Impact of O-H···π Hydrogen Bond on IR and NMR Parameters of Cannabidiol: Theoretical and Experimental Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. DFT Conformational Analysis
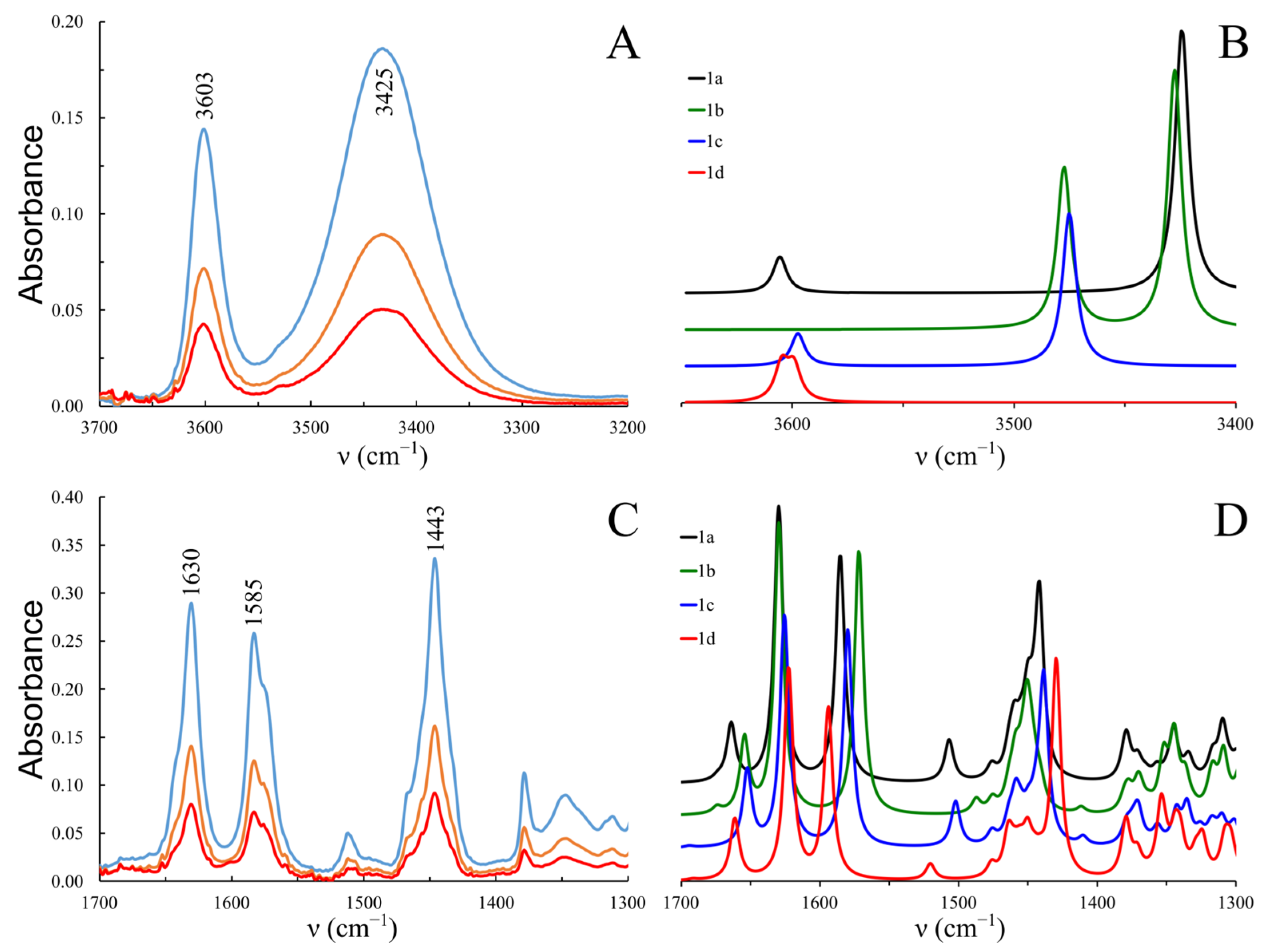
2.2. FTIR Spectra
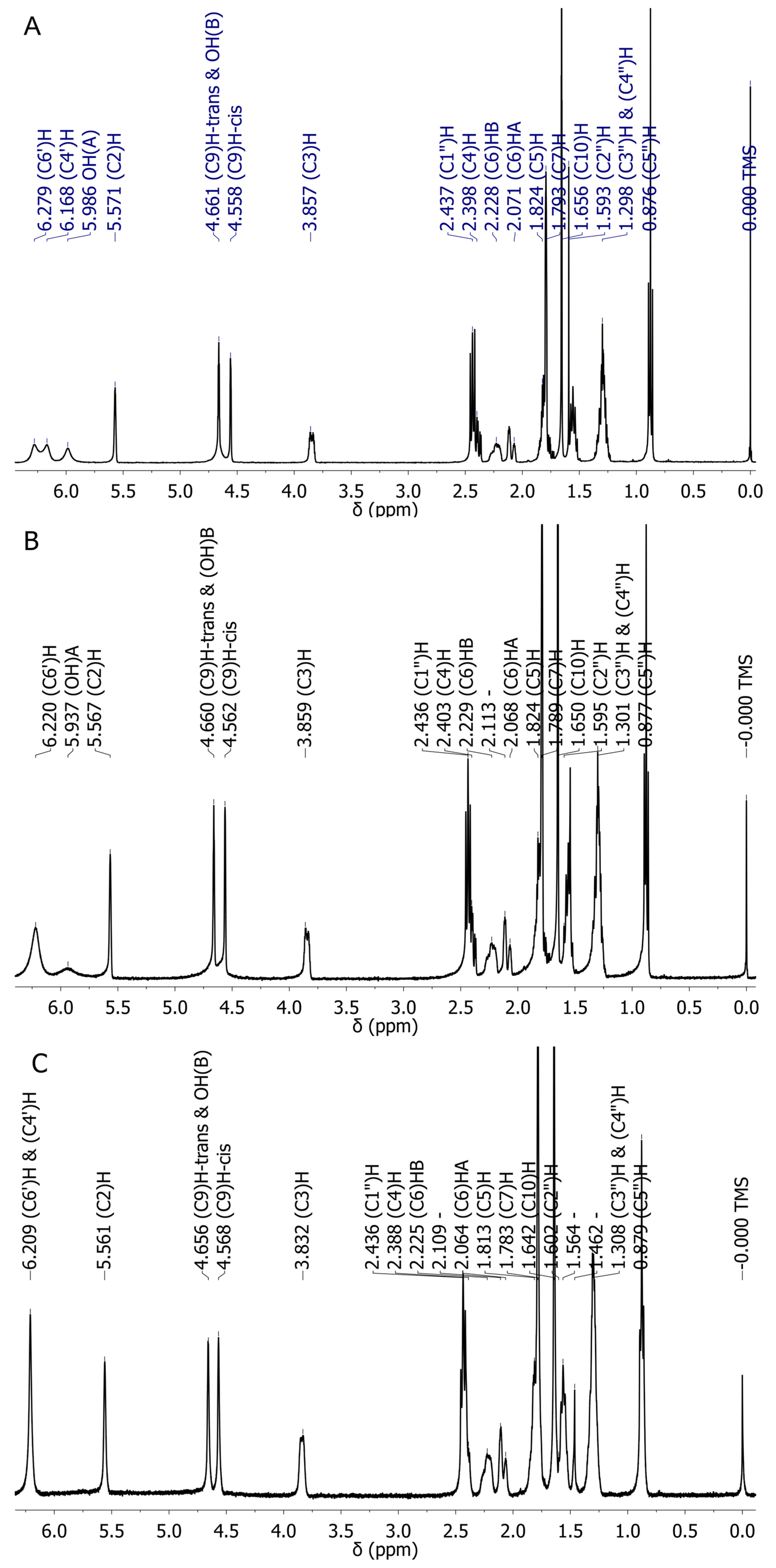
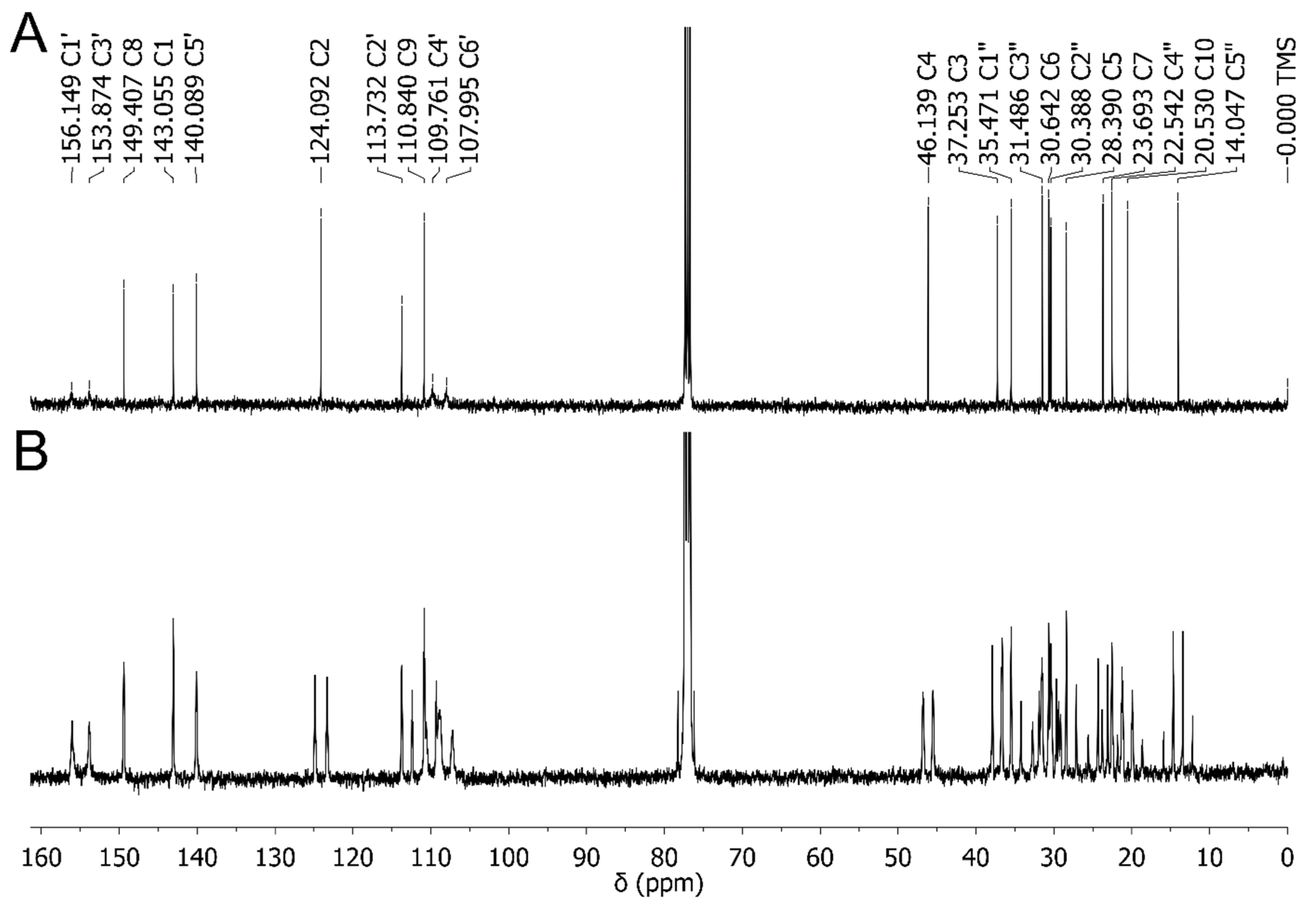
2.3. Experimental NMR Spectra of CBD
2.4. Indirect Spin–Spin Coupling Constants (SSCCs) of CBD Conformers
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental
3.2. Computational Details
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, R.; Hunt, M.; Clark, J.H. Structure of Cannabidiol, a Product Isolated from the Marihuana Extract of Minnesota Wild Hemp. I. JACS 1940, 62, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R.; Shvo, Y. Hashish—I: The structure of Cannabidiol. Tetrahedron 1963, 19, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, B.; Li, H.; Chen, L. An overview on synthetic and biological activities of cannabidiol (CBD) and its derivatives. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 140, 106810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, S. Cannabidiol (CBD) and its analogs: A review of their effects on inflammation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, T.W. Cannabinoid-based drugs as anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanti, S.; Malfitano, A.M.; Ciaglia, E.; Lamberti, A.; Ranieri, R.; Cuomo, G.; Abate, M.; Faggiana, G.; Proto, M.C.; Fiore, D.; et al. Cannabidiol: State of the art and new challenges for therapeutic applications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 175, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, S.; Jarocka-Karpowicz, I.; Skrzydlewska, E. Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Cannabidiol. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulebd, H.; Pereira, D.M.; Amine Khodja, I.; Hoa, N.T.; Mechler, A.; Vo, Q.V. Assessment of the free radical scavenging potential of cannabidiol under physiological conditions: Theoretical and experimental investigations. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 346, 118277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.S.; Batista, J.; Viana, R.B.; Baetas, A.C.; Orestes, E.; Andrade, M.A.; Honório, K.M.; Da Silva, A.B.F. Understanding the Molecular Aspects of Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol as Antioxidants. Molecules 2013, 18, 12663–12674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, E.; Marsh, E.; Mazurkiewicz-Beldzinska, M.; Halford, J.J.; Gunning, B.; Devinsky, O.; Checketts, D.; Roberts, C. Cannabidiol in patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome: Interim analysis of an open-label extension study. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Shibata, M.; Kimura, Y.; Ishikawa, M.; Higurashi, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Ichise, E.; Chiyonobu, T.; Ishii, A. Application of induced pluripotent stem cells in epilepsy. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 108, 103535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihailova, L.; Tchekalarova, J.; Shalabalija, D.; Geskovski, N.; Stoilkovska Gjorgievska, V.; Stefkov, G.; Krasteva, P.; Simonoska Crcarevska, M.; Glavas Dodov, M. Lipid nano-carriers loaded with Cannabis sativa extract for epilepsy treatment—In vitro characterization and in vivo efficacy studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 3384–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iseger, T.A.; Bossong, M.G. A systematic review of the antipsychotic properties of cannabidiol in humans. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 162, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seltzer, E.S.; Watters, A.K.; MacKenzie, D.; Granat, L.M.; Zhang, D. Cannabidiol (CBD) as a Promising Anti-Cancer Drug. Cancers 2020, 12, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chang, S.-L.; Chang, T.-R.; You, Y.; Wang, X.-D.; Wang, L.-W.; Yuan, X.-F.; Tan, M.-H.; Wang, P.-D.; Xu, P.-W.; et al. Inclusion complexes of cannabidiol with β-cyclodextrin and its derivative: Physicochemical properties, water solubility, and antioxidant activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espel Grekopoulos, J. Construction and Validation of Quantification Methods for Determining the Cannabidiol Content in Liquid Pharma-Grade Formulations by Means of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Partial Least Squares Regression. Med. Cannabis Cannabinoids 2019, 2, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borille, B.T.; Marcelo, M.C.A.; Ortiz, R.S.; Mariotti, K.d.C.; Ferrão, M.F.; Limberger, R.P. Near infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometrics for growth stage classification of cannabis cultivated in a greenhouse from seized seeds. Spectrochim. Acta A 2017, 173, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, L.-L.; Hulse, J.; Paroli, R.M. FTIR and Raman spectroscopic characterization of cannabinoids. Can. J. Chem. 2022, 100, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geskovski, N.; Stefkov, G.; Gigopulu, O.; Stefov, S.; Huck, C.W.; Makreski, P. Mid-infrared spectroscopy as process analytical technology tool for estimation of THC and CBD content in Cannabis flowers and extracts. Spectrochim. Acta A 2021, 251, 119422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggio, P.H. Endocannabinoid binding to the cannabinoid receptors: What is known and what remains unknown. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1468–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Atawneh, S.; Goldblum, A. Candidate Therapeutics by Screening for Multitargeting Ligands: Combining the CB2 Receptor With CB1, PPARγ and 5-HT4 Receptors. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 812745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buczek, A.; Rzepiela, K.; Broda, M.A.; Kupka, T.; Strodel, B.; Fatafta, H. Water modulated influence of intramolecular hydrogen-bonding on the conformational properties of Cannabidiol (CBD). J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 423, 127033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.G. The structures of heterocyclic complexes ruled by hydrogen bonds and halogen interactions: Interaction strength and IR modes. Spectrochim. Acta A 2014, 124, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczek, A.; Wałęsa, R.; Broda, M.A. β-turn tendency in N-methylated peptides with dehydrophenylalanine residue: DFT study. Biopolymers 2012, 97, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broda, M.A.; SiodŁak, D.; Rzeszotarska, B. Conformational investigation of α,β-dehydropeptides. XV: N-acetyl-α,β-dehydroamino acid N ′N ′-dimethylamides: Conformational properties from infrared and theoretical studies. J. Pept. Sci. 2005, 11, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, T.; Grassl, T.; Korber, N.; Christoffel, V.; Bodensteiner, M. Cannabidiol revisited. IUCrData 2017, 2, x170276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaremko, Ł.; Jaremko, M.; Buczek, A.; Broda, M.A.; Kupka, T.; Jackowski, K. 1H and 13C shielding measurements in comparison with DFT calculations performed for two 2-(acetyloamino)-N,N-dimethyl-3-phenylacrylamide isomers. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2015, 627, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, B.D.; Srivastava, A.; Honorato, S.B.; Tandon, P.; Pessoa, O.D.L.; Fechine, P.B.A.; Ayala, A.P. Study of molecular structure, vibrational, electronic and NMR spectra of oncocalyxone A using DFT and quantum chemical calculations. Spectrochim. Acta A 2013, 113, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, I.; Scharinger, A.; Golombek, P.; Kuballa, T.; Lachenmeier, D.W. A Quantitative (1)H NMR Method for Screening Cannabinoids in CBD Oils. Toxics 2021, 9, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, L.; Brighenti, V.; Rossi, M.C.; Sperlea, J.; Pellati, F.; Bertelli, D. Use of (13)C-qNMR Spectroscopy for the Analysis of Non-Psychoactive Cannabinoids in Fibre-Type Cannabis sativa L. (Hemp). Molecules 2019, 24, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Long, R.; Cao, F.; Zhao, X.; Lan, T.; Xu, D. Development of Pure Certified Reference Material of Cannabidiol. Molecules 2024, 29, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colella, M.F.; Salvino, R.A.; Gaglianò, M.; Litrenta, F.; Oliviero Rossi, C.; Le Pera, A.; De Luca, G. NMR Spectroscopy Applied to the Metabolic Analysis of Natural Extracts of Cannabis sativa. Molecules 2022, 27, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuki, T.; Friesen, J.B.; Chen, S.N.; McAlpine, J.B.; Pauli, G.F. Selective Preparation and High Dynamic-Range Analysis of Cannabinoids in “CBD Oil” and Other Cannabis sativa Preparations. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.S.; Gordon, W.H.; Morgan, J.B.; Williamson, R.T. Calculated and Experimental 1 H and 13 C NMR Assignments for Cannabicitran. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2021, 60, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdemir, H.U. Effects of intramolecular hydrogen bonding on nuclear magnetic resonance, electron paramagnetic resonance and molecular docking studies: Mexiletine molecule. J. Mol. Model. 2024, 30, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mololina, A.A.; Sobornova, V.V.; Belov, K.V.; Krestyaninov, M.A.; Khodov, I.A. Role of non-covalent interactions in the conformational stability of bicalutamide in different solvent environments: Insights from quantum-chemical calculations and NMR spectroscopy. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 423, 126921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstoy, P.M.; Tupikina, E.Y. IR and NMR Spectral Diagnostics of Hydrogen Bond Energy and Geometry. In Spectroscopy and Computation of Hydrogen-Bonded Systems; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim Germany, 2023; pp. 345–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oparin, R.D.; Kiselev, M.G. A near-infrared spectroscopic study of the conformational equilibria of lidocaine molecules in a highly concentrated lidocaine solution in supercritical CO2. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 396, 123916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, R.C.; Filho, V.S.; Portes, S.A.; Colherinhas, G.; Oliveira, L.B.A. Solvent effects on the spectroscopic properties of cannabinoids derivatives: A theoretical study using PCM. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2024, 124, e27417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denhez, C.; Lameiras, P.; Berber, H. Intramolecular OH/π versus C–H/O H-Bond-Dependent Conformational Control about Aryl–C(sp3) Bonds in Cannabidiol Derivatives. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 6855–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, R.J.; Mobli, M. An NMR, IR and theoretical investigation of 1H Chemical Shifts and hydrogen bonding in phenols. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2007, 45, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Hazekamp, A.; Peltenburg-Looman, A.M.; Frédérich, M.; Erkelens, C.; Lefeber, A.W.; Verpoorte, R. NMR assignments of the major cannabinoids and cannabiflavonoids isolated from flowers of Cannabis sativa. Phytochem. Anal. 2004, 15, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, C.; Bartella, L.; Mazzotti, F.; Aiello, D.; Napoli, A.; De Luca, P.; Temperini, A. 1H NMR quantification of cannabidiol (CBD) in industrial products derived from Cannabis sativa L. (hemp) seeds. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 572, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupka, T.; Makieieva, N.; Jewgiński, M.; Witek, M.; Blicharska, B.; Rahmonov, O.; Doležal, K.; Pospíšil, T. Caffeine—Legal Natural Stimulant with Open Research Perspective: Spectroscopic and Theoretical Characterization. Molecules 2024, 29, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, C 0.1; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi, J.; Mennucci, B.; Cammi, R. Quantum Mechanical Continuum Solvation Models. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2999–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.P.; Radom, L. Harmonic vibrational frequencies: An evaluation of Hartree-Fock, Møller-Plesset, quadratic configuration interaction, density functional theory, and semiempirical scale factors. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 16502–16513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
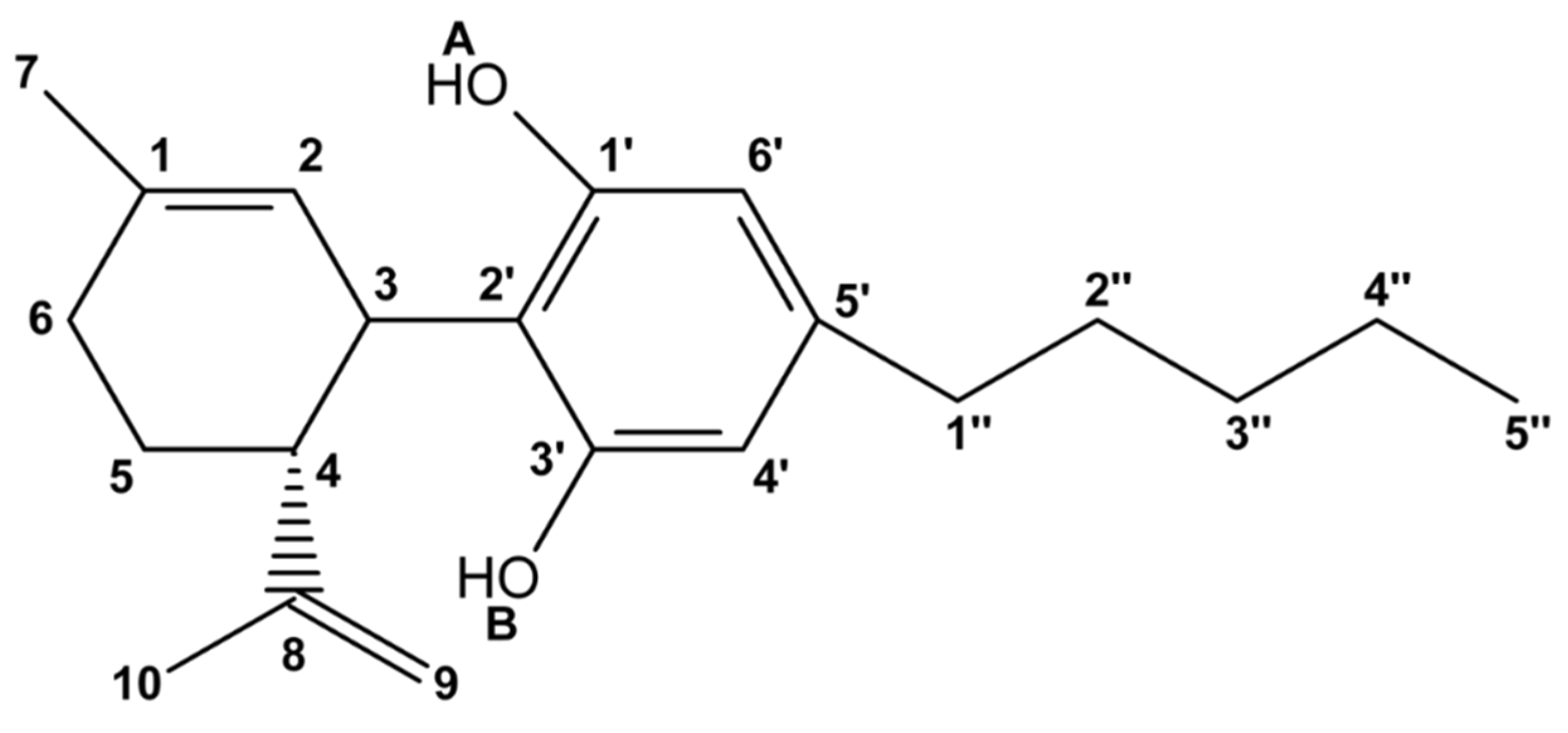
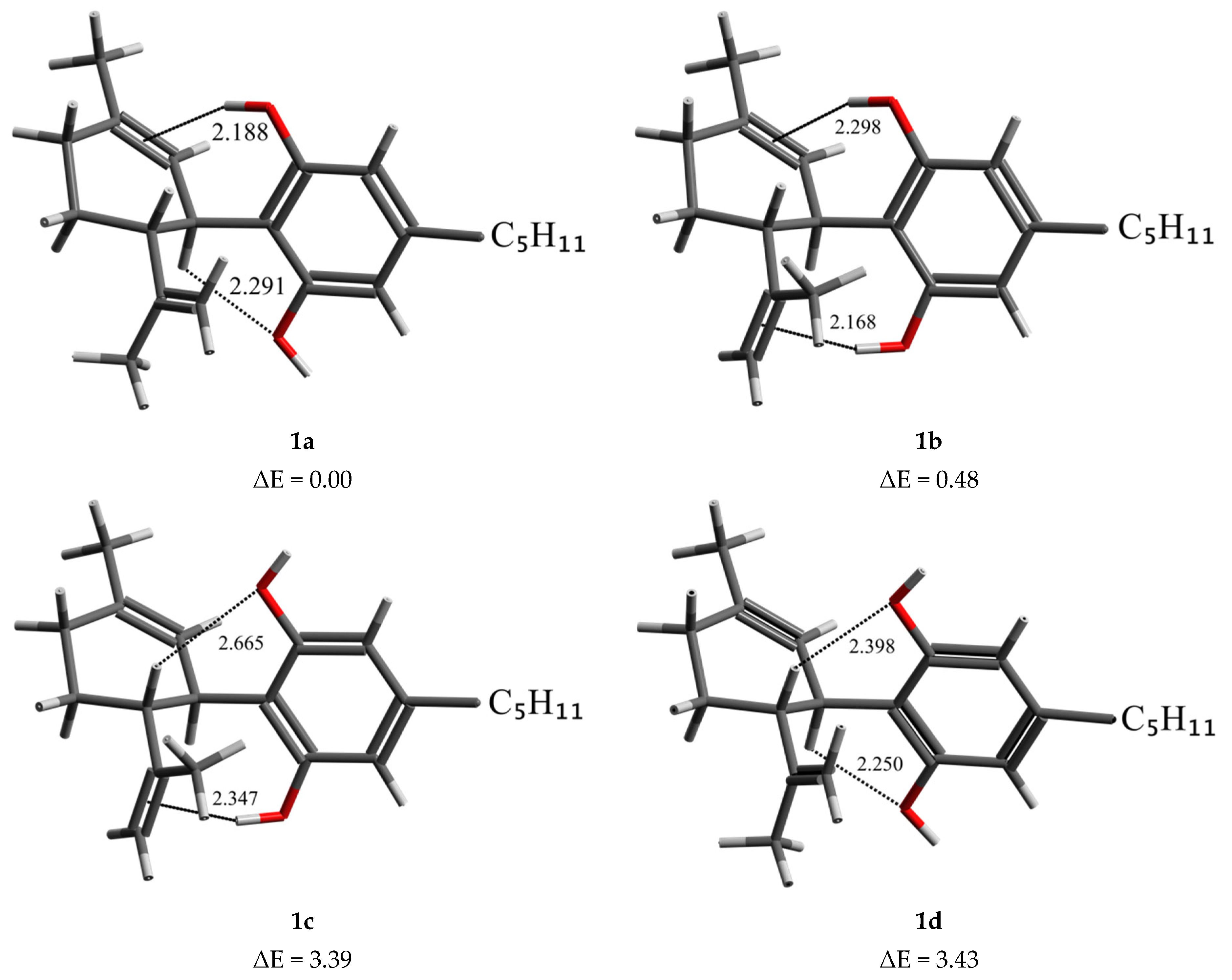
| Gas Phase | Chloroform | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conformer | H-Bond Type | ΔE | Distance | ΔE | Distance |
| 1a | C3-H…O-H(B) | 0.00 | 2.284 | 0.00 | 2.291 |
| O-H(A)…C1=C2 | 2.202 | 2.188 | |||
| 1b | O-H(B)…C8=C9 | 0.49 | 2.335 | 0.48 | 2.298 |
| O-H(A)…C1=C2 | 2.185 | 2.168 | |||
| 1c | O-H(B)…C8=C9 | 3.46 | 2.374 | 3.39 | 2.347 |
| C4-H…O-H(A) | 2.646 | 2.665 | |||
| 1d | C3-H…O-H(B) | 3.97 | 2.257 | 3.43 | 2.250 |
| C4-H…O-H(A) | 2.418 | 2.398 | |||
| Atom | 1a | 1b | 1c | 1d | Exp. a | Lit. [42] | Lit. [29] | Lit. [43] | Lit. [32] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (OA)H | 6.60 | 6.55 | 4.44 | 4.42 | 5.99 | 5.99 | 5.95 | 6.22 | |
| (OB)H | 4.34 | 5.78 | 5.78 | 4.47 | 4.66 | 5.02 | 4.6 | ||
| (C2)H | 5.40 | 5.27 | 5.05 | 5.11 | 5.57 | 5.57 | 5.57 | 5.56 | 5.57 |
| (C3)H | 4.15 | 3.76 | 3.68 | 4.24 | 3.86 | 3.9 | 3.84 | 3.86 | 3.86 |
| (C4)H | 2.51 | 2.27 | 2.50 | 3.21 | 2.40 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.40 | |
| (C5)H | 1.81 | 1.88 | 1.89 | 1.83 | 1.82 | 1.84 | 1.82 | 1.78–1.84 | |
| (C6)H | 2.27 | 2.28 | 2.19 | 2.20 | H6a = 2.07 H6b = 2.23 | 2.21 | 2.09 | H6a = 2.05–2.09 H6b = 2.22 | |
| (C7)H | 1.92 | 1.92 | 1.81 | 1.79 | 1.79 | 1.79 | 1.79 | 1.79 | |
| (C9)H-trans | 4.10 | 4.78 | 4.73 | 4.04 | 4.66 | 4.64 | 4.67 | 4.66 | 4.64 |
| (C9)H-cis | 3.75 | 4.74 | 4.64 | 4.00 | 4.56 | 4.54 | 4.6 | 4.57 | 4.53 |
| (C10)H | 1.88 | 1.53 | 1.50 | 1.88 | 1.66 | 1.66 | 1.65 | 1.66 | |
| (C4′)H | 5.53 | 5.94 | 5.96 | 5.63 | 6.17 | 6.16 | 6.19 | 6.16 | |
| (C6′)H | 5.85 | 5.98 | 5.71 | 5.56 | 6.28 | 6.26 | 6.25 | 6.26 | |
| (C1″)H | 2.53 | 2.59 | 2.57 | 2.52 | 2.44 | 2.43 | 2.44 | 2.43 | |
| (C2″)H | 1.52 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 1.52 | 1.59 | 1.55 | 1.56 | 1.52–1.61 | |
| (C3″)H | 0.82 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.85 | 1.30 | 1.29 | 1.3 | 1.27–1.32 | |
| (C4″)H | 1.18 | 1.19 | 1.19 | 1.19 | 1.30 | 1.29 | 1.3 | ||
| (C5″)H | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.86–0.88 | |
| RMS | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.50 | 0.54 |
| Atom | 1a | 1b | 1c | 1d | Exp. a | Lit. [42] | Lit. [18] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 147.20 | 147.46 | 135.47 | 137.45 | 143.06 | 134.2 | |
| C2 | 125.88 | 124.83 | 128.17 | 128.23 | 124.09 | 127.3 | 124.14 |
| C3 | 41.98 | 50.42 | 51.07 | 41.96 | 37.25 | 37.5 | 37.01 |
| C4 | 53.66 | 49.69 | 49.29 | 51.76 | 46.14 | 46.4 | |
| C5 | 33.30 | 34.39 | 34.95 | 34.51 | 28.39 | 31.7 | 28.35 |
| C6 | 35.92 | 35.86 | 35.56 | 36.05 | 30.64 | 30.7 | 30.36 |
| C7 | 26.86 | 26.93 | 26.43 | 26.43 | 23.69 | 23.7 | 23.69 |
| C8 | 155.26 | 168.10 | 169.01 | 158.00 | 149.41 | 150.3 | |
| C9 | 109.19 | 106.03 | 103.95 | 107.03 | 110.84 | 110.5 | 110.81 |
| C10 | 20.76 | 29.95 | 29.98 | 20.35 | 20.53 | 19.5 | 20.30 |
| C1′ | 159.83 | 159.86 | 158.42 | 157.52 | 156.15 | 157.5 | |
| C2′ | 112.35 | 114.82 | 116.23 | 114.69 | 113.73 | 115.9 | |
| C3′ | 156.83 | 157.25 | 158.18 | 157.26 | 153.87 | 150.3 | |
| C4′ | 105.13 | 109.98 | 110.25 | 102.81 | 109.76 | 108.3 | 107.92 |
| C5′ | 145.31 | 145.84 | 145.15 | 145.03 | 140.09 | 142.7 | |
| C6′ | 105.58 | 107.25 | 104.94 | 107.70 | 107.99 | 108.3 | 109.56 |
| C1″ | 41.68 | 41.38 | 41.09 | 41.33 | 35.47 | 36.6 | 35.46 |
| C2″ | 38.54 | 38.50 | 38.69 | 38.60 | 30.39 | 32.0 | 30.65 |
| C3″ | 36.69 | 36.82 | 36.76 | 37.67 | 31.49 | 32.6 | 31.48 |
| C4″ | 29.80 | 29.85 | 29.99 | 29.33 | 22.54 | 23.6 | 22.54 |
| C5″ | 17.23 | 17.12 | 17.05 | 16.81 | 14.05 | 14.4 | 14.04 |
| RMS this work | 4.70 | 6.85 | 7.30 | 5.06 |
| B3LYP | PBE0 | CAM-B3LYP | B3LYP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas | CHCl3 | Gas | CHCl3 | Gas | Gas | ||||
| Coupling Constants | 1a | 1b | 1c | 1d | Lit. [33] | ||||
| 4J(H6′ H4′) | 1.26 | 1.27 | 1.07 | 1.08 | 1.04 | 1.49 | 1.32 | 1.12 | 3.03 |
| 4J(H2 H6A) | −3.39 | −3.40 | −3.81 | −3.82 | −3.69 | −3.39 | −3.16 | −3.20 | −1.45 |
| 4J(H2 H6B) | −1.16 | −1.17 | −1.44 | −1.44 | −1.36 | −1.20 | −1.68 | −1.63 | 1.35 |
| 4J(H2 H7) | −1.72 | −1.12 | −1.96 | −1.96 | −1.89 | −1.73 | −1.78 | −1.78 | −1.12 |
| 2J(H9A H9B) | 3.07 | 3.29 | 0.96 | 1.17 | 2.69 | 2.15 | 2.39 | 3.47 | 2.13 |
| 3J(H3 H2) | 2.92 | 2.88 | 3.28 | 3.23 | 3.31 | 2.84 | 2.58 | 2.62 | 2.85 |
| 3J(H3 H4) | 10.84 | 10.83 | 10.33 | 10.32 | 11.11 | 10.85 | 10.80 | 11.00 | 10.28 |
| 5J(H3 H7) | 3.27 | 3.24 | 3.32 | 3.30 | 3.43 | 3.22 | 3.12 | 3.22 | 2.49 |
| 2J(H6B H6A) | −19.20 | −19.44 | −19.61 | −19.85 | −19.58 | −19.40 | −18.66 | −18.51 | −17.75 |
| 2J(H5A H5B) | −13.45 | −13.53 | −14.01 | −14.10 | −13.61 | −13.91 | −13.73 | −13.19 | −12.88 |
| 3J(H6A H5B) | 5.99 | 5.99 | 5.69 | 5.70 | 6.05 | 6.09 | 6.20 | 6.23 | 5.21 |
| 3J(H6A H5A) | 12.70 | 12.70 | 11.95 | 11.95 | 12.89 | 12.64 | 12.61 | 12.63 | 11.36 |
| 3J(H6B H5B) | 1.97 | 1.98 | 1.90 | 1.91 | 2.00 | 1.87 | 1.84 | 1.86 | 2.12 |
| 3J(H6B H5A) | 5.66 | 5.65 | 5.34 | 5.32 | 5.76 | 5.64 | 5.85 | 5.92 | 4.94 |
| 4J(H6A H7) | −1.64 | −1.62 | −1.85 | −1.83 | −1.94 | −1.65 | −1.72 | −1.69 | −1.84 |
| 4J(H6B H7) | −0.65 | −0.65 | −0.83 | −0.82 | −0.82 | −0.65 | −0.76 | −0.78 | −1.25 |
| RMS(H) | 1.15 | 1.17 | 1.27 | 1.29 | 1.30 | 1.15 | 1.16 | 1.21 | |
| Coupling Constants | 1a | 1b | 1c | 1d | Exp. in CDCl3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1J (C2H2) | 161.42 | 162.54 | 164.14 | 162.48 | 155.14 |
| 1J (C3H3) | 135.76 | 132.57 | 129.40 | 132.80 | 128.22 |
| 1J (C4H4) | 133.66 | 133.20 | 135.27 | 136.23 | 127.12 |
| 1J (C5H5) | 132.01 | 133.13 | 132.23 | 131.28 | 127.04 |
| 1J (C6H6) | 130.02 | 130.18 | 129.39 | 129.24 | 124.75 |
| 1J (C7H7) | 130.36 | 130.63 | 129.59 | 129.39 | 126.44 |
| 1J (C9H9) | 162.05 | 161.72 | 161.37 | 161.30 | 154.76 |
| 1J (C10H10) | 130.26 | 131.51 | 131.04 | 130.11 | 126.00 |
| 1J (C4′H4′) | 159.91 | 164.00 | 157.81 | 158.08 | 166.94 |
| 1J (C6′H6′) | 164.46 | 166.68 | 167.00 | 160.12 | 161.33 |
| 1J (C1″H1″) | 130.56 | 130.67 | 130.75 | 130.58 | 125.80 |
| 1J (C2″H2″) | 130.17 | 129.98 | 129.69 | 129.89 | 123.54 |
| 1J (C3″H3″) | 128.78 | 128.71 | 128.93 | 128.98 | 120.19 |
| 1J (C4″H4″) | 128.61 | 128.54 | 128.44 | 128.52 | 125.44 |
| 1J (C5″H5″) | 129.12 | 129.09 | 129.22 | 129.26 | 124.54 |
| RMS | 5.82 | 5.65 | 6.12 | 5.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buczek, A.; Rzepiela, K.; Kupka, T.; Broda, M.A. Impact of O-H···π Hydrogen Bond on IR and NMR Parameters of Cannabidiol: Theoretical and Experimental Study. Molecules 2025, 30, 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122591
Buczek A, Rzepiela K, Kupka T, Broda MA. Impact of O-H···π Hydrogen Bond on IR and NMR Parameters of Cannabidiol: Theoretical and Experimental Study. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122591
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuczek, Aneta, Kacper Rzepiela, Teobald Kupka, and Małgorzata A. Broda. 2025. "Impact of O-H···π Hydrogen Bond on IR and NMR Parameters of Cannabidiol: Theoretical and Experimental Study" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122591
APA StyleBuczek, A., Rzepiela, K., Kupka, T., & Broda, M. A. (2025). Impact of O-H···π Hydrogen Bond on IR and NMR Parameters of Cannabidiol: Theoretical and Experimental Study. Molecules, 30(12), 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122591









