A Closed-Loop Process for Rapid and Selective Lithium Extraction and Resynthesis from Spent LiFePO4 Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
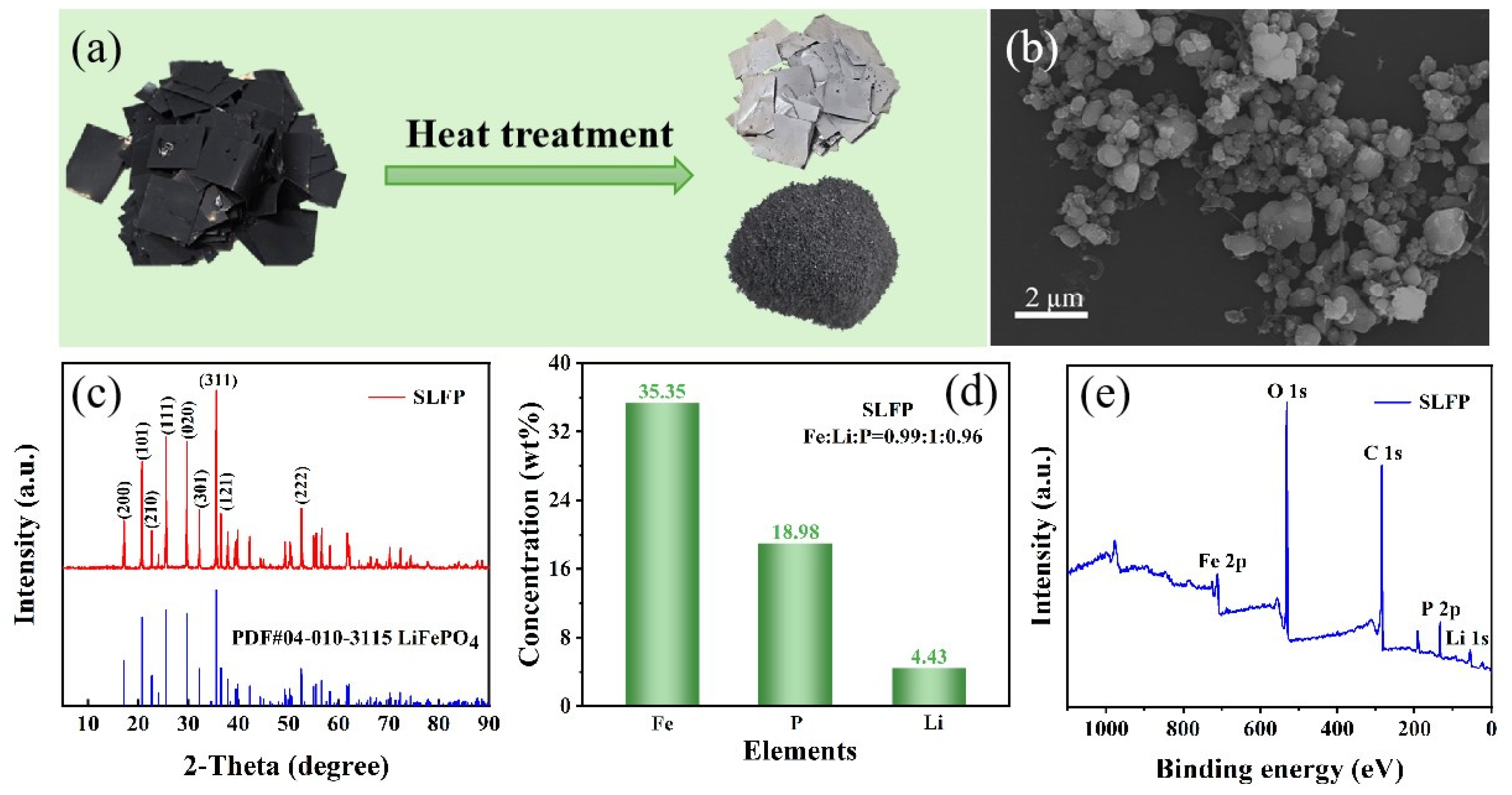
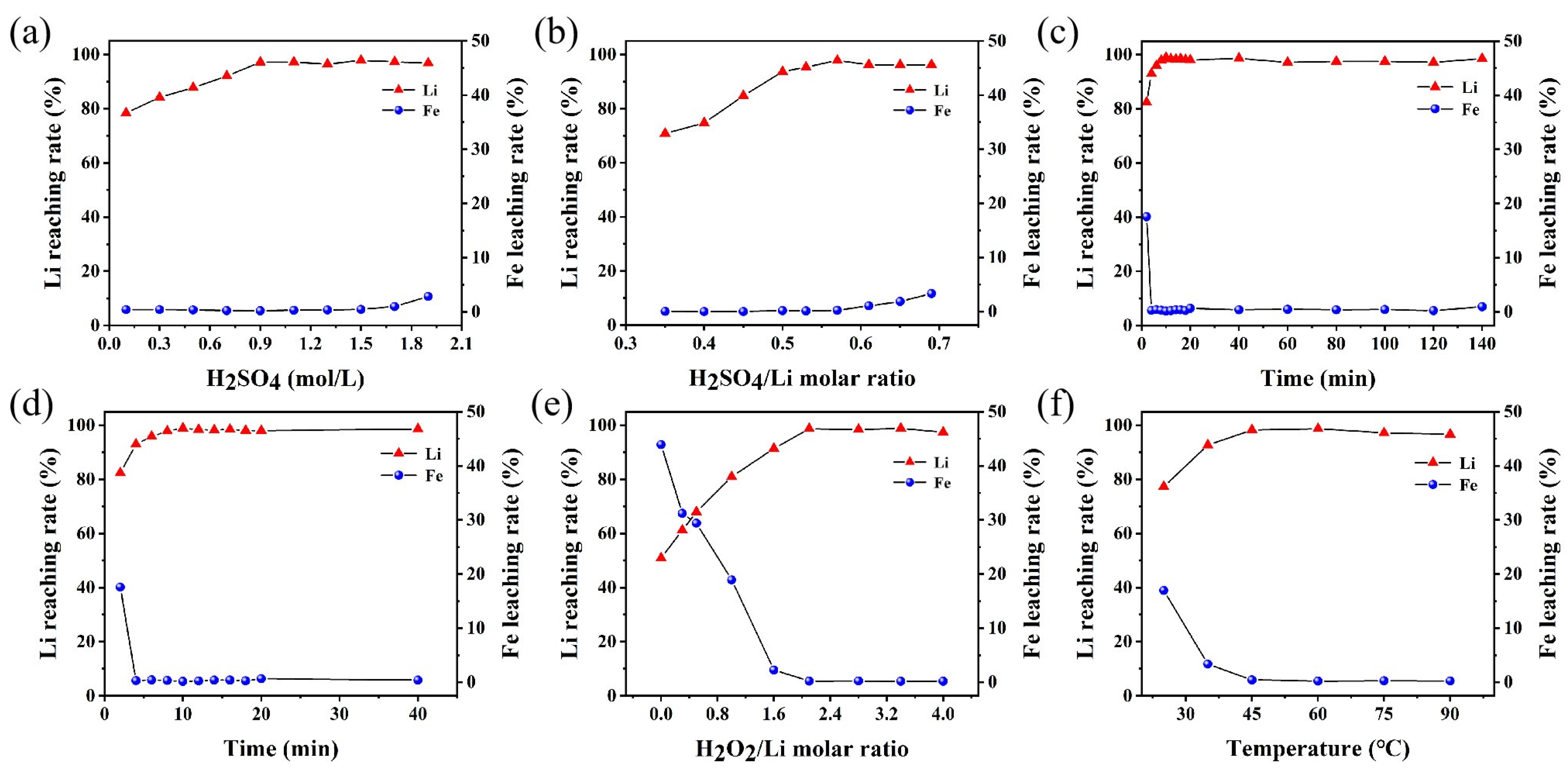
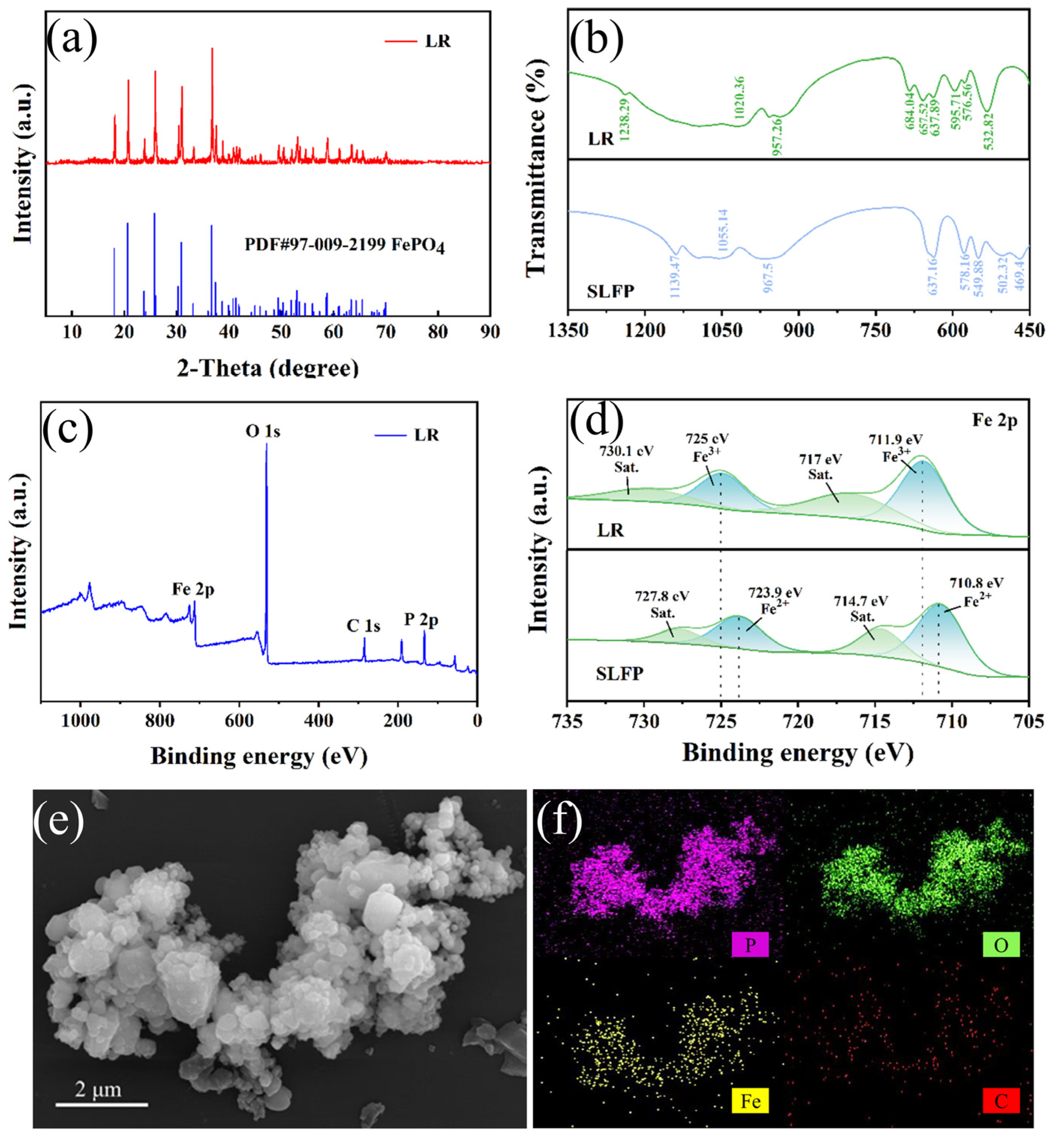
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Pretreatment
3.2. Instrumentation and Analysis Method
3.3. Leaching and Resynthesis Processes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; He, R.; Liu, Z.; Pan, J.; Zhang, J. A Deep Dive into Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: From Degradation Diagnostics to Sustainable Material Recovery. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2024, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Jie, Y.; Hu, F.; Yang, S.; Chang, D.; Fang, G.; Ding, J.; Qu, X.; Wu, G.; Zhu, H.; et al. From Waste to Material Strategy: A Closed-Loop Regeneration Process of Spent LiFePO4 Batteries. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, X.; Fan, E.; Chen, R.; Wu, F.; Li, L. Carbon Neutrality Strategies for Sustainable Batteries: From Structure, Recycling, and Properties to Applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 745–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, B.; Madhuri, W. A Comprehensive Investigation on the Electrochemical Performance, Synthesis, Modification, and Recycling Methods of LiFePO4 for Sustainable Future. J. Energy Storage 2024, 98, 112851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, H.; Valio, J.; Tynjala, P.; Lassi, U.; Suominen, P. Life Cycle of LiFePO4 Batteries: Production, Recycling, and Market Trends. ChemPhysChem 2024, 25, e202400459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Ma, T.; Jia, F.; Zhan, C. A Critical Review on the Recycling Strategy of Lithium Iron Phosphate from Electric Vehicles. Small Methods 2023, 7, 2300125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordor Intelligence. Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/lfp-battery-pack-market (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Wu, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Tian, M. High-Efficiency Leaching Process for Selective Leaching of Lithium from Spent Lithium Iron Phosphate. Waste Manag. 2024, 190, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhou, K.; Zhou, H.; Chen, T.; Zhang, G.; Chen, W. Impact and Removal of Fluorine Impurity in the Comprehensive Recovery of Spent LiFePO4/C. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 362, 131766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Goikolea, E.; De Larramendi, I.R.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Zhang, Q. Recycling Methods for Different Cathode Chemistries—A Critical Review. J. Energy Storage 2022, 56, 106053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Lei, H.; Lu, X.; Zhu, C.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ji, X.; Sun, W.; Yang, Y.; Ge, P. Li-Fe Anti-Sites Defects in LiFePO4: Mechanism, Characterization and Cathode-Regeneration Applications. Energy Storage Mater. 2025, 74, 103947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Zeng, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Yu, X.; Liu, X. A Facile Route for the Efficient Leaching, Recovery, and Regeneration of Lithium and Iron from Waste Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathode Materials. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 342, 127069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xiao, S.; Xu, W.; Liu, D.; Ren, G. A Green and Simplified Method for Selective Recovery of Lithium from the Cathode Scraps of Spent LiFexMn1-xPO4 Batteries. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 341, 126848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, F.; Dai, Y.; Ren, S.; Hou, Y.; Wu, W. A Green Recyclable Process for Selective Recovery of Li and Fe from Spent Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries by Synergistic Effect of Deep Eutectic Solvent and Oxygen. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, Z.; Yao, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Sun, Q.; Jin, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, M.-D. A Method of Efficiently Regenerating Waste LiFePO4 Cathode Material after Air Firing Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 65119–65130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Tran, T.T.; Lee, M.S. A Review on the Recovery of Lithium and Iron from Spent Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2024, 45, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Lv, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhou, D.; Sun, L.; Cheng, H.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Tang, C.-M.; et al. Green and Efficient Selective Lithium Extraction from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using a Self-Pressurizing-Assisted Oxidative Fixation System. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 362, 131716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Yuan, S.; Dong, Z.; Gao, P.; Ding, H.; Lei, S.; Liu, Q. Mechanism and Process Study of Spent Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries by Medium-Temperature Oxidation Roasting Strategy. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 356, 129987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Chemistry Evolution of LiFePO4-NaHSO4⋅H2O System during Roasting and Recovery of Li and Fe. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1007, 176376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Shi, M.; Hu, X.; Yang, H.; Yan, X. Comparison of Life Cycle Assessment of Different Recycling Methods for Decommissioned Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2024, 68, 103871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Fang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Du, W.; Qi, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, R.; et al. A Room-Temperature Lithium-Restocking Strategy for the Direct Reuse of Degraded LiFePO4 Electrodes. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202409929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Han, Q.; Xie, L.; Zhu, L.; Cao, X. Ambient-Pressure Relithiation of Spent LiFePO4 Using Alkaline Solutions Enables Direct Regeneration of Lithium-Ion Battery Cathodes. J. Energy Storage 2025, 105, 114721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, C.; Xie, L.; Zhu, L.; Cao, X.; Ji, X. Challenges and Perspectives towards Direct Regeneration of Spent LiFePO4 Cathode. J. Power Sources 2024, 602, 234365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Dong, P. Direct Regeneration of Degraded LiFePO4 Cathode via Reductive Solution Relithiation Regeneration Process. Molecules 2024, 29, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Liu, R.; Li, J.; Sun, W.; Yang, Y. Regeneration of LiFePO4 from Spent Materials: Control and Influence of Al Impurity. ChemSusChem 2025, 18, e202401432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Shi, D.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Song, F.; Xie, S.; Peng, X. A Closed-Loop Coupling Process of Leaching and Solvent Extraction for Li2CO3 and FePO4 Recovery from Spent LiFePO4. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 39, e00827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Mahandra, H.; Choi, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, A. A Clean and Sustainable Method for Recycling of Lithium from Spent Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Powder by Using Formic Acid and Oxygen. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 170930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Fan, E.; Lin, J.; Sun, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, R.; Wu, F.; Li, L. Acid-Free Mechanochemical Process to Enhance the Selective Recycling of Spent LiFePO4 Batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Iqbal, N.; Noor, T.; Zaman, N. Selective Lithium Recovery from Spent LFP Li-Ion Batteries Using Organic Acids. Ionics 2024, 31, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xiao, L.; Shen, L.; Ran, J.-J.; Zhong, H.; Zhu, Y.-R.; Chen, H. Recent Advancements in Hydrometallurgical Recycling Technologies of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Cathode Materials. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 879–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Xu, B.; Yan, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Z. Advances and Challenges in Recycling Spent LiFePO4 Batteries. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 362, 131780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Yao, T.; Zhai, W.; Zhang, M.; Song, L.; He, J. Advances in Degradation Mechanism and Sustainable Recycling of LiFePO4-Type Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2024, 71, 103623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, S.; Li, R.; Zhou, C.; Wang, C.; Ma, K.; Song, L.; Yue, H. All-Component Recycling and Reuse Process for Spent LiFePO4 Cathodes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 6847–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Zhao, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Mu, D.; Li, R.; Dai, C. Optimized Li and Fe Recovery from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries via a Solution-Precipitation Method. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 43613–43625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, M.; Ma, F.; Qin, M.; Zhong, W.; Chen, X.; Zeng, Z.; Cheng, S.; Xie, J. Direct Lithium Extraction from Spent Batteries for Efficient Lithium Recycling. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Zhang, T.; Wu, D.; Li, W.; Ma, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Z. Oxidation Pressure Leaching of Lithium Iron Phosphate: Kinetic Aspects, Leaching Mechanism, and the Behavior of Lithium and Iron. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, S.; Yin, Y.; Wang, B.; He, W. Selective Recovery of Lithium from Spent Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries. Waste Manag. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, L.; Shi, P.; Ren, Z.; Zhou, Z. Selective Recovery of Lithium from Lithium Iron Phosphate. J. Power Sources 2024, 598, 234158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Zhao, M.-C.; Li, Y.; Atrens, A.; Zhang, F. Recycling of Spent Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries: Research Progress Based on Environmental Protection and Sustainable Development Technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Tran, T.T.; Lee, M.S. Recovery of Iron Phosphate and Lithium Carbonate from Sulfuric Acid Leaching Solutions of Spent LiFePO4 Batteries by Chemical Precipitation. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2024, 60, 189463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Yuan, S.; Dong, Z.; Ding, H.; Gao, P. Recycling of Spent Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Cathode Materials: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 474, 143625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Yao, Y.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Hu, J. Selective Lithium Recovery and Regeneration of LiFePO4 from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: An Efficient and Green Process. J. Power Sources 2025, 631, 236179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Salah, A.; Jozwiak, P.; Zaghib, K.; Garbarczyk, J.; Gendron, F.; Mauger, A.; Julien, C.M. FTIR Features of Lithium-Iron Phosphates as Electrode Materials for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2006, 65, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Gong, D.; Lin, S.; Yu, J. Effect of pH-Dependent Intermediate on the Performance of LiFePO4/C Cathode Material. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 449, 137830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.-H.; Zhang, C.-C.; Zhang, W.-B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.-S. Recycling Phosphorus from Spent LiFePO4 Battery for Multifunctional Slow-Release Fertilizer Preparation and Simultaneous Recovery of Lithium. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Jing, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Facile and Efficient Recovery of Lithium from Spent LiFePO4 Batteries via Air Oxidation–Water Leaching at Room Temperature. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xing, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, H.; Kuang, G. Recovery of Lithium, Iron, and Phosphorus from Spent LiFePO4 Batteries Using Stoichiometric Sulfuric Acid Leaching System. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 8017–8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yuan, L.; Yan, S.; Ma, X. Self-Activation of Ferro-Chemistry Based Advanced Oxidation Process towards in-Situ Recycling of Spent LiFePO4 Batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tang, J.; Su, M.; Xu, J.; Shih, K. Design and Optimization of an Economically Viable and Highly Efficient Strategy for Li Recycling from Spent LiFePO4 Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 16124–16132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, M.; Francia, C.; Fiore, S. Selective Leaching for the Recycling of Lithium, Iron, and Phosphorous from Lithium-Ion Battery Cathodes’ Production Scraps. Batteries 2024, 10, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerold, E.; Lerchbammer, R.; Antrekowitsch, H. Parameter Study on the Recycling of LFP Cathode Material Using Hydrometallurgical Methods. Metals 2022, 12, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Yang, G.; Cai, F.; Wang, B.; Jiang, B.; Chen, H.; Tan, C. Recovery and Reuse of Spent LiFePO4 Batteries. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2019, 22, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Materials | Amount per Batch | Cost Per Ton (USD) Market Price in China in 2024 | Cost Per Batch (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waste LFP battery black powder (kg) | 1.0 | 1390.1 | 1.3901 |
| H2SO4 (L) | 0.196 | 37.14 | 0.0073 |
| Leaching water (L) | 5.154 | 0.41 | 0.0021 |
| Washing water (L) | 3.165 | 0.41 | 0.0013 |
| H2O2 (L) | 1.343 | 112.90 | 0.1516 |
| NaOH (kg) | 0.032 | 372.33 | 0.0119 |
| Na2CO3 (kg) | 0.332 | 273.51 | 0.0908 |
| Glucose (kg) | 0.227 | 345.18 | 0.0784 |
| N2 (L) | 5.400 | 61.85 | 0.3340 |
| Electricity | 0.107/KW h | 0.5580 | |
| Leaching–heating/stirring (KW h) | 0.222 | ||
| Leaching–filtration/drying (KW h) | 0.650 | ||
| Calcination of filter residue (KW h) | 0.410 | ||
| Precipitation–evaporation (KW h) | 0.143 | ||
| Precipitation–drying (KW h) | 0.650 | ||
| Ball milling (KW h) | 1.380 | ||
| Synthetic calcination (KW h) | 1.760 | ||
| Total electricity calculation (KW h) | 5.215 | ||
| Total | 2.6255 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, S.; Du, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L. A Closed-Loop Process for Rapid and Selective Lithium Extraction and Resynthesis from Spent LiFePO4 Batteries. Molecules 2025, 30, 2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122587
Liu R, Liu Y, Li J, Chen Y, Zhu Y, Zhang K, Zhao S, Du L, Zhu X, Zhang L. A Closed-Loop Process for Rapid and Selective Lithium Extraction and Resynthesis from Spent LiFePO4 Batteries. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122587
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ruijing, Yuxiao Liu, Jianjiang Li, Yuanlin Chen, Yule Zhu, Kunzheng Zhang, Shuxian Zhao, Liang Du, Xiaoyi Zhu, and Lei Zhang. 2025. "A Closed-Loop Process for Rapid and Selective Lithium Extraction and Resynthesis from Spent LiFePO4 Batteries" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122587
APA StyleLiu, R., Liu, Y., Li, J., Chen, Y., Zhu, Y., Zhang, K., Zhao, S., Du, L., Zhu, X., & Zhang, L. (2025). A Closed-Loop Process for Rapid and Selective Lithium Extraction and Resynthesis from Spent LiFePO4 Batteries. Molecules, 30(12), 2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122587






