Rapid Classification and Quantitative Prediction of Aflatoxin B1 Content and Colony Counts in Nutmeg Based on Electronic Nose
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
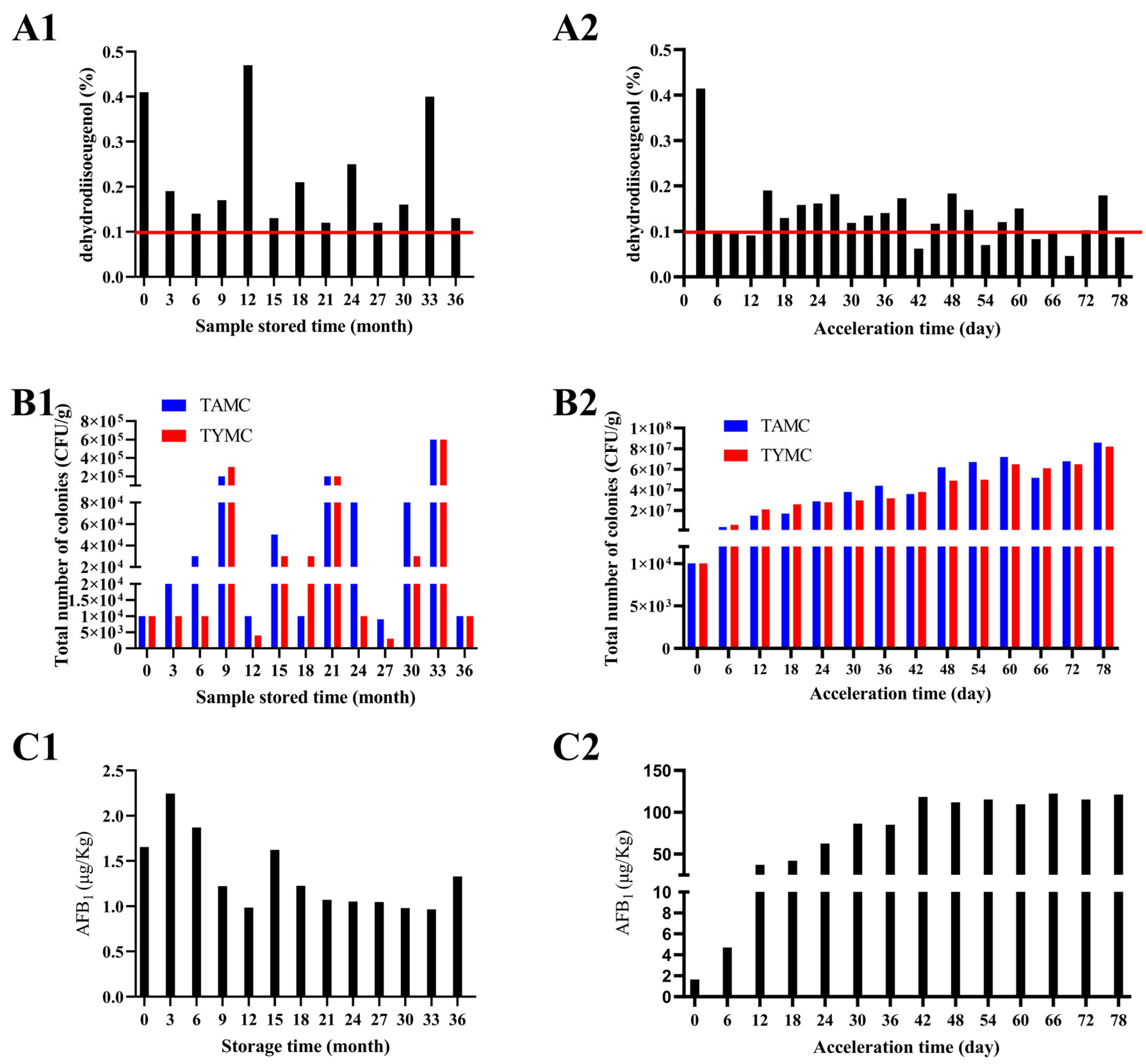
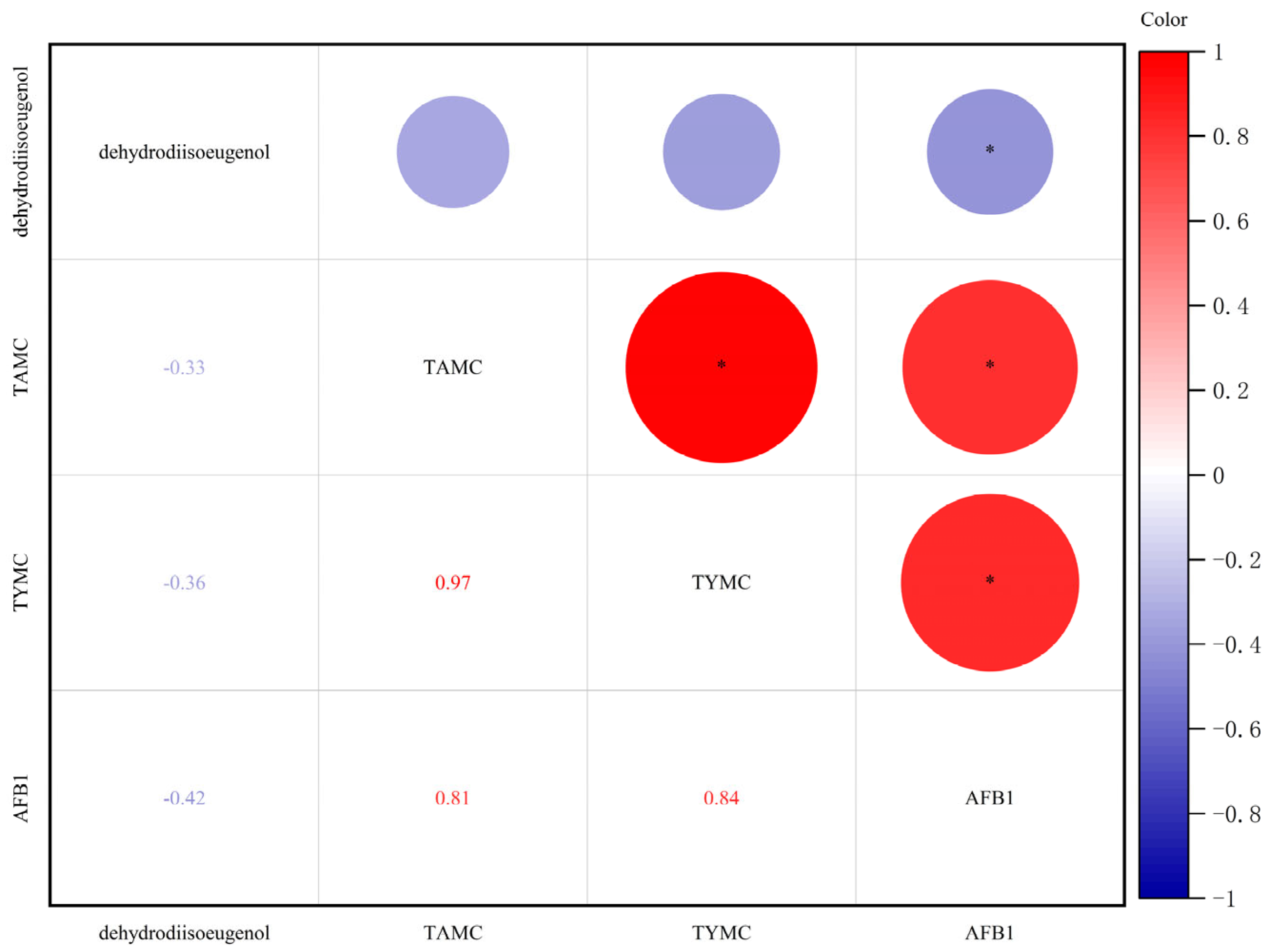
2.1. Changes in Physicochemical Indexes During Storage of Nutmeg
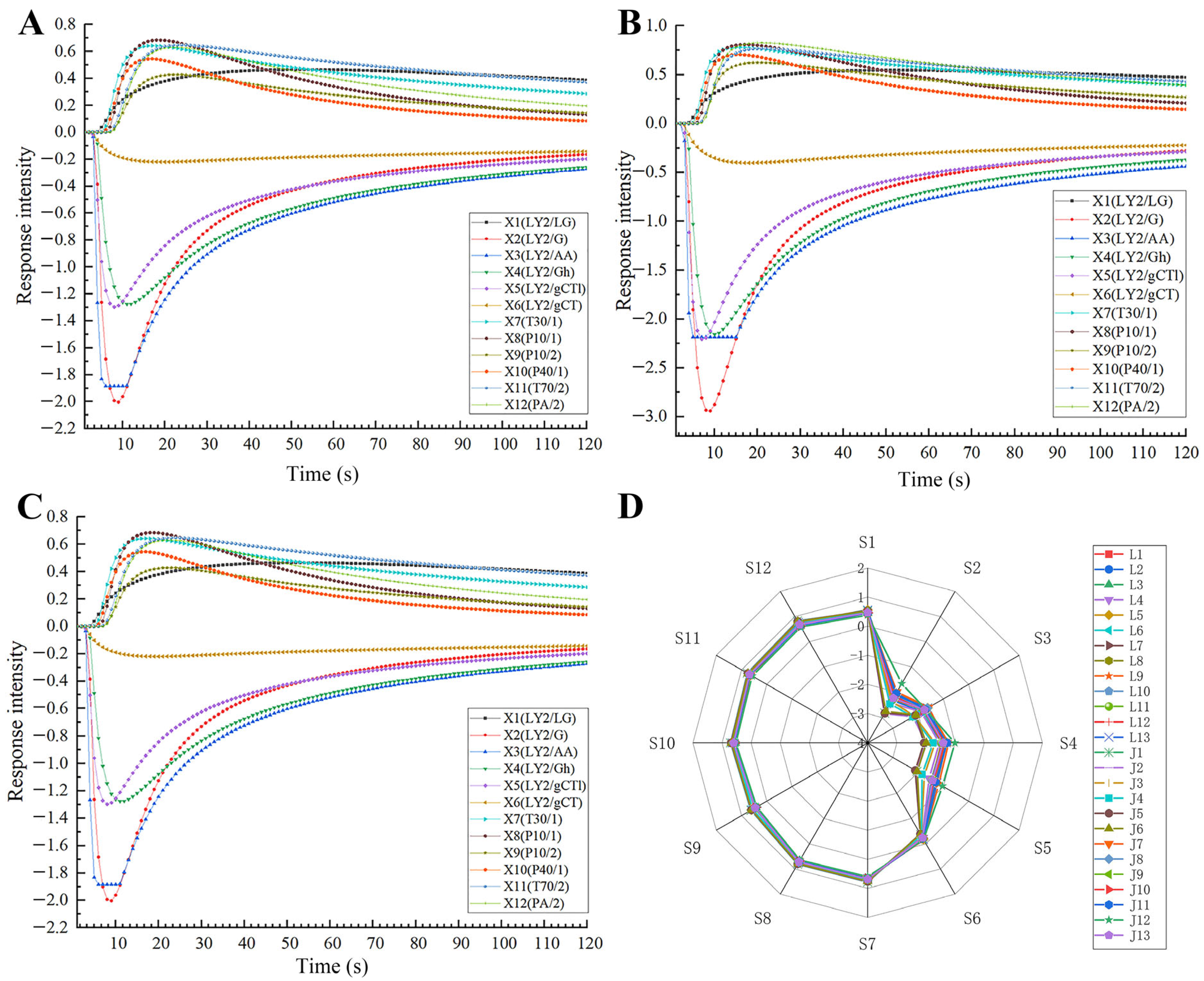
2.2. Odor Characteristics
2.3. Qualitative Classification of Mold Degree of Nutmeg
2.4. Quantitative Prediction of Physicochemical Indexes of Nutmeg
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Reagents and Materials
3.2. Samples Collection
3.3. Physicochemical Identification
3.3.1. Determination of Dehydrodiisoeugenol Content
3.3.2. Microbial Counting Protocols
3.3.3. Determination of AFB1 Content
3.4. E-Nose Analysis
3.5. Data Analysis
3.5.1. Physicochemical Analysis
3.5.2. Classification Analysis
3.5.3. Prediction Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFB1 | Aflatoxin B1 |
| TAMC | Total aerobic microbial count |
| TYMC | Total yeast and mold count |
| E-nose | Electronic nose |
| BPNN | Back Propagation Neural Network |
| SMO | Sequential Minimal Optimization |
| IBK | Instance-based Learning |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RT | Random Tree |
| CC | Correlation coefficient |
| RAE | Relative absolute error |
References
- Abourashed, E.A.; El-Alfy, A.T. Chemical Diversity and Pharmacological Significance of the Secondary Metabolites of Nutmeg (Myristica fragrans Houtt.). Phytochem. Rev. 2016, 15, 1035–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matulyte, I.; Jekabsone, A.; Jankauskaite, L.; Zavistanaviciute, P.; Sakiene, V.; Bartkiene, E.; Ruzauskas, M.; Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Santini, A.; Bernatoniene, J. The Essential Oil and Hydrolats from Myristica fragrans Seeds with Magnesium Aluminometasilicate as Excipient: Antioxidant, Antibacterial, and Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Foods 2020, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calliste, C.A.; Kozlowski, D.; Duroux, J.L.; Champavier, Y.; Chulia, A.J.; Trouillas, P. A New Antioxidant from Wild Nutmeg. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, M.M.; Tabanca, N.; Wedge, D.E.; Tarawneh, A.H.; Cutler, S.J. Antifungal Compounds from Turmeric and Nutmeg with Activity against Plant Pathogens. Fitoterapia 2014, 99, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, R.; Bora, P.K.; Saikia, J.; Kemprai, P.; Saikia, S.P.; Haldar, S.; Banik, D. Nutmegs and Wild Nutmegs: An Update on Ethnomedicines, Phytochemicals, Pharmacology, and Toxicity of the Myristicaceae Species. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 4632–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.; Pöhlmann, C.; Dietrich, R.; Märtlbauer, E.; Elßner, T. An Electrochemical Fiveplex Biochip Assay Based on Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies for Fast On-Site Detection of Bioterrorism Relevant Low Molecular Weight Toxins. Toxins 2019, 11, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medicine Science and Technology Press of China. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, Volume 4, 2020 Edition; Medicine Science and Technology Press of China: Beiing, China, 2020; p. 857. ISBN 978-7-5214-1599-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Li, Q.; Qin, F.; Liu, H.; Yang, M. Comparative Study of Microbial Limit Test and Criteria of TCM Decoction Pieces among United States Pharmacopeia, European Pharmacopeia, Japanese Pharmacopeia and Chinese Pharmacopeia. China Pharm. 2020, 31, 2695–2700. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, K.; Liang, T.; Liu, Q.; Yan, J.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, K.; Ma, S.; Wang, D. Comparative Analysis of Acanthopanacis Cortex and Periplocae Cortex Using an Electronic Nose and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Coupled with Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Molecules 2022, 27, 8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ari, D.; Alagoz, B.B. An Effective Integrated Genetic Programming and Neural Network Model for Electronic Nose Calibration of Air Pollution Monitoring Application. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 12633–12652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Gu, Y. A Machine Learning Method for the Quantitative Detection of Adulterated Meat Using a MOS-Based E-Nose. Foods 2022, 11, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Yadav, B.K. Electronic Nose for Detection of Food Adulteration: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 846–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V.R., N.; Mohapatra, A.K.; V.K., U.; Lukose, J.; Kartha, V.B.; Chidangil, S. Post-COVID Syndrome Screening through Breath Analysis Using Electronic Nose Technology. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 3617–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, W.; Wu, M.; Mao, J.; Sha, R. Application of E-Nose Combined with ANN Modelling for Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Benzoic Acid in Cola-Type Beverages. Food Meas. 2021, 15, 5131–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gu, Y.; Lin, W.; Zhang, Q. Rapid Quantitative Authentication and Analysis of Camellia Oil Adulterated with Edible Oils by Electronic Nose and FTIR Spectroscopy. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 100732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, J.; Mishra, H.N. Recent Advances in Sensors for Detecting Food Pathogens, Contaminants, and Toxins: A Review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 1125–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hooti, H.S.; Al-Bulushi, I.M.; Al-Attabi, Z.H.; Rahman, M.S.; Al-Subhi, L.K.; Al-Habsi, N.A. Efficiency of Electronic Nose in Detecting the Microbial Spoilage of Fresh Sardines (Sardinella longiceps). Foods 2024, 13, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Upadhyay, A.; Xiao, Z.; Luo, Y. Machine Learning-Supported Sensor Array for Multiplexed Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria Detection and Identification. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 154, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonah, E.; Huang, X.; Hongying, Y.; Aheto, J.H.; Yi, R.; Yu, S.; Tu, H. Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium Contamination Levels in Fresh Pork Samples Using Electronic Nose Smellprints in Tandem with Support Vector Machine Regression and Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithms. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 3861–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camardo Leggieri, M.; Mazzoni, M.; Fodil, S.; Moschini, M.; Bertuzzi, T.; Prandini, A.; Battilani, P. An Electronic Nose Supported by an Artificial Neural Network for the Rapid Detection of Aflatoxin B1 and Fumonisins in Maize. Food Control 2021, 123, 107722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godínez-Chaparro, B.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, S.; Pérez-Ramos, J.; Heyerdahl-Viau, I.; Hernández-Vázquez, L. Synthesis and Biological Activities of Dehydrodiisoeugenol: A Review. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, K.; Pan, G.; Ji, H.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, R.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Correction: Dehydrodiisoeugenol Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Growth by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Autophagic Pathways. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S. Research on Storage Specification of Traditional Chinese Medicines of Being Moldy with Malt, Lotus Seeds and Nutmeg as the Models. Master’s Thesis, Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Zou, H.; Yan, Y. Validation on Microbiological Counting Test of Myristicae Semen and Determination of Total Number of Colonies in Mildew. World Sci. Technol./Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Medica 2019, 21, 248–253. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Ouyang, S.; Yu, S.; Zou, H.; Yan, Y. Detection of Mildewed Nutmeg Internal Quality during Storage Using an Electronic Nose Combined with Chemical Profile Analysis. Molecules 2023, 28, 6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, K.; Sheikh Khozani, Z.; Cooper, J.R. Predicting Stable Gravel-Bed River Hydraulic Geometry: A Test of Novel, Advanced, Hybrid Data Mining Algorithms. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 144, 105165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhu, V.-H.; Shahabi, H.; Nohani, E.; Shirzadi, A.; Al-Ansari, N.; Bahrami, S.; Miraki, S.; Geertsema, M.; Nguyen, H. Daily Water Level Prediction of Zrebar Lake (Iran): A Comparison between M5P, Random Forest, Random Tree and Reduced Error Pruning Trees Algorithms. IJGI 2020, 9, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Hu, N.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Jia, T. Study on the Individual Differences among the Seed Kernels of Nutmeg. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2013, 30, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Dong, J.; Tian, Y.; Lin, Y.; Fang, G.; Wang, S. Identification of Mouldy Rice Using an Electronic Nose Combined with SPME-GC/MS. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2022, 95, 101921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xu, C.; Shen, Z.; Yu, C.; Li, Y. Application of Machine Learning Techniques for Clinical Predictive Modeling: A Cross-Sectional Study on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in China. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, e4304376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbiani, S.; Lotesoriere, B.J.; Dellacà, R.L.; Capelli, L. Physical Confounding Factors Affecting Gas Sensors Response: A Review on Effects and Compensation Strategies for Electronic Nose Applications. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, A.M.; Raisi-Estabragh, Z.; Galazzo, I.B.; Radeva, P.; Petersen, S.E.; Lekadir, K.; Menegaz, G. A Perspective on Explainable Artificial Intelligence Methods: SHAP and LIME. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2025, 7, 2400304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Natural Retention Samples | Accelerated Test Samples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Number | AFB1 (μg/kg) | Mold Degree | Sample Number | AFB1 (μg/kg) | Mold Degree |
| L1 | 1.6530 | Class 1 | J1 | 4.7052 | Class 1 |
| L2 | 2.2458 | Class 1 | J2 | 37.2449 | Class 2 |
| L3 | 1.8692 | Class 1 | J3 | 42.2726 | Class 2 |
| L4 | 1.2226 | Class 1 | J4 | 62.6829 | Class 2 |
| L5 | 0.9841 | Class 1 | J5 | 86.3746 | Class 2 |
| L6 | 1.6227 | Class 1 | J6 | 85.0230 | Class 2 |
| L7 | 1.2259 | Class 1 | J7 | 118.3960 | Class 3 |
| L8 | 1.0726 | Class 1 | J8 | 111.7690 | Class 3 |
| L9 | 1.0500 | Class 1 | J9 | 115.0944 | Class 3 |
| L10 | 1.0461 | Class 1 | J10 | 109.6292 | Class 3 |
| L11 | 0.9798 | Class 1 | J11 | 122.3826 | Class 3 |
| L12 | 0.9661 | Class 1 | J12 | 115.0990 | Class 3 |
| L13 | 1.3292 | Class 1 | J13 | 121.3189 | Class 3 |
| Classification | External Testing Set Validation | Ten-Fold Cross-Validation | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kappa Statistic | TPR | Precision | Recall | F-Measure | Kappa statistic | TPR | Precision | Recall | F-Measure | ||
| Function | BPNN | 0.8971 | 0.935 | 0.95 | 0.935 | 0.937 | 0.9544 | 0.973 | 0.973 | 0.973 | 0.973 |
| SMO | 0.6415 | 0.79 | 0.824 | 0.79 | 0.771 | 0.6111 | 0.78 | 0.825 | 0.78 | 0.749 | |
| Lazy | IBK | 0.9469 | 0.968 | 0.969 | 0.968 | 0.968 | 0.9908 | 0.995 | 0.995 | 0.995 | 0.994 |
| Kstar | 0.921 | 0.952 | 0.955 | 0.952 | 0.952 | 0.9908 | 0.995 | 0.995 | 0.995 | 0.994 | |
| Trees | RF | 0.8955 | 0.935 | 0.943 | 0.935 | 0.937 | 0.9544 | 0.973 | 0.973 | 0.973 | 0.973 |
| RT | 0.8938 | 0.935 | 0.935 | 0.935 | 0.935 | 0.8637 | 0.918 | 0.919 | 0.918 | 0.918 | |
| Classification | External Testing Set Validation | Ten-Fold Cross- Validation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | RAE | CC | RAE | ||
| Dehydrodiisoeugenol | BPNN | 0.4856 | 149.1% | 0.3734 | 111.9% |
| IBK | 0.5595 | 80.08% | 0.4212 | 79.67% | |
| RF | 0.4646 | 91.04% | 0.5061 | 82.14% | |
| TAMC | BPNN | 0.9443 | 27.82% | 0.934 | 27.60% |
| IBK | 0.9344 | 10.96% | 0.9671 | 7.90% | |
| RF | 0.9010 | 27.60% | 0.9184 | 23.26% | |
| TYMC | BPNN | 0.9685 | 23.69% | 0.9598 | 21.83% |
| IBK | 0.9214 | 13.31% | 0.9571 | 9.83% | |
| RF | 0.8985 | 27.66% | 0.9035 | 25.36% | |
| AFB1 | BPNN | 0.9776 | 15.83% | 0.9792 | 15.41% |
| IBK | 0.9552 | 6.76% | 0.9861 | 3.09% | |
| RF | 0.9395 | 22.96% | 0.9340 | 20.87% | |
| Natural Retention Samples | Accelerated Test Samples | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Batch | Numbers | Storage Time (Month) | Sampling Time | Temperature (°C) | Humidity (%) | Sample Batch | Numbers | Acceleration Time (Day) |
| 2018.01 | L1 | 0 | 2018.01 | 15 | 40 | 2018.01 | L1 | 0 |
| 2018.01 | L2 | 3 | 2018.03 | 18 | 42 | 2018.01 | J1 | 6 |
| 2018.01 | L3 | 6 | 2018.06 | 26 | 50 | 2018.01 | J2 | 12 |
| 2018.01 | L4 | 9 | 2018.09 | 25 | 60 | 2018.01 | J3 | 18 |
| 2018.01 | L5 | 12 | 2018.12 | 16 | 38 | 2018.01 | J4 | 24 |
| 2017.01 | L6 | 15 | 2018.03 | 18 | 42 | 2018.01 | J5 | 30 |
| 2017.01 | L7 | 18 | 2018.06 | 26 | 50 | 2018.01 | J6 | 36 |
| 2017.01 | L8 | 21 | 2018.09 | 25 | 60 | 2018.01 | J7 | 42 |
| 2017.01 | L9 | 24 | 2018.12 | 16 | 38 | 2018.01 | J8 | 48 |
| 2016.01 | L10 | 27 | 2018.03 | 18 | 42 | 2018.01 | J9 | 54 |
| 2016.01 | L11 | 30 | 2018.06 | 26 | 50 | 2018.01 | J10 | 60 |
| 2016.01 | L12 | 33 | 2018.09 | 25 | 60 | 2018.01 | J11 | 66 |
| 2016.01 | L13 | 36 | 2018.12 | 16 | 38 | 2018.01 | J12 | 72 |
| 2018.01 | J13 | 78 | ||||||
| No. | Type of Sensor | Sensitive Substance |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | LY2/LG | Oxidizing gas |
| S2 | LY2/G | Ammonia, carbon monoxide |
| S3 | LY2/AA | Ethanol |
| S4 | LY2/GH | Ammonia/organic amine |
| S5 | LY2/gCTL | Hydrogen sulfide |
| S6 | LY2/gCT | Propane/butane |
| S7 | T30/1 | Organic solvents |
| S8 | P10/1 | Hydrocarbons |
| S9 | P10/2 | Methane |
| S10 | P40/1 | Fluorine |
| S11 | T70/2 | Aromatic compounds |
| S12 | PA/2 | Ethanol, ammonia/organic amine |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, R.; Zhu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zou, H.; Yan, Y. Rapid Classification and Quantitative Prediction of Aflatoxin B1 Content and Colony Counts in Nutmeg Based on Electronic Nose. Molecules 2025, 30, 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122538
Yang R, Zhu K, Zhao Y, Guo X, Wang Y, Wang J, Zou H, Yan Y. Rapid Classification and Quantitative Prediction of Aflatoxin B1 Content and Colony Counts in Nutmeg Based on Electronic Nose. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122538
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ruiqi, Keyao Zhu, Yuanyu Zhao, Xingyu Guo, Yushi Wang, Jiayu Wang, Huiqin Zou, and Yonghong Yan. 2025. "Rapid Classification and Quantitative Prediction of Aflatoxin B1 Content and Colony Counts in Nutmeg Based on Electronic Nose" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122538
APA StyleYang, R., Zhu, K., Zhao, Y., Guo, X., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Zou, H., & Yan, Y. (2025). Rapid Classification and Quantitative Prediction of Aflatoxin B1 Content and Colony Counts in Nutmeg Based on Electronic Nose. Molecules, 30(12), 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122538






