; Bekhit, A.E.D.A. Use of fungal and bacterial protease preparations to enhance extraction of lipid from fish roe: Effect on lipidomic profile of extracted oil. Food Chem. 2022, 16, 100499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskovic, B.; Bozovic, O.; Prodanovic, R.; Niketic, V.; Polovic, N. Identification, purification and characterization of a novel collagenolytic serine protease from fig (Ficus carica var. Brown Turkey) latex. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 118, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.Y.; Yoon, K.Y. Conditions for hydrolysis of perilla seed meal protein for producing hydrolysates and ultrafiltered peptides and their antioxidant activity. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2018, 25, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshima, H.; Hirata, S.; Ayabe, S. Antioxidative and anti-hydrogen peroxide activities of various herbal teas. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Pan, D.; Guo, Y.; Li, J. Purification of chicken breast protein hydrolysate and analysis of its antioxidant activity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3397–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athukorala, Y.; Kim, K.N.; Jeon, Y.J. Antiproliferative and antioxidant properties of an enzymatic hydrolysate from brown alga, Ecklonia cava. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, N.-E.; Lee, D.-H.; Hwang, J.; Son, W.-Y.; Kim, K.-S.; Kim, G.-Y.; Kim, H.-W. Proteolytic Activity of Silkworm Thorn (Cudrania tricuspidata) Fruit for Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Food Proteins. Molecules 2024, 29, 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030693
Yang N-E, Lee D-H, Hwang J, Son W-Y, Kim K-S, Kim G-Y, Kim H-W. Proteolytic Activity of Silkworm Thorn (Cudrania tricuspidata) Fruit for Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Food Proteins. Molecules. 2024; 29(3):693. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030693
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Na-Eun, Da-Hoon Lee, Jun Hwang, Woo-Young Son, Kyeong-Soo Kim, Gwang-Yeon Kim, and Hyun-Wook Kim. 2024. "Proteolytic Activity of Silkworm Thorn (Cudrania tricuspidata) Fruit for Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Food Proteins" Molecules 29, no. 3: 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030693
APA StyleYang, N.-E., Lee, D.-H., Hwang, J., Son, W.-Y., Kim, K.-S., Kim, G.-Y., & Kim, H.-W. (2024). Proteolytic Activity of Silkworm Thorn (Cudrania tricuspidata) Fruit for Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Food Proteins. Molecules, 29(3), 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030693






